Lecture Exam 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
1
New cards
mutation
any change in nucleotide sequence
2
New cards
insertions/deletions and substitution
major kinds of mutations
3
New cards
point mutation
when a single base pair is added, deleted or changed
4
New cards
kinds of point mutations
Silent mutations, missense mutations and nonsense mutations
5
New cards
silent mutation
no change in amino acid sequence of polypeptide
6
New cards
missense mutation
* Slightly different amino acid sequence
* Sickle cell
* 1 single base pair to be substituted in hemoglobin chain
* Sickle cell
* 1 single base pair to be substituted in hemoglobin chain
7
New cards
nonsense mutation
* Codes for stop codon
* Polypeptide synthesis ceases
* Usually result in loss of fitness (reproduction)
* Polypeptide synthesis ceases
* Usually result in loss of fitness (reproduction)
8
New cards
frameshift insertion/deletion
Major difference in amino acid sequence
9
New cards
physical mutagens
Ionizing radiation
* penetrates deeply
* Destabilizes it
* Destroys DNA of cells
\
Nonionizing radiation
* UV light
* Thymine dimers
* Double thymine's stick together and then gets cut out causing frameshift mutations
* penetrates deeply
* Destabilizes it
* Destroys DNA of cells
\
Nonionizing radiation
* UV light
* Thymine dimers
* Double thymine's stick together and then gets cut out causing frameshift mutations
10
New cards
chemical mutagens
* Nucleotide analogs - Disrupt DNA and RNA replication
* Bromouracil can replace thymine
