Biology Unit (Painful and Torturous)
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6 H2O + energy
cellular respiration definition
The process of converting glucose into a form of energy (ATP) that is useable by cells
glycolysis
Begins initial breakdown of glucose
Occurs in the cytoplasm
Breaks glucose molecule into 2 pyruvate molecules
Creates NADH from NAD+
Creates 2 ATP molecules
Does not require oxygen
pyruvate
The molecules created from the initial breakdown of glucose during glycolysis
cytoplasm
site of glycolysis
NAD+
molecule that brings electrons and H via NADH to the electron transport chain to create ATP
created during reactions that breakdown glucose
FAD
molecule that brings electrons and H via FADH2 to the electron transport chain to create ATP
created during reactions that breakdown glucose
aerobic cellular respiration
metabolic pathway that requires oxygen (Kreb's --> ETC); complete breakdown of glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water
anaerobic cellular respiration
metabolic pathway that does not use oxygen (AKA fermentation); breakdown of pyruvate into lactic acid or alcohol and CO2
Kreb's cycle
AKA citric acid cycle
occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion
completes the breakdown of glucose into carbon dioxide
generates NADH and FADH2 that carry H to the electron transport chain
creates 2 ATP
electron transport chain (ETC)
occurs along the inner membrane of the mitochondrion
NADH and FADH2 deliver electrons that are passed across the membrane to create 32 ATP
oxygen is final electron acceptor to form water
ATP
adenosine triphosphate
the "energy currency of the cell"
the form of energy that is useable by cells
breaks into ADP when used by cells
ADP
adenosine diphosphate
accepts a phosphate group to store energy in the form of ATP
fermentation
anaerobic respiration
follows glycolysis and converts pyruvate into either alcohol and CO2 (yeast, bacteria) or lactic acid (muscles)
occurs in the cytoplasm
mitochondrion
site of aerobic cellular respiration
glucose in respiration
reactant that is broken down in first stage (glycolysis) into pyruvate
oxygen in respiration
reactant that is used to accept electrons in ETC
carbon dioxide in respiration
product of final breakdown of glucose in Kreb's cycle
water in respiration
product created from oxygen and electrons from ETC
photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
photosynthesis definition
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in the bonds of a glucose molecule.
ENERGY ACQUIRING
light dependent reactions
series of reactions that uses energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
takes in H2O and gives off O2 as a waste product
occurs in the thylakoids of the chloroplast
light independent reactions
AKA Calvin cycle or dark cycle
series of reactions that do not require light
uses CO2, and energy from ATP & NADPH to build glucose
occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast
NADP+
molecule that transfers electrons Calvin cycle to build glucose
chloroplast
the site of photosynthesis
water in photosynthesis
reactant split during the light dependent reactions
carbon dioxide in photosynthesis
reactant that is used to build glucose in light independent reactions
glucose in photosynthesis
product that is built in the light independent reactions
molecule that stores chemical energy within the chemical bonds between the atoms
oxygen in photosynthesis
product that is formed in the light dependent reactions from the breakdown of water
autotroph
An organism that is able to capture energy from sunlight and transform it into an organic molecule of glucose
AKA producer
Plants and plant-like protists
heterotroph
An organism that obtains organic food molecules by eating other organisms
AKA consumer
Animals, Fungi, animal-like protists, most bacteria
photosynthetic organisms
Plants
Plant-like protists
Some bacteria
Must contain a chloroplast or chlorophyll
respiration organisms
ALL organisms MUST perform some type of respiration (aerobic or anaerobic) to convert glucose into ATP
inputs of cellular respiration
glucose and oxygen
outputs of cellular respiration
Co2 and water
inputs of photosynthesis
Co@ and water
outputs of photosynthesis
glucose and oxygen
energy is converted from what to what in the process of photosynethesis
sunlight to glucose
exothermic
heat is released
endothermic
heat is absorbed
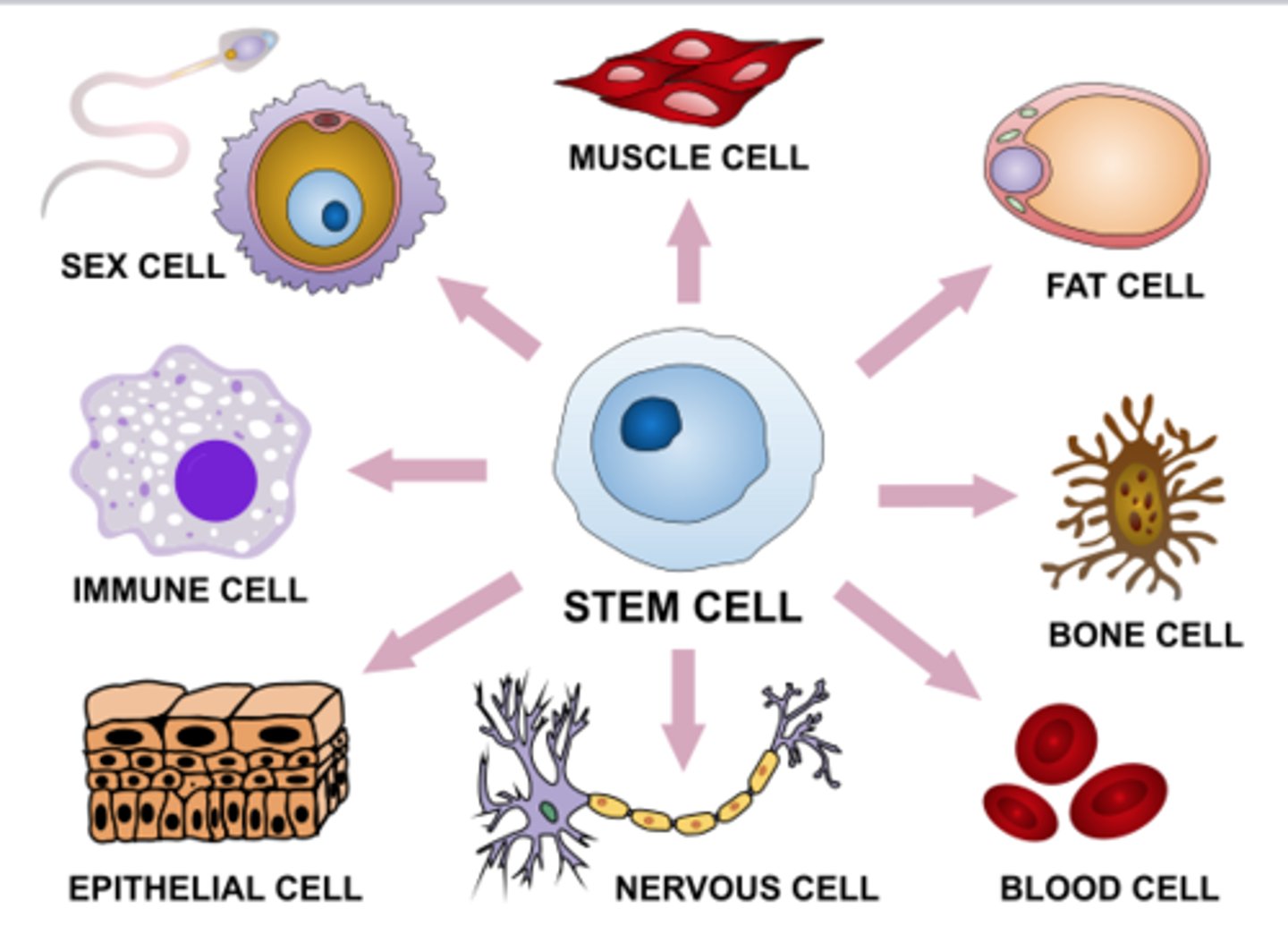
cell differentiation/specialization
an immature, unspecialized (no job) cell develops into a specialized cell type (nerve, muscle, blood cell) with unique structure helping to build tissue
Integumentary System
Organs: skin ,hair, nails
FUNCTIONS: protects against pathogens; receives stimuli from the environment; helps control body temperature; produces vitamin D; removes some waste (sweat)
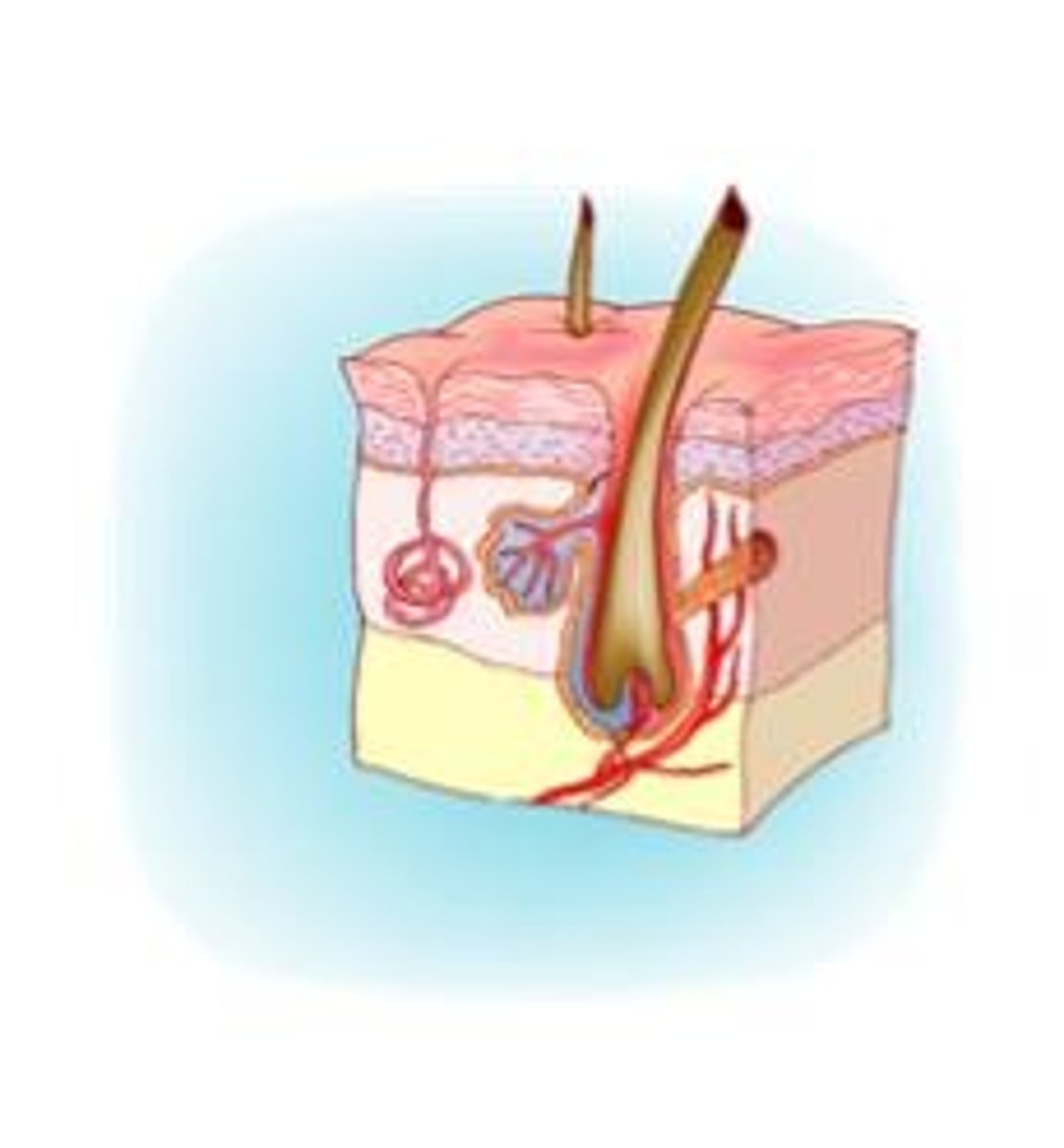
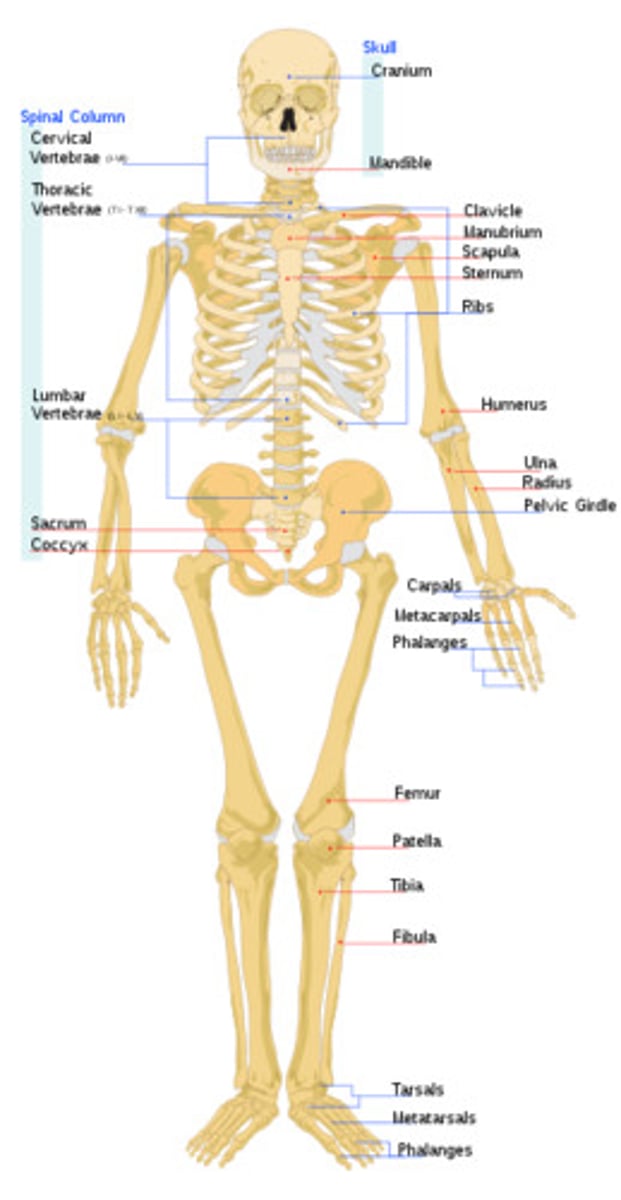
Skeletal System
Organs: bones, ligaments, tendons, cartilages
FUNCTIONS: Creates framework of the body, protects internal organs, produces red blood cells, acts as levers for muscles to provide mobility, stores minerals
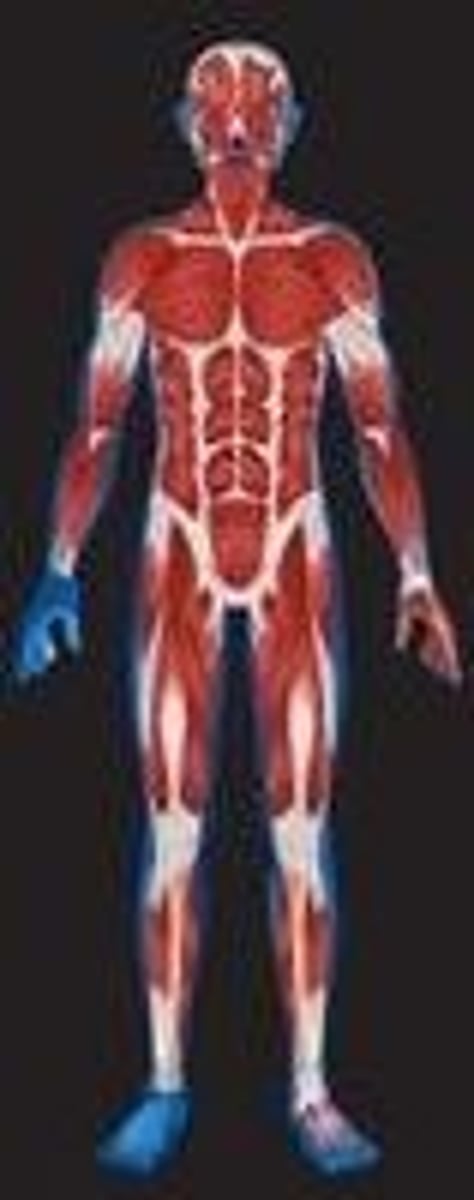
Muscular System
Organs: Cardiac Muscle, Skeletal Muscl and Smooth Muscle
FUNCTIONS: Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression. Maintains posture & produces heat.
