Biology 3201 - End of Term 1st Term Assessment - Review MC
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
During which stage of the cell cycle does DNA replicate?
A. G1 Phase
B. S Phase
C. G2 Phase
D. Mitosis
B
How does cytokinesis differ between plant and animal cells?
A. Animal cells do not form a cleavage furrow
B. Animals cells build a tough and rigid cell plate
C. Plant cells form a cleavage furrow
D. Plant cells build a tough and rigid cell plate
D
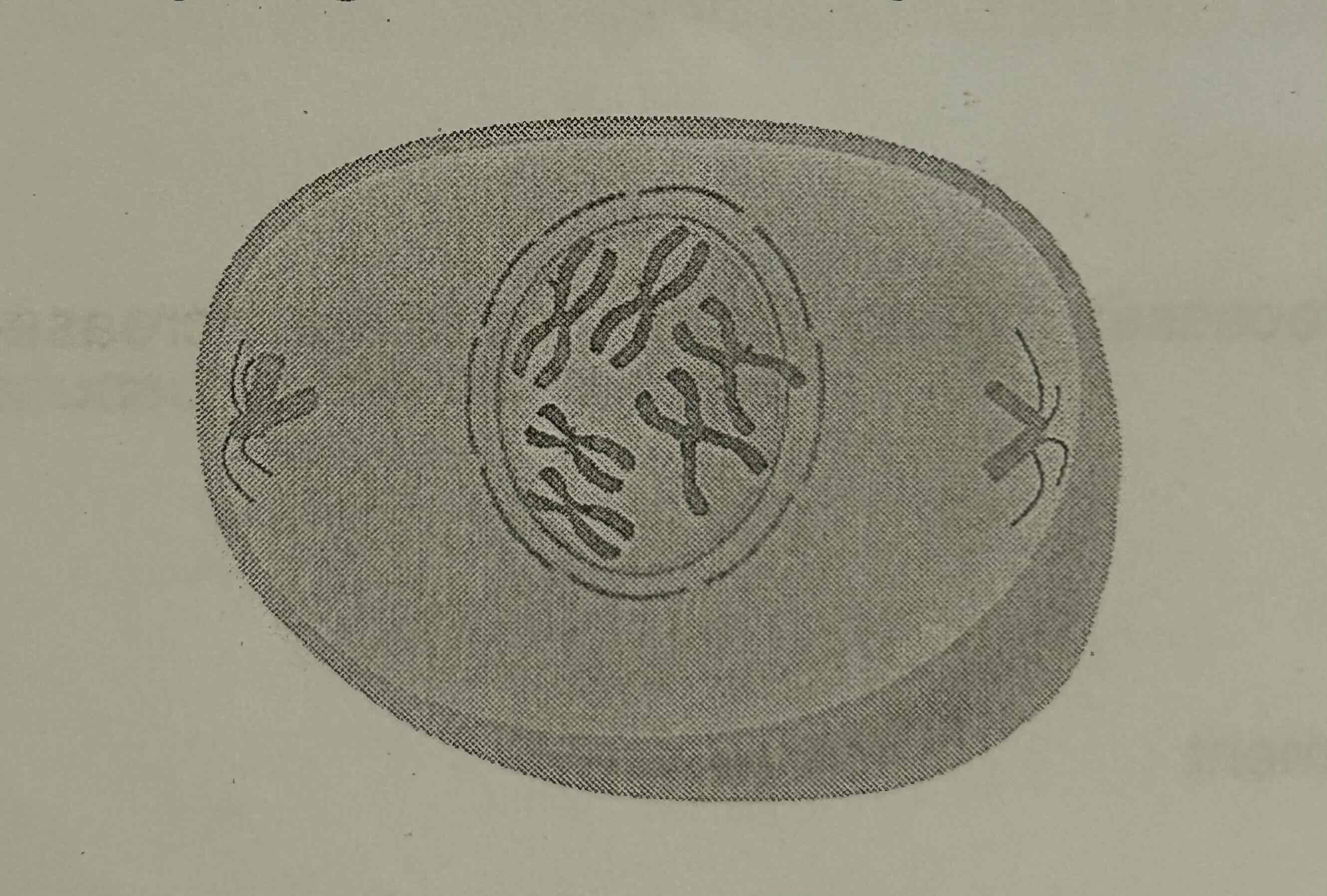
Which stage of mitosis is illustrated in the diagram?
A. Prophase
B. Metaphase
C. Anaphase
D. Telophase
A
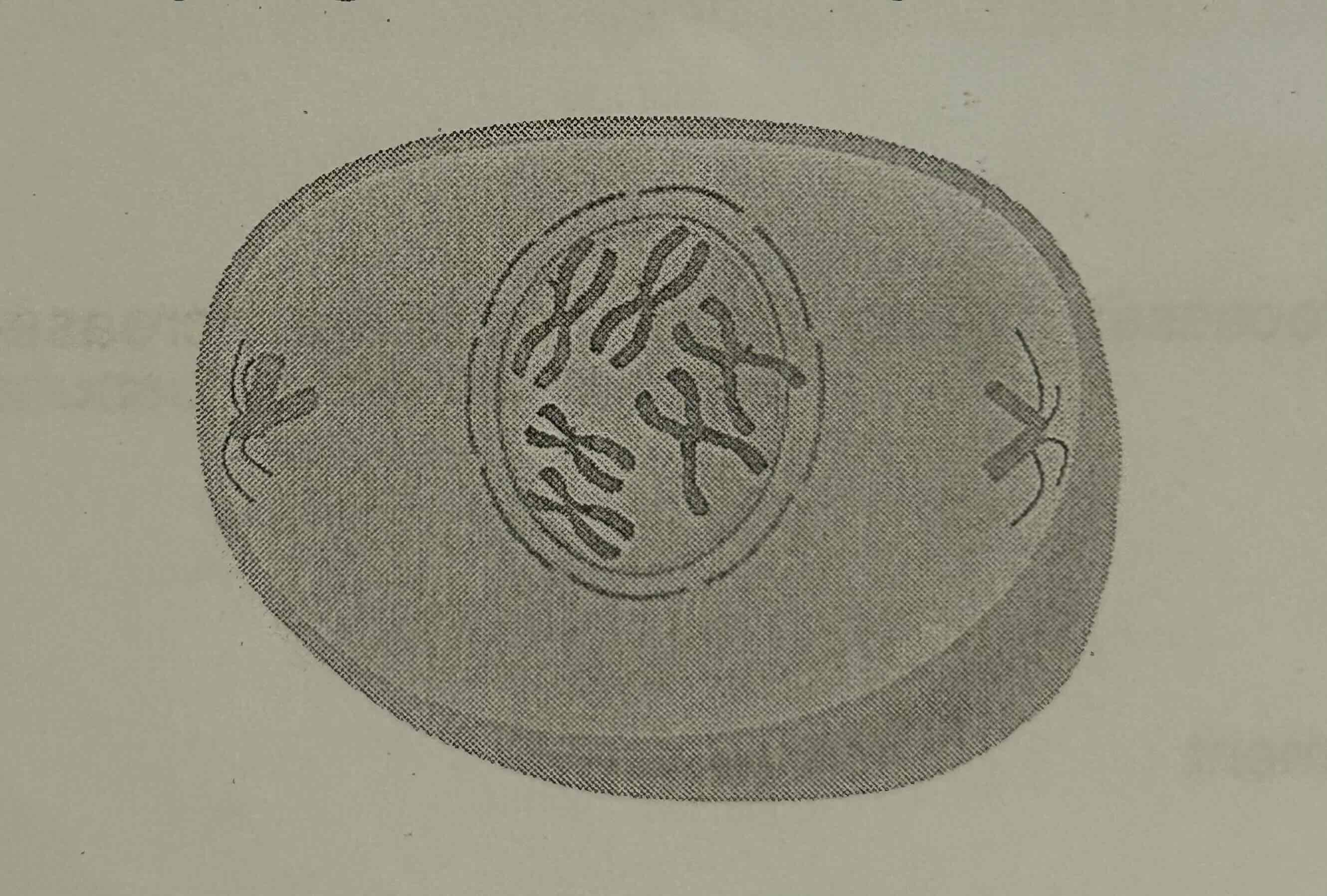
How many chromatids are present in the cell?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 6
D. 12
D
Which of the following is not a function of mitosis?
