Cardiac Conduction System
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LO: 1. Define the conduction system of the heart. 2. Explain the normal sequence of cardiac activation (depolarization) from the sinoatrial node to the Purkinje fibers. 3. Describe the sinoatrial node and its importance and explain the ionic mechanism of pacemaker automaticity. 4. Explain neural and humoral factors that influence pacemaker rate. 5. Explain the function of the atrioventricular node.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
_____________
the “pacemaker” of the heart, where the normal heartbeat is initiated.
located at the junction of the right atrium (RA) and the superior vena cava.
The signal sent out from it is conducted through the RA and LA but not the ventricles
The sinoatrial (SA) node
the “pacemaker” of the heart, where the normal heartbeat is initiated.
located at the junction of the right atrium (RA) and the superior vena cava.
The signal sent out from it is conducted through the RA and LA but not the ventricles
The signal from the SA to the RA is conducted the LA through ____________________, a specialized myocyte conduction pathway. It cannot go directly to the ventricles, since they are “walled off” from the atria by fibrous, nonconducting connective tissue. Instead, the signal is routed to the gatekeeper, the atrioventricular (AV) node.
The signal from the SA to the RA is conducted the LA through Bachmann’s bundle, a specialized myocyte conduction pathway. It cannot go directly to the ventricles, since they are “walled off” from the atria by fibrous, nonconducting connective tissue. Instead, the signal is routed to the gatekeeper, the atrioventricular (AV) node.