Nervous System
Organs: brain, spinal cord, nerves, sense organs
FUNCTIONS: receives and interprets stimuli and transmits impulses to the effector organs.
Fast acting control system; provides communication throughout the body.
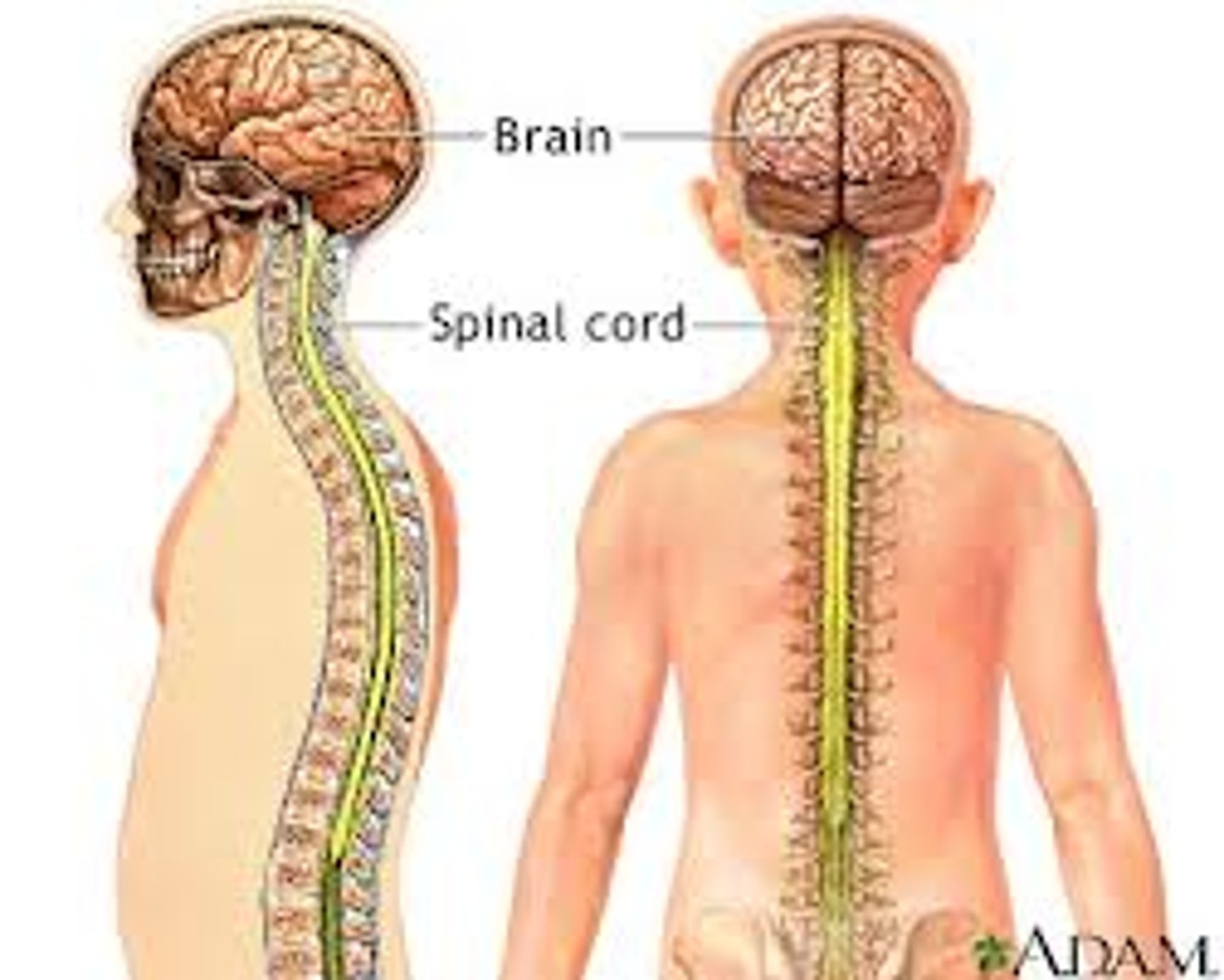
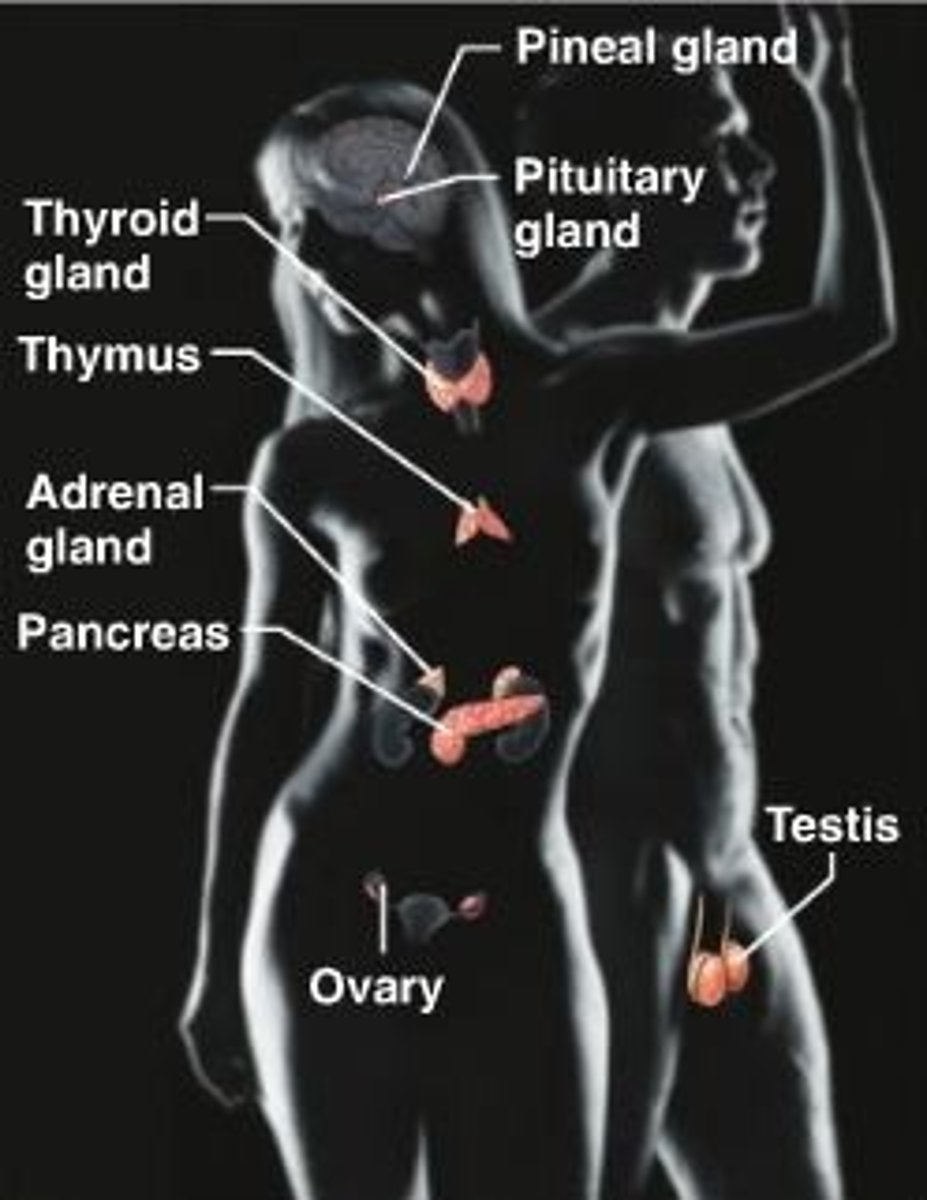
Endocrine System
Organs: pituitary gland, thyroid and adrenal glands.
FUNCTIONS: Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells.
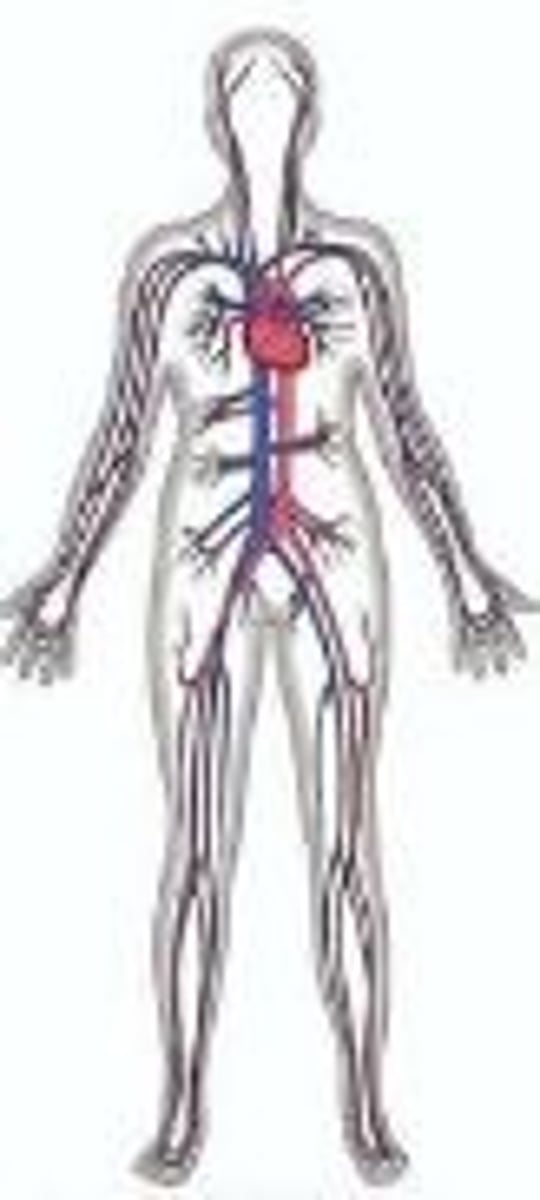
Cardiovascular System
Organs: Heart, arteries, capillaries, veins, blood
FUNCTIONS: The transport system of the body responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body and carrying away carbon dioxide and other wastes
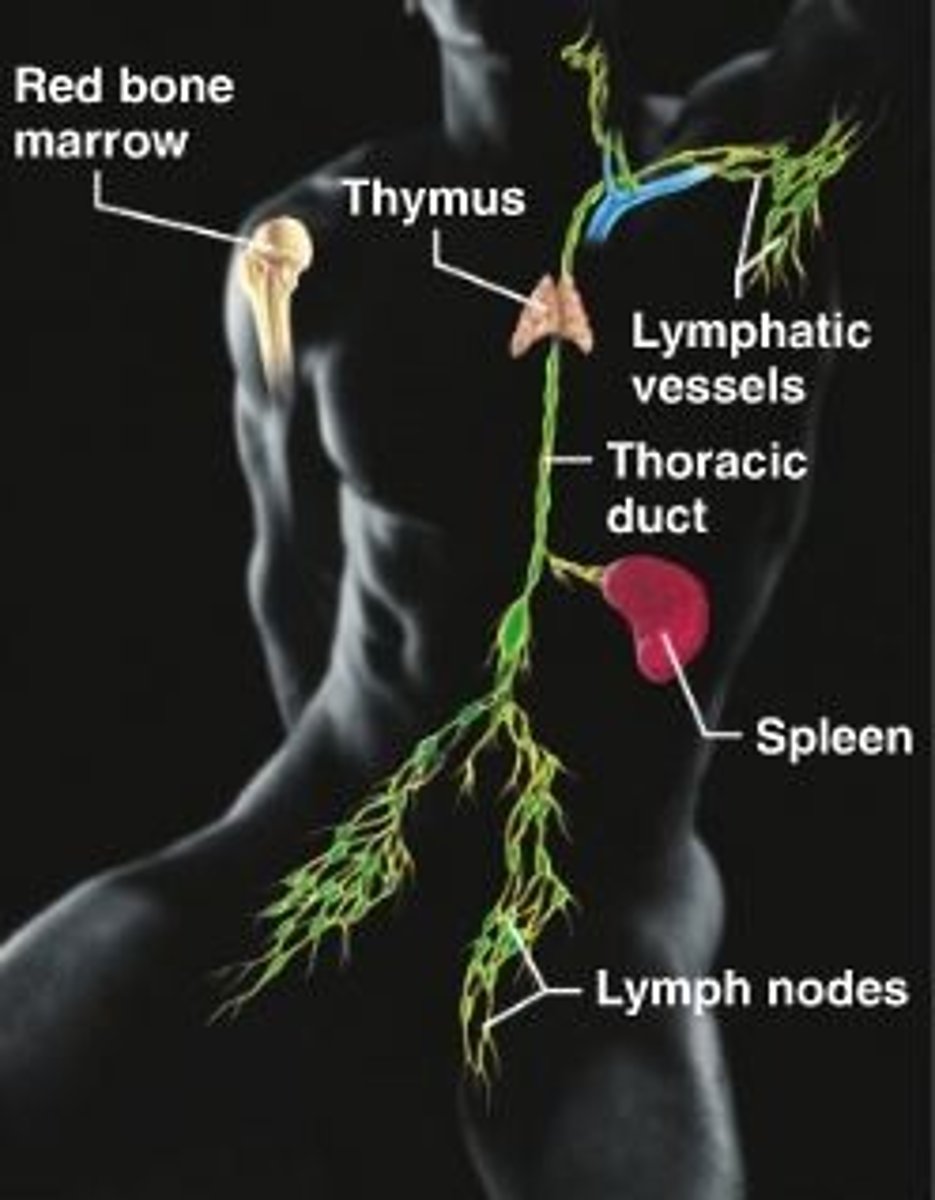
Lymphatic System
Organs: Lymph nodes, spleen and Lymphatic Vessels
FUNCTIONS: Acts like a "drain" to remove the body's excess fluid and return portions to the blood. Contains lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) that protect the body against disease.
