Anatomical Terminology for Lab Exam - BIO 1314
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
anatomical position
stand erect with feet flat on the floor, feet forward, arms at side with palms facing forward, head facing forward
sagittal plane
vertical division of the body into right and left portions
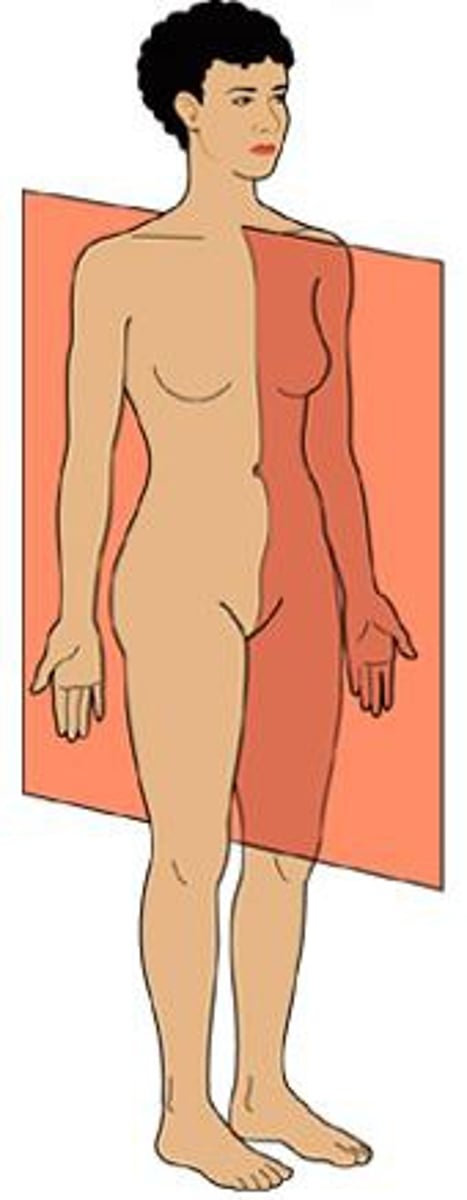
midsagittal plane
divides the body into equal left and right halves
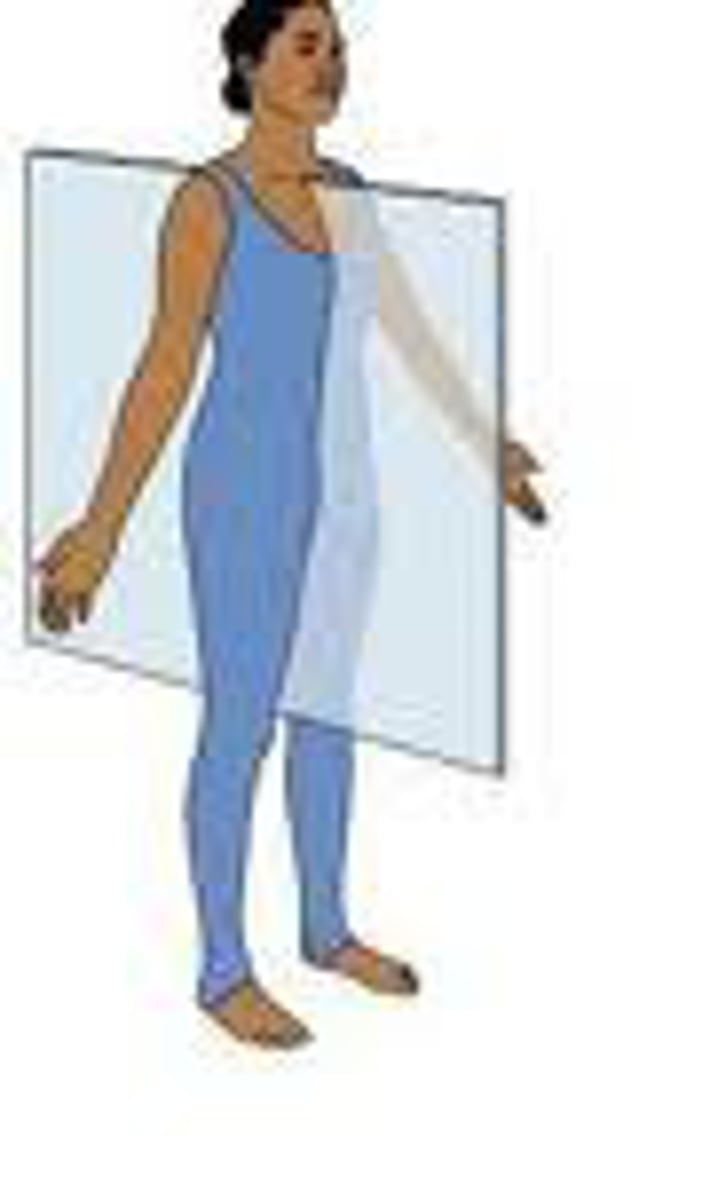
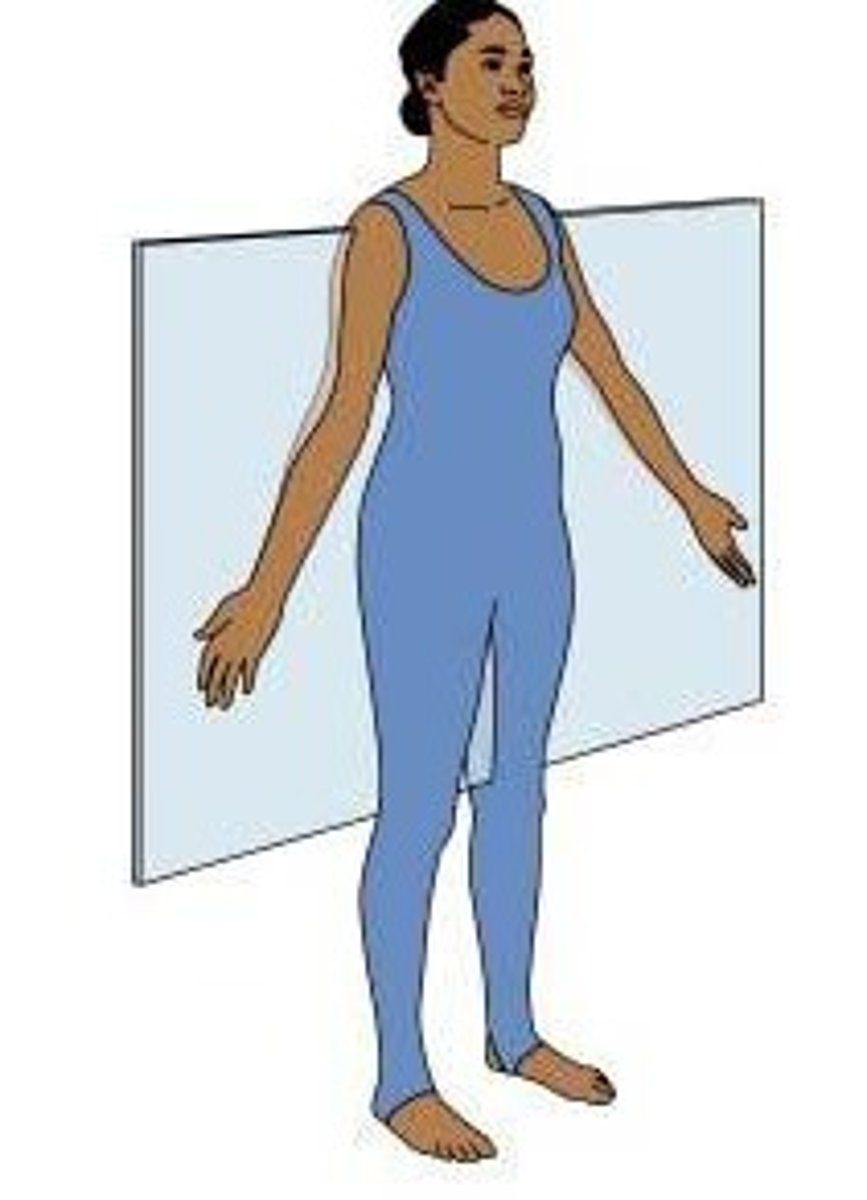
frontal (coronal) plane
extends vertically, but is perpendicular to the sagittal plane and divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions
Contents of the _________ and __________ cavities are most commonly shown as frontal sections
thoracic; abdominal
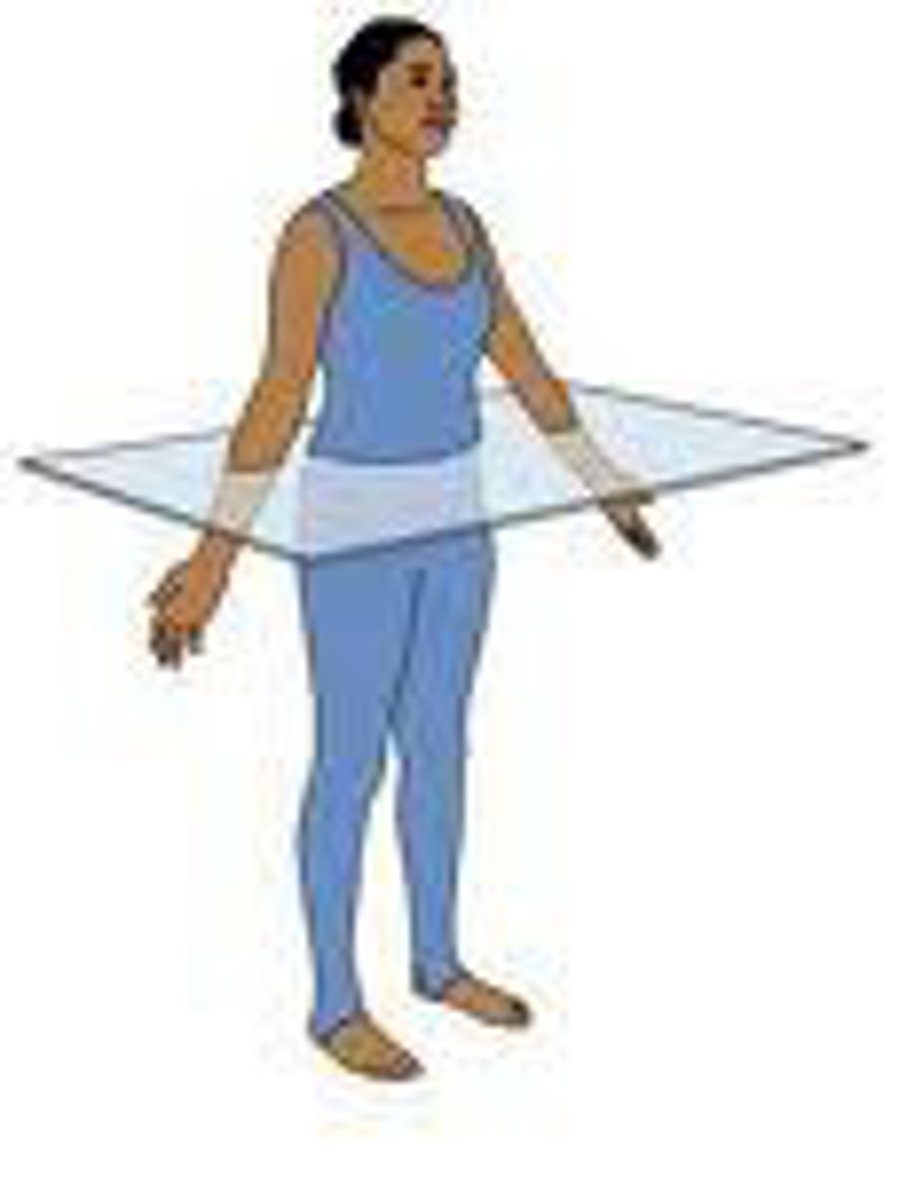
transverse (horizontal) plane
passes across the body or an organ perpendicular to its long axis; it divides the body or organ into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) portions
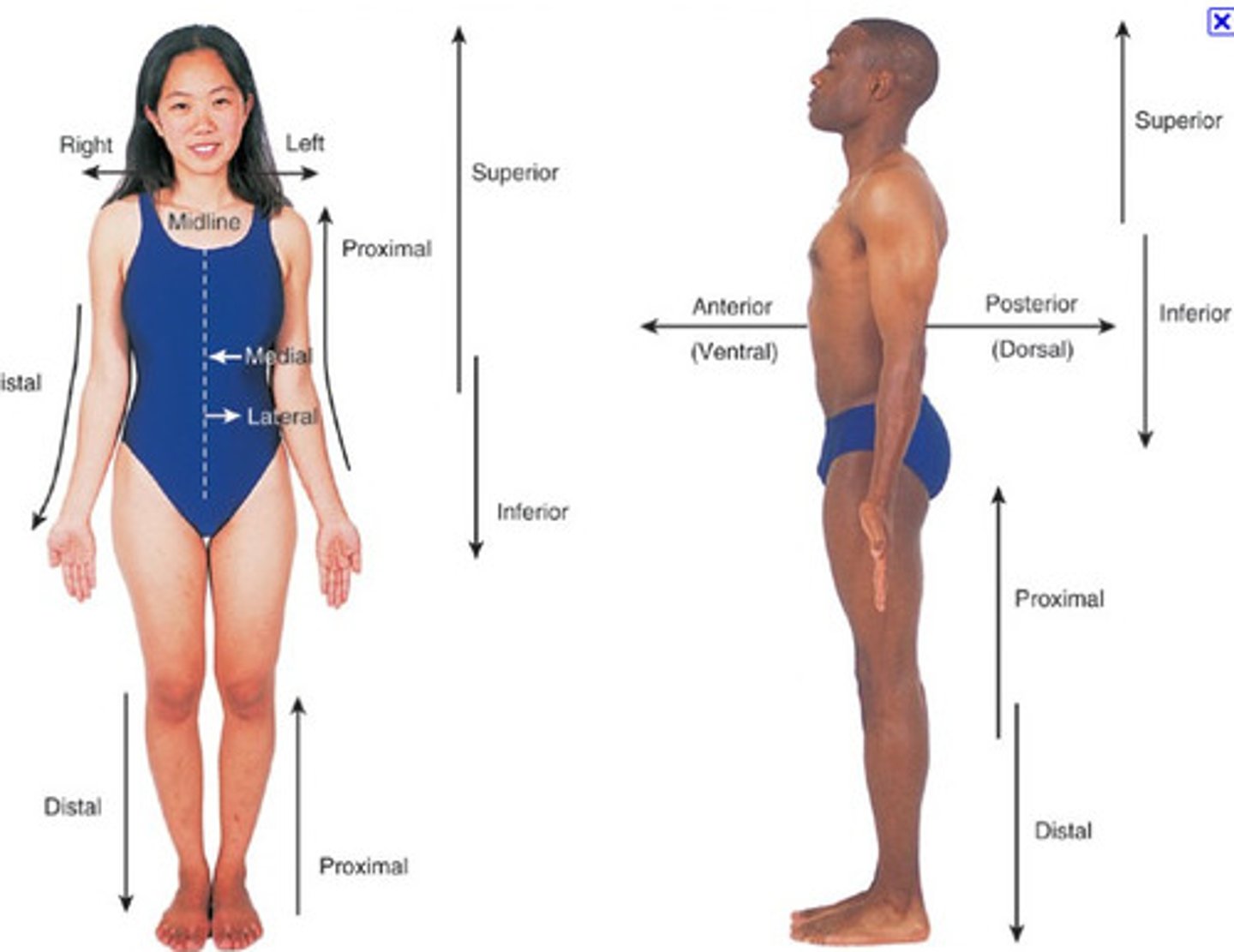
Directional Terms
Terms used to explain where one body structure is in relation to another
Ventral
Toward the belly or front
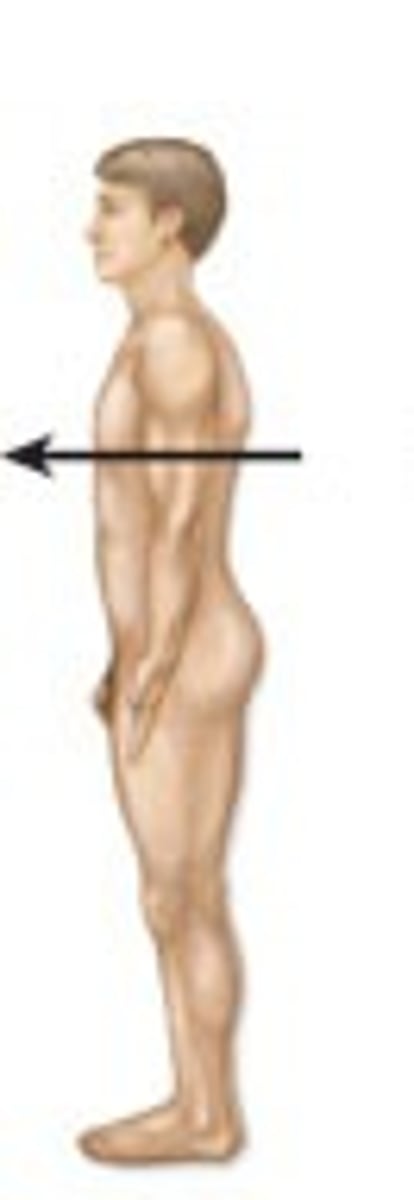
Dorsal
toward the back
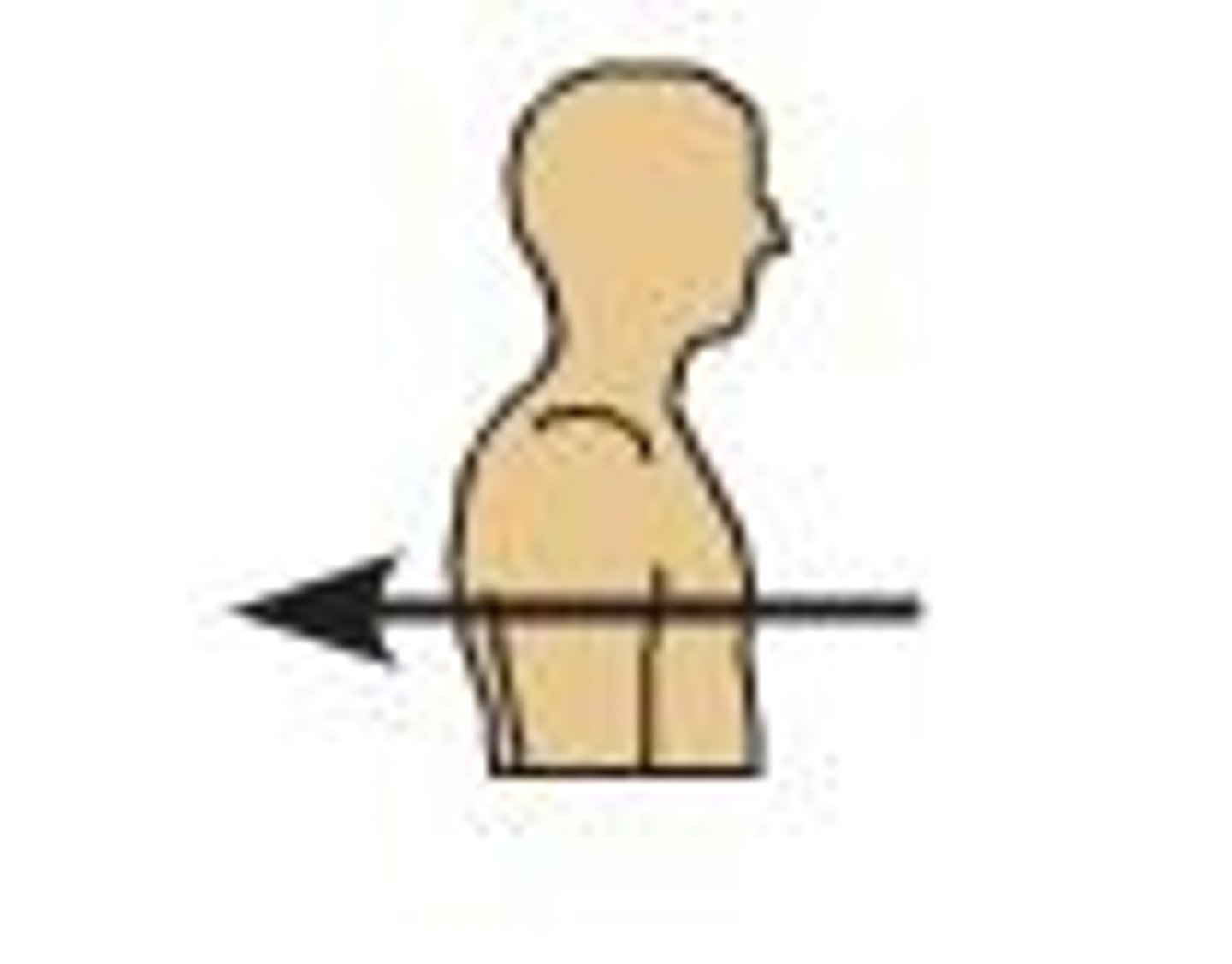
Anterior
toward the ventral side