A. Gamete production
B. Physical growth of an organism
C. Cellular maintenance
D. Cellular repair
A
Which of the following cell structures produces the spindle fibers responsible for pulling chromosomes to opposite ends of the cell during mitosis?
A. Centromeres
B. Centrioles
C. Cell membrane
D. Nuclear membrane
B
Which of the following is true regarding interphase?
A. Each chromosome replicates
B. It is also called the resting stage
C. It lasts from the end of anaphase to the beginning of telophase
D. The cells does not grow
A
Which of the following is true about the number of chromosomes found in each daughter cell at the end of both mitosis and meiosis?
D
Which of the following cell types would meiosis produce?
A. Hair cells
B. Muscle cells
C. Egg cell
D. Neural cells
C
Which of the following processes directly contributes to the increased genetic variety between sex cells?
A. Cytokinesis
B. Synapsis
C. Independent assortment
D. Oogenesis
C
If an oogonium with a diploid number (2n) of 50 chromosomes undergoes oogenesis, how many chromosomes are present in its daughter cells?
A. 4
B. 25
C. 50
D. 100
B
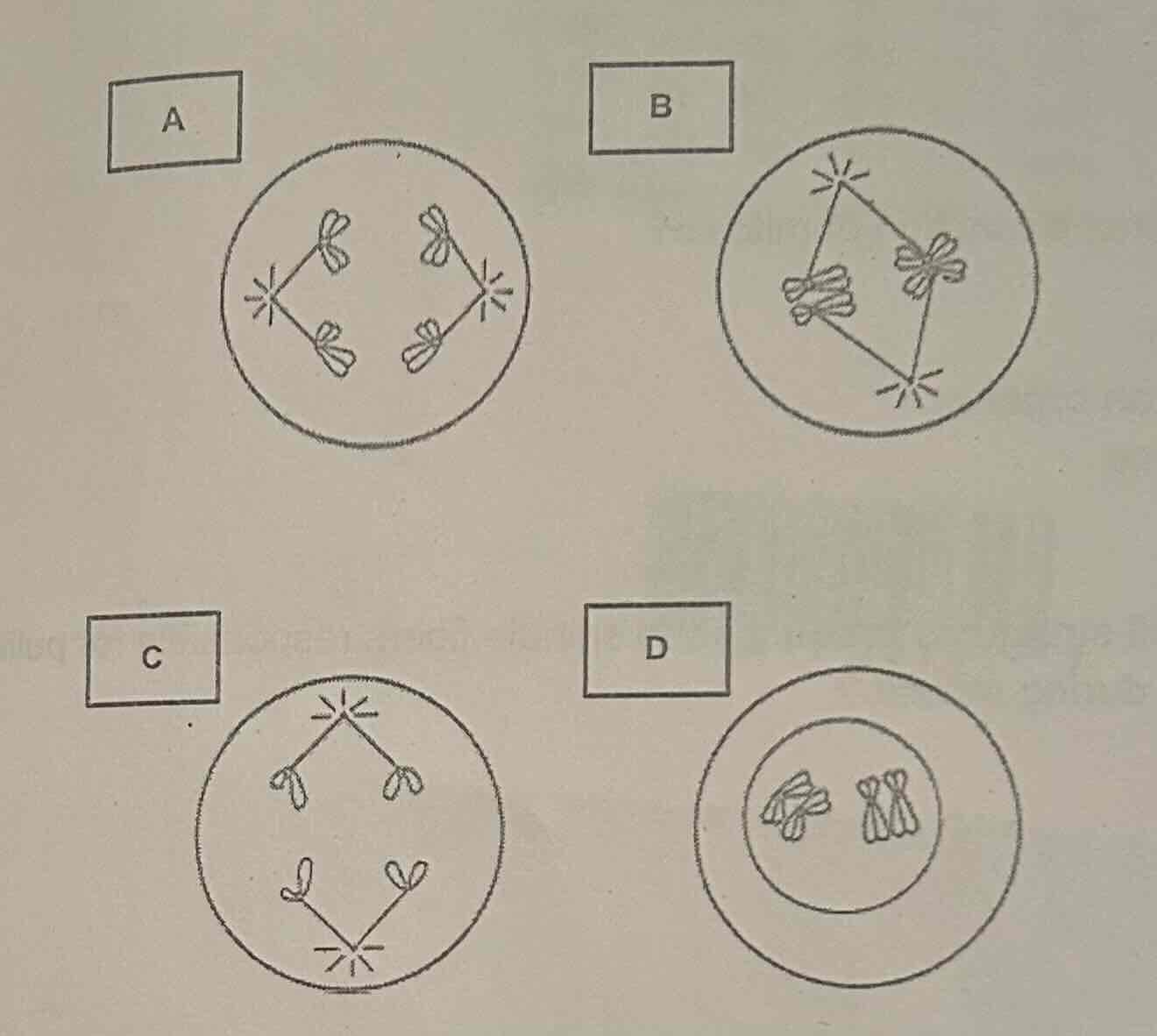
Which following stages of meiosis illustrates Anaphase?
