Bio 2 Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/181
Earn XP
Last updated 3:26 AM on 9/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
1
New cards
What is science?
aims to understand the natural world through observation and reasoning
* begins with organisms
* classification of all life
* human genome sequencing
* begins with organisms
* classification of all life
* human genome sequencing
2
New cards
hierarchical classification?
organisms grouped into clusters
* Kingdom > Phylum > Class > Order > Family > Genus > Species
* shift from identifying and naming to constructing hypotheses to explain relatedness of species
* Kingdom > Phylum > Class > Order > Family > Genus > Species
* shift from identifying and naming to constructing hypotheses to explain relatedness of species
3
New cards
binomial scientific name?
Genus \[capital\], Species \[lowercase\]
4
New cards
how to identify hierarchical classification?
1. latin
2. 2 parts
3. lowercase
4. capitalize
5
New cards
Scientific Method step 1
Observations
6
New cards
scientific method step 2
Hypothesis
7
New cards
what is hypothesis
* a possible explanation for an observation
* statement
* has dependent and independent variables (control variables)
* statement
* has dependent and independent variables (control variables)
8
New cards
what is null hypothesis
* no changes
* all the same
* all the same
9
New cards
what is independent variable?
the experimenter will ==manipulate== to see how it affects the dependent variable
10
New cards
what is the dependent variable?
What is actually being ==measured/affected== in the experiment
11
New cards
scientific method step 3
experiment
* tests the hypothesis at a time
* includes a control (no part of the experiment)
* tests the hypothesis at a time
* includes a control (no part of the experiment)
12
New cards
scientific method step 4
analysis
13
New cards
scientific method step 5
draw conclusions
14
New cards
why are many hypotheses are supported?
it is because of theory
15
New cards
what is theory?
* broad explanation
* body of interconnected concepts
* supported by lots of scientific evidence
* body of interconnected concepts
* supported by lots of scientific evidence
16
New cards
Can supernatural be studied?
No
* it cannot be studied or explained by science
* it cannot be measured
* it cannot be studied or explained by science
* it cannot be measured
17
New cards
What cannot provide value judgments?
ethics, morals, faith
18
New cards
what is evolution?
challenge in allelic frequencies in a given population over time
* darwin’s “descent with modification”
* darwin’s “descent with modification”
19
New cards
Aristotle’s ideology: scala naturae
scale of nature
‘life may have changed gradually over time, but .. life forms arranged on a ladder of increasing complexity’
‘life may have changed gradually over time, but .. life forms arranged on a ladder of increasing complexity’
20
New cards
Carolus Linnaeus?
* scientist who classify life “for the greater glory of God”
* developed ==Binomial nomenclature==: Nested classification
* long thought to have been created recently and to be unchanging
* change is hard to see at the scale of a human lifetime
* developed ==Binomial nomenclature==: Nested classification
* long thought to have been created recently and to be unchanging
* change is hard to see at the scale of a human lifetime
21
New cards
From static worldview to an evolutionary worldview- what happened?
1700s-1800s: accumulation of fossils showed that life on earth had changed enormously
22
New cards
==what is catastrophism?==
==extinctions (and other major changes on earth) are due to periodic catastrophes (sudden change)==
* big change
* big change
23
New cards
==Georges Cuvier (1769-1832)?==
==french scientist: extinct species were evidence of past catastrophes 1798==
24
New cards
==James Hutton & Charles Lyell?==
* ==scottish geologists==
* ==geological evidence that current events were the key to understanding the past==
* ==geological evidence that current events were the key to understanding the past==
25
New cards
==what is uniformitarianism?==
==processes operating in the world today are the same ones that have operated in the past (constant change)==
* processing change
* processing change
26
New cards
what is gradualism?