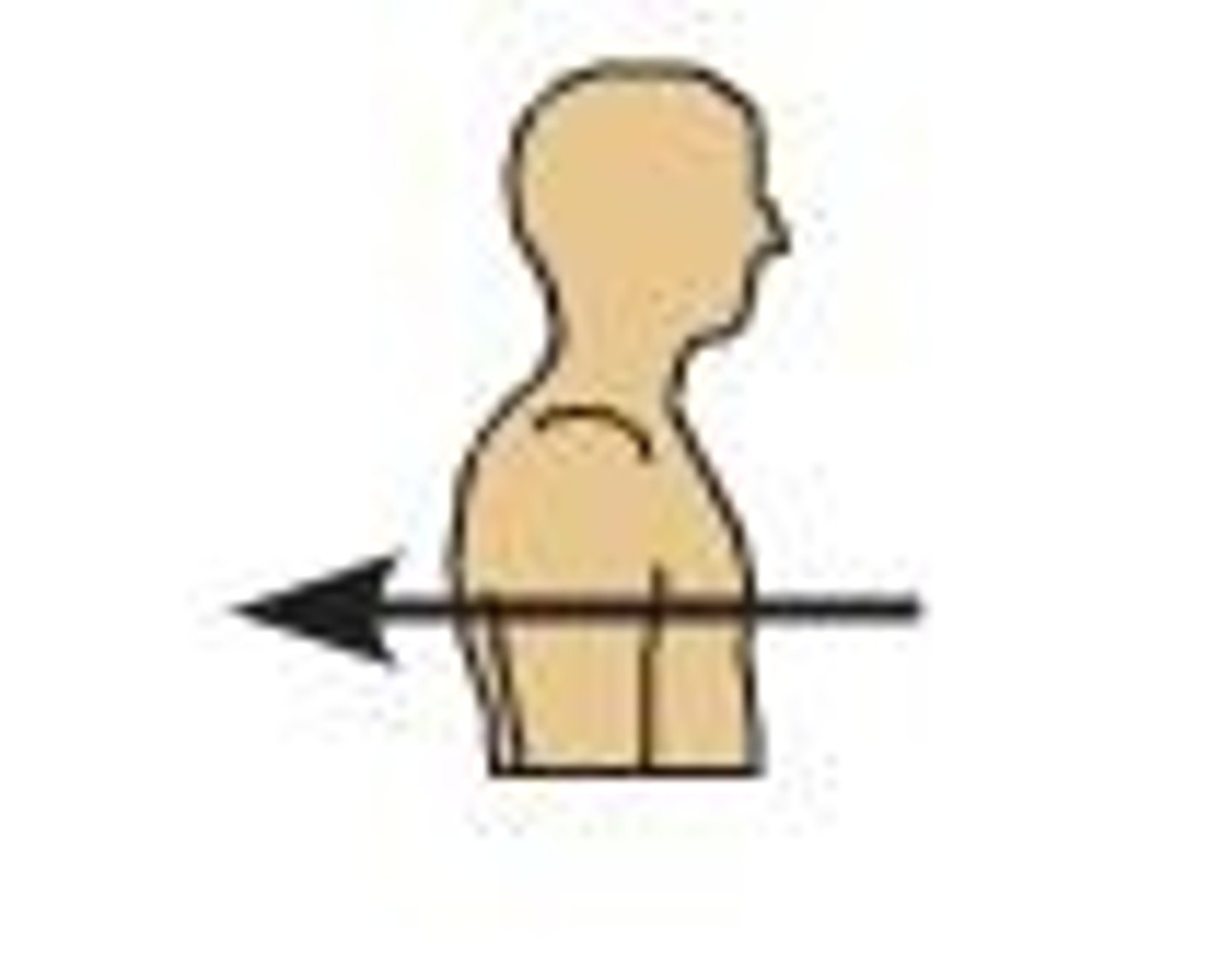
Posterior
toward the dorsal side
Cephalic
toward the head
Rostral
toward the forehead or nose
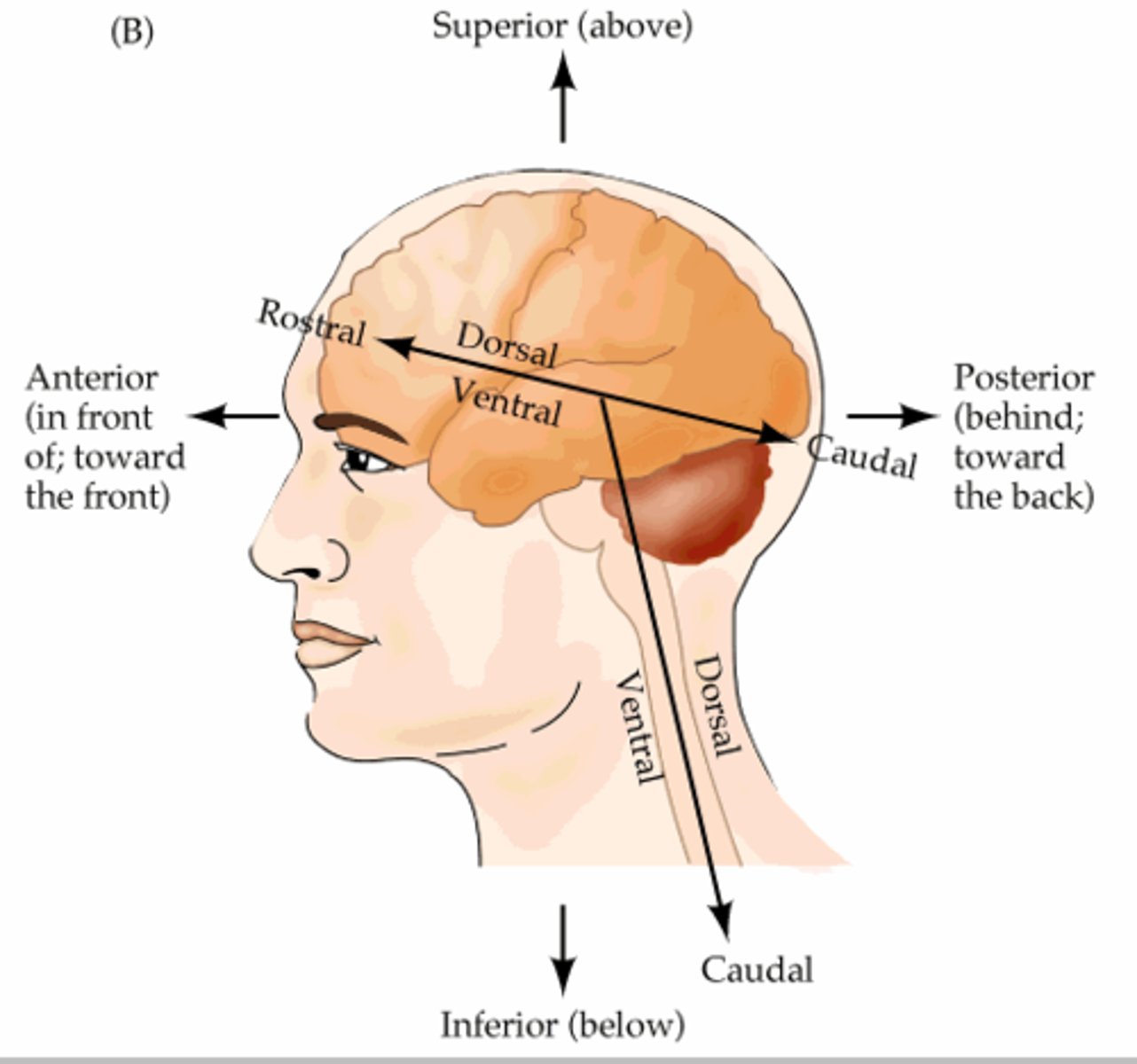
Caudal
toward the tail or inferior end
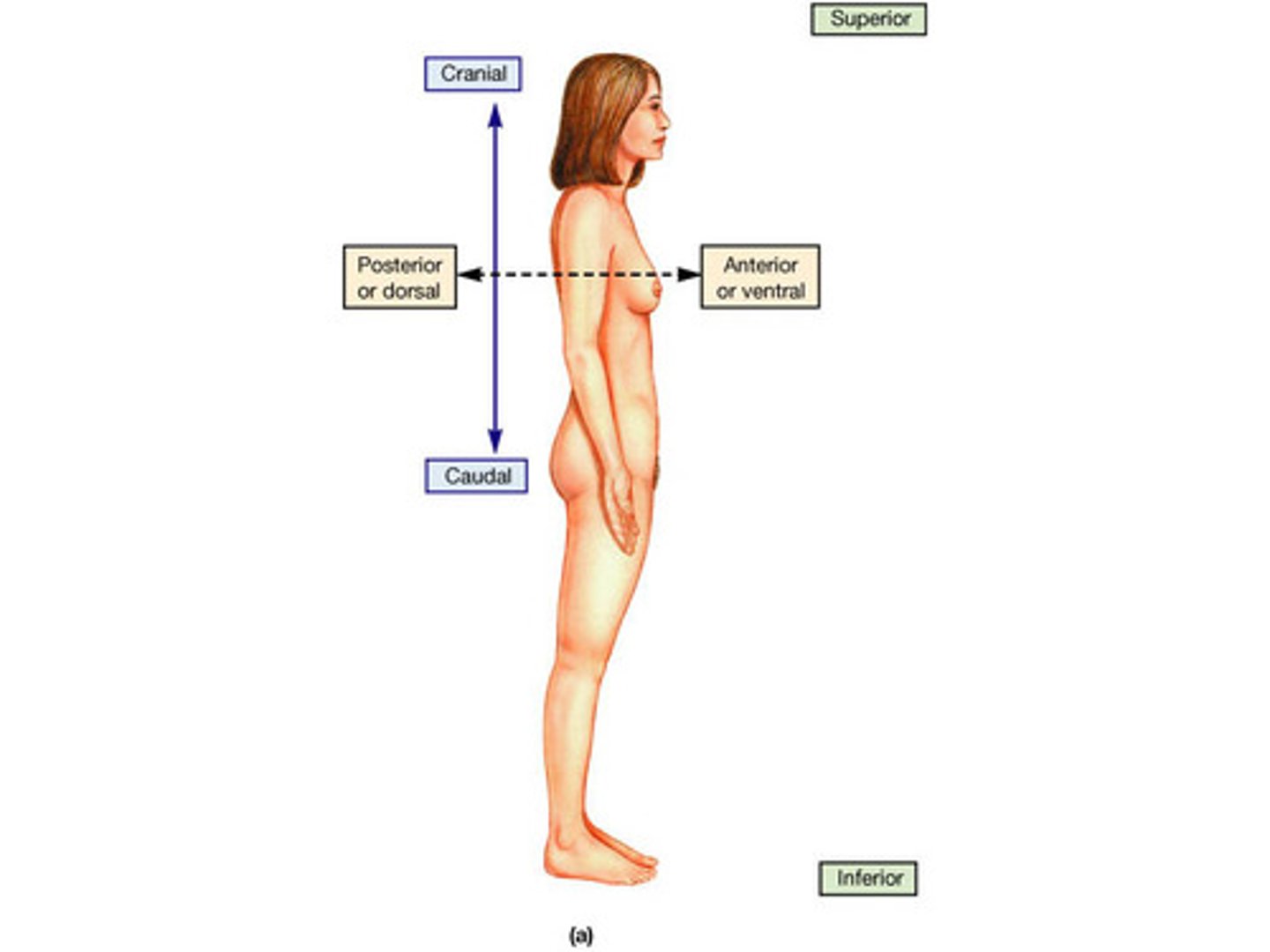
Superior
Higher on the body, nearer to the head
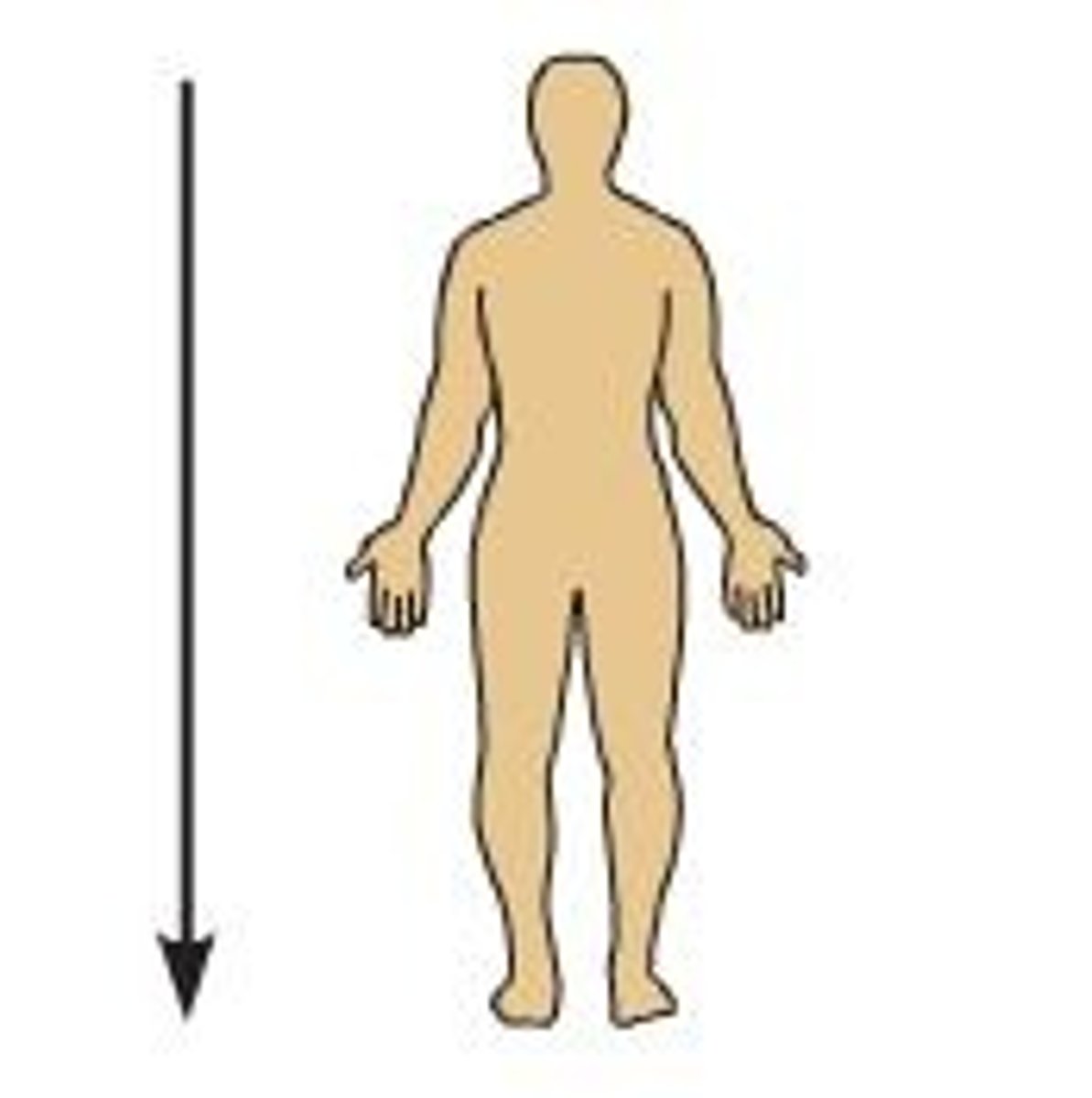
Inferior
Lower on the body, farther from the head
Medial
toward the median plane
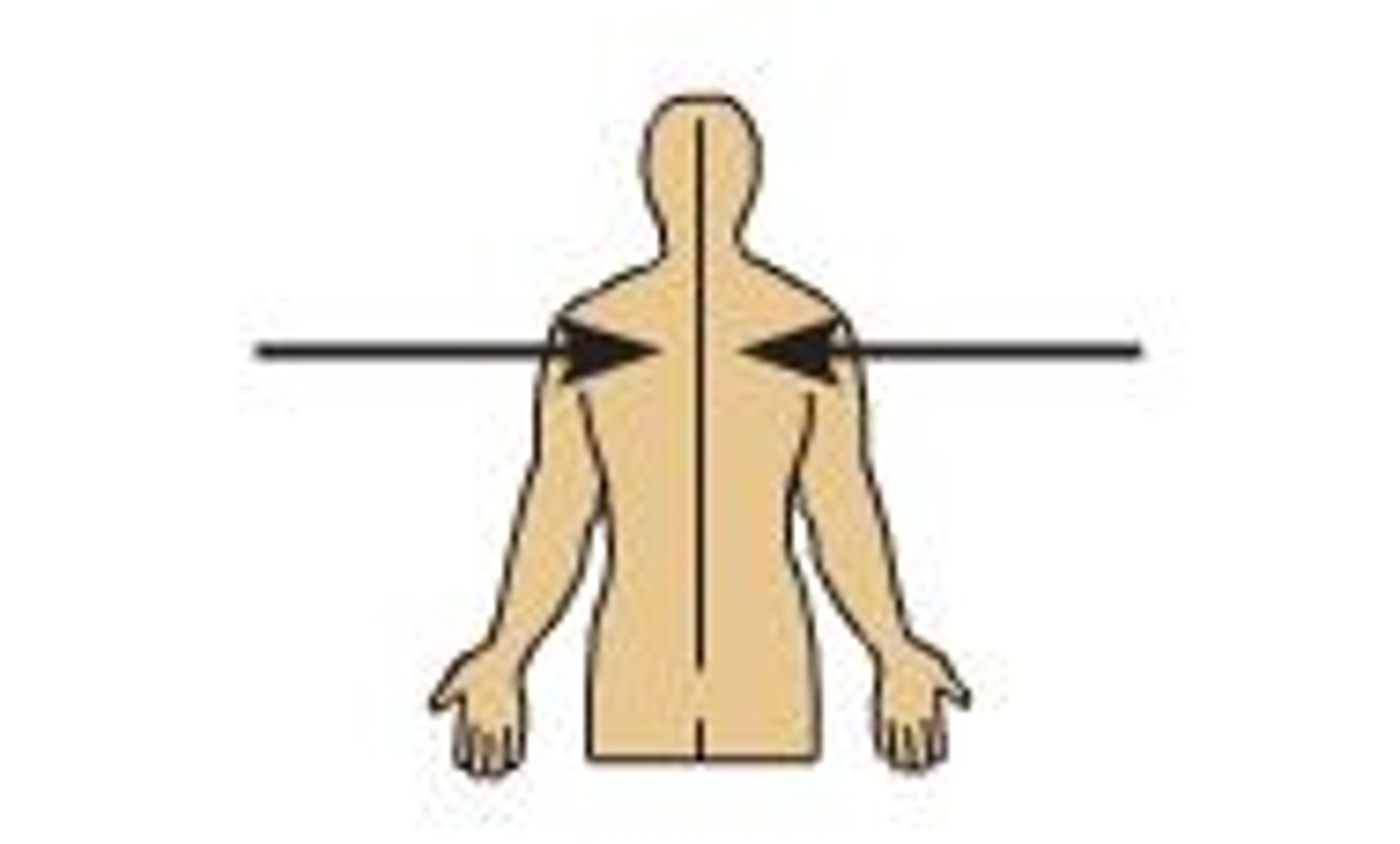
Lateral
Away from the midline (median) of the body
Proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
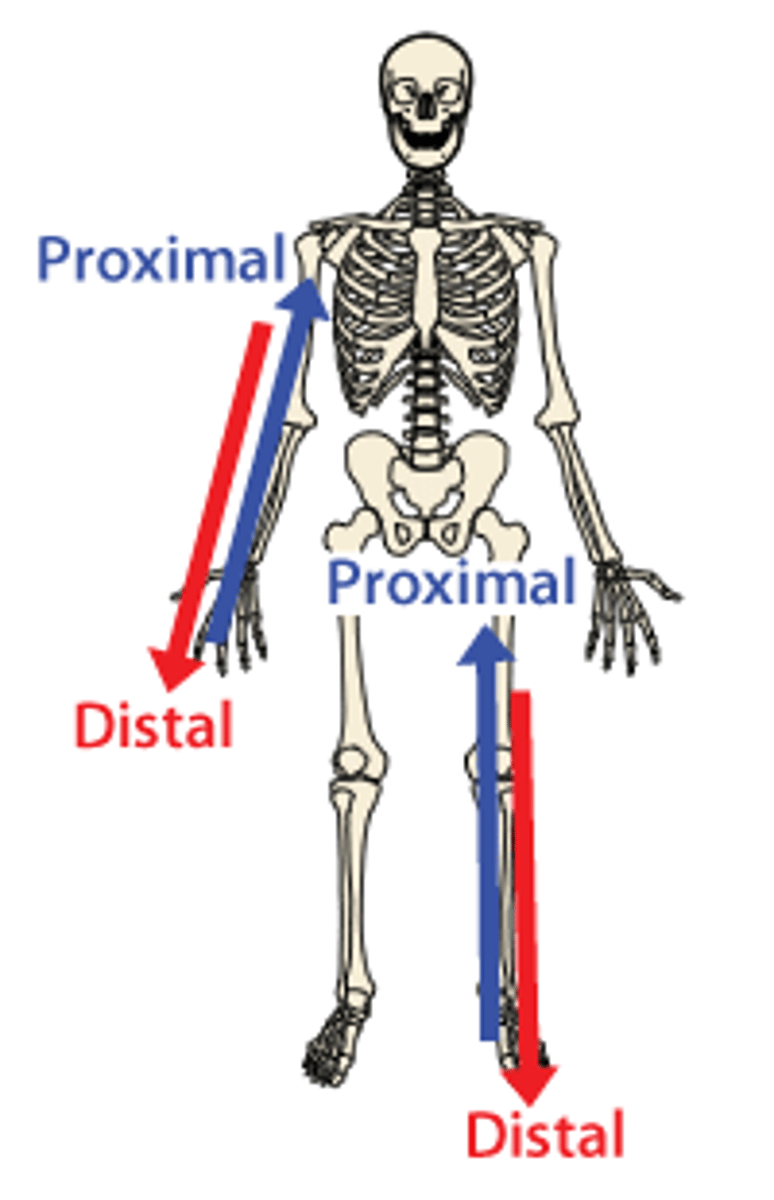
Distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
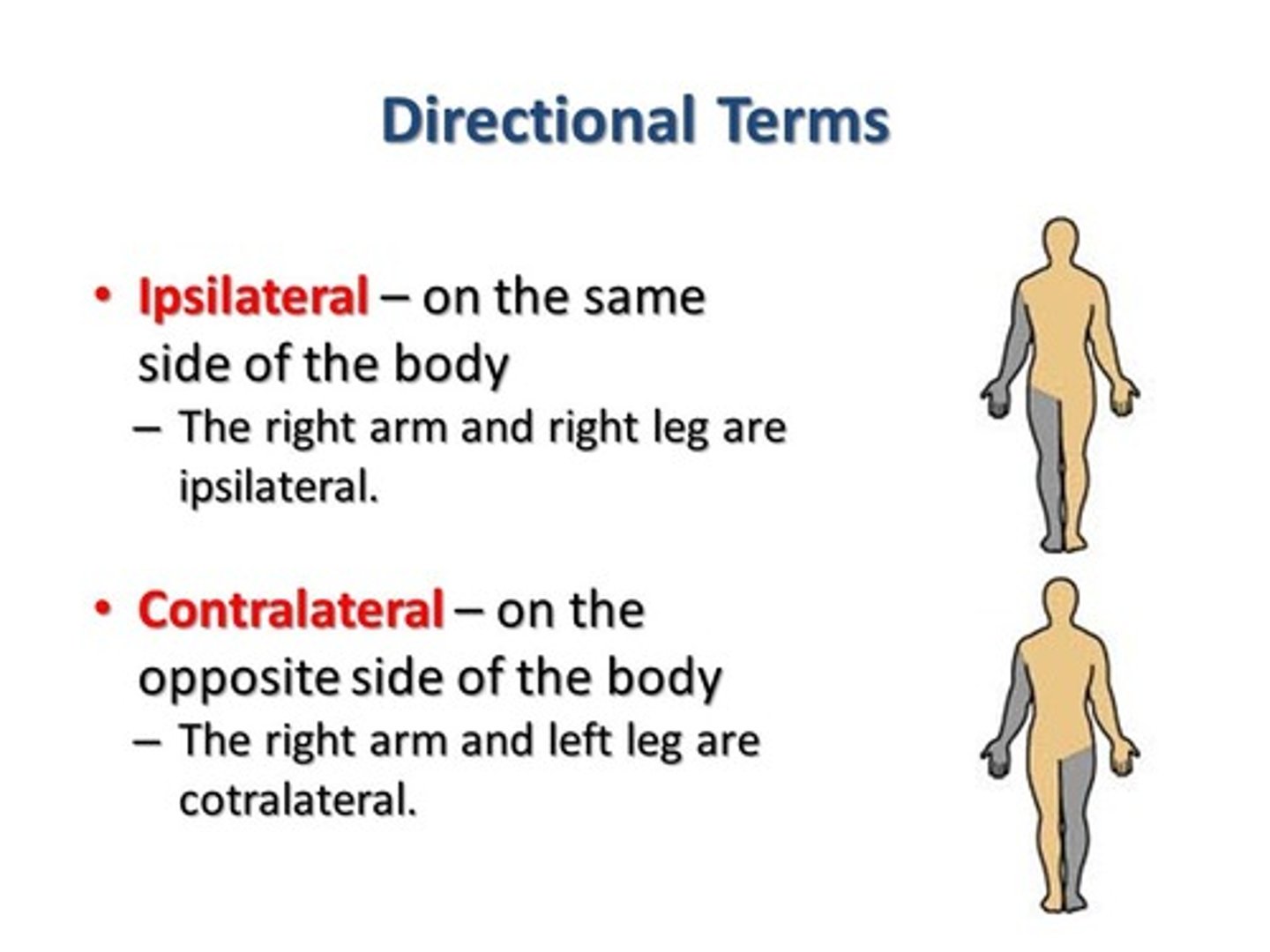
Ipsilateral
on the same side of the body as another structure
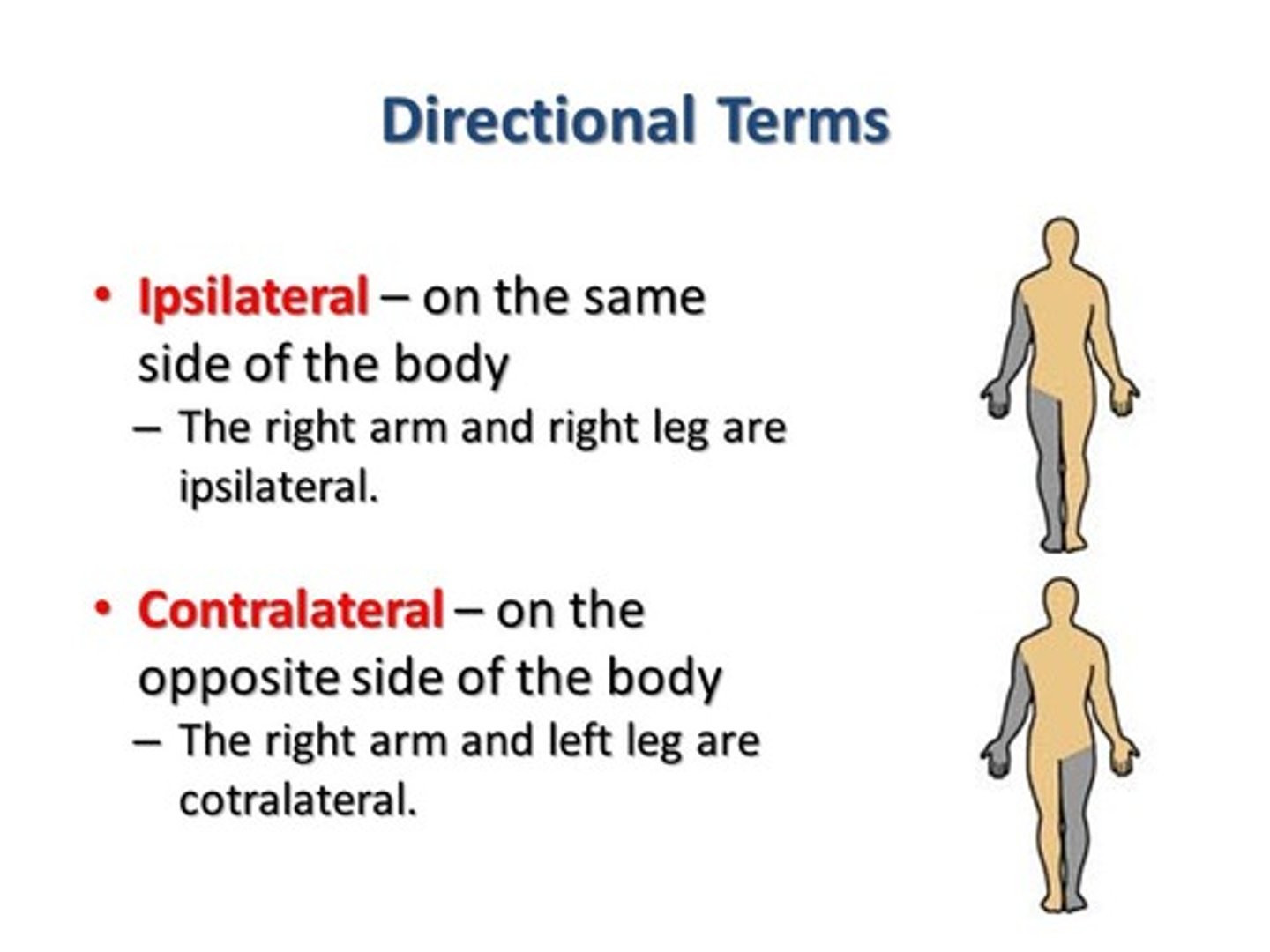
Contralateral
on the opposite side of the body from another structure
superficial
closer to the surface of the body
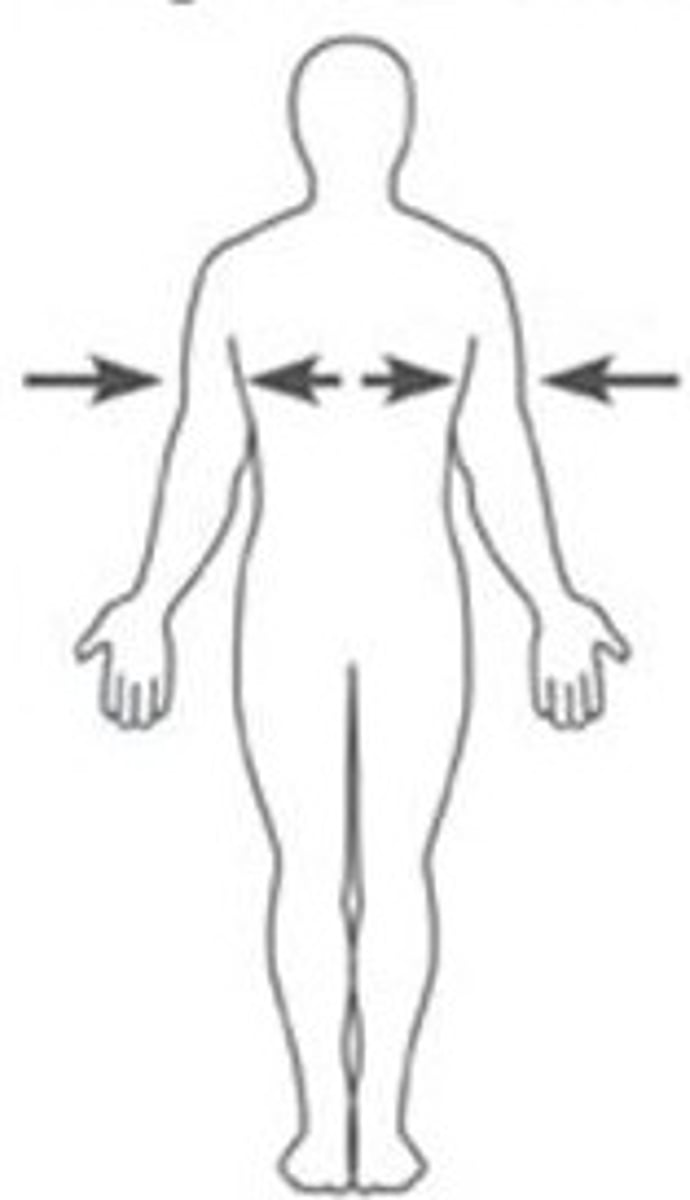
Deep
Away from the body surface; more internal

dorsum
the back
upper surface of the foot and back of the hand
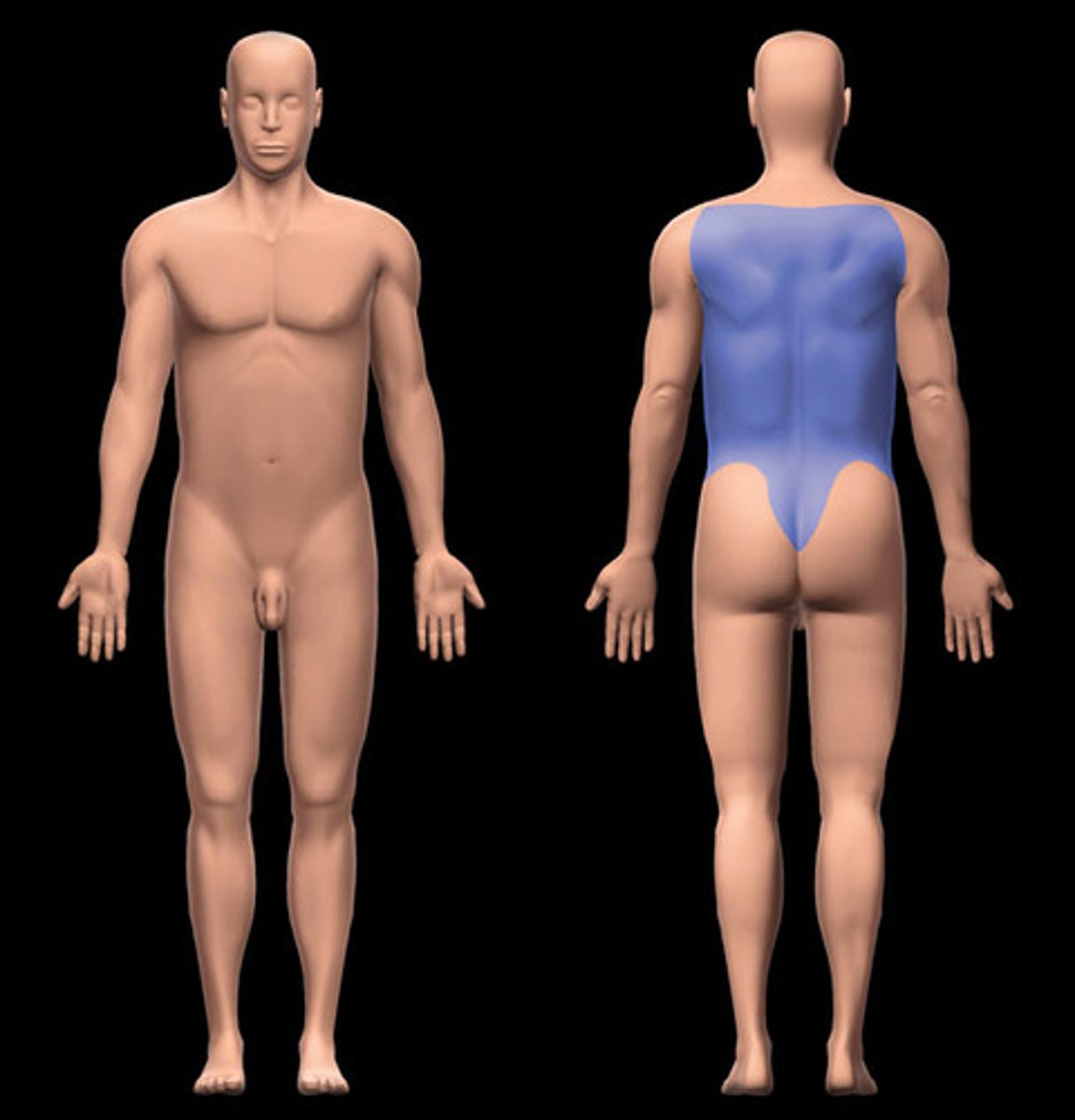
axial region
Head, neck, and trunk
Forms the main vertical axis of the body
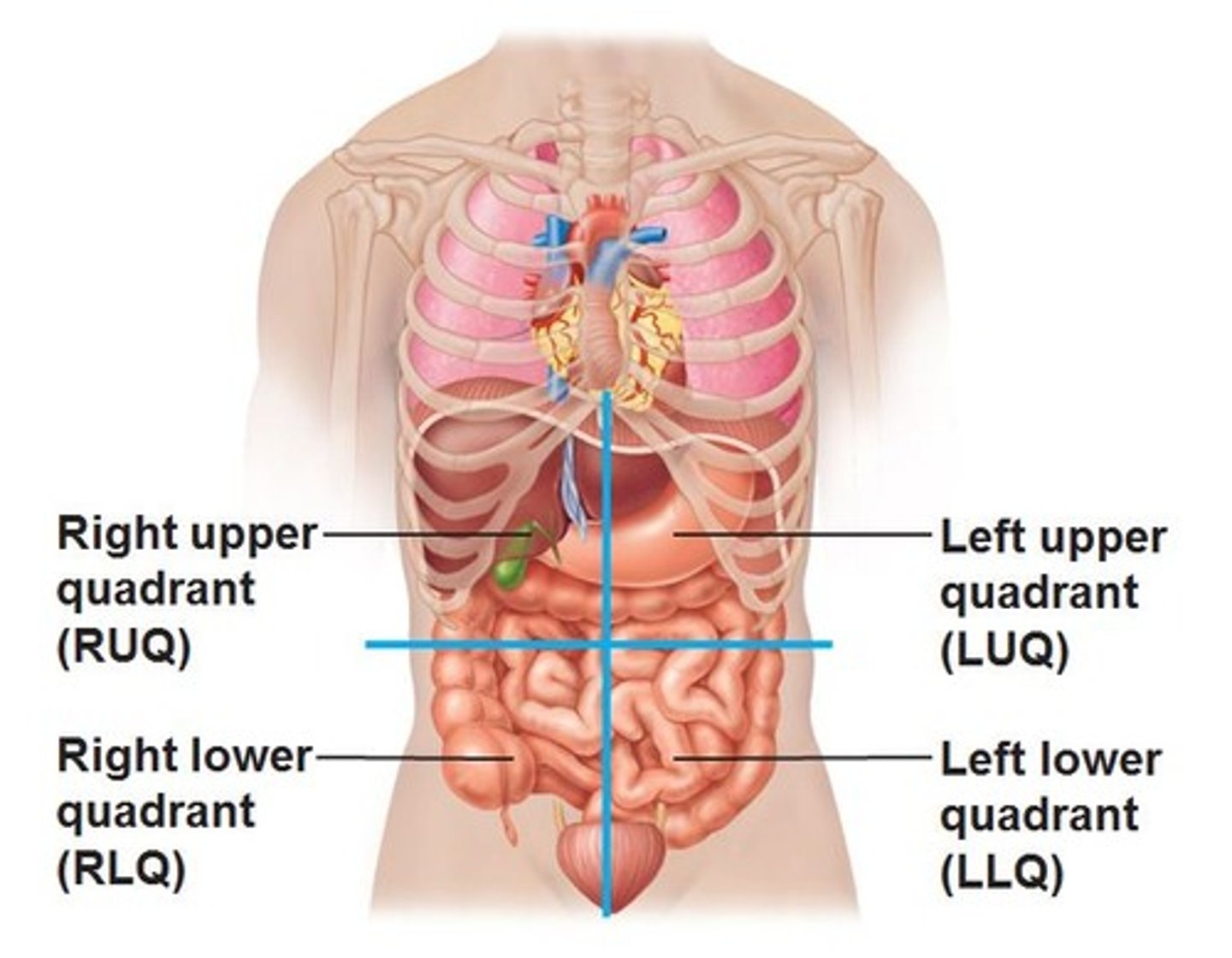
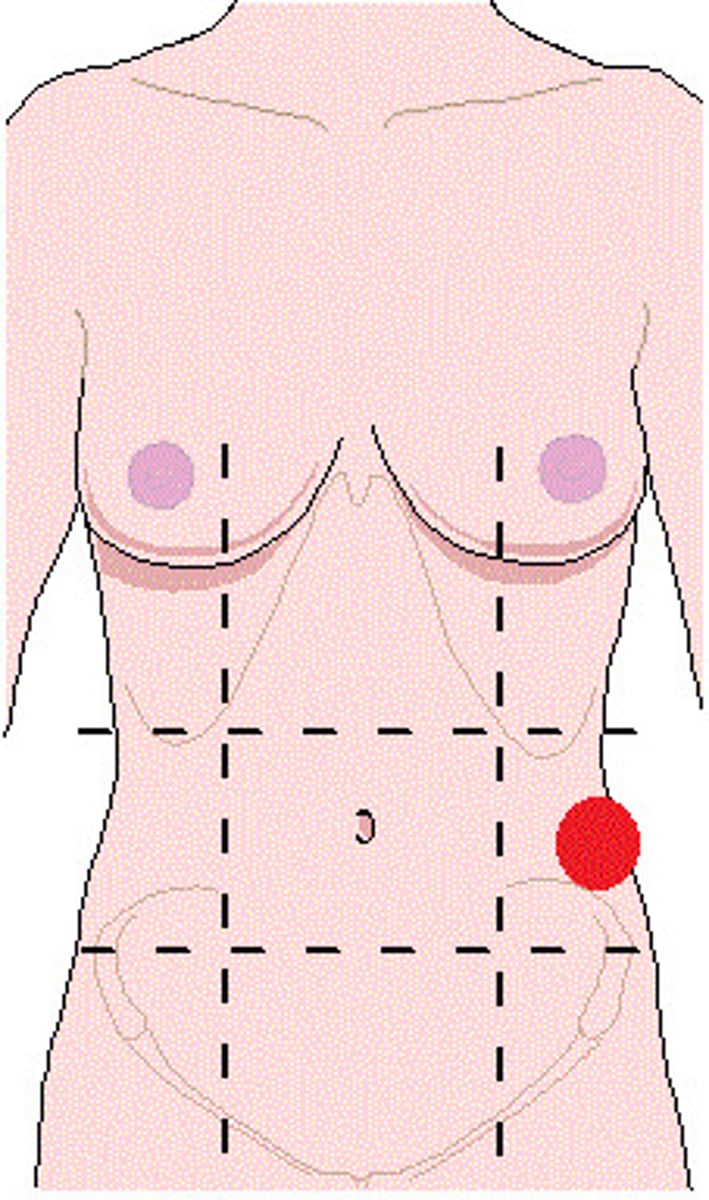
Abdominopelvic quadrants
