CompTIA A+ Core 1 Exam
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Input, Output, Processing, and Storage
The four main functions any computer has
Hardware
The physical parts of a computer
Software
The programs, operating systems, and drivers that instruct hardware on what to do
Firmware
Software that is embedded within hardware that must be updated through flashing
Bits
A storage unit of data that is either a 1 or 0 and is used to measure transfer data
Bytes
A storage unit of data made up of 8 bits that is used to measure storage data

USB Type A
What is this cable?

USB 2.0 Type B
What is this cable? It is often used for printers, scanners, and external drives.

USB 2.0 Type B Mini
What is this cable? It is often used for digital cameras, MP3 players, early phones, and GPS.

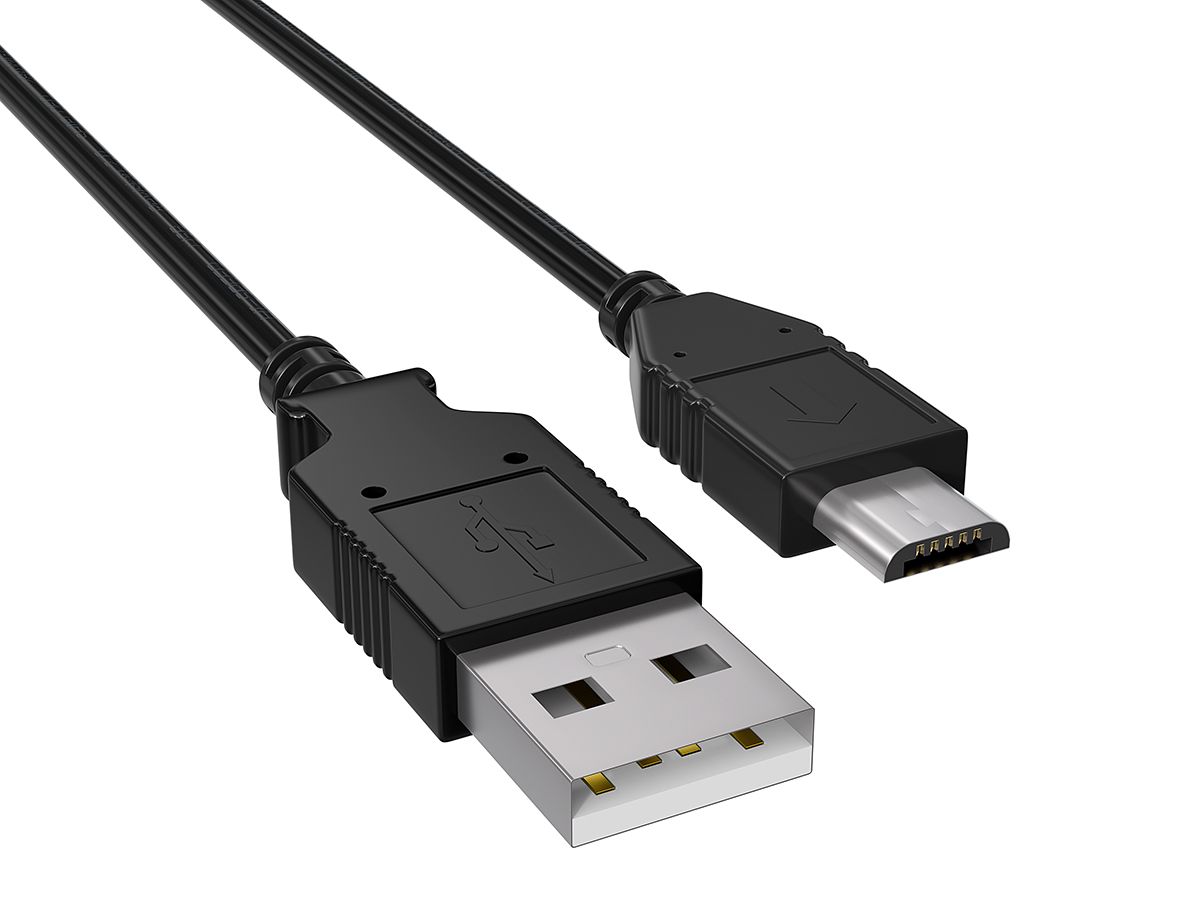
USB 2.0 Type B Micro
What is this cable? It is often used for older phones, console controllers, and some Raspberry Pi controllers.

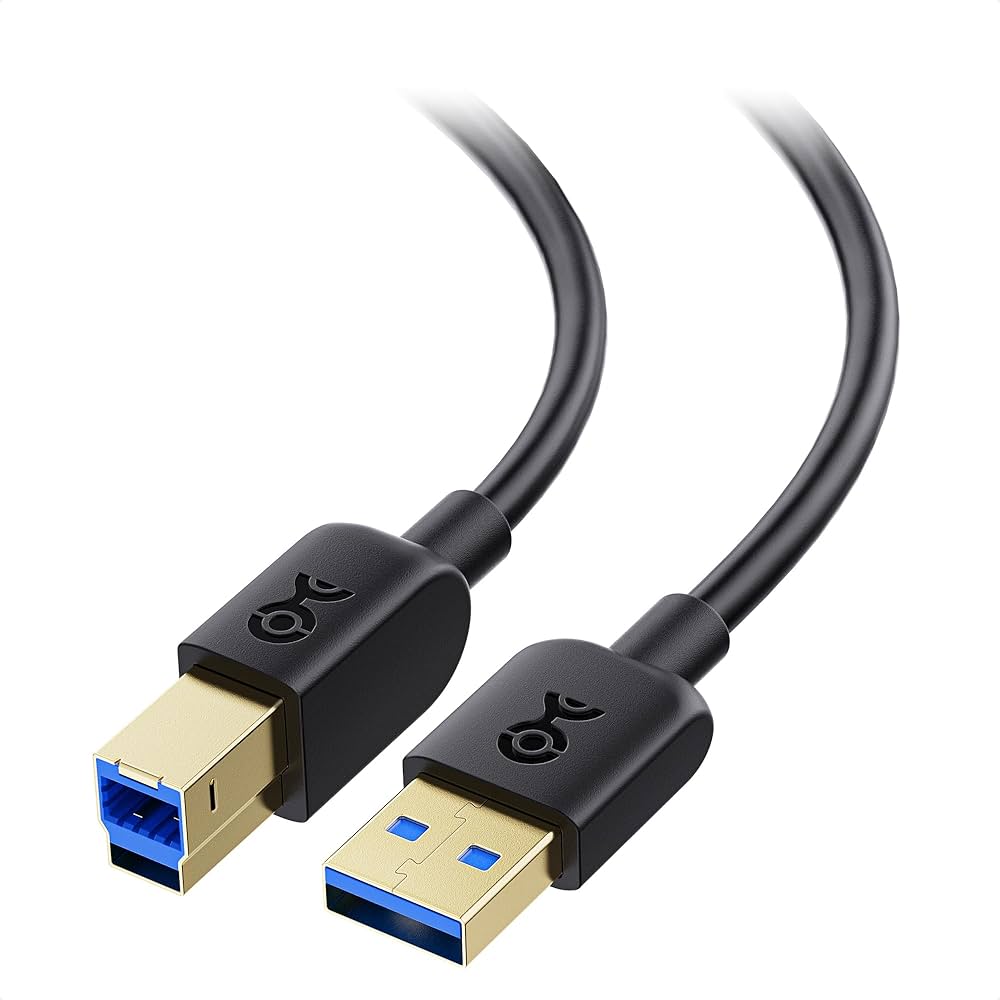
USB 3.0
What is this cable? It is used for external hard drives, webcams, printers, scanners, large audio equipment, and USB docking stations.

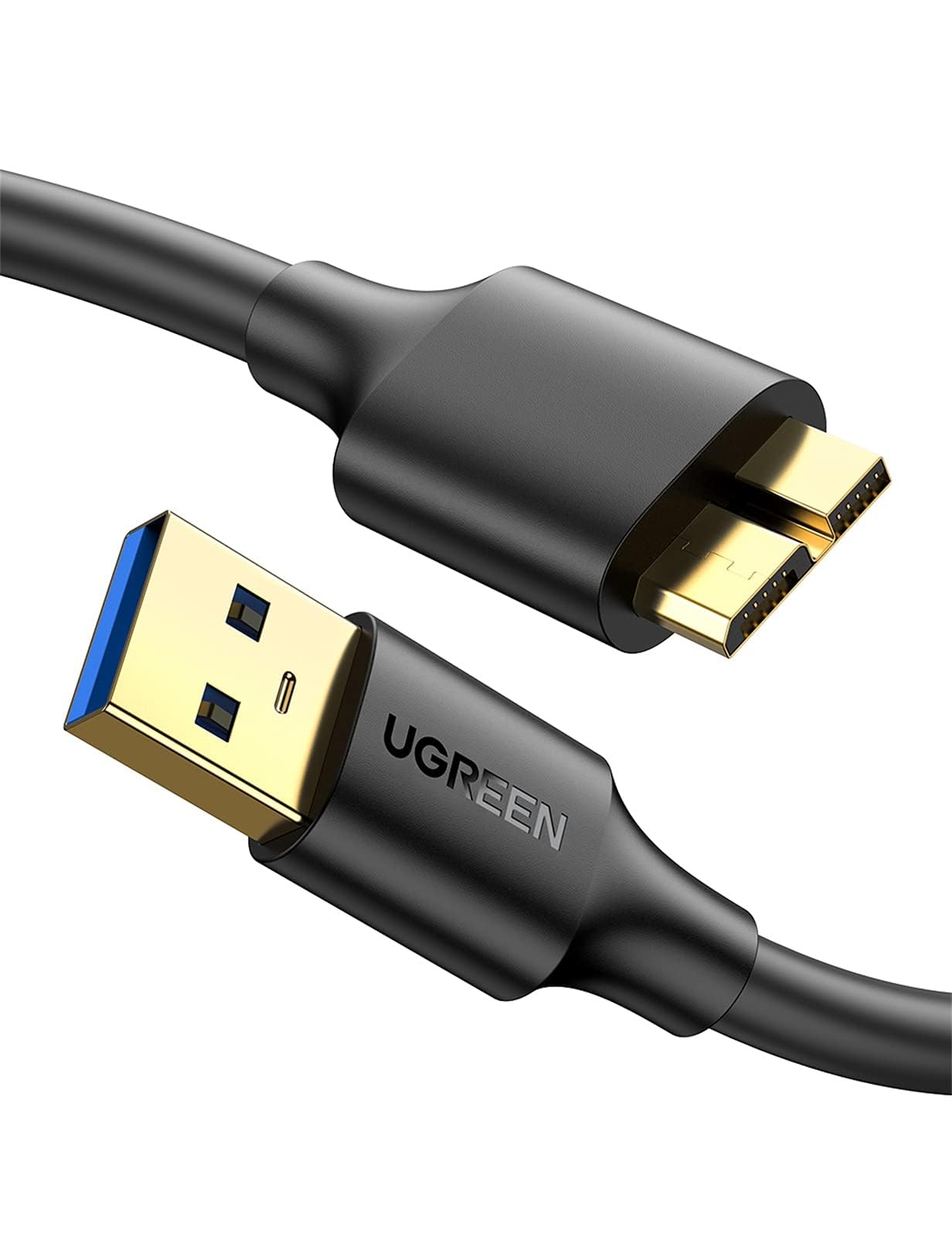
USB 3.0 Micro
What is this cable? It was used for older phones, digital cameras, GPS devices, external hard drives, and KVM switches.