==processes that result in geological change operate slowly (gradually) over huge spans of time==
* implies much time has passed and earth is VERY OLD
* age/time… takes a while
* implies much time has passed and earth is VERY OLD
* age/time… takes a while
27
New cards
Darwin was not the first to?
propose a theory of evolution
28
New cards
Darwin proposed?
proposed mechanism of evolution: ==natural selection 1859==
29
New cards
Darwin’s perception?
a radical, leftist, atheist who was happy to overthrow the existing worldview
* facts are a little more mundane
* facts are a little more mundane
30
New cards
Extra facts on Darwin
* fainted at the sight of blood
* went to clergy school
* naturalist
* took notes in voyage of HMS beagle
* in the mainland is not the same in the islands
* with Captain Fitzroy
* idea came out in ‘59
* went to clergy school
* naturalist
* took notes in voyage of HMS beagle
* in the mainland is not the same in the islands
* with Captain Fitzroy
* idea came out in ‘59
31
New cards
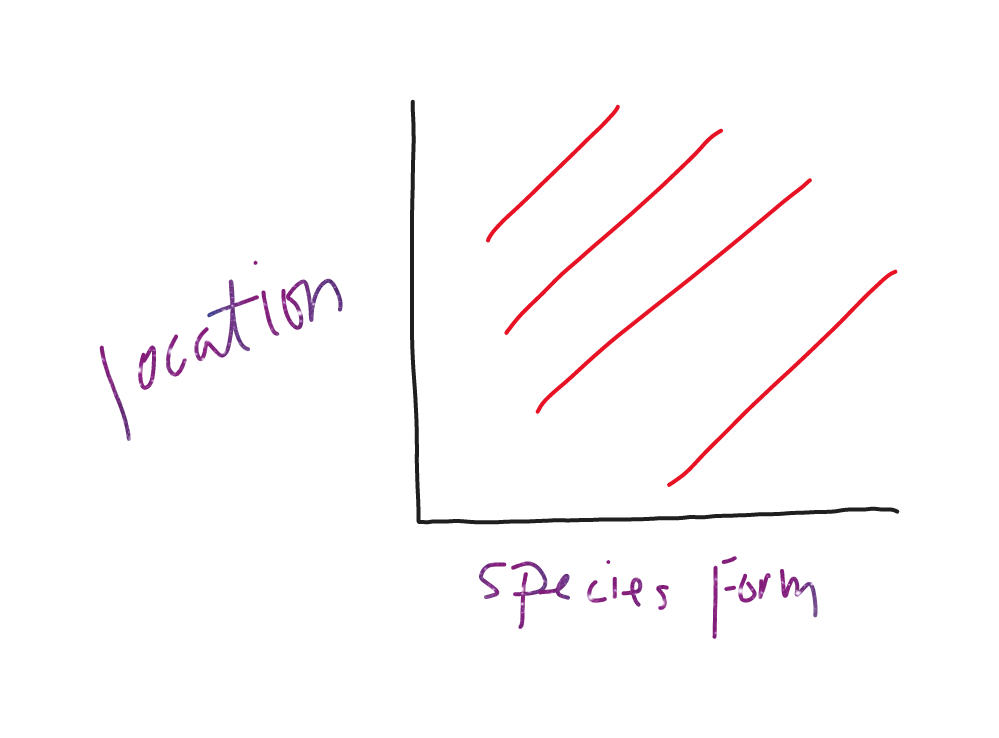
==Buffon’s theory== 1749
species change as they spread from their original location
32
New cards
==Lamarck’s theory== 1809
acquired variation is passed on to descendants
* new species come from existing species through environmental forces
* change over time
* new species come from existing species through environmental forces
* change over time
33
New cards
==Darwin’s theory==
natural selection or genetically-based variation leads to evolutionary change
34
New cards
Darwin’s focus on adaptation
* influenced by Thomas Malthus (most significant, made essays)
* adaptation to the environment and the origin of new species as closely related processes
* adaptation to the environment and the origin of new species as closely related processes
35
New cards
natural selection?
the match between organisms and their environment
* has to match environment to survive
* has to match environment to survive
36
New cards
agricultural selection?
results from generations of ==human selection== for desirable phenotypic traits, they reproduce and pass genes
* ex: larger corn ear size
* ex: larger corn ear size
37
New cards
Domestication?
