mid-term biology exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/241
Earn XP
Description and Tags
make sure you change the settings to "answer with definition"
Last updated 7:08 PM on 12/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
242 Terms
1
New cards
long piece on top of microscope
body tube
2
New cards
holds and spins objectives on microscope
revolving nose piece
3
New cards
smallest objective on microscope
low power objective
4
New cards
second largest objective on microscope
medium power objective
5
New cards
largest objective on microscope
high power objective
6
New cards
holds slide on microscope
stage clips
7
New cards
controls the amount of light on microscope
diaphragm
8
New cards
what you look through on microscope
occular/eyepiece
9
New cards
what the slide is set on on the microscope
stage
10
New cards
biggest focus knob
coarse focus
11
New cards
smallest focus knob
fine focus
12
New cards
bottom of microscope
base
13
New cards
which objective is used to focus?
low power objective
14
New cards
how do you calculate total magnifacation?
occular magnification x objective magnifacation
15
New cards
what is a compound microscope?
a microscope using two lenses
16
New cards
first step of the scientific method:
problem or question
17
New cards
second step of the scientific method:
research
18
New cards
third step of the scientific method:
hypothesis
19
New cards
fourth step of the scientific method:
experiment
20
New cards
fifth step of the scientific method:
analysis
21
New cards
sixth step of the scientific method:
conclusion
22
New cards
seventh step of the scientific method:
prediction
23
New cards
the "things" that are changed in an experiment
variable
24
New cards
the "things" that stay the same in an experiment
constant
25
New cards
the one "thing" a scientist changes in an experiment
independent variable
26
New cards
the "things" that change due to the independent variable
dependent variable
27
New cards
what axis does the independent variable go on?
x
28
New cards
what axis does the dependent variable go on?
y
29
New cards
an educated guess made before an experiment
hypothesis
30
New cards
used as a basis of accepting or rejecting the hypothesis
null hypothesis
31
New cards
a group that gets a fake treatment without knowing it.
placebo group
32
New cards
a group actively participating in an experiment. getting a treatment
experimental group
33
New cards
gets no treatment or gets "normal treatment"
control group
34
New cards
a statement that summarizes exactly what happened in an experiment
conclusion
35
New cards
what does a chi square test?
the observed data with the expected data
36
New cards
what is the rule to accept a null hypothesis?
if the x^2 is less than the critical value
37
New cards
what is the rule to reject a null hypothesis?
if the x^2 is more than the critical value
38
New cards
membrane surrounding nucleus
nuclear envelope
39
New cards
control center of the cell. contains DNA
nucleus
40
New cards
dense circular structure within nucleus
nucleolus
41
New cards
when DNA is in long thin strands inside nucleus
chromatin
42
New cards
gel like fluid that contains nucleus and other organelles
cytoplasm
43
New cards
holds cells together, transports substances into/out of cell
cell membrane
44
New cards
outermost layer of plant cells, surrounds cell membrane
cell wall
45
New cards
clean up crew of cell
lysosomes
46
New cards
how do you calculate total magnification on microscope
occular magnification x objective magnification
47
New cards
what is a compound microscope?
a microscope using two lenses
48
New cards
first step of scientific method
the problem or question
49
New cards
second step of scientific method
research
50
New cards
third step of scientific method
hypothesis
51
New cards
fourth step of scientific method
experiment
52
New cards
fifth step of scientific method
analysis
53
New cards
sixth step of scientific method
conclusion
54
New cards
seventh step of scientific method
prediction
55
New cards
one thing a scientist changes in an experiment
variable
56
New cards
the "things" that stay the same in an experiment
constant
57
New cards
the one thing a scientist manipulates in an experiment
independent variable
58
New cards
the "thing" that changes because of the independent variable
dependent variable
59
New cards
which axis does the independent variable go on?
x
60
New cards
which axis does the dependent variable go on?
y
61
New cards
an educated guess made before an experiment. answers the question or problem
hypothesis
62
New cards
used as a basis of accepting or rejecting the hypothesis
null hypothesis
63
New cards
a group that gets a fake treatment without knowing it.
placebo group
64
New cards
a group actively participating in the experiment. they get a treatment
experimental group
65
New cards
gets no treatment or gets "normal treatment", not experimental treatment
control group
66
New cards
a statement that summarizes exactly what happened in an experiment
conclusion
67
New cards
what does a chi square test?
the observed data with the expected data
68
New cards
a series of membranes that attach sugars to proteins and wrap them in a vesicle
golgi body
69
New cards
storage structures for food, water, or waste products
vacuole
70
New cards
storage structures that can move molecules in/out of cell
vesicles
71
New cards
a series of tubes surrounding nucleus. has attached ribosomes
rough ER
72
New cards
a series of tubes surrounding RER and nucleus. transports materials to and from nucleus
smooth ER
73
New cards
found in plant cells only. contains chlorophyll
chloroplast
74
New cards
contains chlorophyll. is a disk shaped membrane
thylakoid
75
New cards
an entire stack of thylakoids
grana
76
New cards
the watery space between thylakoids
stroma
77
New cards
cell particles made of RNA that are scattered throughout cytoplasm
ribosome
78
New cards
oval shaped with a double membrane. make energy by cellular respiration.