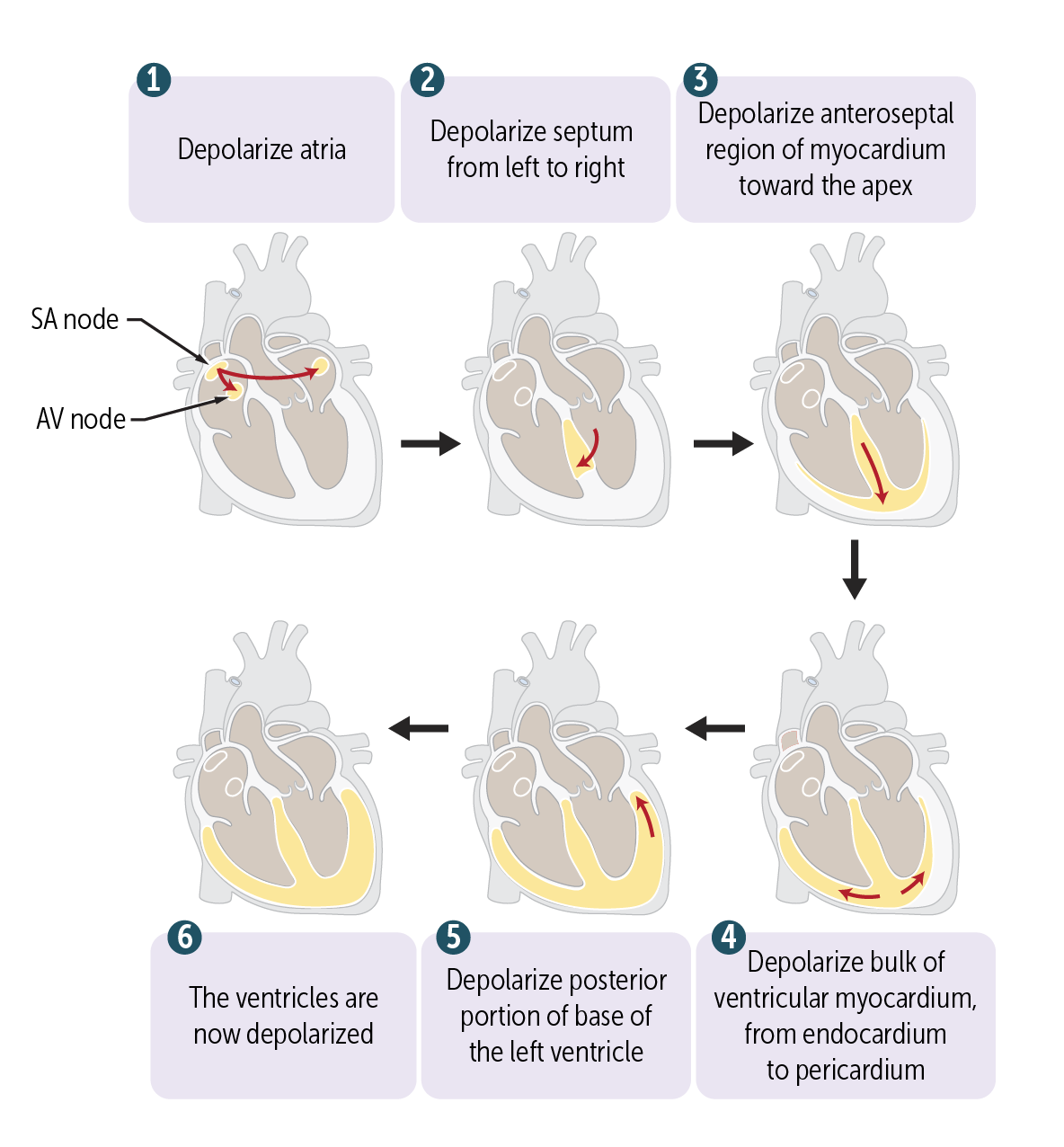
The conduction cells called the __________ node depolarize with an action potential, like in the SA node, but the conduction velocity is slower. This slowing allows the ventricles to depolarize after, not along with, the atria. This allows the ventricles to fill with blood from the atria prior to their depolarization and contraction for optimal pumping of blood
The conduction cells called the Atrioventricular (AV) node depolarize with an action potential, like in the SA node, but the conduction velocity is slower. This slowing allows the ventricles to depolarize after, not along with, the atria. This allows the ventricles to fill with blood from the atria prior to their depolarization and contraction for optimal pumping of blood
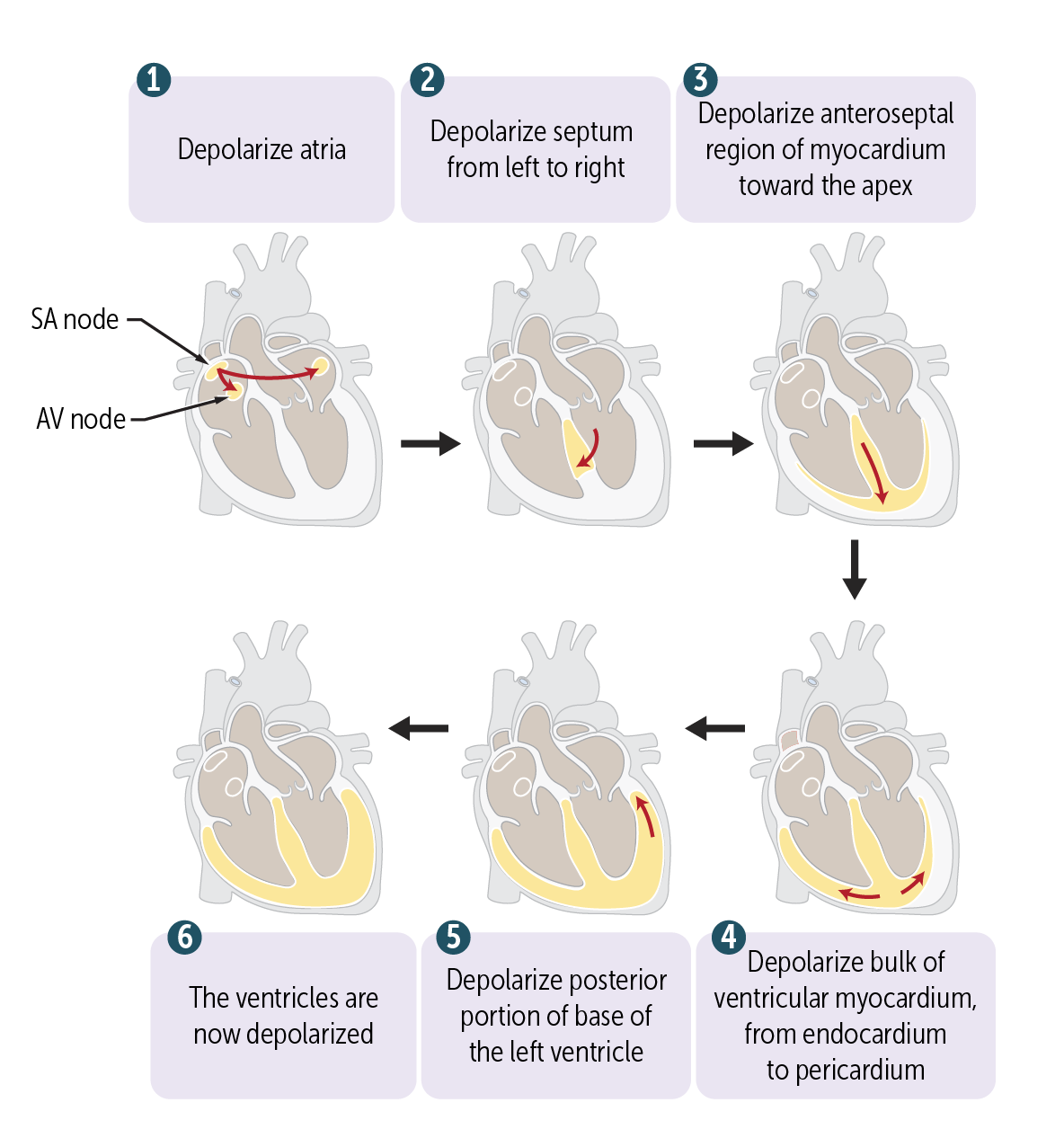
The AV node exhibits a property called _____________, which refers to an increased slowing of impulses through the AV node at higher atrial contraction rates. This serves as a protective mechanism to ensure that the ventricles do not contract too rapidly in cases of atrial tachyarrhythmias, such as atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation, by allowing the transmission of only some but not all beats through the AV node.
The AV node exhibits a property called decremental conduction, which refers to an increased slowing of impulses through the AV node at higher atrial contraction rates. This serves as a protective mechanism to ensure that the ventricles do not contract too rapidly in cases of atrial tachyarrhythmias, such as atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation, by allowing the transmission of only some but not all beats through the AV node.