human-imposed selection has produced a variety of cats, dogs, pigeons, etc
* breeds developed for specific purposes
* dachshunds for badger pursuit
* breeds developed for specific purposes
* dachshunds for badger pursuit
38
New cards
Evidence of evolution: direct observations
* nature - soapberry bugs
* evolution of drug-resistant bacteria
* resist to penicillin 1945, 2 yrs after widely used
* resist to methicillin, 2 yrs after widely used
* MRSA now resistant to many antibiotics
* evolution of drug-resistant bacteria
* resist to penicillin 1945, 2 yrs after widely used
* resist to methicillin, 2 yrs after widely used
* MRSA now resistant to many antibiotics
39
New cards
Evidence of evolution: anatomical evidence
* homologous structures
* vestigial structures
* early embryonic development
* molecular evidence
* vestigial structures
* early embryonic development
* molecular evidence
40
New cards
homologous structures?
structures derived from ==same== body part; ==may or may not have same function==
* ex: forelimb bones in mammals are same
* ex: forelimb bones in mammals are same
41
New cards
vestigial structures?
structures ==have no apparent function==, but resemble structures their ancestors possessed
* ex: human ear wiggling muscles
evolutionary relicts
* ex: human ear wiggling muscles
evolutionary relicts
42
New cards
early embryonic development?
comparisons of how organisms develop
* embryos similar early on → different as develop
* humans: glands and ducts
* embryos similar early on → different as develop
* humans: glands and ducts
43
New cards
molecular evidence?
==DNA relatedness== - compare anatomy, genomes, or proteins
* more related → less changes
* less related → more changes
* more related → less changes
* less related → more changes
44
New cards
Evidence of evolution: fossil record
differed from present-day organisms
* shed light on new groups
* support hypothesis based on DNA
* document transition fossils
* measured; determines how they move
* shed light on new groups
* support hypothesis based on DNA
* document transition fossils
* measured; determines how they move
45
New cards
Animal closest relation to whales?
Hippopotamuses
46
New cards
evidence of evolution: biogeography
* plate tectonic
* convergent evolution
* convergent evolution
47
New cards
what is biogeography?
study of species geographic distribution
* different geographical areas exhibit similar plants and animals even though organisms may be distantly related
* different geographical areas exhibit similar plants and animals even though organisms may be distantly related
48
New cards
plate tectonic?
shifting continents drift isolated organisms, promoting divergence
49
New cards
convergent evolution?
parallel evolutionary adaptation in similar environments
50
New cards
Similar forms evolved in different, isolated areas because of?
similar selective pressures in similar environments
51
New cards
==analogous structures?==
similar function, not same form (evolutionary-ancestral traits)
52
New cards
divergence?
moving apart from each other
53
New cards
Genetic variation?
differences in alleles of genes found within individuals in a population
* raw material for natural selection
* raw material for natural selection
54
New cards
meiosis creates variation. why?
* independent assortment
* recombination
* random fertilization
* recombination
* random fertilization
55
New cards
independent assortment?
shuffles chromosomes
56
New cards
recombination?
shuffles genes on chromosomes
* meiosis metaphase phase 1
* meiosis metaphase phase 1
57
New cards
random fertilization?
picks two cards out of the deck at random
* one couple can create >70 trillion unique combinations (not including crossing over)
* one couple can create >70 trillion unique combinations (not including crossing over)
58
New cards
Raw material?
no selection takes place without heritable variation
59
New cards
How do you get raw material?