* Nucleotide-altering chemicals - Result in base-pair substitutions and missense mutations
* Frameshift mutagens - Result in nonsense mutations
* Bromouracil can replace thymine
* Nucleotide-altering chemicals - Result in base-pair substitutions and missense mutations
* Frameshift mutagens - Result in nonsense mutations
11
New cards
base excision repair
Can remove incorrect nucleotides
12
New cards
light repair
Can produce photolyase to repair and get rid of thymine dimers by using natural light to produce photolyase
13
New cards
nucleotide excision repair
Can cut out multiple nucleotides to repair thymine dimers and repair the strand
14
New cards
mismatch repair
Can remove large parts of a single strand to repair incorrect nucleotide repair
15
New cards
error-prone repair
an inefficient mechanism for repairing DNA damage that often results in mutations
16
New cards
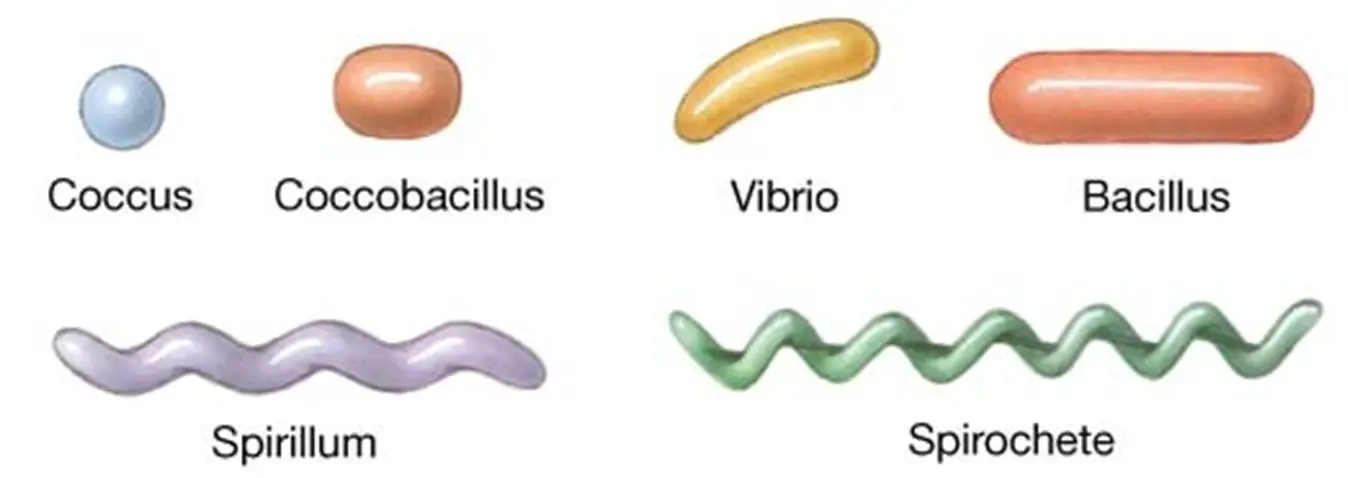
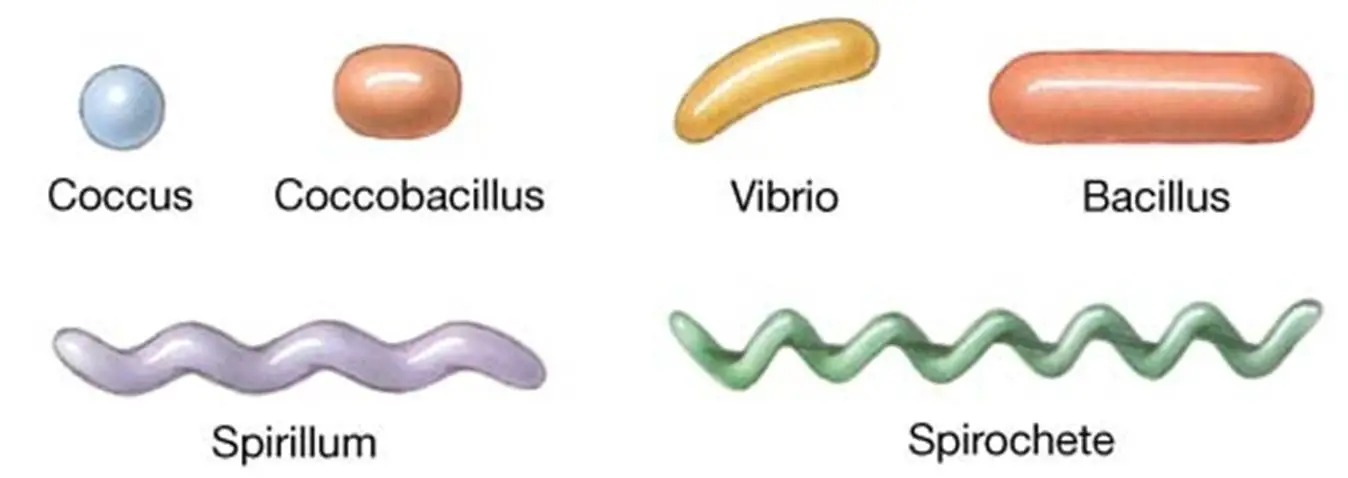
cocci
circular bacteria
17
New cards
bacillus
rod shaped bacteria
18
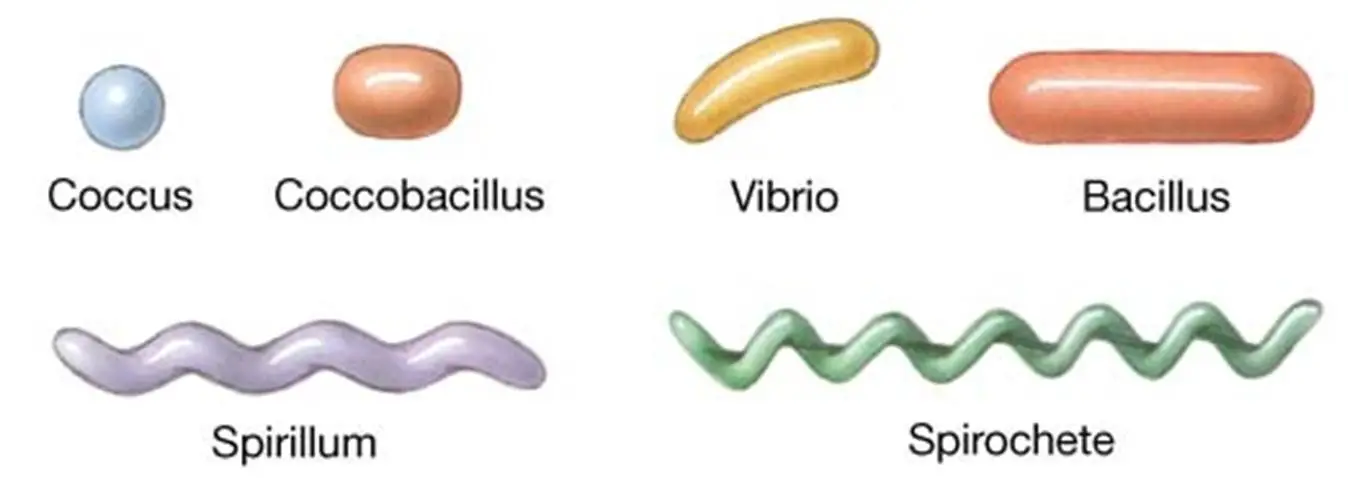
New cards
vibrio
comma shaped bacteria
19
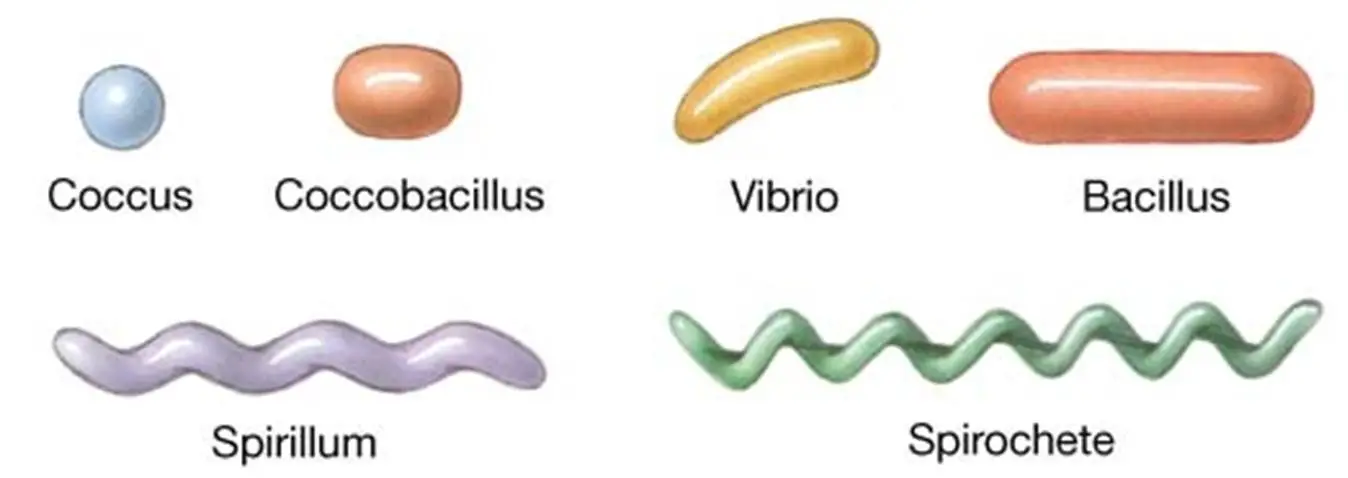
New cards
spirochete
corkscrew like bacteria
20
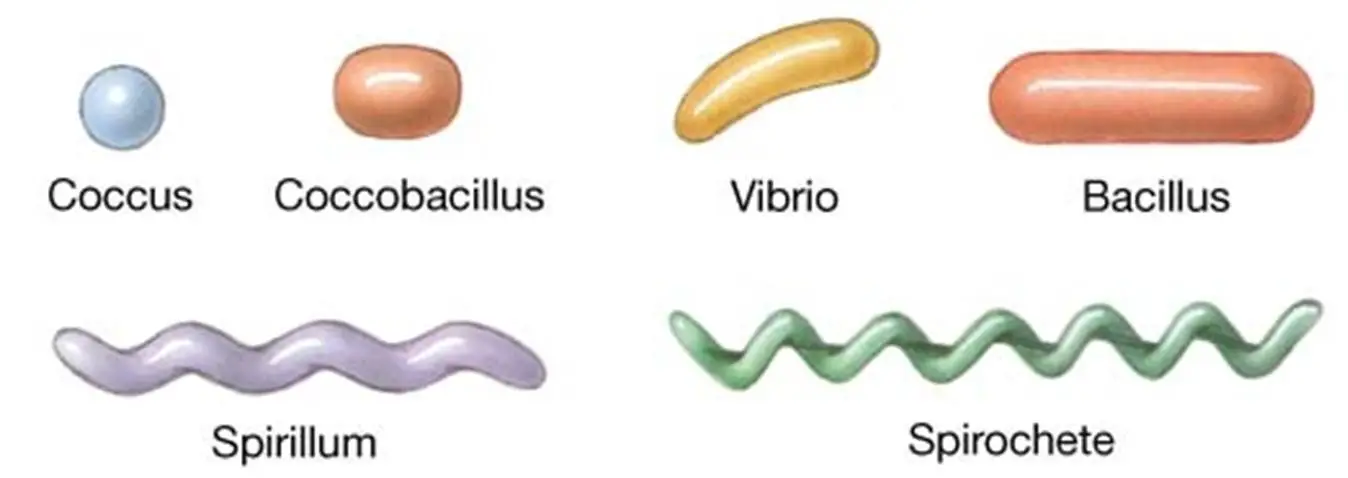
New cards
spirilium
wavy like bacteria
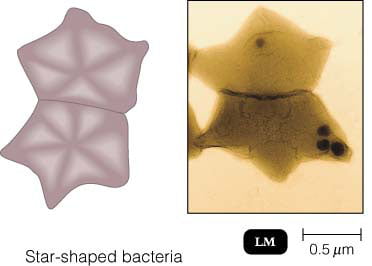
21
New cards
star
22
New cards
pleomorphic
can change shape
23
New cards
endospores
formation
* when there is a severe lack of nutrients
\
function
* allows the bacterium to produce a dormant and highly resistant cell to preserve the cell's genetic material in times of extreme stress.