right upper quadrant (RUQ)
right lower quadrant (RLQ)
left upper quadrant (LUQ)
left lower quadrant (LLQ)
abdominopelvic regions
right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right iliac, hypogastric, left iliac
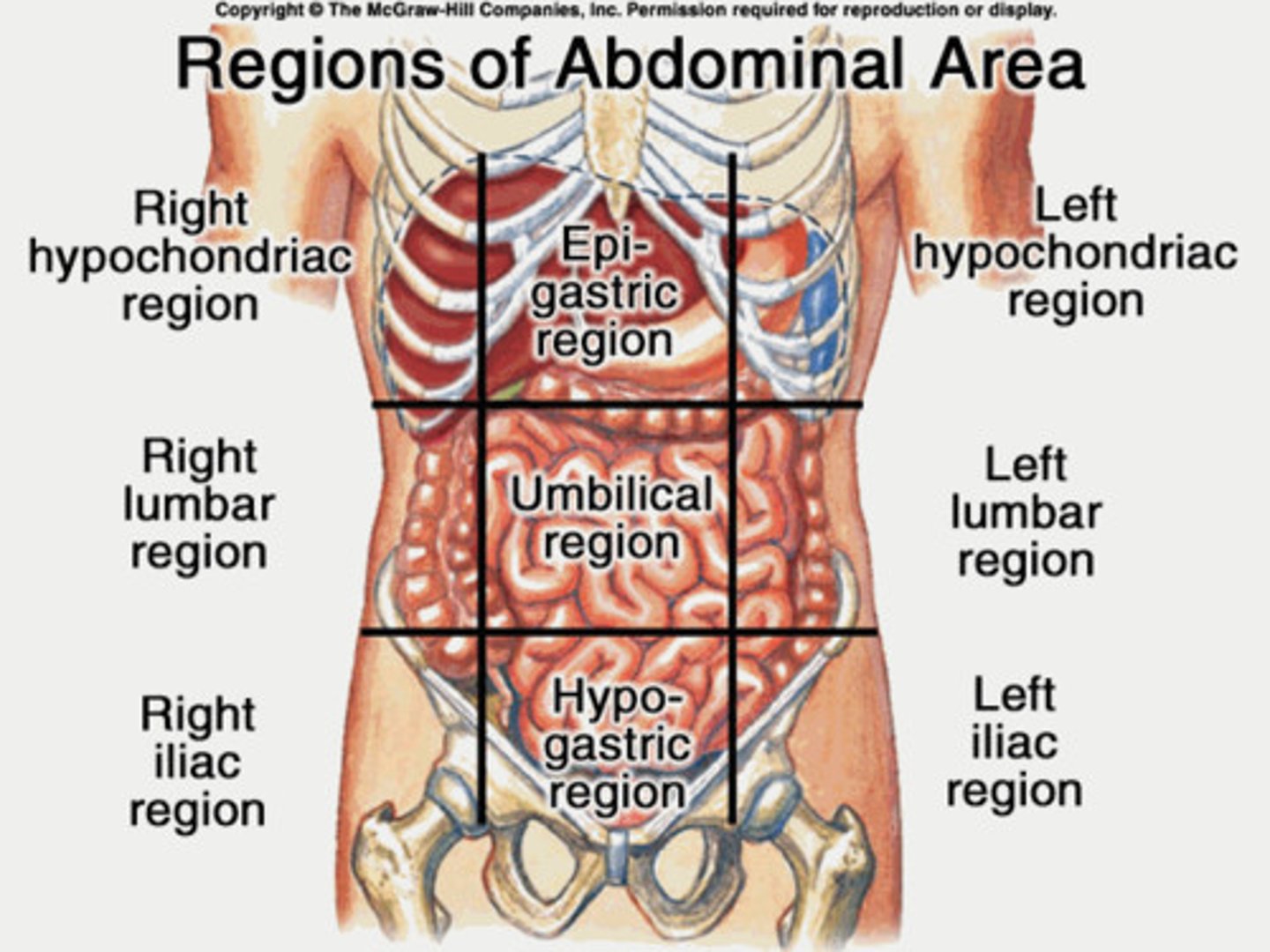
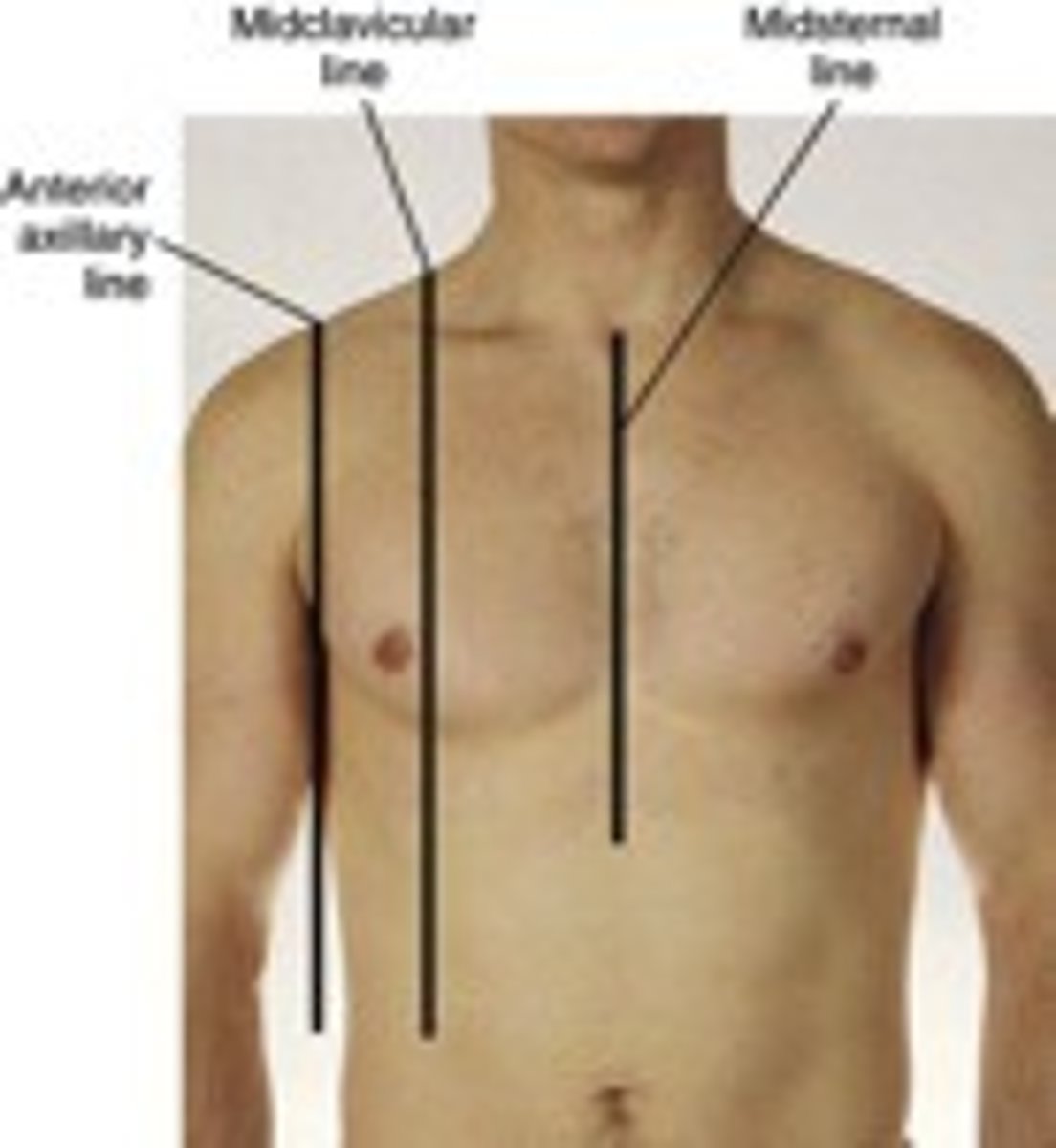
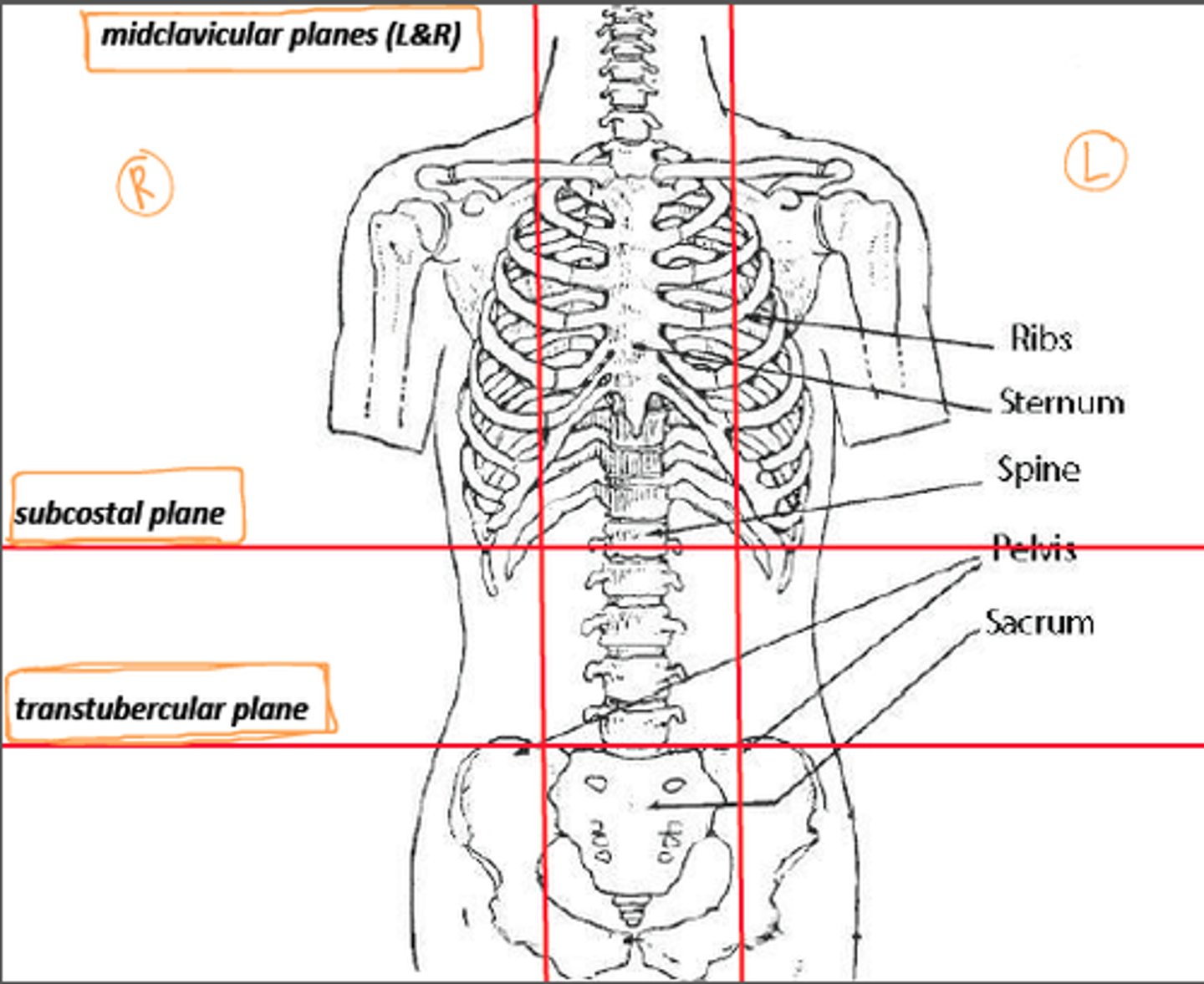
The abdomen is divided into nine regions defined by four lines that intersect like tic tac toe; each vertical line is called a _____________ line because it passes through the midpoint of the clavicle.
The superior horizontal line is called the __________ line because it connects the inferior borders of the lowest costal cartilages
midclavicular; subcostal
Intertubercular lines
the inferior horizontal line that passes from left to right between the tubercles (anterior superior spines) of the pelvis- two points of bone located about where the front pockets open on most pants
What are the three lateral regions of the abdominopelvic region grid?
hypochondriac, lumbar, and inguinal
What are the three medial regions from upper to lower on the abdominopelvic region grid?
epigastric, umbilical, and hypogastric (pubic)
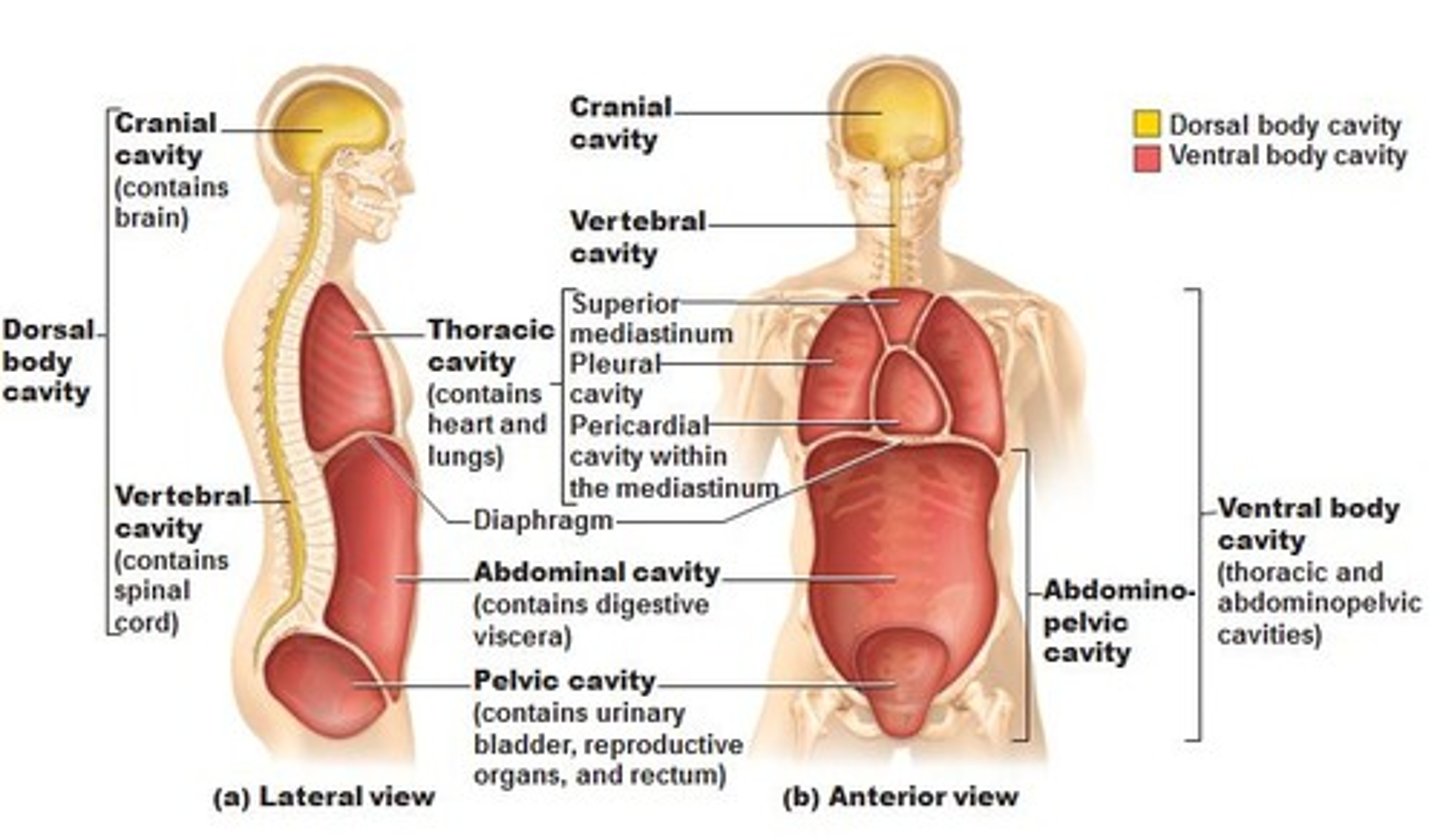
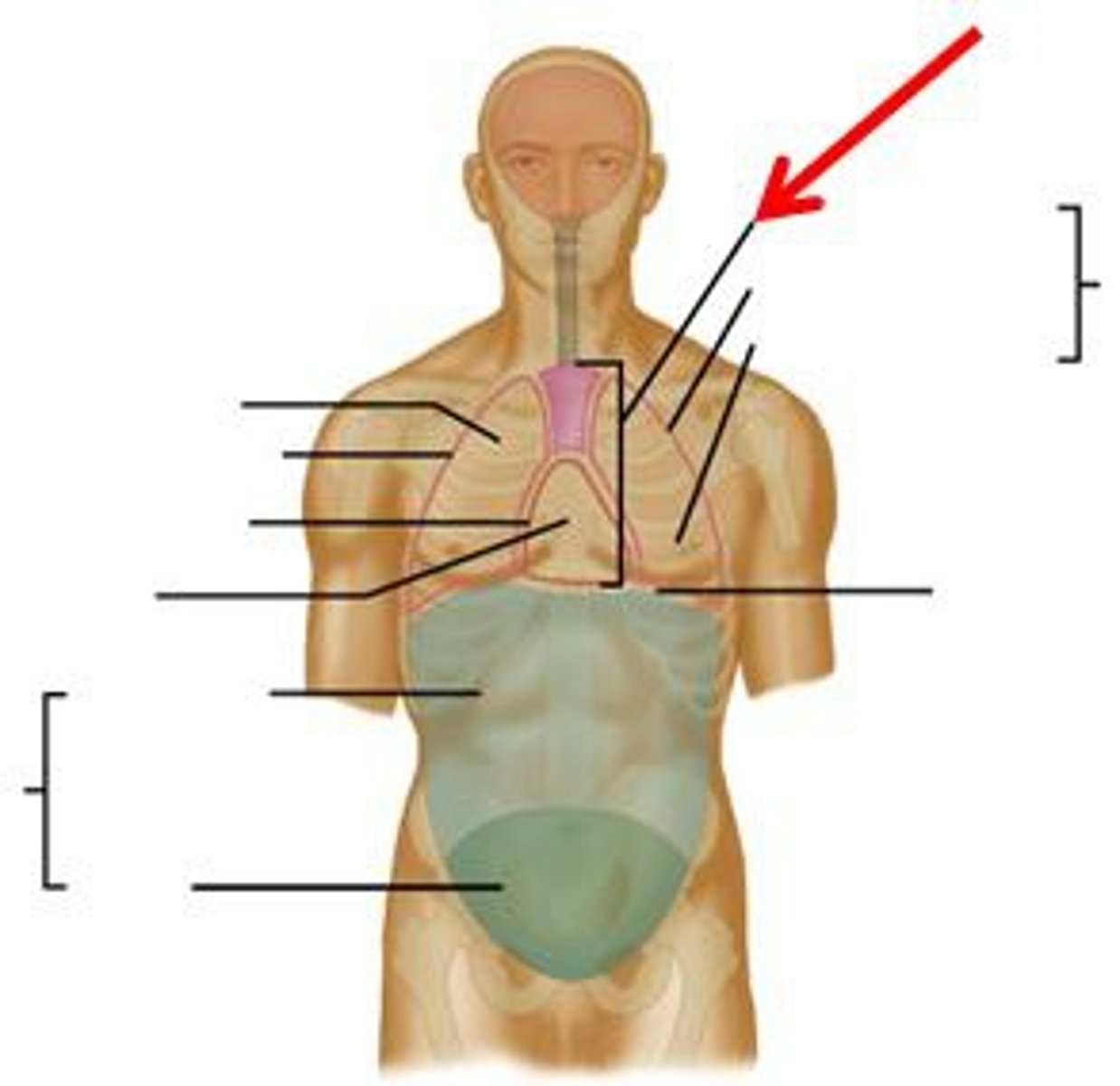
dorsal cavity
includes the cranial and spinal cavities.
