Skills Final Exam
5.0(4)
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
Hypothermia:
- abnormally low body temperature
2
New cards
Hyperthermia:
- abnormally high body temperature
3
New cards
Shock:
- increased risk when you lose too much blood
- cause extracellular fluid loss
- cause extracellular fluid loss
4
New cards
Signs of Shock:
- hypotension
- tachycardia
- restlessness and apprehension
- skin cold, moist, pale, cyanotic
- decreased O2 sat.
- decreased circulating volume
- tachycardia
- restlessness and apprehension
- skin cold, moist, pale, cyanotic
- decreased O2 sat.
- decreased circulating volume
5
New cards
Heat stroke:
- continued exposure to extreme heat that raises the core body temperature to 105° or higher.
- altered mental state, nausea, vomiting, slurred speech
- altered mental state, nausea, vomiting, slurred speech
6
New cards
Tachycardia:
- increased HR
7
New cards
Pyrexia:
- fever
- raised body temp
- raised body temp
8
New cards
- proximal to it
When doing vitals, if a distal pulse is absent, check the pulse:
9
New cards
- apical pulse
If the radial pulse is low check the:
10
New cards
Acidosis:
- pH below 7.35
11
New cards
Alkalosis:
- pH above 7.45
12
New cards
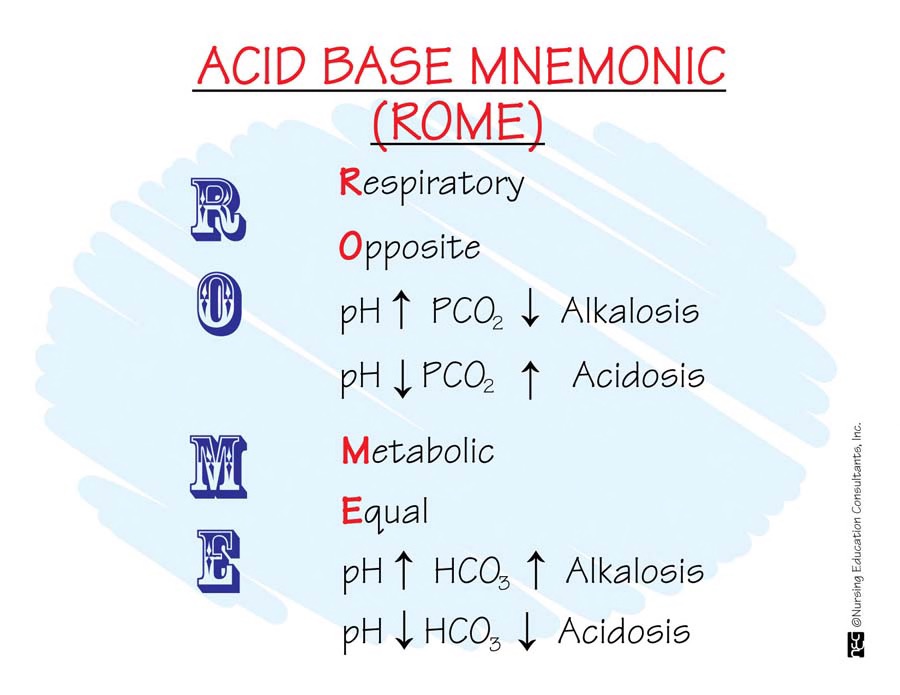
R.O.M.E. acronym
- Respiratory Opposite: high pH=low CO2, low pH=high CO2
- Metabolic Equal: high pH=high HCO3, low pH=low HCO3
- Metabolic Equal: high pH=high HCO3, low pH=low HCO3
13
New cards
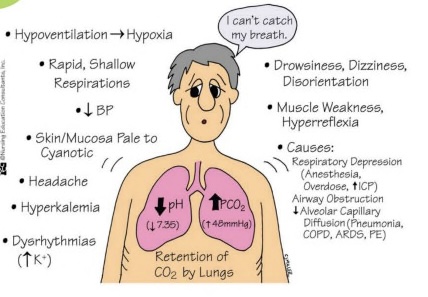
Respiratory Acidosis:
- low pH, high CO2
- hypoxia, decreased BP, muscle weakness, dizziness, increased potassium
- causes: COPD, pneumonia, atelectasis
- hypoxia, decreased BP, muscle weakness, dizziness, increased potassium
- causes: COPD, pneumonia, atelectasis
14
New cards
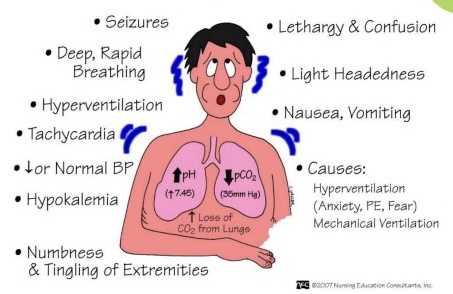
Respiratory Alkalosis:
- high pH, low CO2
- seizures, confusion, nausea, decreased/normal BP, decreased potassium
- causes: hyperventilation (stress), mechanical ventilation
- seizures, confusion, nausea, decreased/normal BP, decreased potassium
- causes: hyperventilation (stress), mechanical ventilation
15
New cards
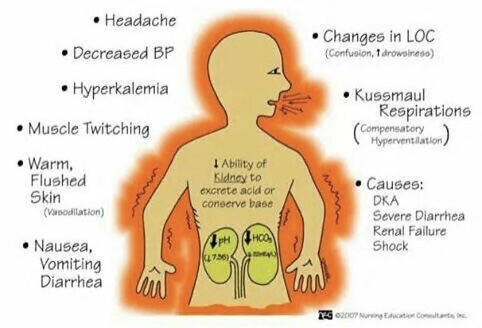
Metabolic Acidosis:
- low pH, low HCO3
- Kussmauls, headache, decreased BP, warmth, decreased LOC
- causes: DKA, severe diarrhea, renal failure, shock
- Kussmauls, headache, decreased BP, warmth, decreased LOC
- causes: DKA, severe diarrhea, renal failure, shock
16
New cards
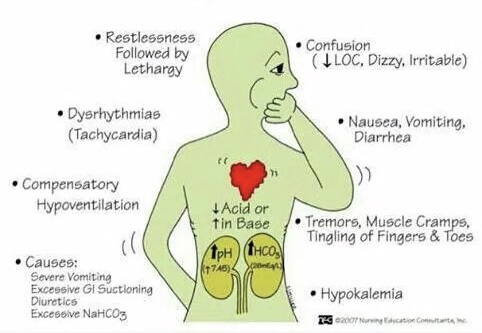
Metabolic Alkalosis:
- high pH, high HCO3
- restlessness, tachycardia, confusion, tremors, muscle cramps
- causes: severe vomiting, excessive GI suctioning, diuretics, excessive NaHCO3