_____________ is a bundle of specialized cardiac muscle fibers run from the AV node down the interventricular septum that divides the left and right ventricles. It then divides into two bundle branches.
Bundle of His is a bundle of specialized cardiac muscle fibers run from the AV node down the interventricular septum that divides the left and right ventricles. It then divides into two bundle branches.
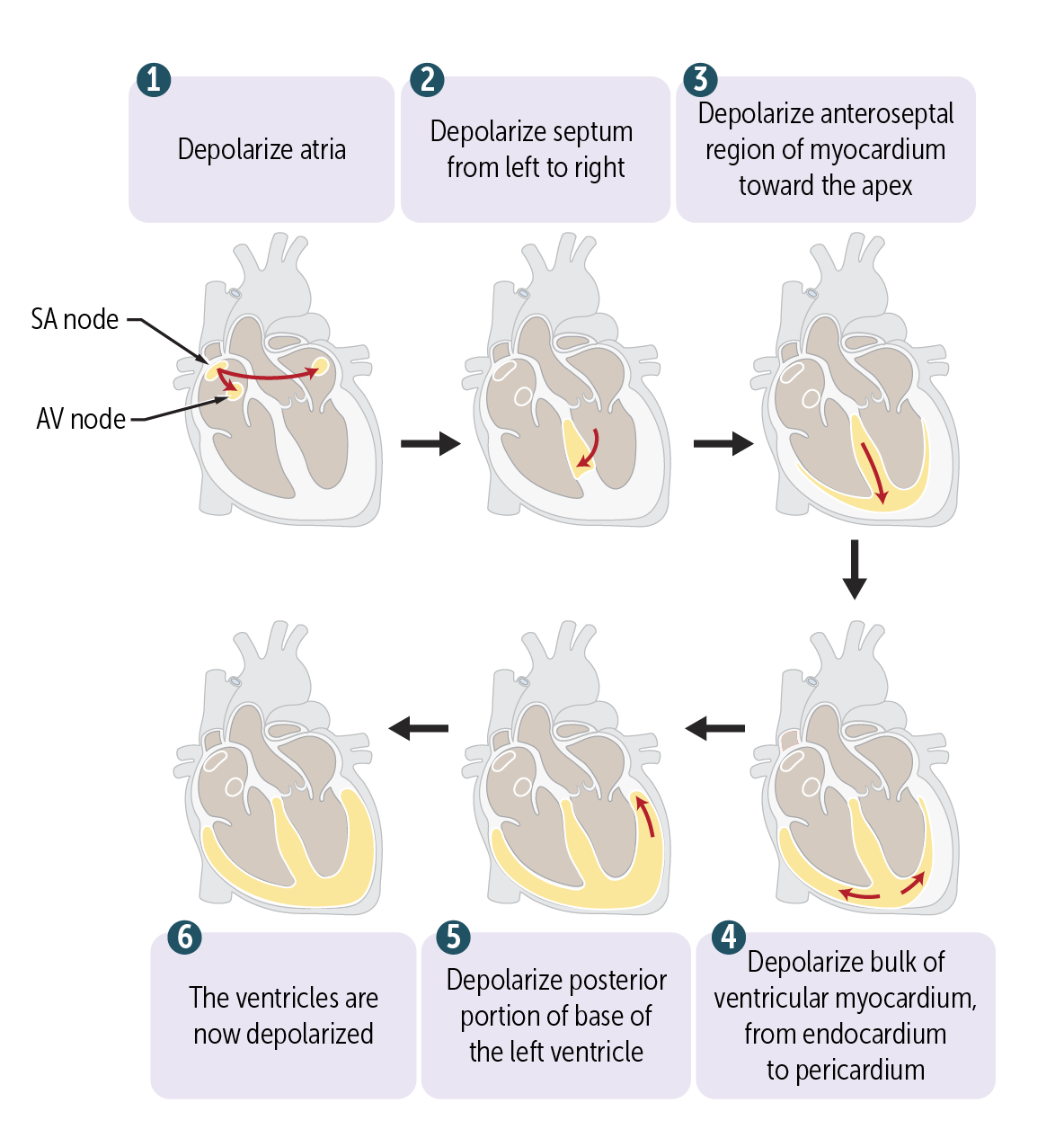
The _______ bundle branch has a posterior and an anterior fascicle that transmits impulses to the LV.
The left bundle branch has a posterior and an anterior fascicle that transmits impulses to the LV.
The bundle branches divide into the intricate ___________, which is responsible for depolarizing ventricular cardiac muscle cells (myocardium), causing the ventricular muscle to contract.
The bundle branches divide into the intricate Purkinje fiber system, which is responsible for depolarizing ventricular cardiac muscle cells (myocardium), causing the ventricular muscle to contract.
