UTS midterm
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Psychology
The study of how our minds work and how they influence our actions. It helps us understand our thoughts and behaviors better.
Sense of Self
The way a person thinks about and views his or her traits,
beliefs and purpose within the world.
Sigmund Freud
Has a theory about the unconscious and also, about sexual development.
ID, EGO, SUPER EGO
FREUD’S PERSONALITY COMPONENTS
ID
-Operates on the pleasure principle.
-It focuses on immediate gratification or satisfaction of its needs.
-Too much leads to impulsive behavior.
EGO
-Operates using the reality principle.
-It is aware that others have also needs to meet.
-It is practical since it reasons and considers the best response to situations.
SUPER EGO
-It embodies a person’s moral aspect ; operates on the morality principle.
-It is likened to conscience because it exerts influence on what one considers right or wrong.
The Unconscious, The Conscious, The Subconscious, Nonconscious
TOPOGRAPHICAL MODEL
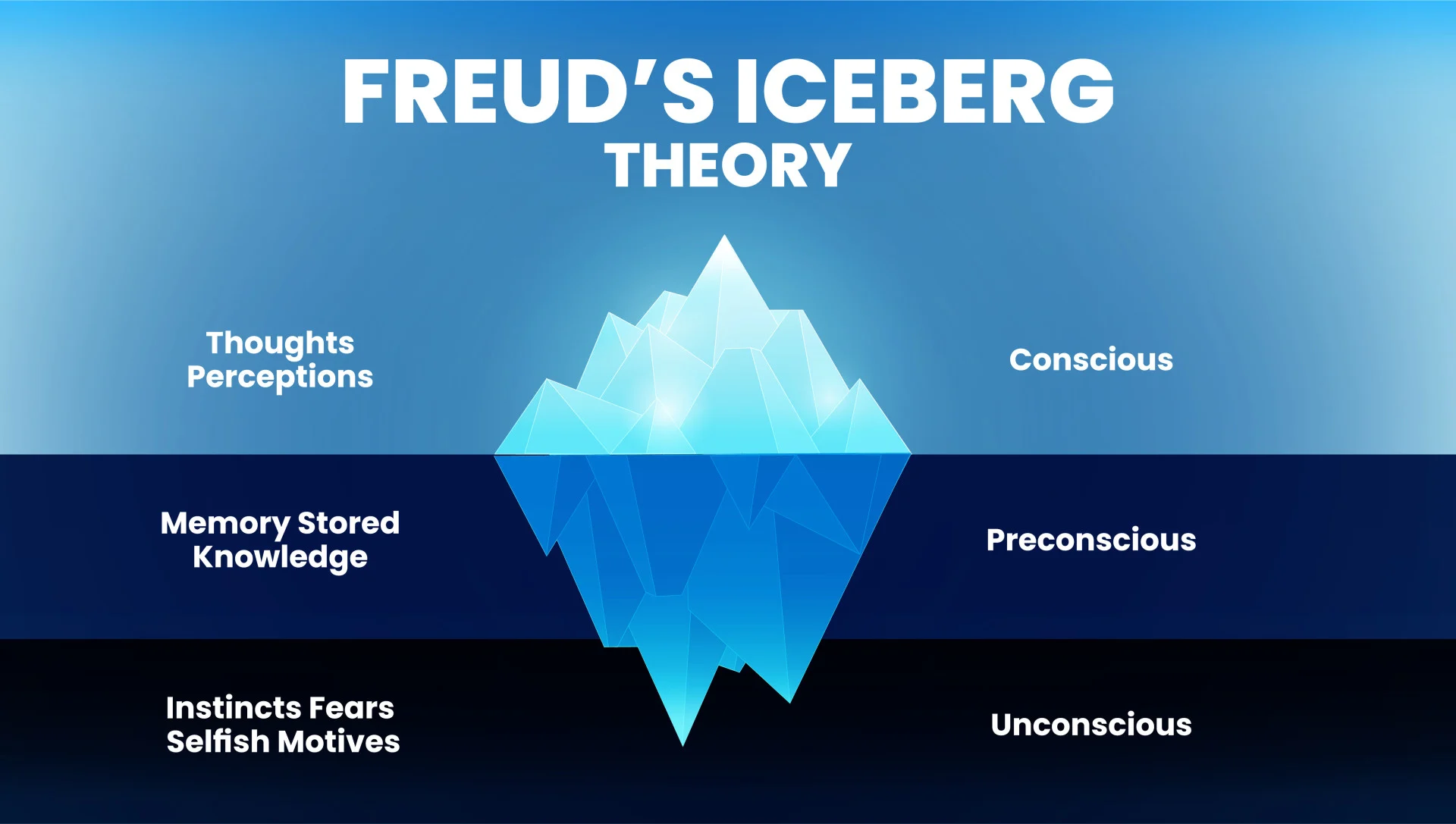
The Unconscious
-Most of what influences us.
