Fetal Development, Adaption to Pregnancy, Prenatal Care
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Presumptive signs of pregnancy
Makes client think they might be pregnant
- Nausea, vomiting, fatigue, missed period
Probable signs of pregnancy
Makes examiner suspect client is pregnant
- Positive pregnancy test
- Goodell sign: soft cervix, increased vascularity
- Chadwick sign: voilet-blue vaginal mucosa and cervix
- Hegar sign: softening of lower uterine segment
Positive signs of pregnancy
Signs only explained by pregnancy
- Fetal heart sounds, visualizing fetus, fetal movement palpated by examiner
Uterus adaptations
high levels of estrogen and progesterone stimulate growth in 1st trimester
- May show by 14 weeks
- After 3rd month, growth is result of pressure of growing fetus
Cardiovascular adaptations
- Slight cardiac enlargement due to increased blood volume and CO
- pulse increase 10-15 bpm between 14-20 wks
- Arterial BP highest when sitting, lowest when lying left lateral
- Diastolic BP decreased in 1st and 2nd trimester, then gradually increase
- Blood volume increase 40-50%
- RBCs increase 20-30% (less proportionally to plasma)
- Increased clotting factors
Cardiovascular discomforts
- Varicose veins and LE edema: elevate legs, support hose, no leg crossing
- Supine hypotension: left lateral or semi-sitting position
- Faintness: avoid sudden position change and hypoglycemia, compression hose
Respiratory adaptations
- Rib cage relaxes for chest expansion
- Diaphragm displaces as much as 4cm
- Increased oxygen consumption due to uterine-placental-fetal unit
