College Bio Cellular Respiration
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is the overall reaction?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 = 6 CO2 + 6 H2O (ATP)
function of mitochondria
Mitochondria function as the cell's "powerhouse" by producing the energy molecule ATP through cellular respiration.
its involved in other critical processes including cell signaling, adaptation to stress, and regulating cell death (apoptosis).
strictly anaerobic respiration
organisms obtain energy from food without oxygen, using inorganic or organic molecules as the final electron acceptor instead of oxygen
facultative anaerobic respiration
organisms that can switch between anaerobic (without oxygen) and aerobic respiration (using oxygen)
what is fermentation in cellular respiration?
Fermentation is an anaerobic process that occurs in the absence of oxygen, allowing cells to produce a small amount of energy (2 ATP) from glycolysis alone
has 2 types lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation
what is alcohol fermentation in cellular respiration?
converts glucose into pyruvate to make ethanol and carbon dioxide, producing only 2 net ATP per glucose molecule
what is lactic acid fermentation in cellular respiration?
converts glucose into pyruvate to make 2 ATP and NADH
both forms of anaerobic respiration (alcohol and lactic) produce 2 ATP per glucose, rather than 36 ATP made in aerobic respiration.
what part of the aerobic respiration process is utilized by fermentation?
Fermentation utilizes the glycolysis stage of aerobic respiration, which breaks down glucose into pyruvate to produce a net of 2 ATP and 2 NADH molecules.
While aerobic respiration continues with the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, fermentation does not; instead, it uses the pyruvate and NADH from glycolysis to regenerate NAD+ so glycolysis can continue.
how much ATP is made per glucose in anaerobic respiration?
2 ATP molecules per glucose molecule
how much ATP is made per glucose in aerobic respiration?
36 ATP per glucose molecule
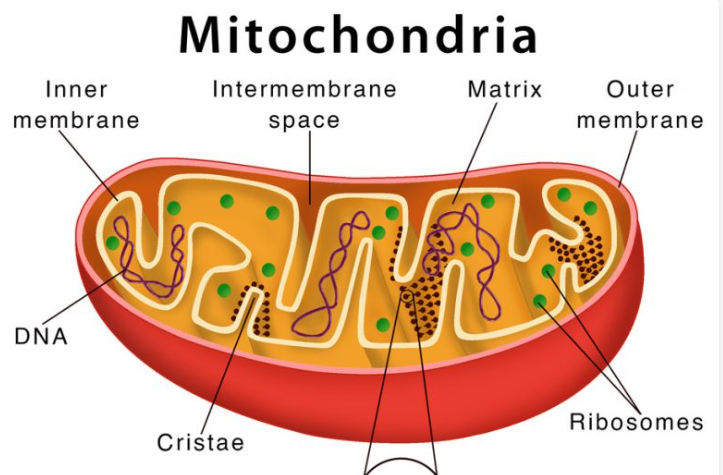
structure of mitochondria
what role does oxygen play in aerobic respiration?
In aerobic respiration, oxygen's primary role is to act as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. This function allows the chain to continue operating, enabling the process to efficiently break down glucose and convert its energy into ATP, with water and carbon dioxide as byproducts.
where are reactants used and products produced within the stages of respiration?
glucose is used in glycolysis
oxygen is used in the ETC
2 carbon dioxide are produced in the preparatory reaction while the other 4 carbon dioxide are made in the Krebs cycle
Water is produced in the ETC
Glycolysis
the first stage of cellular respiration
glucose, 2 ADP+2 Phosphate, 2 NAD+H+ are used. The overall reactant glucose is used.
2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH are made. none of the overall products are made.
enzymes accomplish the work of this stage
this occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell
preparatory reaction
the second stage of cellular respiration
2 pyruvate, 2 CoA and NAD+H+ are used. none of the overall reactants are used
2 acetyl-CoA, 2 CO2, NADH are made. The overall product CO2 is made
enzymes accomplish the work of this stage
takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria
The Krebs Cycle
The Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) is the third stage of cellular respiration
2 acetyl-CoA, OAA, 2 FADH+H+, 6 NAD+H+ are used in this stage. none of the overall reactants are used
OAA, 4 CO2, 2 FADH2, 6 NADH, 2 ATP are made. the overall product CO2 is made
enzymes accomplish the work in this stage
This is happening in the Matrix of the mitochondria
Electron Transport Chain
The fourth stage of cellular respiration
NADH, FADH2, and O2 are used in this stage. The overall reactant oxygen is used. H+ are in the matrix.
NAD+H+, FADH+H+. H+ are pumped from the matrix into the intermembrane space. The overall product H2O is made
NADH and FADH2 dehydrogenase and ETC proteins accomplish the work in this stage
this happens in the inner membrane of the mitochondria (cristae)
ATP Synthetase
This is the fifth stage of cellular respiration
ADP+Phosphate are used. none of the overall reactants are used. H+ are in the inner membrane space
32 ATP are produced. none of the overall products are made. H+ return to the matrix
the ATP synthetase enzyme accomplishes the work of this stage
this is happening in the inner membrane (cristae) of mitochondria
where are the important energy intermediates ATP, NADH, and FADH2 used and made?
ATP is made in glycolysis, kreb’s cycle, and ATP synthetase. ATP is not used in any stage.
2 NADH are made in glycolysis. 1 is made in preparatory reaction. 6 are made in Krebs cycle. 1 is used in ETC
2 FADH2 are made in Krebs cycle. 1 is used in ETC
NADH and FADH2 are also co-enzymes that aid in ETC
PGAL
During glycolysis, a glucose molecule is first split into two molecules of PGAL, which are then converted into pyruvate in the second half of glycolysis.
where is oxygen required in cellular respiration?
the ETC
what organisms do lactic acid fermentation and ethanol fermentation?
bacteria and yeasts
Where do H+ accumulate in order to power the ATP synthase step?
the intermembrane space. they are actively pumped from the matrix to the inner membrane space
what supplies energy to the mitochondrial ETC?
high energy electrons from the electron carriers NADH and FADH2
which step of cellular respiration is separate from mitochondria
glycolysis