synaptic plasticity
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
prenatal development
pattern of connections emerges as a result of cell recognition events
an axon guidance mechanism gets axons in approximately the right place
there is a coarse retinotopic map, but the result is not nearly as good as normal retinotopy found in the adult → requires a second stage in development
postnatal development
prenatal coarse pattern of connections refined by activity dependent mechanisms
based on interactions between organism and its environment
the influence on the environment on the brain changes with age
ocular dominance columns
L/R segregated in layer 4C
don’t see it in newborn cat
above and below layer 4, binocular, but dominated by one eye or the other
extend from pia to white matter
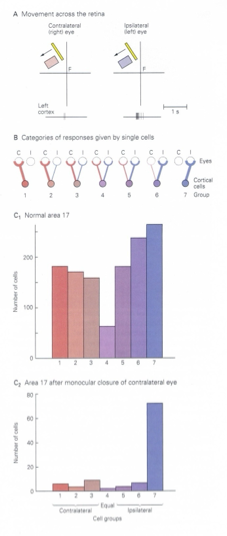
Hubel and Weisel OD column demonstration
divided OD columns into 7 groups
1-7 contralateral → ipsilateral
experiment: sutured one eye shut at birth, raised monkey to 6 months, removed sutures and tested deprived animal’s visual responses
V1 cells only driven by non-deprived eye
monocular deprivation from birth-6 weeks in monkey, 12-13 weeks in cat → no binocular interactions
after this critical period, no effect of monocular deprivation
critical period in development
time period in dvlpment when genetically determined patterns of brain circuitry are subject to environmental refinement
cortex can change its wiring to appreciate the different input from the two eyes
