life at cellular level
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
nucleus
contains cell DNA
nucleoli
sites of ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosomal assembly
nuclear membrane/envelope
encloses nucleus
phospholipid bilayer
endoplasmic reticulum
membrane bound
rough and smooth varieties
RER
has ribosomes attached
modifies proteins
SER
lipid and steroid hormone production and metabolism of toxins
ribosome
synthesise proteins
golgi apparatus
packages up protein in preparation for transport out of the cell
lysosome
bound vesicles containing enzymes
enzymes are degradative
digest biological materials or engulfed particles
peroxisome
bound vesicles containing enzymes
enzymes degrade long chain fatty acids and other foreign toxic molecules (eg H2O2)
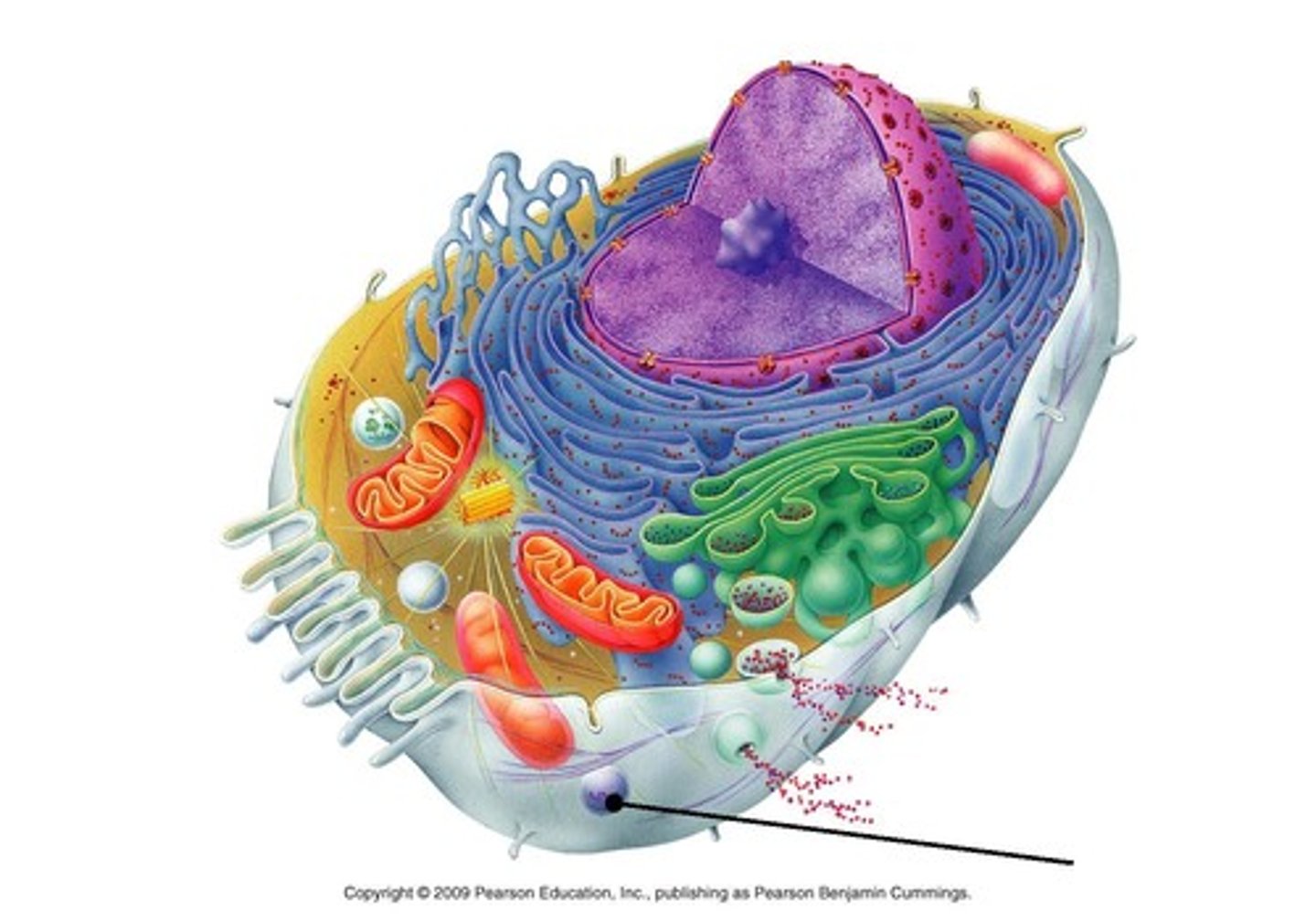
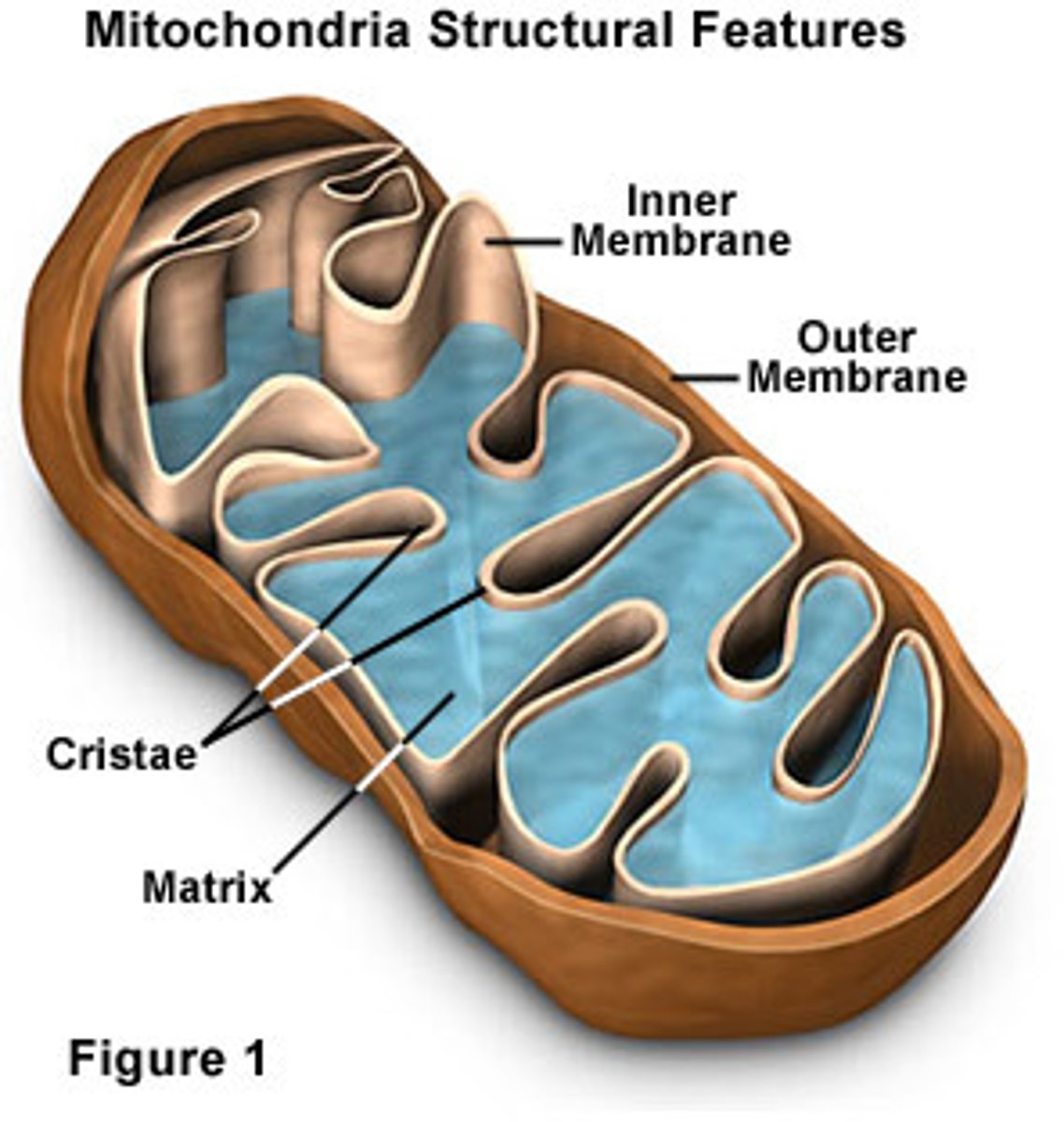