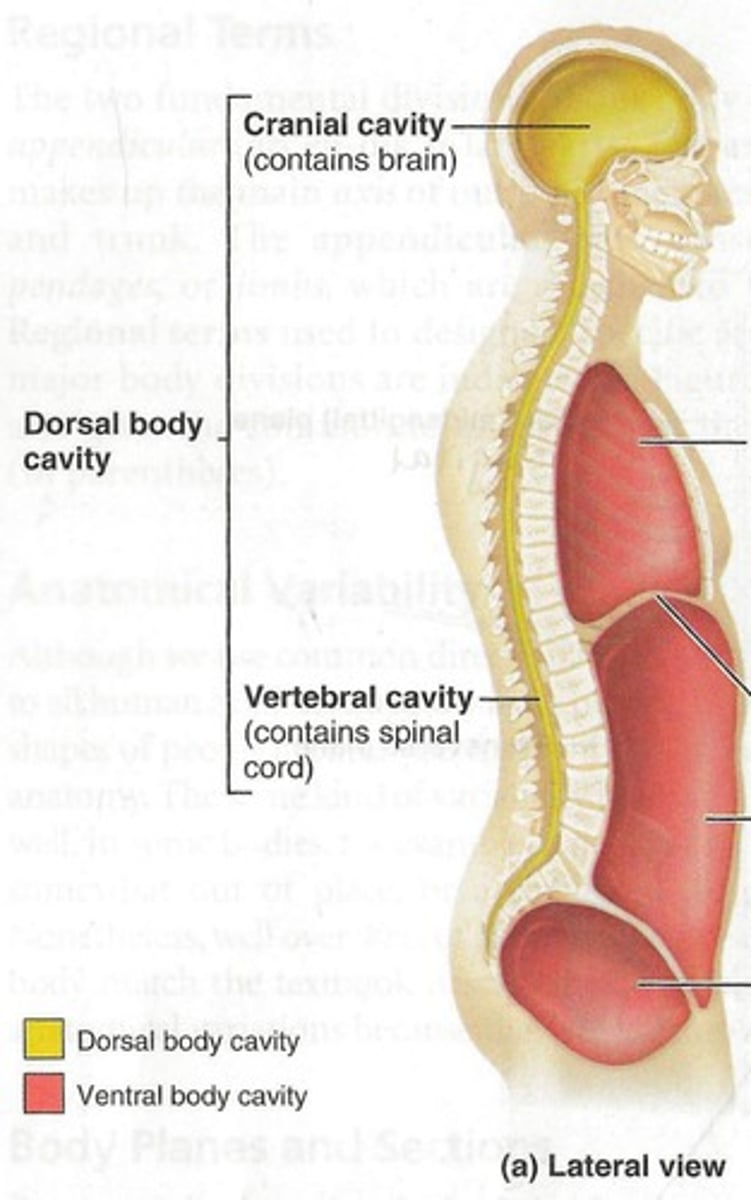
cranial cavity
contains the brain
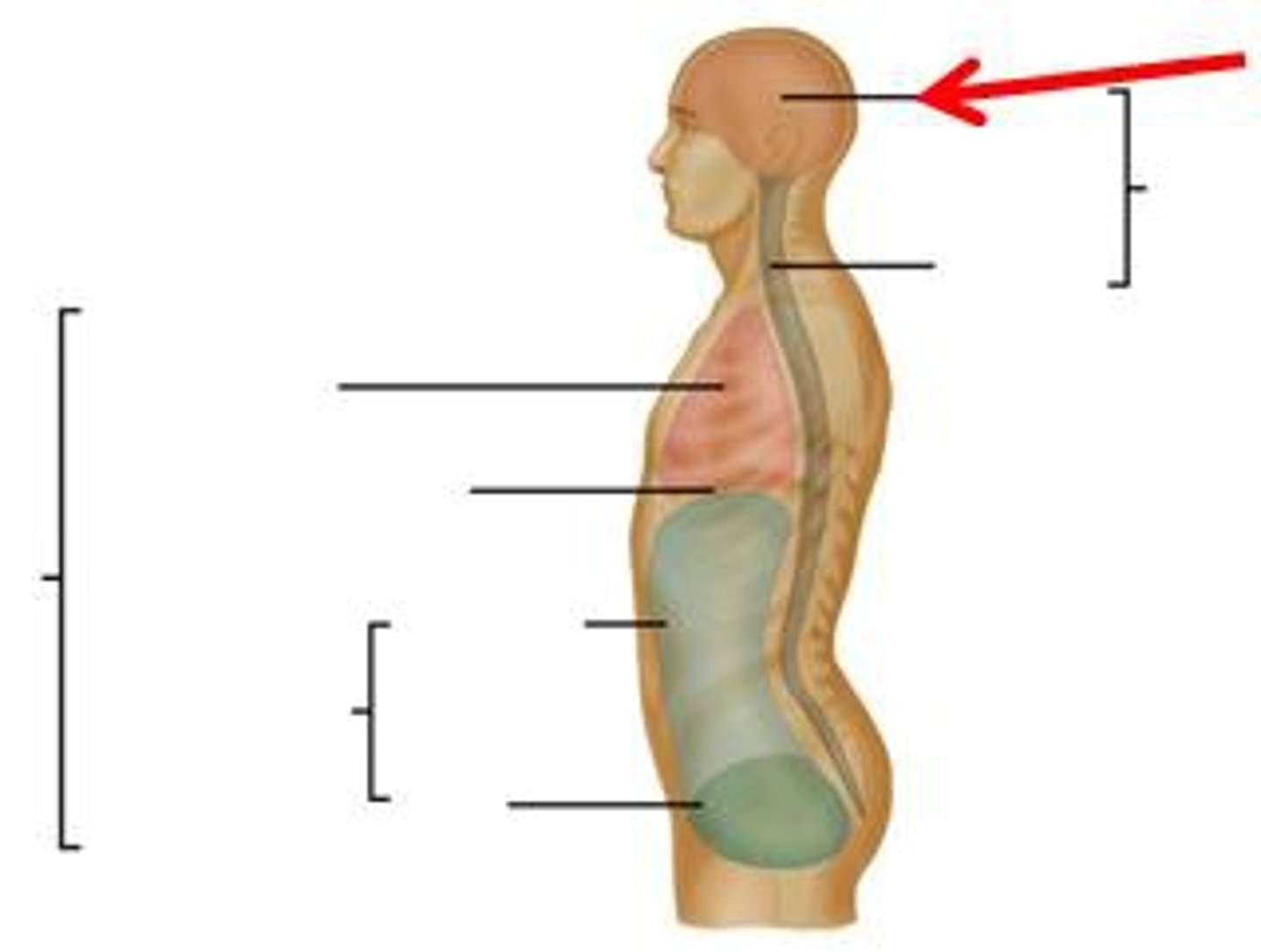
vertebral cavity
contains the spinal cord
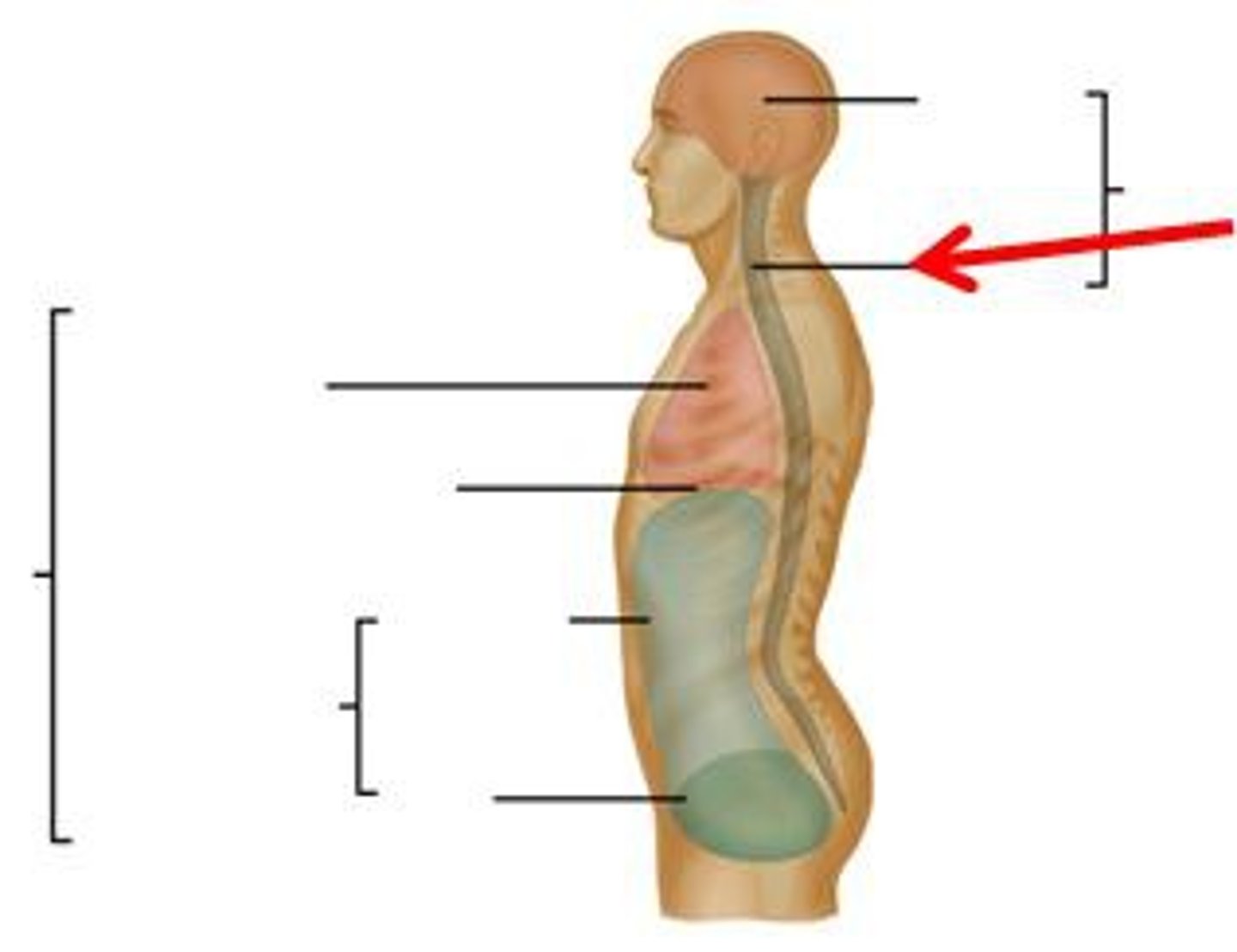
ventral cavity
thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity
located along the front of the body, contains the body organs that sustain homeostasis
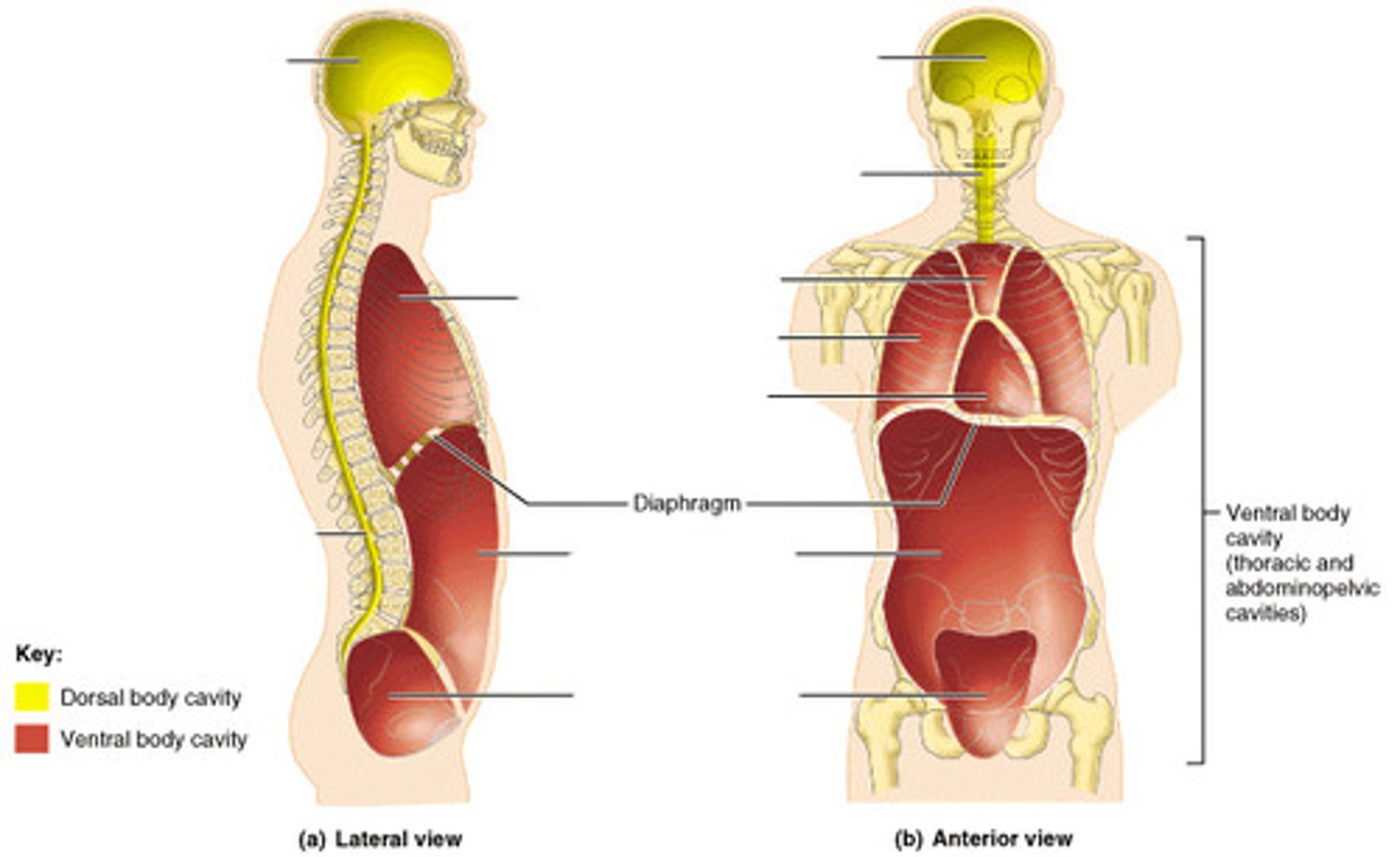
thoracic cavity
contains heart and lungs
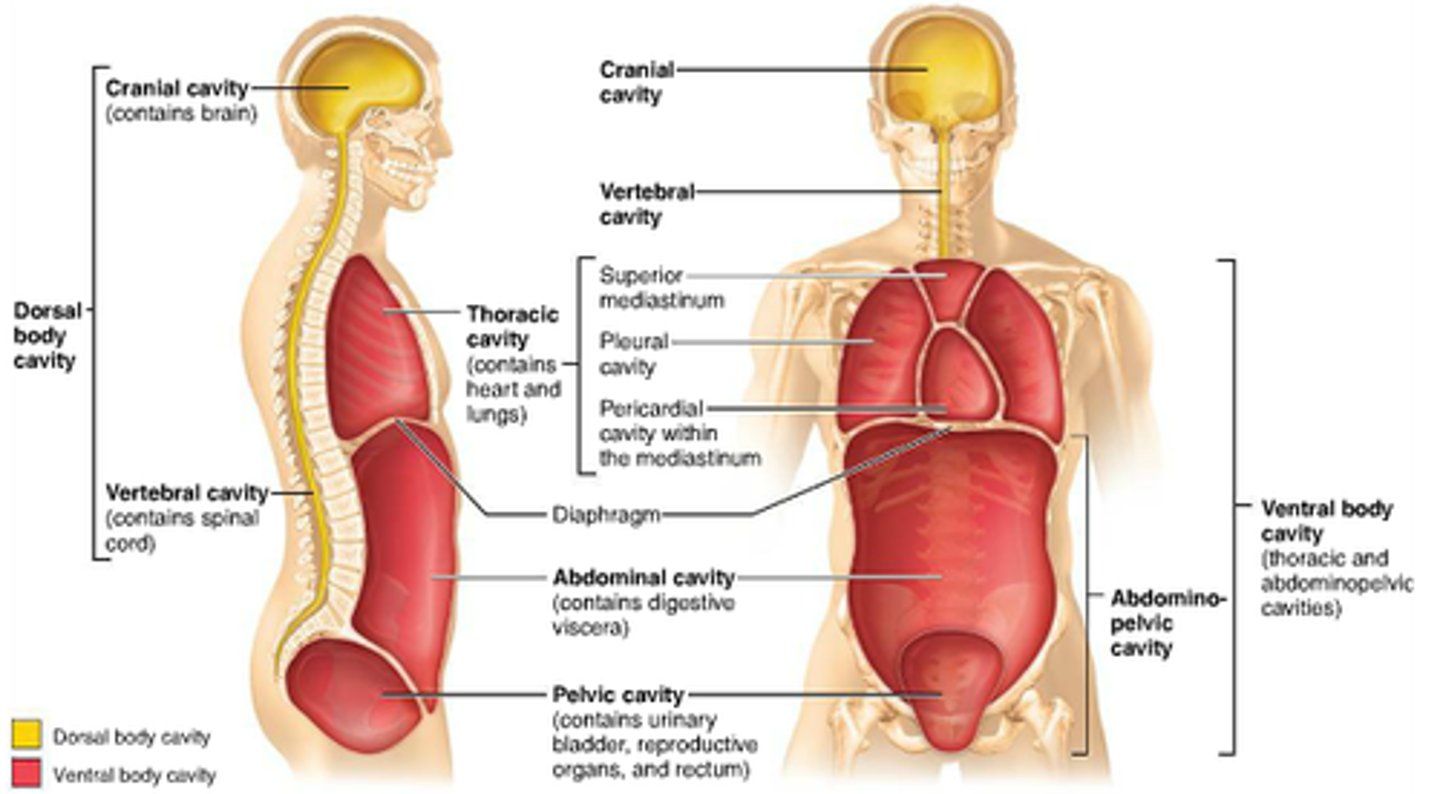
mediastinum cavity
a thick median wall dividing the thoracic cavity. This is the region between the lungs, extending from the base of the neck to the diaphragm
It is occupied by the heart, the major blood vessels connected to it, the esophagus, the trachea and bronchi, and a gland called the thymus
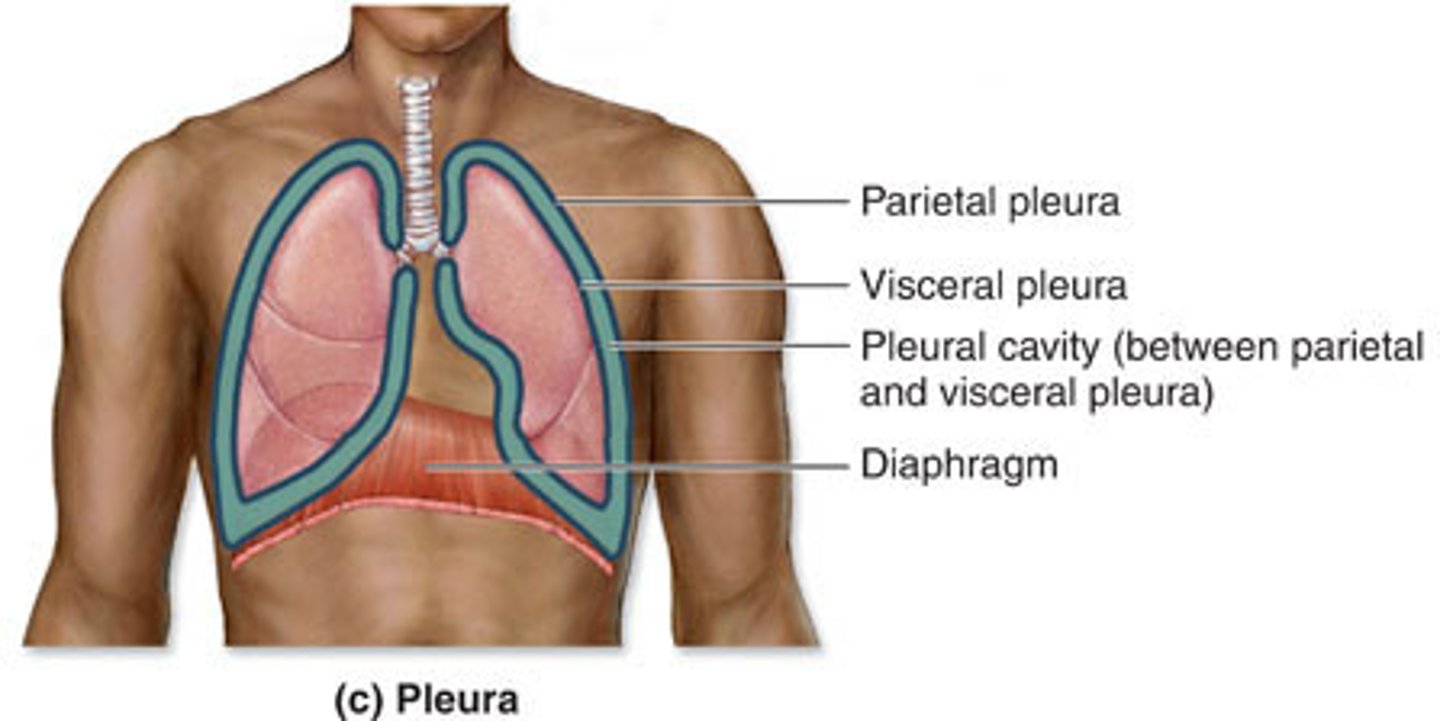
pleural cavity
a fluid filled space that surrounds the lungs. It is found in the thorax, separating the lungs from its surrounding structures such as the thoracic cage and intercostal spaces, the mediastinum and the diaphragm.
It is bounded by a double layered serous membrane called pleura.
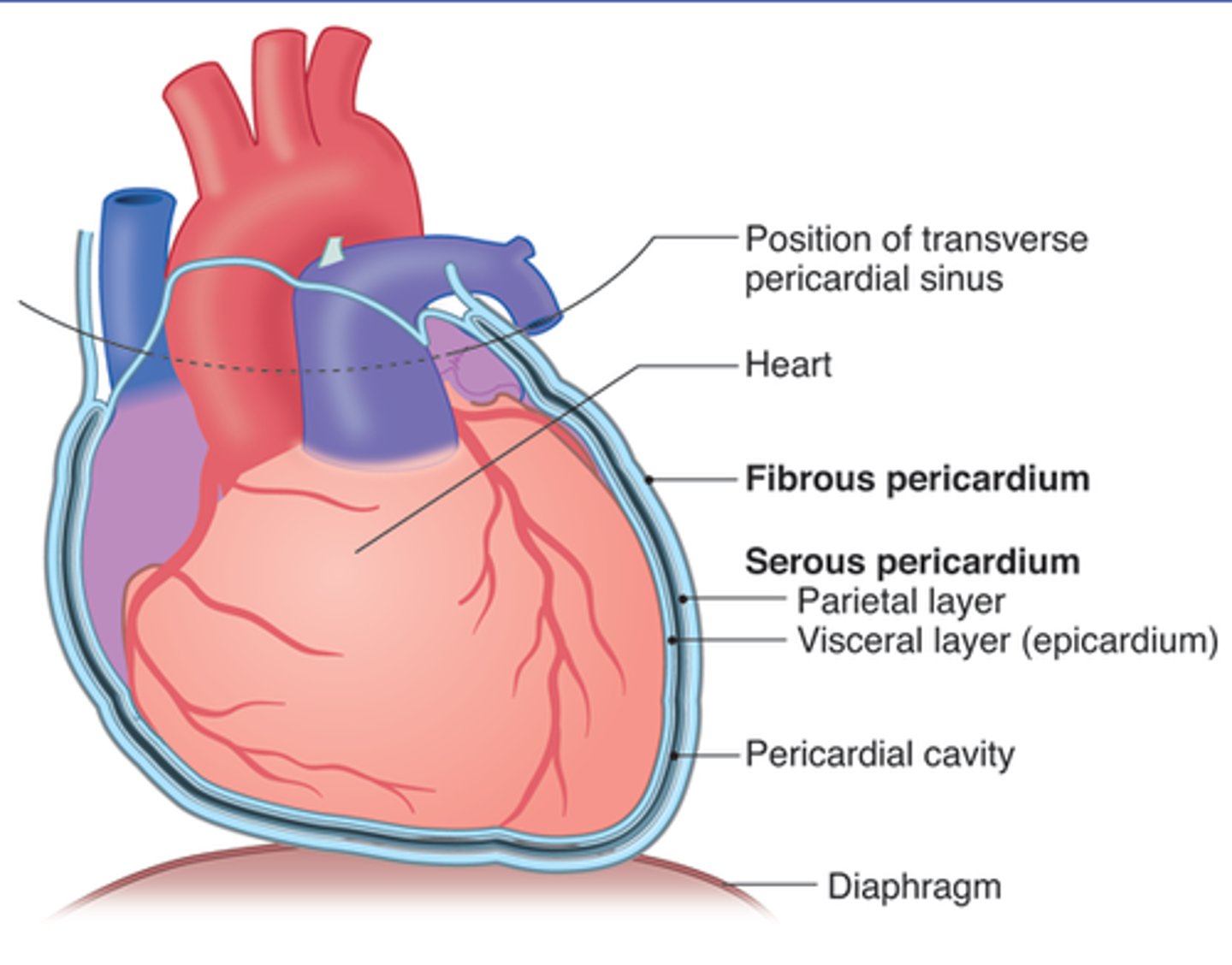
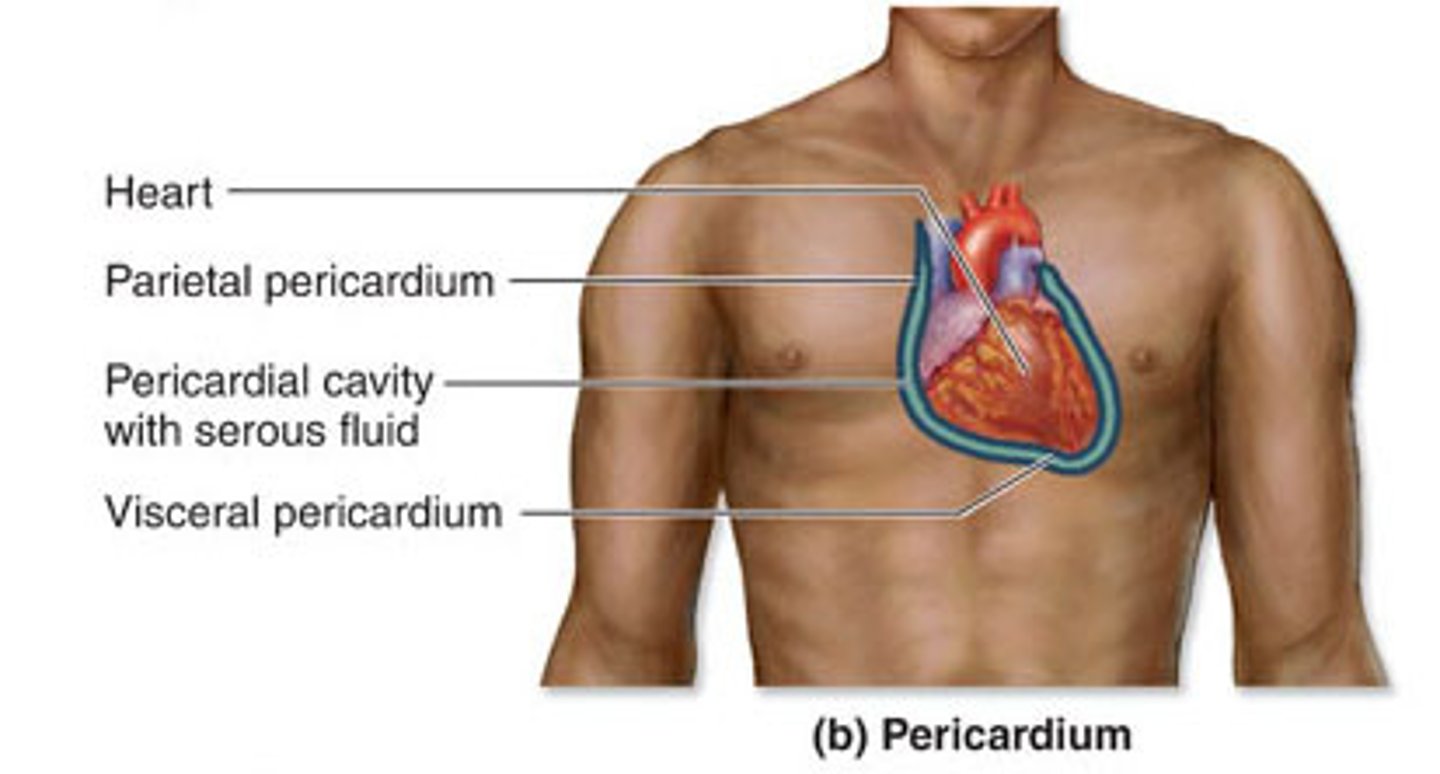
pericardial cavity
an anatomical space located between the outside surface of the heart and the pericardium of the heart, which is a tough fibrous membrane that surrounds and protects the muscle of the heart. Usually this cavity is deflated and only contains a small amount of fluid.
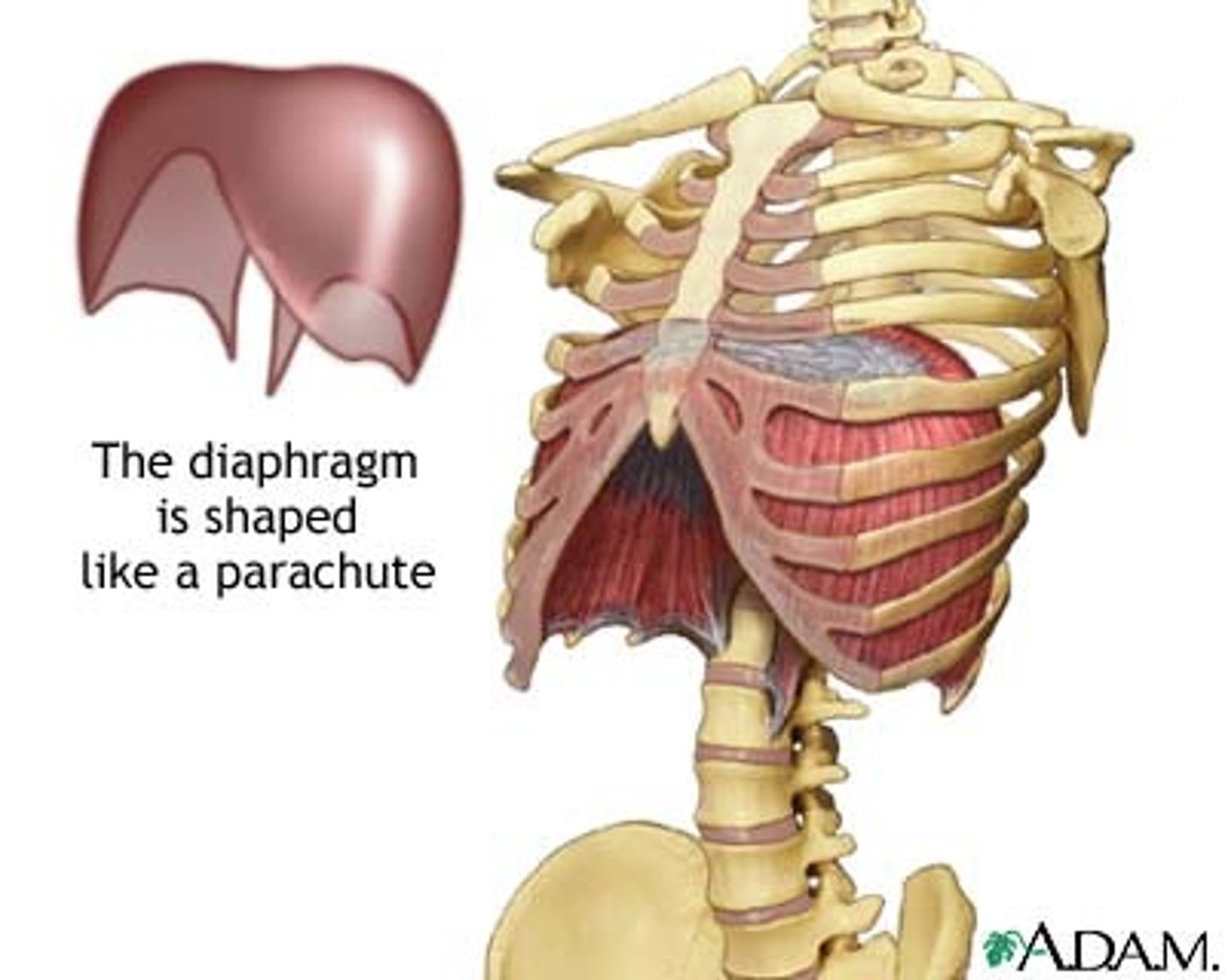
diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
What are the 10 regions and structures of the head and neck?