Respiratory discomforts
- Gingivitis, nasal stuffiness, nosebleeds: brush teeth gently, humidifier, saline nose drops
- SOB and dyspnea: good posture, small meals, no smoking
Renal adaptations
- Muscle relaxation and dilated ureters
- Increased UTI risk and urinary frequency
- Side lying position increases renal perfusion, which increases urine output and decreases edema
- Glycosuria
- Proteinuria during labor or after birth
Renal discomforts
- Urgency and frequency: pee often, kegels, pad, limit fluid before bed
- UTI: wipe front to back, pee after sex
Integumentary adaptations
- Hyperpigmentation (nipple, areolae, vulva)
- Melasma
- Linea nigra
- Striae gravidum
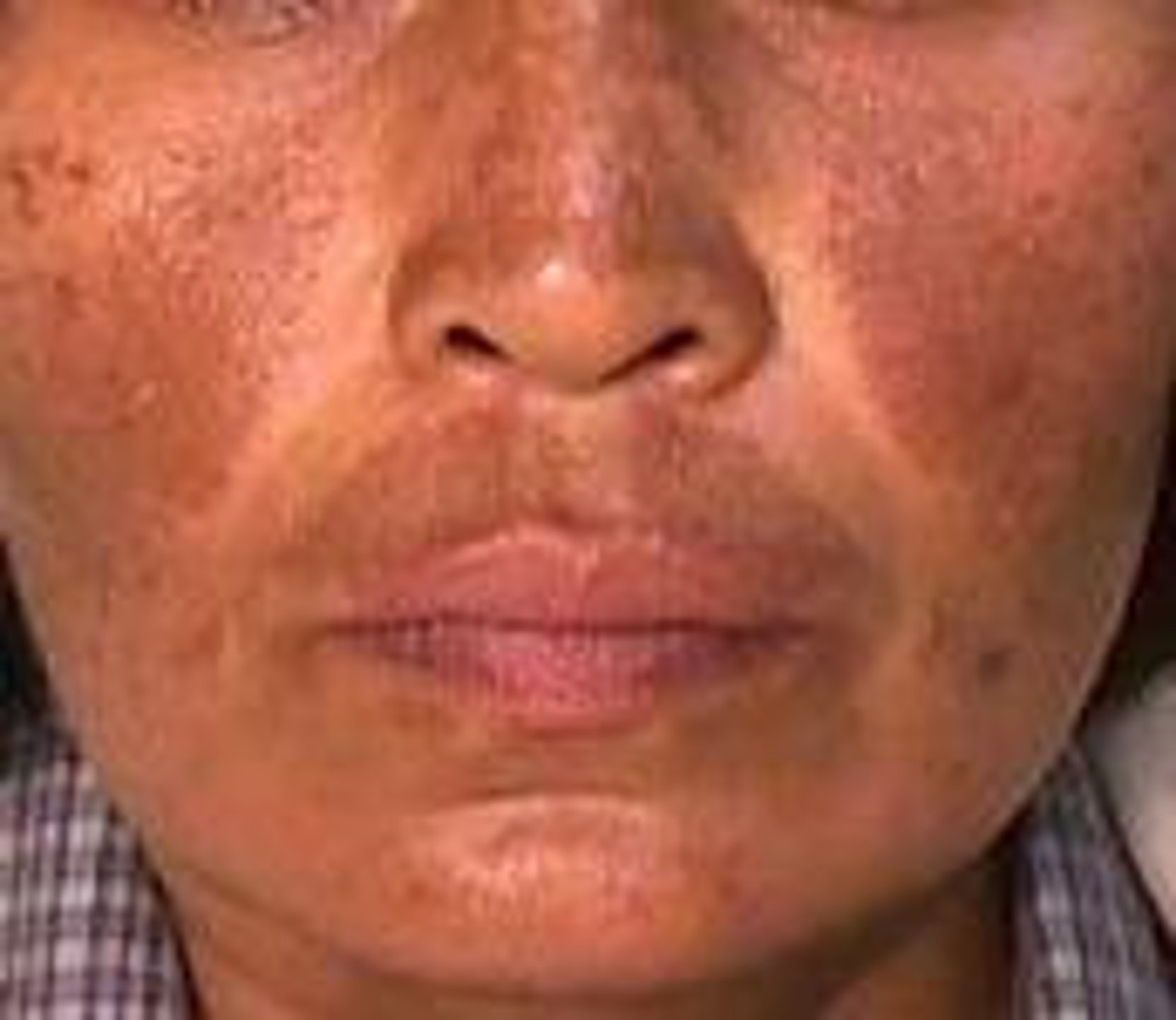
Melasma
hyperpigmentation of cheeks, nose, and forehead
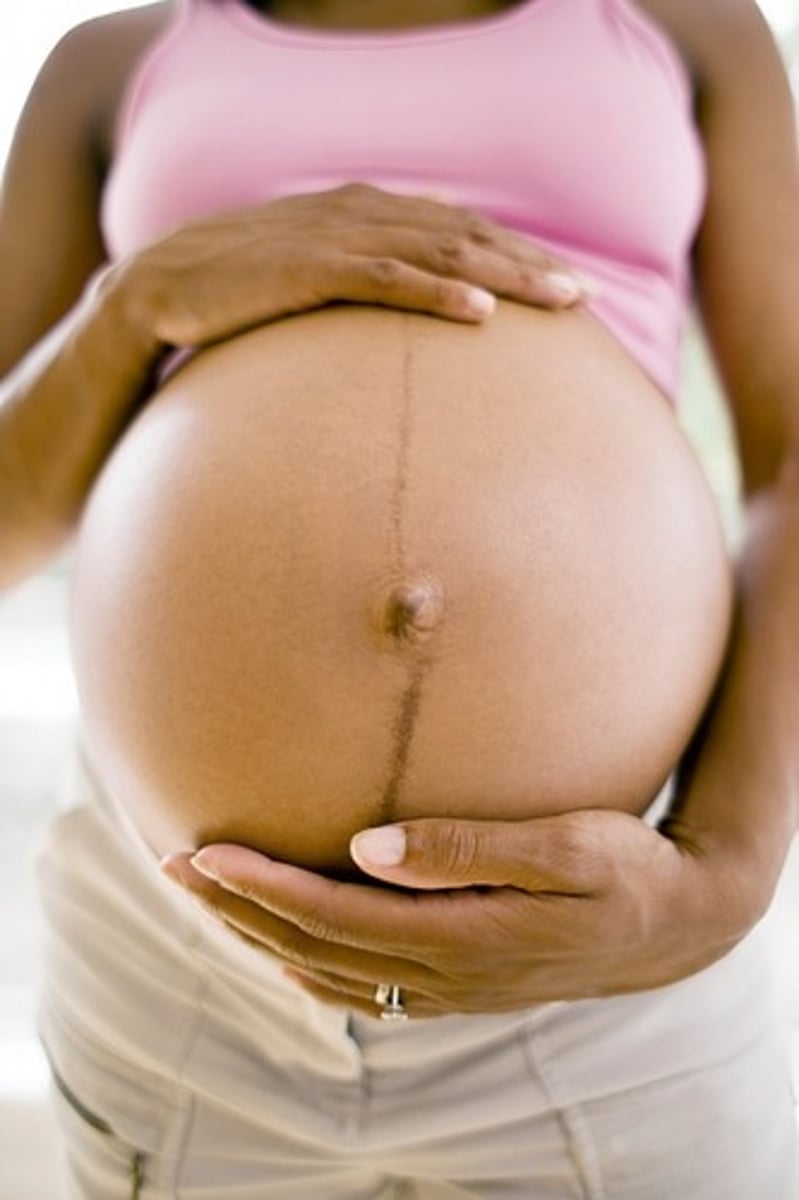
Linea nigra
pigmented line on stomach's midline

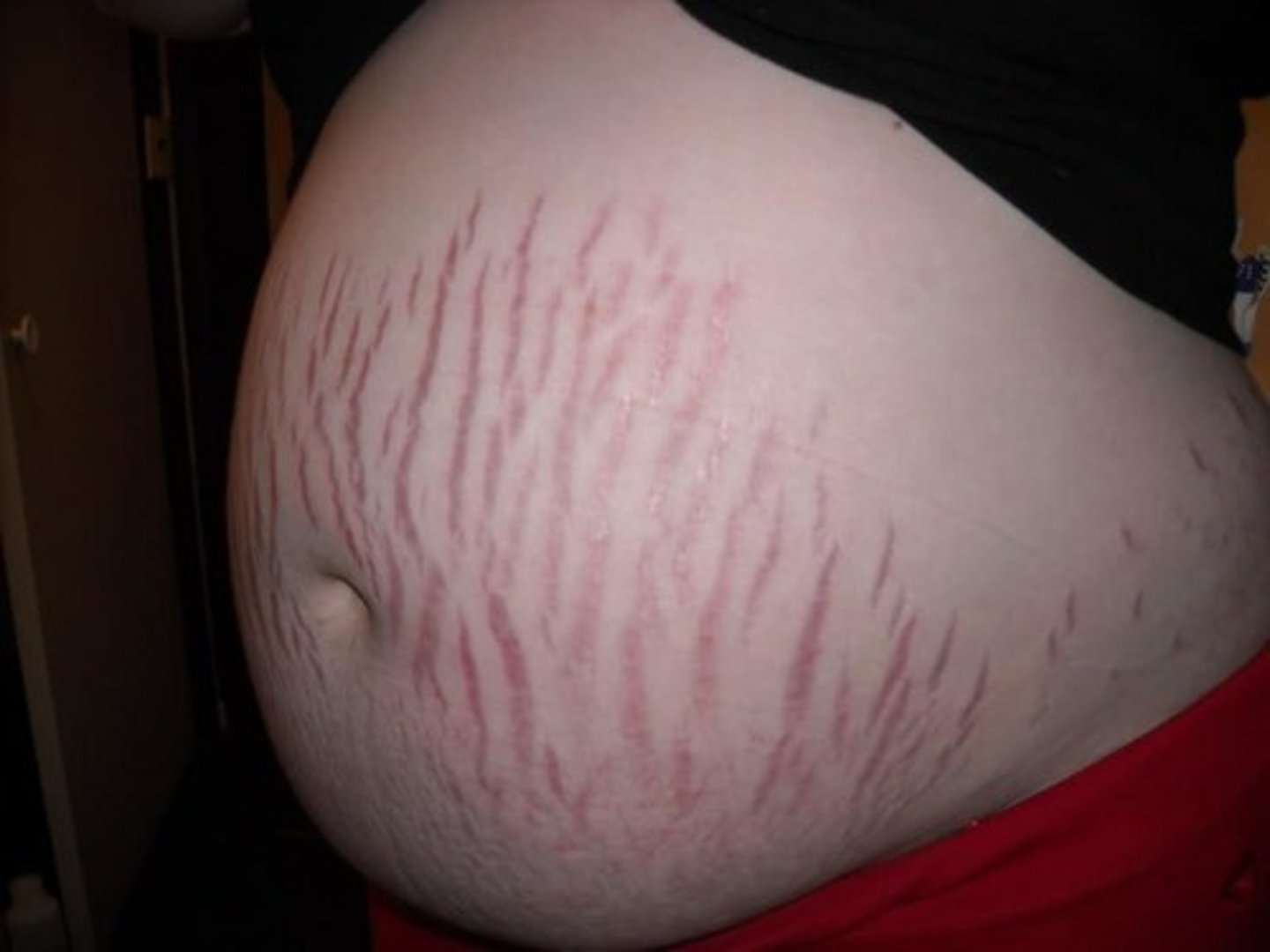
Striae gravidum
stretch marks
Musculoskeletal adaptations
- As abdomen grows, center of gravity shifts
- Increased lumbosacral curve
- Increased mobility of pelvic joints
- Rectus abdominis muscles may seperate
Musculoskeletal discomforts
- Round ligament pain (sharp stabbing pain in upper leg/lower abdomen): rest and good posture
- Joint pain and backache: good posture and low heels
- Leg cramps: dorsiflex foot
Neurologic adaptations
- Compression of pelvic nerves --> sensory leg changes
- Carpal tunnel
- Hypocalcemia causing muscle cramps
GI adaptations
- Constipation due to increased progesterone causing smooth muscle relaxation and decreased peristalsis
- Pica