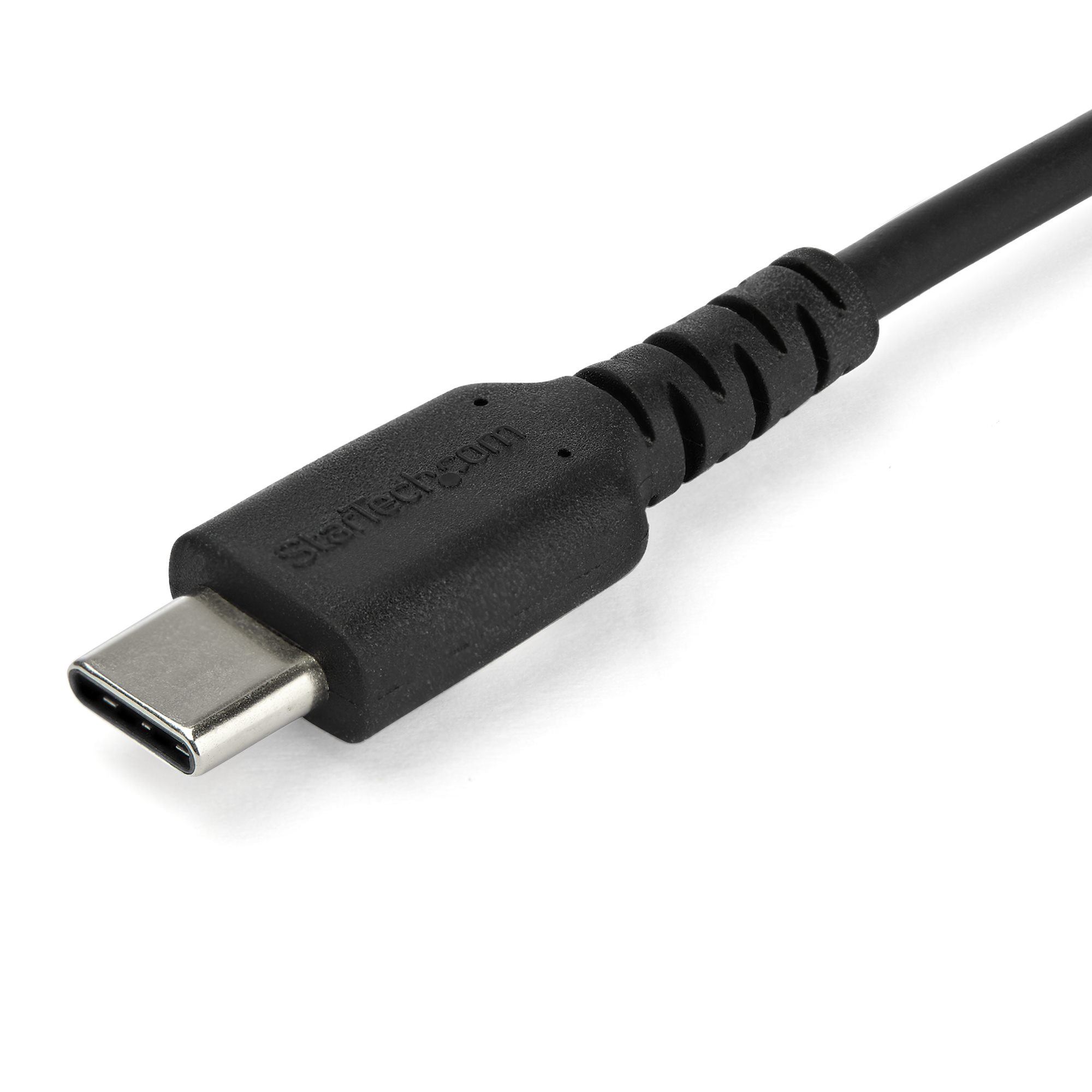
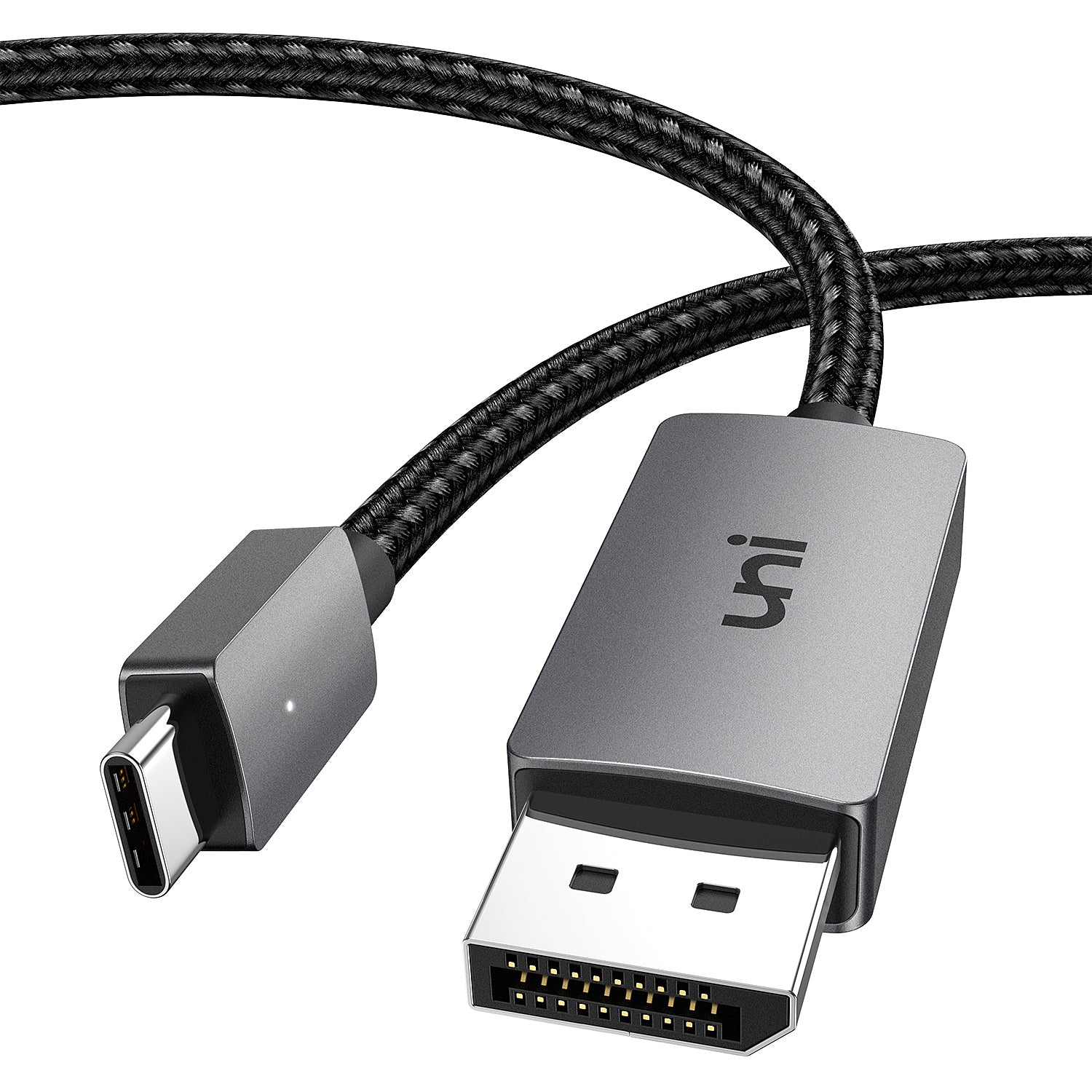
USB C
What is this cable? It is used for just about everything nowadays, utilizing USB 3.0 and 4.0 speeds. Can utilize the strength of USB to make a daisy chain of up to 127 devices. Can carry power, data, and audio/video.

