Ray Tracing and Sign Conventions in Optics
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the focal point in ray tracing for spherical mirrors?
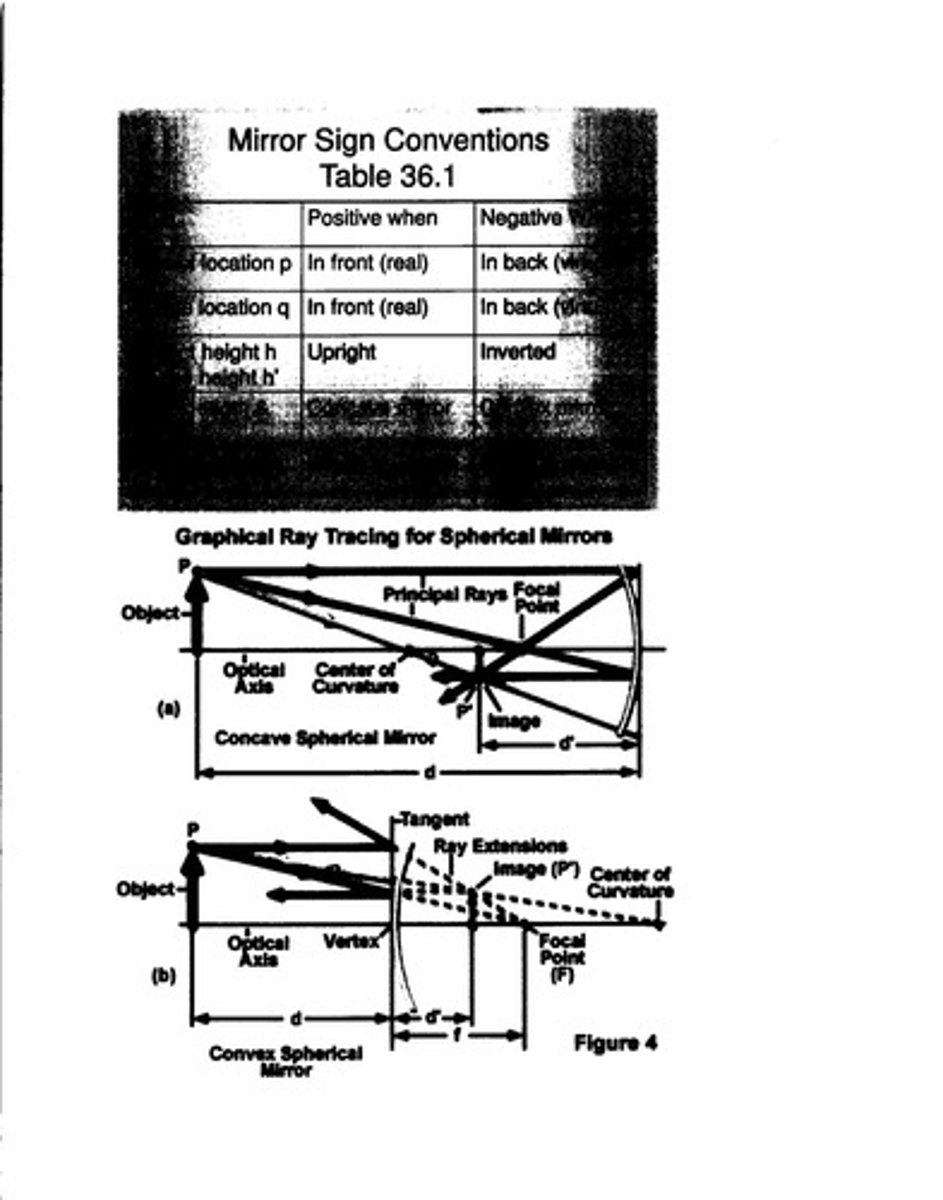
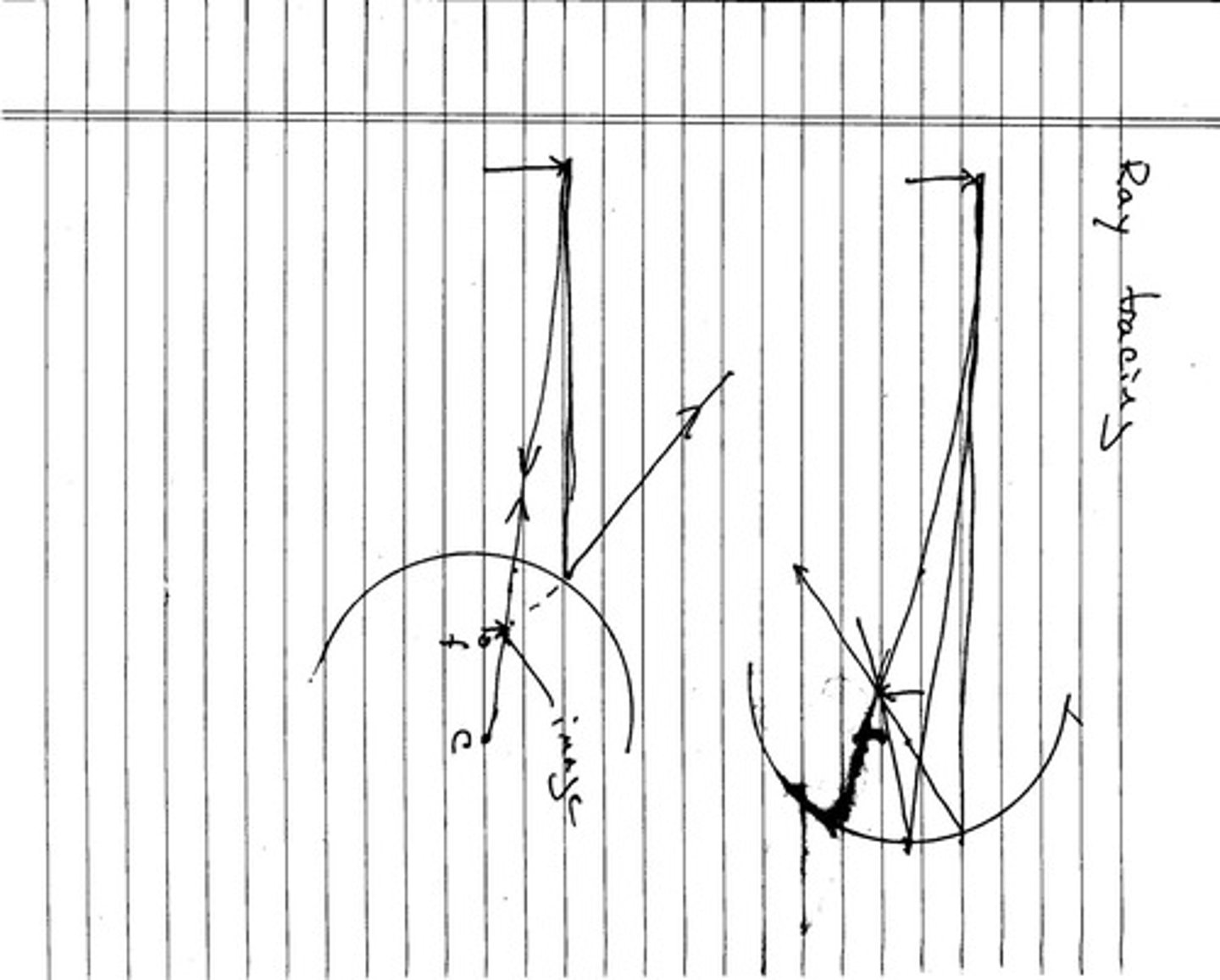
The focal point (F) is where parallel rays of light converge after reflecting off a concave mirror.
What are the sign conventions for object and image locations in mirror optics?
Object location (p) is positive when in front of the mirror (real), while image location (q) is positive when in front (real) and negative when behind (virtual).
What does a positive focal length indicate about a lens?
A positive focal length indicates that the lens is converging.
What does a negative focal length indicate about a lens?
A negative focal length indicates that the lens is diverging.
What is the magnification (M) formula for mirrors?
Magnification (M) is given by M = -q/p, where q is the image distance and p is the object distance.
How do you determine the nature of an image formed by a concave mirror?
If the image distance (q) is positive, the image is real and inverted; if negative, the image is virtual and upright.
What is the relationship between object distance (p), image distance (q), and focal length (f) for mirrors?
The relationship is given by the mirror equation: 1/f = 1/p + 1/q.
What is the significance of the center of curvature in spherical mirrors?
The center of curvature (C) is the point from which the mirror surface is curved, and it is located at a distance equal to the radius of curvature (R) from the mirror's vertex.
What is the optical vertex in the context of spherical mirrors?
The optical vertex is the point on the mirror's surface that is closest to the optical axis.
What is the ray tracing technique for determining image formation?
Ray tracing involves drawing rays from the object to the mirror, reflecting them according to the laws of reflection to locate the image.
What is the principle of superposition in wave interference?
The principle of superposition states that when two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the sum of the individual waves.
What conditions are necessary for constructive interference to occur?
Constructive interference occurs when waves meet in phase, resulting in increased amplitude.
