AP Physics Unit13_1: Reflection And Refraction
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
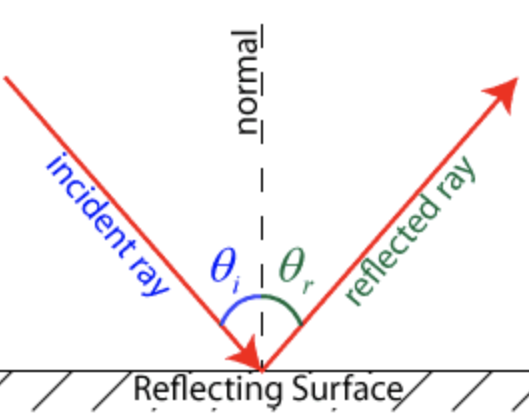
What is the Law of Reflection?
θ1=θ1′
The angle of incidence (θ1) equals the angle of reflection (θ1′).
Key Notes:
All angles are measured from the normal (perpendicular to the surface).
Incident, reflected, and refracted rays lie in the same plane.
Works for any smooth surface (e.g., mirrors, glass, water).
Example:
If light hits a mirror at 30∘ from the normal, it reflects at 30∘ on the opposite side.
Define index of refraction (n) and its formula.
c = speed of light in vacuum (3×108 m / s).
v = speed of light in the medium.
Key Notes:
Always ≥ 1 (light slows down in materials).
No units (it’s a ratio).
Higher n = slower light = more bending.
Example:
Air: n≈1.0
Water: n=1.33
Glass: n≈1.5
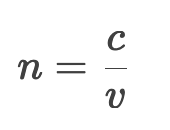
State Snell’s Law and its implications.