mitochondria
79
New cards
folded inner membrane of mitochondria
cristae
80
New cards
plays a key role in the oxidation of specific molecules
peroxisome
81
New cards
chromatins coiling around proteins and forming an X
chromosome
82
New cards
two bundles of microtubes near nucleus that pull apart chromosomes during mitosis/meiosis
centriole
83
New cards
internal skeleton made of protein fibers. keeps organelles organized, helps cell move, helps organelles move
cytoskeleton
84
New cards
only on animal cells. like a tail. helps with movement
flagella
85
New cards
only on animal cells. like smaller flagella. helps cell move
cilia
86
New cards
prokaryote or eukaryote?: 0.1-0.5 micrometers
prokaryote
87
New cards
prokaryote or eukaryote?: no nucleus or organelles
prokaryote
88
New cards
prokaryote or eukaryote?: evolved first
prokaryote
89
New cards
prokaryote or eukaryote?: bacteria
prokaryote
90
New cards
prokaryote or eukaryote?: 10-100 micrometers
eukaryote
91
New cards
prokaryote or eukaryote?: membrane bound nucleus and organelles
eukaryote
92
New cards
prokaryote or eukaryote?: evolved second
eukaryote
93
New cards
prokaryote or eukaryote?: protozoans
eukaryote
94
New cards
prokaryote or eukaryote?: fungi
eukaryote
95
New cards
prokaryote or eukaryote?: animals
eukaryote
96
New cards
prokaryote or eukaryote?: plants
eukaryote
97
New cards
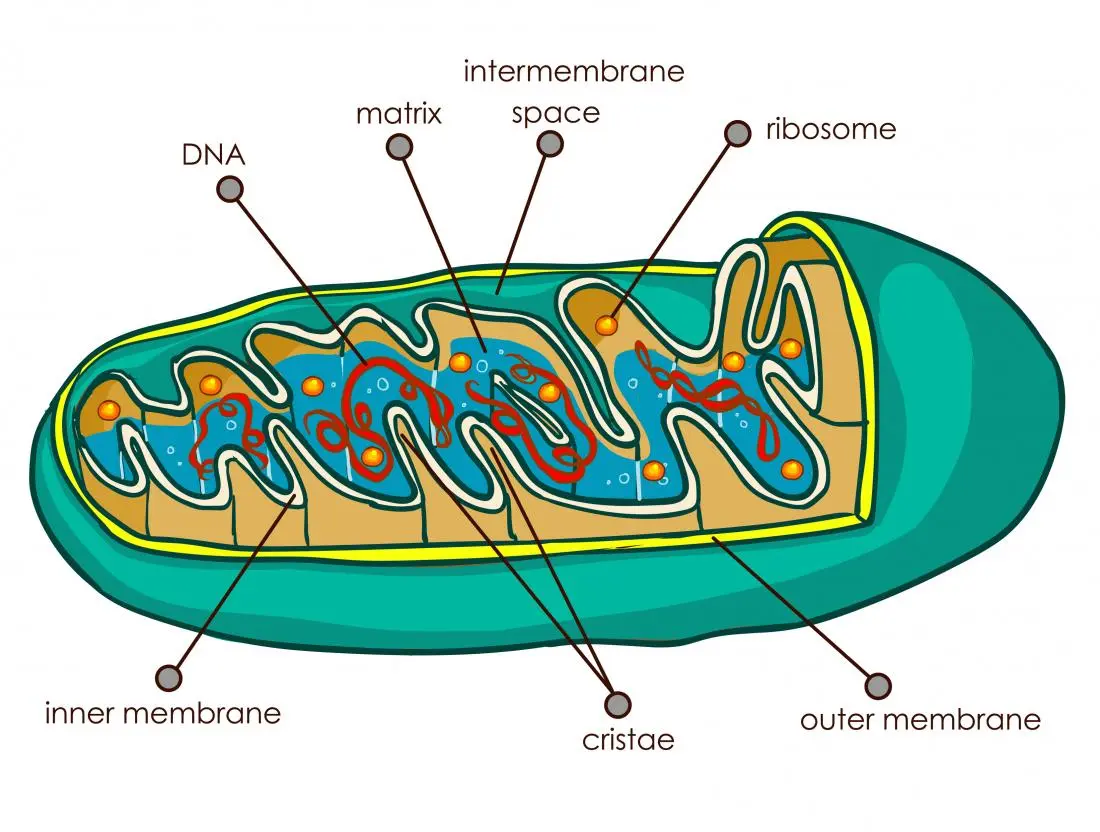
identify this organelle
mitochondria
98
New cards
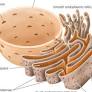
identify this organelle (not the nucleus)
rough endoplasmic reticulum
99
New cards
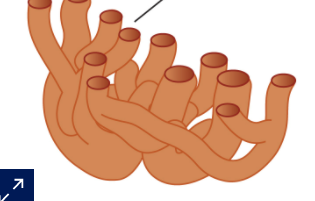
identify this organelle
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
100
New cards
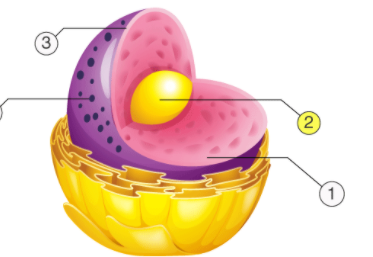
identify this organelle (yellow dot)
nucleolus