Mutation & Recombination
60
New cards
Mutation?
a heritable change in DNA
* has to be inherited
* 0.003 === 64== mutations per genome per cell generation
* has to be inherited
* 0.003 === 64== mutations per genome per cell generation
61
New cards
recombination?
a molecule (DNA/RNA) is broken and then joined to a different one \[crossing over\]
62
New cards
population genetics?
study of properties of genes in a population
63
New cards
==gene pool?==
sum total of all the genes in a population at a given time
* all alleles at all loci (locations within)
* all alleles at all loci (locations within)
64
New cards
who is Mendel 1860s?
he showed that inheritance is caused by “particles” that are passed unchanged from generation to generation according to the rules of probability
* plant breeding experiments
* plant breeding experiments
65
New cards
==Mendel’s Laws?==
1. Law of segregation
2. Law of independent assortment
3. Law of dominance
66
New cards
==Law of segregation?==
pair of alleles separate during cell divisions for any particular trait (assumes diploidy)
67
New cards
==Law of independent assortment?==
separate genes for separate traits are passed independently of one another
68
New cards
Law of dominance?
one allele masks other allele
* RR or rr
* RR or rr
69
New cards
how many chromosomes combinations in humans?
8 million
70
New cards
True breeding cross P1
1 Homo dominant, 1 Homo recessive \[Rr\]
71
New cards
F1 generation
100% heterozygous
72
New cards
F2 generation genotypic ratio
1:2:1
73
New cards
Phenotype
physical characteristics/appearance
74
New cards
Genotype
actual genetic typing
75
New cards
homologous chromosomes?
2 copies of alleles of the gene for a given individual (genotype)
76
New cards
homozygous alleles?
alleles are the same
* AA, aa
* AA, aa
77
New cards
heterozygous alleles?
alleles are different
* Aa
* Aa
78
New cards
population-level variation describe as?
* allele frequencies (one)
* genotype frequencies (two)
* genotype frequencies (two)
79
New cards
==Hardy-Weinberg Principle?==
genotypic frequencies remain constant from generation
to generation under constant conditions
to generation under constant conditions
80
New cards
Conditions of the Hardy-Weinberg Principle?
1. No mutation takes place
2. No gene flow (no immigration \[in\] or emigration \[out\])
3. Random mating is occurring
4. Large population size
5. No natural selection = no change
1. a way to examine changes in allele frequency = null hypothesis (no change)
81
New cards
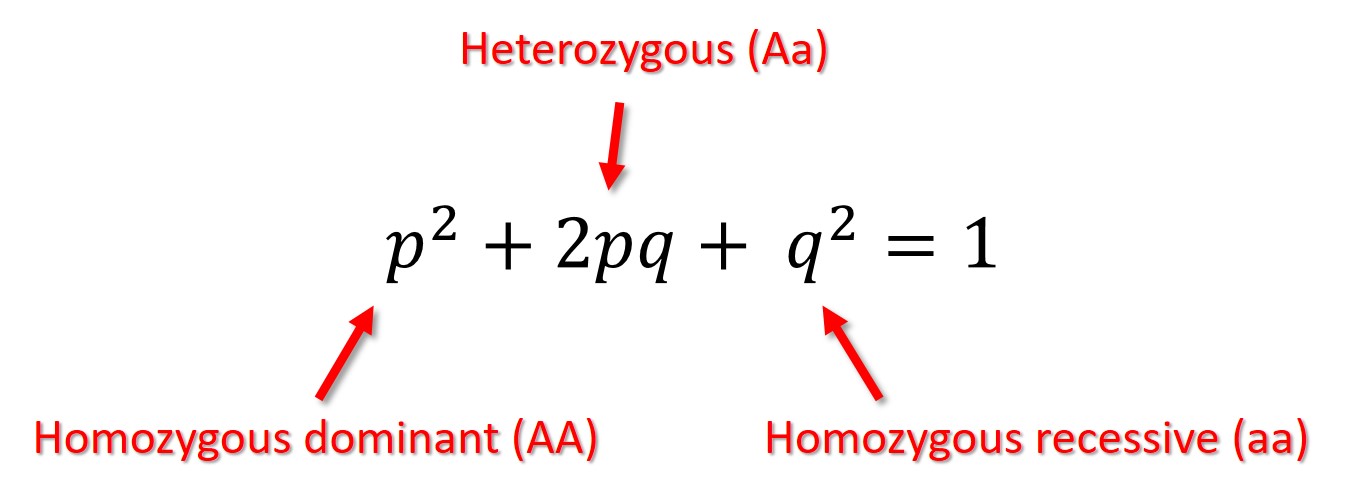
Hardy-Weinberg Principle Equation
p + q = 1
* p = homo dominant
* q = homo recessive
* pq = heterozygous
* p = homo dominant
* q = homo recessive
* pq = heterozygous
82
New cards
In reality, most populations will not meet all 5 assumptions/conditions. why?
==Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction alone will NOT change allele and genotype frequencies in a population (will NOT cause evolution)==
83
New cards
==what process/processes cause changes to the frequencies?==
==evolution results in the change of a population’s genetic composition==
84
New cards
5 agents of evolutionary change
1. Mutation
2. Gene flow
3. Genetic drift
4. Nonrandom mating
5. Selection
85
New cards
==Agent Mutation==
* totally random
* ultimate source of genetic variation
* makes evolution possible
* rates generally low
* other evolutionary processes usually more important in changing allele frequency
* ultimate source of genetic variation
* makes evolution possible
* rates generally low
* other evolutionary processes usually more important in changing allele frequency
86
New cards
==Agent Gene flow==
movement of alleles from one population to another
* random
* drifting of gametes or immature stages
* mating of individuals from adjacent populations
* random
* drifting of gametes or immature stages
* mating of individuals from adjacent populations
87
New cards
==Agent Genetic Drift==
describes how allele frequencies fluctuate unpredictably
* random-uncommon alleles are vulnerable
* bottleneck effect
* founder effect
* random-uncommon alleles are vulnerable
* bottleneck effect
* founder effect
88
New cards
==Bottleneck Effect?==
catastrophic event reduces population size
* survivors are a random genetic sample of original
* results in loss of genetic variability
* parent population gone
* survivors are a random genetic sample of original
* results in loss of genetic variability
* parent population gone
89
New cards
==Founder effect?==
small number of individuals drift from population
* can lead to the loss of alleles in isolated populations
* foundling
* parent population is still there
* isolation
* can lead to the loss of alleles in isolated populations
* foundling
* parent population is still there
* isolation
90
New cards
==Agent Nonrandom Mating==
1. Assortative mating
2. Disassortative mating
91
New cards
Assortative mating?
phenotypically similar individuals mate
* increases homozygosity
* increases homozygosity
92
New cards
Disassortative mating?
phenotypically different individuals mate
* increases heterozygosity
* increases heterozygosity
93
New cards
==Agent Selection==
some individuals leave behind more progeny than others
* rate = favorable phenotype/behavior
* non random
* natural selection
* artificial selection
* rate = favorable phenotype/behavior
* non random
* natural selection
* artificial selection
94
New cards
what is the result of evolution by natural selection?
populations become better adapted to their environment
* organisms start to blend in their environment
* organisms start to blend in their environment
95
New cards
Conditions for natural selection?
1. Variation ==must exist== in population
2. Variation must result in ==numerical differences== of offspring survival
3. Variation must be ==genetically inherited==
96
New cards
Natural selection is not equal to evolution. why?
* Evolution is a subset to natural selection
* Natural selection is a process (4 other processes)
* Evolution = historical record of change through time
* Natural selection is a process (4 other processes)
* Evolution = historical record of change through time
97
New cards
what is fitness?
individuals of one phenotype leave more surviving offspring in the next generation than individuals with an alternative phenotype
98
New cards
what ==relative concept== is misleading?
the most fit phenotype = one that produces, on average, the greatest number of offspring
99
New cards
components of fitness?
* traits favored for one, a disadvantage for others - ==variation==
* number of offspring per mating - ==heritability==
* sexual selection = ==more successful at mates==
* ==survival!==
* number of offspring per mating - ==heritability==
* sexual selection = ==more successful at mates==
* ==survival!==
100
New cards
selection favors phenotypes with the greatest fitness. why?
phenotype with greater fitness usually increases frequency