Digestive System
Organs: mouth, tongue, esophagus, stomach, liver, small intestines,
colon= large intestines, and anus
FUNCTIONS: Breaking down food into simple nutrient form so that it can be utilized by the body and eliminate the waste from the body
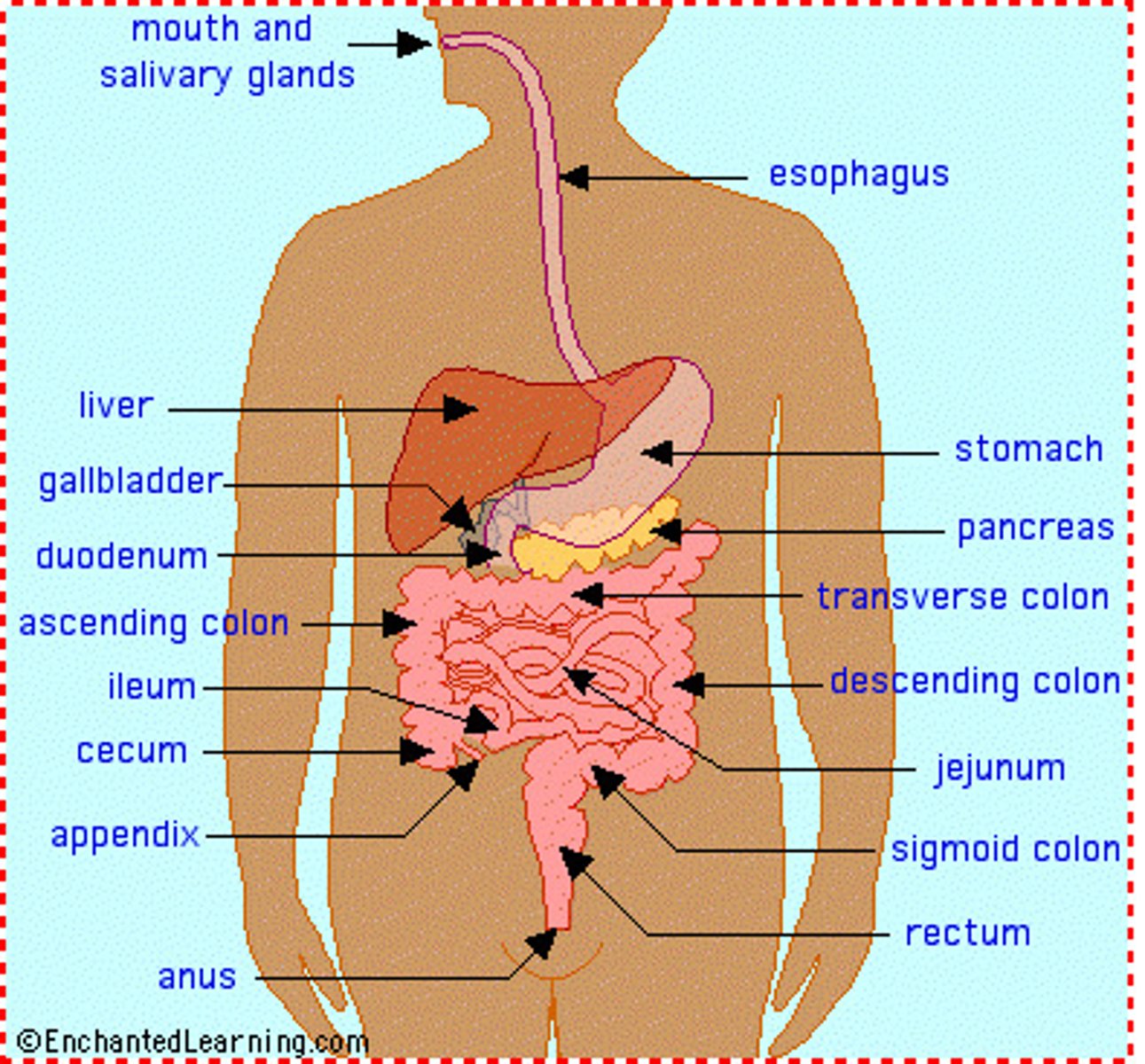
Respiratory System
Organs: nasal cavity, trachea, lungs, and alveoli.
FUNCTIONS:
A group of organs that work together to transfer oxygen from the atmosphere to the blood and transfer carbon dioxide from the blood to the atmosphere.
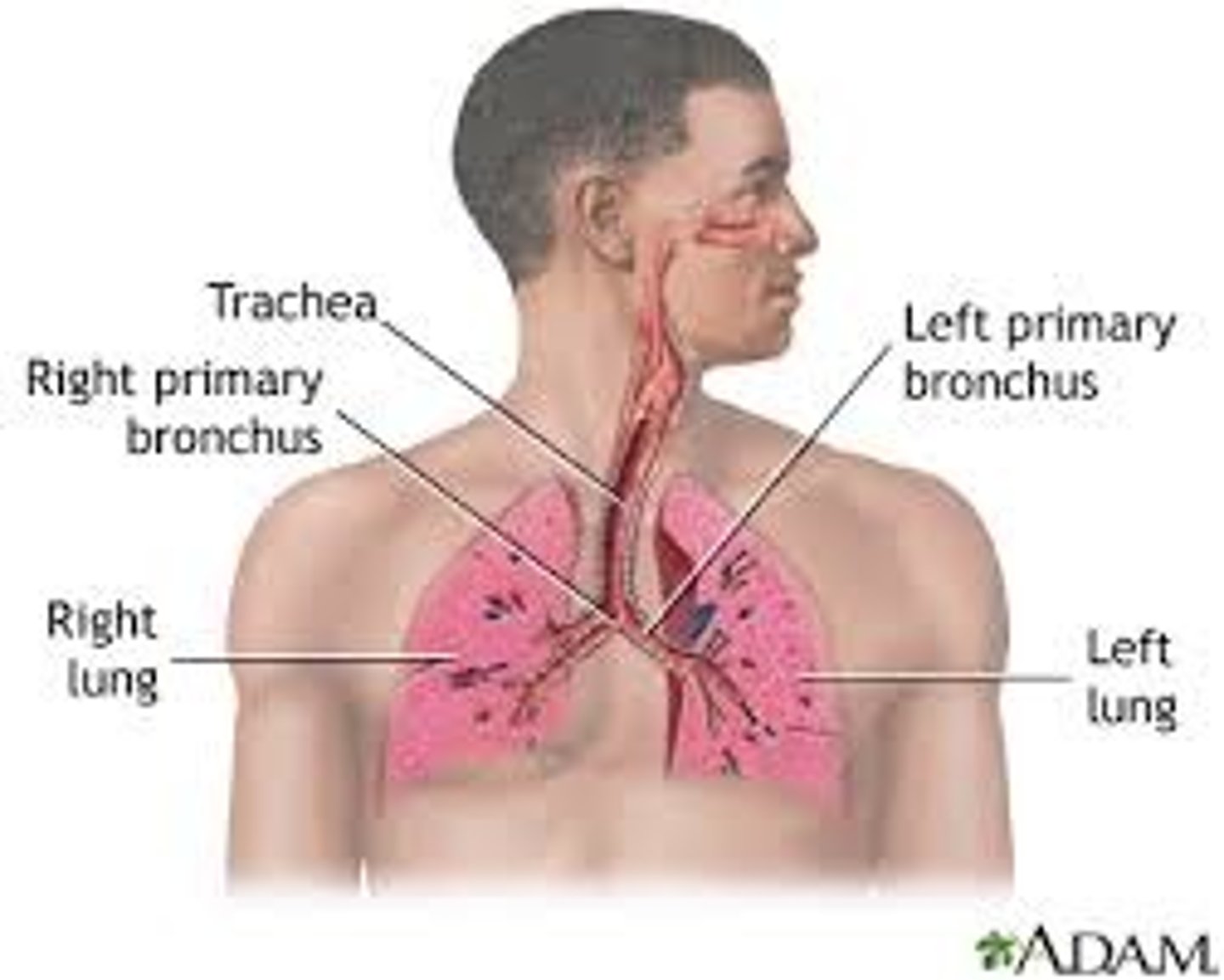
Urinary System
Organs: 2 kidneys, 2 ureters, 1 urinary bladder and 1 urethra
FUNCTIONS: Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body. Regulates water, electrolyte and acid-base balance of the blood.
Reproductive System
Organs: ovaries, testes, uterus
FUNCTIONS: Reproduce offspring- produce male sex cells (sperm) and female sex cells (oocytes)

Purpose of mitosis
organisms' growth, damage repair, replacing dead cells
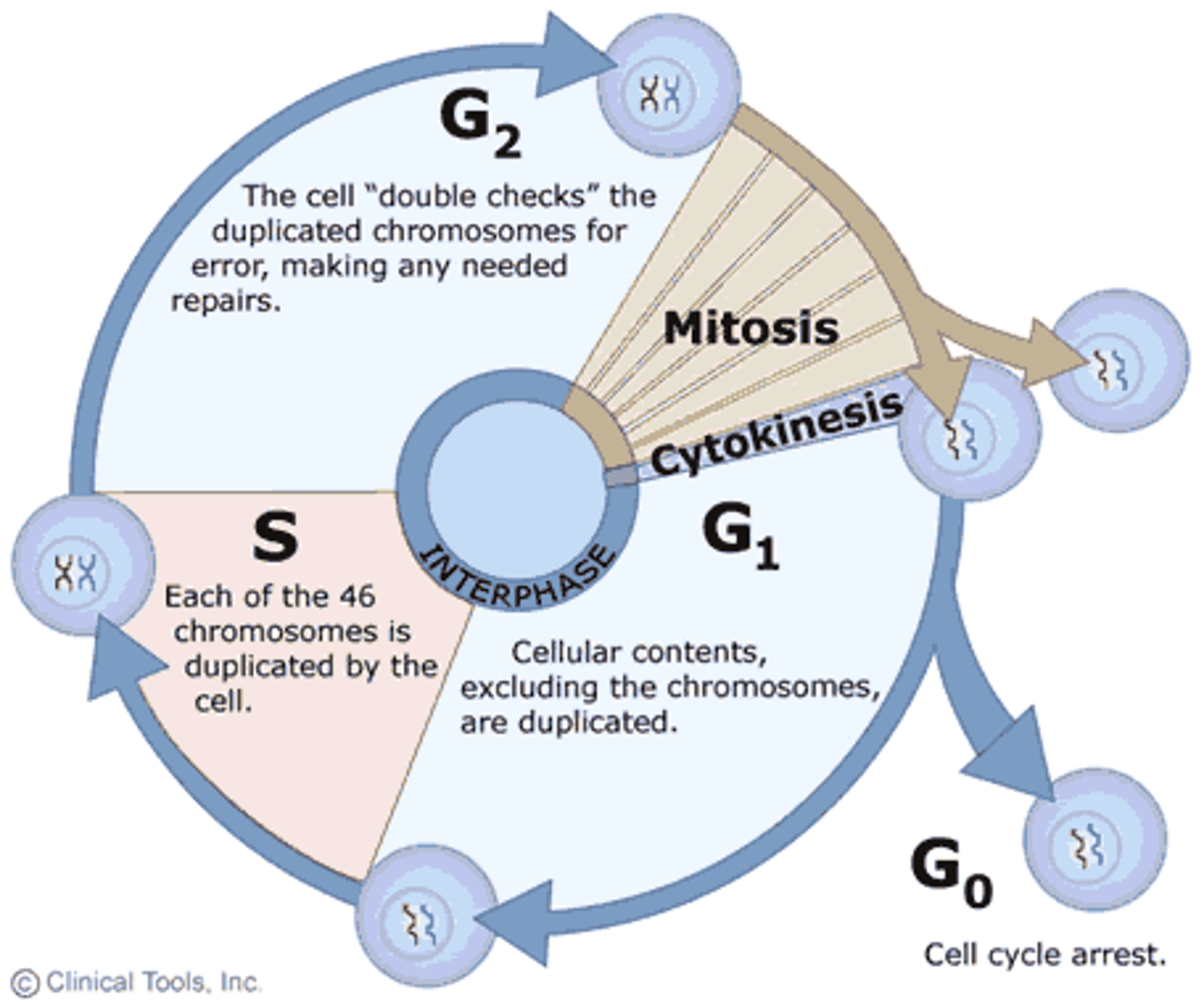
TERM
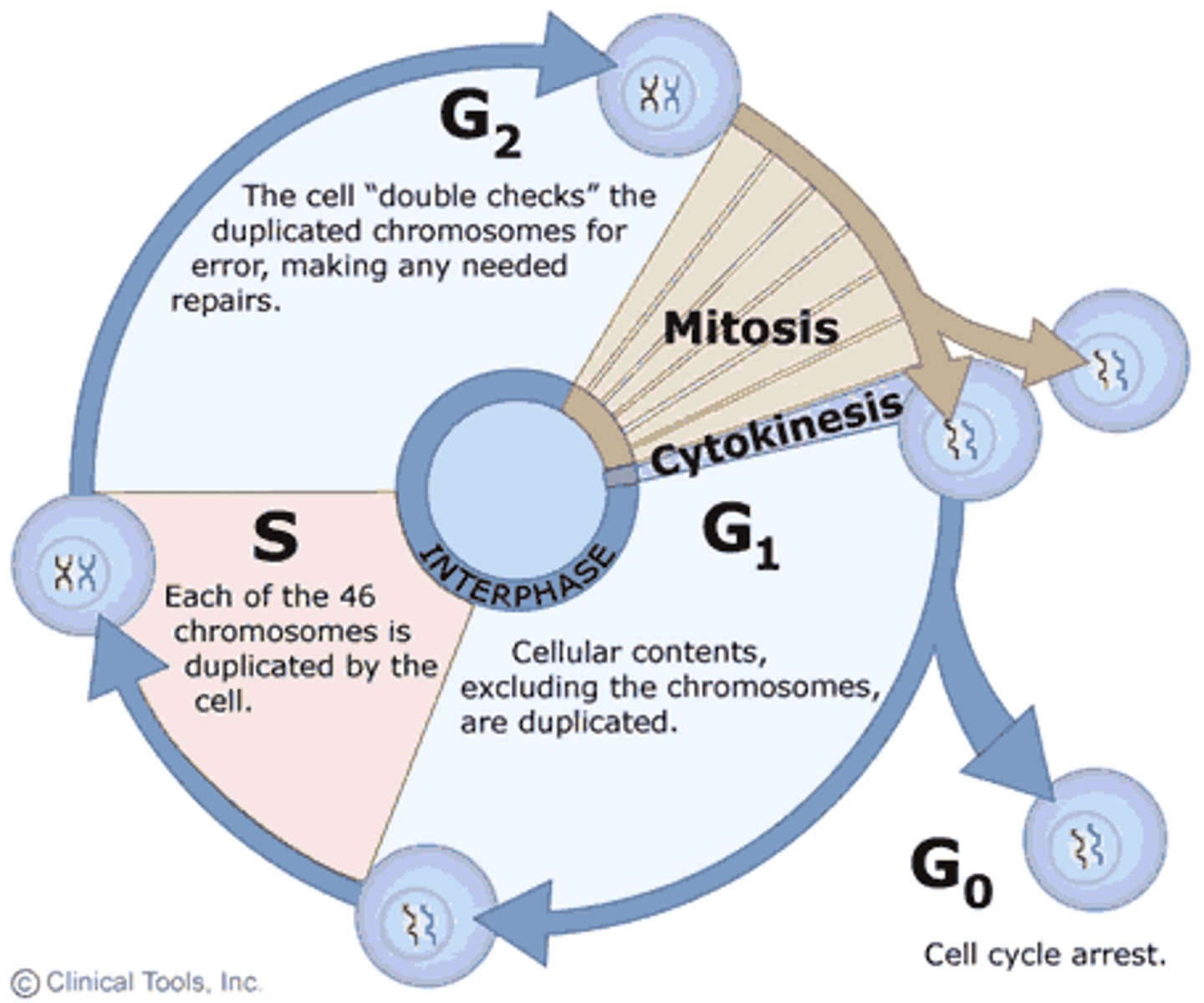
Interphase
DEFINITION
Major Phase of The Cell Cycle in which cells grow (G1), maintain normal activities (G0) and replicate DN (S), and get ready for division (G2).