- restlessness, tachycardia, confusion, tremors, muscle cramps
- causes: severe vomiting, excessive GI suctioning, diuretics, excessive NaHCO3
17
New cards
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen):
- indicates renal function and hydration status
18
New cards
Normal Range of BUN:
- 10-20 mg/dL
19
New cards
Critical Range of BUN:
- above 100 mg/dL
20
New cards
Symptoms of Increased BUN:
- dehydration
- impaired renal function
- excessive protein intake
- impaired renal function
- excessive protein intake
21
New cards
Symptoms of Decreased BUN:
- malnutrition
- overhydration
- liver damage
- overhydration
- liver damage
22
New cards
Creatinine:
- increased level of this may be a sign of poor kidney function
- 0.7 to 1.3 mg/dL for men
- 0.6 to 1.1 mg/dL for women
- 0.7 to 1.3 mg/dL for men
- 0.6 to 1.1 mg/dL for women
23
New cards
Hemoglobin:
- protein in RBCs that carries oxygen to your body's organs and tissues and transports CO2 from your organs and tissues back to your lungs
24
New cards
Signs of Low Hemoglobin:
- tiredness and lack of energy
25
New cards
How to treat a pt. w/ C. Diff:
- antibiotics
- place in a private room
- wear gloves and gown
- use soap and water for hand hygiene
- use Clorox wipes for surfaces
- place in a private room
- wear gloves and gown
- use soap and water for hand hygiene
- use Clorox wipes for surfaces
26
New cards
Urinalysis:
- looks for bacteria that causes UTIs
27
New cards
- an antibiotic sensitivity test
If you have a UTI, what test can pinpoint the bacteria?
28
New cards
- identifying yourself and your patient
- bed locked
- bed lowered
- side rails up
- call light near
- bed locked
- bed lowered
- side rails up
- call light near
General Safety Checks include:
29
New cards
- YES
Do you need an order to use restraints?
30
New cards
- why the restraint is being used
If you use a restraint, what is one thing you must document?
31
New cards
- checking the circulation
- color and nerve pain
- color and nerve pain
What is a nursing priority with restraints?
32
New cards
Circadian Rhythm:
- responses to light and dark
- internal clock
- tired at night; awake during the day
- internal clock
- tired at night; awake during the day
33
New cards
- excessive daytime sleepiness
Patients with sleep apnea have:
34
New cards
- CPAP machine
Treatment for Sleep Apnea:
35
New cards
Insomnia:
- persistent problems with falling and staying asleep
36
New cards
- give them earplugs
- play music
- limit noise and distractions
- dim lights
- play music
- limit noise and distractions
- dim lights
What actions can you take to help a pt. with insomnia?