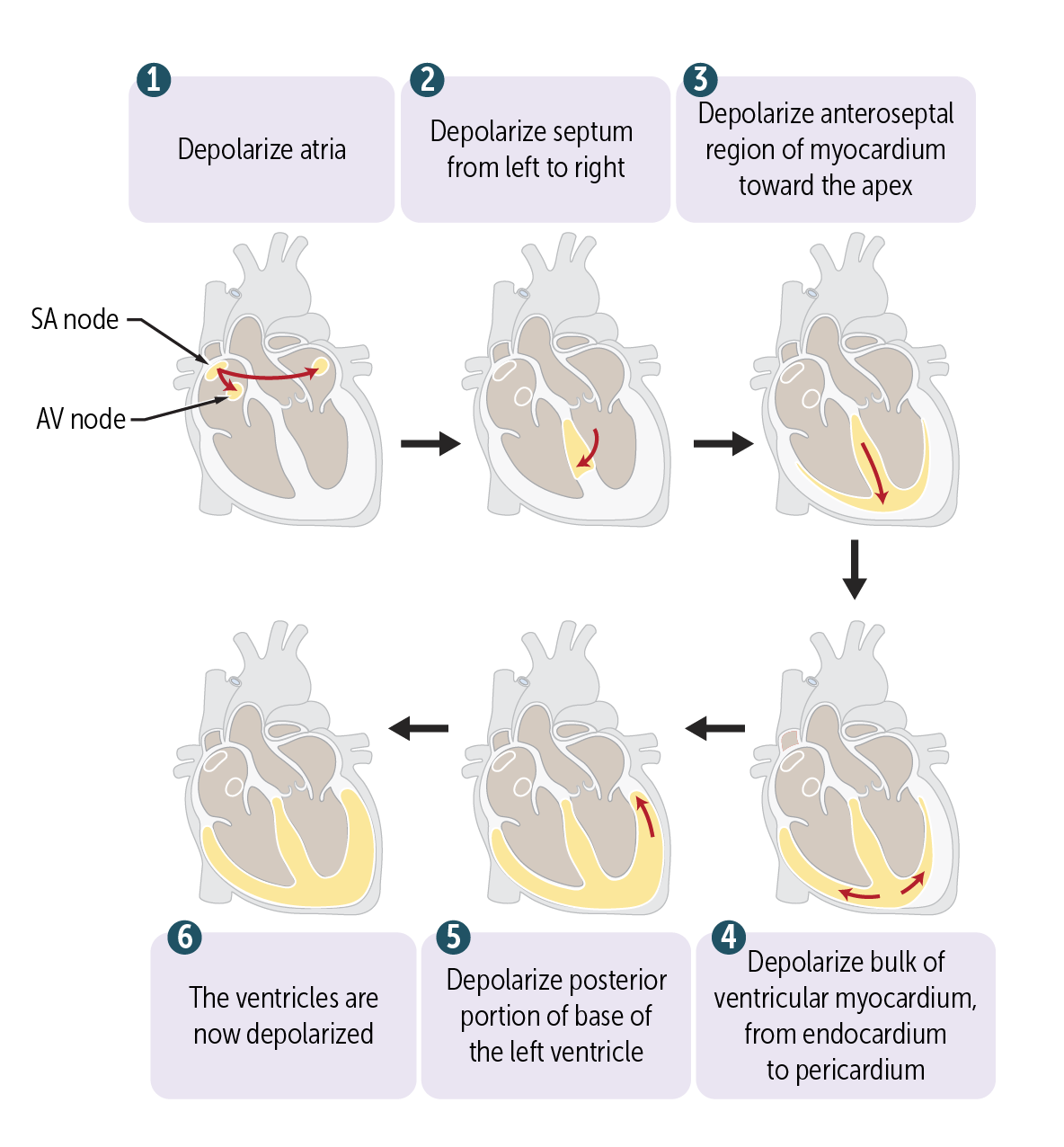
What is the last parts of the heart to depolarize?
Posterior left ventricle
Unlike most cells, the muscle cells of the SA node have _________ that demonstrate automaticity, meaning they depolarize spontaneously and with a regular rhythm
Unlike most cells, the muscle cells of the SA node have pacemaker cells that demonstrate automaticity, meaning they depolarize spontaneously and with a regular rhythm
Phase 4 presents the spontaneous depolarization unique to the pacemaker cells of the heart. These cells have a special pacemaker current, also known as the________________. This is a slow inward movement of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) into the cell.
Phase 4 presents the spontaneous depolarization unique to the pacemaker cells of the heart. These cells have a special pacemaker current, also known as the If current (f for funny, or odd, as it was first referred to). This is a slow inward movement of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) into the cell.