* when there is a severe lack of nutrients
\
function
* allows the bacterium to produce a dormant and highly resistant cell to preserve the cell's genetic material in times of extreme stress.
24
New cards
types of reproduction
budding
* cell elongates to form a bud that eventually breaks off mother cell
\
binary fission
* Most common method of cell division
\
snapping division
* Elongates and older outer cell wall snaps to reveal new cell wall
* cell elongates to form a bud that eventually breaks off mother cell
\
binary fission
* Most common method of cell division
\
snapping division
* Elongates and older outer cell wall snaps to reveal new cell wall
25
New cards
arrangements of prokaryotes
diplo
* two
\
strepto
* chain
\
tetrads
* clusters of 4 arranged in same plane (cocci)
\
sarcinae
* large brick like arrangements
\
staphylo
* big clumps of cells
\
palisade
* only bacilli
* fence like structure
\
v shape
* form a v
* two
\
strepto
* chain
\
tetrads
* clusters of 4 arranged in same plane (cocci)
\
sarcinae
* large brick like arrangements
\
staphylo
* big clumps of cells
\
palisade
* only bacilli
* fence like structure
\
v shape
* form a v
26
New cards
mycoplasma
* live in osmotically protected environments
* lack of cell wall makes them naturally more antibiotic-resistant
* antibiotics that act by degrading cell walls cannot kill mycoplasma
* lack of cell wall makes them naturally more antibiotic-resistant
* antibiotics that act by degrading cell walls cannot kill mycoplasma
27
New cards
Clostridium
detrimental
* Form endospores
* Vegetative cells produce toxins
* Medically relevant members
* C. tetani – causes tetanus
* C. perfrigens – causes gas gangrene
* C. botulinum – causes botulism & and is used in botox
* C. dificile (C. diff)– causes severe diarrhea and is resistant to most antibiotics
* Make hydrogen sulfide gas – smells like rotten eggs
* Form endospores
* Vegetative cells produce toxins
* Medically relevant members
* C. tetani – causes tetanus
* C. perfrigens – causes gas gangrene
* C. botulinum – causes botulism & and is used in botox
* C. dificile (C. diff)– causes severe diarrhea and is resistant to most antibiotics
* Make hydrogen sulfide gas – smells like rotten eggs
28
New cards
Bacillus
* *B. cereus* – causes food poisoning
* *B. anthracis* – causes anthrax by producing toxins that kill surrounding tissues
* Was used in bioterrorism attack in 2001
* Cutaneous, inhalation
* If untreated, \~20% & 100% fatal (inhalation), respectively
* Inhalation anthrax needs to be picked up within 24 hours of inhalation
* *B. anthracis* – causes anthrax by producing toxins that kill surrounding tissues
* Was used in bioterrorism attack in 2001
* Cutaneous, inhalation
* If untreated, \~20% & 100% fatal (inhalation), respectively
* Inhalation anthrax needs to be picked up within 24 hours of inhalation
29
New cards
Listeria
* Can contaminate milk & meat
* Causes food poisoning
* Able to reproduce when refrigerated
* Evades host immune response
* Causes food poisoning
* Able to reproduce when refrigerated
* Evades host immune response
30
New cards
Streptococcus
* Strep pyogenes common cause of strep throat
* Gram-positive catalase negative
* Strep pneumonae
* Can cause middle ear infections
* Strep mutans
* Takes hold and can overpopulate and lead to cavities
* Ferments sugar to produce acids
* These acids destroy tooth enamel
* Can cause diseases including pharyngitis, impetigo (more common manifestation of strep in young children; cutaneous), pneumonia, necrotizing fasciitis, etc.
* Gram-positive catalase negative
* Strep pneumonae
* Can cause middle ear infections
* Strep mutans
* Takes hold and can overpopulate and lead to cavities
* Ferments sugar to produce acids
* These acids destroy tooth enamel
* Can cause diseases including pharyngitis, impetigo (more common manifestation of strep in young children; cutaneous), pneumonia, necrotizing fasciitis, etc.
31
New cards
Staphylococccus
* S. aureus can cause diseases such as toxic shock, pneumonia, etc.