A
B
C
D
A
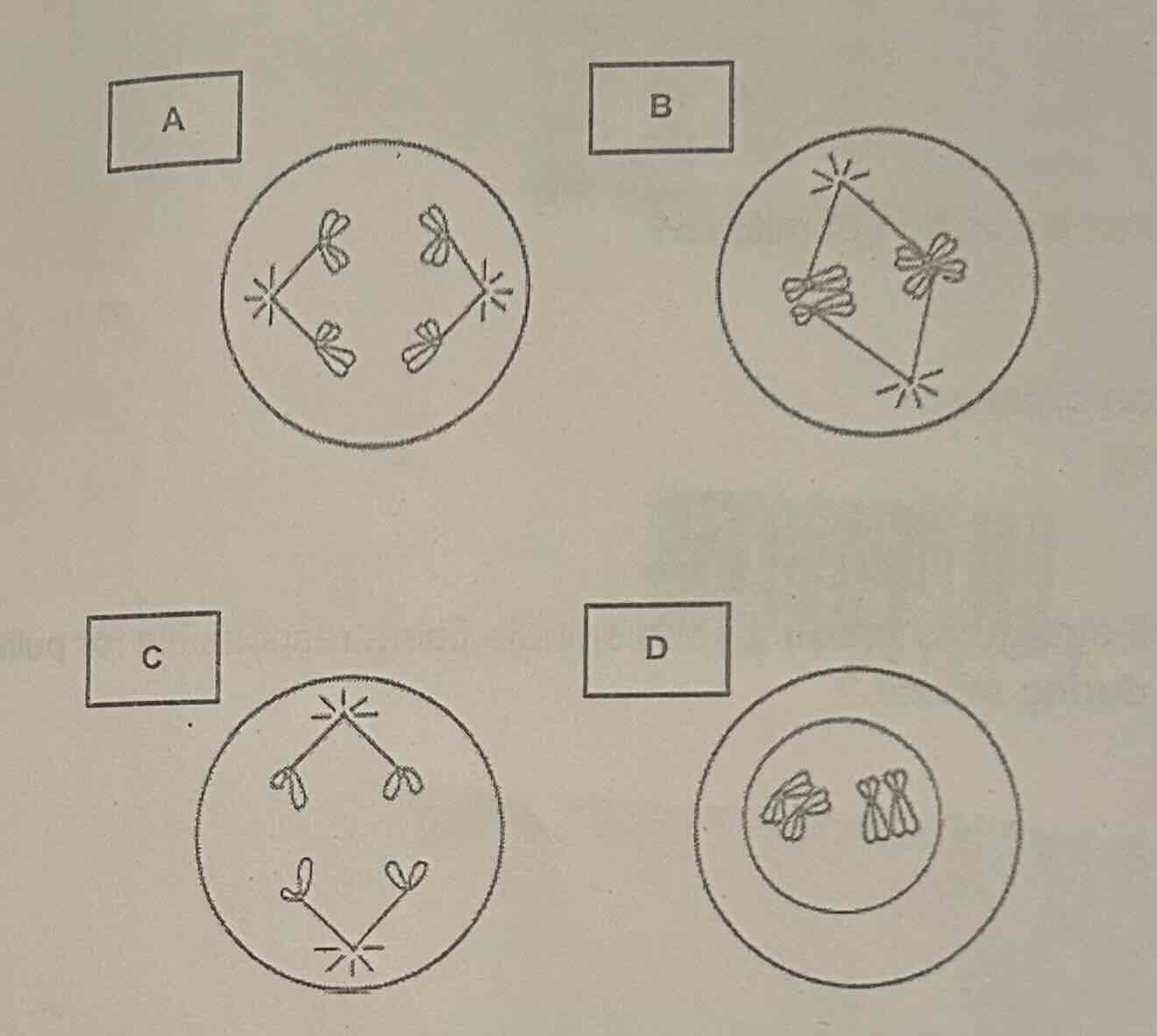
In which of the following stages of meiosis did synapsis occur?
A
B
C
D
D
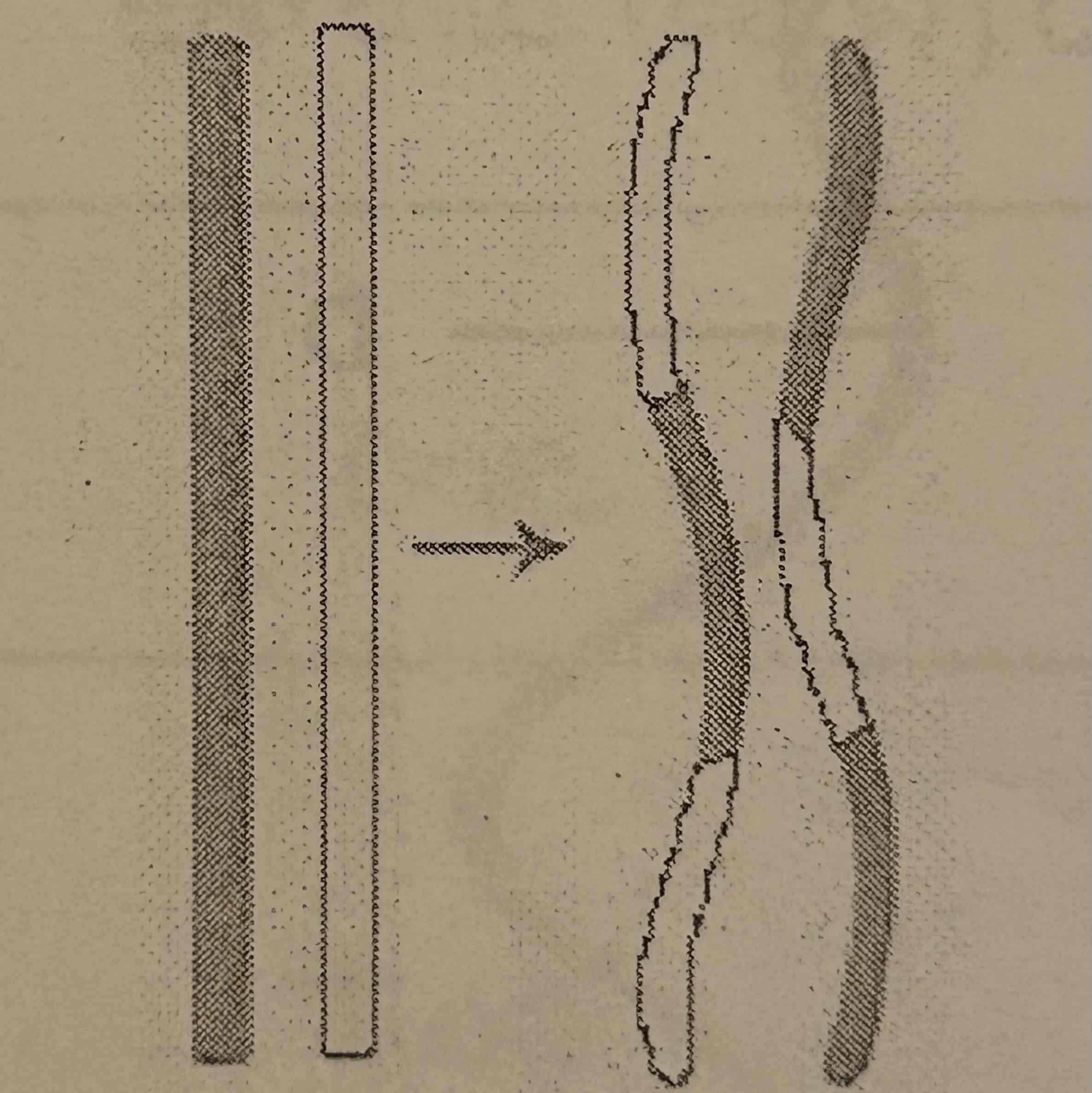
Which process is illustrated in the diagram below?
A. Crossing over
B. Independent assortment
C. Oogenesis
D. Spermatogenesis
A
How many polar bodies are produced during oogenesis?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
C
How many sperm are produced if 4 spermatogonia undergo meiosis?
A. 1
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
D
Homologous chromosomes are similar in that they:
A. Remain paired during meiosis
B. Are genetic replicas of each other
C. Carry genetic information for the same traits
D. Come from the same parent
C
Why is there only one functional egg cell produced at the end of oogenesis?