imprinting
critical period is 2 days after hatching
ambliopia
animals cortically blind in deprived eye
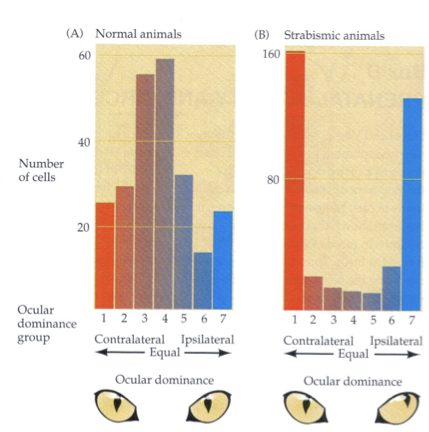
Comparing monocular, binocular, and alternating deprivation
Monocular: ambliopia
Binocular: normal distribution, but cells not quite normal → poor acuity
Alternating: OD bands sharper than normal, no binocular vision
alternating deprivation
no binocular cells, no 3D depth perception
strabismus (eye misalignment) gives same results → eventually lead to ambliopia
critical period for normal binocular vision development in humans
2-4 years
Child with strabismus
initially has good vision (acuity), but cannot fuse image in 2 eyes because they favor one eye
opthamologists used to delay correcting until 8/9, after critical period → children got amblopia
mild strabismus: patch good eye for a few hours/day, strengthens eye muscles for alignment
severe strabismus: surgical intervention to realign eyes
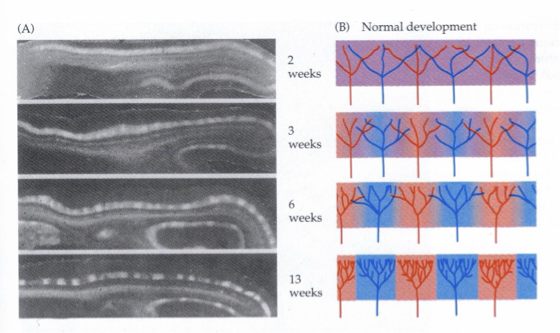
Formation of ocular dominance columns
each projection initially spread out over full neural space of layer 4, trying to form their own topographical map of the retina
In monocularly deprived eyes during critical period, deprived eye is at competitive disadvantage→ non-deprived eye continues to occupy cortical space they normally would have given up to the other eye
competition for target space between fibers from the 2 eyes
cooperation between fibers from the same eye