DB9
What is this cable? It was used for serial communication to connect to older peripherals and other devices like mice, keyboards, modems, and printers. Serial connections only allowed for one device to one serial port, making it difficult to add many things.
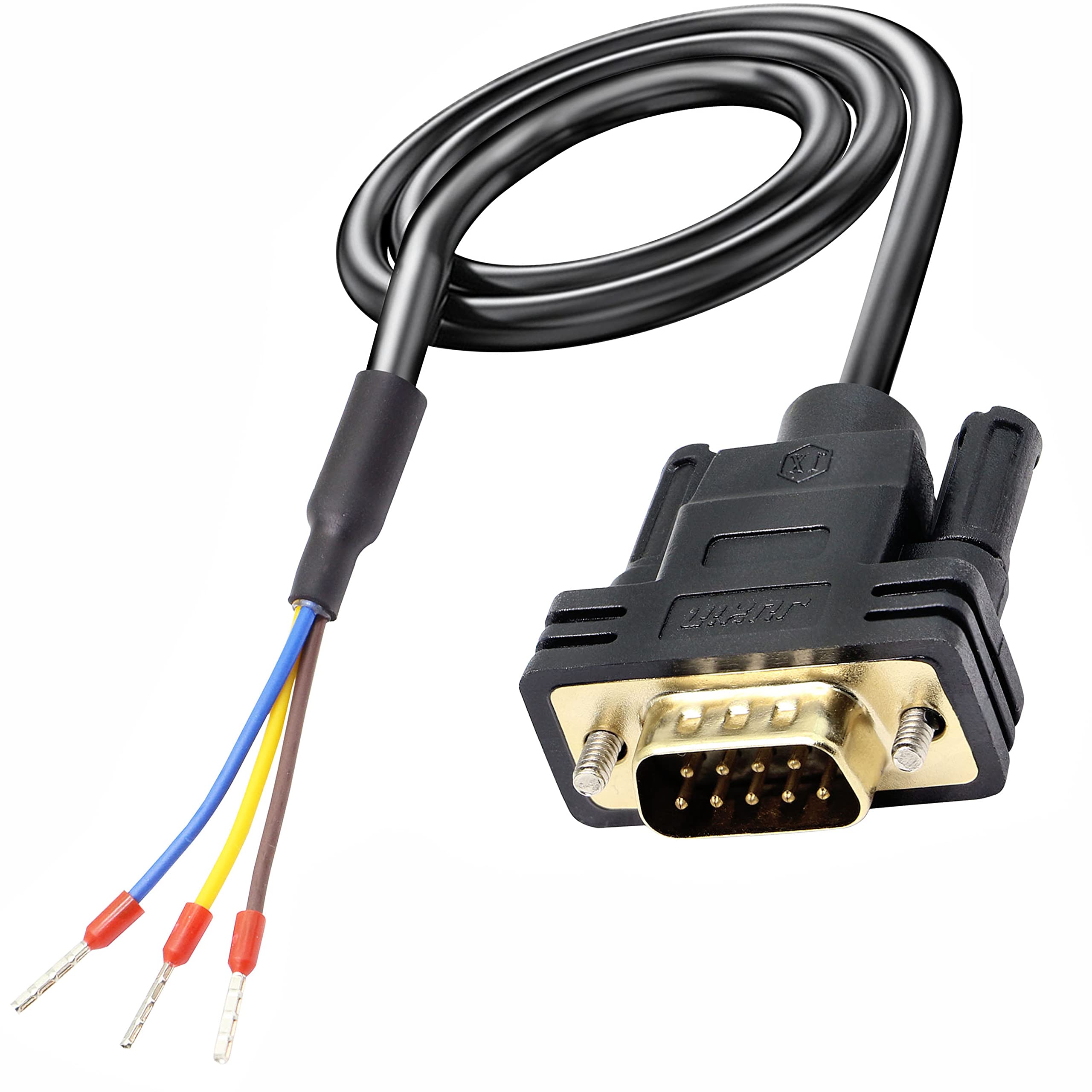

HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
What is this cable? It is a widely used video interface that allows for High Definition video and sound. Supports HDCP which is a big snitch. Has several different connector sizes for different equipment, and certain versions that specialize in high quality or data transfer.
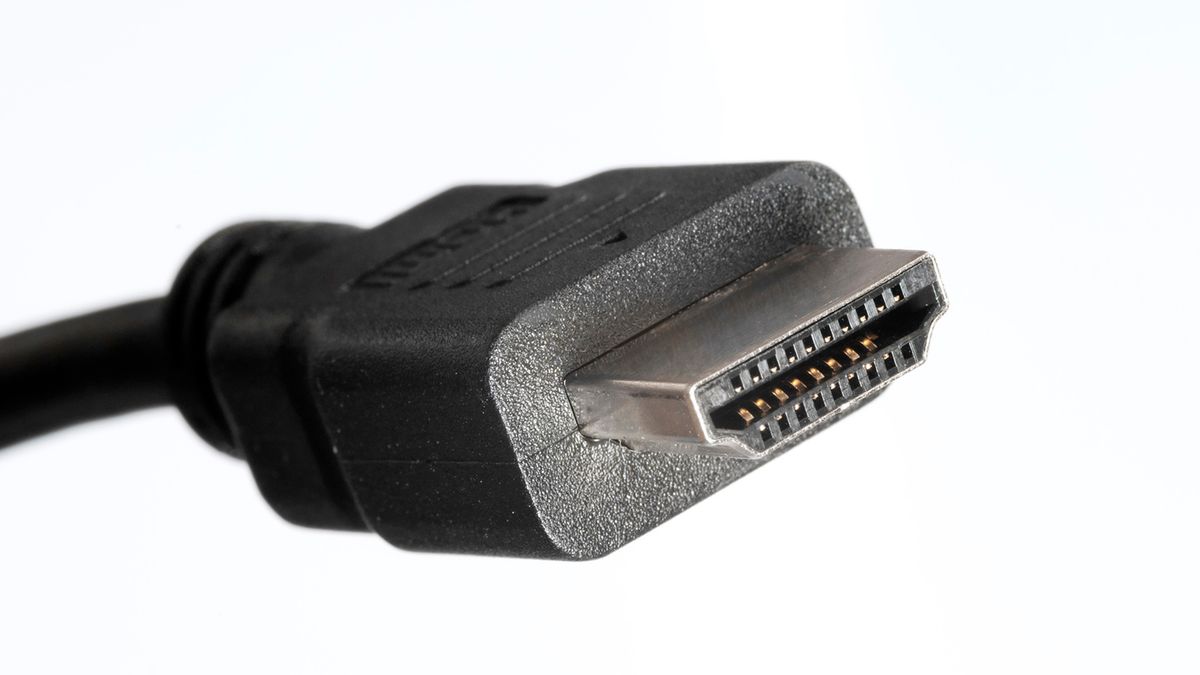

SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment)
What is this cable? It is a standard method of connecting a storage device to the motherboard inside of a desktop computer. Also used by optical drives. A 7-pin cable transfers data only and a 15-pin connector provides power only.
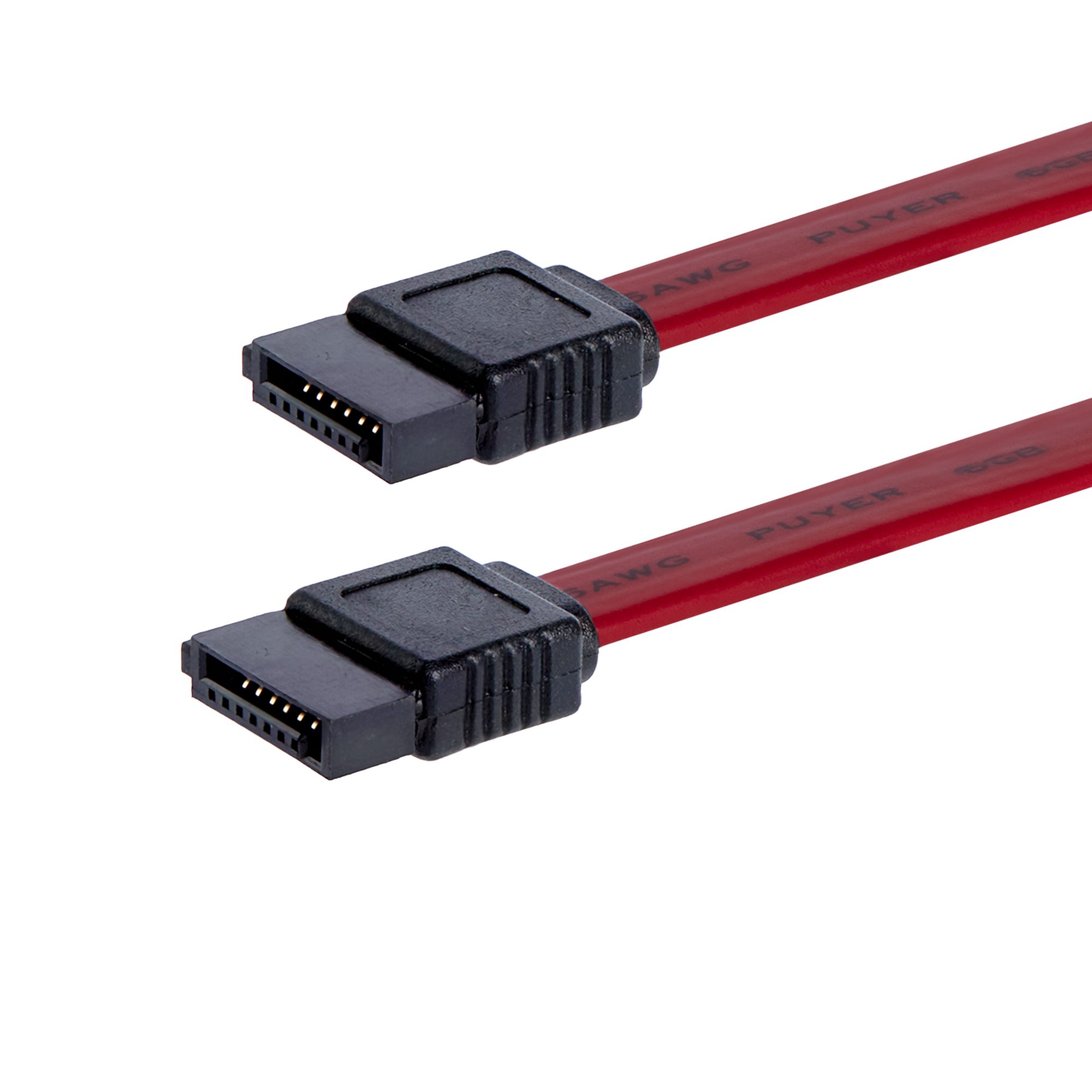