37
New cards
- extra sleep
When a patient is under stress, they need:
38
New cards
- look them in the eye when speaking to them
- use tools like amplified telephones
- use tools like amplified telephones
If a patient is hard of hearing, what can you do to help them?
39
New cards
Glaucoma:
- a gradual increase of intraocular pressure to the nerve of the eye
- produces very poor eyesight
- peripheral vision is poor
- produces very poor eyesight
- peripheral vision is poor
40
New cards
- identify yourself
- stay in their field of vision
- make sure the room is clutter free
- be on guard for falls
- stay in their field of vision
- make sure the room is clutter free
- be on guard for falls
What are some things you can do to try to protect a patient that has problems with their vision?
41
New cards
Vertigo:
- dizziness
- feels like the room is spinning
- feels like the room is spinning
42
New cards
- Snellen chart
Tools to evaluate vision:
43
New cards
- tuning fork
Tools to evaluate hearing:
44
New cards
PCA Pump:
- patient-controlled analgesic
45
New cards
- morphine, fentanyl, hydromorphone
What drugs are used in PCA pumps?
46
New cards
Features on PCA Pumps:
- a loaded dose
- predetermines safety limits
- lockout mechanisms
- predetermines safety limits
- lockout mechanisms
47
New cards
- cancer patients
Morphine is commonly used in:
48
New cards
- handles and perceives pain
Coping styles can determine how a patient:
49
New cards
- elderly
- paraplegics
- patients incontinent of urine or feces
- patients that are very ill and cannot move much
- comatose patients
- paraplegics
- patients incontinent of urine or feces
- patients that are very ill and cannot move much
- comatose patients
What kind of patients are prone to pressure ulcers?
50
New cards
- oxygen and protein
For a pressure ulcer to heal it must have:
51
New cards
- infections due to bacteria getting into the open wound
Patients with pressure ulcers are at higher risk for:
52
New cards
- a wound vac
What can you use to help with a pressure ulcer?
53
New cards
Eschar:
- a black substance on pressure ulcers
54
New cards
- debridement
How is Eschar treated?
55
New cards
SBAR
- situation
- background
- assessment
- recommendation
- background
- assessment
- recommendation
56
New cards
Respiratory process:
- ventilation
- perfusion
- diffusion
- perfusion
- diffusion
57
New cards
Ventilation:
- moving gases into and out of the lungs
58
New cards
Perfusion:
- ability of cardiovascular system to pump oxygenated blood to the tissues and return deoxygenated blood to the lungs
59
New cards
Diffusion:
- exchange of respiratory gases in the alveoli and capillaries
60
New cards
Albumin:
- protein made by your liver
61
New cards
- albumin levels
If you want to look at statistic of a patients protein levels, what will you draw?
62
New cards
TPN infusions:
- high in fluids, electrolytes, minerals, vitamins, and fats
63
New cards
How is a TPN infusion inserted?
- IV access
- Central line
- PIC line
- Central line
- PIC line
64
New cards
- 24 hour period
TPN is given over a:
65
New cards
Tonicity:
- measurement of concentration of IV solutions with osmolality of bodily fluids
66
New cards
Hypertonic:
- sodium and volume replacement
- used for hypernatremia (water insufficiency)
- go slow
- cells shrink
- used for hypernatremia (water insufficiency)
- go slow
- cells shrink
67
New cards
Hypotonic:
- isotonic until INSIDE the body
- used for hyponatremia (water excess) and hypoglycemia
- don't give to infants or head injury patients (cerebral edema may occur)
- cells swell
- used for hyponatremia (water excess) and hypoglycemia
- don't give to infants or head injury patients (cerebral edema may occur)
- cells swell
68
New cards
Isotonic:
- expands the volume, dilutes medications, and keeps veins open
- same osmolarity as body fluid
- same osmolarity as body fluid
69
New cards
How to identify extracellular fluid volume deficit:
- sudden weight loss
- postural hypotension
- tachycardia
- thready pulse
- dry mucuous membranes
- poor skin turgor
- slow vein filling
- flat neck veins
- dark yellow urine
- postural hypotension
- tachycardia
- thready pulse
- dry mucuous membranes
- poor skin turgor
- slow vein filling
- flat neck veins
- dark yellow urine
70
New cards
Laboratory findings for fluid volume deficit:
- increased hematocrit
- increased BUN above 20 mg/dL
- urine specific gravity above 1.030
- increased BUN above 20 mg/dL
- urine specific gravity above 1.030
71
New cards
How to identify extracellular fluid volume overload:
- sudden weight gain
- edema
- full neck veins
- crackles in lungs
- confusion
- pulmonary edema
- edema
- full neck veins
- crackles in lungs
- confusion
- pulmonary edema
72
New cards
Laboratory findings for fluid volume Overload:
- decreased hematocrit
- decreased BUN below 10 mg/dL
- decreased BUN below 10 mg/dL
73
New cards
- their Oxygen
If a patient with CHF has an infection that increases their body temperature, what do you need to increase?