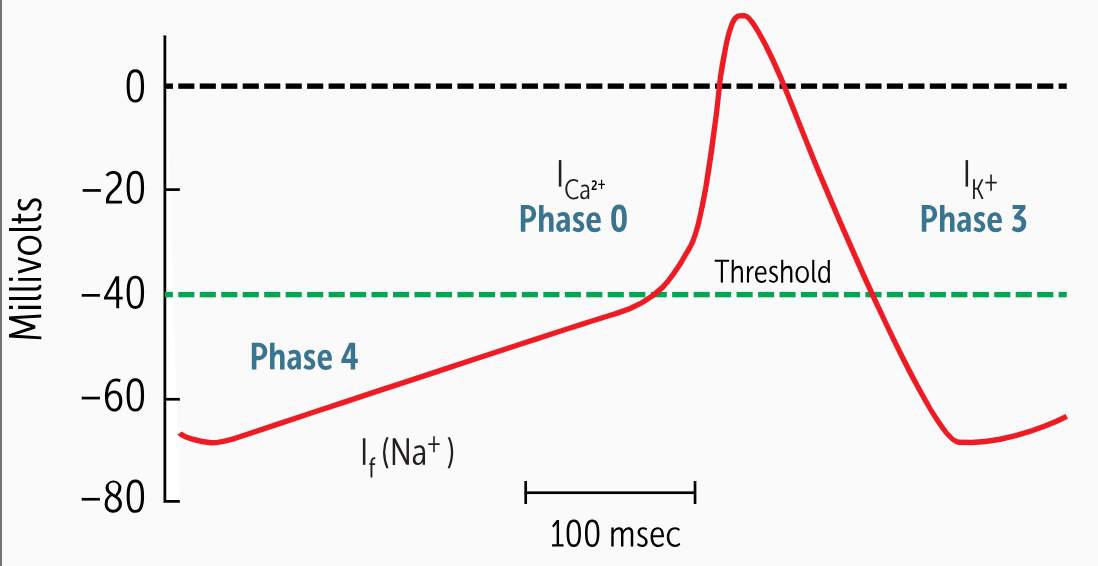
As Na+ and K+ flow into the cell, it slowly depolarizes and reaches the threshold potential of –40 mV, at which point, the L-type calcium channels start opening and calcium influx occurs, and _____________ starts.
As Na+ and K+ flow into the cell, it slowly depolarizes and reaches the threshold potential of –40 mV, at which point, the L-type calcium channels start opening and calcium influx occurs, and phase 0 depolarization starts.
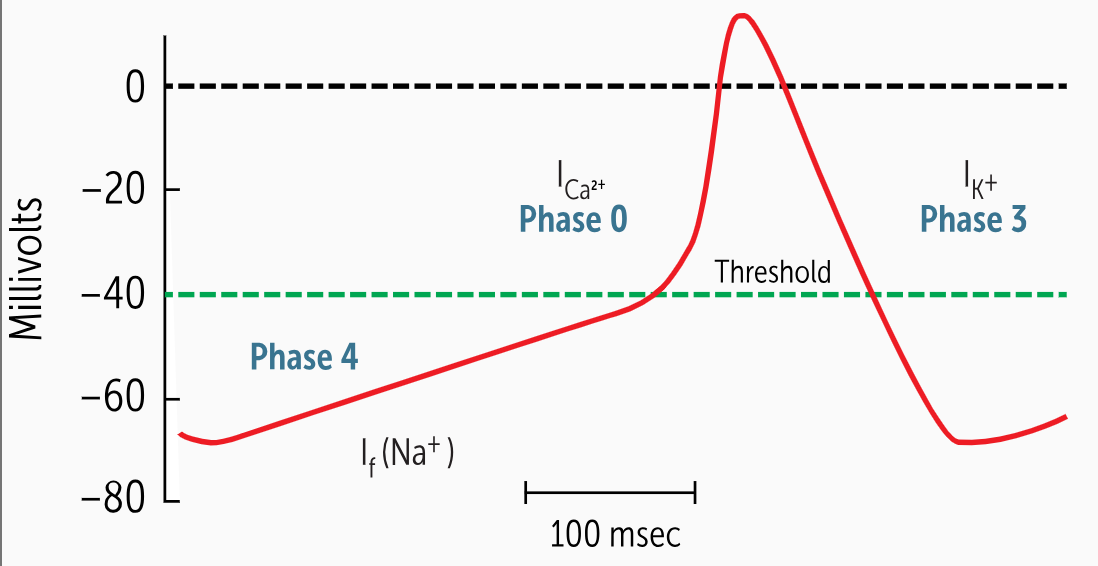
The upward slope of phase 4 is adjustable, and the slope will determine how fast a new phase 0 depolarization occurs. A steeper slope means less time elapses until phase 0 and a more rapid heart rate. A flatter slope means _______________
The upward slope of phase 4 is adjustable, and the slope will determine how fast a new phase 0 depolarization occurs. A steeper slope means less time elapses until phase 0 and a more rapid heart rate. A flatter slope means a slower heartbeat.
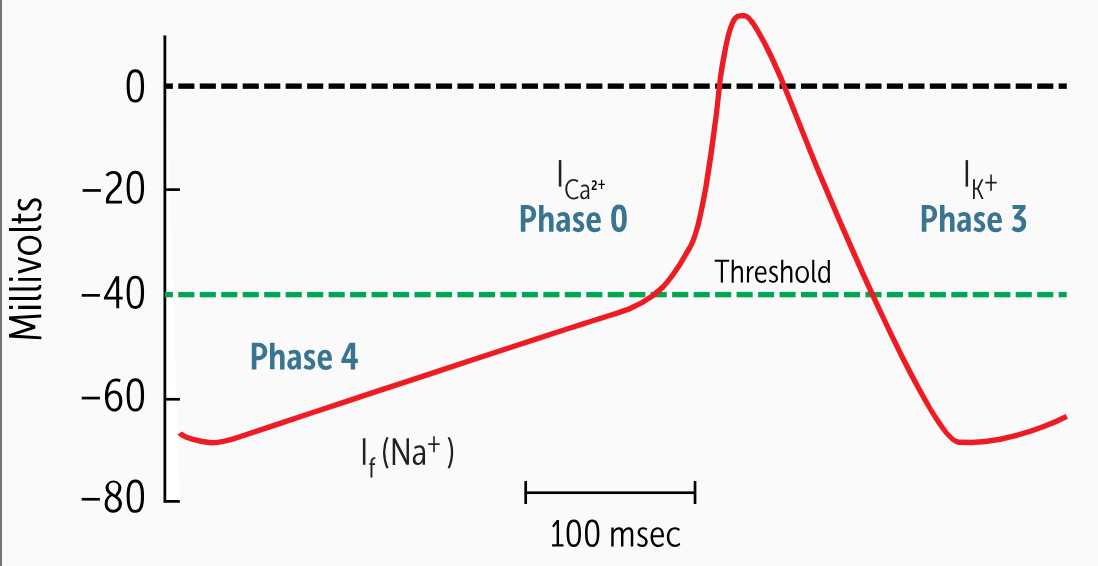
___________________ are also present in the AV node, in the bundle of His, and throughout the ventricular conduction system.