eSATA (external Serial Advanced Technology Attachment)
What is this cable? It is a method of connecting an external storage device to your computer. Faster than USB 2.0 but not as fast USB 3.0.
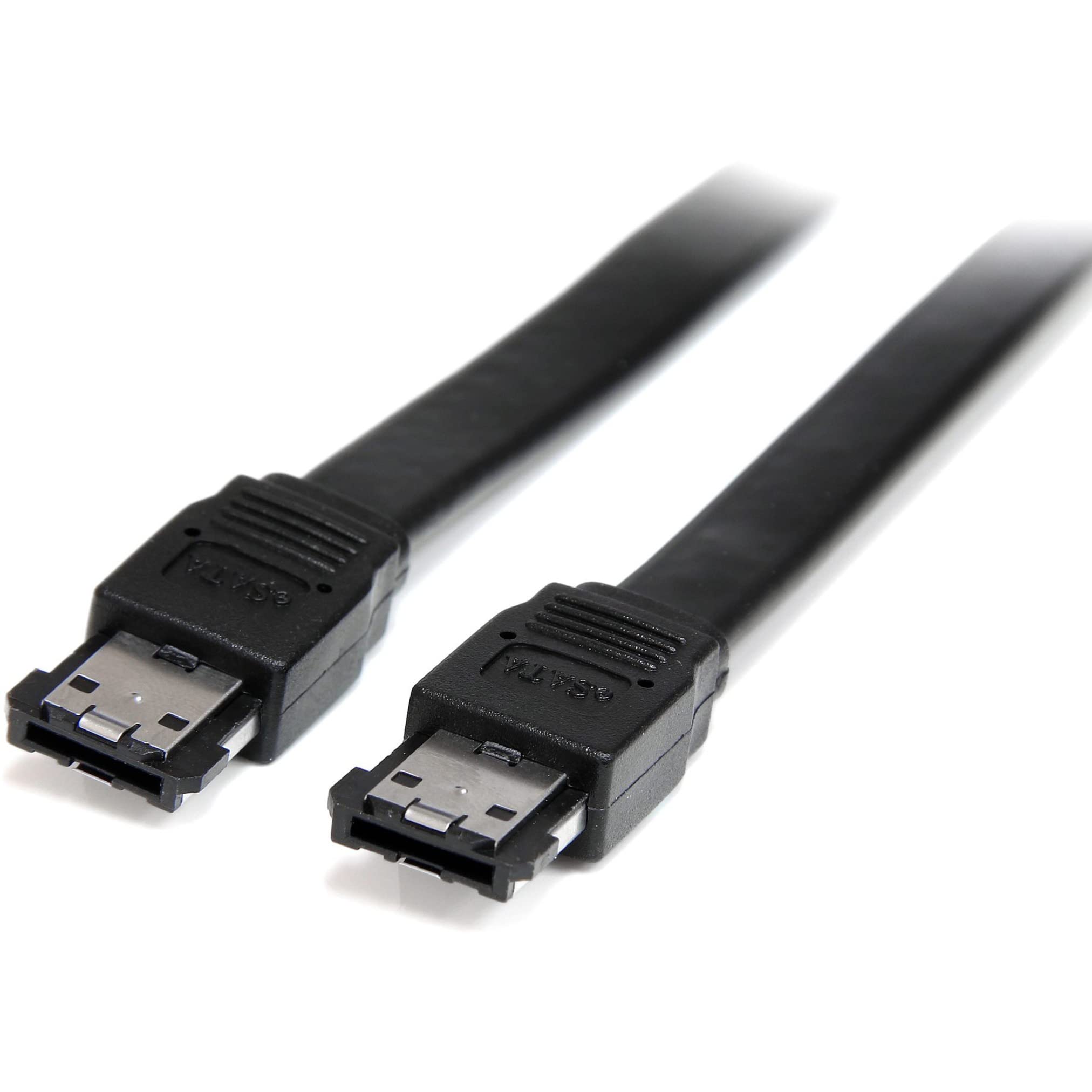

SAS (Serial Attached SCSI (Small Computer Systems Interface))
What is this cable? It was a high performance data transfer technology used mainly in enterprise environments for connecting storage devices to servers and workstations. Supported daisy chaining and backward compatible with SATA drives.
DisplayPort
What is this cable? It was developed to be a direct competitor to HDMI and can do everything that HDMI can. Has different form factors for different sizes of devices.

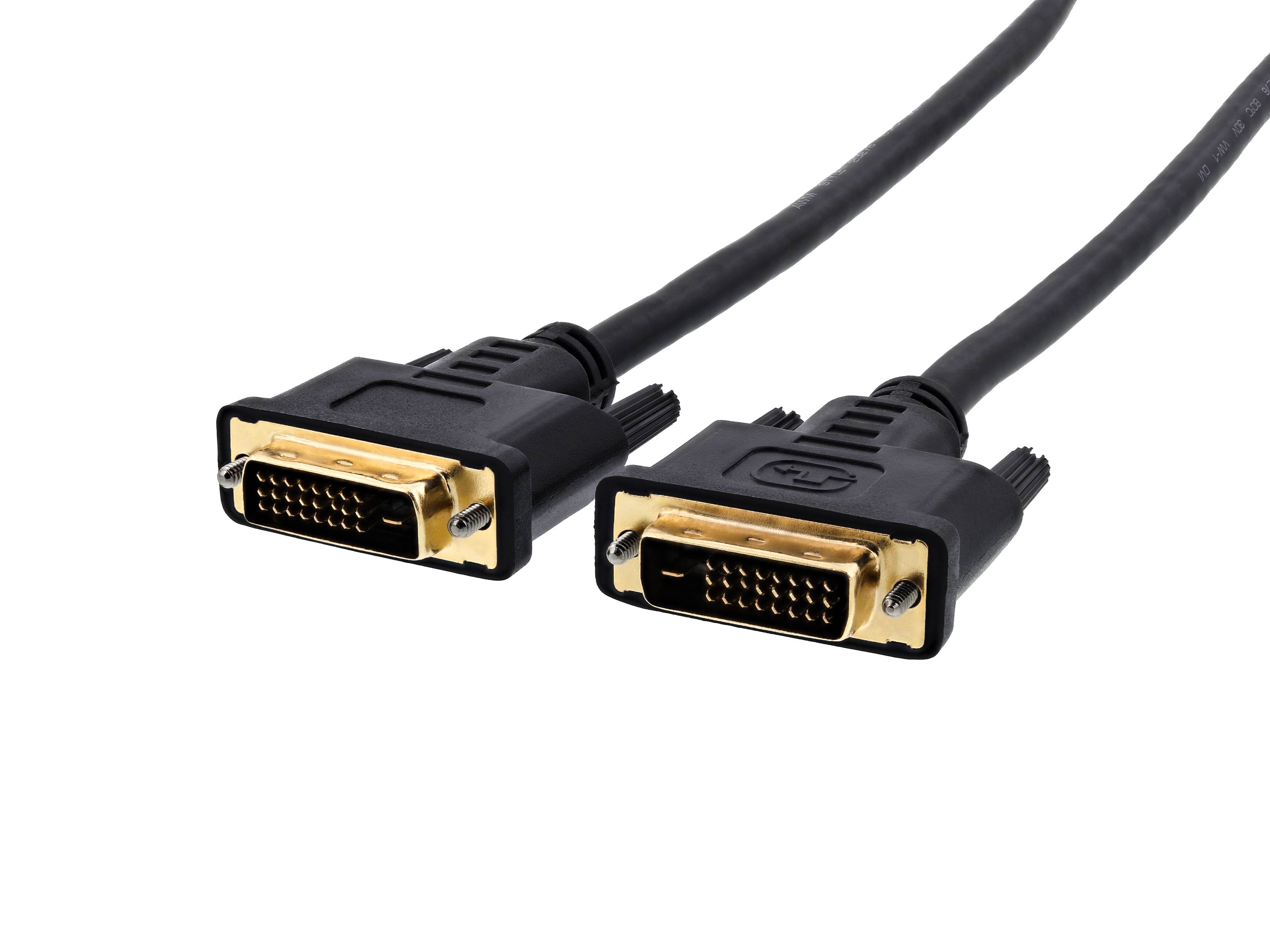
DVI (Digital Visual Interface)
What is this cable? It has versions to support analog inputs, digital inputs, or both. 29 pins for the dual analog/digital version.

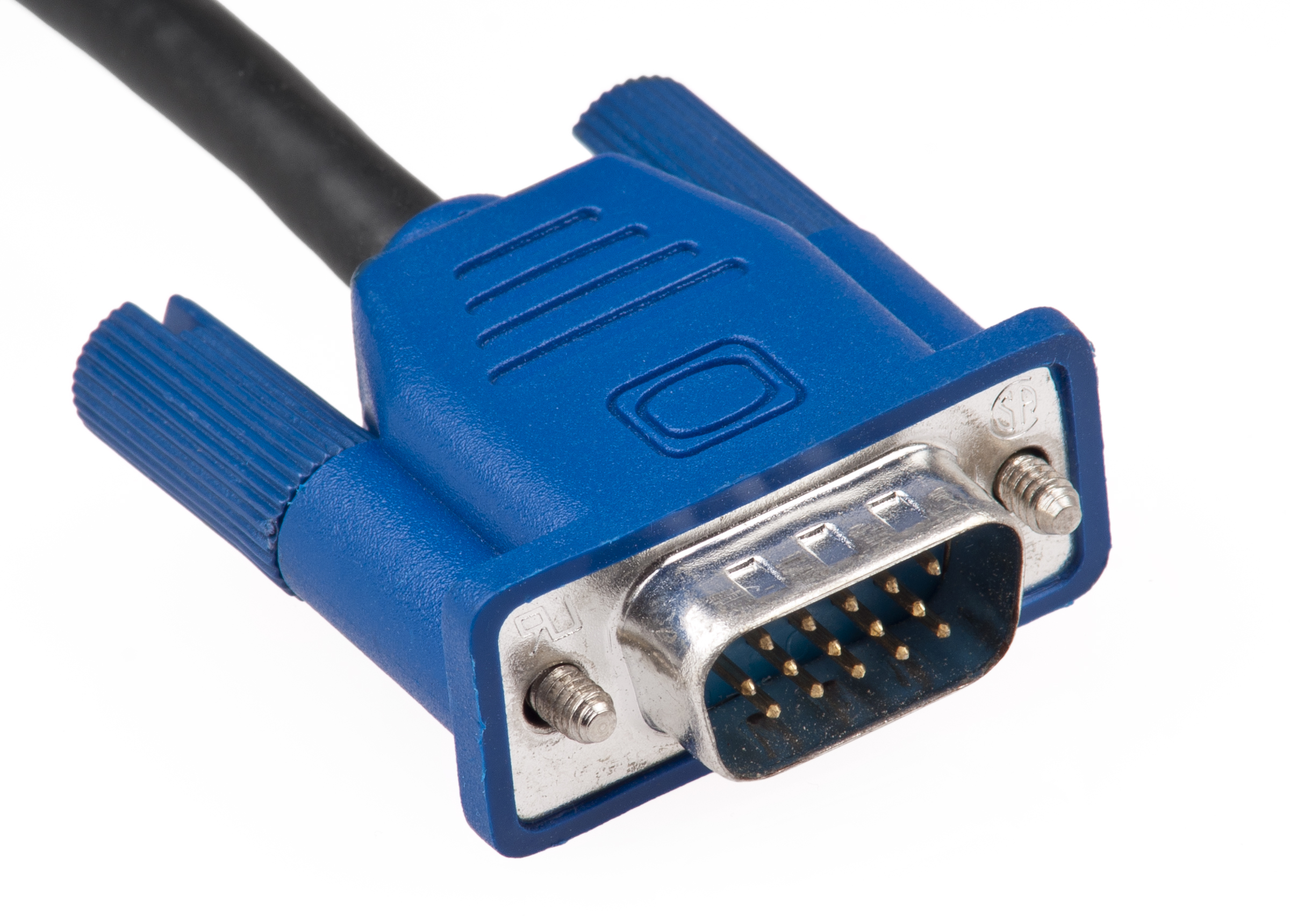
VGA (Video Graphics Array)
What is this cable? It used a 15-pin standard analog video interface port, and is usually blue!

