Tarleton Genetics 3303 Dr. Pfau FINAL EXAM
1/265
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
266 Terms
Where do sister chromatids come from?
Homologous or non-homologous chromosomes?
DNA replication, identical copies
Homologous chromosomes: (same size, shape, and gene. one from mom/dad= inheritance)
Gene
A specific Stretch of DNA (only a portion) containing the info to produce an RNA molecule, which may or may not be used to make a polypeptide, which may or may not be a protein.
Purines have ___ carbon rings and Pyrimidines have ___ carbon rings. which nitrogenous bases fall into each category?
Purines = 2 carbon rings and their nitrogenous bases are A & G
Pyrimidines = 1 carbon ring and their nitrogenous bases are C & T
Name all 4 non-functional genetic sequences and describe each.
Pseudogenes: from ancestors
Viral Sequences: virus inserted into DNA
Repetitive Sequences: 3' CAG 5' ---> 3' CAAAGGG 5'
Transcribed Elements: "copy/paste" anywhere
What are the 3 roles of DNA as a hereditary material?
Replication: (not 100%) ---> mutations
Information Content
Ability to change/adapt to environment
Variations of one gene are known as
Alleles
the Packaging of DNA is Hierarchical. The double stranded DNA strand is wrapped around proteins known as _____. These "beads on a string" are referred to as ________.
Histones
Nucleosomes
Continuous Variation
complex traits
ex: hair color in humans
Discontinuous variation
simple traits
ex: dog lab coat colors
which DNA strand is Identical to
3' CAGTCCAGATC 5' ?
5' CTAGACCTGAC 3'
which DNA strand is complementary to
3' CAGTCCAGATC 5'
5' GTCAGGTCTAG 3'
What kind of cells have introns and exons?
Eukaryotic Cells ONLY
intron
A stretch of DNA within a gene that does not contain info to be translated, "interfering", "no purpose"
exon
expressed gene, "good stuff"
loci and/or locus
A specific location on a chromosome
Hydrogen bonds
the bonds between two complementary strands of DNA
The bonds that link nucleotides on a single strand of DNA are
Phosphodiester Bonds (covalent)
Heterochromatin
tightly packaged DNA
Euchromatin
loosely packaged DNA
Purines pair with _____
pyrimidines
A strand of DNA contains 17% Thymine, what is the amount of Guanine?
33%
Karyotype
A representation of chromosomes in the cell, large to small except x/y
How many Hydrogen bonds are in the DNA below?
3' CATTGCCTA 5'
5' CTAACGGAT 3'
22
A cell contains 3 unreplicated chromosomes. Following DNA replication, how many replicated chromosomes will it contain?
3
Nuclear Genome
linear, intron
Organelle Genome (Mitochondria/Chloroplast)
Circular, Endosymbiosis
Viral Genome
RNA/DNA, Circular/Linear
Prokaryotic Genome
Circular, Plasmids
mRNA
"Messenger RNA"
sends information to ribosomes
tRNA
"Transfer RNA"
Brings Amino Acids for translation
rRNA
regulates gene expression
How is DNA faithfully replicated?
template strand
double-stranded
Telocentric Chromosome
Centromere located at end
Acro-Centric Chromosome
Centromere located close to end
Sub-Metacentric Chromosome
Centromere located off centered
Metacentric Chromosome
Centromere in the middle
T/F: Sex chromosomes are either X or Y
False
what are the 2 ways that mutations can occur?
SNP's: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
Indels: INsertion, DEletion
Where do Kinetochores attach to?
the centromere
what are Base pairs (bp)
how DNA is measured
A cell contains 5 unreplicated chromosomes, immediately after DNA replication how many strands of DNA would the cell contain?
10
list the 3 functional regions of a gene and describe them
promoter: start region
Transcribed Region: Transcription
Termination: Stop region
List the 4 ways genomes can differ among species
Number of Chromosomes
Amount of DNA
Format of DNA
Organization of genes
what usually has the most DNA?
Nucleus
What type of chromosomes contain different versions of the same genes?