A. Failure of chromatids to separate
B. Failure of homologous chromosomes to separate
C. Insufficient amount of genetic material
D. Unequal division of cytoplasm during meiosis I and meiosis lI
D
Which is true for an egg cell?
A. They are larger than sperm cells
B. They are motile
C. They are smaller than sperm cells
D. They contain a diploid number of chromosomes
A
Which type of cell division immediately occurs following fertilization of an egg cell?
A. Mitosis
B. Meiosis
C. Cytokinesis
D. Oogenesis
A
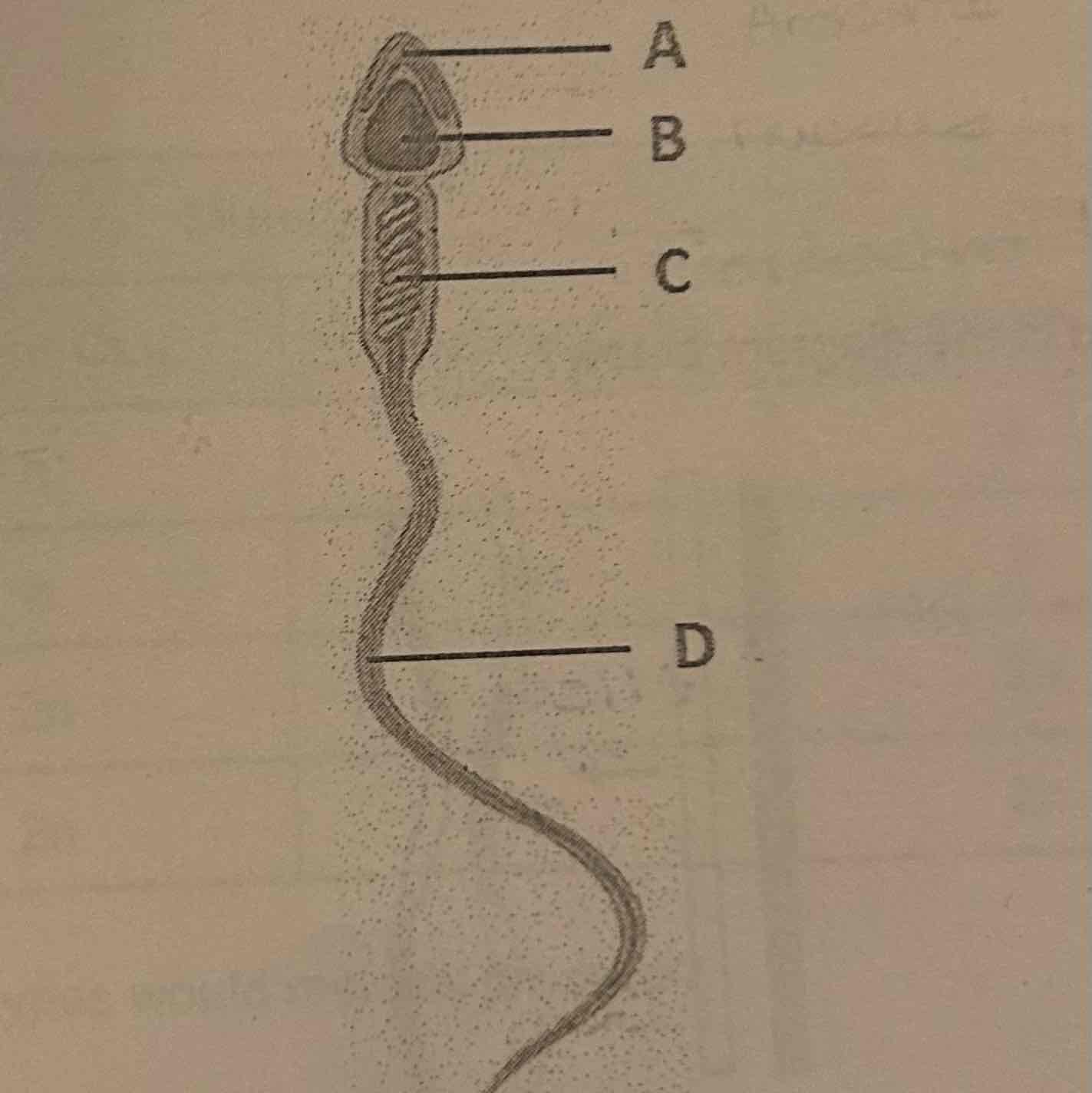
Which of the following is the correct function of the structure labeled 'C'?
A. Help the sperm cell penetrate the egg during fertilization b.
B. Help propel the sperm through the female body
C. House the genetic material of the sperm cell
D. Produce and provide energy for the metabolic function of the sperm cell
D
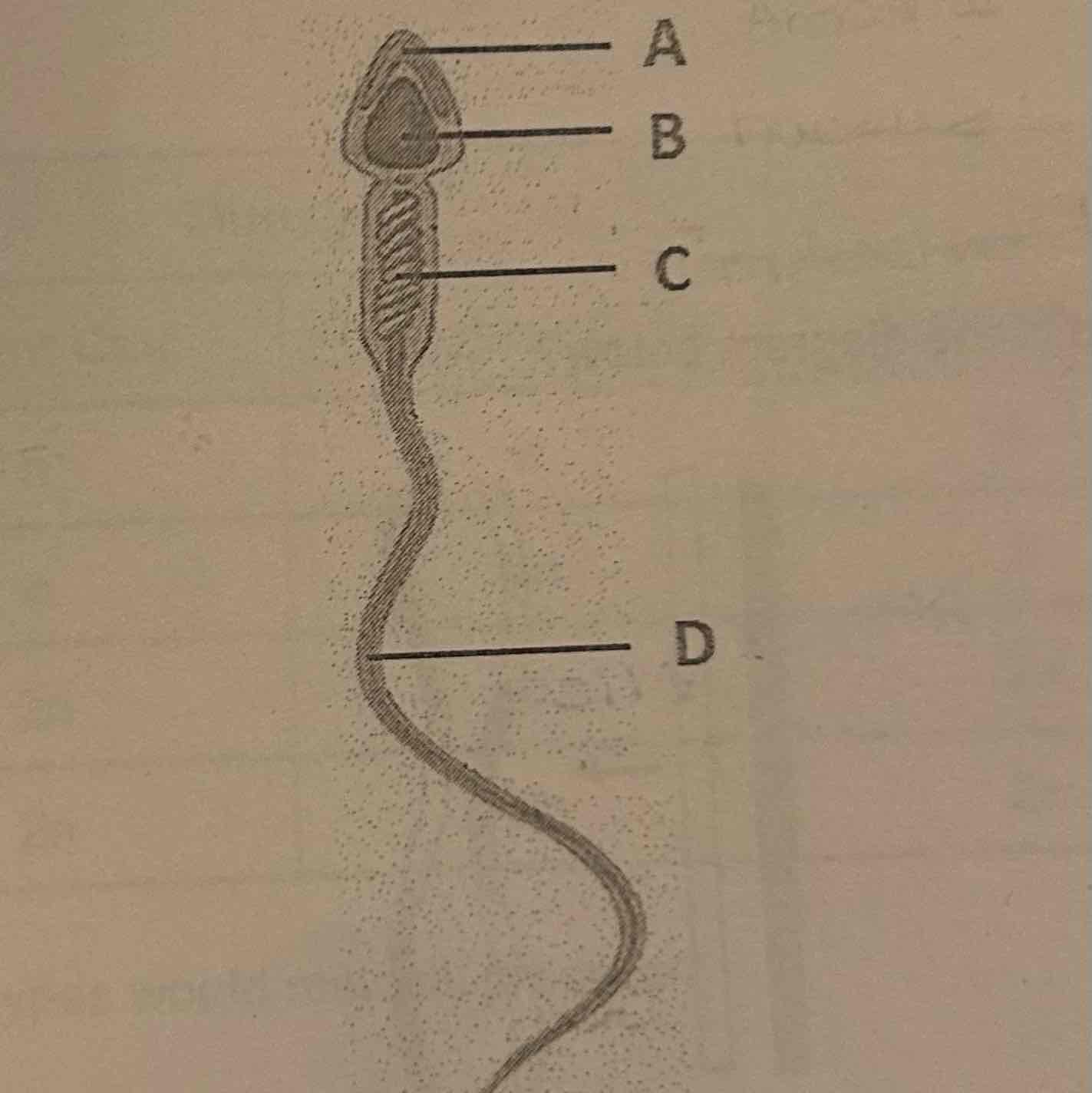
The structure labeled 'A' is called the:
A. Acrosome
B. Nucleus
C. Midpiece
D. Flagella
A
Bees and wasps can produce offspring from unfertilized eggs, which reproductive strategy is this?