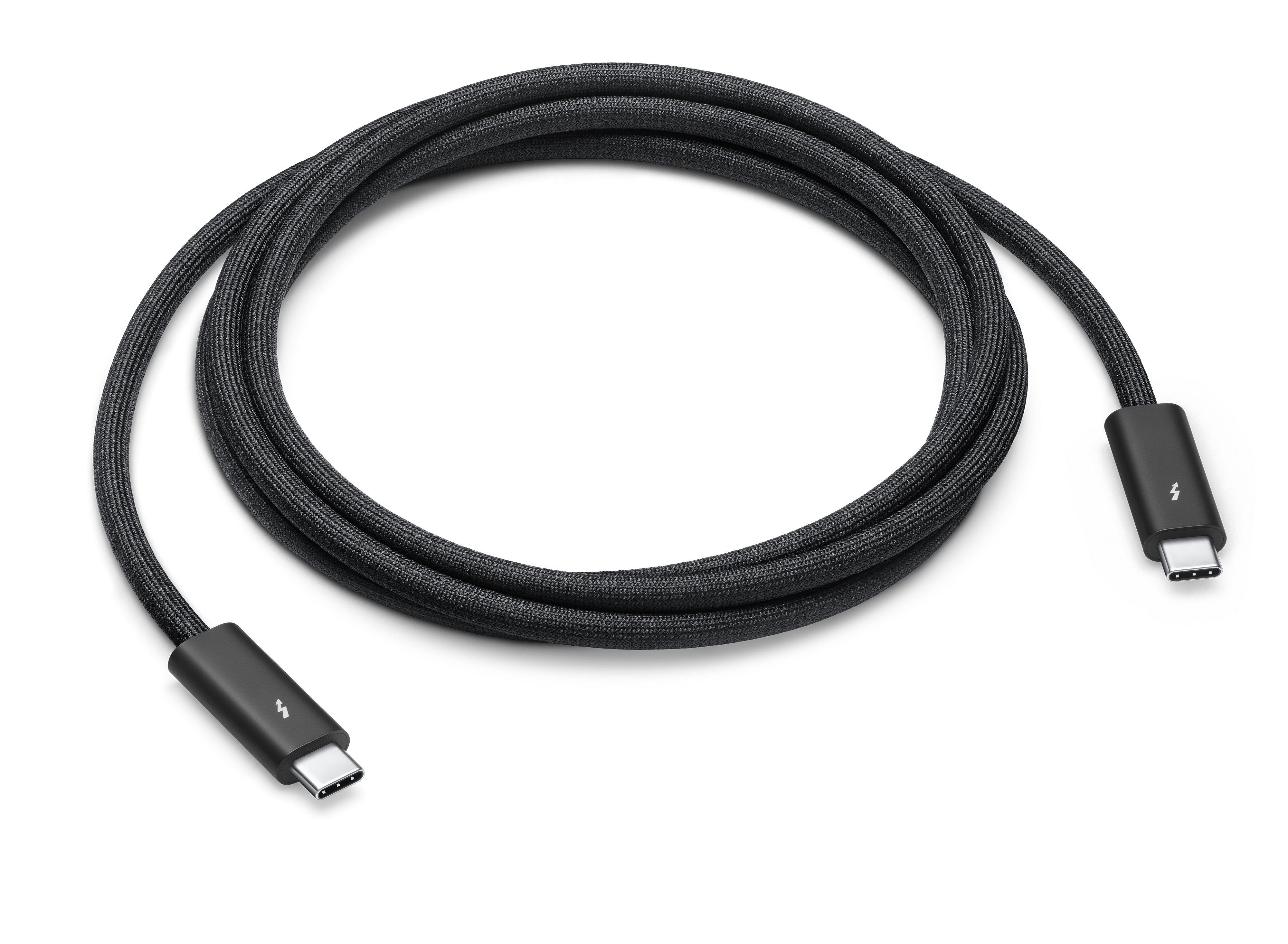
Thunderbolt
What is this cable? It can either acts as a display cable or a data transfer cable. Doesn't always work in USB-C ports but all USB-C cables will work on these ports. Supports daisy chaining. Tends to be better than USB-C but is more proprietary.

Lightning
What is this cable? It was a proprietary Apple cable used to charge and sync Apple devices.
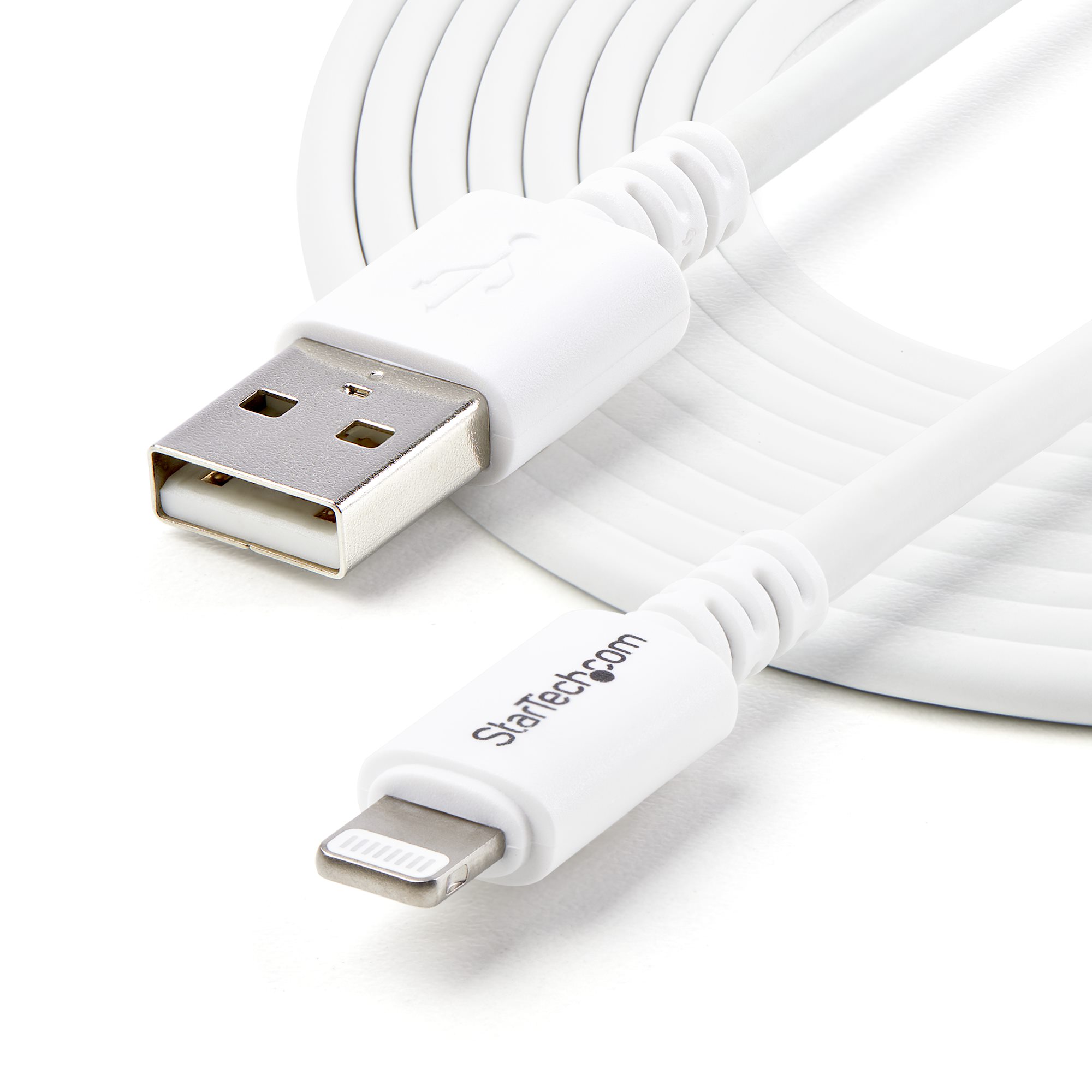