secondary pacemaker cells are also present in the AV node, in the bundle of His, and throughout the ventricular conduction system.
The SA nodal rate triggers the activation of these secondary pacemaker cells before they have a chance to automatically depolarize, a phenomenon known as ______________________.
The SA nodal rate triggers the activation of these secondary pacemaker cells before they have a chance to automatically depolarize, a phenomenon known as overdrive suppression.
When the SA node is nonfunctional (eg, sick sinus syndrome), or the impulse from the SA node is blocked from triggering the rest of the conduction system (eg, complete heart block), the secondary pacemakers start depolarizing and send out impulses at their slower intrinsic rate (eg, 50-60 beats/min for the AV node, 30 beats/min for Purkinje fibers). This will result in a slow heartbeat, and the secondary pacemakers are then known as ________________________
When the SA node is nonfunctional (eg, sick sinus syndrome), or the impulse from the SA node is blocked from triggering the rest of the conduction system (eg, complete heart block), the secondary pacemakers start depolarizing and send out impulses at their slower intrinsic rate (eg, 50-60 beats/min for the AV node, 30 beats/min for Purkinje fibers). This will result in a slow heartbeat, and the secondary pacemakers are then known as ectopic pacemakers (normal pacemakers).
The automaticity rate of the SA node, without outside influences, is ______ beats per minute, faster than the actual heart rate.