Homologous Chromosomes
The only words used to describe chromosomes are?
Homologous
non-Homologous
Why must the expression of genes be regulated?
Different genes must be regulated at different times, locations, and quantities (genes get turned on and off)
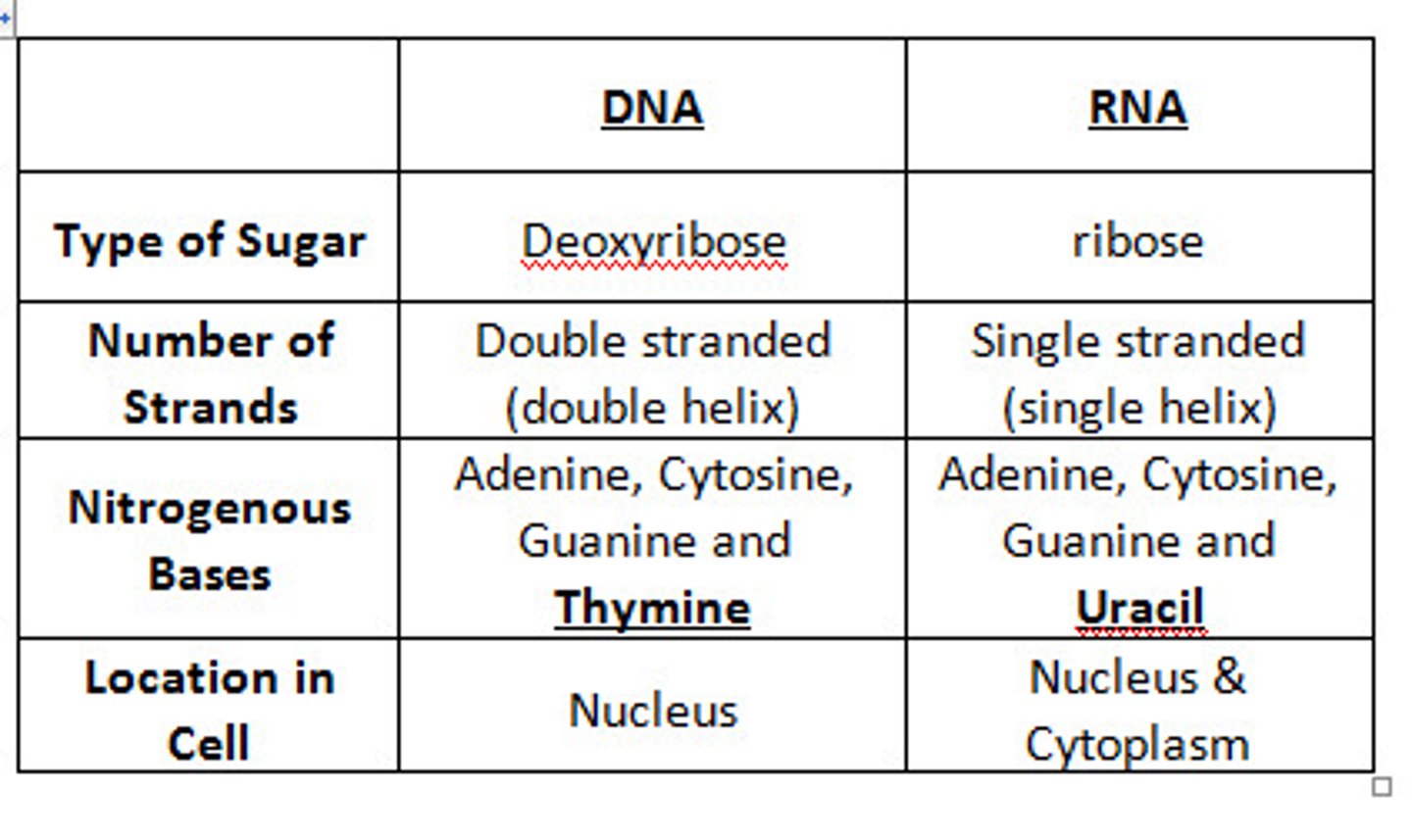
Compare and contrast DNA and RNA
During the process of transcription, what enzyme adds nucleotides?