Chromatid
Two chromosomes combined by a centromere
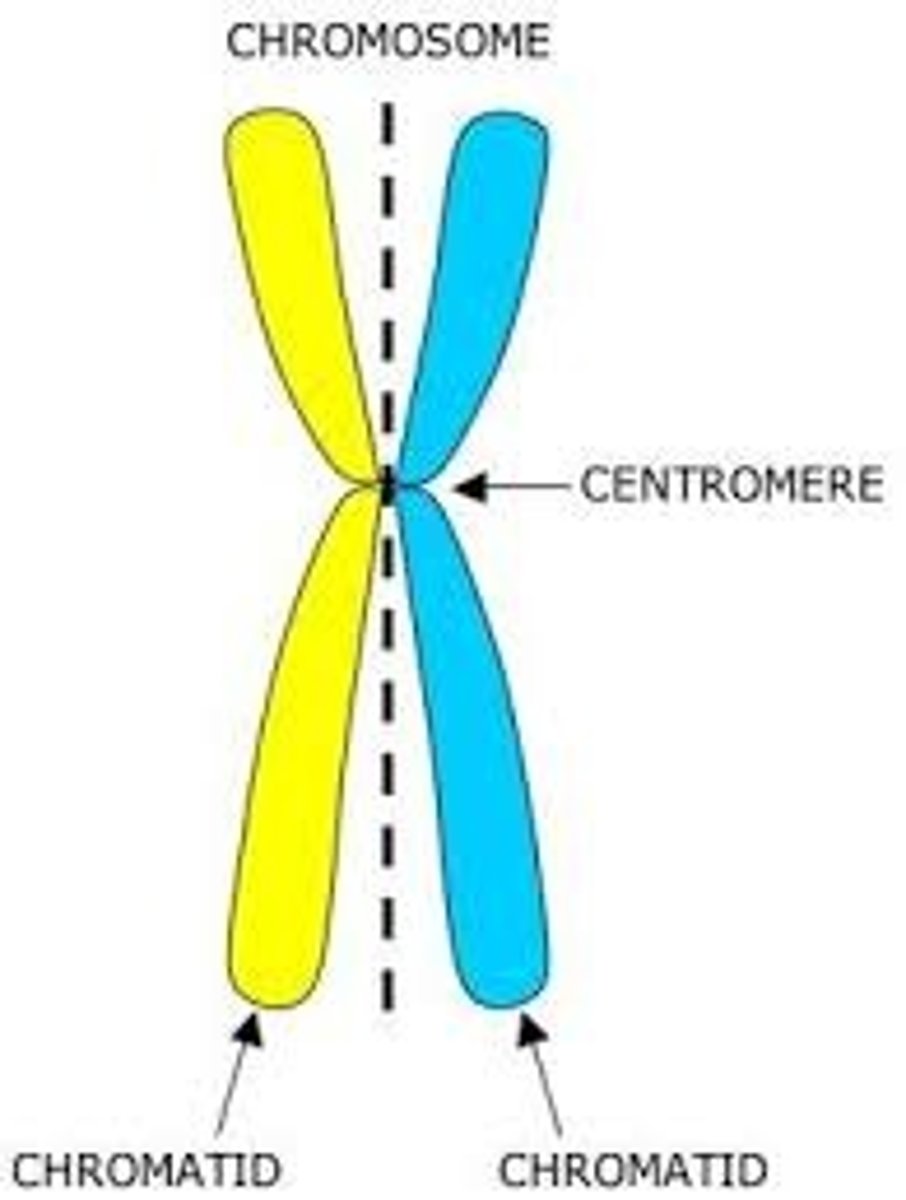
Chromosome
Condensed chromatin

Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
Cell cycle
An ordered sequence of events in the life of a cell which includes cell division
TERM
Mitosis
DEFINITION
Major Stage of The Cell Cycle where the cell divides
46
How many chromosomes does a human have?
4
A parent cell with four chromosomes before mitosis, will have how many chromosomes after mitosis?
TERM
G0
DEFINITION
"Going to work"- the cell's normal everyday functions
TERM
SYNTHESIS
DEFINITION
DNA is replicated, aka copied
TERM
G1
DEFINITION
