Topic 11 - static electricity
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what is static electricty, charges
a property of all matter
positive and negative charges exist
if a body has the same amount of positive and negative charge, they cancel out, forming a neutral body (ie. protons and electrons in a neutral atom)
like charges repel
opposite charges attract
conducting electricity
insulators do not conduct electricity
their electrons cannot flow throughout the material, they are fixed
conductors can conduct electricity
their electrons can flow, and are not fixed (they are delocalised)
what is static electricity
when two insulators are rubbed together it can be charged by friction
electrons are transferred from one object to the other
forming a positive charge on one object and a negative charge on the other
if conductors were rubbed, electrons will flow in/out of them cancelling out any effect, so they stay neutral
insulators become charged because the electrons cannot flow
a positive static charge forms on object which loses electrons
a negative static charge forms on object which gains electrons
which object loses/gains electrons depends on the materials involved
sparking occurs when enough charge builds up, and the objects are close but not touching
the “spark” is when the charge jumps through the air from the highly negative object to the highly positive object, to balance out the charges
lightning occurs when the charge difference between clouds and the Earth becomes so great, and a massive spark (lightning) jumps across to balance the charge
forces exerted
the charged objects experiences a force - electrostatic force (of attraction/repulsion)
greater charge = greater force (eg. a more positive object, a more negative object)
closer together = greater force (force is proportional to the inverse square of the distance)
it is a noncontact force, as force can be felt even when the objects are not touching
like charges repel, unlike charges attract
a positively charged balloon next to a wall attracts electrons in the wall
this induction causes the balloon to stick to the wall
comb charged induces the opposite charge in small pieces of paper, so picks them up
earthing
this allows electrons to flow to the earth, removing excess charge
this allows materials to stay neutral
application of this
insecticide sprays are sprayed from aircraft, and given a charge
this means the spray droplets repel each other
so the droplets spread evenly, and are attracted to the earth
if not charged, there is a risk that some droplets will blow away, or spray will fall unevenly
dangers of sparks
if charge builds up and a spark forms when fuelling cars, it could ignite and cause a massive explosion
as fuel passes through a hose to the vehicle, a static charge can build up
when it is too large a spark might form
a resulting spark might ignite the fuel
the hoses are earthed to stop this occuring
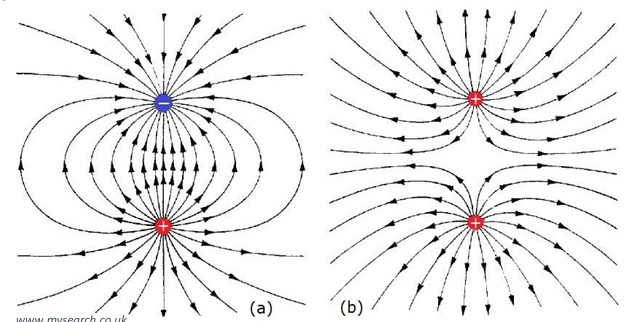
electric fields
like magnetic fields for magnets, electric fields are for charges
an electric field is the region where an electric charge experiences a force
they point in the direction a positive charge would go
ie. away from positive charges, and towards negative charges
they point to charges at right angles to the surface
stronger the charge, the more field lines present and the stronger the force felt
parallel plates have a uniform field