74
New cards
- requirement for oxygen
If the metabolic rate goes up, so does the:
75
New cards
Normal Sodium level:
- 135-145
76
New cards
Hypernatremia:
- 145 or higher
- decreased LOC (confusion, lethargy, coma)
- thirst
- seizures
- decreased LOC (confusion, lethargy, coma)
- thirst
- seizures
77
New cards
Hyponatremia:
- 135 or below
- decreased LOC (confusion, lethargy coma)
- seizures
- decreased LOC (confusion, lethargy coma)
- seizures
78
New cards
Normal Potassium Level:
- 3.5-5
79
New cards
Hyperkalemia:
- 5.1 or higher
- bilateral muscle weakness in quadriceps
- transient abdominal cramps
- diarrhea
- dysrhythmias
- cardiac arrest
- bilateral muscle weakness in quadriceps
- transient abdominal cramps
- diarrhea
- dysrhythmias
- cardiac arrest
80
New cards
Hypokalemia:
- 3.5 or lower
- bilateral muscle weakness that begins in quadriceps and ascends to respiratory muscles
- abdominal distensionion
- decreased bowel sounds
- constipation
- dysrhythmias
- bilateral muscle weakness that begins in quadriceps and ascends to respiratory muscles
- abdominal distensionion
- decreased bowel sounds
- constipation
- dysrhythmias
81
New cards
Dysuria:
- pain during urination
82
New cards
Ketosis:
- a metabolic state that occurs when your body burns fat for energy instead of glucose
83
New cards
Spironolactone:
- decreases sodium in the body, saving potassium
- removes H2O and Na
- used for hypertension and edema due to CHF
- if systolic is
- removes H2O and Na
- used for hypertension and edema due to CHF
- if systolic is
84
New cards
Lasix:
- gets rid of potassium, saving sodium
- removes H2O and K+
- treats hypertension, edema due to CHF, and ascites
- if systolic is
- removes H2O and K+
- treats hypertension, edema due to CHF, and ascites
- if systolic is
85
New cards
- dehydrated
If fluid labs are high when a patient is on Lasix, that means they are:
86
New cards
- in fluid overload
If fluid labs are low when a patient is taking Lasix, that means they are:
87
New cards
Kayexalate:
- lowers potassium
- need to get rid of potassium or it can kill you
- watch for constipation, gastric irritation, diarrhea, sodium retention, and hypokalemia
- need to get rid of potassium or it can kill you
- watch for constipation, gastric irritation, diarrhea, sodium retention, and hypokalemia

88
New cards
- their heart rate
What bodily function do we monitor when a patient is taking Kayexalate?
89
New cards
- Normal Saline 0.9%
What solution is hung with blood during a blood transfusion?
90
New cards
- stop transfusion immediately and notify the prescriber
- change the IV tubing
- treat symptoms if present (O2, fluids, epi)
- change the IV tubing
- treat symptoms if present (O2, fluids, epi)
What steps do you take if a patient is having a blood transfusion reaction?
91
New cards
- with an ampule
When do we use a filter needle?
92
New cards
Infiltration:
- occurs when IV catheter becomes dislodged and vein ruptures so IV fluids inadvertently enter subcutaneous tissue around the IV site
- potentially dangerous
- potentially dangerous
93
New cards
- to decrease pain
Why do we inject IV medications slowly?
94
New cards
- add an NSAID to the regime to give better relief
- decrease opioid intake
- decrease opioid intake
How do we get a surgical patient off of morphine?
95
New cards
- the surgeon and the patient
Who signs the informed consent forms for surgery?
96
New cards
- before the surgery
When are informed consent forms signed?
97
New cards
Primary Healing:
- edges of wound are pulled together and approximated with sutures or staples
- healing occurs by connective tissue deposition
- healing occurs by connective tissue deposition
98
New cards
Secondary Healing:
- wound edges are not approximated
- healing occurs by granulation tissue formation and contraction of the wound edges
- healing occurs by granulation tissue formation and contraction of the wound edges
99
New cards
Evisceration:
- protrusion of the internal organs through an incision
100
New cards
Dehiscence:
- when a wound opens (partially or totally)
- may see bleeding, pain, swelling, fever, and broken sutures
- maybe use a wound vac
- may see bleeding, pain, swelling, fever, and broken sutures
- maybe use a wound vac