Cell organelles are copied and cell growth occurs
TERM
G2
DEFINITION
Materials needed for cell division are made.
TERM
Daugher cells
DEFINITION
Have the SAME AMOUNT OF CHROMOSOMES AS THE PARENT CELL
TERM
Check Point 1
DEFINITION
To make sure all organelles have been divided and there are no mutations
TERM
Check Point 2
DEFINITION
Check DNA for mutations
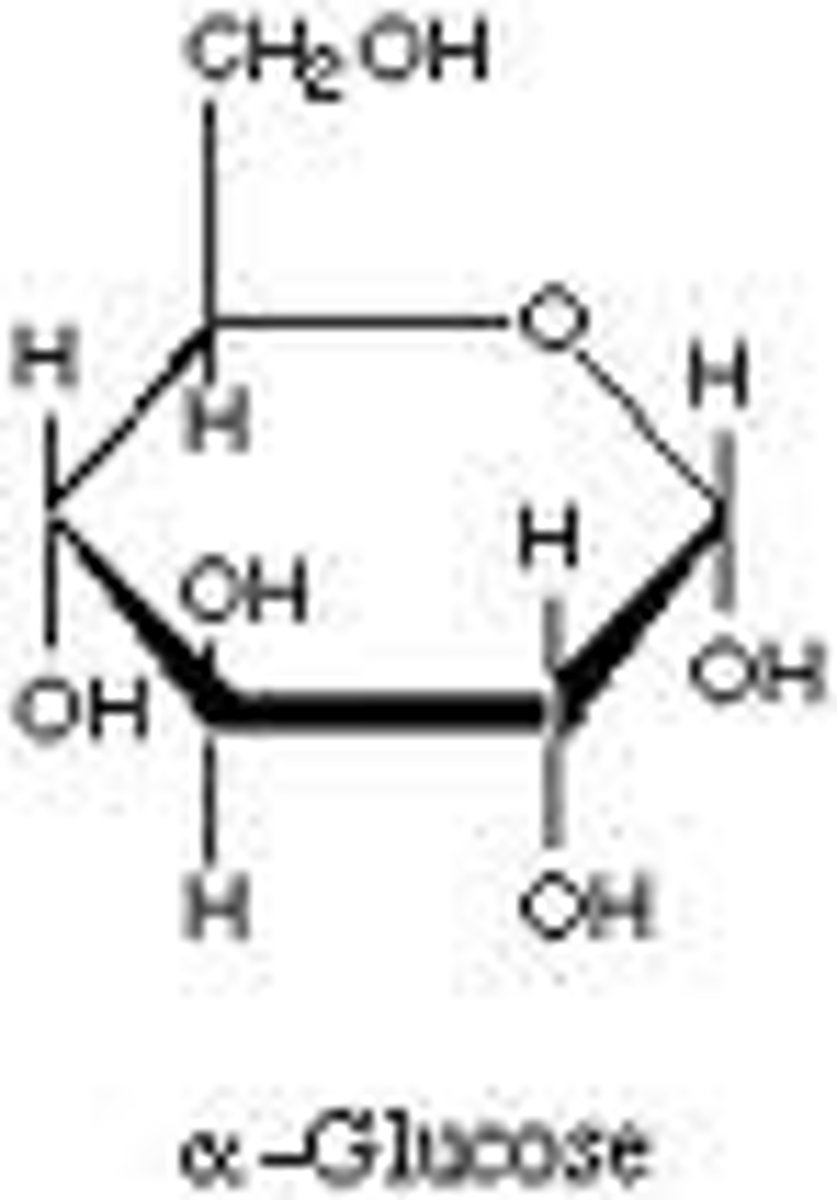
carbohydrate
main source of quick energy for most organisms
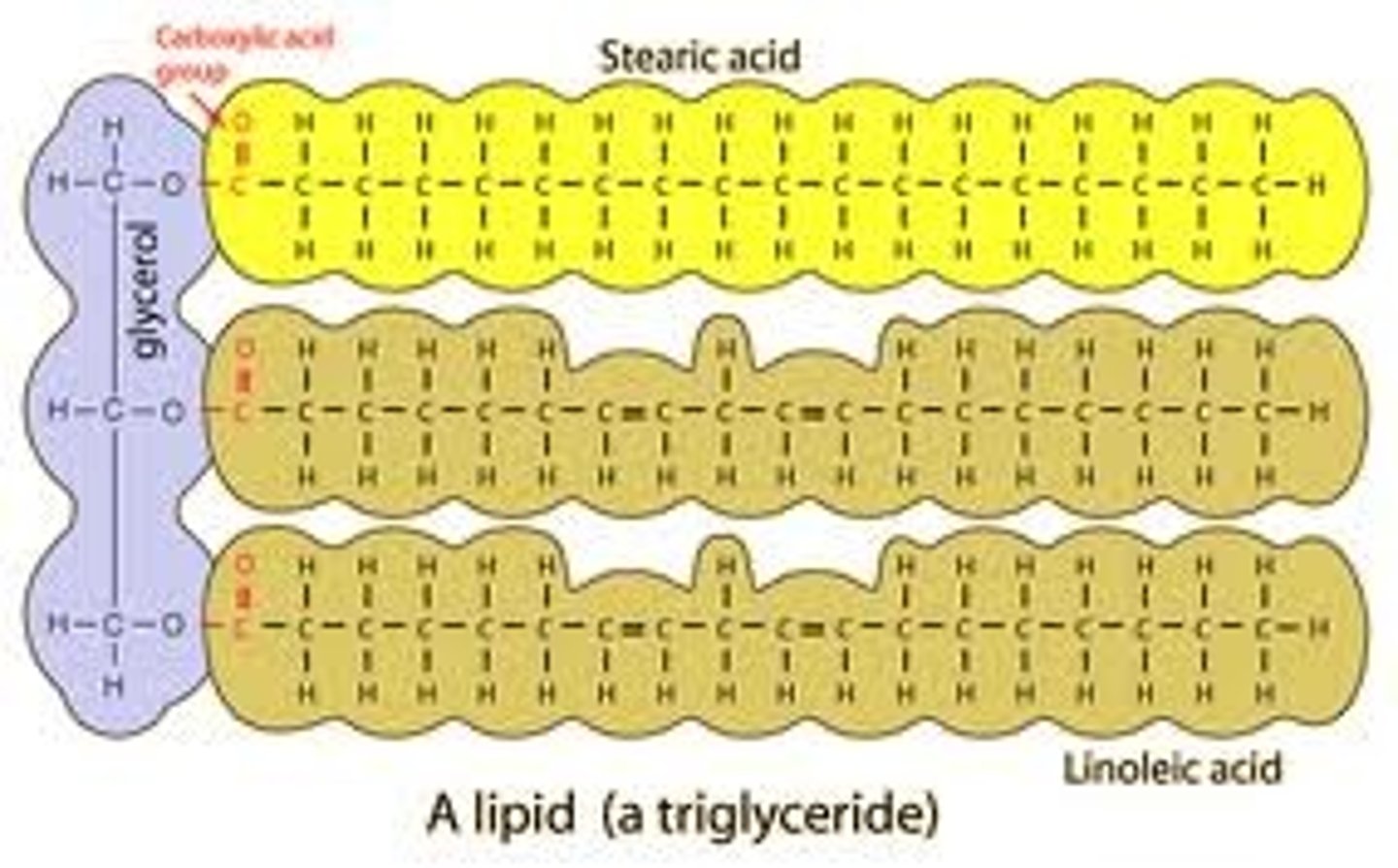
lipid
long-term energy storage; part of biological membranes; waterproof coverings/barriers
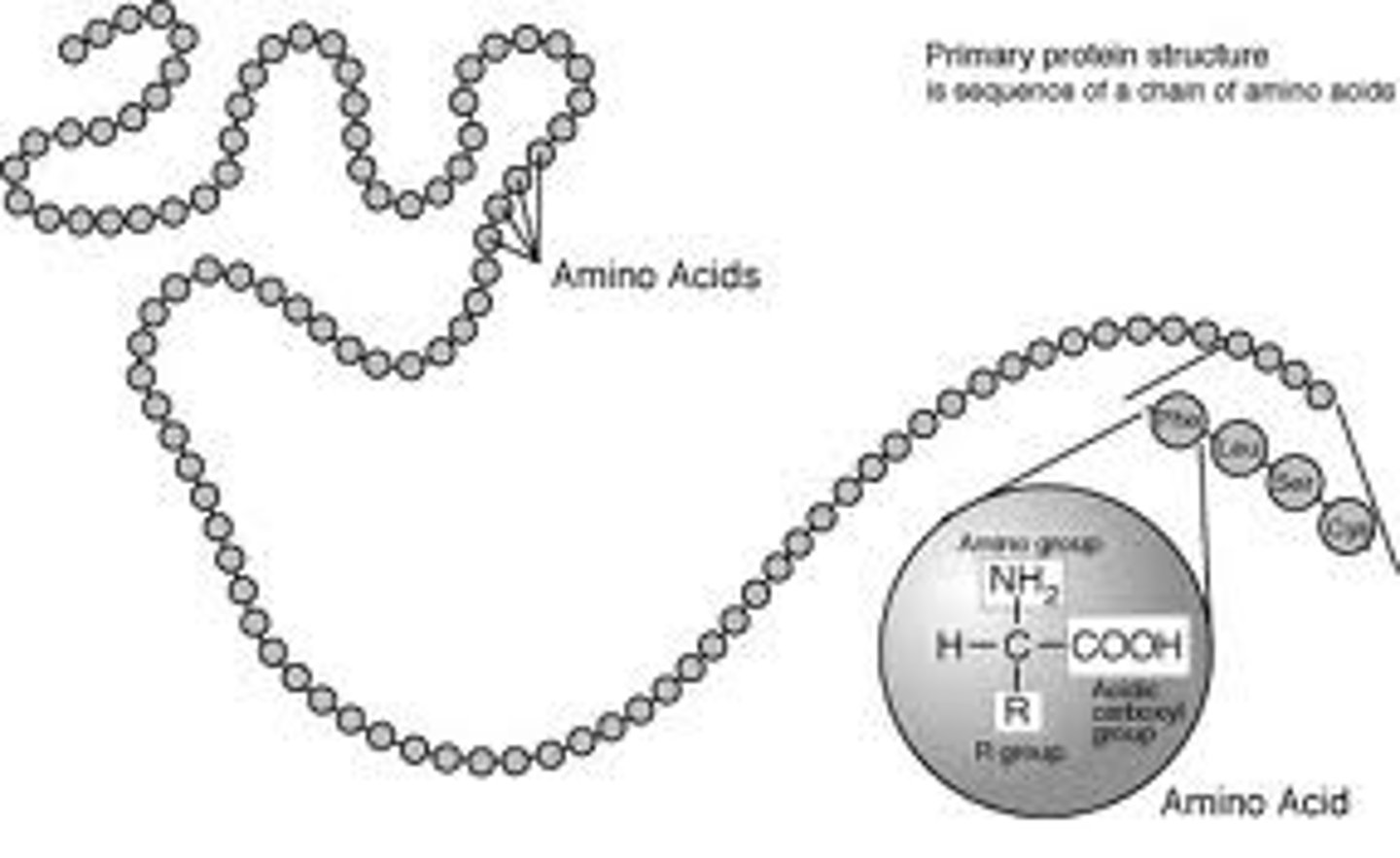
protein
Enzymes are an example of this macromolecule.