1. Cephalic
2. Frontal
3. Orbital
4. Otic
5. Nasal
6. Buccal
7. Oral
8. Mental
9. Occipital
10. Cervical
Cephalic
pertaining to the head; superior in position
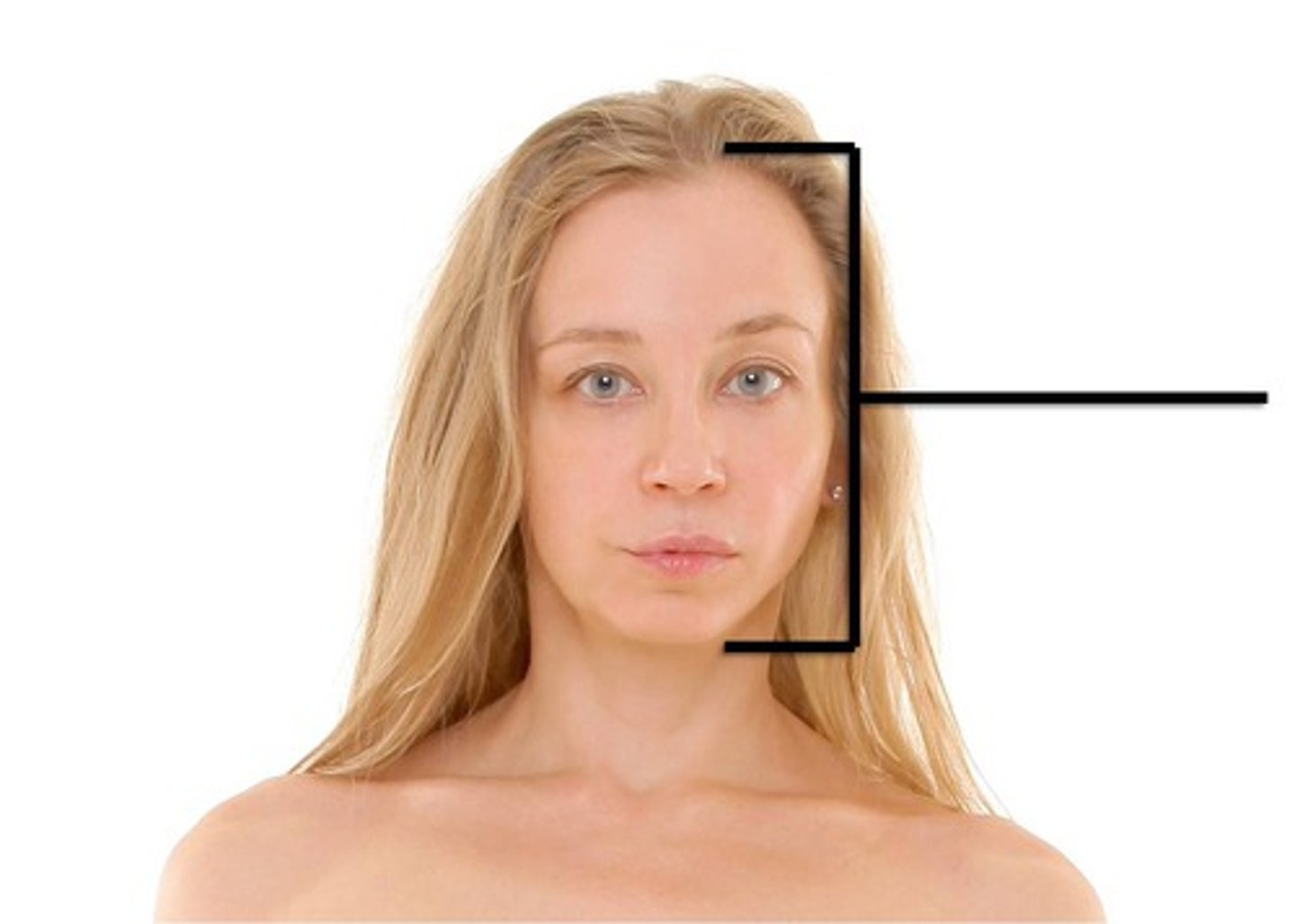
Frontal
pertaining to the forehead
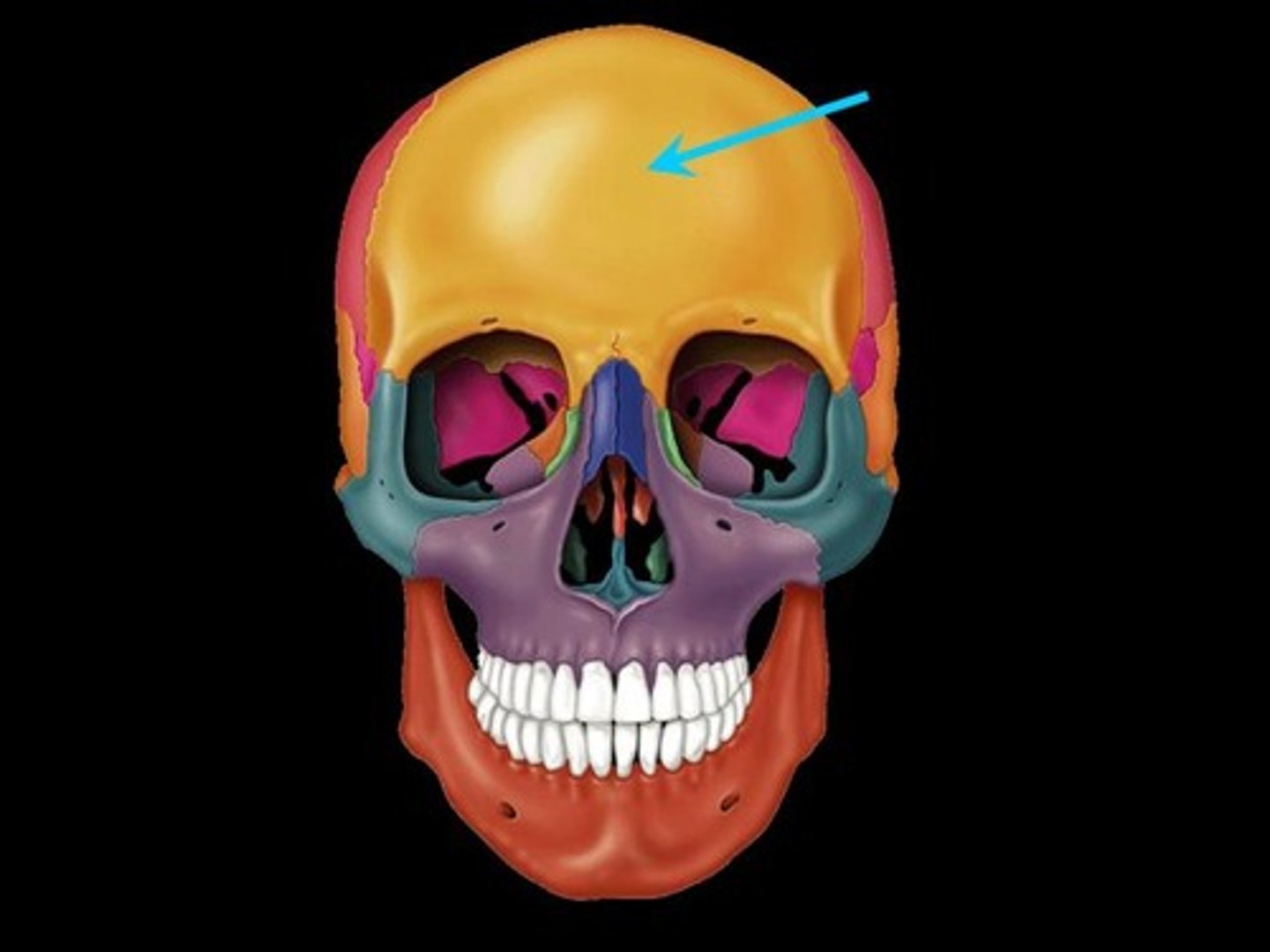
Orbital
eye area
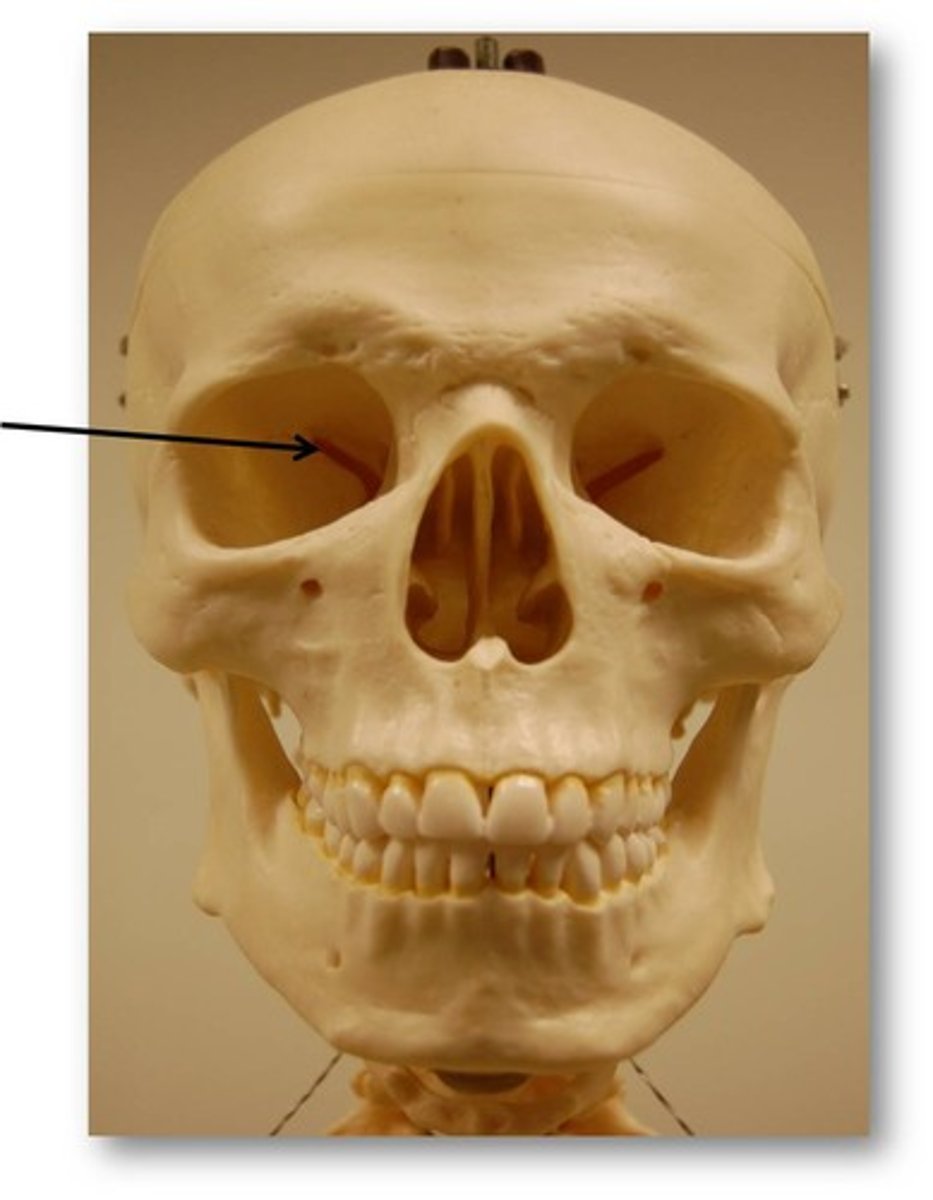
Otic
pertaining to the ear, also called auricular
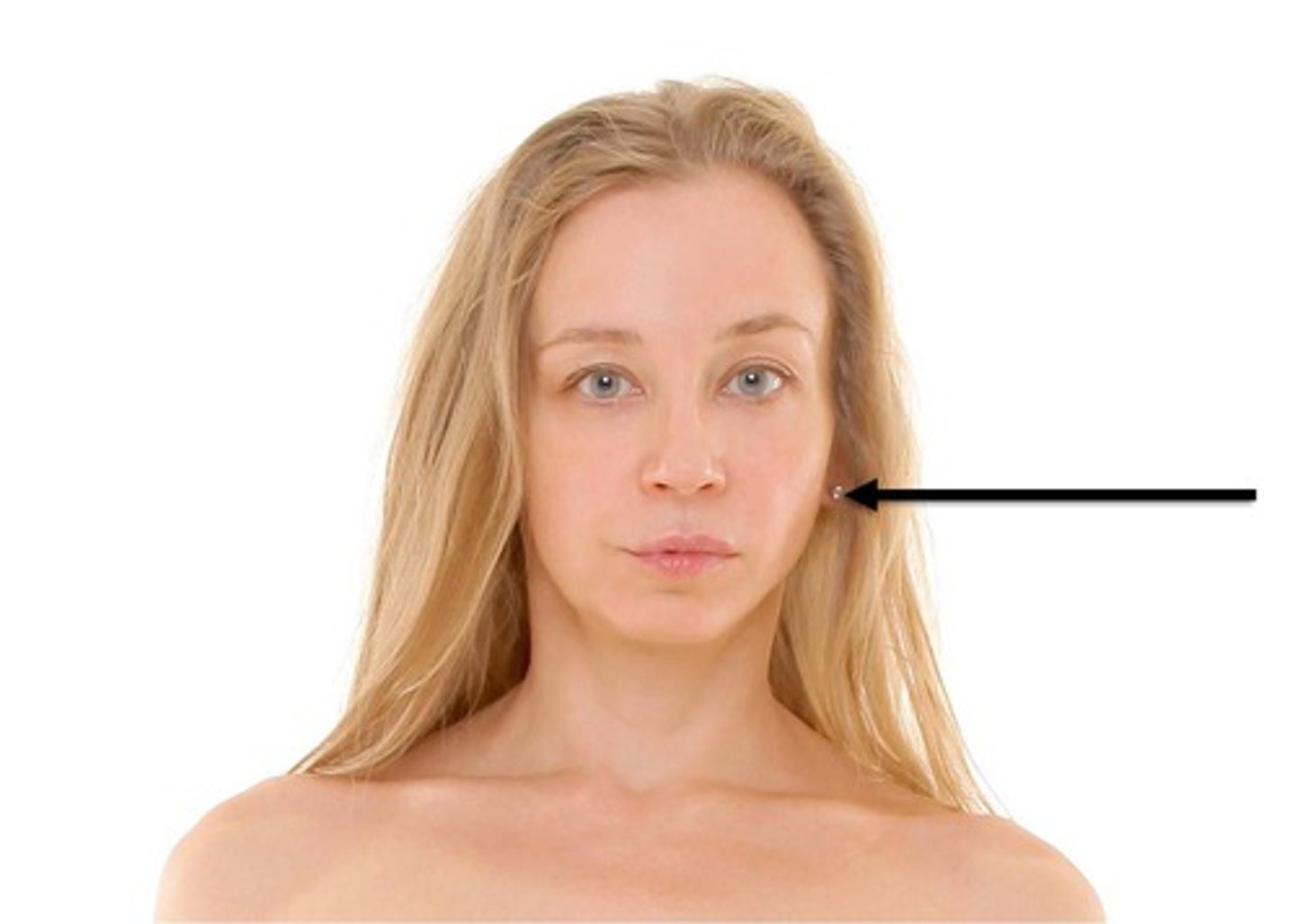
Nasal
pertaining to the nose
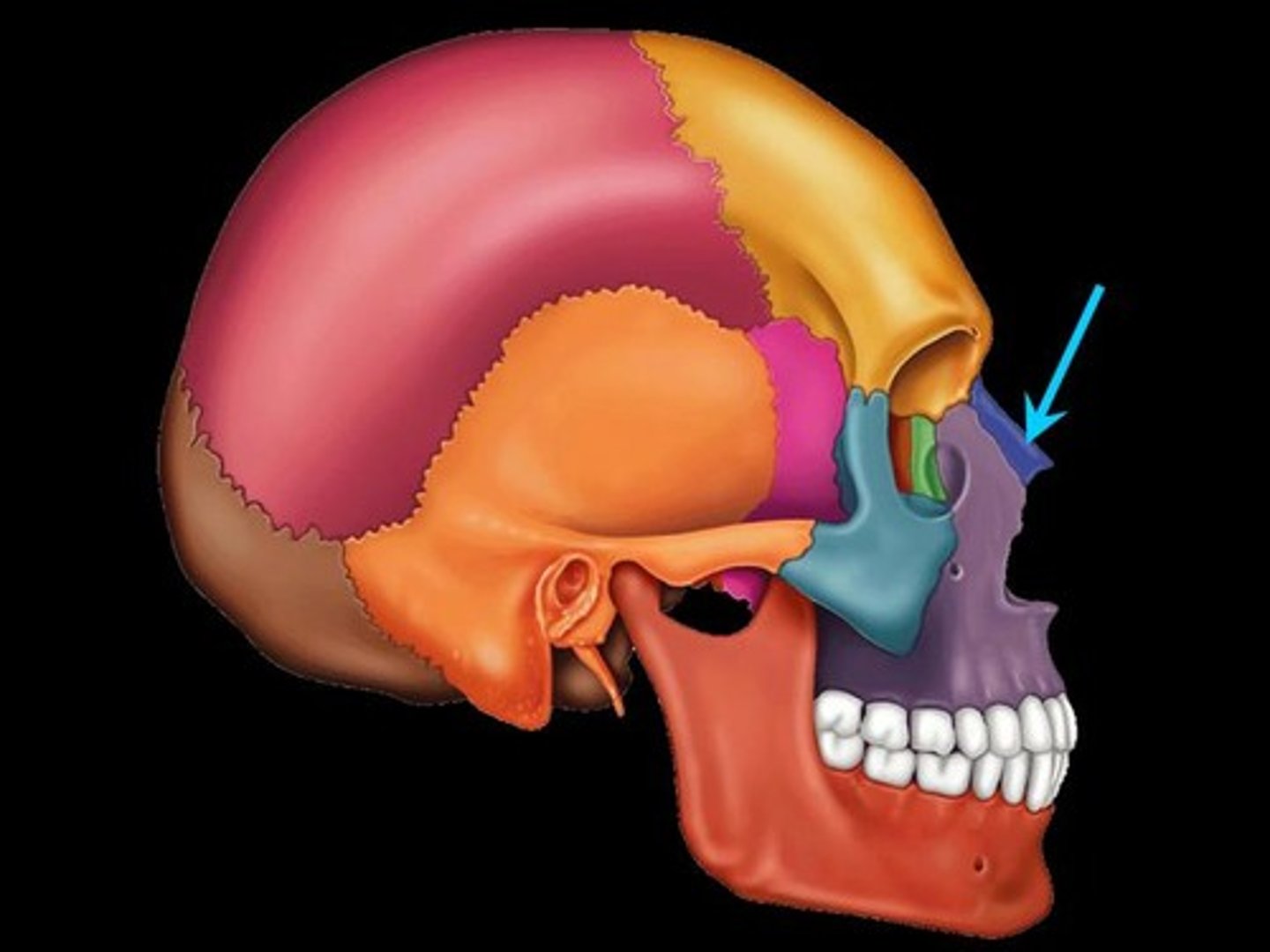
Buccal
pertaining to the cheek
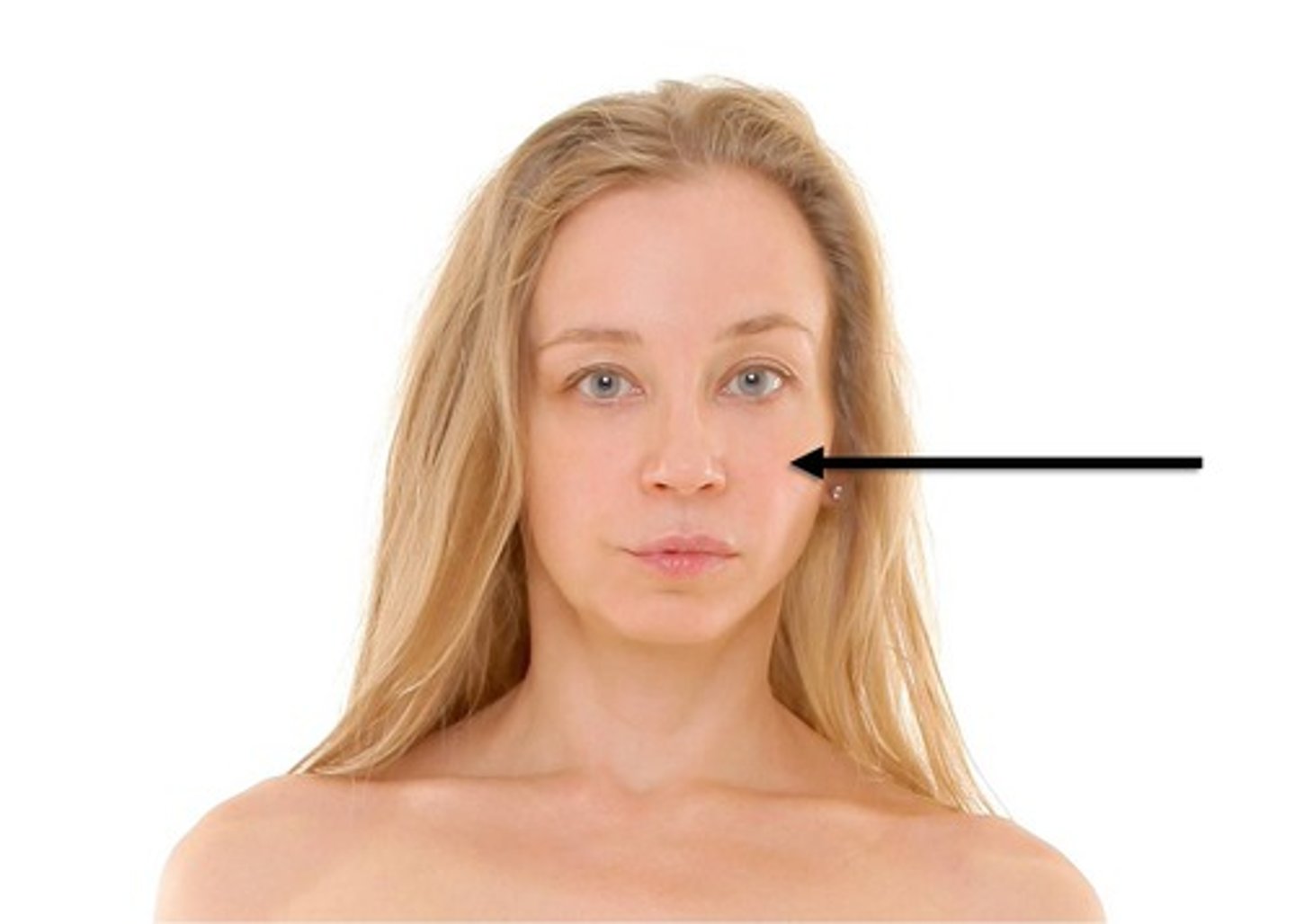
Oral
pertaining to the mouth
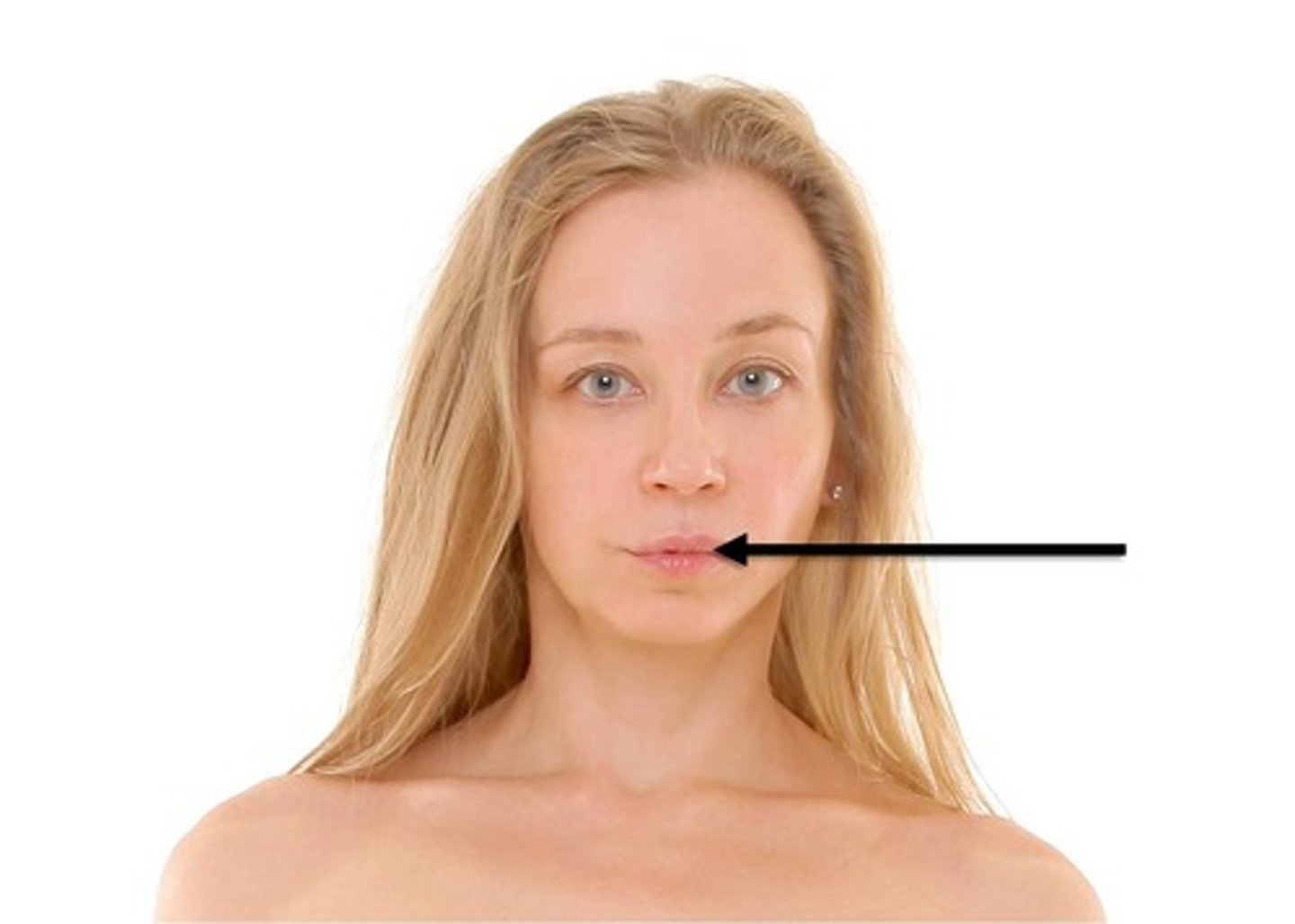
Mental
pertaining to the chin
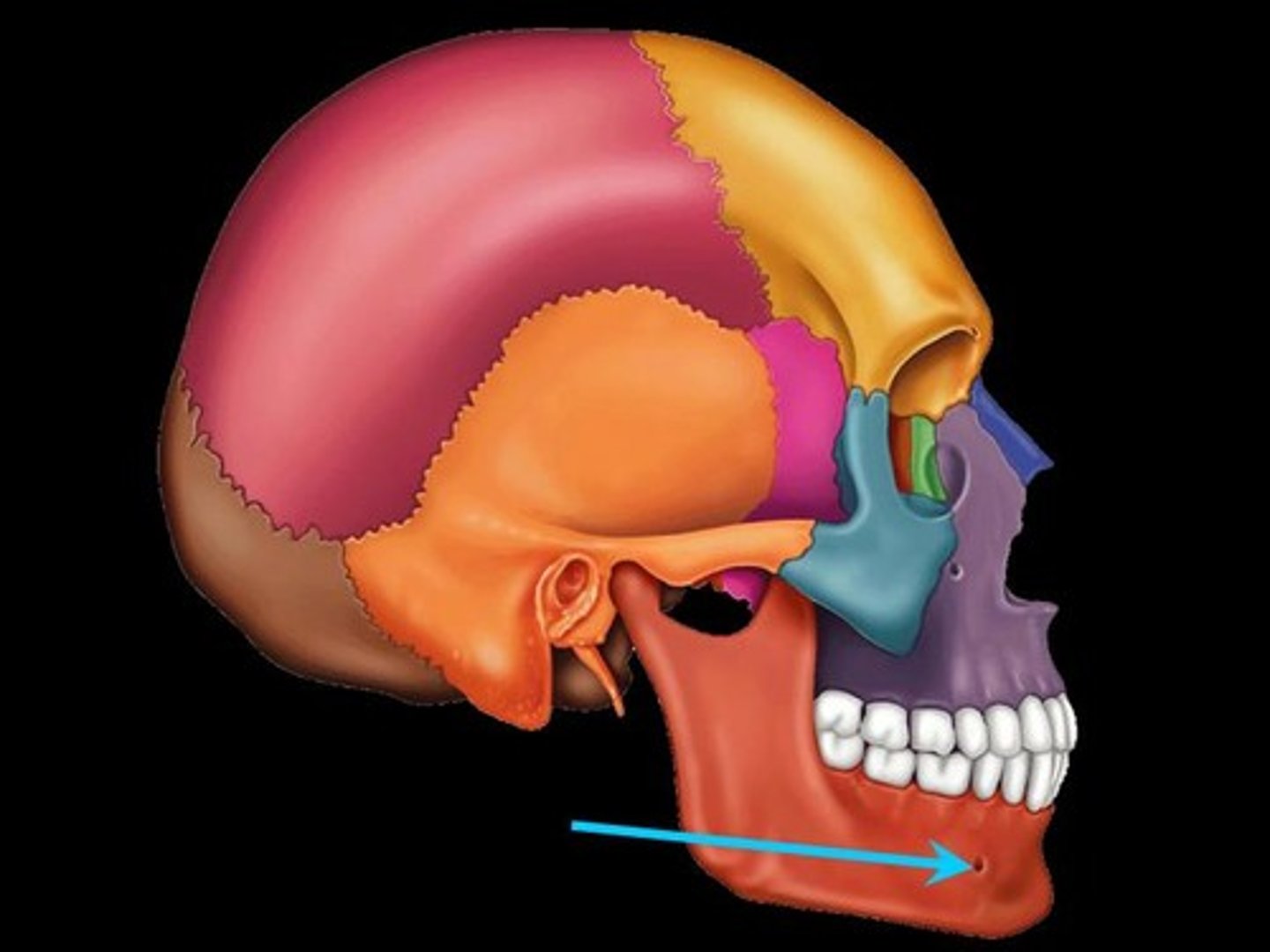
Occipital
base of skull
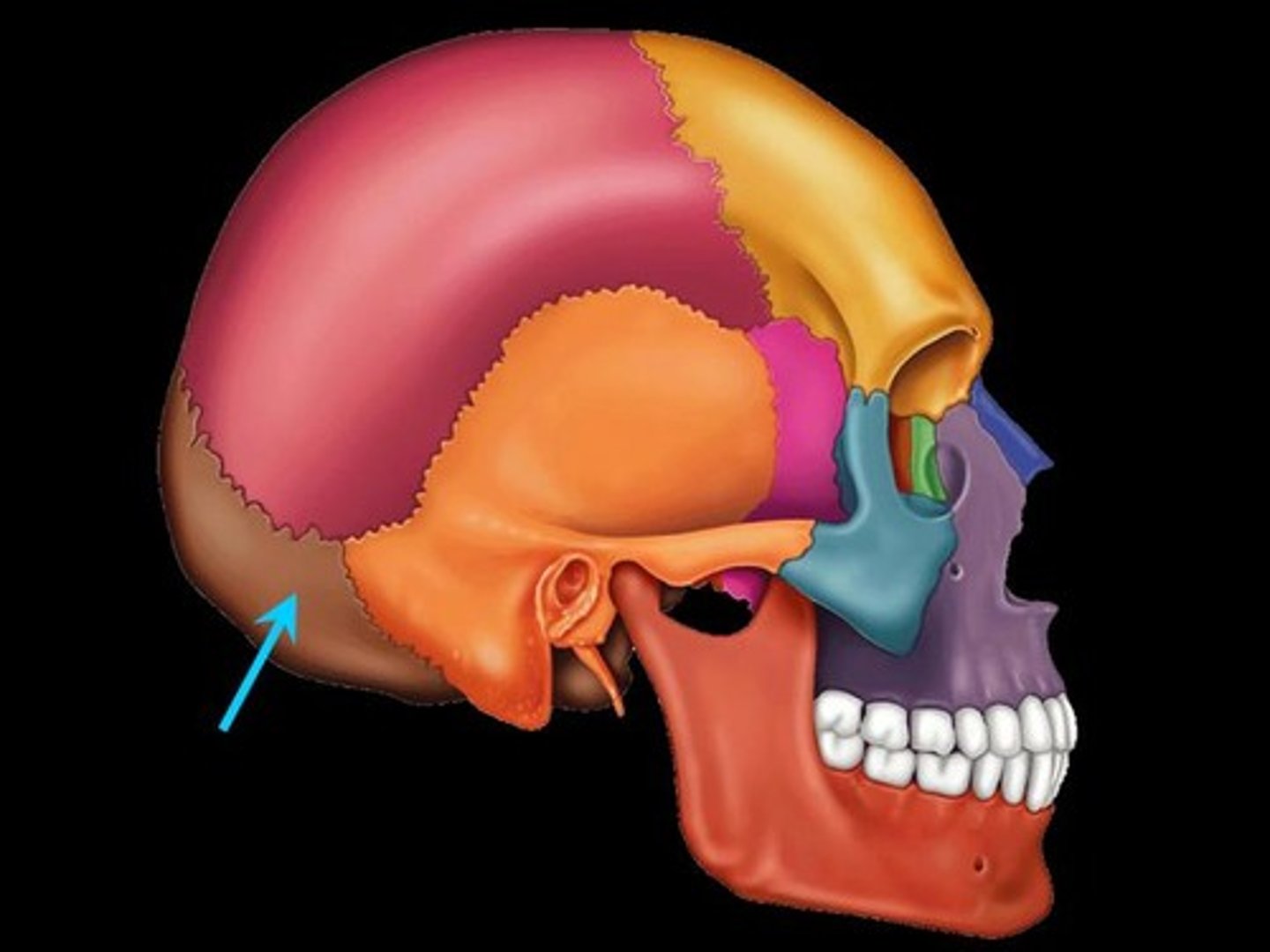
Cervical
pertaining to the neck
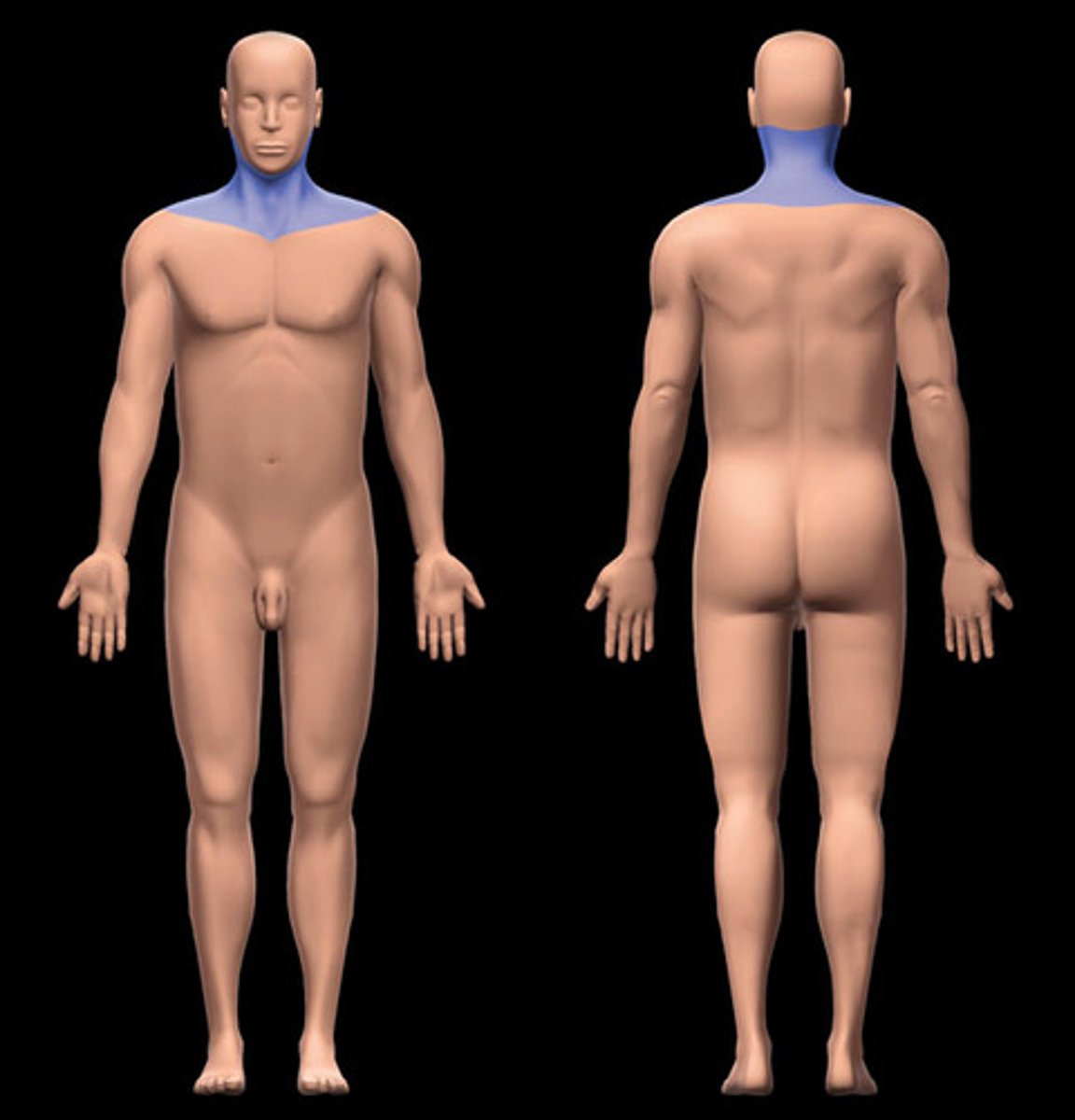
What are the 15 regions and structures of the Torso?