neural activity: critical factor regulating both competition and cooperation
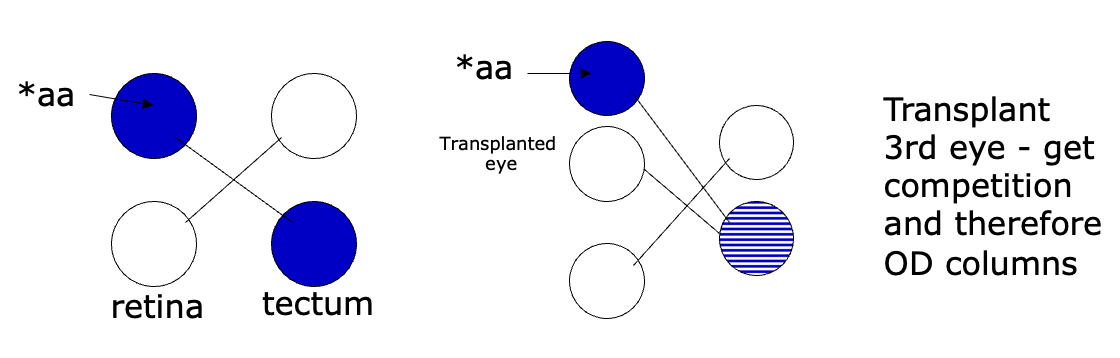
Evidence of competition for target space between fibers from the 2 eyes
monocular deprivation → competition reduced
inputs from open eye form complete topographic map
frog optic tectum: no competition → no columns
evidence for cooperation between fibers from the same eye
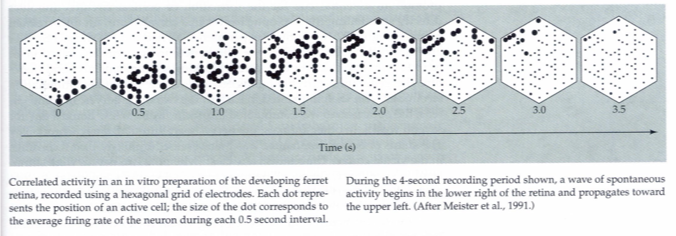
retinal fibers spontaneously active in utero
retinal neighboring cells tend to be active together, firing in synchronous bursts
neighboring cells have similar patterns of activity (correlated activity) → LGN → cortex
activity patterns in two eyes not correlated with each other
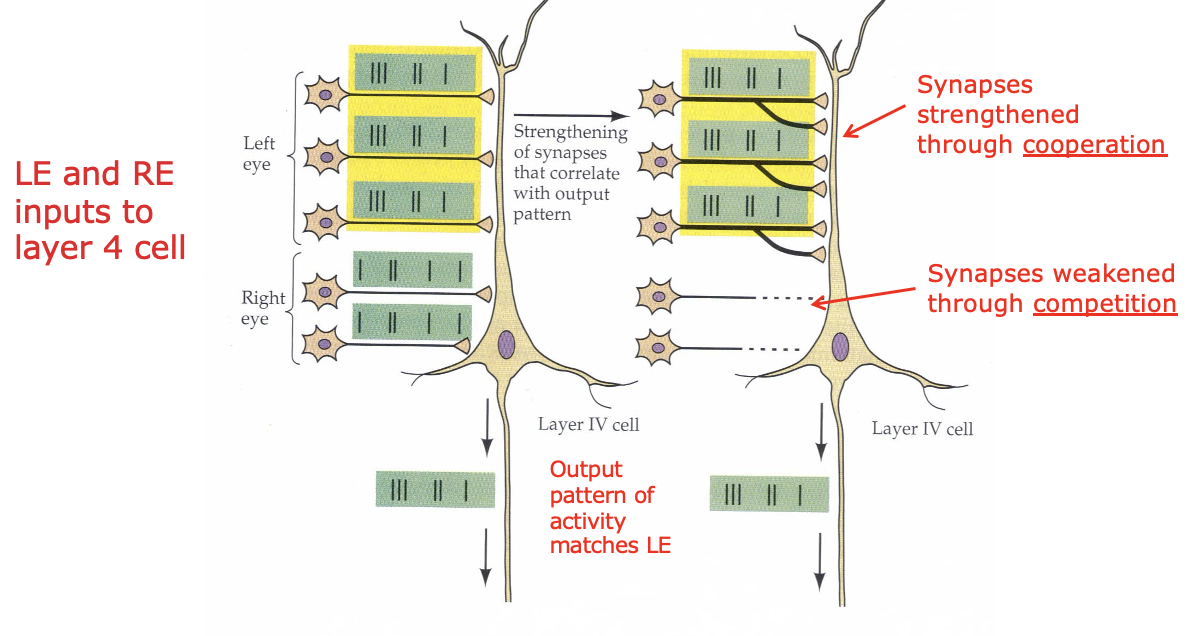
Strengthening/weakening synapses through cooperation/competition
excited neurons synapses that are active together strengthened
inactive/out of synchrony synapse fibers weakened
results in precise retinotopic map and segregation of L/R eye influences in layer 4C
Hebb’s postulate for learning
coincident activity in pre and postsynaptic elements of a synapse leads to its strengthening
things that fire together, wire together
strengthening of synapses in developing V1 is mediated by NMDA-receptor dependent mechanism
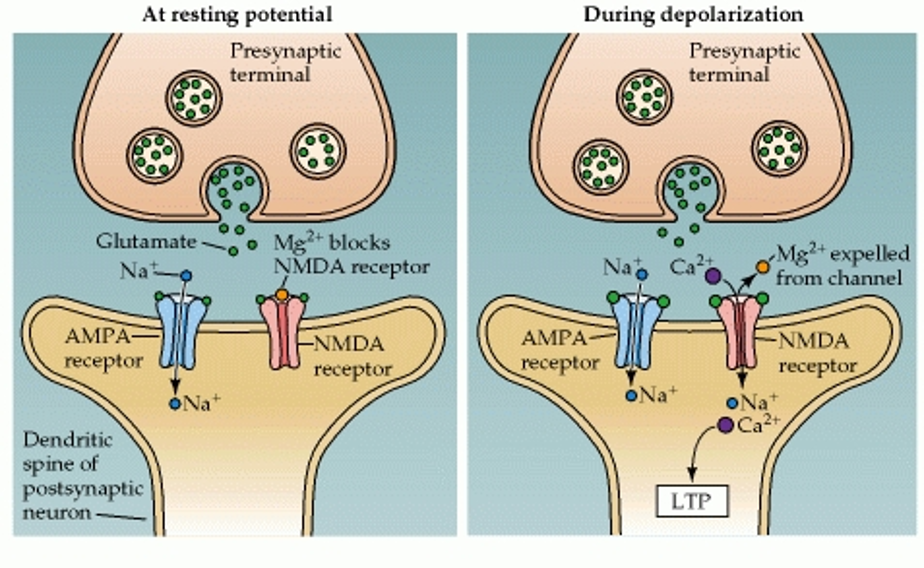
NMDA receptor
glutamate receptor
ligand and voltage gated ion channel (coincidence detector)
at resting Vm, Mg2+ blocks channel