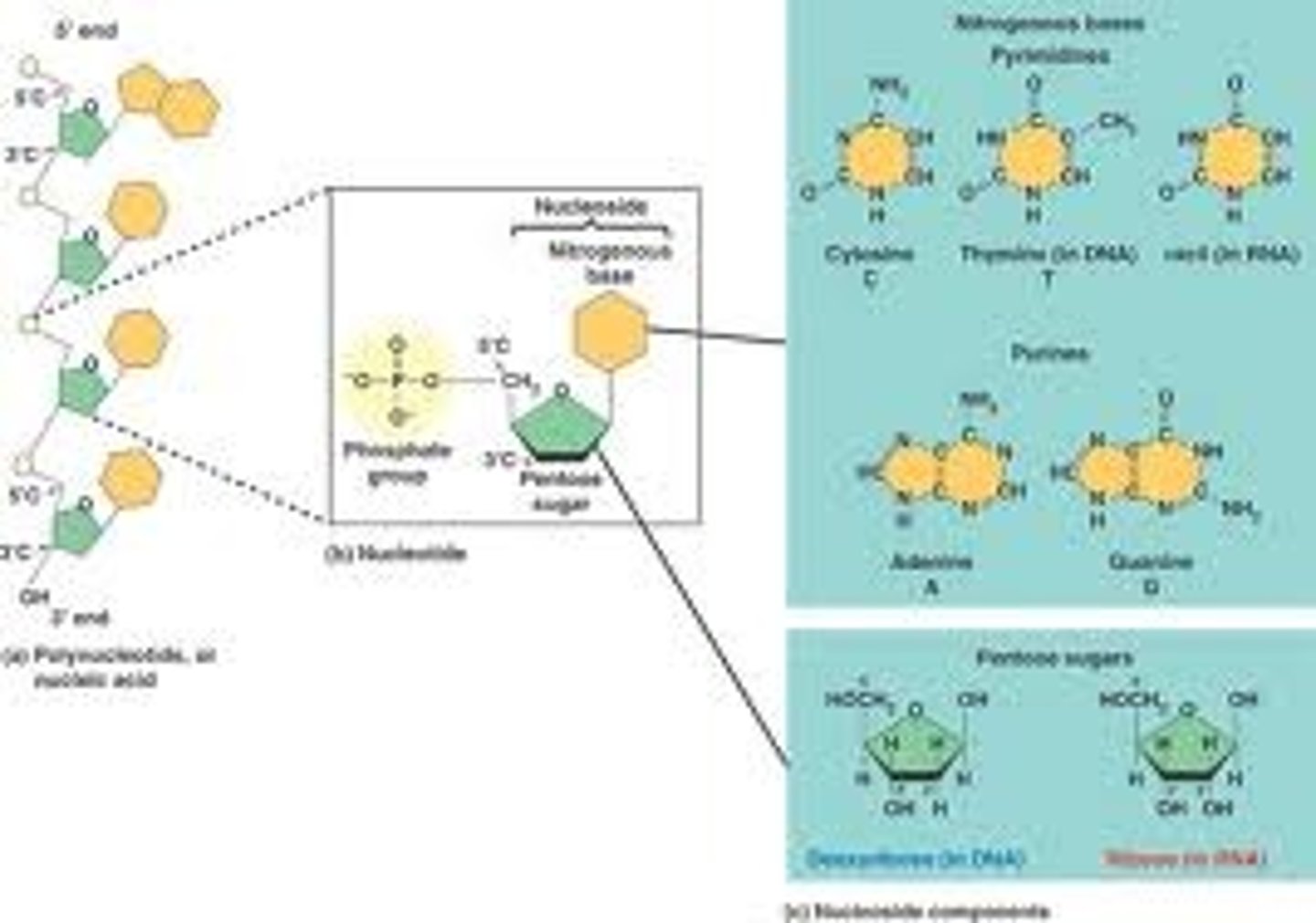
nucleic acid
store and transmit hereditary/genetic information
C,H,O,N
elements in protein

C,H,O
elements in carbohydrates and lipids
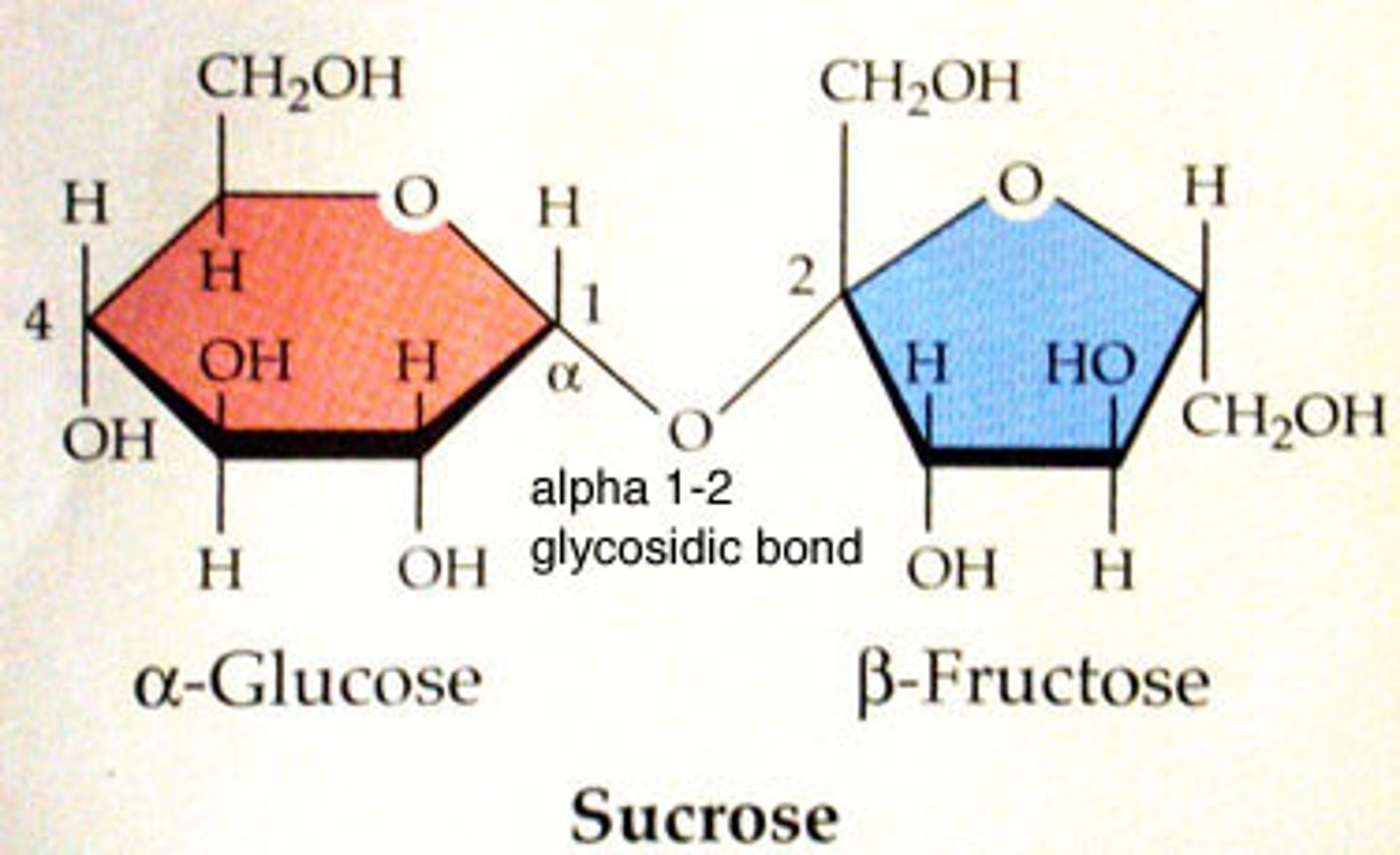
Disaccharide
2 sugar molecule, such as sucrose
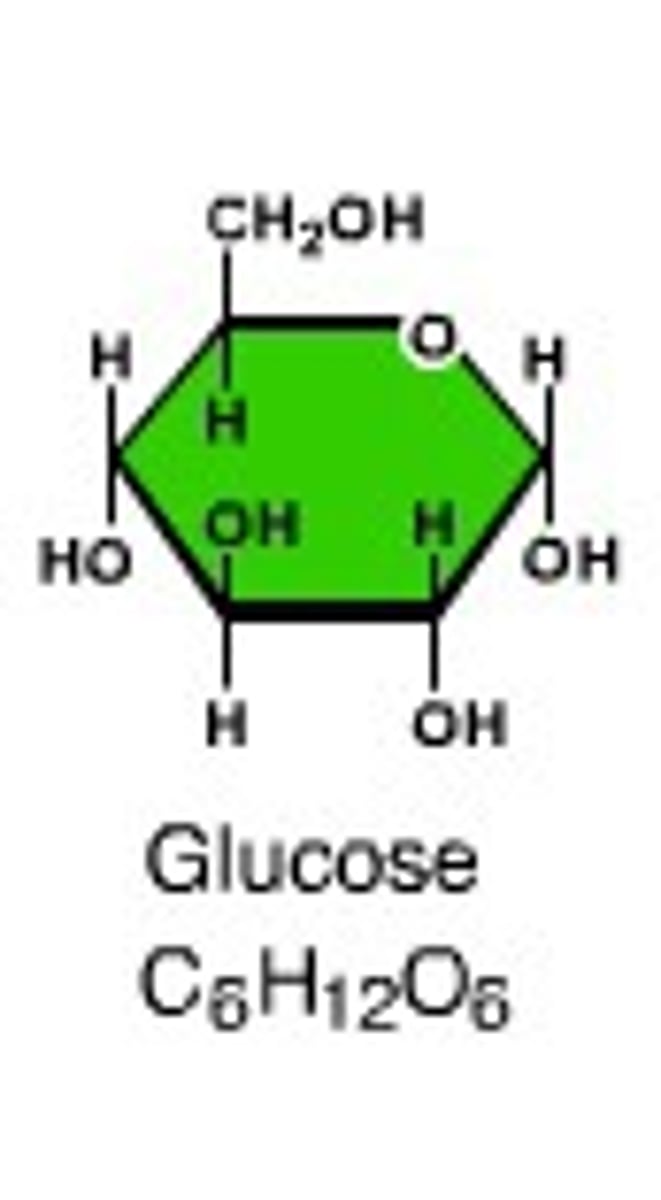
Monosaccharide
1 sugar molecule, such as glucose
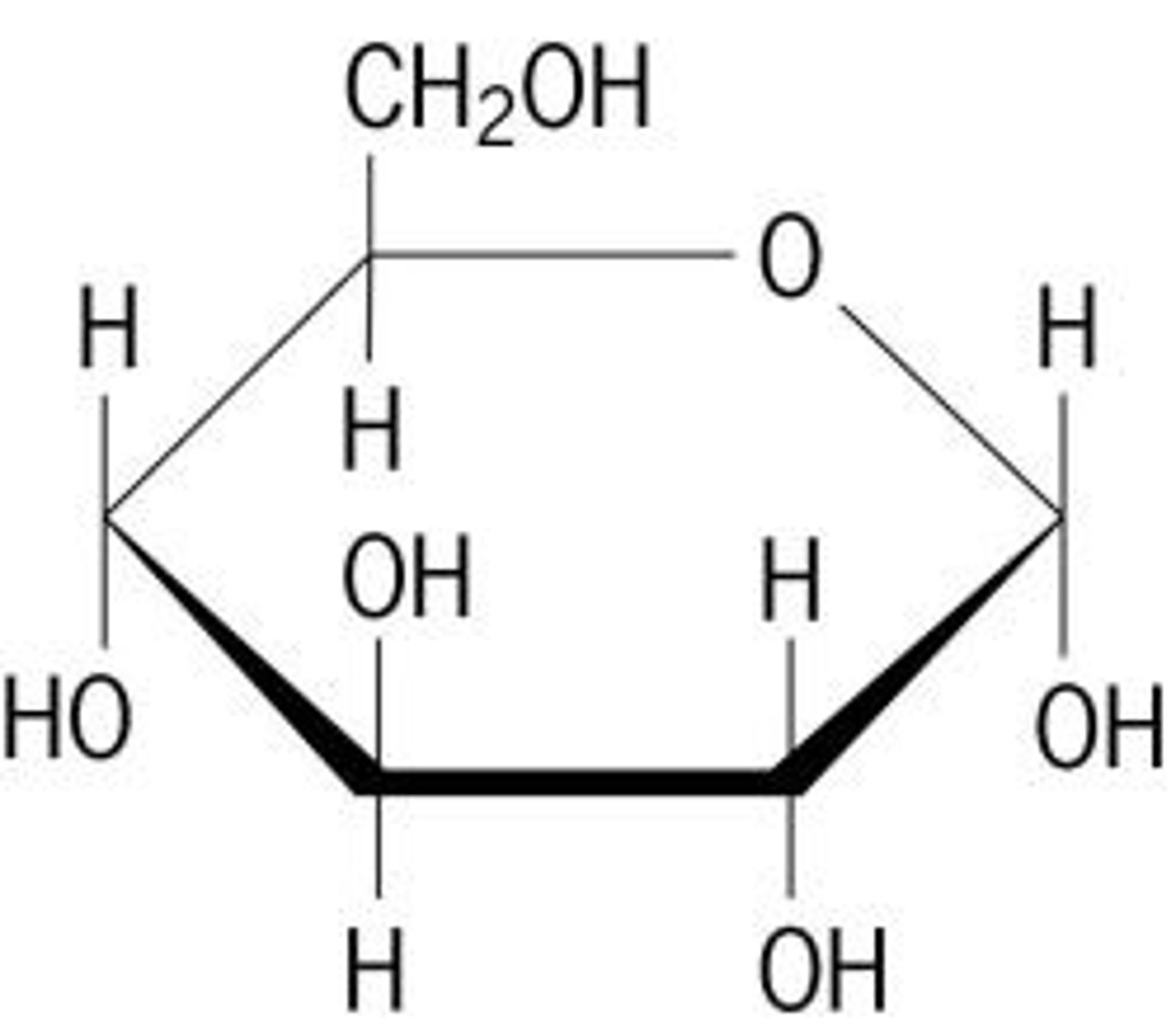
carbohydrate monomers
monosaccharides
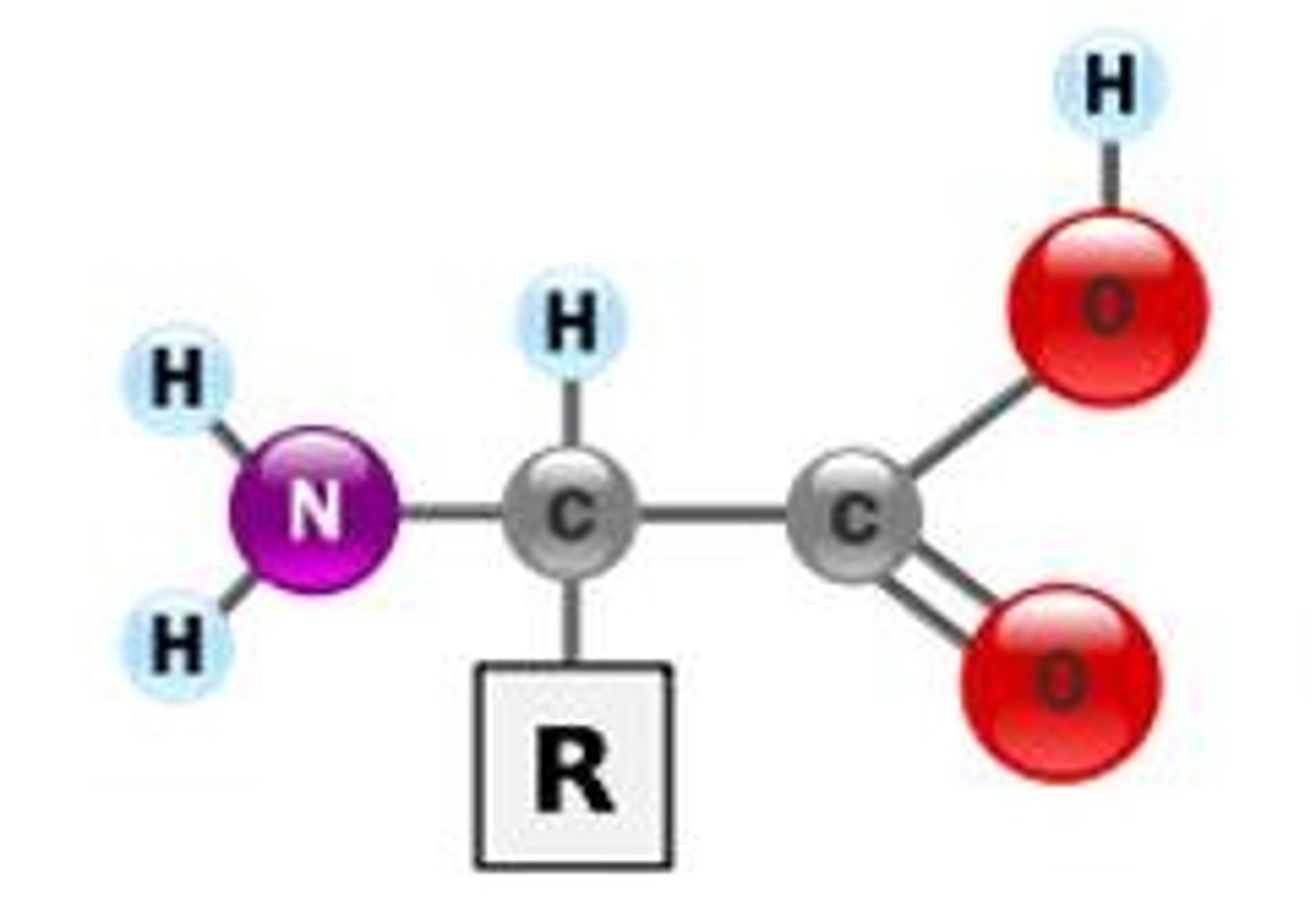
protein monomers
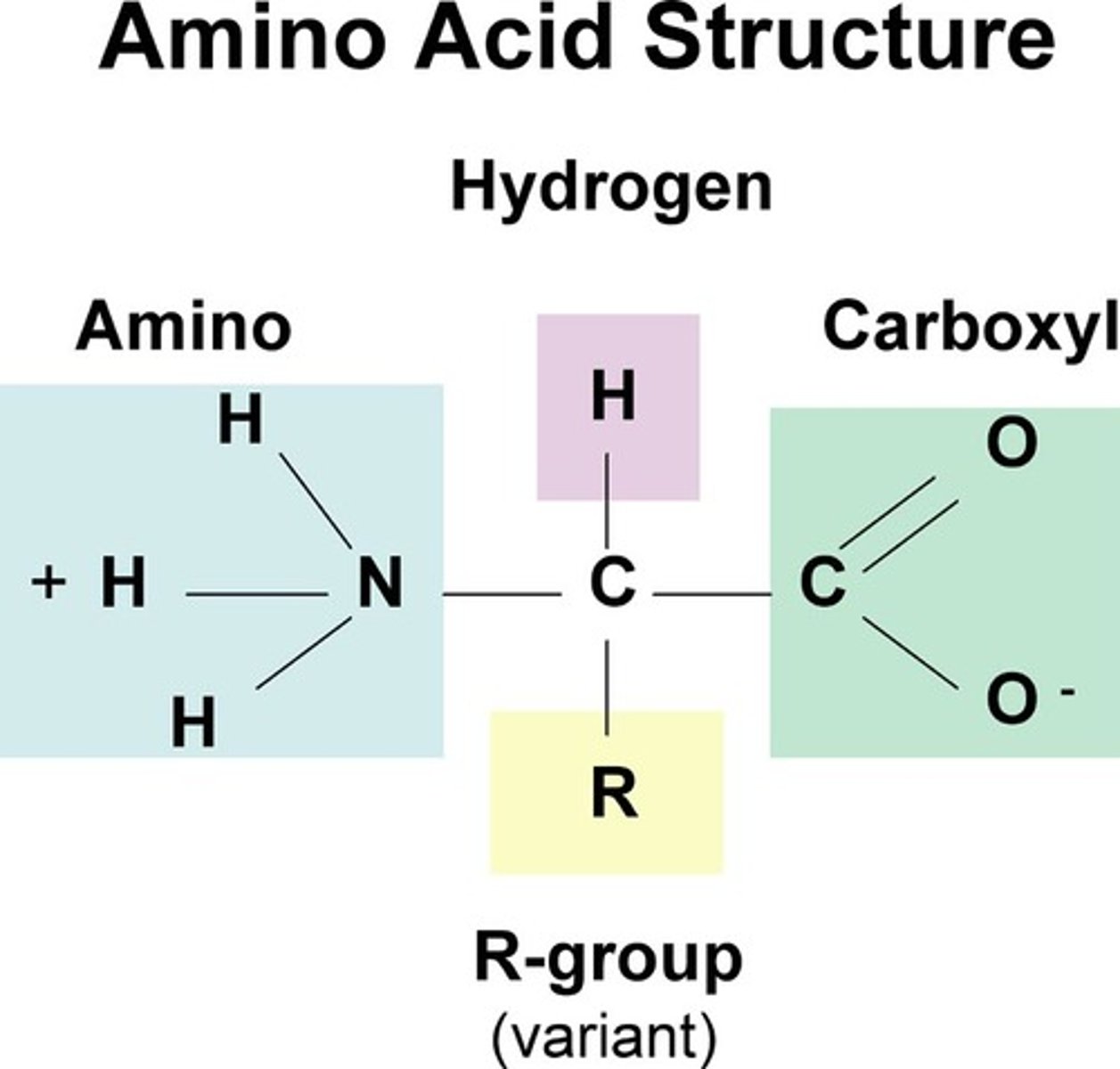
amino acids
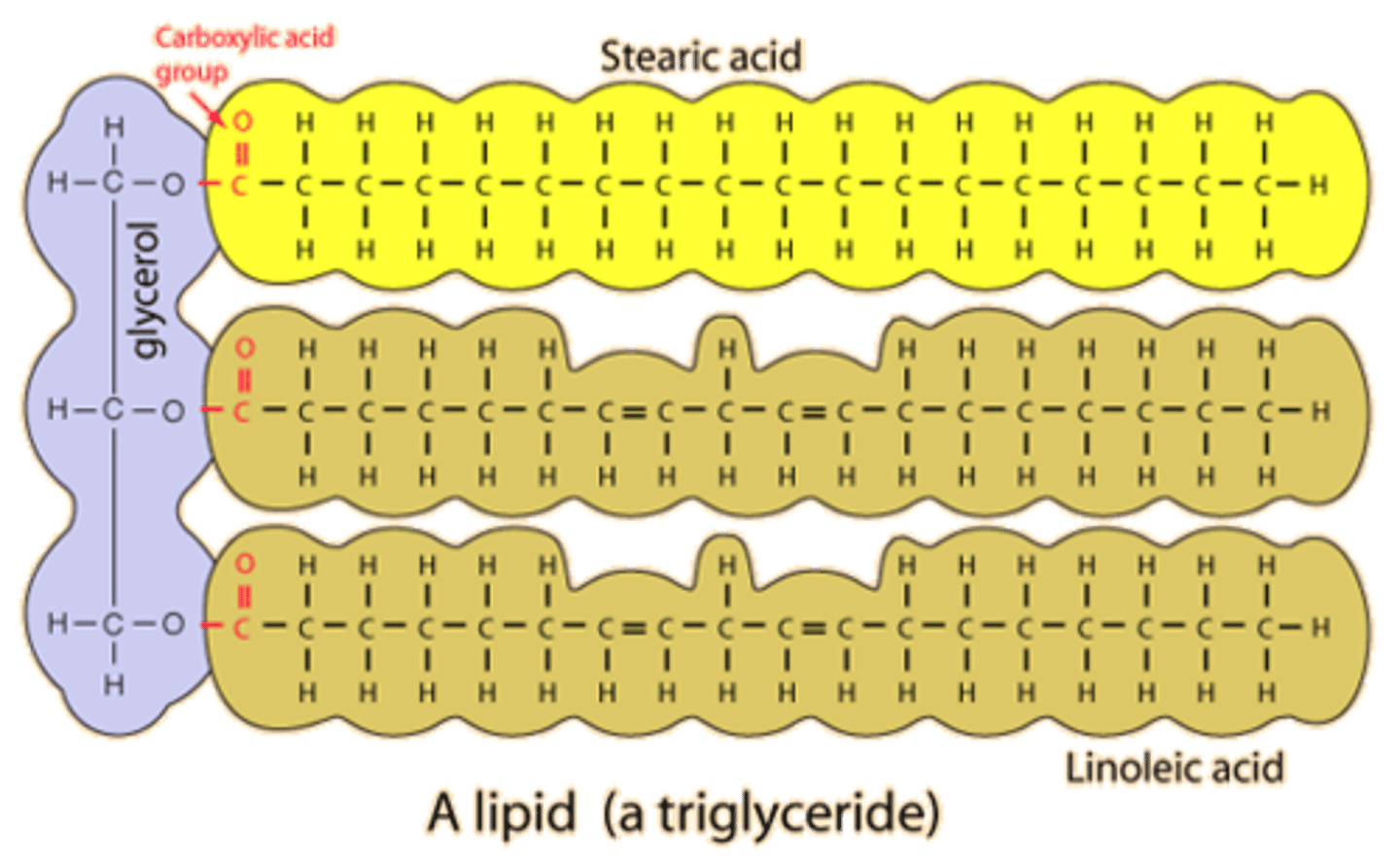
lipid monomers
glycerol and 3 fatty acids
monomers of nucleic acids are