The automaticity rate of the SA node, without outside influences, is ~100 beats per minute, faster than the actual heart rate.
At the cellular level, the ANS primarily alters the heart rate by changing the slope of phase ___.
At the cellular level, the ANS primarily alters the heart rate by changing the slope of phase 4.
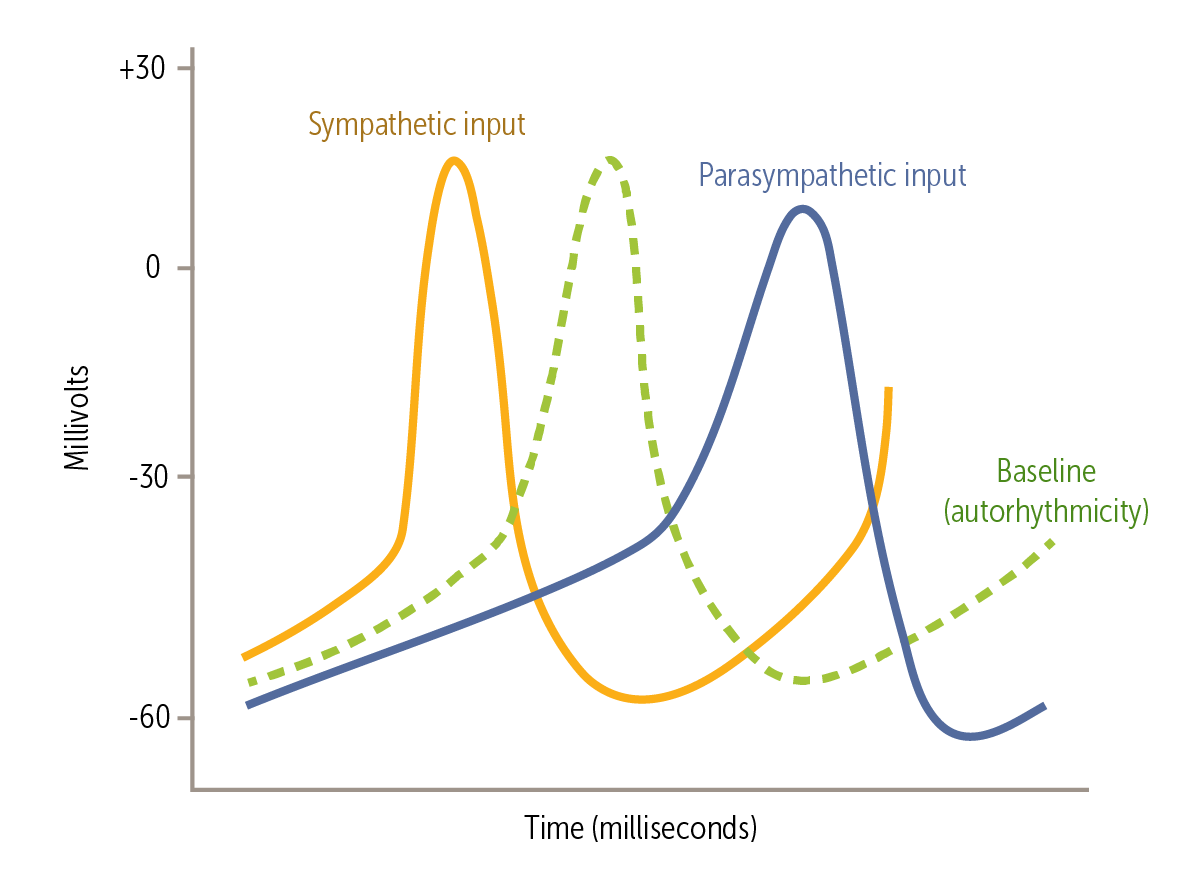
At rest, the PSNS dominates, giving us a resting heart rate of 60-100 beats/min. The PSNS does this via innervation by the ____________. The vagus increases the threshold for triggering phase 0 (ie, less negative threshold), causes hyperpolarization at the end of phase 3, and decreases the slope of phase 4
At rest, the PSNS dominates, giving us a resting heart rate of 60-100 beats/min. The PSNS does this via innervation by the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X). The vagus increases the threshold for triggering phase 0 (ie, less negative threshold), causes hyperpolarization at the end of phase 3, and decreases the slope of phase 4
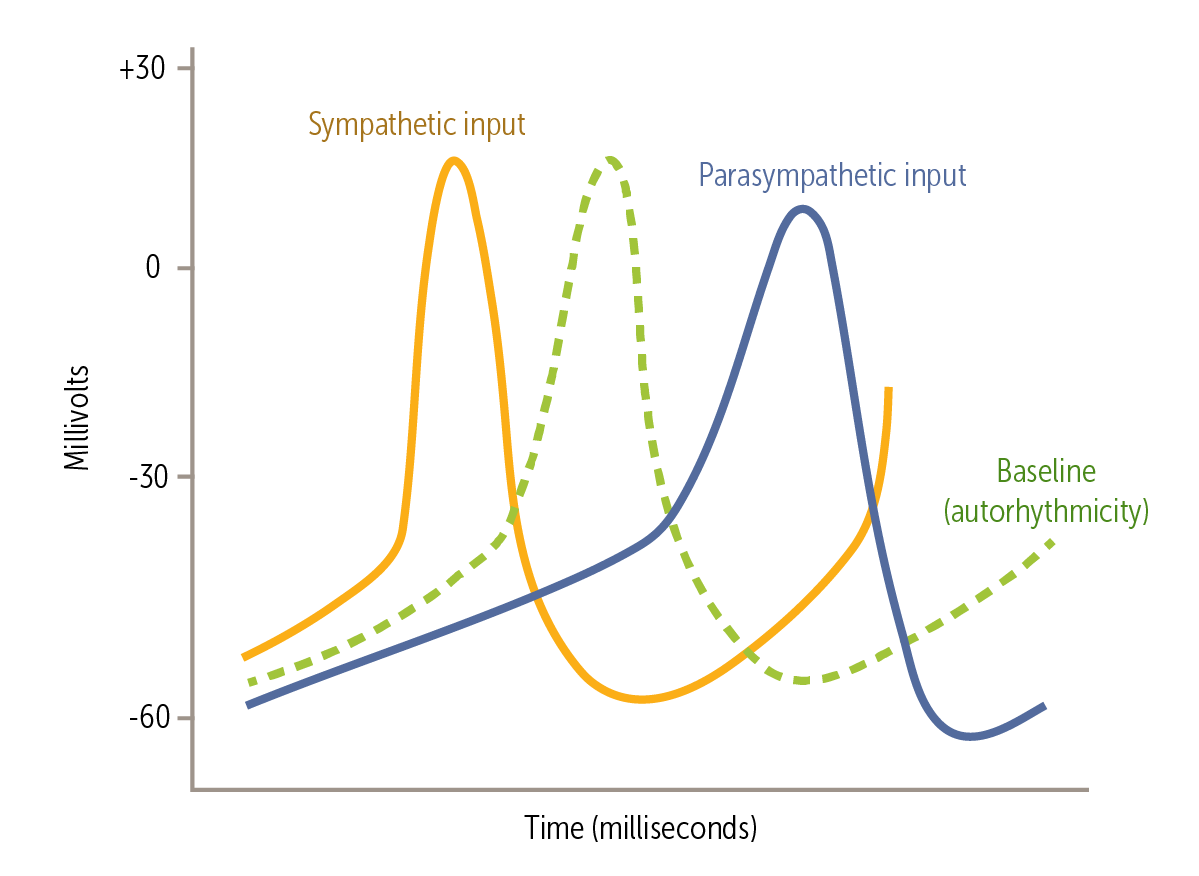
How does the vagus nerve influence the changes of the heart seen with PSNS?
In phase 4, the released parasympathetic neurotransmitter acetylcholine increases conductance of potassium (K+) channels and decreases conductance of calcium (Ca2+) channels. This decreases the If current, thus decreasing the slope of phase 4 depolarization. This effect delays phase 0 depolarization
Why do heart transplant recipients have a resting heart rate of 100-110 beats/min?