-Influences our thinking, feeling, and doing in perhaps dramatic ways.
Teacher's examples: Traumas - "Why am I afraid?"
The Conscious
-All that we are aware of.
-Only comprises a very small part of who we are.
-Hidden and out of reach.
The Subconscious
Part of us that we can reach if prompted but it is not our active conscious. (some things trigger it)
Nonconscious
All that we are not aware of, have not experienced, and have not been made part of our personalities. (you're literally not aware)
Wilhelm Wundt
Father of psychology
William James
IDK
leads to impulsive behavior.
what happens if the id is dominant?
Easily taken advantage of
what happens if the superego is dominant?
indecisiveness
what happens if the ego is dominant?
William James
He defined psychology as the study of consciousness, believing it is what makes mental life possible. He aimed to understand how human consciousness helps people survive and adapt to their environment. (external self - Freud was internal)
I and Me
Two aspects of the self: according to William James
I (Self-as-a-subject)
-"The thinker does the thinking."
-Pure ego (It isn’t an object like hair, clothes, or reputation; it’s the ongoing sense of being the subject.)
-Knows who he is and what he has done in his life.
Outside teacher’s explanation:
-It is a subjective self that is aware of its own actions - the performer of the action
Me (Self-as-an-object)
-"The empirical me." (observation)
-Separate object or individual a person refers to when describing his personal experience. (Naka kita kog kulog, kulot sad baya ko)
Outside teacher’s explanation:
-It is the self that is an object or the self you can describe.
“They think of me as ugly.” “They think of me as friendly.” “They think of me as religious. “
The material self
The social self
The spiritual self
James Theory of the Self
The material self
The core of the blank is the body. Blank, as described by William James, refers to the physical possessions and relationships a person considers as part of their identity. These include the body, clothing, family, home, and other personal belongings, which reflect and express who the individual is. (external - everything you can call your own)
The social self
Represent the different ways we behave based on the social contexts we find ourselves in. For instance, a person might act formally and reserved at work with their boss, but be relaxed and informal when hanging out with friends, showing that we adapt behavior to fit various social situations. (different personas)
The spiritual self
For William James, blank represents who we truly are at our core, encompassing aspects like personality, values, and conscience that remain stable throughout life. He believed that deeply understanding this inner self, through introspection and self-reflection, is more fulfilling than focusing on social status or material possessions. (your core, the voice inside yourself = internal > values and principles)
Western culture
Individualistic
Emphasizes the individual
Western Culture’s focus
Loose associations, less loyalty to groups
Western Culture’s group relations
Straightforward and forceful
Western Culture’s communication style
competitive, promoting fair competition
Western Culture’s decision making
Emphasis on individual equality and rising above others
Western Culture’s values
Focus: Emphasizes the individual
Western Culture:
People value personal goals, independence, and self-expression over the needs of the group. Success is often measured by personal achievements rather than group accomplishments.
Example: A student chooses a career path in art even if their family prefers business because they prioritize their own passion and identity.
Group relations: Loose associations, less loyalty to groups
Western Culture:
Individuals tend to join groups temporarily and may leave when their personal interests are no longer served. Loyalty to organizations, communities, or even extended families is weaker compared to personal goals.