mitochondrion
bound by phospholipid bilayer
matrix contains most of enzymes for metabolising food
have their own ribosomes, synthesise most of their own proteins
flagellum
surface projection supported by cytoskeleton
longer than cilium
cilium
surface projection supported by cytoskeleton
short
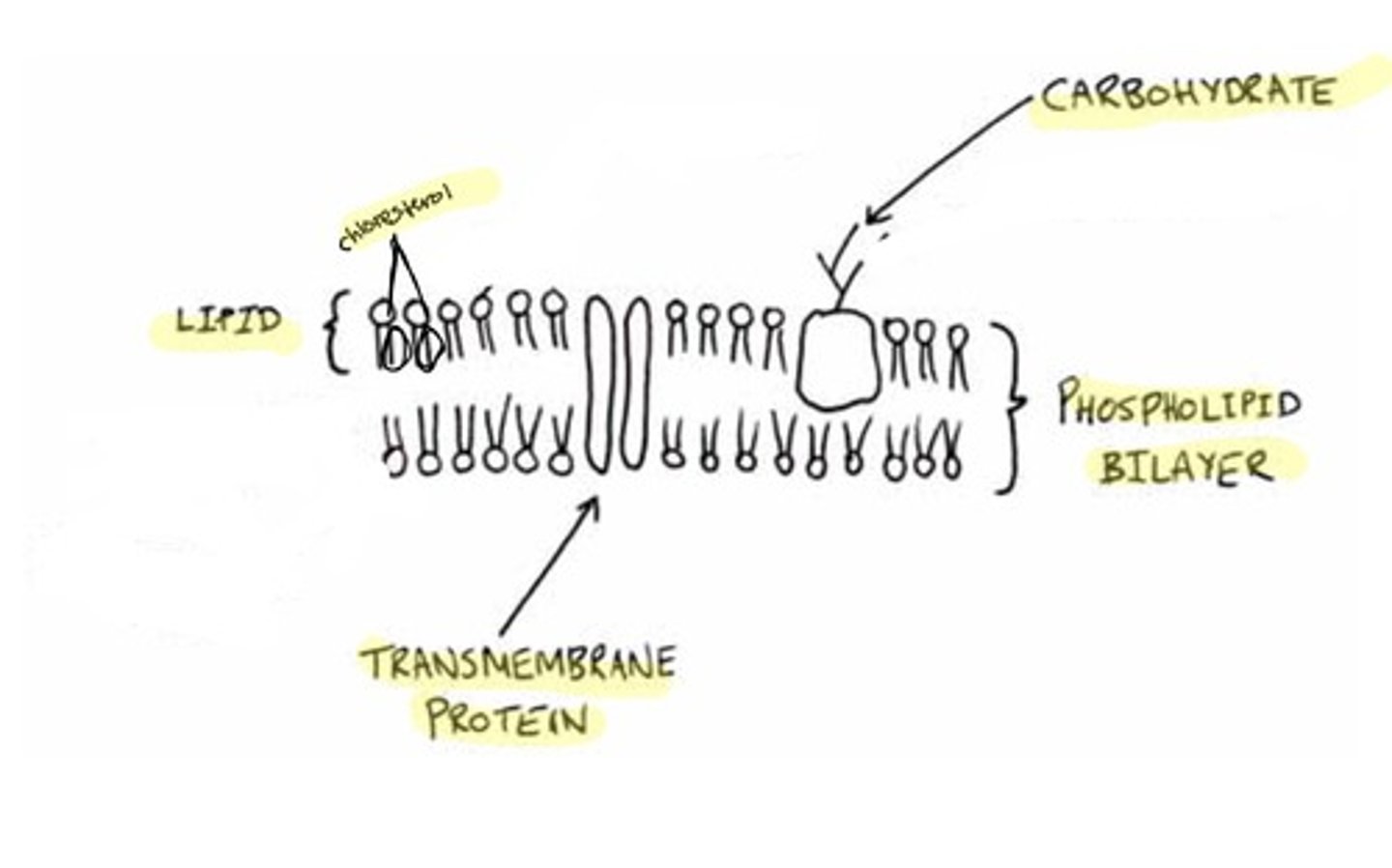
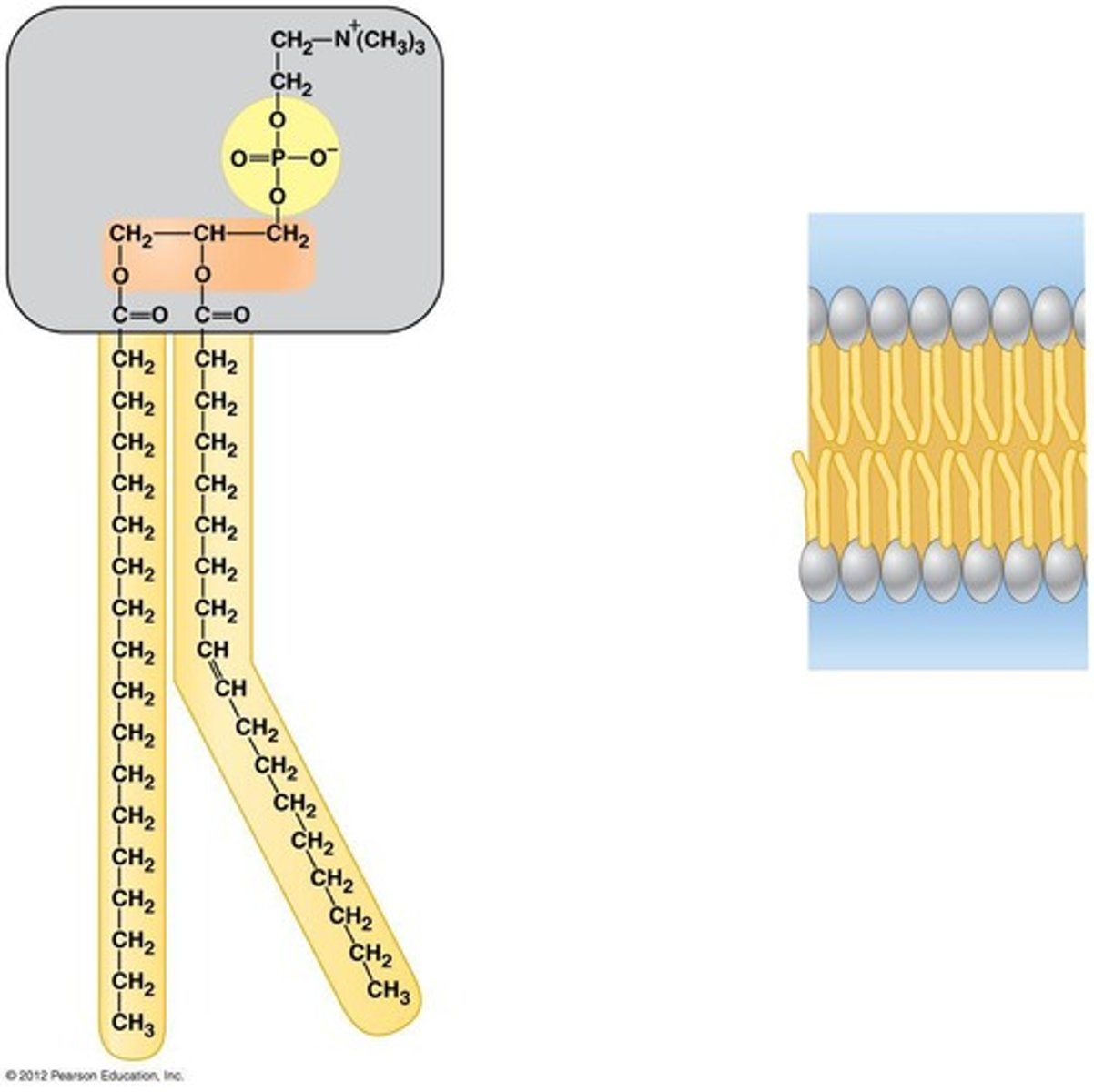
eukaryotic plasma membrane (cell membrane)