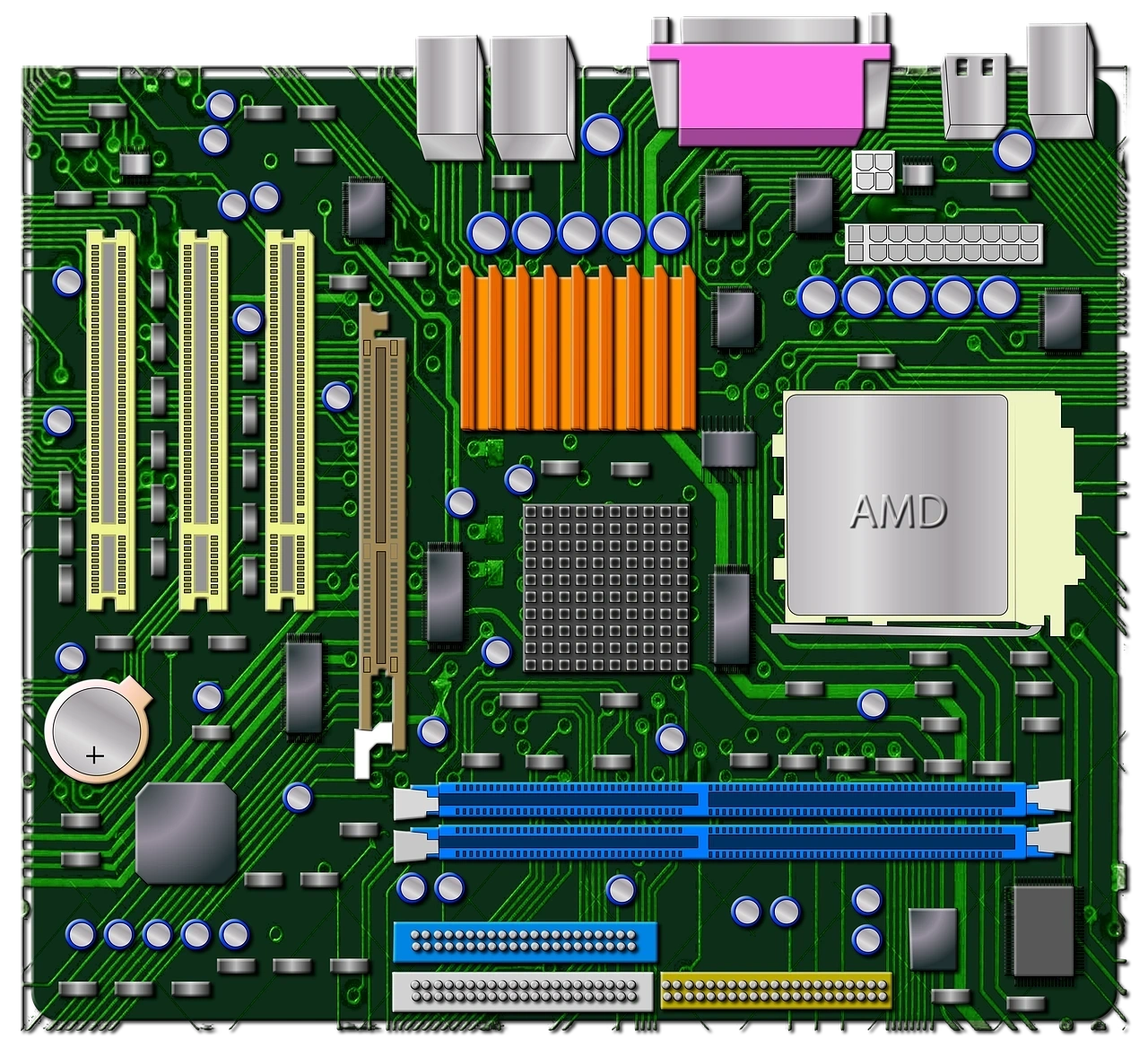
Motherboard
What is this component? A printed circuit board that provides a place to physically house and connect the components of your computer. Transfers electricity between components. Often classified by the speed that they can transfer data in MHz and GHz.
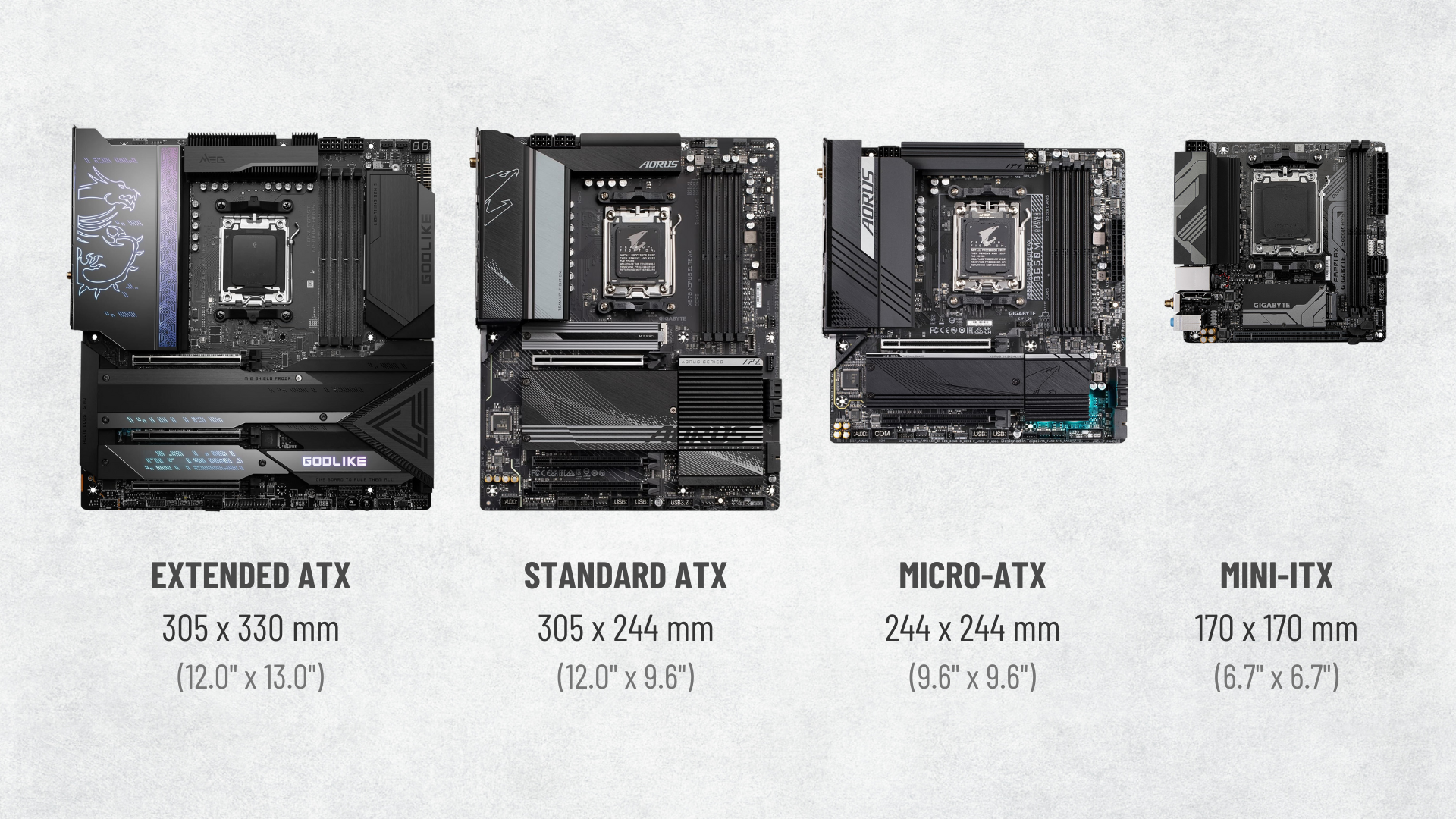
ATX and it's different versions, and mini-ITX
What are the primary motherboard form factors?
LGA (Land Grid Array) has pins on the motherboard and PGA (Pin Grid Array) has pins on the CPU.
Intel and AMD are the two primary CPU manufacturers. They both use a ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) system to connect the pins between the CPU and the motherboard safely. AMD uses a PGA and Intel uses a LGA, what are the difference between the two?
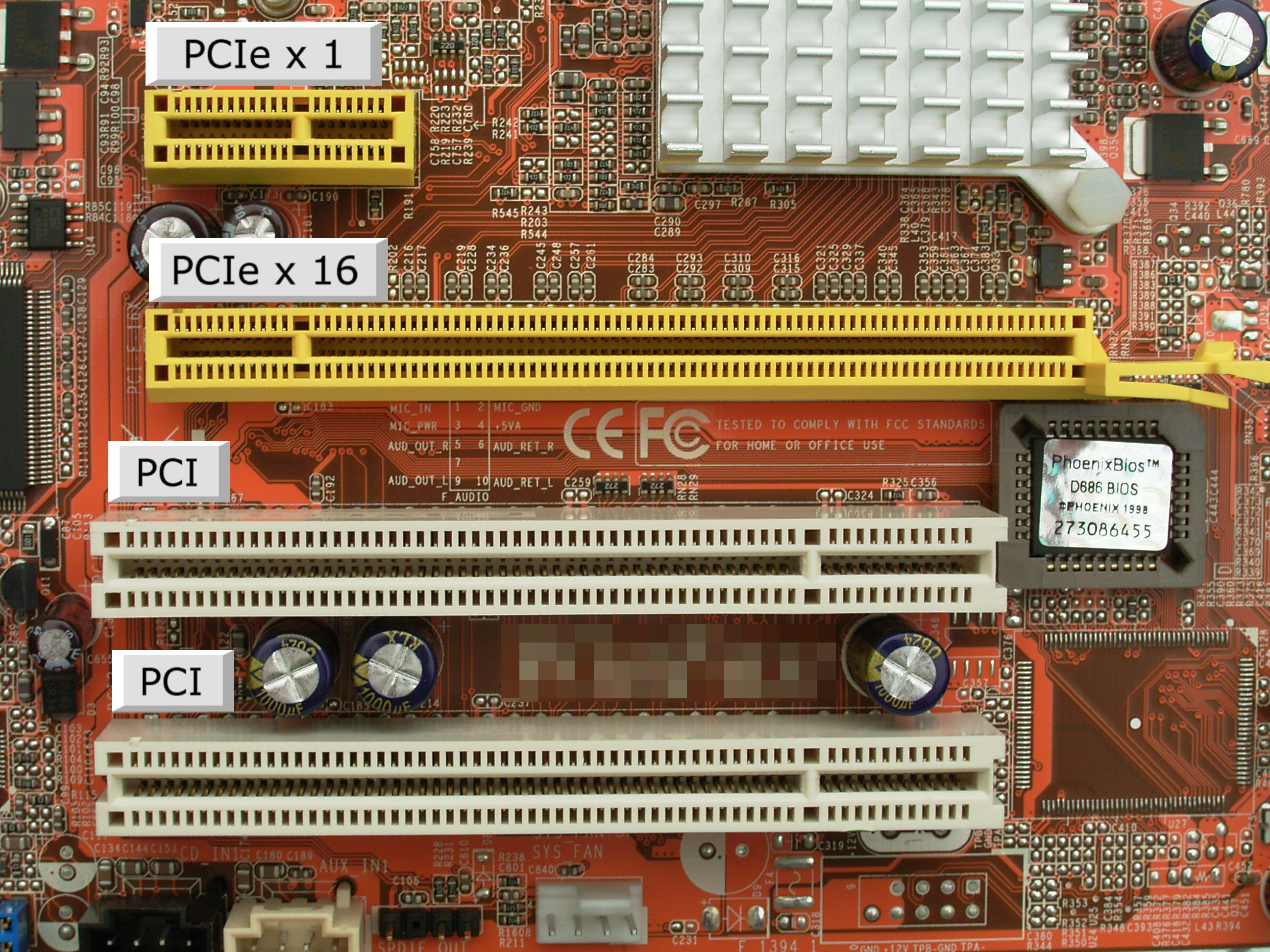
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect express).
This replaced PCI, PCI-X, and AGP. It provides a direct connection to the motherboard for your different devices. The most common slots are x1 and x16, x1 can fit into x16 but not vice versa, and x16 is faster than x1.
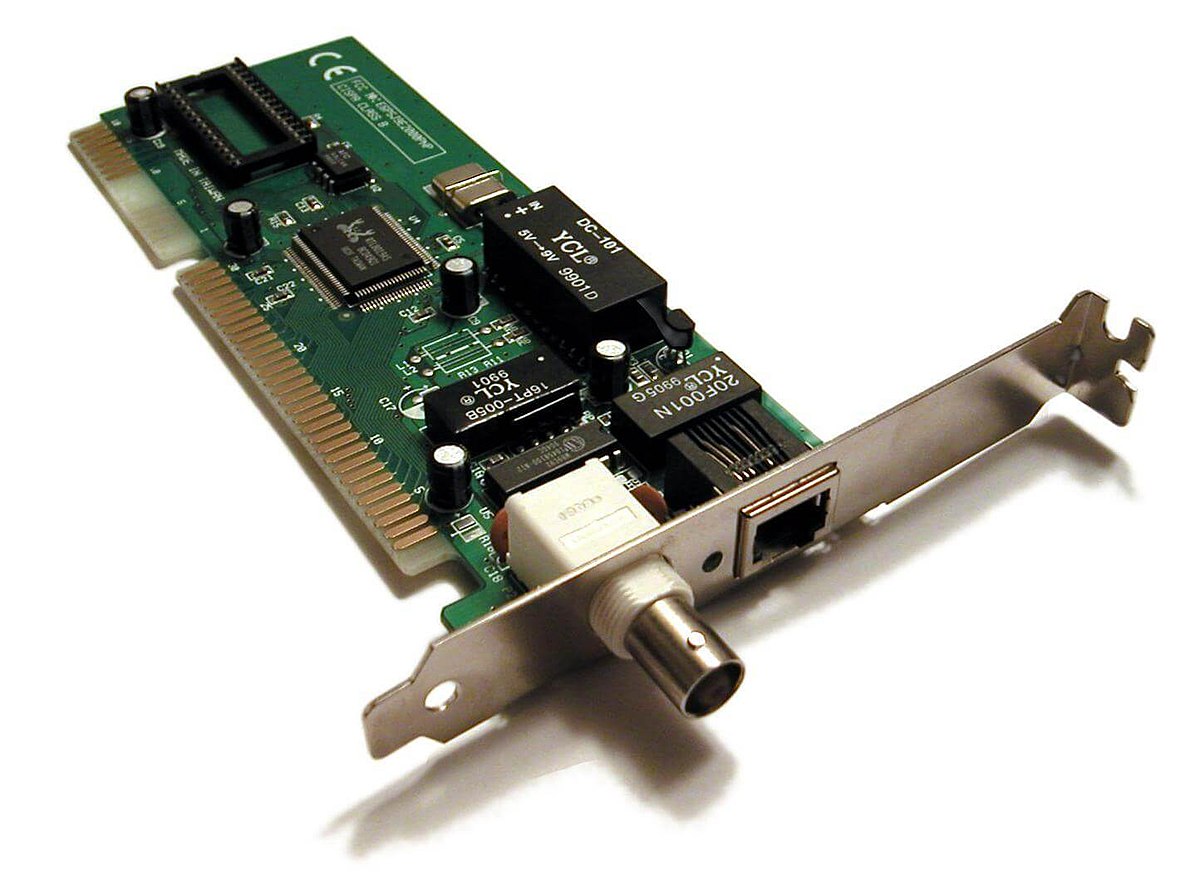
NIC (Network Interface Card)
This component is a piece of hardware that allows a computer or other device to connect to a network.
AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current)
Certain devices need specific forms of power to function. One type cycles between positive and negative charge rapidly, and the other keeps the level and charge consistent which is what the computer needs (+12 VDC, -12 VDC, +3.3 VDC, +5 VDC). A PSU (Power Supply Unit) utilizes a transformer to adjust, filter, and regulate incoming voltage.
The three types of cooling are passive cooling, active cooling, and liquid cooling.
What are the three types of cooling?