1. Thoracic
2. Sternal
3. Mammary
4. Vertebral
5. Dorsum
6. Scapular
7. Abdominal
8. Umbilical
9. Pelvic
10. Coxal
11. Inguinal
12. Pubic
13. Lumbar
14. Perineal
15. Sacral
thoracic region
chest area above the diaphragm
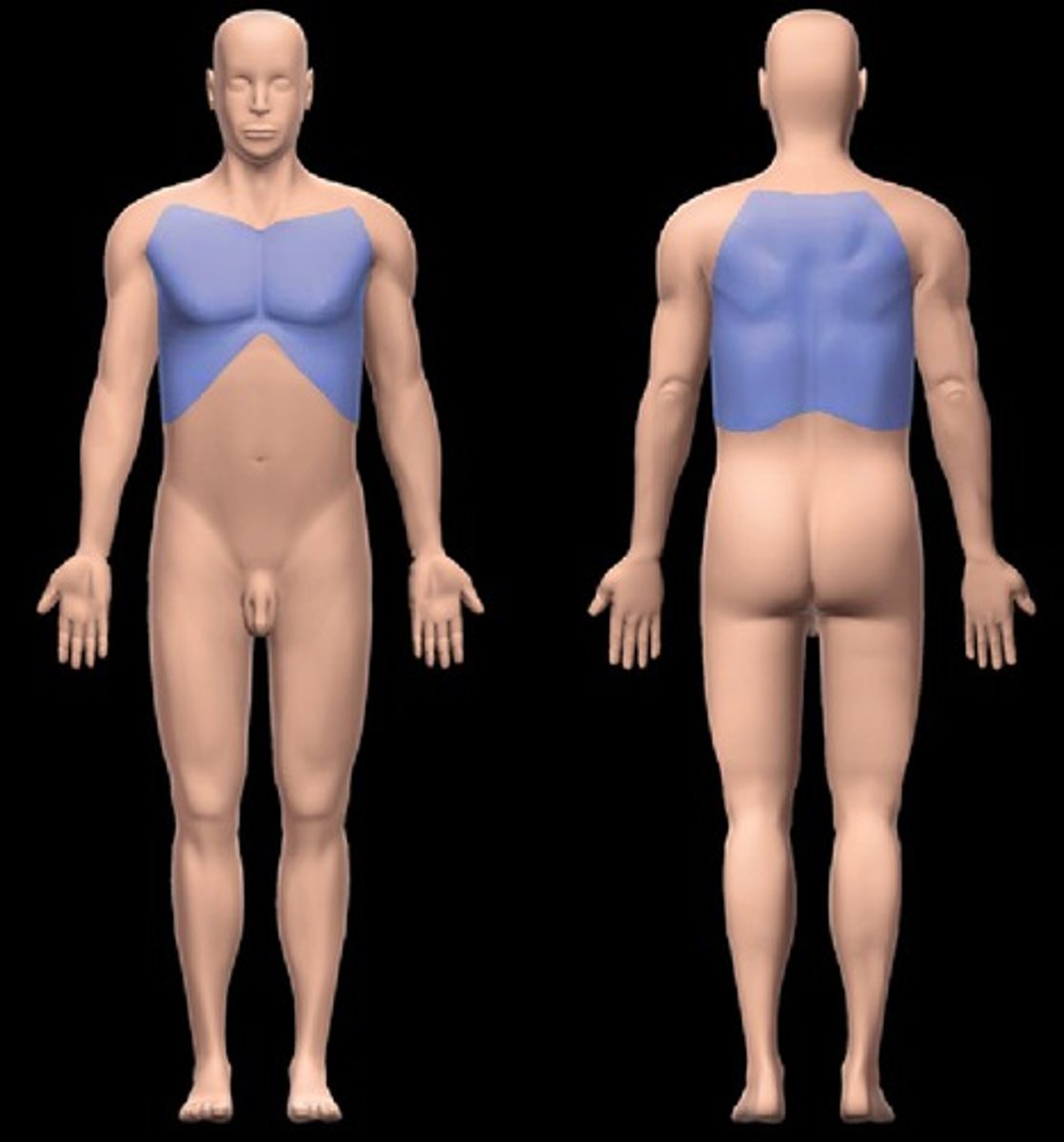
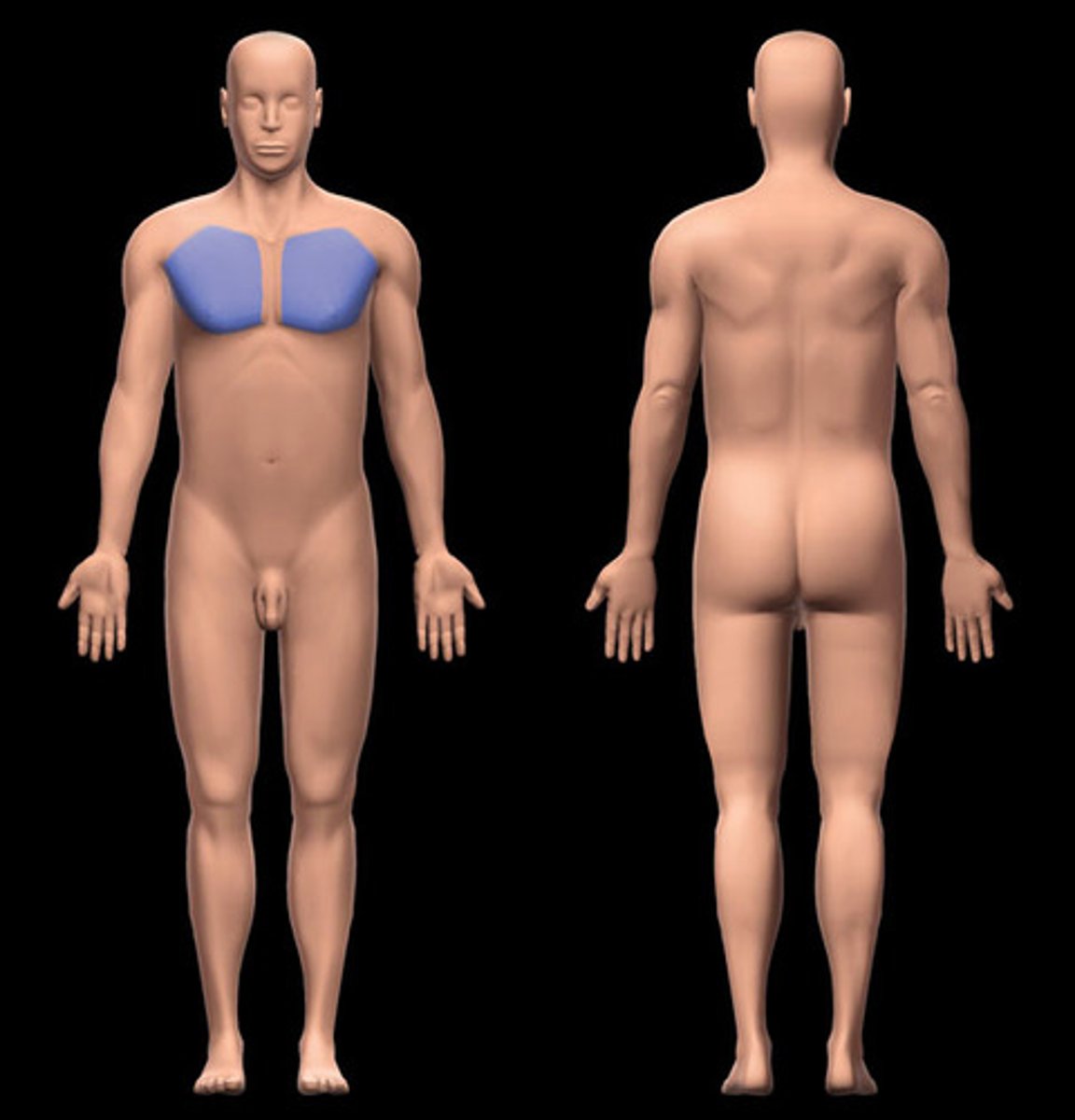
sternal region
the area in the middle of the chest over the sternum
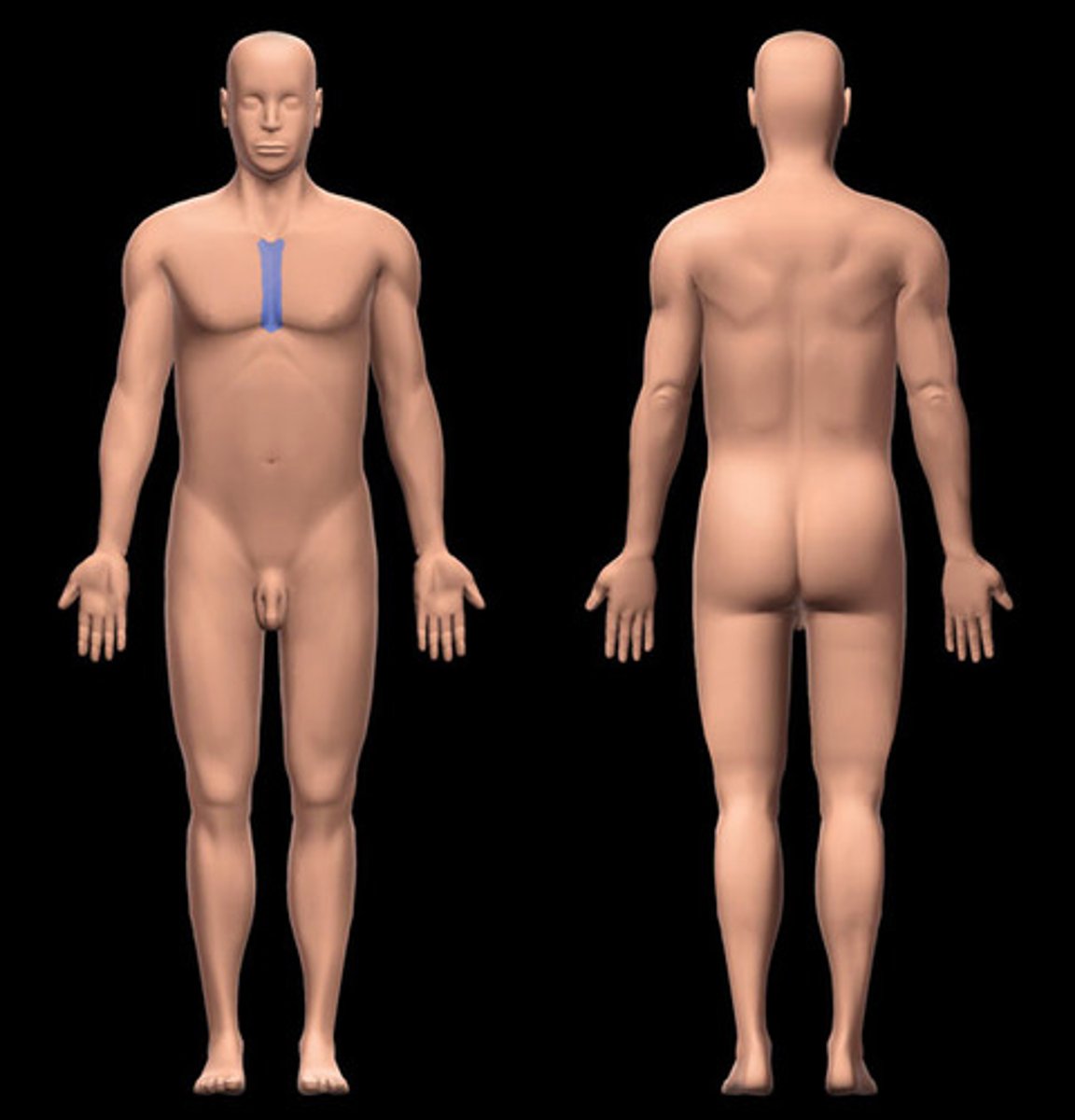
mammary region
the portion of the chest that contains the breasts
vertebral region
overlies spinal column or vertebrae; on posterior side of trunk
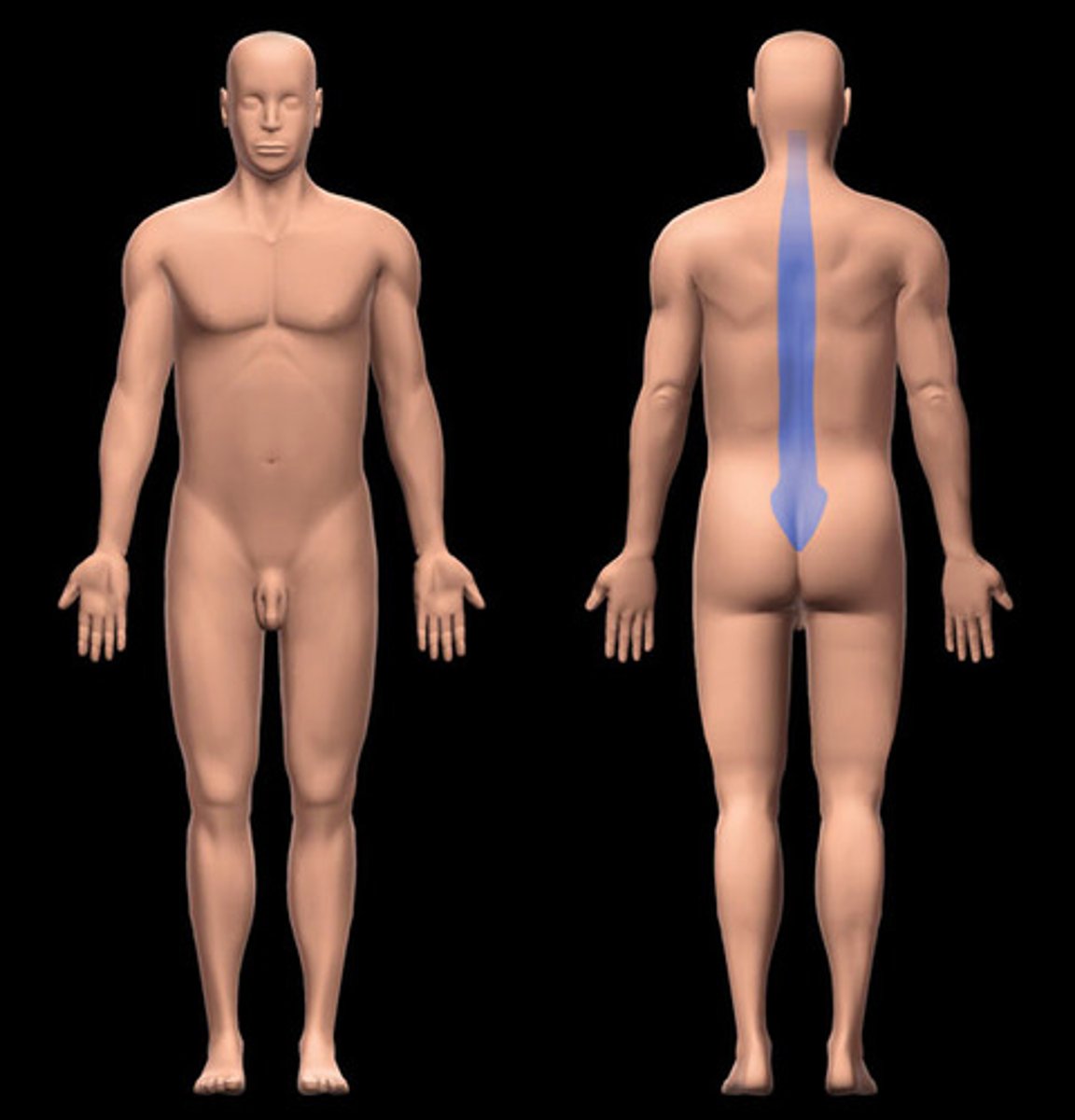
dorsum region
The back
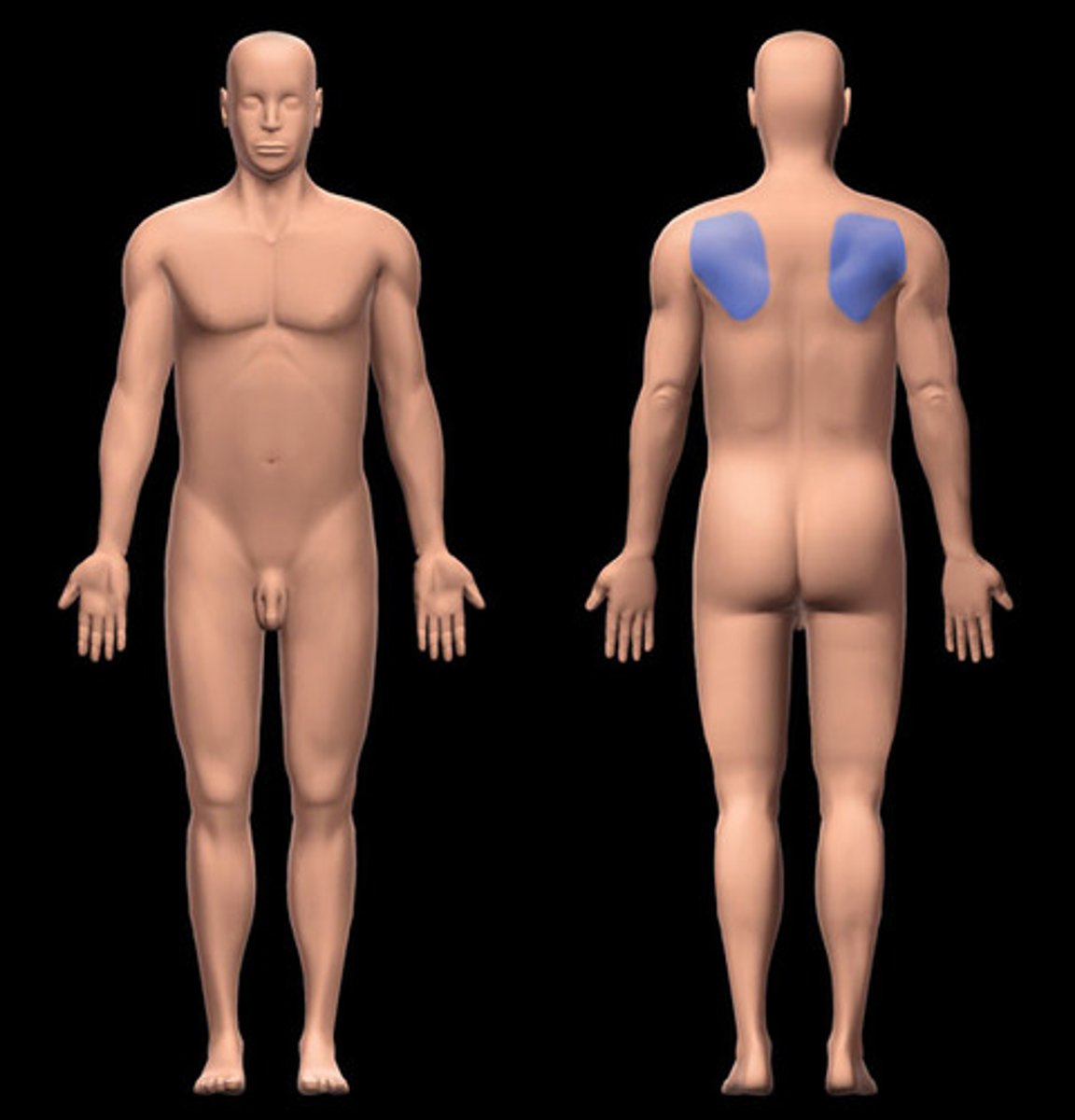
scapular region
shoulder blade region
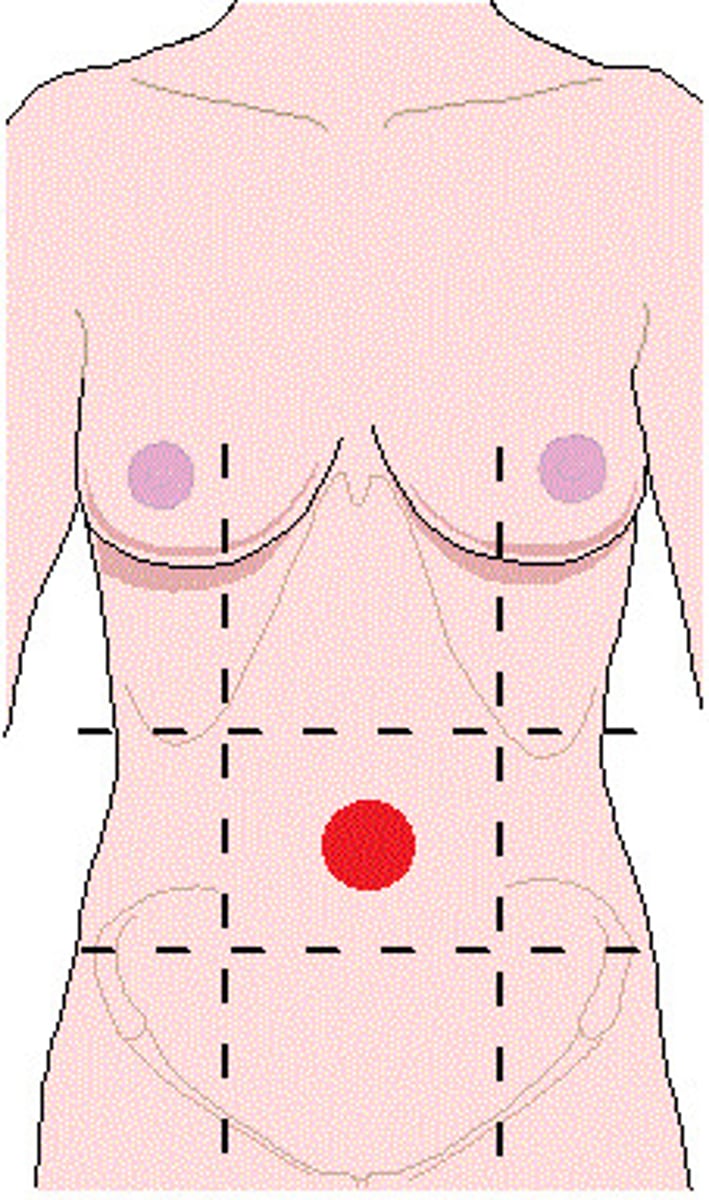
abdominal region
one of nine equal areas of the abdomen that are named and used as reference points when discussing the body
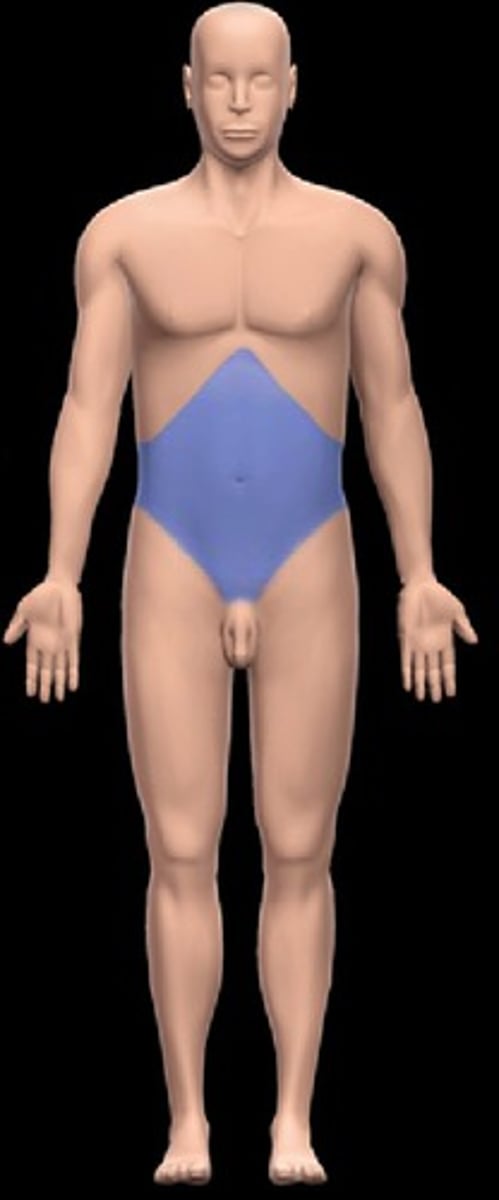
umbilical region
The centermost region, which includes the umbilicus
pelvic region
area of the pelvis below the abdomen
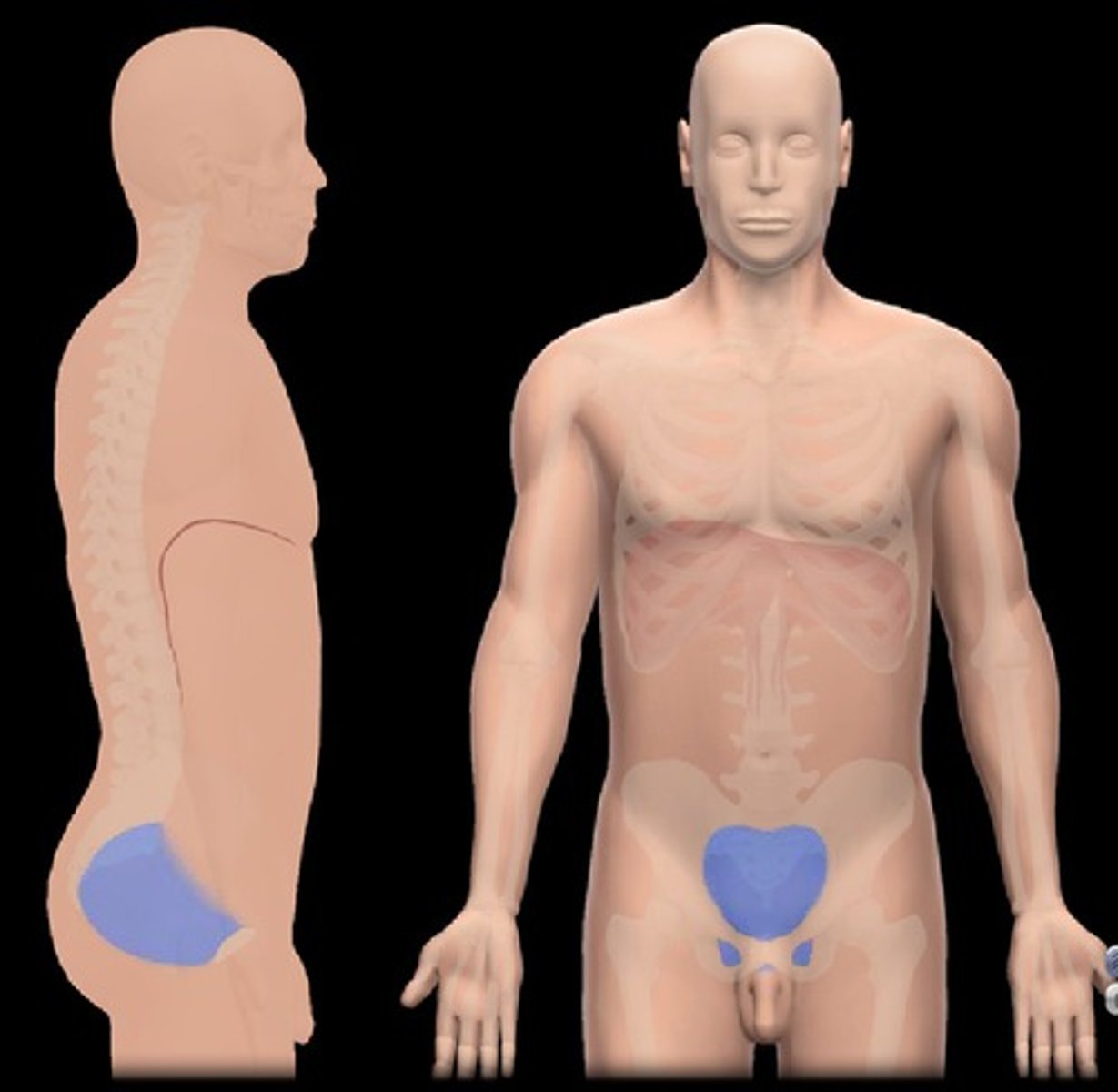
coxal region
hip region
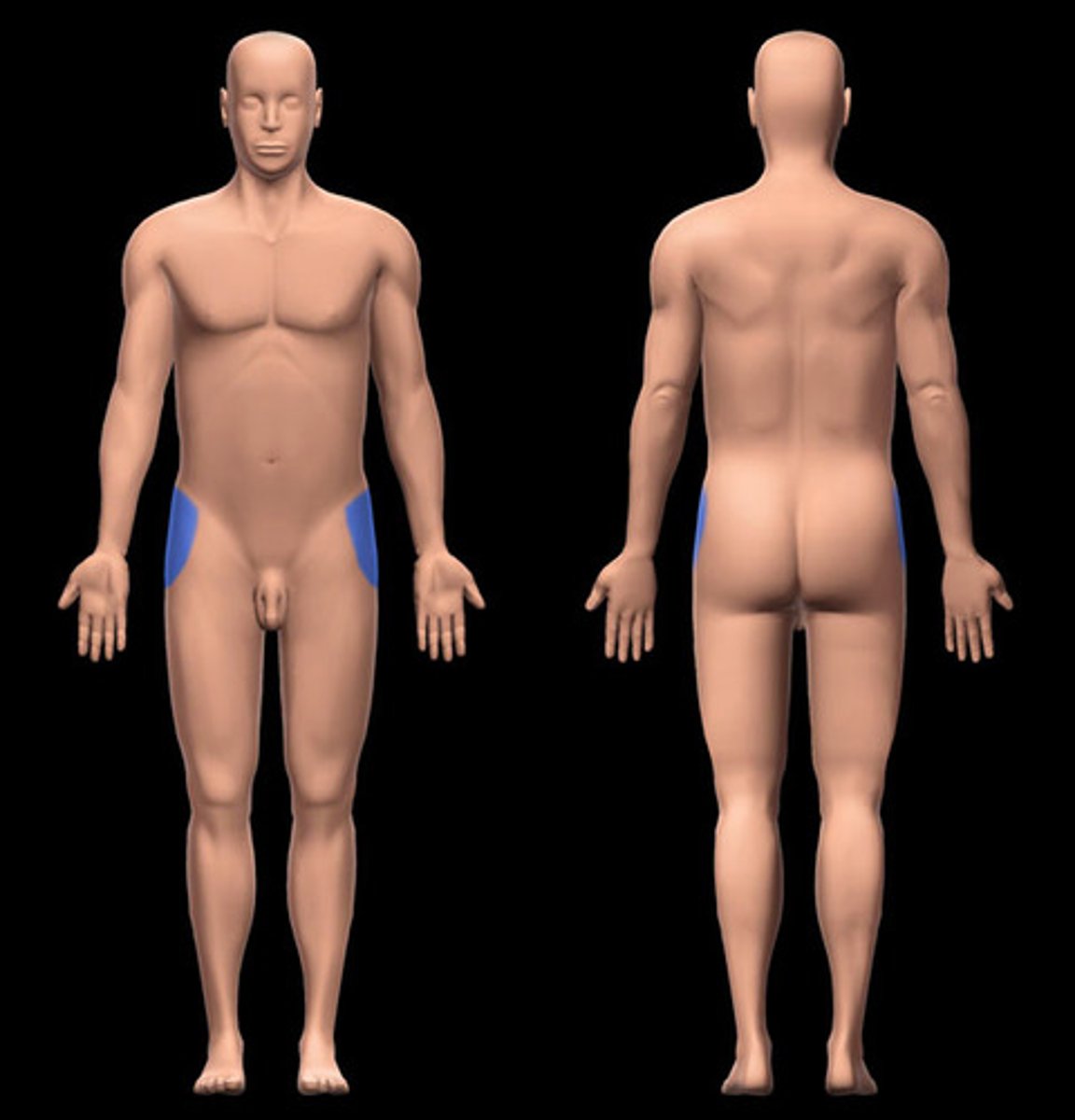