double layer of lipid with attached phosphate groups
phospholipid bilayer
selective barrier
proteins are receptors of chemical messengers
cytoskeleton (5)
cell shape
internal cell order
intracellular transport
movement
assembly of cells into tissues
3 types of cytoskeleton
microfilament
intermediate filament
microtubule
microfilament example and role
actin
cell shape and mobility
intermediate filament example and role
keratin
maintain structure
microtubule example and role
tubulin
intracellular transport
stem cell
cells that can differentiate into many (multipotent) or any (pluripotent) cell types in the body
stem cells are
multipotent and pluripotent
cell differentiation
division of stem cells into identical daughter cells then different cell types depending on gene expression and local cellular environment
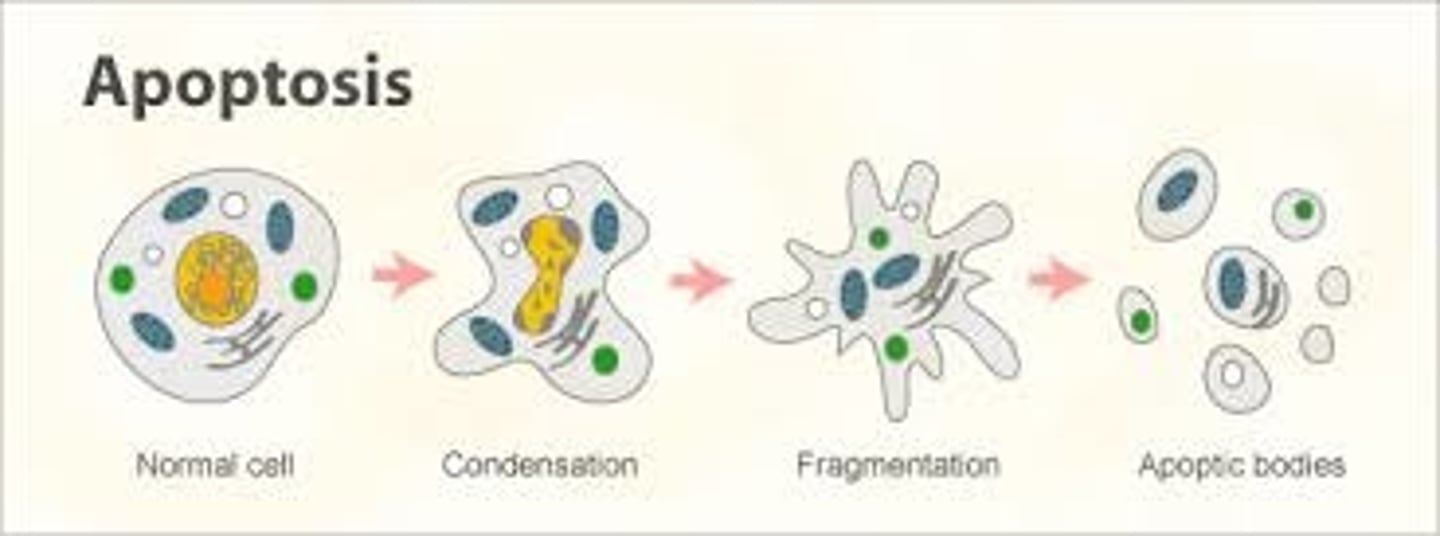
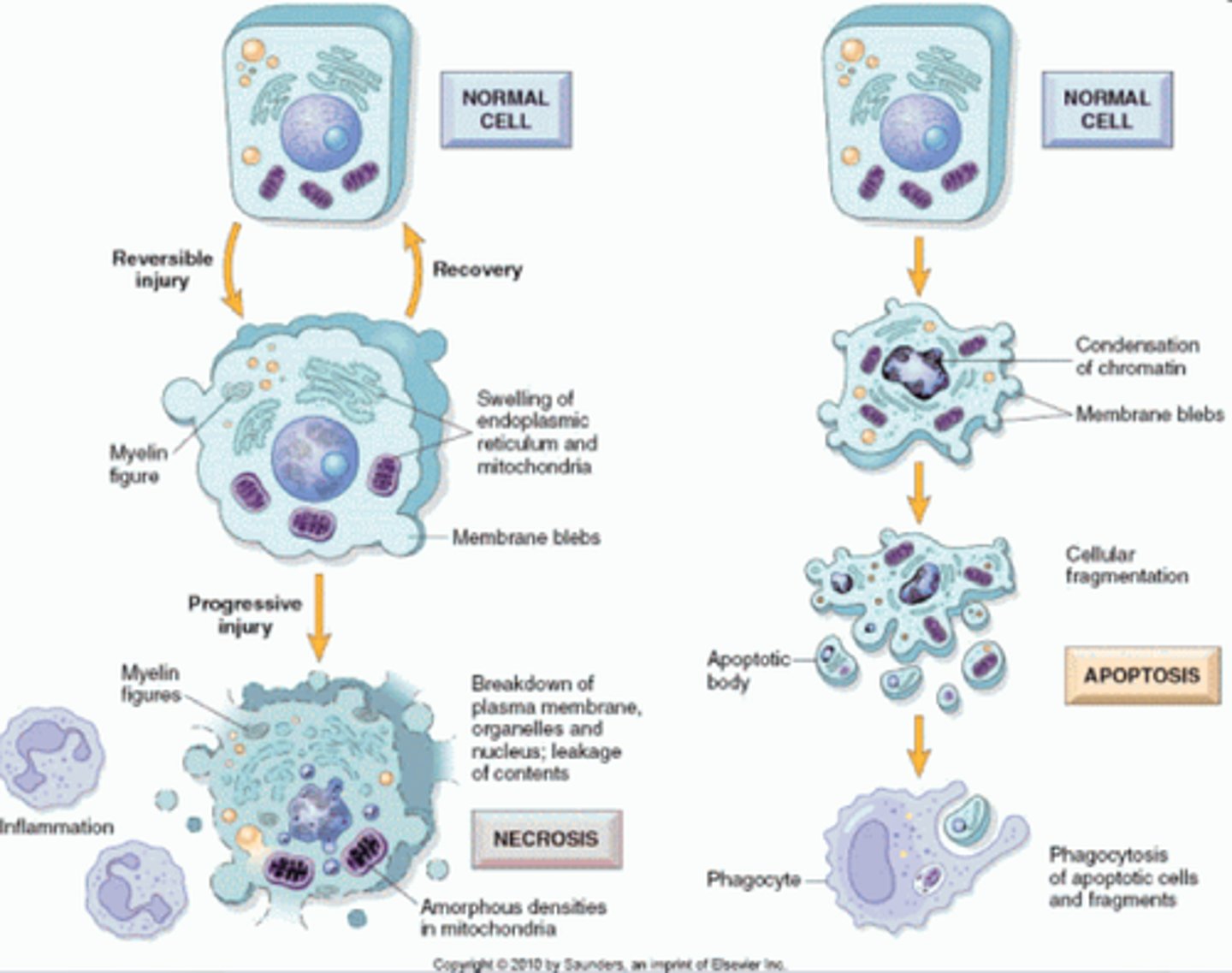