CPU (Central Processing Unit)
What is this component? Versions for Intel and AMD. Uses multithreading to do multiple tasks at once, multiprocessing to have multiple processors to get even more done, and multicore to get extra stuff done even without multiple slots on a motherboard.
Multithreading/Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT)[AMD]/Hyper-Threading(HT)[Intel]
This is the method by which a singular CPU can perform multiple actions at the same time. Intel and AMD have different names for this. If you want it to do 1-5, it might be able to do 1 and 2 at the same time.
Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP)
This is the method by which multiple CPUs can work together on a singular motherboard to get more things done. All of the processors need to be the same type and speed, and the motherboard and OS need to be able to handle multiple processors.
Multicore
This is the method by which one CPU can contain multiple processors in order to have more processing power. It can have up to like 8 cores (dual, quad, hexa, octa) in a single chip. You can combine this with multithreading as each core can have multiple threads.
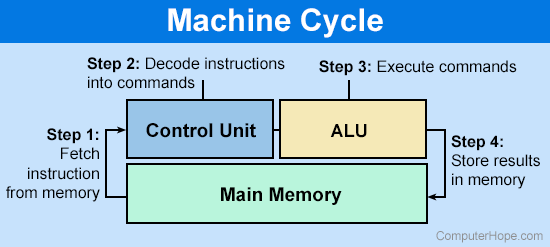
The CPU Machine Cycle
The processor is first going to fetch the next instruction in a sequence from the system memory or the cache inside of the processor.
The control unit will then decode each of those instructions and either executes it or pass it on to a secondary unit that will help it complete that process.
Components like Floating-Point Units (FPU) and Arithmetic Logic Units (ALU) are these secondary units that can help speed up processing by having specialized kits, which can execute their speciality efficiently.
Once it's done computing, that data is stored back in the register, cache, or system memory. It can then be presented to the user and/or be referenced later if necessary.
3 different types of processors
x86 is a 32-bit instruction set with a maximum of 4 (2³² bits) GB of RAM. x64 is a 64-bit instruction set with a maximum of (2^64 bits) a lot GB of RAM. ARM (Advanced RISC Machine) are often used for lower power or more unique devices.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
What is this component? It is primarily used to load applications and files into a non persistent, fast storage area. It provides a necessary function for the processor: a place for it to store data and instructions before it peforms it's computations when it's cache becomes full.
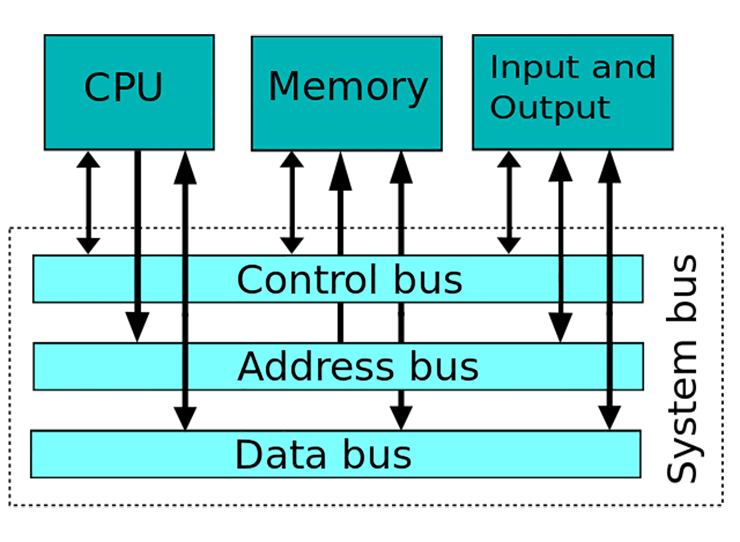
System Bus and Memory Controller
There are two important components to ensuring smooth communication between the CPU, RAM, and Input/Output.
The _______ ___ is split into two distinct sections. The data pathway is used to send and receive information. The address pathway is used to determine where data is located.
The _______ __________ connects the RAM and CPU and facilitates communication between them.
DDR (Dual Data Rate) SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory)
Nearly every manufacturer of RAM uses the same type of RAM. It transfers memory twice per clock cycle, following the speed of the data bus, which will help it catch up to the super fast CPUs.
PC4-16000. Convert this to word form.
16000 MB/s of throughput on a DDR4 module. Covert this to symbol form.
SO-DIMM (Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module)
DDR modules can be decently large, so they cannot fit in laptops. Therefore we have designed a smaller version of the memory modules that fits within smaller form factors.
Multi-Channel Memory
Sometimes your motherboard can have multiple slots for your RAM to fill. Some allow you to have multiple working at the same time. Single-channel uses one memory module on one bus (64-bits). Dual-channel (128-bits), Triple-channel (192-bits), and Quad-channel (256-bits) all allow for multiple memory modules to work together simultaneously. It essentially adds more lanes for your RAM highway.
Parity vs Non-Parity Memory
One type of memory performs basic error checking and ensures that memory contents are reliable. It is slower, but helpful for devices where memory needs to be in top condition, like a server. It can be combined with things like ECC for extra precautions.
The other type of memory is a standard memory that does not check for errors and allows data to be put in or taken out. This is what most memory consists of.
Virtual Memory/Page File/Swap Space/VRAM
There are many different names for this block of space on a hard drive that is allocated by the OS and pretends to be RAM. It is a temporary solution to the problem of not having enough physical RAM, as you generally do not want for this to happen.
BIOS/UEFI
The program that a computers microprocessor used to start and boot after being turned on. It is the most common example of firmware. It takes care of boot order, hardware configuration, and the POST (Power-On Self-Test) which is a diagnostic testing sequence run to check if the hardware is working properly. Additionally offers several security features to properly lock down your computer from attackers.
TPM (Trusted Platform Module) and HSM (Hardware Security Module)
There are two important hardware modules that allow us physical cryptography. They are types of Hardware RoTs (Root of Trusts) which contains all of the keys used for secure boot functions and ensure that the system is not compromised.
The first one is the most common, ensuring a secured boot and storing relevant information for encryption like keys and password hashes.
The second one can pretty much do all of that but better, and also allows for some additional tools.
HDD
What is this component? It is a mass storage device using a spinning magnetic disk to store a large amount of information. It generally comes in 2.5, 3.5, and 5.25 inch form factors. Divided into tracks and sectors: tracks being a ring around the disk and a sector is a portion of a track. Speed is measured in rpm.