nucleotides
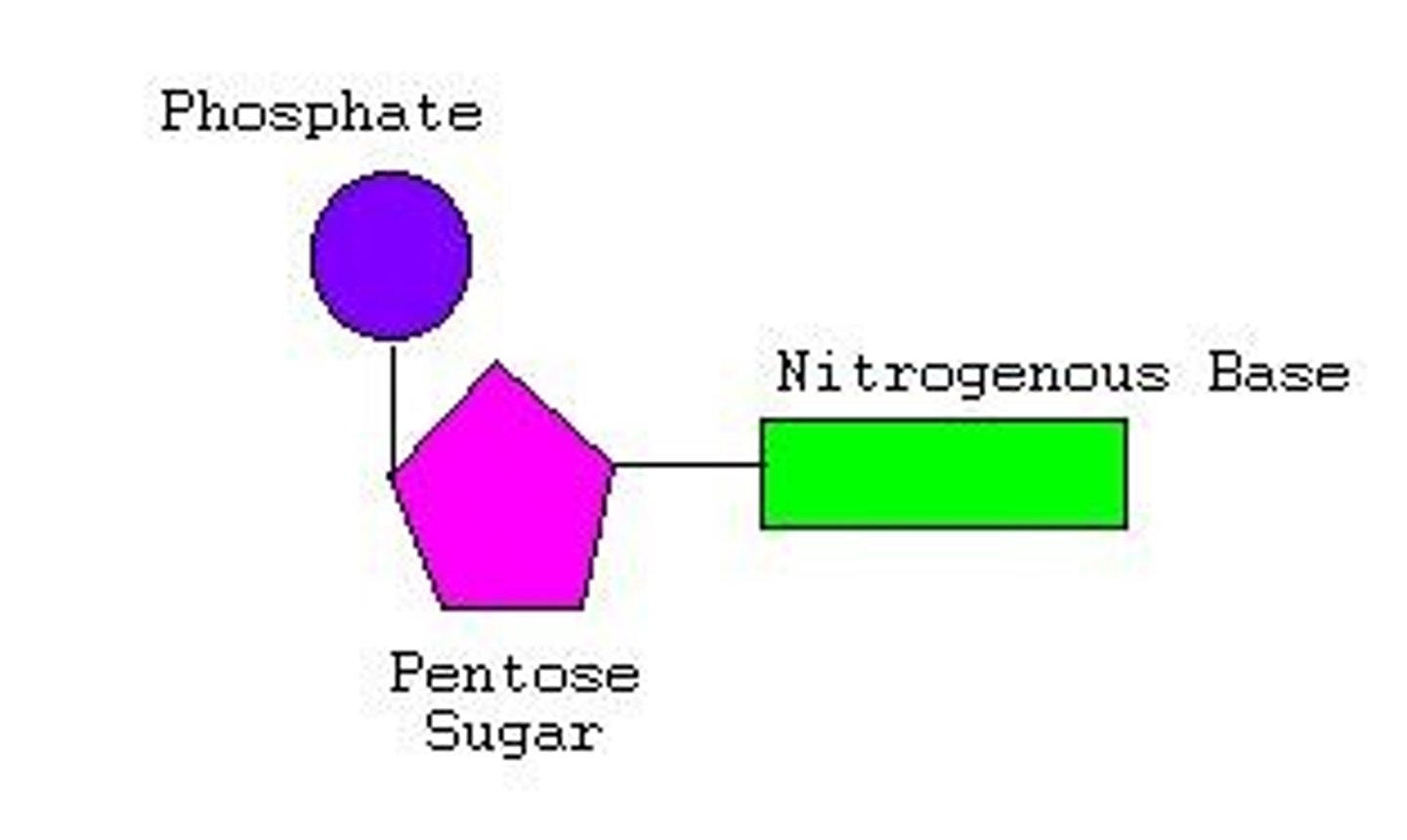
C,H,O,N,P
Elements in Nucleic Acid
Macromolecules can also be called ?
polymers or biomolecules

monomer
the building block of a macromolecule

Condensation reaction (aka dehydration synthesis)
The chemical process used to join monomers to make polymers
Examples of proteins
Keratin, muscles, meat, nuts, hemoglobin
Examples of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
stores genetic information
function nucleic acids
Examples of lipids
Waxy cuticle of plants, oils, butter, phospholipids
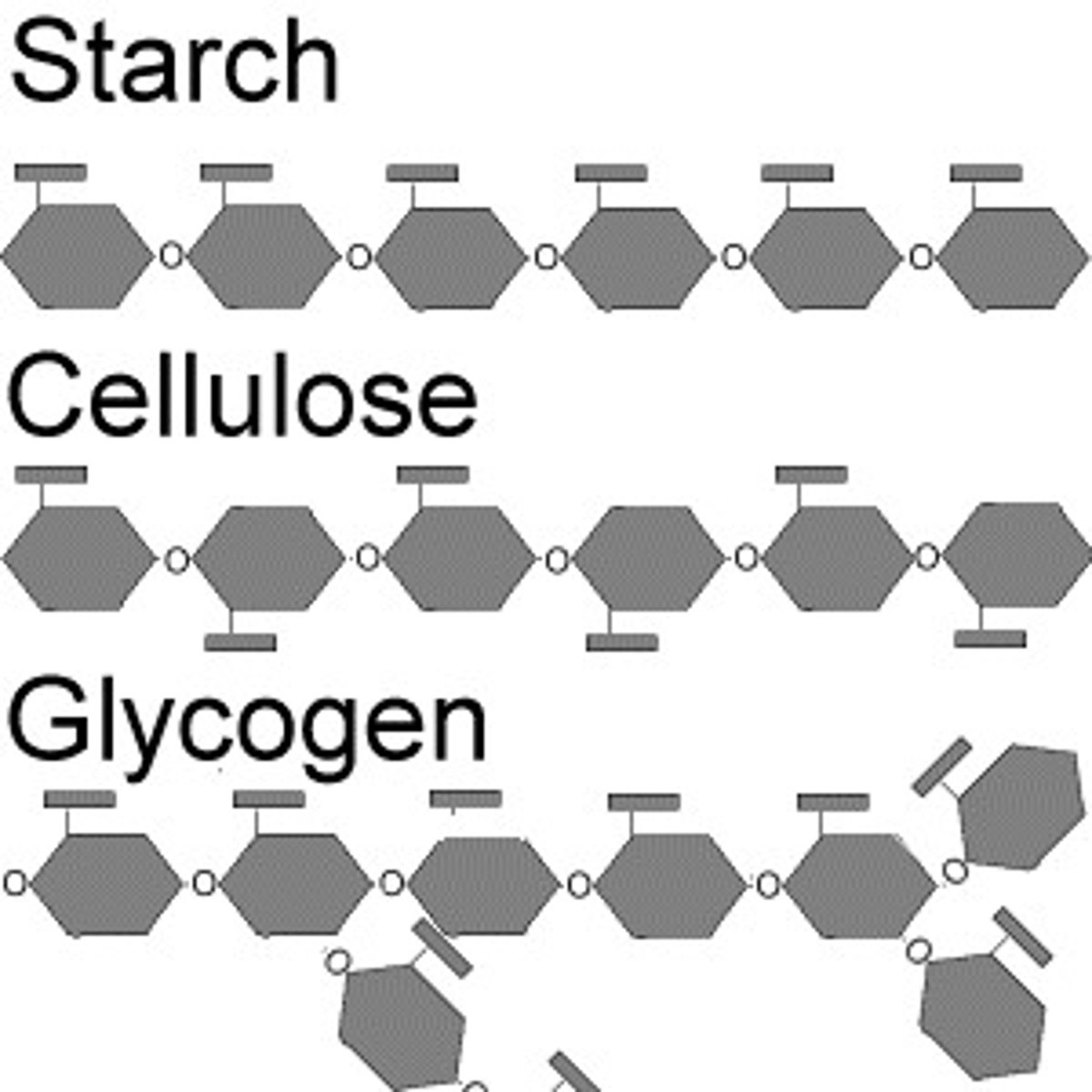
Polysaccharides
Made of many sugars