* MRSA is a serious problem
* MRSA - Methicillin resistant staph. aureus
* MRSA is a serious problem
* MRSA - Methicillin resistant staph. aureus
32
New cards
medically important firmicutes
* low G+C content
* classifys gram positive bacteria
* **E**ager **L**eprechauns **M**unched **S**aucy **S**andwiches **B**efore **C**hrist
* E - enterococcus
* L - Listeria
* M - mycoplasma
* S - streptococcus
* S - staphylococcus
* B - bacillus (spore former)
* C - clostridium (spore former)
* classifys gram positive bacteria
* **E**ager **L**eprechauns **M**unched **S**aucy **S**andwiches **B**efore **C**hrist
* E - enterococcus
* L - Listeria
* M - mycoplasma
* S - streptococcus
* S - staphylococcus
* B - bacillus (spore former)
* C - clostridium (spore former)
33
New cards
Enterococcus
* found in GI track
* Causes nosocomial UTI in immunocompromised patients
* Increase in vancomycin resistant enterococci (VRE)
* Causes nosocomial UTI in immunocompromised patients
* Increase in vancomycin resistant enterococci (VRE)
34
New cards
low vs high G+C content
low G+C
* less than 50% guanine and cytosine nucleotides in their DNA
* similar 16s rRNA sequence
\
high G+C
* more than 50% of guanine and cytosine nucleotides in their DNA
* Gram-positive bacteria
* Identified by a fast acid stain
* Their rRNA is similar
* less than 50% guanine and cytosine nucleotides in their DNA
* similar 16s rRNA sequence
\
high G+C
* more than 50% of guanine and cytosine nucleotides in their DNA
* Gram-positive bacteria
* Identified by a fast acid stain
* Their rRNA is similar
35
New cards
mycobacterium
* slow growth
* M. tuberculosis & M. leprae are pathogenic
* need long term antibiotic treatment because of slow generation time
* M. tuberculosis & M. leprae are pathogenic
* need long term antibiotic treatment because of slow generation time
36
New cards
Corynebacterium
* Corynebacterium are aerobes & facultative anaerobes
* C. diphtheriae causes diphtheria
* Pleomorphic (have different shape)
* Cell wall does not invaginate it snaps
* C. diphtheriae causes diphtheria
* Pleomorphic (have different shape)
* Cell wall does not invaginate it snaps
37
New cards
Actinomyces
* Actinomyces form branching filaments
* A. israelii can destroy tissue
* A. israelii can destroy tissue
38
New cards
Nocardia
cause pneumonia in hospitalized patients
39
New cards
proteobacteria classes
* Alphaproteobacteria
* Betaproteobacteria
* Gammaproteobacteria
* Deltaproteobacteria
* Epsilonproteobacteria
* Betaproteobacteria
* Gammaproteobacteria
* Deltaproteobacteria
* Epsilonproteobacteria
40
New cards
diseases caused by alphaproteobacteria
* Rickettsia rickettsii causes Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
* Brucella causes brucellosis
* Brucella causes brucellosis
41
New cards
pathogenic betaproteobacteria
Neisseria gonorrhoeae & N. meningitidis
* Inhabits mucous membranes of mammals
* Causes gonorrhea, meningitis, pelvic inflammatory disease
\
Bordetella pertussis
* Causes pertussis (whooping cough), usually in children < age 5 years
* Inhabits mucous membranes of mammals
* Causes gonorrhea, meningitis, pelvic inflammatory disease
\
Bordetella pertussis
* Causes pertussis (whooping cough), usually in children < age 5 years
42
New cards
gammapreoteobacteria
* Gram negative rods
* most abundant class of pathogenic proteobacteria
* common pathogens are
* Escherichia coli
* Commensal
* May or may not benefit the host
* GI infections
* Gastroenteritis (stomach flu), UTIs, sepsis, renal failure (hemolytic uremia syndrome)
* Klebsiella pneumoniae
* Nosocomial & community acquired infections
* Pseudomonas aeruginosa
* Wound infections or pneumonia
* sepsis, UTIs (Urinary Tract Infection), ear & lung infections
* 1/10 nosocomial infections
* Biofilms are common in cystic fibrosis
* Yersinia pestis
* Causes the plague
* Most common/well known is bubonic plague
* People would get infection from a flea bite
* Causes buboes (collection of blood, pus, bacteria)
* Also causes gangrene (end stages)
* Mortality rate of 20-50%
* most abundant class of pathogenic proteobacteria
* common pathogens are
* Escherichia coli
* Commensal
* May or may not benefit the host
* GI infections
* Gastroenteritis (stomach flu), UTIs, sepsis, renal failure (hemolytic uremia syndrome)
* Klebsiella pneumoniae
* Nosocomial & community acquired infections
* Pseudomonas aeruginosa
* Wound infections or pneumonia
* sepsis, UTIs (Urinary Tract Infection), ear & lung infections
* 1/10 nosocomial infections
* Biofilms are common in cystic fibrosis
* Yersinia pestis
* Causes the plague
* Most common/well known is bubonic plague