- Heartburn from decreased smooth muscle tone and motility
GI discomforts
- Nausea and vomiting: dry crackers or toast 30 min before rising in morning, avoid empty stomach, fluid between meals
- Constipation: Fiber and water, exercise, apples
- Heartburn: small frequent meals, sit up for 30 min after meals
Visit schedule
Monthly until 7 months
Every 2 weeks until 36 weeks, then weekly
Gravida
women who is pregnant
Parity
number of pregnancies in which fetus reached 20 weeks gestation
Gravidity
all pregnancies including current one
Term
pregnancies reached 38 weeks
Preterm
babies born <36 weeks
Abortion
miscarriage or planned abortion
Living
assume all mentioned pregnancies are living unless told otherwise
GTPAL
Gravida, Term, Preterm, Abortions, Living
Nagele's rule
Determine first day of last period
- Subtract 3 months
- add 7 days and 1 year
Fundal height
height of the fundus from the top of the symphysis pubis to the highest point at the top of the uterus; used to estimate the size of the fetus between 18 and 32 weeks
Initial visit
Comprehensive health history
- Current and previous pregnancy
- Family history
- Psychosocial profile
- Physical assessment including pelvic exam and pap smear
- Diagnostic testing (H&H, blood type, rubella, HIV, urinalysis and culture, RPR/VDRL (syphilis test), folate, CF screen, sickle cell
- Risk assessment
Follow-up visits
Physical exam, fetal assessment, follow up labs.
Routine lab: clean-catch urine
11-14 weeks: screen for chromosomal abnormalities
18-24 weeks: ultrasound for fetal anatomy
35-37 weeks: group B strep test