Removal of the vagus nerve inputs in heart transplant recipients can lead to the heart beating faster.
As SA node input from the SNS increases, the slope of phase 4 increases; and the threshold for triggering phase 0 becomes more negative and occurs earlier. These effects increase pacemaker depolarization frequency. This happens because the released ___________ increases conductance of Ca2+ channels, the If current, and the slope of phase 4 depolarization.
As SA node input from the SNS increases, the slope of phase 4 increases; and the threshold for triggering phase 0 becomes more negative and occurs earlier. These effects increase pacemaker depolarization frequency. This happens because the released norepinephrine increases conductance of Ca2+ channels, the If current, and the slope of phase 4 depolarization.
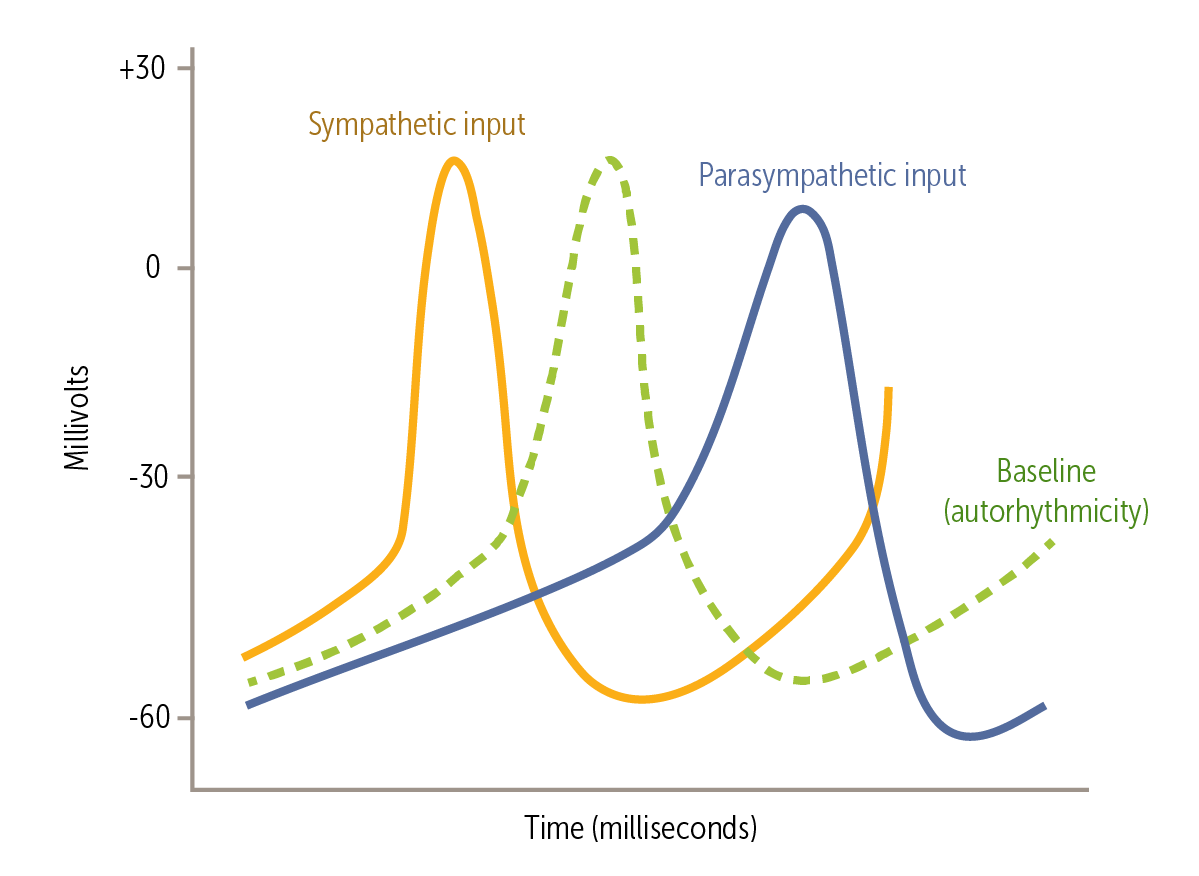
Circulating _______________ such as adrenaline (epinephrine) released from the adrenal medulla act like the SNS to cause the SA node to depolarize at a greater rate, increasing the heart rate.
Circulating catecholamines such as adrenaline (epinephrine) released from the adrenal medulla act like the SNS to cause the SA node to depolarize at a greater rate, increasing the heart rate.
In normal hearts, the ___node is a true gatekeeper, as it is the only pathway by which the electrical signal can pass from the atria to the ventricles. During passage through the ___ node, conduction velocity decreases tenfold.
In normal hearts, the AV node is a true gatekeeper, as it is the only pathway by which the electrical signal can pass from the atria to the ventricles. During passage through the AV node, conduction velocity decreases tenfold.
The decrease conduction of the AV node allows for?
Allow the atria to completely depolarize and contract before the ventricles depolarize and contract (needed for a proper synchronous cardiac contraction)
Limit the passage of electrical signals that could simultaneously activate the ventricles and potentially cause arrhythmias.