* People would get infection from a flea bite
* Causes buboes (collection of blood, pus, bacteria)
* Also causes gangrene (end stages)
* Mortality rate of 20-50%
43
New cards
pathogenic epsilonproteobacteria
Campylobacter jejuni causes acute gastroenteritis (stomach flu)
* Is in the jejunum in small intestine
\
Helicobacter pylori causes gastric ulcers
* Creates bubble around itself that neutralizes acidity
* Is in the jejunum in small intestine
\
Helicobacter pylori causes gastric ulcers
* Creates bubble around itself that neutralizes acidity
44
New cards
chlamydia
* are very small cocci that reproduce only within the cells of mammals
* Obligate intracellular parasites
* Chlamydia trachomatis causes STDs & neonatal blindness
* Common complication is pelvic inflammatory disease
* Inflammation of the fallopian tubes – can cause infertility
* Obligate intracellular parasites
* Chlamydia trachomatis causes STDs & neonatal blindness
* Common complication is pelvic inflammatory disease
* Inflammation of the fallopian tubes – can cause infertility
45
New cards
bacteroides
* Not a spore former
* Obligate anaerobes that normally inhabit the GI tract
* Digest cellulose & other complex carbohydrates that are indigestible by humans
* Bacteroides fragilis can cause abdominal, pelvic, blood & other infections
* Obligate anaerobes that normally inhabit the GI tract
* Digest cellulose & other complex carbohydrates that are indigestible by humans
* Bacteroides fragilis can cause abdominal, pelvic, blood & other infections
46
New cards
spirochetes
* Motile by axial filaments
\
Treponema pallidum
* Causes syphilis
\
Borrelia burgdorferi
* Causes Lyme disease
\
Treponema pallidum
* Causes syphilis
\
Borrelia burgdorferi
* Causes Lyme disease
47
New cards
eukaryotic classification
* Earliest schemes based groups based upon structural similarities
* Linnaeus – Plants and Animals
* 20th century – Fungi, Protista, Plants, Animals, (bacteria were Monerans)
* 21st century – Fungi, Parabasalids, Diplomonads, Euglenazoa, Avleolata, Rhizaria, Amoebozoa, \n Plants and Animals
* Linnaeus – Plants and Animals
* 20th century – Fungi, Protista, Plants, Animals, (bacteria were Monerans)
* 21st century – Fungi, Parabasalids, Diplomonads, Euglenazoa, Avleolata, Rhizaria, Amoebozoa, \n Plants and Animals
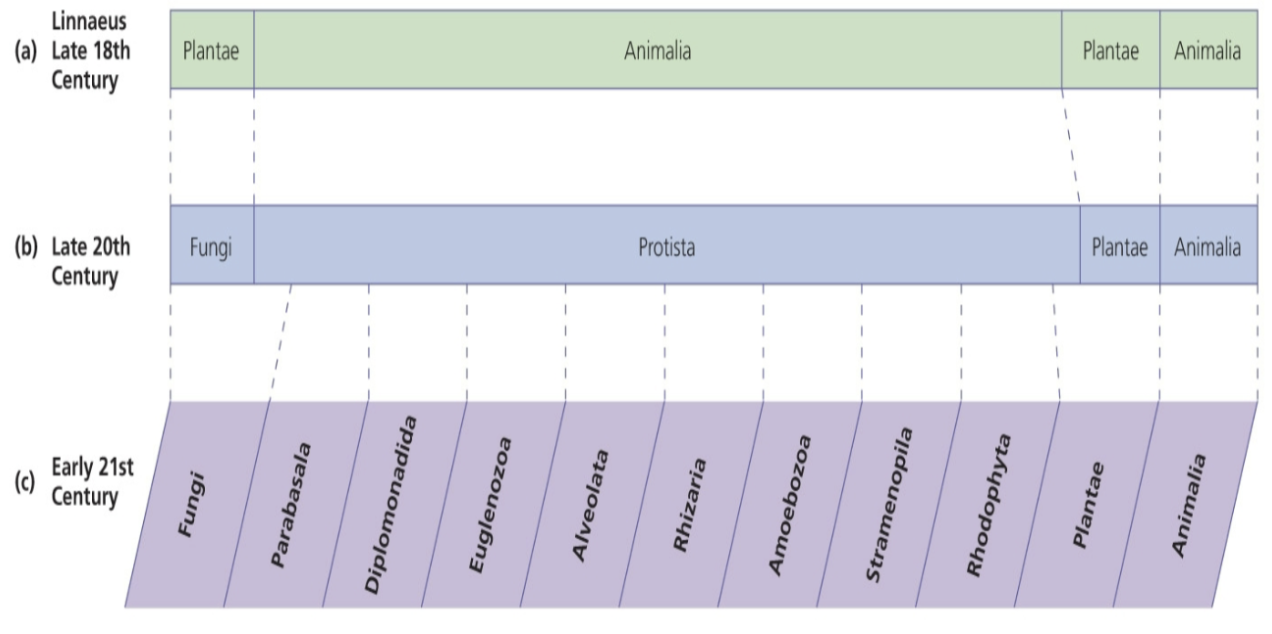
48
New cards
problems with protist classification
* included both large, photosynthetic, multicellular algae and nonphotosynthetic, unicellular protozoa
* abandoned classifying schemes that are so strongly grounded in large-scale structural similarities in favor of schemes based on similarities in nucleotide sequences and cellular ultrastructure
* abandoned classifying schemes that are so strongly grounded in large-scale structural similarities in favor of schemes based on similarities in nucleotide sequences and cellular ultrastructure
49
New cards
protozoa characteristics
* eukaryotic
* unicellular
* lack a cell wall
* unicellular
* lack a cell wall
50
New cards
why there are many different taxonomic schemes for protozoa
* they classify them based on 18S rRNA nucleotide sequencing and features made visible by microscope
* very diverse phylum of organisms
* very diverse phylum of organisms
51
New cards
euglenid
* Characteristics of both plants and animals
* Have both mitochondria and chloroplasts
* Chloroplasts almost identical to those in green plants
* Flagella contain a crystalline rod of unknown function
* Mitochondria have disk-shaped cristae
* Photoautotrophic plant like
* Have both mitochondria and chloroplasts
* Chloroplasts almost identical to those in green plants
* Flagella contain a crystalline rod of unknown function
* Mitochondria have disk-shaped cristae
* Photoautotrophic plant like
52
New cards
alveolates
Apicomplexans
* The most pathogenic
* Non motile protozoa
* Special organelles that allow them to attach and enter host cells
* Do not have cilia, flagella
* Through bite of insect vector
* Plasmodium
* Responsible for causing malaria
* 3 major types
* All transmitted by mosquitos
\
Toxoplasmosis
* Parasite that is carried by cats
* Tell pregnant women to not empty cat litter
* Parasite can get across the placenta
\
Dinoflagellates
* Hard outer shells made of silica
* Photosynthetic and chemoheterotrophs
* Few species that are highly toxic to humans
* Known to cause red tides
* Usually where agricultural runoff goes into the ocean
* Massive bloom from all the fertilizer and extra nutrients
* Produce potent neurotoxin
* Can impact shellfish
* The most pathogenic
* Non motile protozoa
* Special organelles that allow them to attach and enter host cells