RNA polymerase
the genetic code is nearly ____,_____, with ____ codons
universal
redundant
64 codons
What monomers make up proteins?
What bonds link monomers together?
Amino Acids
Peptide bonds
list the components of a ribosome and there function
A site: arrival of tRNA P
P site: paring of Amino Acids
E site: Exit of empty tRNA
In the presence of lactose, a lac operon would be ______. This process occurs in _____ cells.
Transcribed
Eukaryotic Cells
In a diploid cell, how many genotypes are possible in the expression of 2 genes each with 2 alleles?
9
mRNA
contains information to make proteins
rRNA
the structural components of the site of translation
tRNA
clover shaped, transfers amino acids during translation
scRNA
found in cytoplasm, regulates gene expression
snRNA
found in nucleus, makes modifications to mRNA
What determines the function of a protein?
its shape
A specific amino acids sequence describes ____ structure of a protein
primary
Following transcription, the strand of mRNA is identical to ____
non-template
what produces alleles? list the 4 possible effects
Mutations
1) normal protein
2) Protein not functional
3) Different Protein Function
4) No protein produced
what are the components of an Amino Acid
Central Carbon
Hydrogen
Amino Group
Side Carbon
Carboxylic Acid group
Mutant Allele
Uncommon variant often the result of mutation in wild type allele
wildtype allele
most frequent allele associated with the common phenotype
what binds to the promoter genes to regulate gene expression?
activators
repressors
effector molecules
molecules that can bind to transcription factors
steps of transcription and translation
initiation, elongation, termination
name the 3 stop codons
UAA
UAG
UGA
effector molecule
stimulus that regulates transcription factors, transcription factors regulate genes
Norm of Reaction
One genotype produces a wide range of phenotypes
Penetrance
The Proportion of Individuals in which the genotype is expressed
Variable Expressivity
the degree to which a trait is expressed
environmental influences
Phenotypic variation due to factors such as sun and heat
Epigenetics
the addition of molecules to DNA
Polymorphism
Existence of variation
incomplete/partial dominance
Heterozygous phenotype is intermediate of its homozygous.
ex:
LDLR gene, cholesterol
L/L = normal
L/l = moderate
l/l = high
complete dominance/recessiveness
Heterozygous phenotype is identical to one homozygous
ex:
huntingtin gene
MC1R gene (hair color)
Codominance
Heterozygous phenotype is a combo of both homozygotes
ex:
blood type
Relative Allelic interaction
Environmental conditions affect gene expression
ex:
Beta-globulin gene
sickle cell anemia
genes in different pathways
expression of one gene does not affect the expression of others
ex:
corn snake colors
Epistasis
expression of a gene affects the expression of other genes "down stream"
ex:
dog lab coat colors
X and Y linked genes
genes found on either the X or Y chromosome
ex:
X-linked = opsin gene (colorblind)
Y-linked = SRY gene
where do you get Mitochondrial genes from?
mom ONLY
What are two fundamental mechanisms for inheritance?
DNA replication
Cell Division
How many origins of Genetic Diversity are there? list them
2
Mutations
Sex
Reproduction
Production of new cells/organisms
Sex
Production of genetic diversity by recombining from more than one source
sexual reproduction
Reproduction with sex
(Meiosis/Union of Gametes)
asexual reproduction
Reproduction without sex
(Binary Fission/Mitosis)
Helicase
unzipping of DNA
"separates"
Topoisomerase
Relieves tension on DNA Strand
Single-Stranded Binding Proteins
Prevents the rejoining of DNA strands
Primase
Adds RNA primer
DNA polymerase
Adds nucleotides complementary to template strand
Ligase
joins Okazaki fragments
Telomerase
completely replicates DNA ends = Telomeres
(located in gametic cells)
What are Okazaki fragments?
Short lengths of single-stranded DNA made on the lagging strand.
Semi-discontinuous
lagging strand