apoptosis (essential for normal function)
controlled programmed cell death
membranes bleb
necrosis
untimely death of cells in response to injury or infection
membranes rupture
major elements that construct human biomolecules
H C N O
five chemical reactions occurring in living organisms
redox
c-c bonds
internal rearrangements
group transfers
condensation/hydrolysis
protein structure
amino acids joined together
nucleic acid structure
polymers of nucleotide monomers linked with 3',5'-phosphodiester bonds
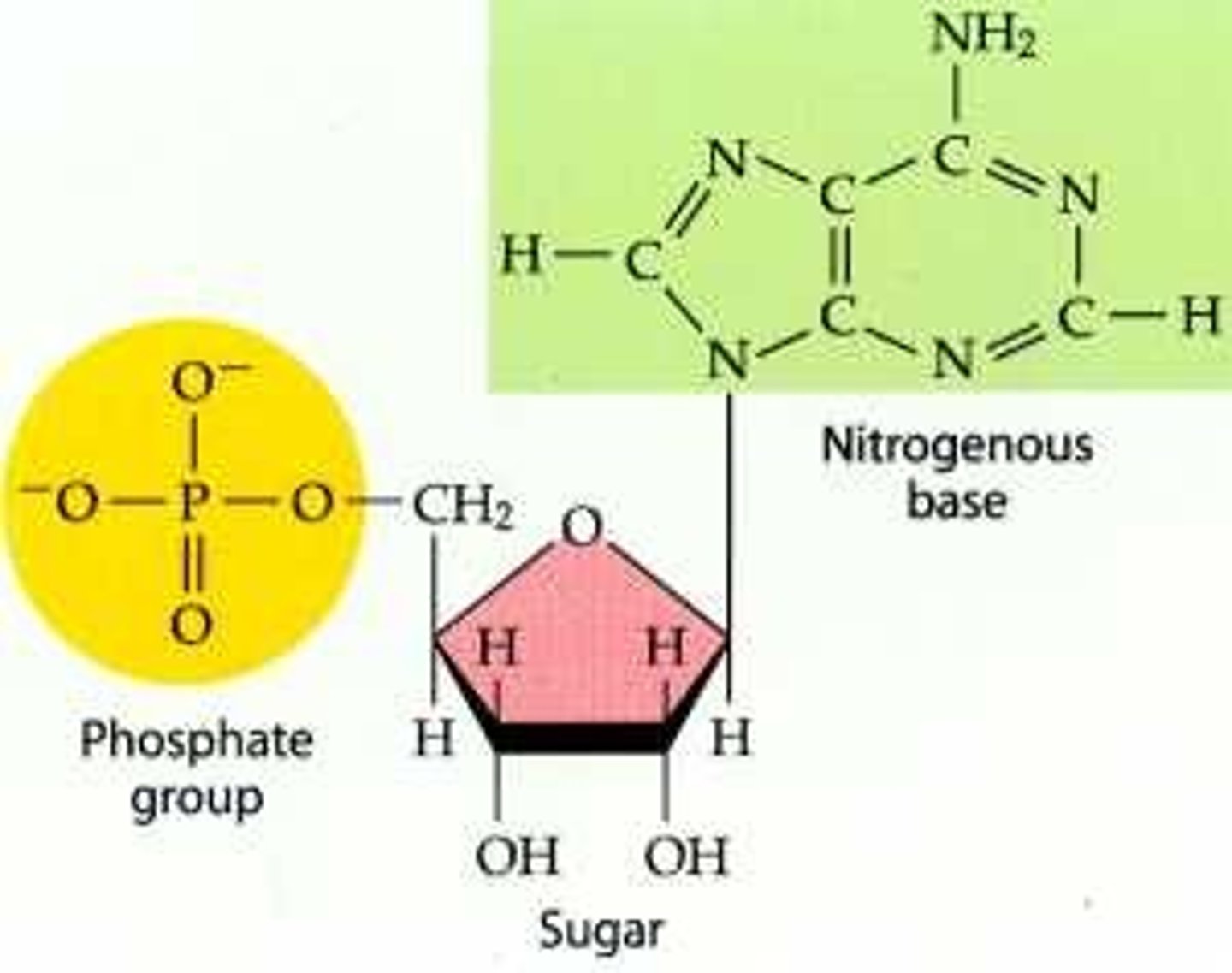
nucleotide
combination of phosphate, nitrogenous base and five carbon sugar
polysaccharide (carbohydrates) structure
monosaccharides (eg glucose) joined together with glycosidic bonds
reaction that forms polysaccharides (eg glycogen)
condensation
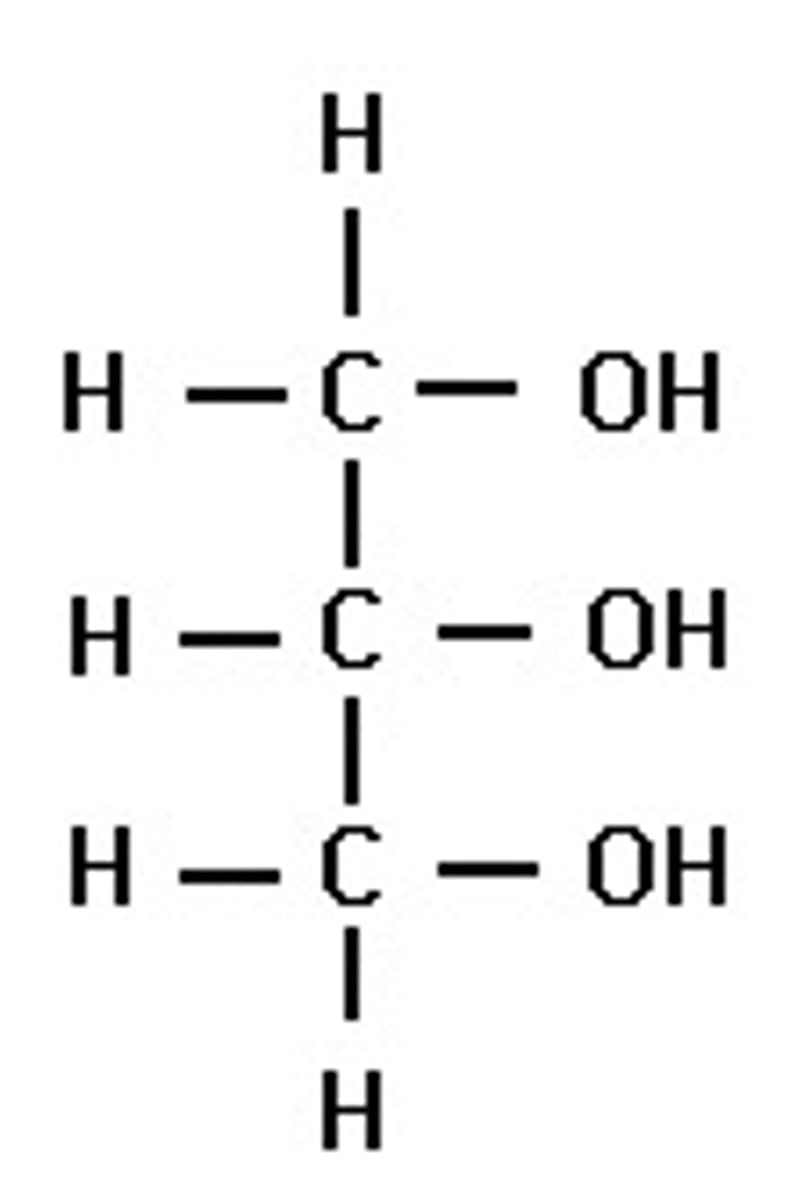
glycerol