* Do not have cilia, flagella
* Through bite of insect vector
* Plasmodium
* Responsible for causing malaria
* 3 major types
* All transmitted by mosquitos
\
Toxoplasmosis
* Parasite that is carried by cats
* Tell pregnant women to not empty cat litter
* Parasite can get across the placenta
\
Dinoflagellates
* Hard outer shells made of silica
* Photosynthetic and chemoheterotrophs
* Few species that are highly toxic to humans
* Known to cause red tides
* Usually where agricultural runoff goes into the ocean
* Massive bloom from all the fertilizer and extra nutrients
* Produce potent neurotoxin
* Can impact shellfish
53
New cards
amoebas
Naegleria
* Brain eating amoeba
* Usually found in the south
* Can burrow through cribriform plate
* 100% fatal
* From people swimming and water sports in bodies of water w muddy bottoms
\
Acanthamoeba
* Can also cause meningitis and encephalitis
\
Entamoeba
* Live in digestive tract of animals
* Can cause amoebic dysentery
* Can cause severe dehydration until it results in death
* Can live in water
* Brain eating amoeba
* Usually found in the south
* Can burrow through cribriform plate
* 100% fatal
* From people swimming and water sports in bodies of water w muddy bottoms
\
Acanthamoeba
* Can also cause meningitis and encephalitis
\
Entamoeba
* Live in digestive tract of animals
* Can cause amoebic dysentery
* Can cause severe dehydration until it results in death
* Can live in water
54
New cards
parabasalids
* One of the simplest types
* Lack mitochondria
* Mitosomes perform similar functions to mitochondria
* Have a single nucleus
* Contain Golgi body–like structure called a parabasal body
* Helps to package proteins
* Important parabasalids – *Trichomonas vaginalis*
* STI
* Lives in vaginal canal
* When pH becomes more alkaline it proliferates
* Lack mitochondria
* Mitosomes perform similar functions to mitochondria
* Have a single nucleus
* Contain Golgi body–like structure called a parabasal body
* Helps to package proteins
* Important parabasalids – *Trichomonas vaginalis*
* STI
* Lives in vaginal canal
* When pH becomes more alkaline it proliferates
55
New cards
diplomonads
* Lack mitochondria
* Have mitosomes in the cytoplasm
* Mitochondrial genes found in the nuclear chromosomes
* Also lack Golgi bodies and peroxisomes
* Have two equal-sized nuclei and multiple flagella
* Whip side to side like a fin
* Do not spin like bacteria flagella
* Important diplomonad: *Giardia intestinalis*
* Parasite found in water
* Extremely hard to get rid of it
* Causes diarrhea (can last a month)
* Have mitosomes in the cytoplasm
* Mitochondrial genes found in the nuclear chromosomes
* Also lack Golgi bodies and peroxisomes
* Have two equal-sized nuclei and multiple flagella
* Whip side to side like a fin
* Do not spin like bacteria flagella
* Important diplomonad: *Giardia intestinalis*
* Parasite found in water
* Extremely hard to get rid of it
* Causes diarrhea (can last a month)
56
New cards
rhizaria
* Amoebae exhibit little uniformity
* Do not make blob-like extensions of their membrane
* Rhizaria are amoebae with threadlike pseudopods
* Foraminifera - Often live attached to the ocean floor
* Most are fossil species
* Radiolaria -Have ornate shells of silica, Live as part of the marine plankton
* Do not make blob-like extensions of their membrane
* Rhizaria are amoebae with threadlike pseudopods
* Foraminifera - Often live attached to the ocean floor
* Most are fossil species
* Radiolaria -Have ornate shells of silica, Live as part of the marine plankton
57
New cards
amoebozoa
* Amoebae with lobe-shaped pseudopods and no shells
* Can form cysts (like endospores – increase resistance)
* Includes some human pathogens
* Found in almost every wet environment
* Most in fresh water
* Can form cysts (like endospores – increase resistance)
* Includes some human pathogens
* Found in almost every wet environment
* Most in fresh water
58
New cards
what distinguishes fungi from other eukarya
* chemoheterotrophs
* Lack chlorophyll
* Fungal walls contain chitin
* Most are not truly multicellular
* Most famous are penicillin and saccharomyces (brewer's yeast)
* Most are aerobes
* Others are facultative anaerobes
* Heterotrophic as saprophytes (decomposers)
* Lack chlorophyll
* Fungal walls contain chitin
* Most are not truly multicellular
* Most famous are penicillin and saccharomyces (brewer's yeast)
* Most are aerobes
* Others are facultative anaerobes
* Heterotrophic as saprophytes (decomposers)
59
New cards
major shapes of fungi
* Molds—composed of long filaments called hyphae