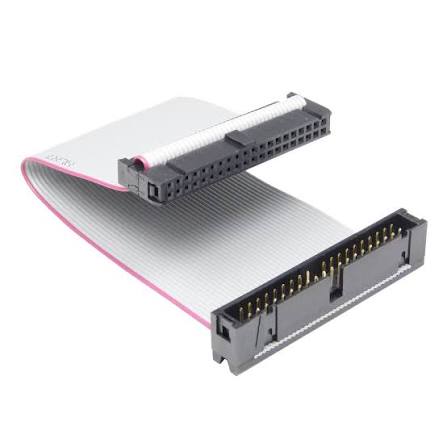
PATA/IDE
What is this cable? It was a 40 wire flat ribbon data cable that connected motherboards to mass storage devices. It's only used in legacy systems, sometimes only having data transfer and other times having data and power transfer.

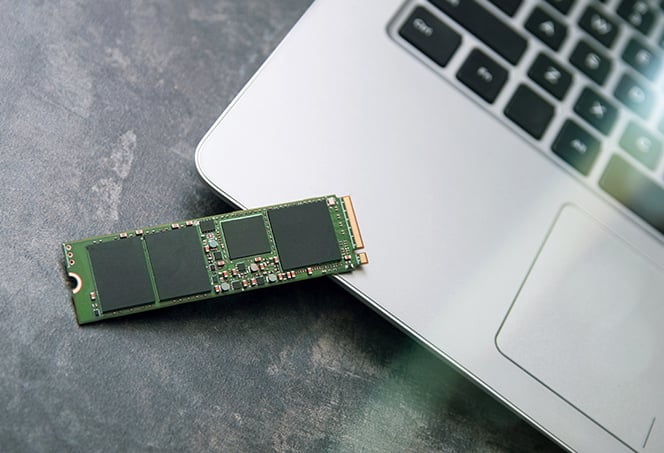
SSD (Solid State Drive/Device)
What is this component? It uses flash memory to implement persistent mass storage. Replaced HDDs in terms of performance. Common form factors are 2.5”, 1.8”, and M.2. SATA connectors used for everything but M.2. M.2 uses NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory express) port.

RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks)
This allows you to combine multiple physical hard disks logically into one.
Version 0 - Striping. Each disk holds half the data, increasing speeds.
Version 1 - Mirrored. Each disk holds a copy of the data, giving redundancy.
Version 5 - Parity. 3 Disks. Two of the disks hold half of the data (A and B), the third disk holds a calculation of the two (AB). If one disk is lost, it can be mathematically reconstructed with the other two.
Version 10 - 4 disks. Both stripes and mirrors the data, allowing for speed and redundancy.
They can be Failure Resistant (if one disk fails you will not lose all data), Fault Tolerant (even if one technology involved in the disk fails, it will still function), and Disaster Tolerant (two independent zones with full access to data at all times)
Optical Drives
There are three different kinds of this component.
CD (Compact Disc) - 650 to 700 MB storage.
DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) - 4.7 GB or 8.4 GB (DL) storage.
BD (Blu-Ray Disc) - 25 GB or 50 GB (DL) storage.
These come in three different types.
Read-only (ROM)
Write-once (R)
Write-many/Erasable (RW, RAM, RE)
Hypervisor
This component is a piece of hardware necessary for virtualization. It is used to manage the distribution of the physical resources of a server or host to different virtual machines. It comes in two types.
Type 1 (bare-bones/bare-metal) runs natively on your hardware. Kind of like making it what your OS runs on.
Type 2 (OS) runs as software within an already running OS.
Containerization does not use a hypervisor.
Virtualization
A concept similar to containerization that allows you to run several different computers from the resources on one computer. It can also be used to remotely access applications and other resources on a computer that is not physically close to you. It can also be used to trick applications into thinking you have hardware that you do not (legacy software, phone on a computer, etc.)
Basic CPU virtualization extensions; Intel: VT-x, AMD: AMD-v
Containerization
A concept similar to virtualization where instead of having multiple OSs on one machine, only one OS is on that machine and instead each user has their own ‘container’ that shares the kernel of the base OS. Uses much less storage space and processing power, since only one OS is running, kind of.
SLAT (Second Level Address Translation)
In addition to AMD’s AMD-V and Intel’s VT-x, this improves performance of virtual memory when running multiple virtual machines on a single physical host.
Intel - EPT (Extended Page Table)
AMD - RVI (Rapid Virtualization Indexing)
Having multiple processors can also assist in having better performance, but that doesn't really have a lot to do with this concept.
Cloud Computing
The practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process data. Consists of Shared Resources and Dedicated Resources.
Shared Resources - multiple customers use the same infrastructure, isolated using virtualization.
Dedicated Resources - resources that are reserved for a single customer, more expensive, often used for highly sensitive organizations.
Metered Utilization
The concept of cloud computing where the user is billed based on the amount of resources used, often involving ingress and egress.
Ingress - Amount of data entering the cloud.
Egress - Amount of data leaving the cloud, where most of the cost comes from. Plan around this accordingly.
4 Key Features of Cloud Computing
Elasticity allows resources to scale upon demand.
Cloud Availability refers to the ability to access data and applications whenever and wherever needed through the use of multiple servers in multiple areas.
File Synchronization is a feature that allows users to keep their files updated across multiple devices in real time.
Multitenancy allows multiple customers to share the same physical resources while their data and resources remain separate.
Cloud Deployment Models
Users can choose what they want their Cloud Computing to operate like with multiple options of models.
Public Cloud is the most common type used today, making it's resources available over the Internet. (Google Drive, Amazon, Microsoft)
Private Cloud is used when a company creates it's own cloud environment, usually when security is very important to the organization.
Hybrid Cloud combines the benefits of both public and private cloud options, the organization can choose what to privatize and what not to.
Community Cloud sees its resources and costs shared among several different organizations that all have a common service need. Like taking multiple private clouds and connecting them.
Cloud Service Models
There are three different service models that your organization might choose from in the realm of Cloud Computing.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) is according to CompTIA focused on the hardware only. Provides you with what you need to run a server.
PaaS (Platform as a Service) adds the OS and the “infrastructure sofeware” like database functionality, web servers, other server software and middleware.
SaaS (Software as a Service) - The service provider gives your organization a complete solution. Hardware, networking, storage, servers, virtualization, OS, middleware, runtime, data processing, application, and software. (Drive, TurboTax, Gmail, etc.)
Exam could get tricky here. Just think that if it's more than IaaS or less than SaaS, it's probably PaaS.
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
A Cloud Computing method that allows a central server to host desktop OSs within a virtualized environment, allowing you to sign in to it with a “dummy” computer. SSD er performs all of the application processing and data storage. Comes in 3 different models:
Centralized Model hosts all of the desktop instances in a single server or server farm.
Hosted Model is where all of the desktops are maintained by a service provider and provided to the end user as a service (DaaS).
Remote Virtual Desktop Model involves copying the desktop image to a local machine prior to being used by an end user.

What is the difference between a hub and a switch?
A hub can only hear one device talking at a time. If two devices talk at the same time they wait a random amount of time to try talking again. Hubs transmit communications to everyone, but the ones not supposed to receive the message just plug their ears.
A switch remembers the MAC addresses of the devices attached to its ports. It's much easier to set up than a hub and mostly self regulates unless you want to customize it. Multiple devices can communicate at the same time, and knowing the MAC address ensures that it doesn't have to send messages to every device.
Patch Panel
What is this device? Connects to network cables in the wall to help facilitate communications within a localized area. Since switches are expensive and only have so many connections, it's more efficient to buy some of these than lots of switches.

PoE (Power over Ethernet)
This supplies electrical power from a switch port over an ordinary data cable to a power device.
802.3 af - 13 W
802.3 at (+) - up to 25 W
802.3 bt (++) up to 51 W (Type 3) or 73 W (Type 4)
Your switch, cabling, and device need to support this in order for you to be able to use this.