A. Fragmentation
B. Parthenogenesis
C. Sexual reproduction
D. Spore production
B
Which reproductive strategy is used when Bacteria exchange genetic material to reproduce?
A. Budding
B. Conjugation
C. Fragmentation
D. Parthenogenesis
B
Which of the following is not considered an advantage to asexual reproduction?
A. Compared to sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction is faster
B. Compared to sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction requires less energy
C. Compared to sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction doesn't promote genetic variety in offspring
D. Compared to sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction almost ensures the production of viable offspring
C
Which of the following are the male reproductive gonads?
A. Penis
B. Vas deferens
C. Seminal vesicles
D. Testes
D
Which of the following hormones are secreted by the ovaries?
A. Estrogen and Follicle Stimulating Hormone
B. Progesterone and Luteinizing Hormone
C. Luteinizing Hormone and Follicle Stimulating Hormone
D. Estrogen and Progesterone
D
What is the function of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
A. Produce seminal fluid
B. Maturation of sperm
C. Produce fructose
D. Transport sperm to the urethra
B
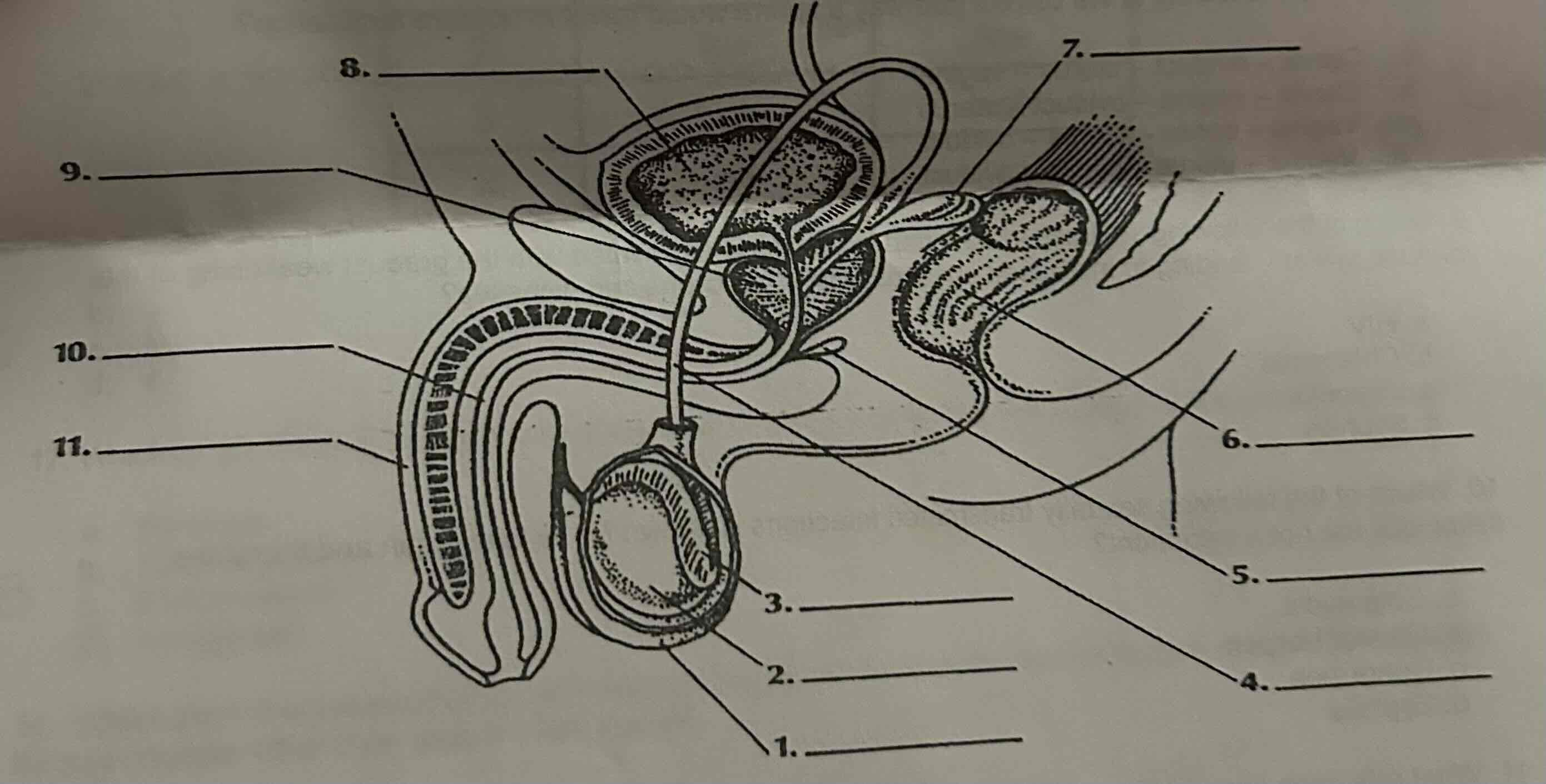
What is the role of the structure labeled '7' in the male reproductive system?