depolarization → Mg2+ removed (+ ion repelled by positively charged inside)
When nearby retinal ganglion cells fire at the same time → combined signals add up in the postsynaptic neuron
postsynaptic neuron’s Vm rises enough to kick out the Mg2+ block
NMDA receptors open → Ca2+ enters
activates signaling pathways inside the neuron → strengthens the synapses that were active
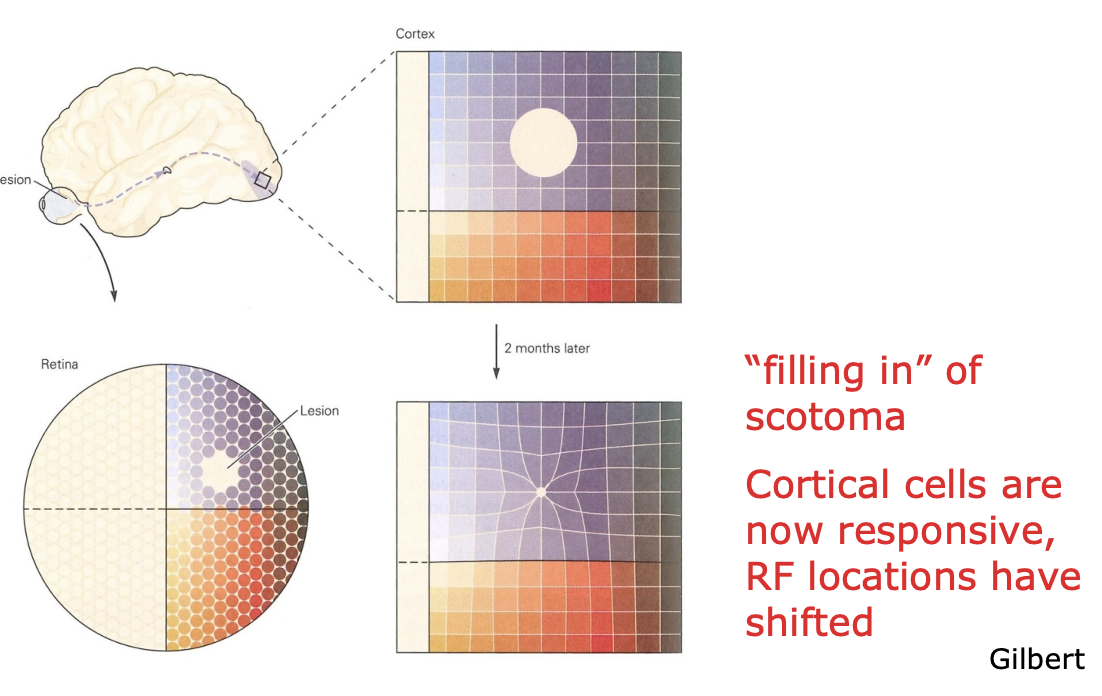
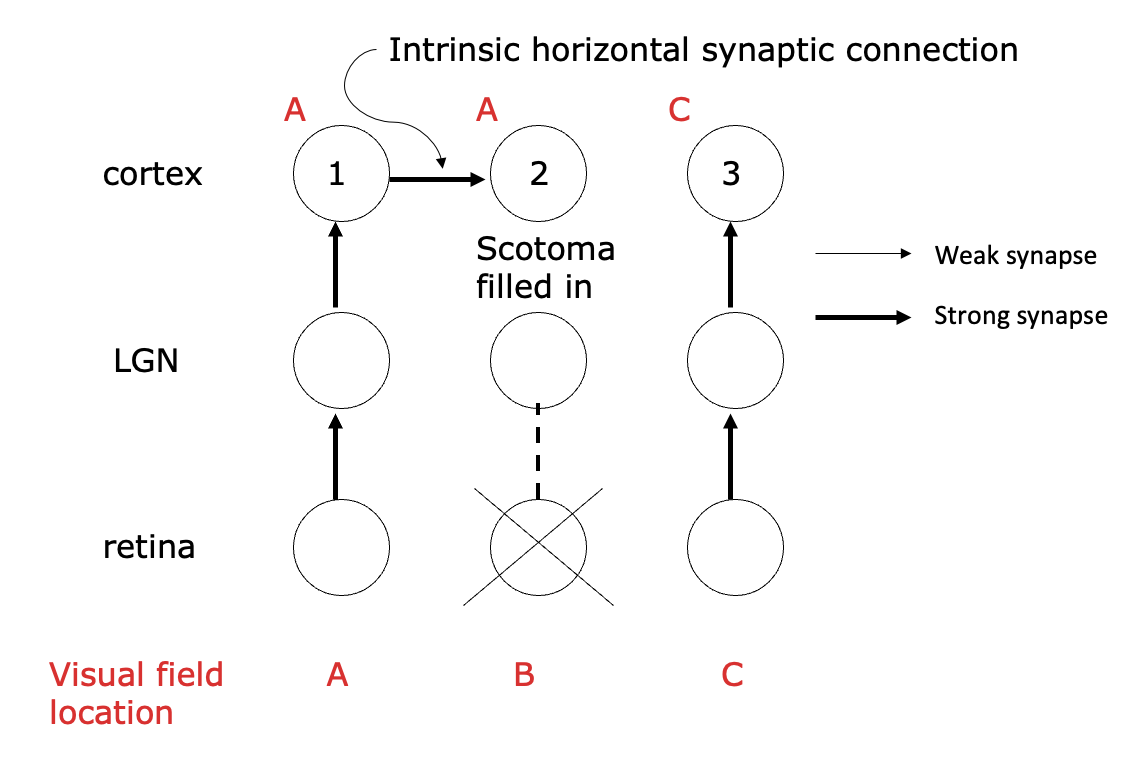
Effect of retinal lesions on cortical topography: plasticity in adult visual system
Visual space is organized like a grid on the retina
A small, targeted retinal lesion is made with a laser.
When the visual cortex is mapped right after, the part that normally gets input from that damaged retinal spot becomes silent (a cortical scotoma).
After about two months, mapping again shows that those previously silent neurons now respond, but to areas just outside the damaged region. Their receptive fields have shifted to the edges of the scotoma.
As a result, the region of cortex representing the area around the lesion becomes enlarged, effectively “filling in” the missing visual space.
intrinsic horizontal synaptic connection
V1 circuits that connect nearby columns with similar orientation tuning
can be strengthened through cortical map modifications
Long-range horizontal connections
Patchy, clustered similar connections linking distant orientation domains
perceptual learning
requires plasticity in cortical connections
task-specific