Polysaccharides examples
starch, glycogen, cellulose
Enzymes are
proteins that function as biological catalysts
Enzyme-substrate complex

Protein structural formula
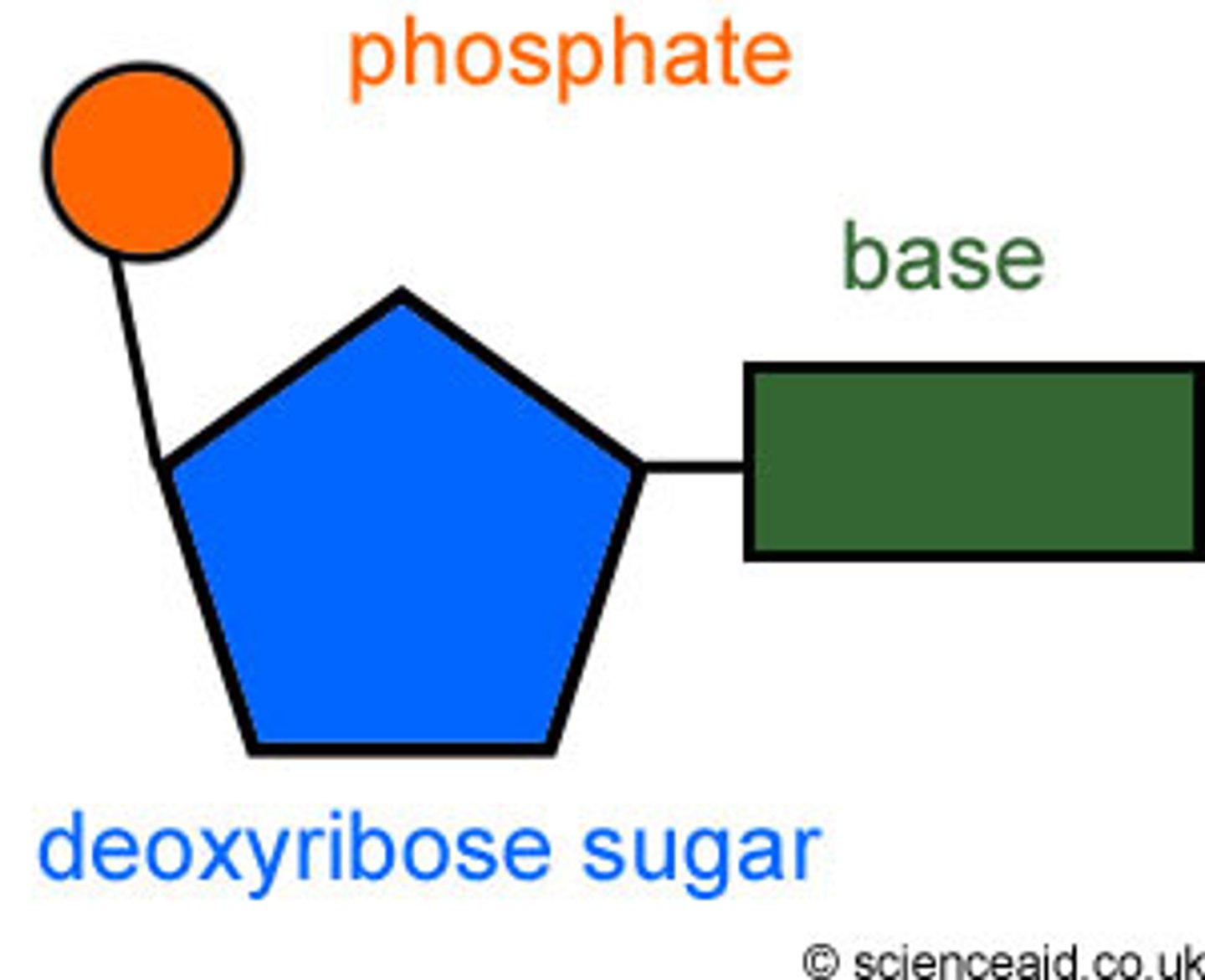
nucleic acid structural formula
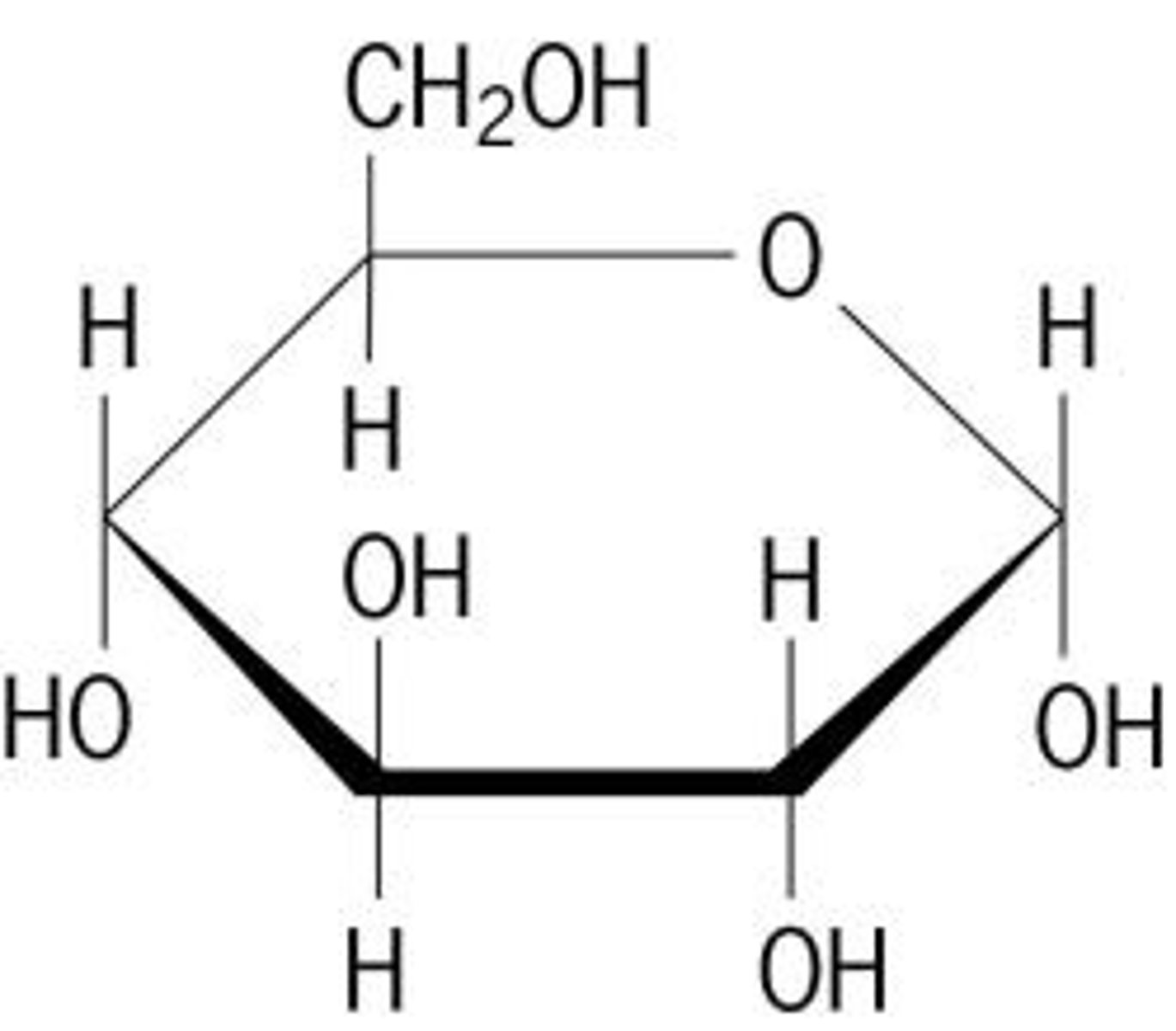
monosaccharide structural formula
polysaccharide structural formula
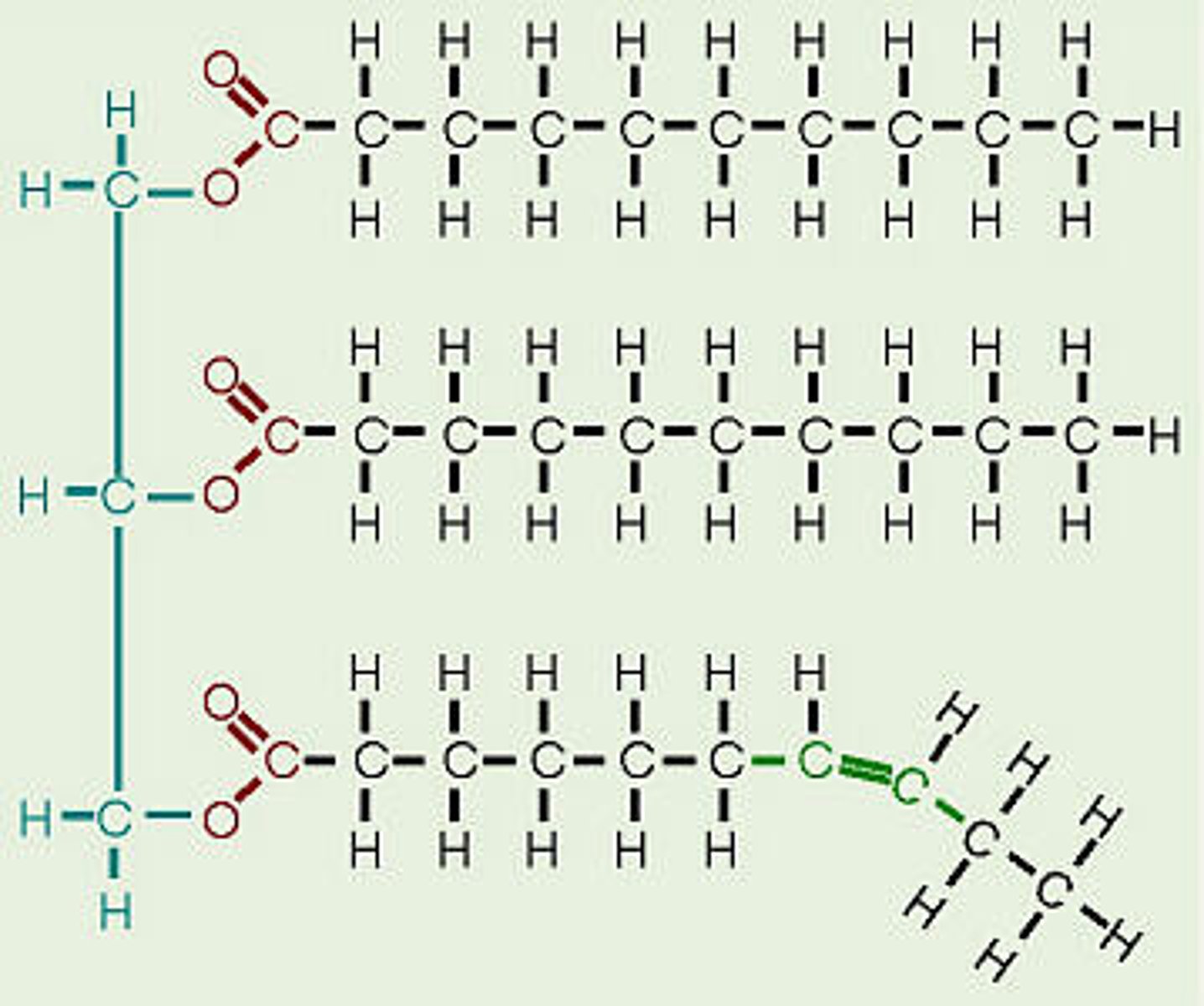
lipid structural formula
Atom
The basic building block of matter
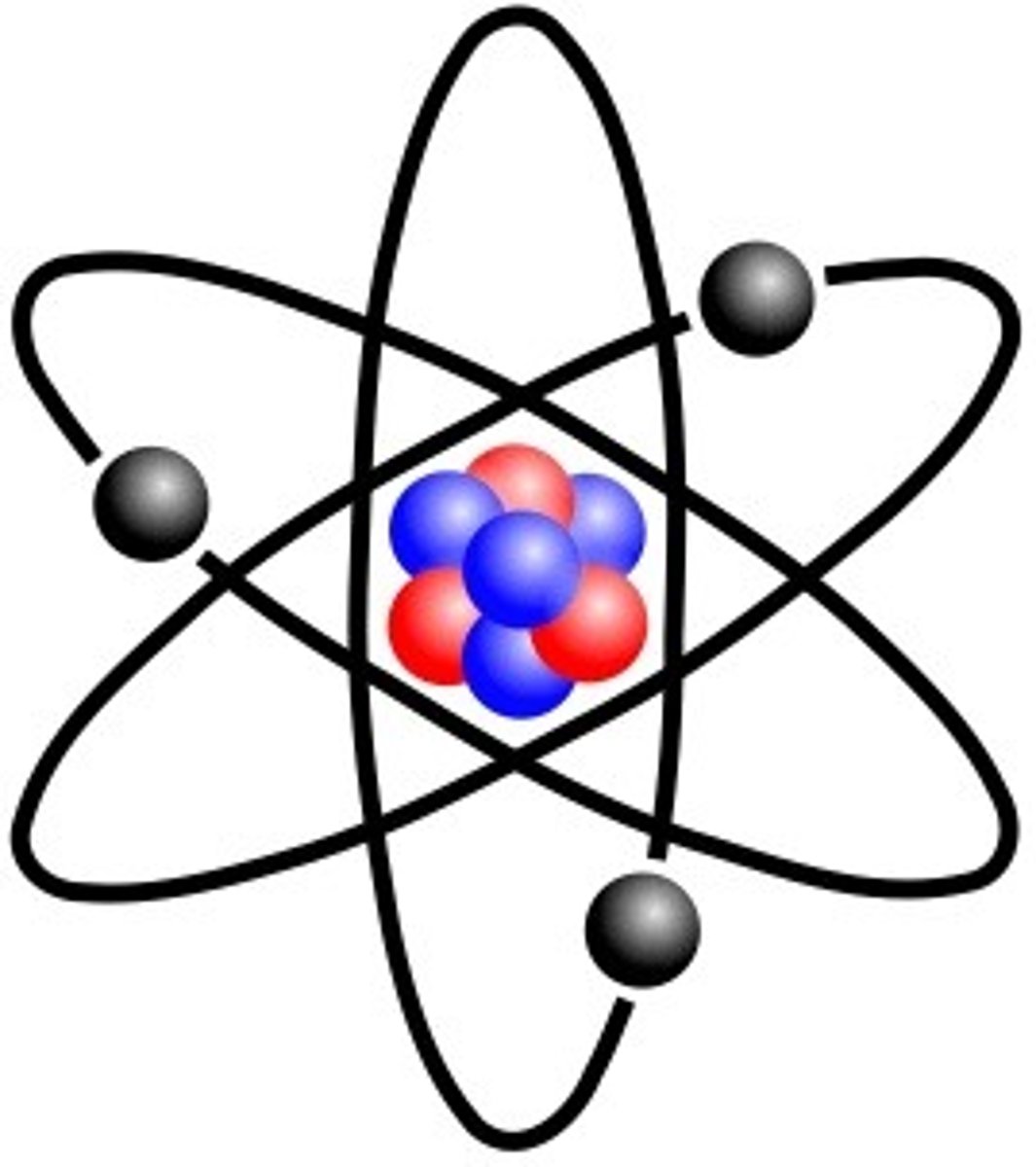
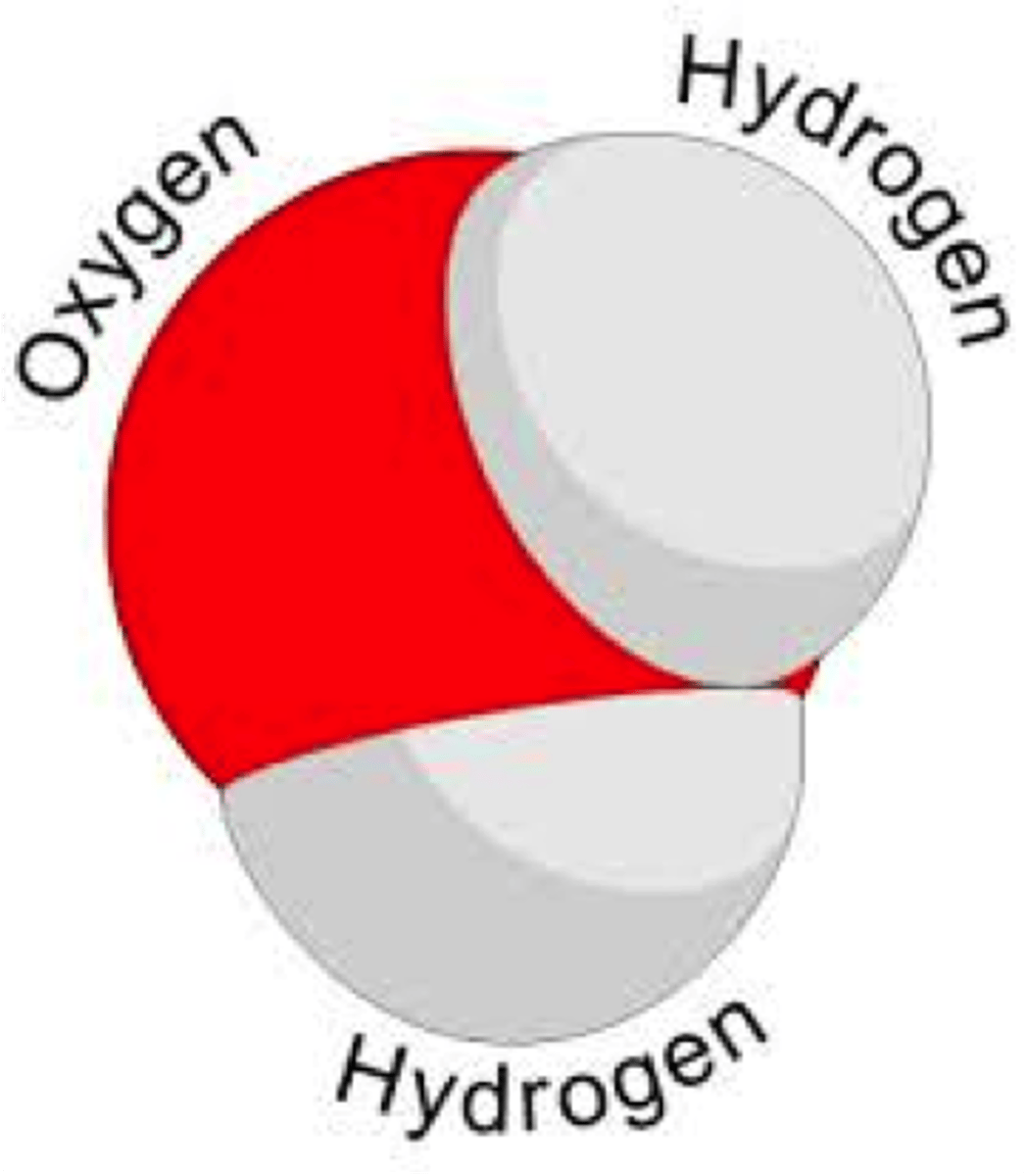
Molecule
Two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
Cell
The basic unit of structure and function in all living things