A. Produce seminal fluid
B. Store sperm
C. Transport sperm from the testes
D. Produce testosterone
A
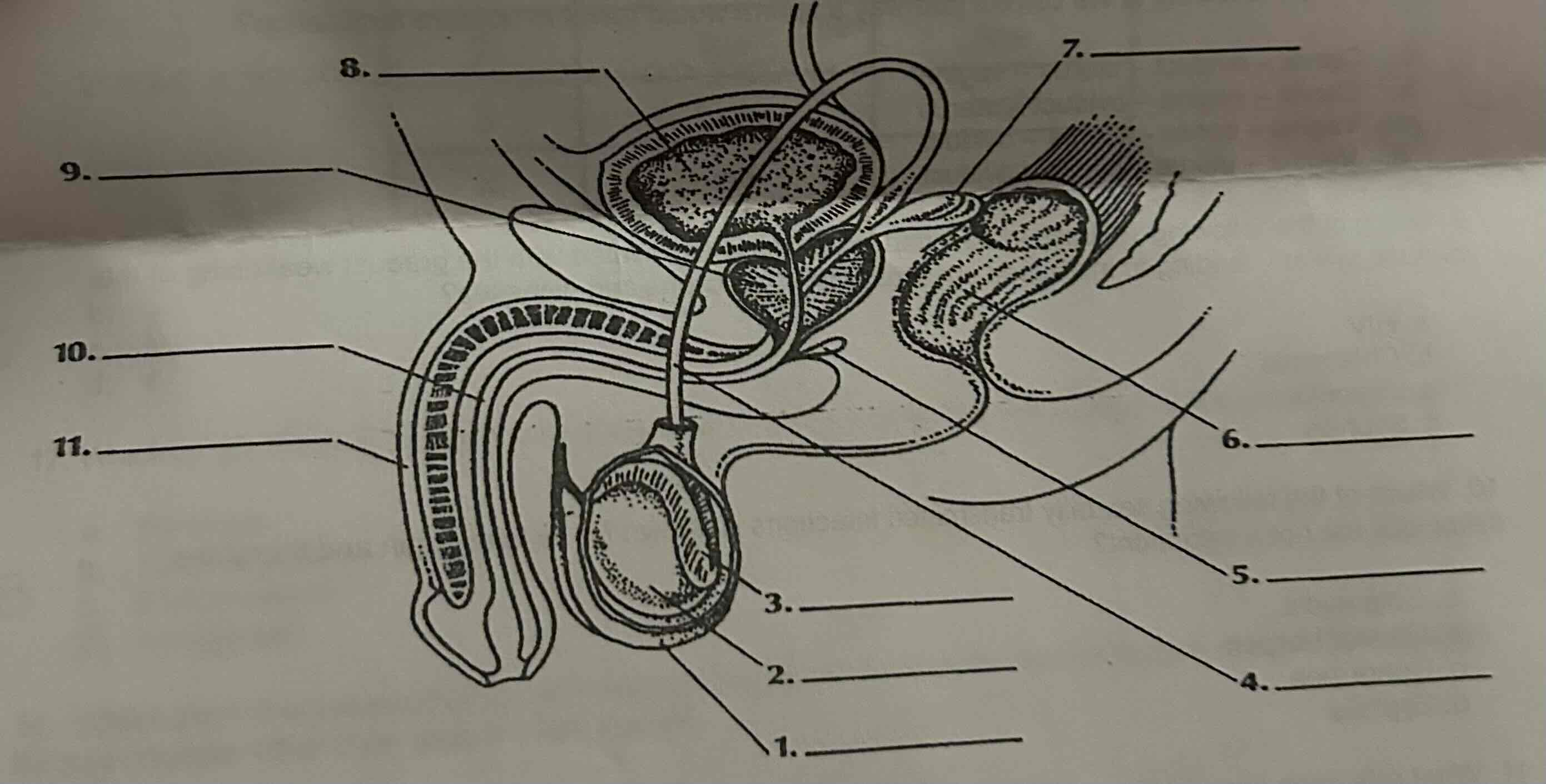
Which of the following structures is the vas deferens?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 9
D. 10
B
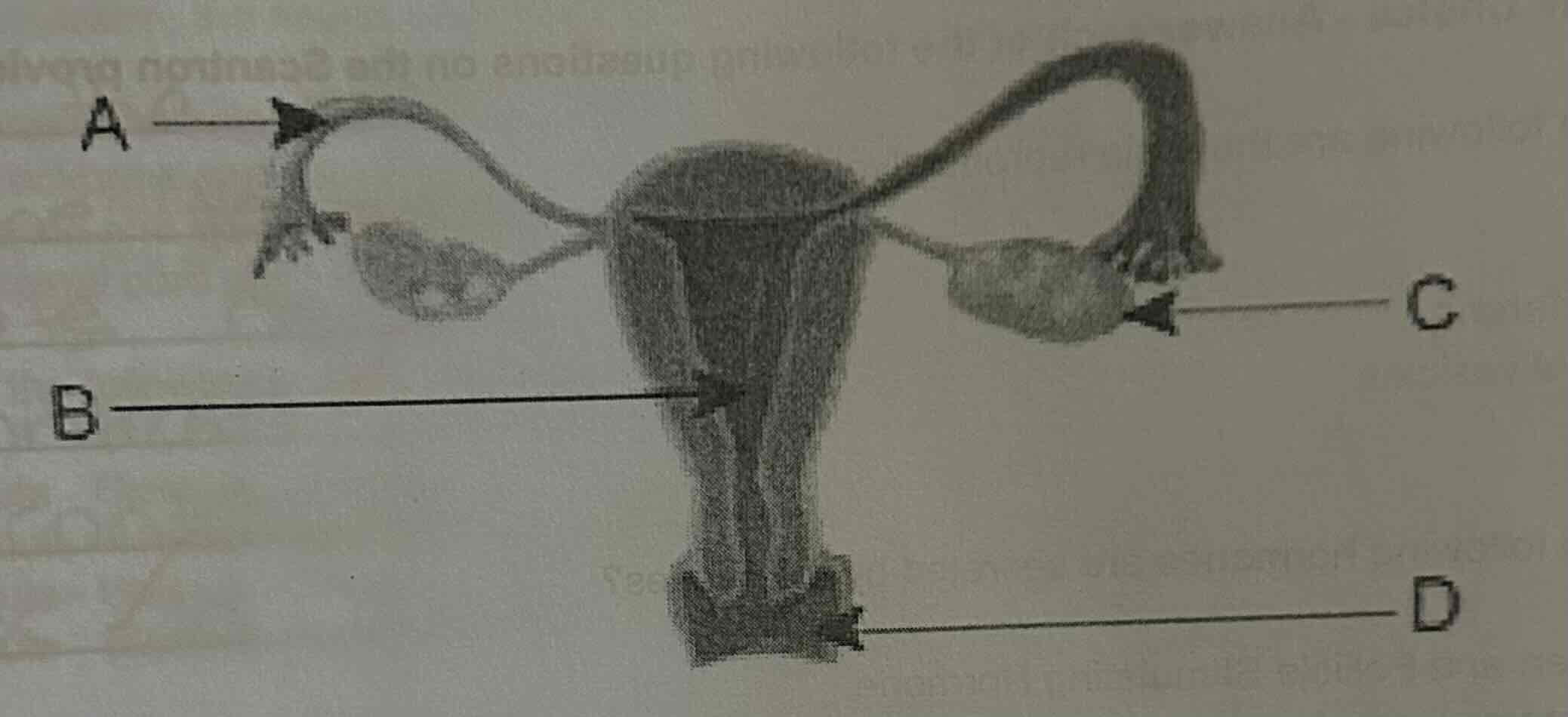
In which of the following structures is the myometrium located?
A.
B.
C.
D.