covalently bonds to fatty acids to make lipids
lipid structures
triacylglycerides, phospholipids, sterols
fatty acids joined together
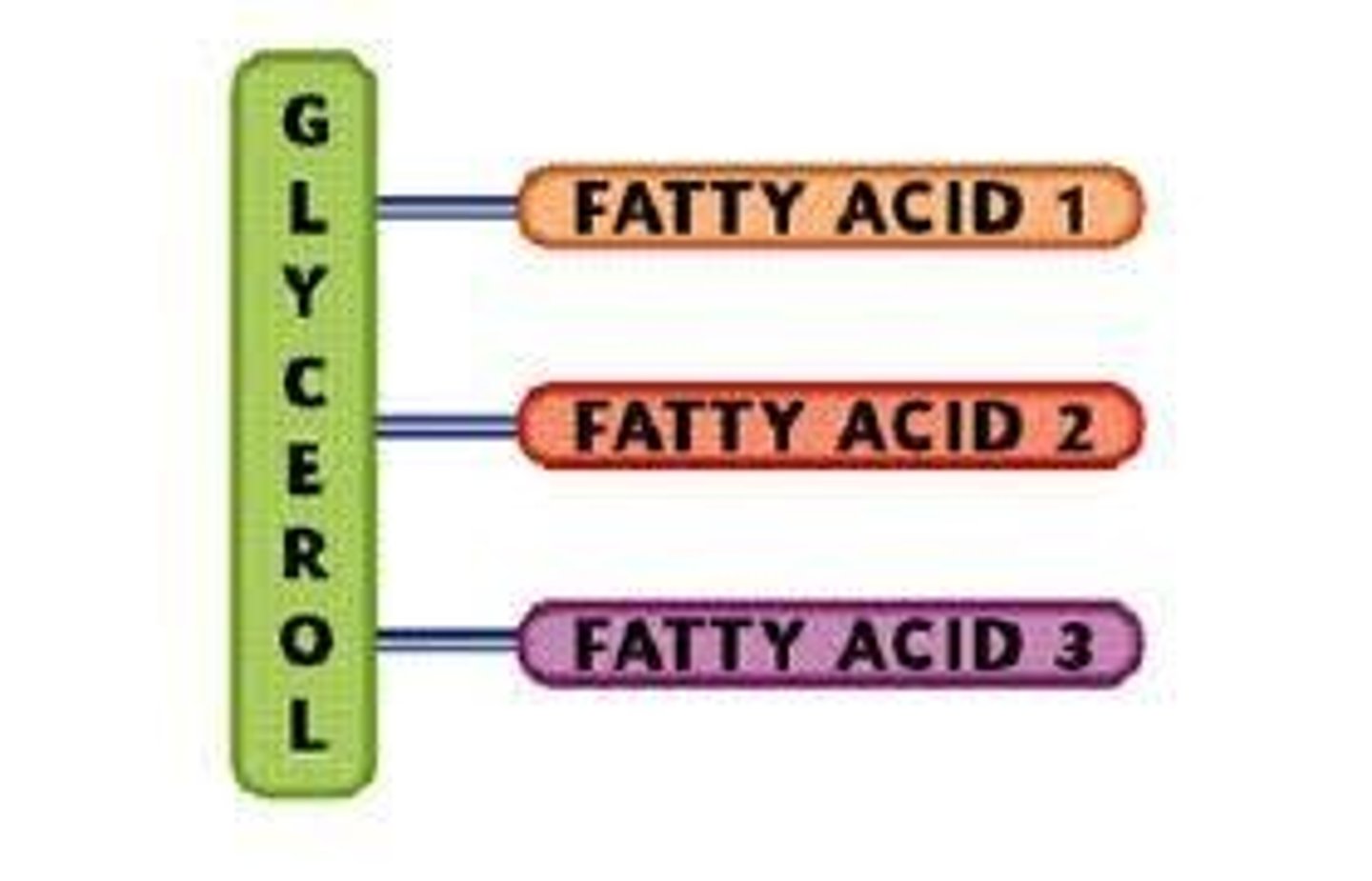
triagylcerides (triglycerides/fats) structure
glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains
phospholipids strucure
glycerol and 2 fatty acid chains and phosphate
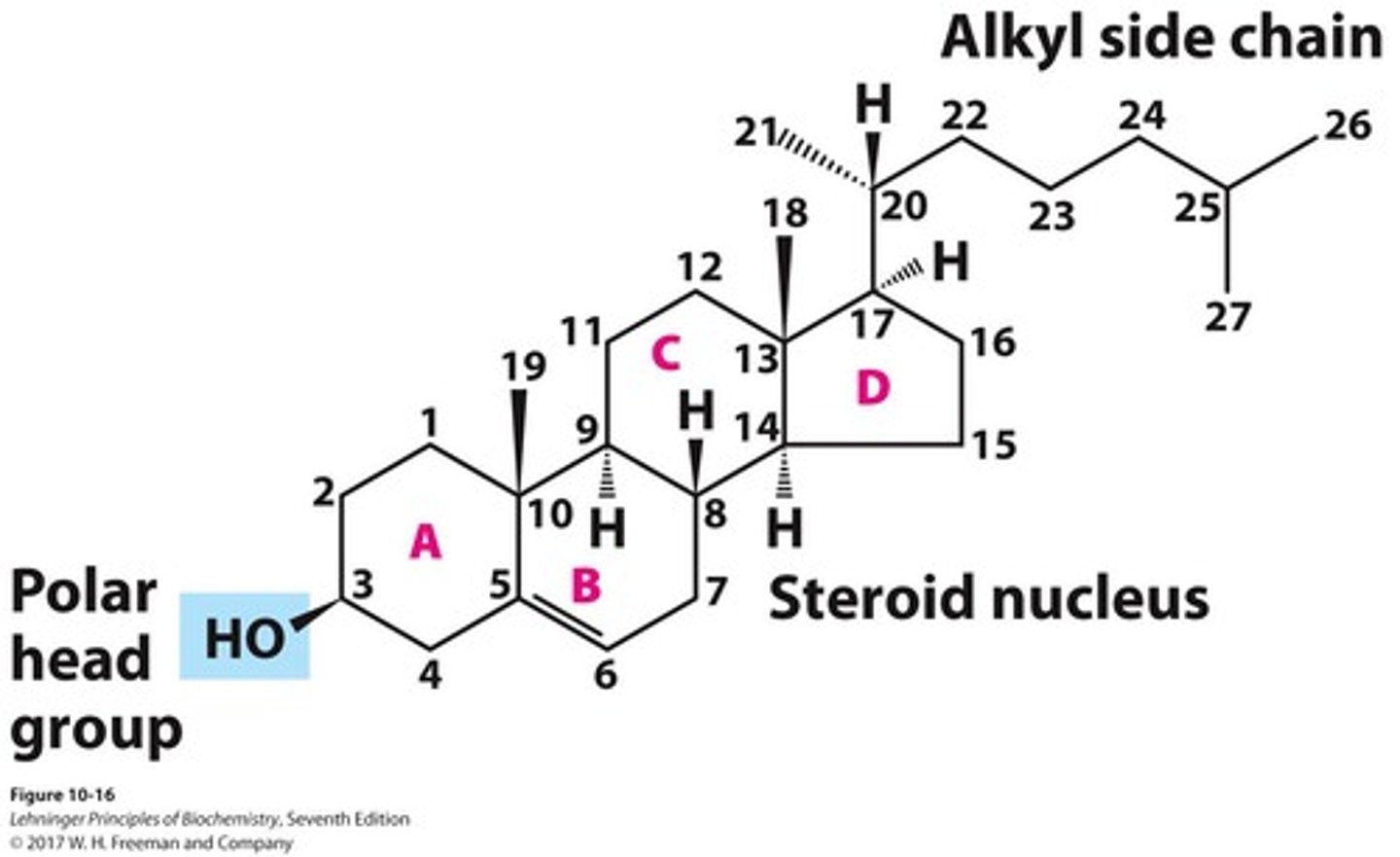
sterols structure
polar head steroid nucleus alkyl side chain