What conditions are necessary for destructive interference to occur?
Destructive interference occurs when waves meet out of phase, resulting in decreased amplitude.
What is Young's double-slit experiment?
Young's double-slit experiment demonstrates the wave nature of light through the observation of interference patterns.
What is the significance of monochromatic light in interference experiments?
Monochromatic light ensures that all waves have the same wavelength and phase, which is essential for clear interference patterns.
How does the wavelength of light affect the interference pattern?
Shorter wavelengths produce closely spaced fringes, while longer wavelengths produce more widely spaced fringes.
What is the effect of a phase shift upon reflection?
A phase shift of 180° occurs upon reflection when light travels from a medium of lower refractive index to one of higher refractive index.
What is the Fresnel equation used for?
The Fresnel equation calculates the fraction of light reflected and transmitted at an interface between two media.
What is the relationship between refractive index and phase change upon reflection?
If light reflects off a medium with a higher refractive index, it undergoes a phase change of 180°; if it reflects off a lower refractive index, there is no phase change.
What is the significance of antireflective coatings?
Antireflective coatings are designed to minimize reflection and maximize transmission of light through lenses.
What is the formula for total magnification in a system of lenses?
Total magnification is the product of the magnifications of individual lenses: M_total = M₁ × M₂.
What does a negative total magnification indicate?
A negative total magnification indicates that the final image is inverted.
What is the role of piezoelectric crystals in imaging systems?
Piezoelectric crystals are used to adjust the focus of the imaging system by applying voltage to change their shape.
How does the distance between slits affect the interference pattern in Young's experiment?
The distance between slits (d) determines the spacing of the interference fringes; smaller d results in wider spaced fringes.
What is the significance of coherent light sources in interference experiments?
Coherent light sources maintain a constant phase relationship, which is necessary for producing stable interference patterns.