inguinal region
right and left lower regions near the groin
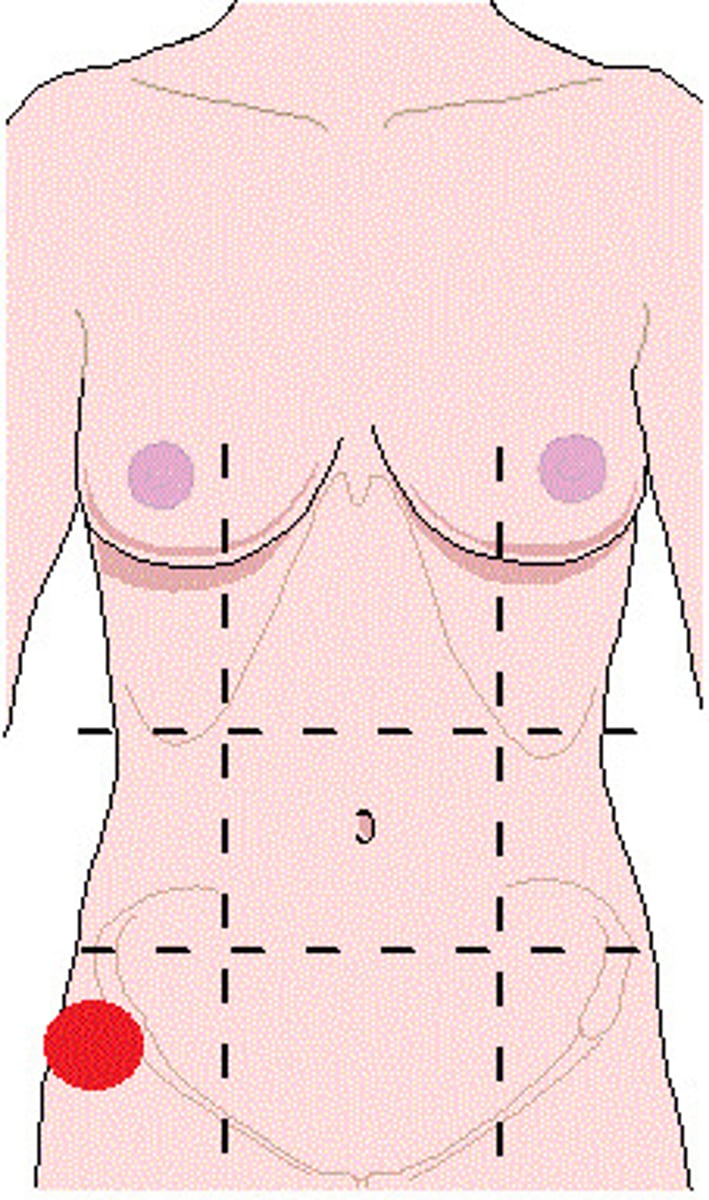
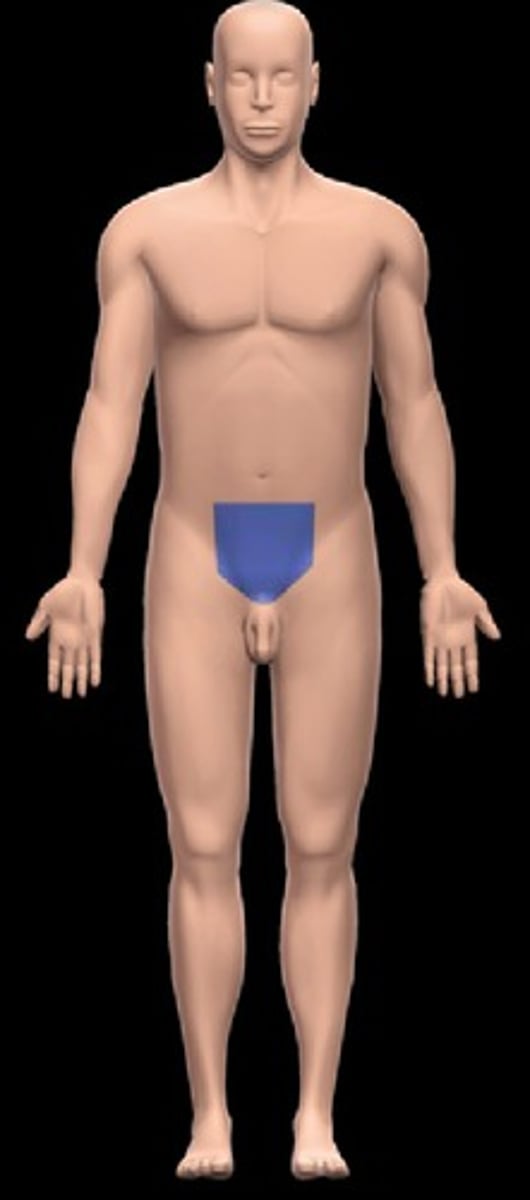
pubic region
genital region, pubis
lumbar region
to the right and left of the umbilical region, near the waist
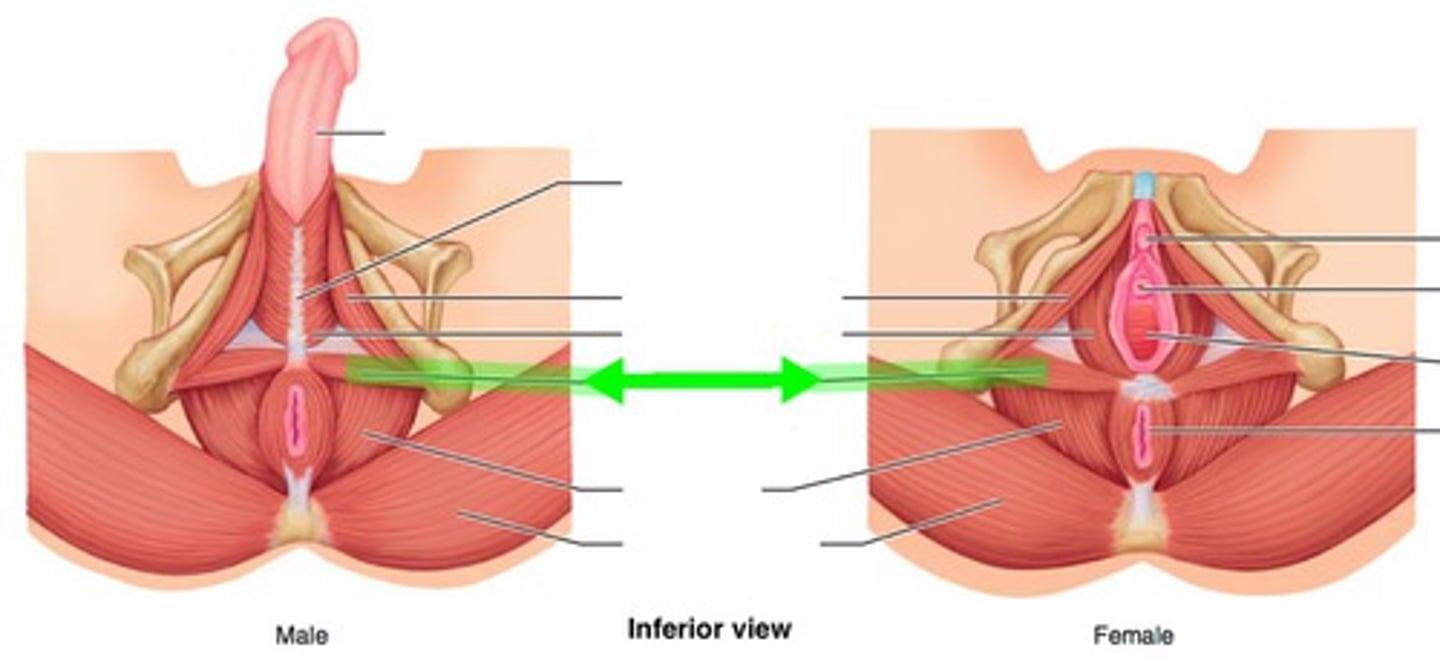
perineal region
Area between anus and genitals
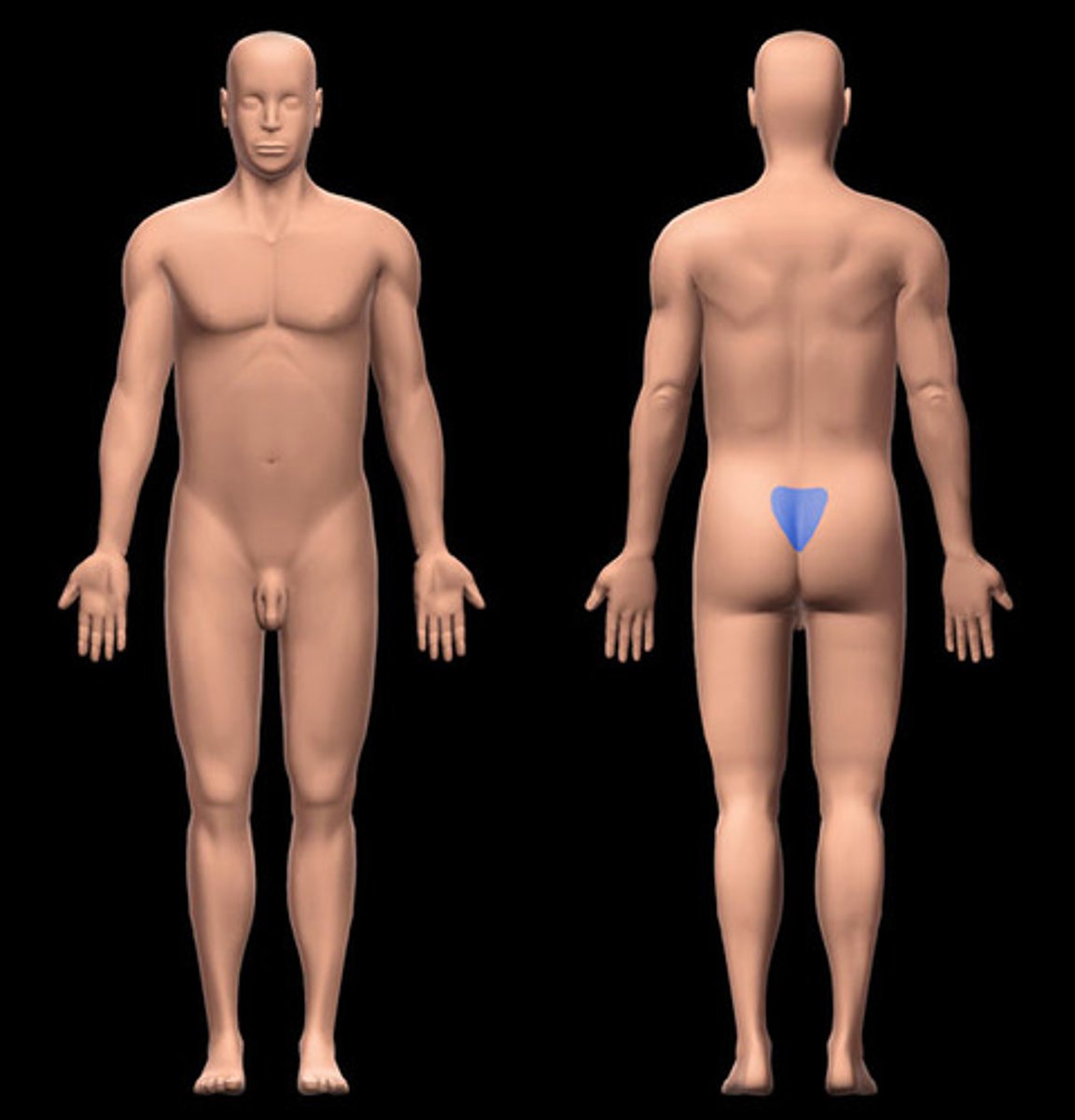
sacral region
the area where the sacrum is located; forms the tail end of the spinal column
What are the 12 regions/structures of the Arm/Wrist/Hand?
1. Acromial
2. Axillary
3. Brachial
4. Antecubital
5. Olecranal
6. Antebrachial
7. Carpal
8. Manus
9. Pollex
10. Palmar
11. Dorsum
12. Digital
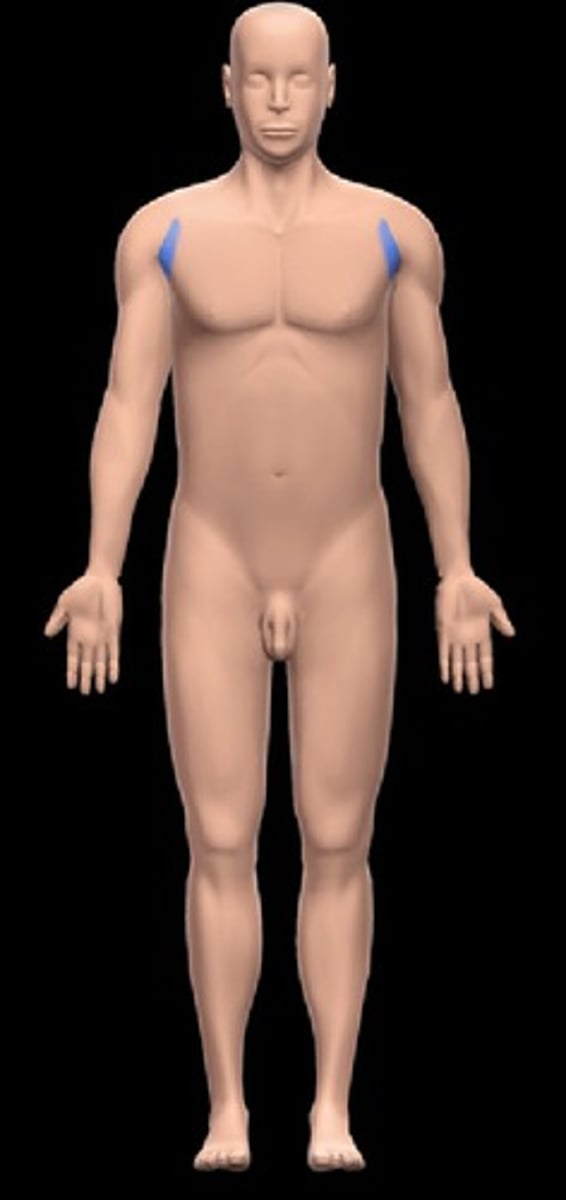
Acromial region
the area over the lateral part of the shoulder that contains the acromion of the scapula
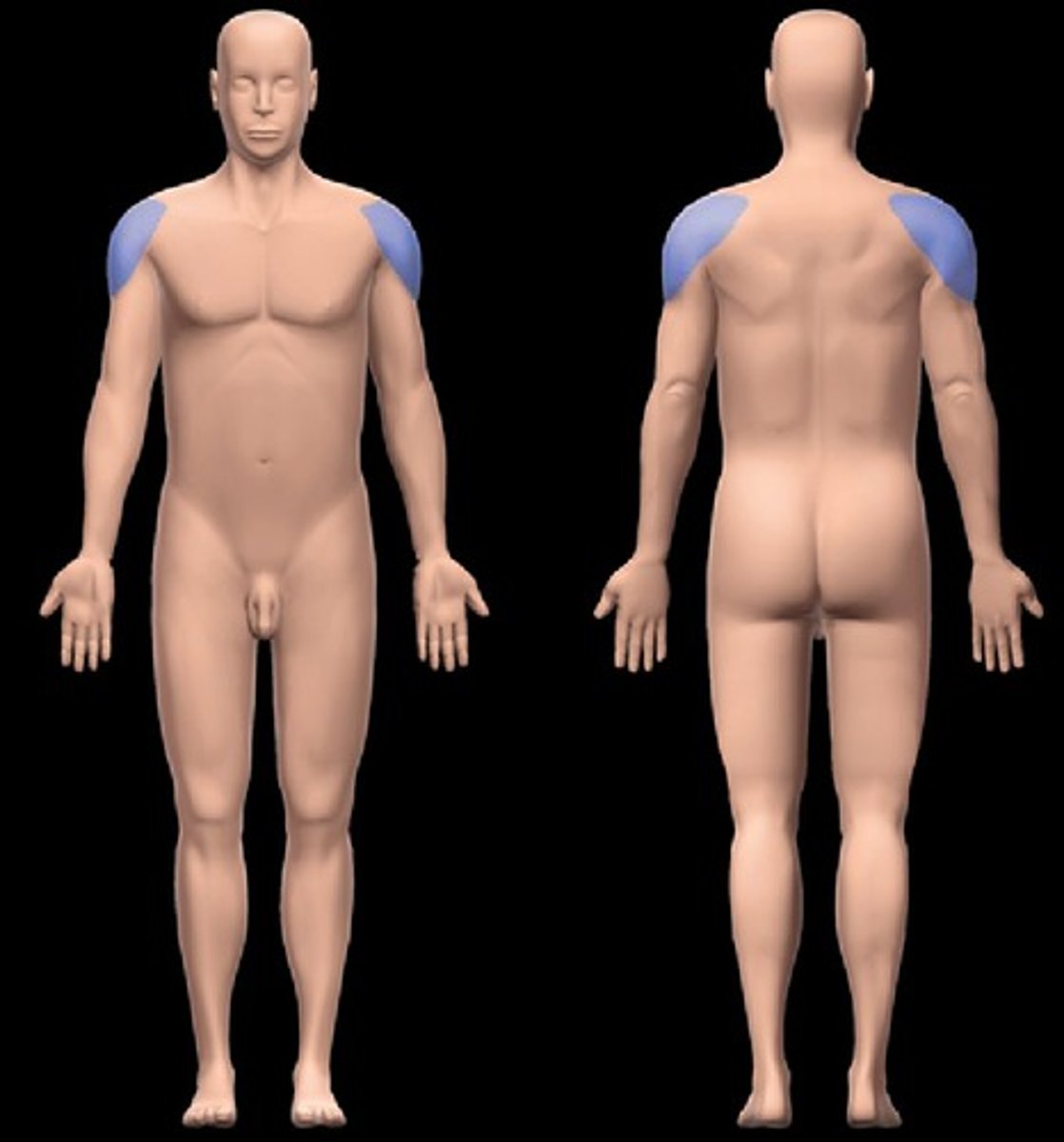
Axillary region
the area in and around the axilla (armpit)
Brachial region
arm (shoulder to elbow)
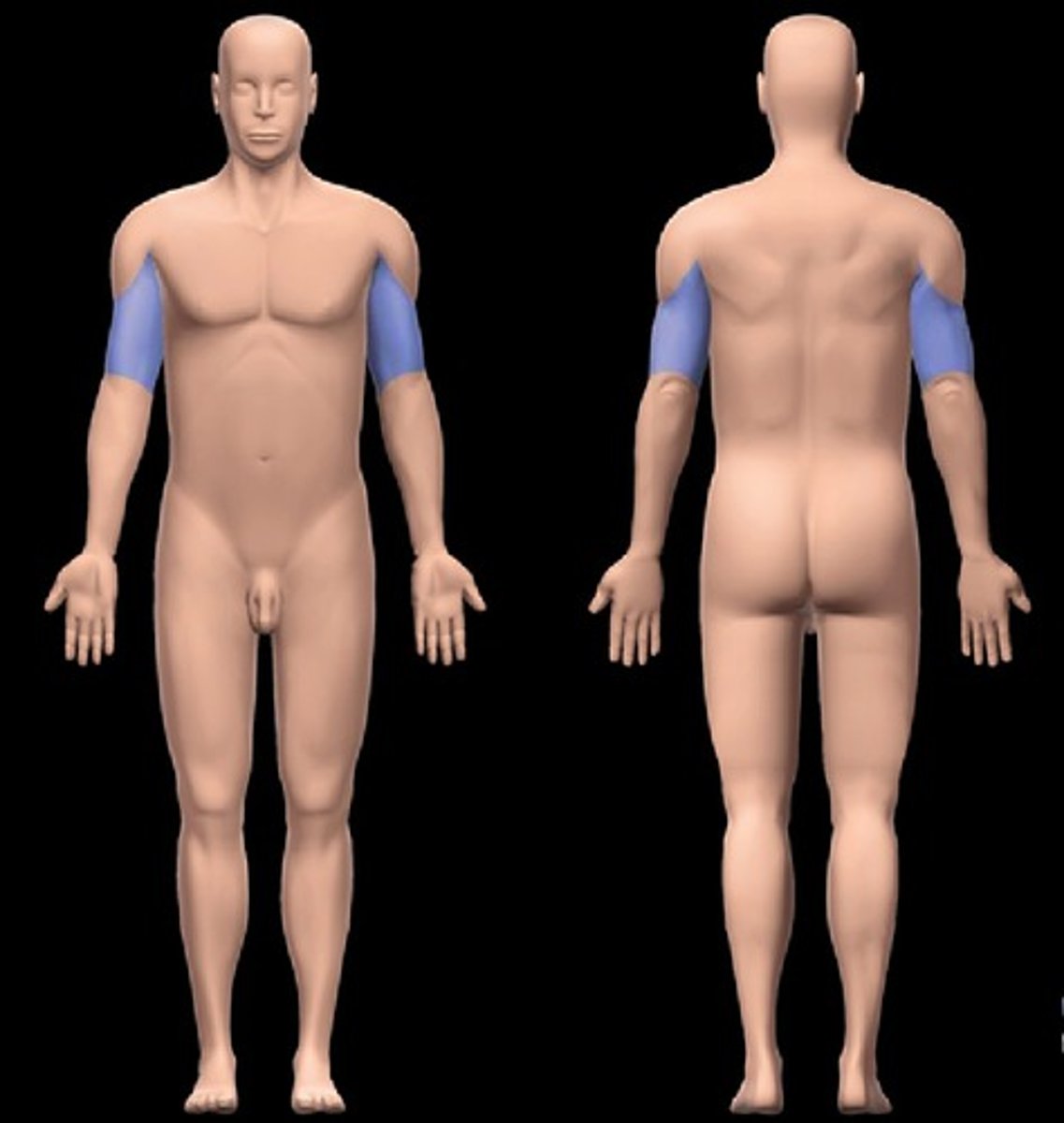
Antecubital Region
the anterior upper limb between the forearm and arm, over the elbow joint
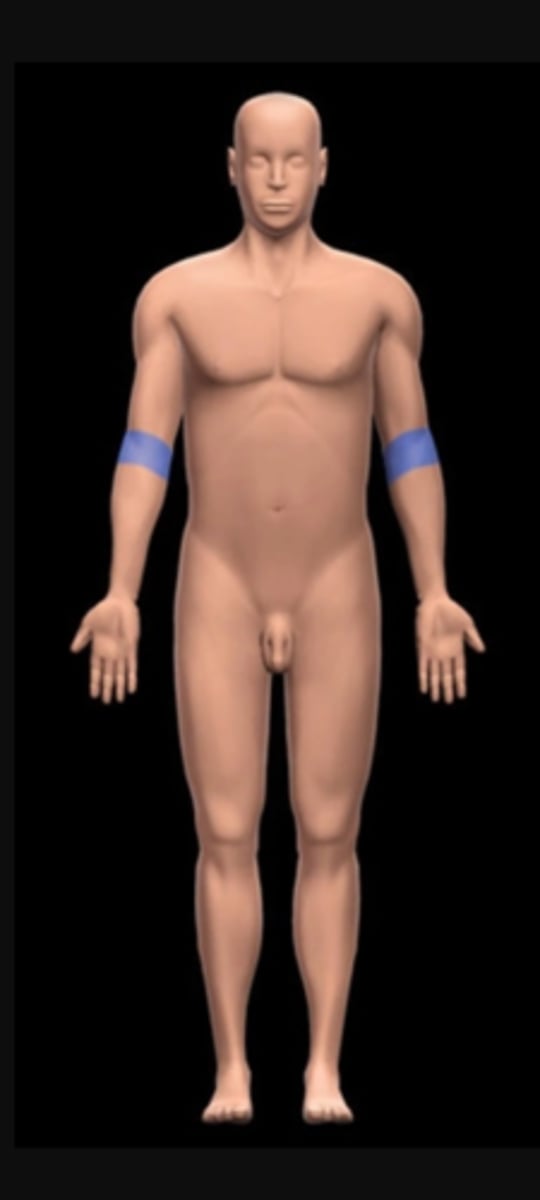