Weight gain
25-35 pounds
Underweight: 28-40 lbs
Overweight: 15-25 lbs
Nutrition needs
- extra 340 cal/day during 2nd trimester
- extra 450 cal/day during 3rd trimester
- Protein
- Iron
- Calcium
- Folic acid
- Fluid
Ovum or preembryonic stage
conception to 14 days
embryo stage
day 14 to 8 weeks
- most crucial time of development
- ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
fetus stage
9 weeks to birth
chorion
fetal side of placenta
amnion
covering umbilical cord and chorion of fetal surface of placenta
amniotic fluid
initially diffuse from maternal blood, then fluid secreted by fetus
- Increased weekly
- 700-1000mL at term
- Functions: filtering waste through placenta, testable fluid, temp, symmetrical growth
Cardiac - 3rd week
heart starts beating
Umbilical cord - 5th week
connecting stalk becomes compressed from both sides and forms umbilical cord
umbilical cord structure
2 arteries and 1 vein
Circulatory - 4th and 5th week
four chambers form
Respiratory - 4-17th week
development of respiratory tract
Respiratory - 32 weeks
Alveolar cells secrete surfactant
Lecithin/sphingomyelin (L/S) ratio
2:1 ratio indicates fetal lung maturity
GI - 5th month
fetus begins swallowing amniotic fluid
GI - 36 weeks
GI system mature
Renal - 5th week
kidneys form
Renal - 9th week
kidneys begin to function
Neuro - 5th week
forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain form
Neuro - 8th week
Brainwaves and nerve fibers run throughout body
Neuro - 24th week
all hearing loss is permanent
Neuro - 5th month
able to distinguish taste
Neuro - 20th week
insulin produced