Example: An employee resigns from a company after receiving a better job offer elsewhere, showing less obligation to stay out of loyalty.
Communication style: Straightforward and forceful
Western Culture:
People are encouraged to express their opinions directly, even if it may sound blunt or confrontational. Honesty and clarity are valued more than preserving harmony in conversations.
Decision making: competitive, promoting fair competition
Western Culture:
People are encouraged to make choices that highlight their strengths and give them an advantage over others. Competition is seen as healthy because it motivates individuals to improve and prove their capabilities. (it means making each other improve using their strengths)
Values: Emphasis on individual equality and rising above others
Western Culture:
Society promotes the idea that everyone has equal rights and opportunities, regardless of background. At the same time, individuals are encouraged to strive harder to stand out and achieve personal success.
Eastern Culture
Collectivistic
Emphasizes the group and social relations
Eastern culture’s focus
Focus: Emphasizes the group and social relations
In collectivistic cultures, the well-being of the group is prioritized over individual desires. People find identity and purpose in harmony within their families, communities, or workplaces.
Strong loyalty to groups
Eastern culture’s group relations
Group relations: Strong loyalty to groups
Members of a group, such as family, friends, or organizations, are expected to remain loyal and supportive. Betraying or abandoing a group is seen as dishonorable and damaging to relationships.
More compromising, indirect, hoping for understanding
Eastern culture’s communication style
Communication style: More compromising, indirect, hoping for understanding
People often communicate in ways that avoid confrontation and preserve harmony. Subtle hints, tone of voice, and nonverbal cues are used to express meaning rather than blunt words.
Values cooperation, emphasis on hierarchy for harmony
Eastern culture’s decision making
Decision making: Values cooperation, emphasis on hierarchy for harmony
In collectivistic cultures, decisions are often made with group consensus in mind. Prioritizing cooperation over competition. Respect for elders or leaders plays a key role, as their authority helps maintain unity and order.
Example: mananghid daan before mo lakaw
Emphasis on maintaining harmony and order within the group
Eastern culture’s values
Values: Emphasis on maintaining harmony and order within the group
Group stability is more important than individual ambition, so actions are guided by what will preserve peace. Avoiding conflict and showing respect for traditions are central to maintaining good relationships.
Confucianism, Taoism, Buddhism
Religious beliefs
Confucianism (Code of ethical conduct)
Emphasizes a moral framework that teaches people how to live with integrity, respect, and responsibility. It provides rules of behavior that shape personal character and guide interactions within society.
Example: a student shows respect by bowing to their teacher and listening attentively, reflecting proper conduct taught by Confucian values.
Guide's how people should act in their relationships for a harmonious social life - the philosophy stresses the importance of fulfillng one's role in family, community, and society to create order and peace. Harmony is achieved when everyone understands their duties and behaves according to respect, loyalty, and kindness.
Taoism
Living in harmony with the TAO (universe) - It teaches that people should align themselves with the natural flow of the universe rather than resist it. By following the universe, one finds peace, balance, and simplicity in life.
Rejects fixed definitions, seeing the Tao as free-flowing, relative, unified, and paradoxical - The Tao cannot be strictly defined because it represents the ever-changing interconnected essence of life. It embraces flexibility, paradox, and openness to multiple truths rather than rigid rules.
Yin and yang is under Taoism.
Universe
What is Tao?
Buddhism
Sees the self as an illusion - it teaches the idea of a permanent, unchanging self not real; instead, we are constantly changing through experiences and conditions. Clinging to the illusion of "self" creates attachment and prevents true understanding.
Self arises from ignorance and a desire to control, leading to suffering - suffering comes from ignorance of reality and the constant craving to satisfy desires or control outcomes. By letting go of attachment and practicing mindfulness, one can reduce suffering and find peace. (letting go of the unneeded baggage)
(Culture > (Society (everyone around you) > (Self (you're influenced)
The three circles
Others-awareness
Empathy > mindful of your surroundings
Confucianism
Following the book of Confucius - code of ethics