B
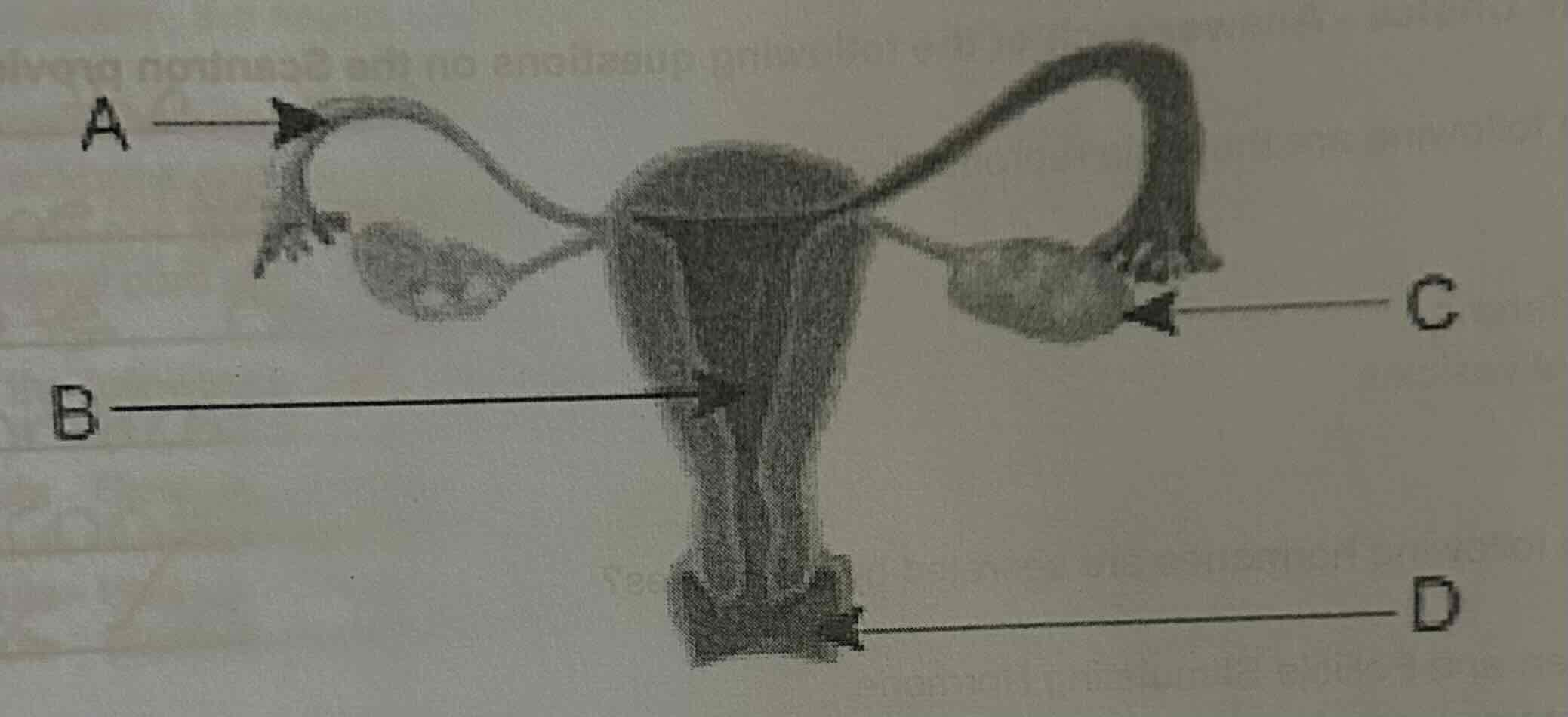
In which of the following structures is fertilization of an egg cell supposed to occur?
A.
B.
C.
D.
A
Which of the following is the correct pathway a sperm would travel to achieve fertilization?
A. Cervix - oviduct - uterus - vagina
B. Cervix - vagina - oviduct - uterus
C. Vagina - uterus - oviduct - ovary
D. Vagina - cervix - uterus - oviduct
C
Which of the following sexually transmitted infections is associated with the gradual weakening of the immune system, leading to increased susceptibility to infections and diseases?
A. HIV
B. Chlamydia
C. Hepatitis
D. Syphilis
A
Which of the following sexually transmitted infections is known for its viral origin and therefore antibiotics are not a treatment?
A. Chlamydia
B. Genital Herpes
C. Gonorrhea
D. Syphilis
B
What role does luteinizing hormone play in the regulation of the male reproductive system?
A. Stimulates sperm production
B. Promotes testosterone synthesis
C. Suppresses FSH secretion
D. Triggers ejaculation
B
The hypothalamus is responsible for the secretion of which hormone?
A. Testosterone
B. GnRH
C. FSH
D. LH
B
Which hormone is responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics characteristics during puberty?
A. Follicle Stimulating Hormone
B. Luteinizing Hormone
C. Oxytocin
D. Estrogen
D
Which of the following hormones is responsible for the maintenance of the uterine lining during pregnancy?
A. Progesterone
B. Follicle Stimulating Hormone
C. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
D. Prolactin
A
Which of the following stimulates ovulation?
A. Increase in FSH
B. Increase in LH
C. Increase in Estrogen
D. Increase in Progesterone
B
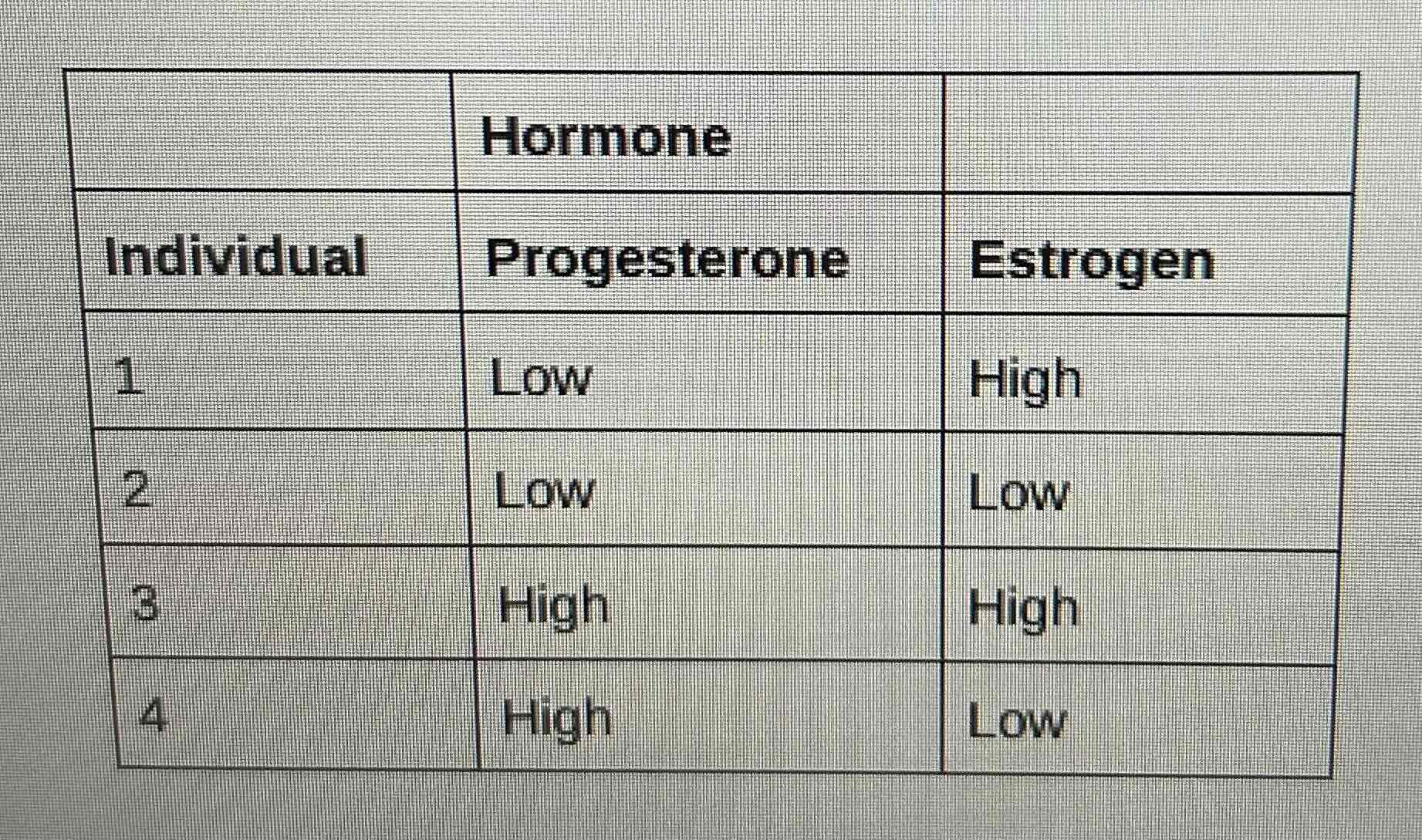
Which individual is in the luteal stage of the menstrual cycle?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
C
Which of the following develops from an ovarian follicle during the luteal stage of the menstrual cycle?