What are the conditions for Total Internal Reflection (TIR)?
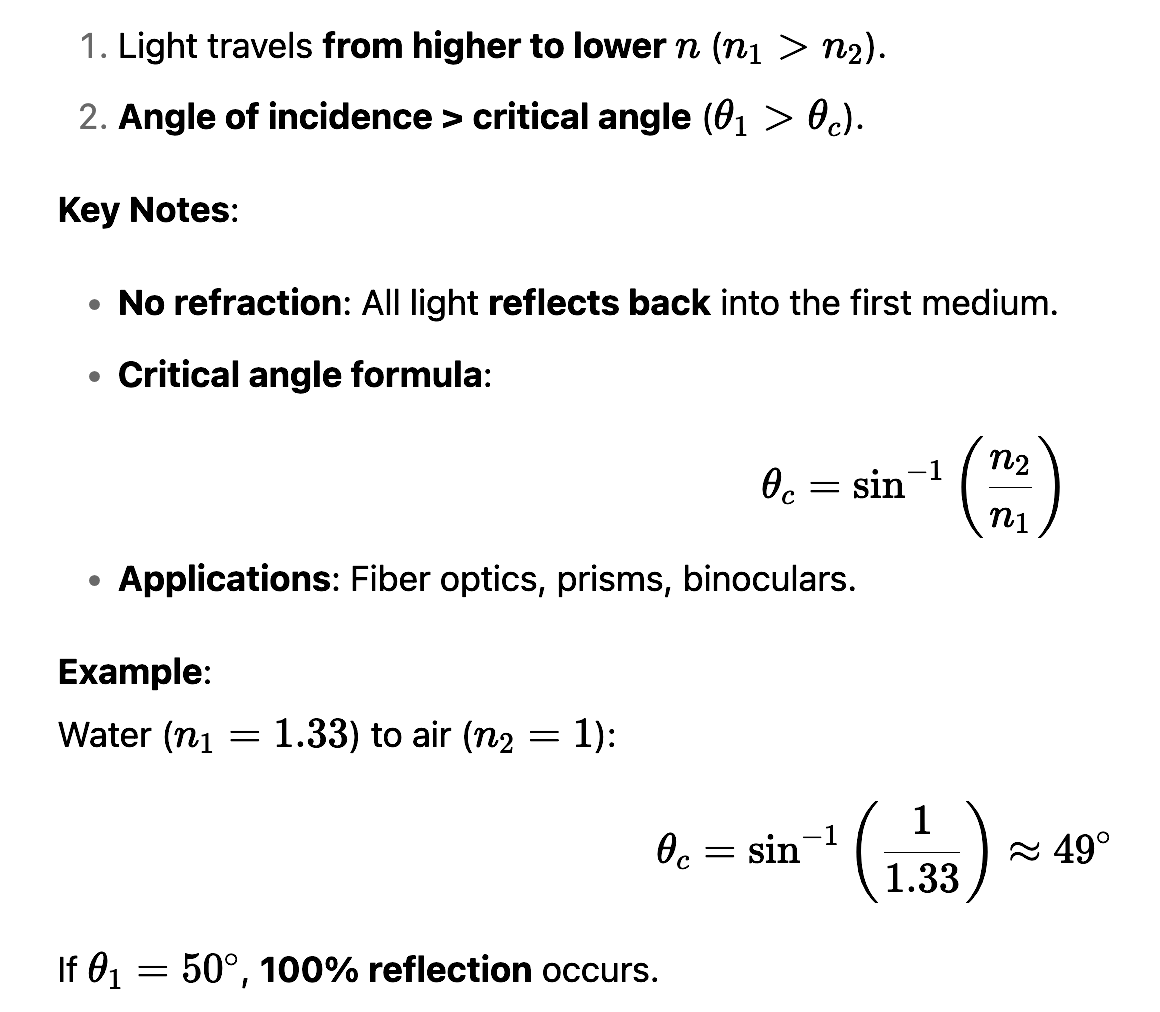
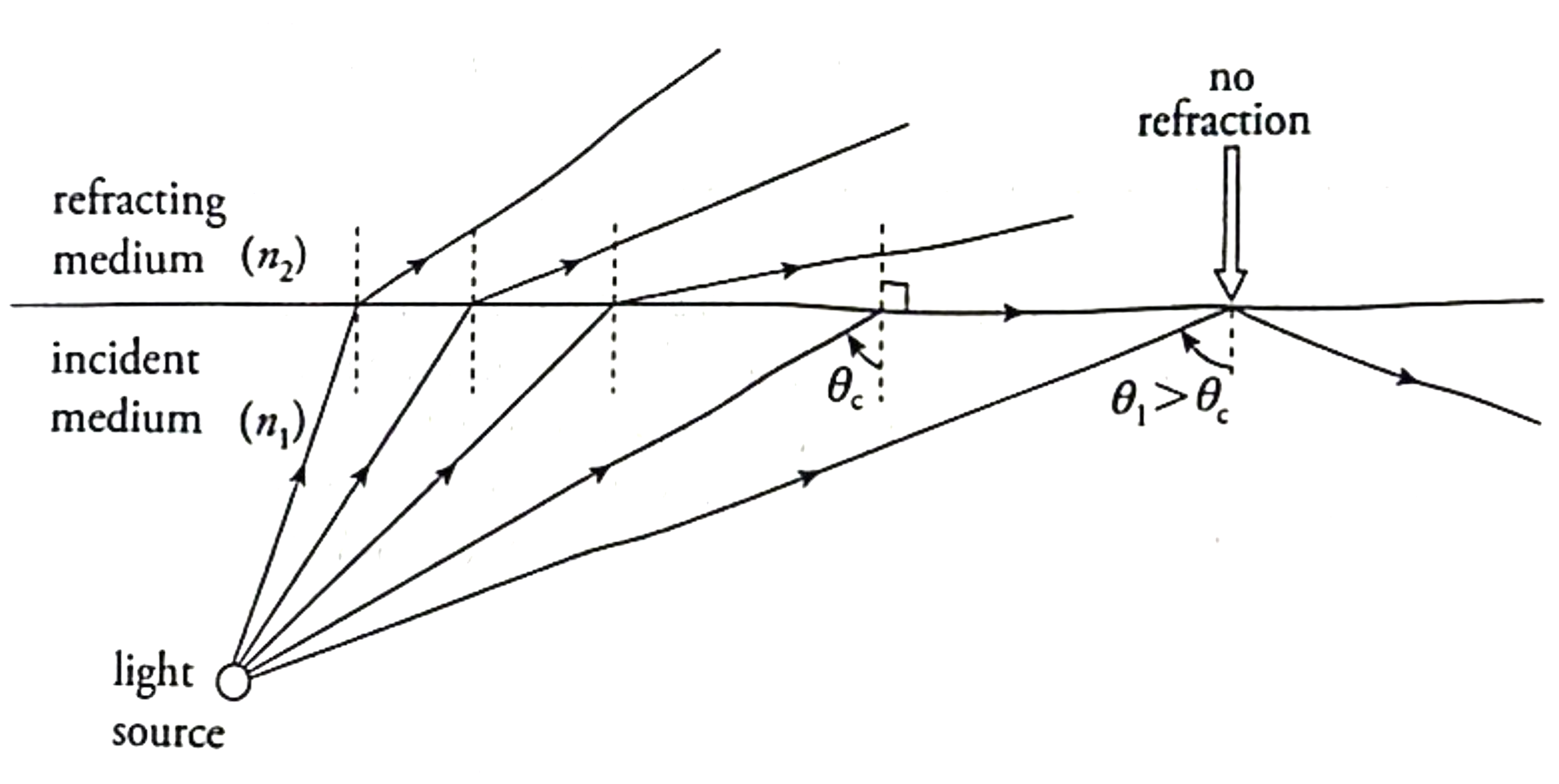
How do you find θc?

Why does a submerged object look shallower?

How far can a fisherman see a submerged light?

How does TIR work in a prism?

Key Problem-Solving Tips