* Yeasts—small, globular, and composed of a single cell
* Yeasts—small, globular, and composed of a single cell
60
New cards
dimorphic
* Produce both yeastlike and moldlike shapes
* Change in response to environmental conditions
* Change in response to environmental conditions
61
New cards
fungi nutrition
* Saprophytic Nutrition: The absorption of food from dead or decaying organic matter
* Parasitic Nutrition: The absorption of food from living organisms
* Parasitic Nutrition: The absorption of food from living organisms
62
New cards
mold nutrition
* secretes digestive juices (enzymes) directly on the food
* enzymes cause the food to become soluble, which it is then absorbed by the mold
* enzymes cause the food to become soluble, which it is then absorbed by the mold
63
New cards
asexual fungi reproduction
Spores
* Asexual
* Can bud
* Asexual
* Can bud
64
New cards
sexual fungi reproduction
Gametophytes
* Contain half the chromosomes
* Come together to form sporocysts
* Contain half the chromosomes
* Come together to form sporocysts
65
New cards
algae
* Simple, photosynthetic organisms that photosynthesize similarly to plants
* Different from plants in that every cell can become a gamete (a sex cell)
* Can be unicellular or colonial
* All aquatic
* Different from plants in that every cell can become a gamete (a sex cell)
* Can be unicellular or colonial
* All aquatic
66
New cards
why microbiologist study parasitic worms
Larvae are microscopic and are usually the diagnostic features of many parasitic worms.
67
New cards
vectors
a living organism that transmits an infectious agent from an infected animal to a human or another animal
68
New cards
arachnids
* Can be mechanical or biological vectors of disease
* Ticks and mites are the most common biological vectors
* Adult stages have eight legs, two body parts and mouthparts made to burrow
* Ticks and mites are the most common biological vectors
* Adult stages have eight legs, two body parts and mouthparts made to burrow
69
New cards
tick and mite diseases
Lyme disease, Rocky mountain spotted fever, tularemia, tick-borne encephalitis
70
New cards
fleas disease
Plague
71
New cards
lice diseases
Vectors for typhus
72
New cards
flies diseases
Leishmaniasis, Sleeping sickness
73
New cards
mosquito diseases
* Most important arthropod vectors of disease
* Malaria, Yellow fever, Dengue fever, Viral encephalitis, Rift valley fever, West nile, Zika
* Malaria, Yellow fever, Dengue fever, Viral encephalitis, Rift valley fever, West nile, Zika
74
New cards
kissing bug diseases
Chagas disease
75
New cards
mechanical vector
insect or arachnid tracks through something and it is transmitted to us through touch
76
New cards
biological vector
involves getting bitten by insect or arachnid
77
New cards
virus
when a virion enters a host cell
78
New cards
virion
* When a virus is not inside a host cell
* nucleic acid (single- or double-stranded RNA or DNA) and a protein coat, the capsid
* nucleic acid (single- or double-stranded RNA or DNA) and a protein coat, the capsid
79
New cards
viral genetic material
Either DNA or RNA, never both
* dsDNA
* Double stranded
* ssDNA
* Single stranded
* ssRNA
* DsRNA
* dsDNA
* Double stranded
* ssDNA
* Single stranded
* ssRNA
* DsRNA
80
New cards
virus specificity
* depends on capsid or envelope structure
* Many viruses infect certain cell or tissue types within the host (tissue tropism)
* The virus needs a specific receptor to invade the host cell
* all organisms are susceptible to viruses
* Many viruses infect certain cell or tissue types within the host (tissue tropism)
* The virus needs a specific receptor to invade the host cell
* all organisms are susceptible to viruses
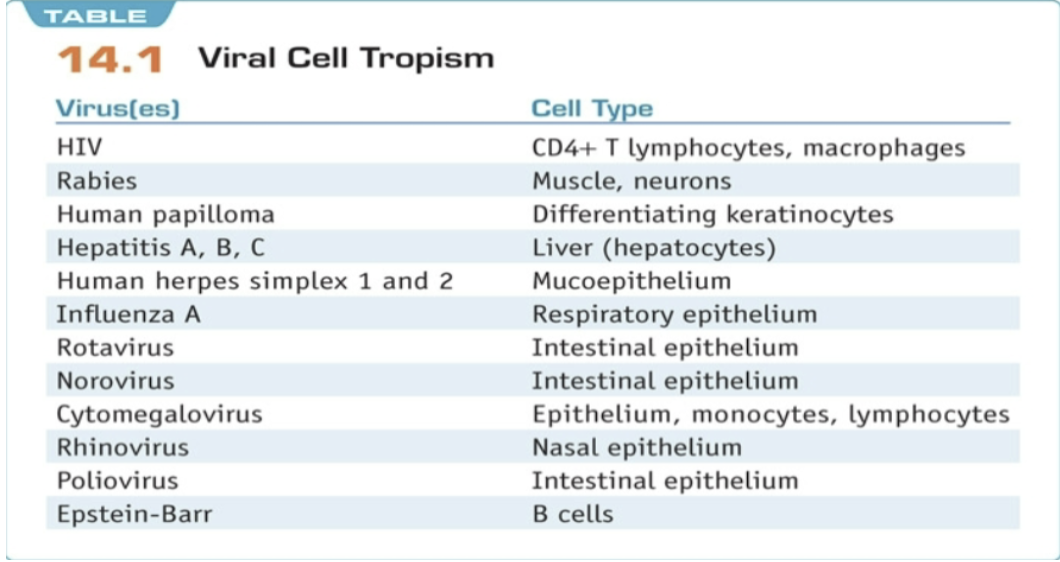
81
New cards
viral envelope
* Have a cell membrane around the outside of them
* Cell membrane from the host cell
* Phospholipid bilayer
* Obtain it through budding
* Pushed out of the cell and gain a membrane through it
* Does not do transport, diffusion, osmosis
* Typically, it's easier to get rid of enveloped viruses
* More susceptible to lysol, bleach, disinfectants
* Proteins that stick out
* Can be part of the cells glycocalyces
* Can be hard to detect because it has host characteristics
* Cell membrane from the host cell
* Phospholipid bilayer
* Obtain it through budding
* Pushed out of the cell and gain a membrane through it
* Does not do transport, diffusion, osmosis
* Typically, it's easier to get rid of enveloped viruses
* More susceptible to lysol, bleach, disinfectants
* Proteins that stick out
* Can be part of the cells glycocalyces
* Can be hard to detect because it has host characteristics