A. Fimbriae
B. Corpus luteum
C. Endometrium
D. An egg cell
B
Which reproductive technology involves the introduction of sperm into the female reproductive system through means other than sexual intercourse?
A. Artificial Insemination
B. In Vitro Fertilization
C. Surrogacy
D. Superovulation
A
Which hormone does a pregnancy test identify?
A. Progesterone
B. Follicle Stimulating Hormone
C. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
D. Prolactin
C
Which of the following is true of cleavage in embryological development?
A. Fusion of male sperm and female egg
B. Rapid division of zygote cells by mitosis
C. Implantation of the blastula in the uterus
D. Differentiation and specialization of cells
B
During neurulation, the neural tube develops into:
A. The brain and backbone
B. The backbone and spinal cord
C. The brain and spinal cord
D. The spinal cord and notochord
C
Which of the following is the correct sequence of embryonic development?
A. Morula - Gastrula - Blastula - Neurula
B. Blastula - Morula - Neurula - Gastrula
C. Morula - Blastula - Neurula - Gastrula
D. Morula - Blastula - Gastrula - Neurula
D
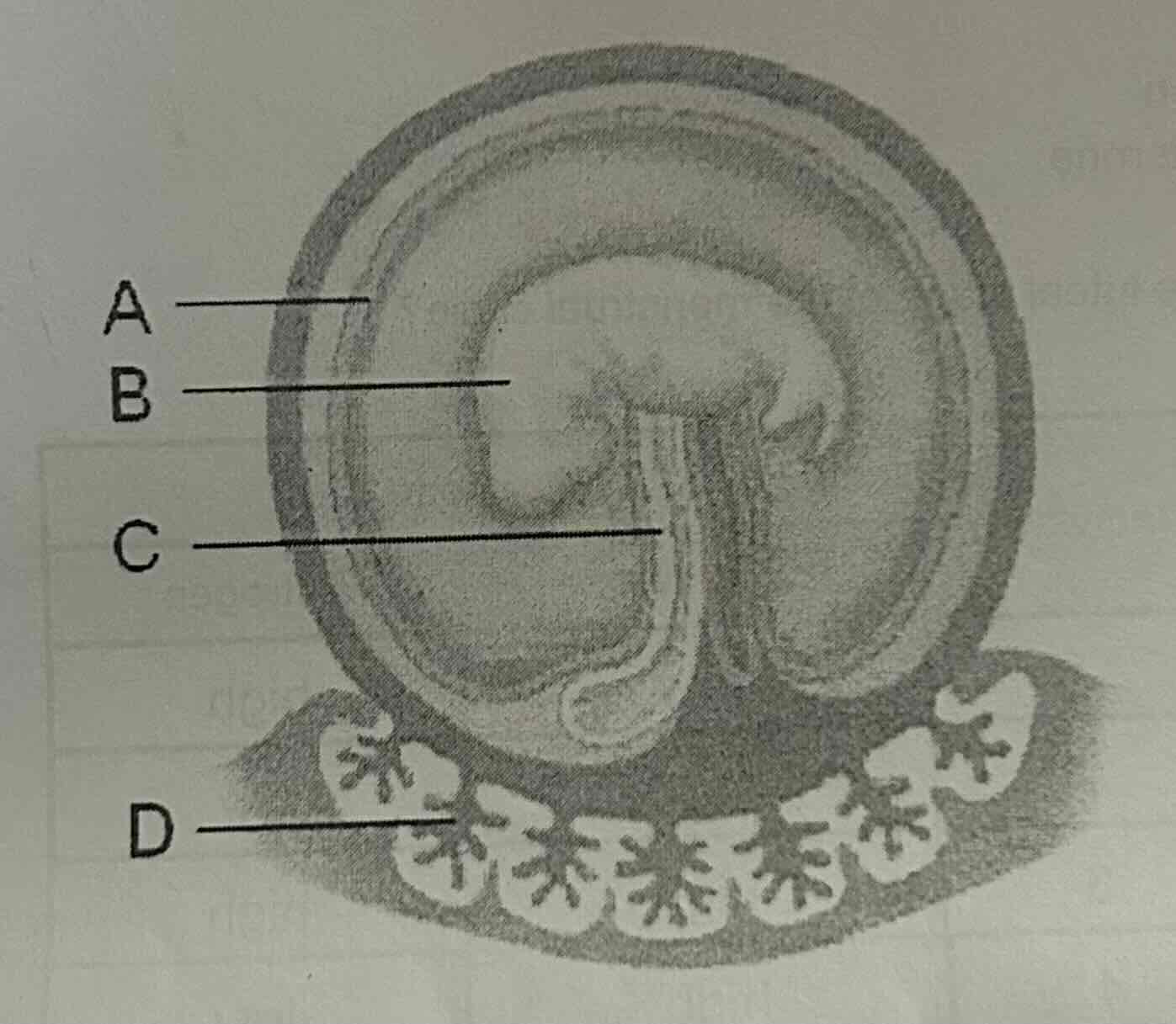
In the diagram, which structure is the site of metabolic exchange between the fetus and its mother?
A.
B.
C.
D.
D
Fraternal twins are also called:
A. Monozygotic twins
B. Dizygotic twins
C. Trizygotic twins
D. Zygotic twins
B
During which stage of parturition does a female's 'water break'?
A. Dilation
B. Expulsion
C. Placental
D. After birth
A