82
New cards
viral capsids
* Protein case that encloses genetic material
* Protects it when outside of a host
* Helical
* Screw
* Icosahedral/polyhedral
* Anywhere from 10-20 sides
* Complex viruses have both helical and icosahedral symmetry
* Protects it when outside of a host
* Helical
* Screw
* Icosahedral/polyhedral
* Anywhere from 10-20 sides
* Complex viruses have both helical and icosahedral symmetry
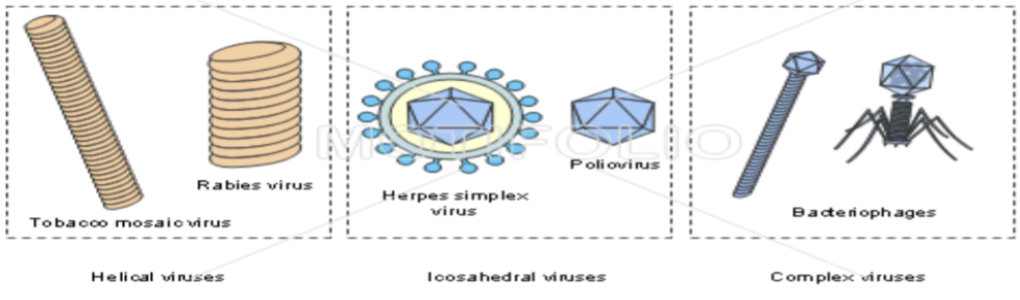
83
New cards
viral classification
based on
* Type of nucleic acid
* Presence of an envelope
* Shape
* Size
\
Viral genera have only been organized into families
Relationships among viruses are not well understood by taxonomists
* Type of nucleic acid
* Presence of an envelope
* Shape
* Size
\
Viral genera have only been organized into families
Relationships among viruses are not well understood by taxonomists
84
New cards
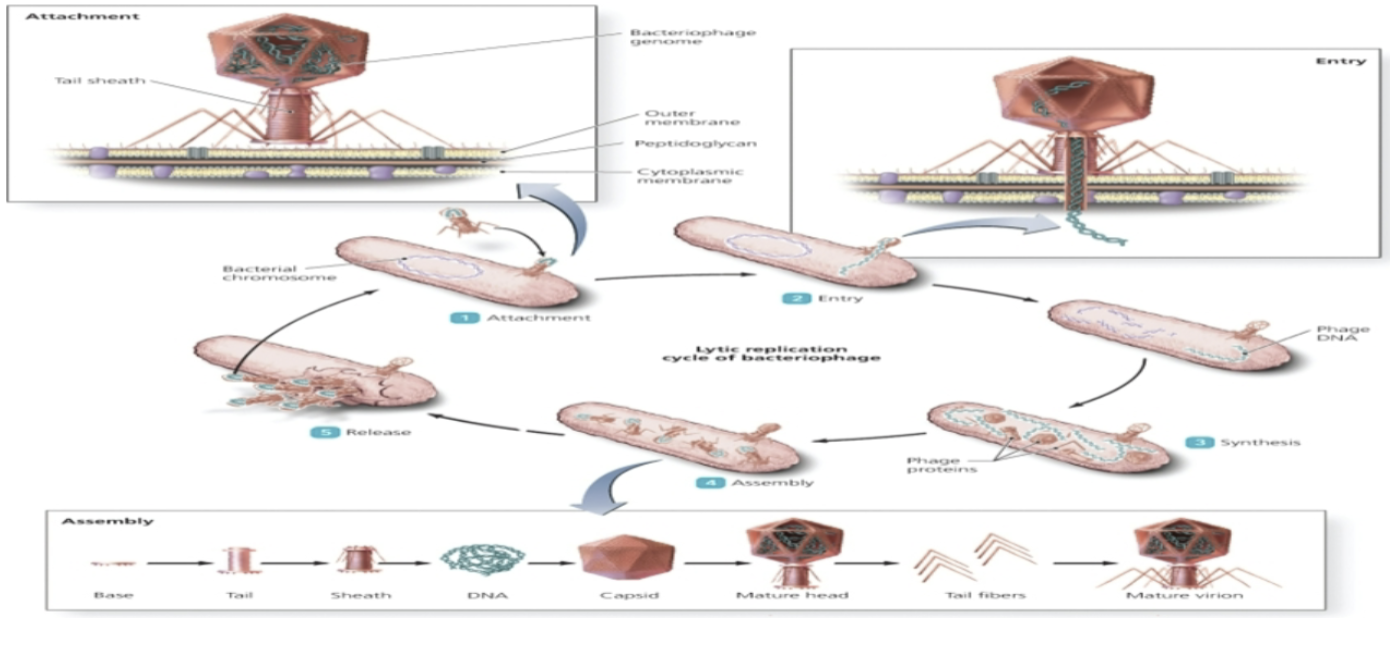
lytic cycle
*only in bacteriophages*
Attachment
* Nonmotile
* Contact with host cell is random
* Dependent upon chemical attraction between tail fibers and receptors on host membrane
* Will only attach to pili, cell wall, or flagella for E. coli
\
Entry
* To break through cell wall, it releases lysozyme to dissolve outer part of cell wall
* Helical part contracts and squirts nucleic acid into bacteria
* After entry viral enzymes begin to degrade bacterial DNA
\
Synthesis
* Begins to create viral genome for new viruses
* For dsDNA viruses, the viral genome directs the synthesis of new capsid proteins, tail, viral polymerase, and lysozyme
\
Assembly
* Capsid proteins begin to assemble inside the host cell
* Tails and tail fibers begin to assemble and attach to head
* Capsids form around viral genomes, or the genomes are pumped into the newly formed capsid
\
Release
* As lysozymes weakens the cell wall of the bacterium the new virions can burst free from the cell
Attachment
* Nonmotile
* Contact with host cell is random
* Dependent upon chemical attraction between tail fibers and receptors on host membrane
* Will only attach to pili, cell wall, or flagella for E. coli
\
Entry
* To break through cell wall, it releases lysozyme to dissolve outer part of cell wall
* Helical part contracts and squirts nucleic acid into bacteria
* After entry viral enzymes begin to degrade bacterial DNA
\
Synthesis
* Begins to create viral genome for new viruses
* For dsDNA viruses, the viral genome directs the synthesis of new capsid proteins, tail, viral polymerase, and lysozyme
\
Assembly
* Capsid proteins begin to assemble inside the host cell
* Tails and tail fibers begin to assemble and attach to head
* Capsids form around viral genomes, or the genomes are pumped into the newly formed capsid
\
Release
* As lysozymes weakens the cell wall of the bacterium the new virions can burst free from the cell
85
New cards
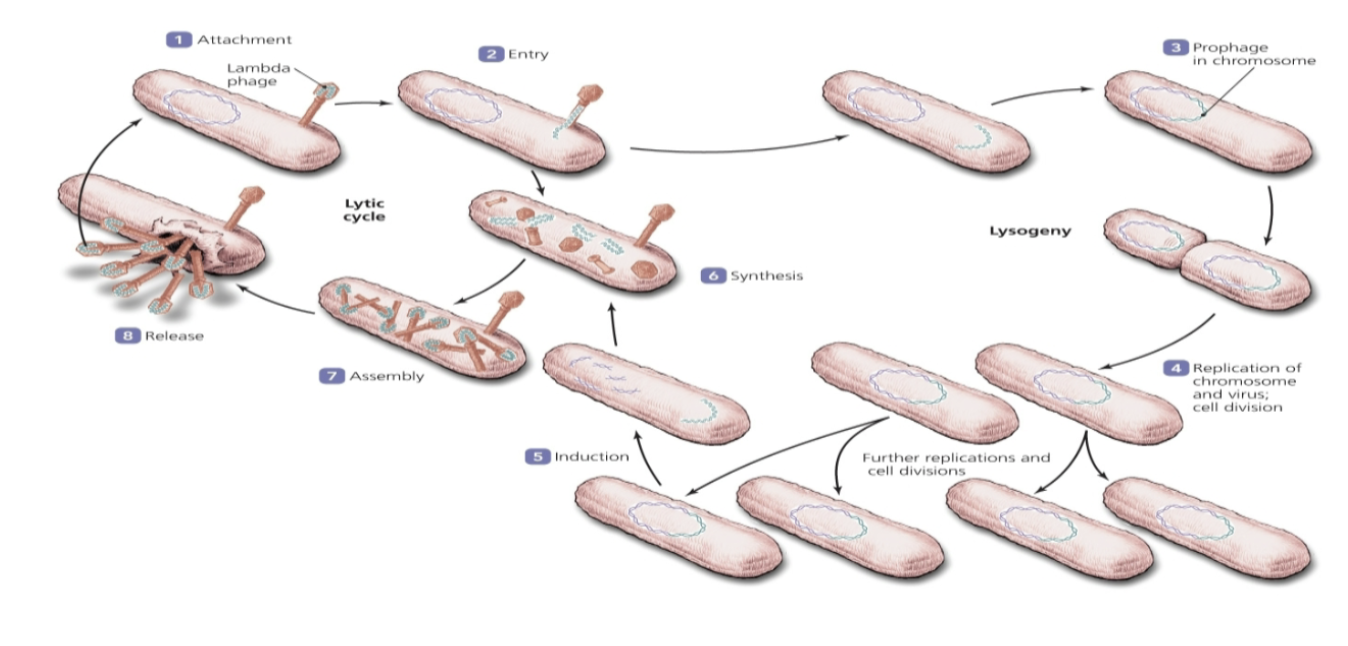
lysogenic cycle
Attachment
* Same as in lytic cycle, but the host cell’s DNA is not destroyed
\
Entry
* Viral DNA remains silent as a prophage
\
Prophage entry
* Prophage incorporates itself in the host cell’s DNA
\
Lysogeny
* Every time the bacterial chromosome replicates, the viral DNA is copied along with it
* All daughter cells will now carry the prophage
* Lysogenic phages can cause the phenotype of the bacterium to change from harmless into pathogenic
\
Induction
* At some point the prophage may be excised from the host DNA
* At this point it reenters the lytic phase
* Inductive agents include physical and chemical agents that damage bacterial DNA
\
Steps 6-8 are Synthesis
\
Assembly and Release
* occurs just as in lytic cycle
* Same as in lytic cycle, but the host cell’s DNA is not destroyed
\
Entry
* Viral DNA remains silent as a prophage
\
Prophage entry
* Prophage incorporates itself in the host cell’s DNA
\
Lysogeny
* Every time the bacterial chromosome replicates, the viral DNA is copied along with it
* All daughter cells will now carry the prophage
* Lysogenic phages can cause the phenotype of the bacterium to change from harmless into pathogenic
\
Induction
* At some point the prophage may be excised from the host DNA
* At this point it reenters the lytic phase
* Inductive agents include physical and chemical agents that damage bacterial DNA
\
Steps 6-8 are Synthesis
\
Assembly and Release
* occurs just as in lytic cycle
86
New cards
animal viruses
* Can be enveloped or non-enveloped
* Replication of animal viruses within a host share the same 5 stages as lytic cycle
* Few changes
* Replication of animal viruses within a host share the same 5 stages as lytic cycle
* Few changes