Olecranal region
posterior elbow
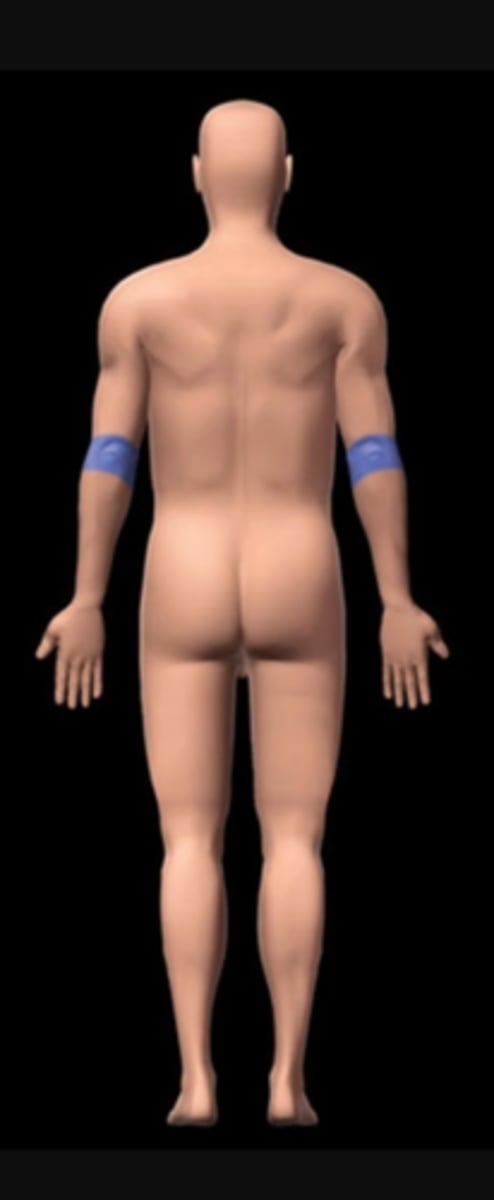
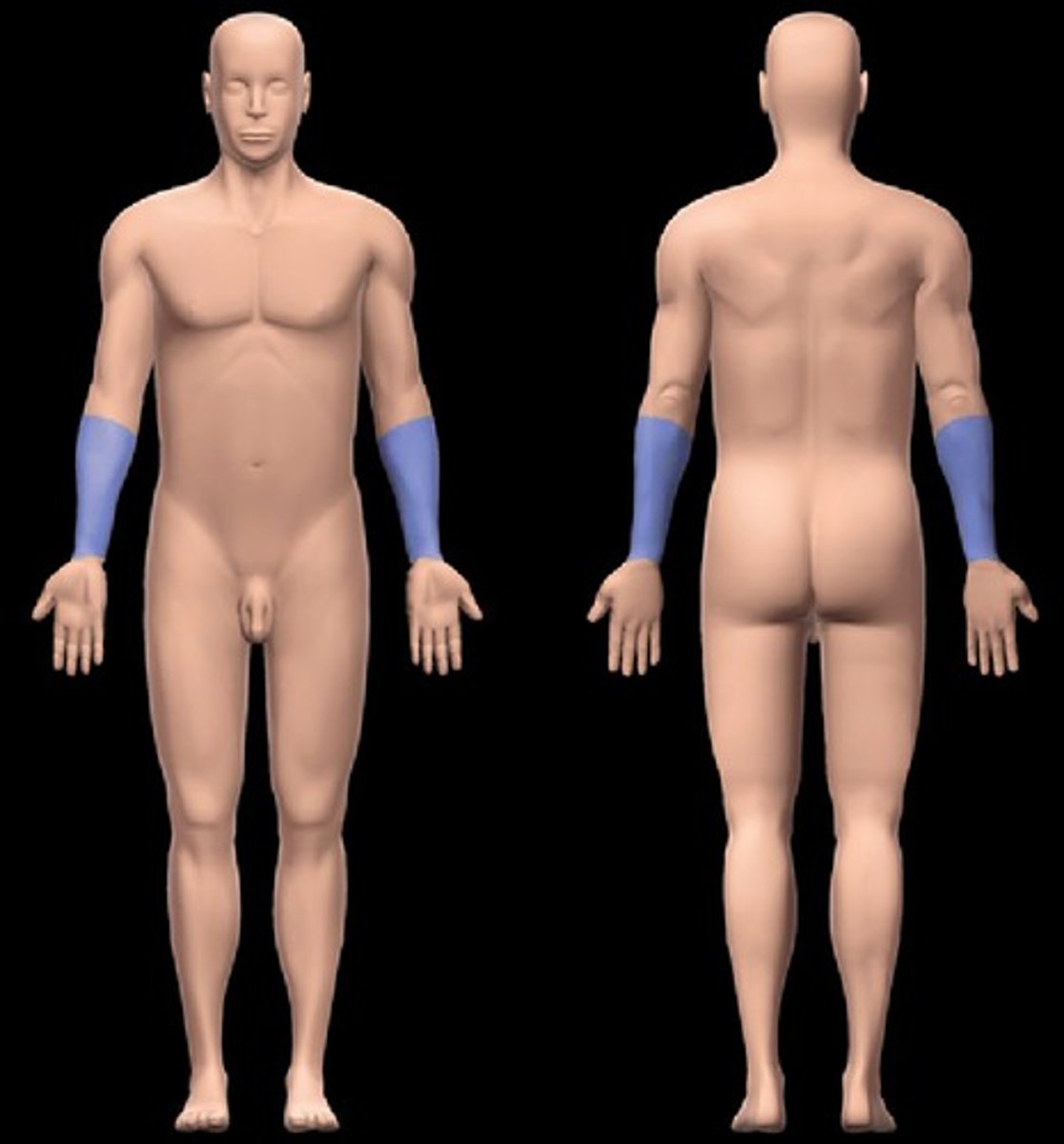
Antebrachial region
forearm (elbow to wrist)
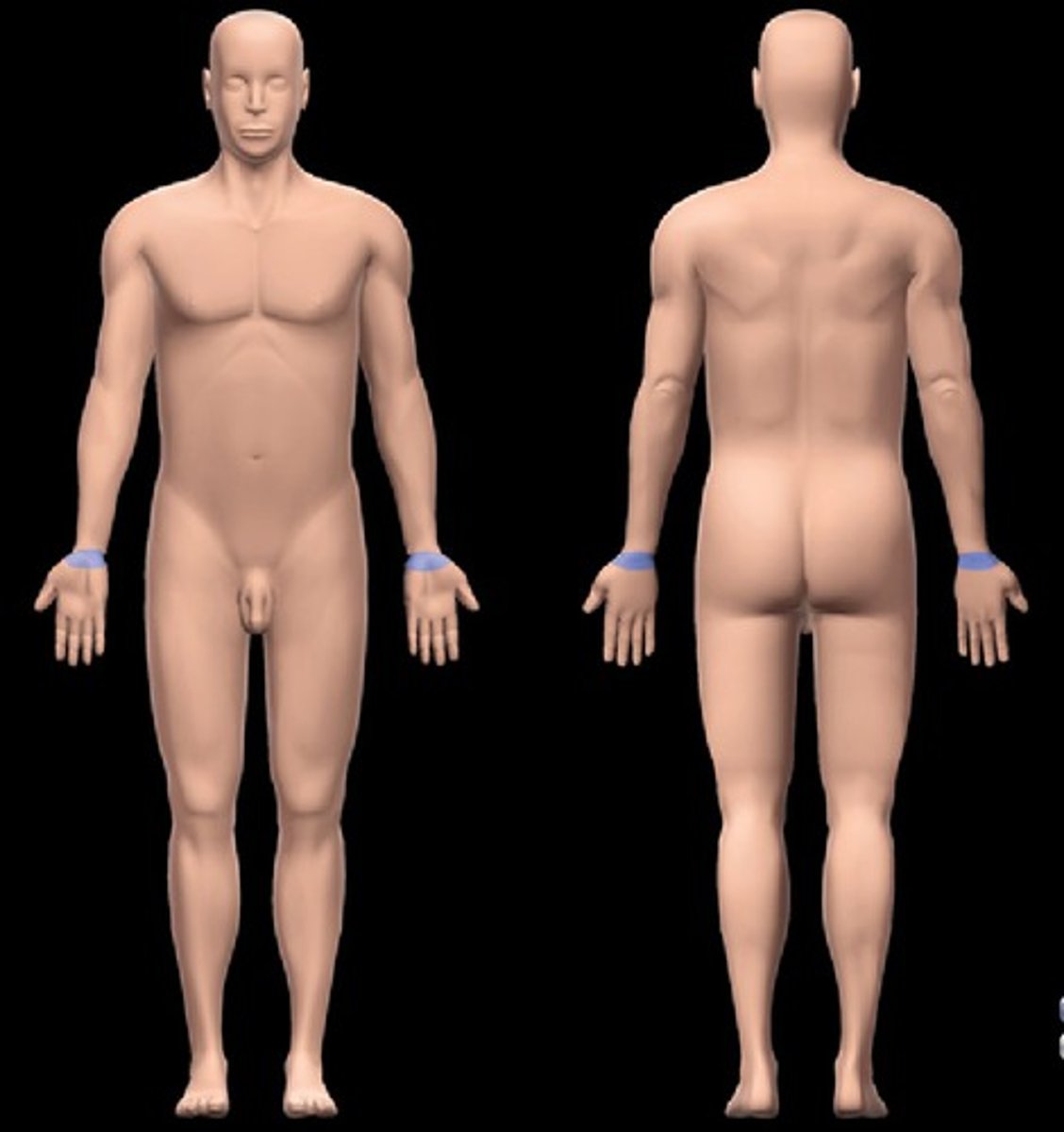
Carpal region
carpus (wrist)
Manus region
hand region
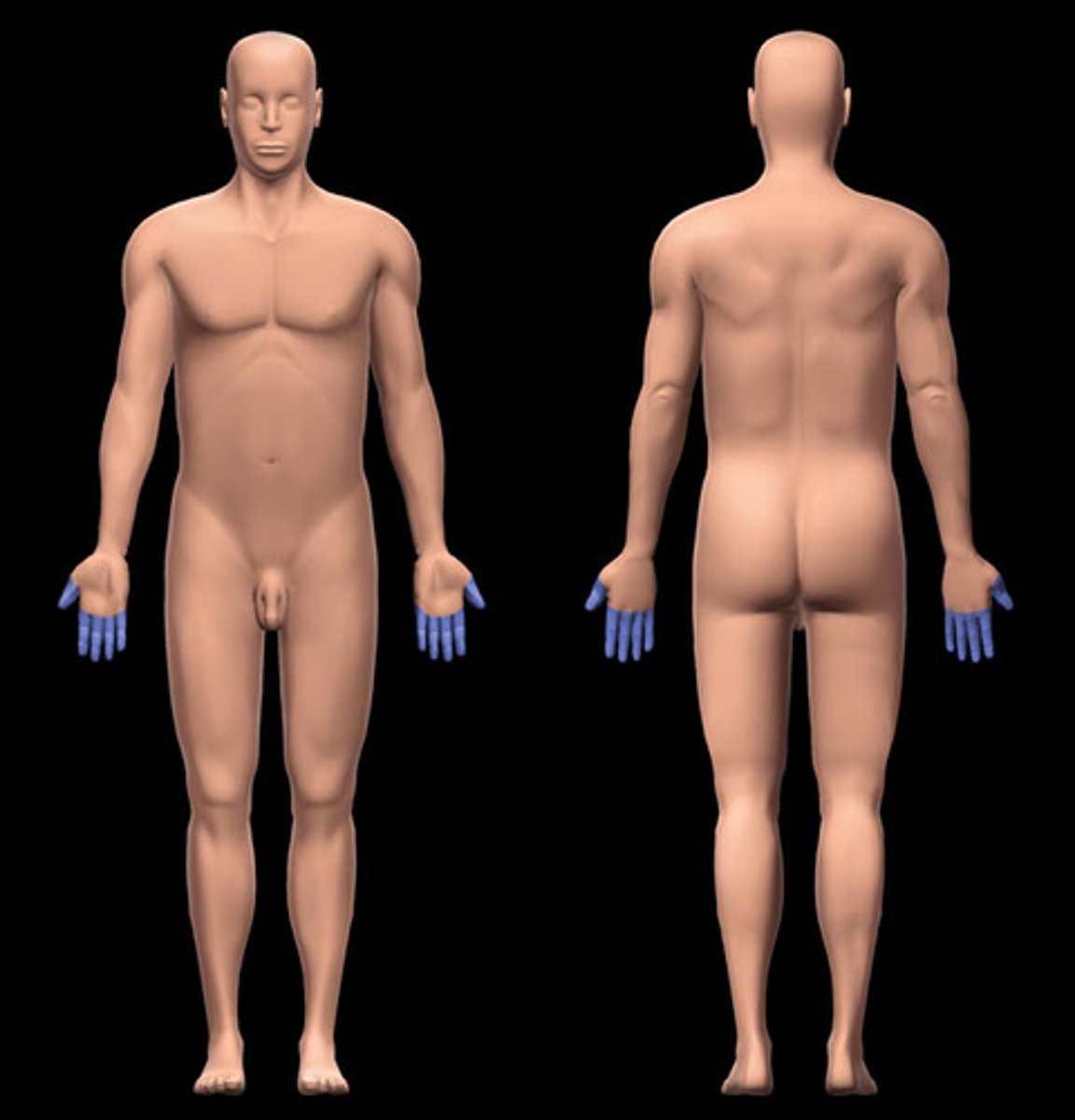
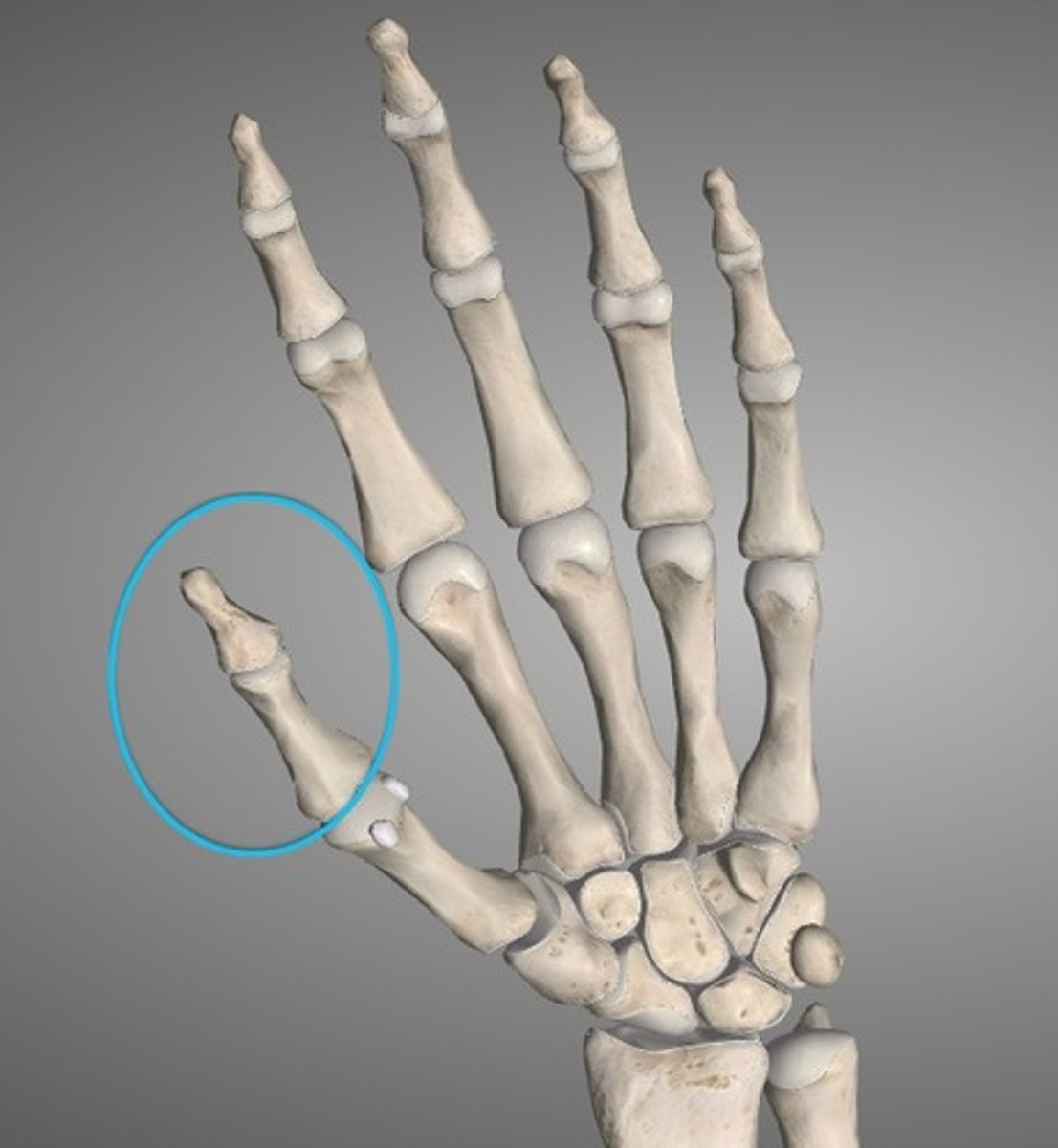
Pollex region
pertaining to the thumb
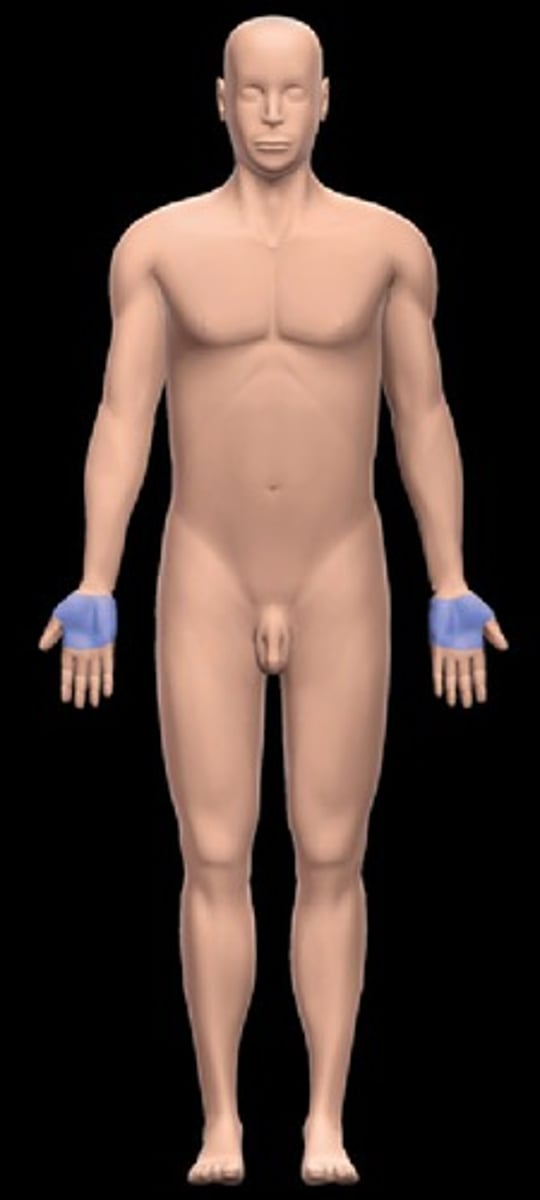
Palmar region
the anterior hand (the palm of the hand)
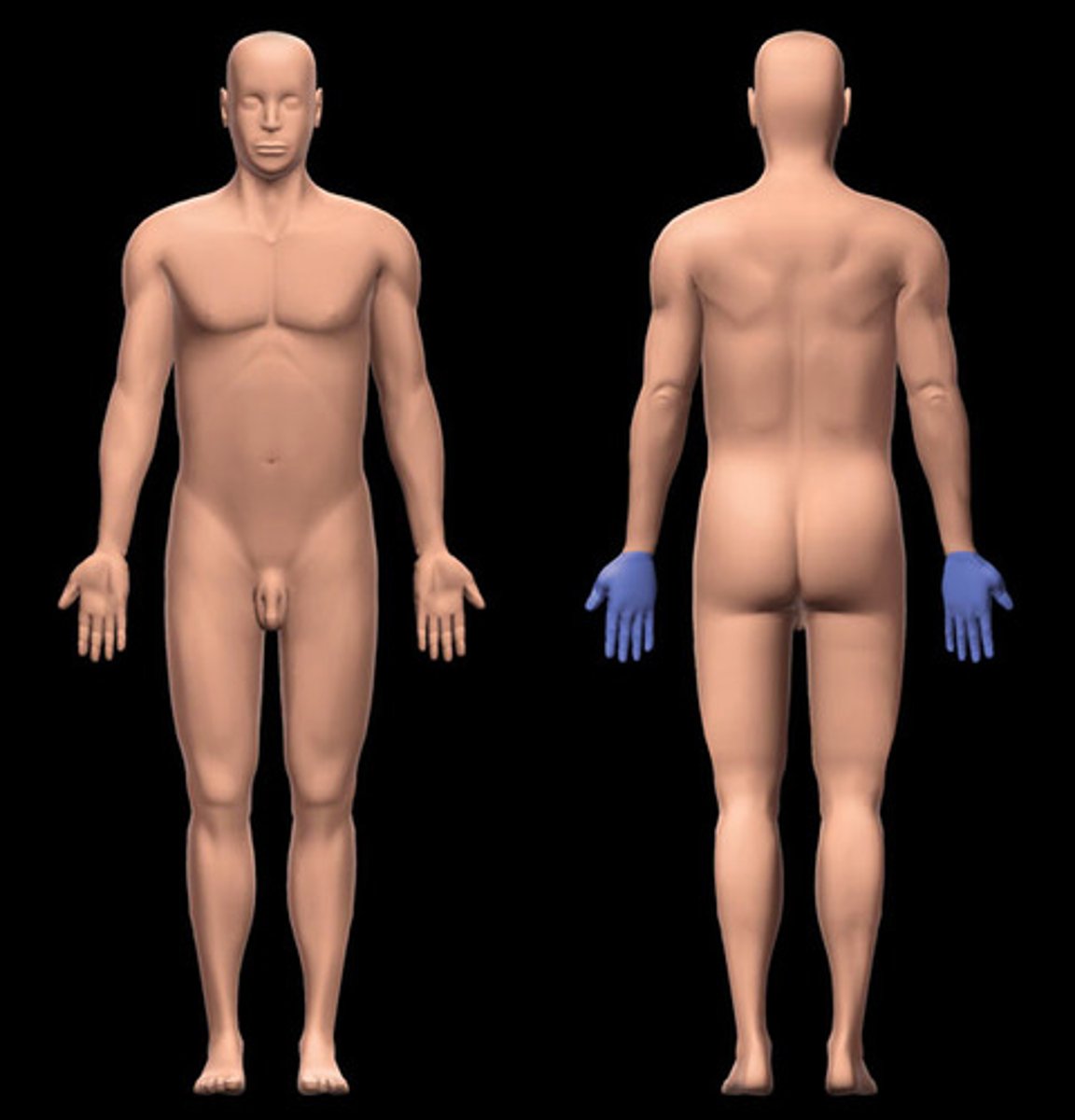
Dorsum region
back of hand
Digital region
fingers, toes

What are the 12 regions of the Leg/Ankle/Foot?
1. Gluteal
2. Femoral
3. Popliteal
4. Patellar
5. Peroneal
6. Pedal
7. Tarsal
8. Calcaneal
9. Hallux
10. Digital
11. Plantar
12. Dorsum
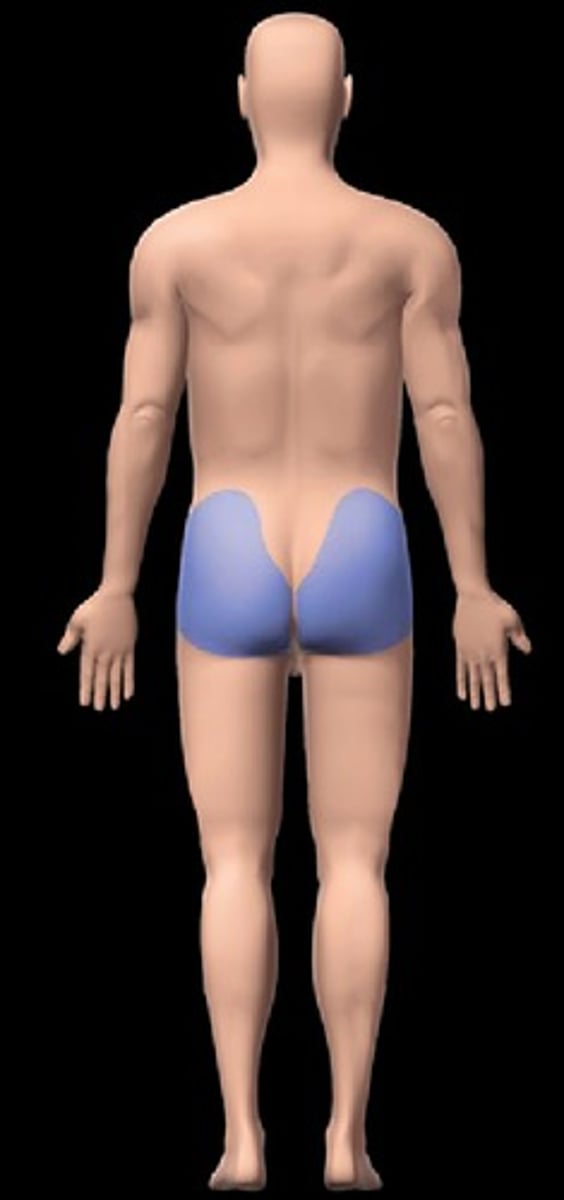
Gluteal region
buttocks; on posterior side of trunk
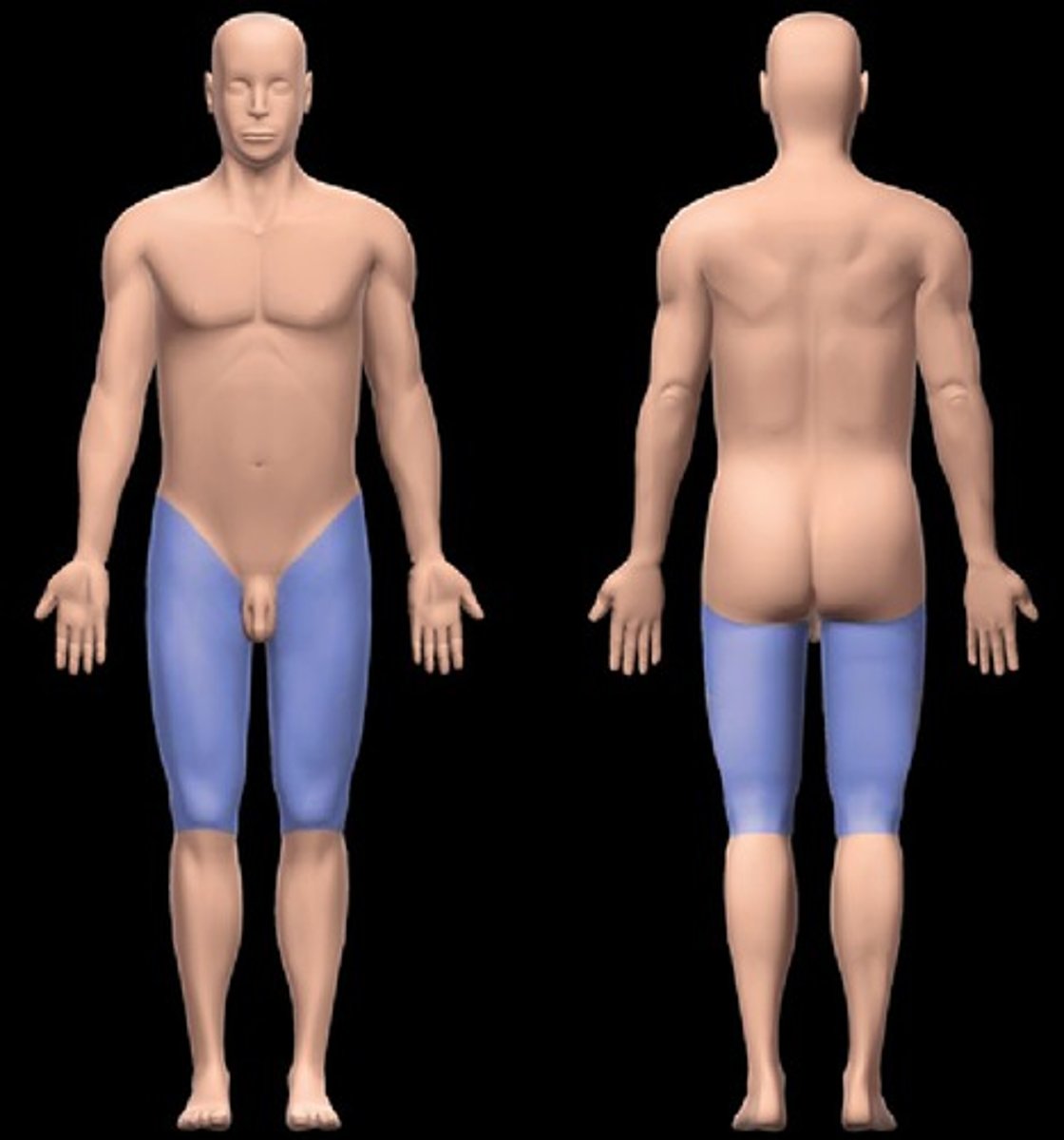
Femoral region
thigh region (hip to knee)
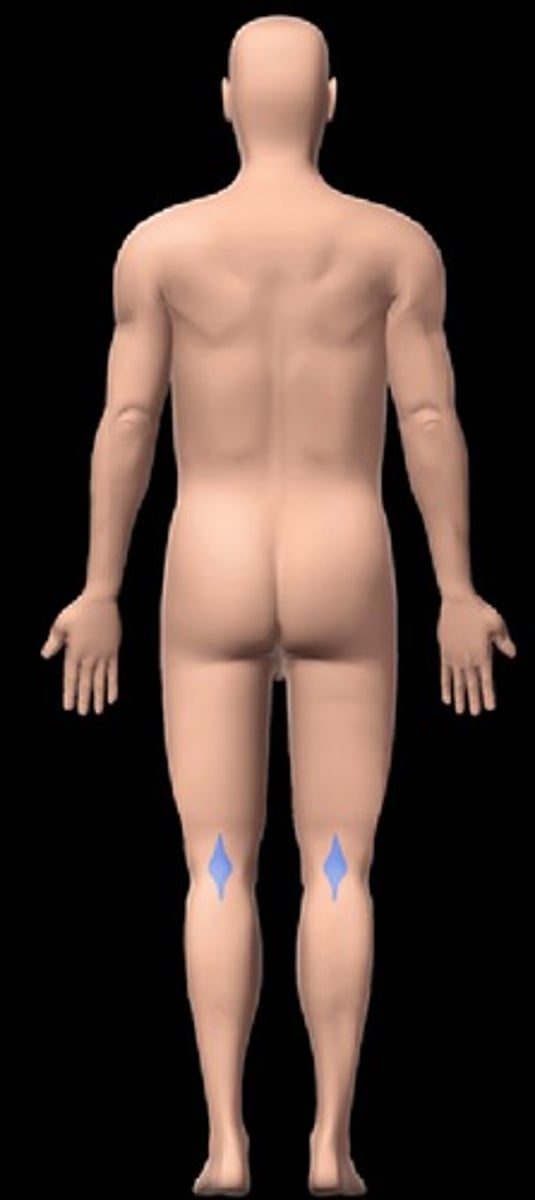
Popliteal region
the posterior side of the knee joint
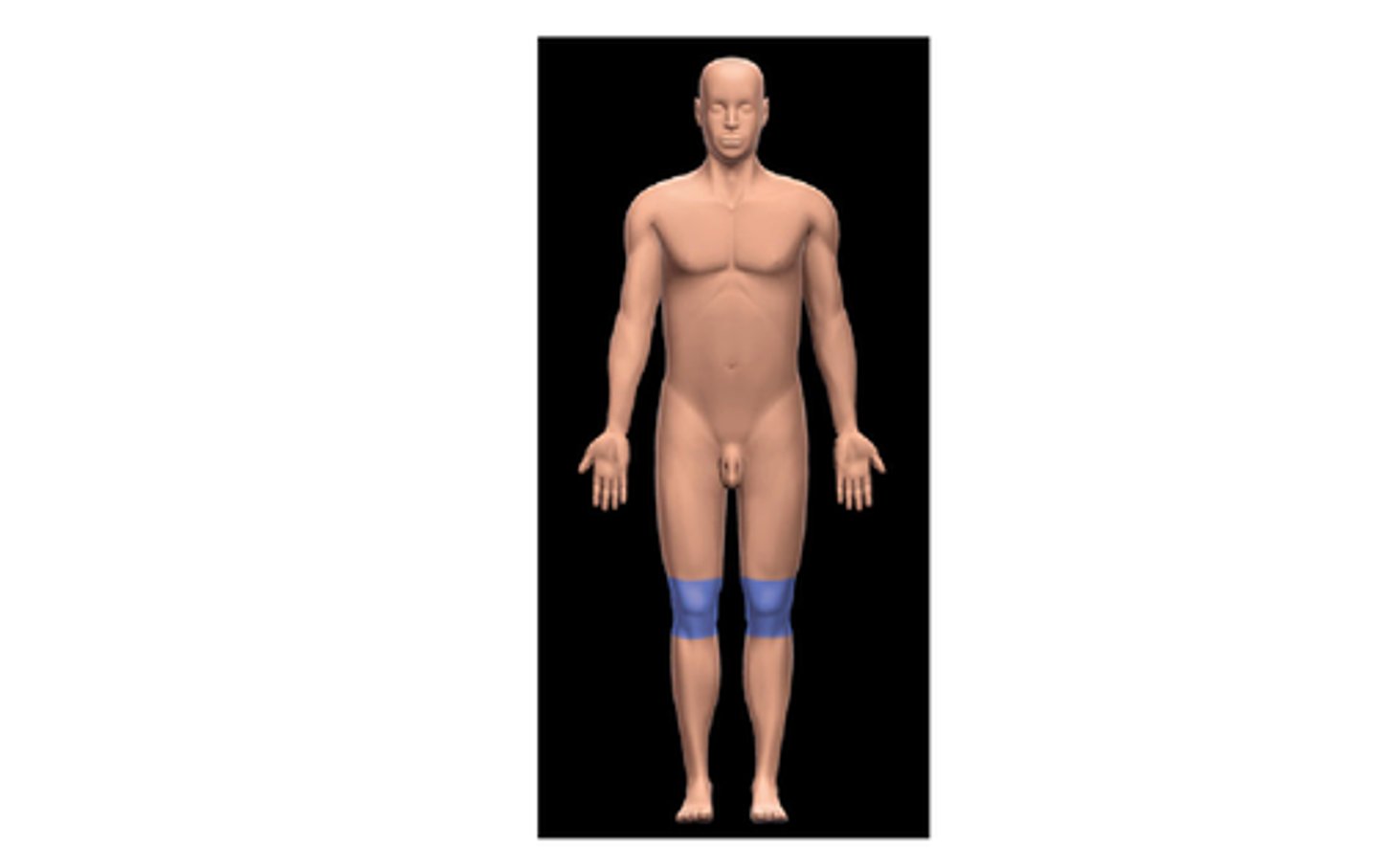
Patellar region
front of knee
Peroneal region
lateral side of leg-knee to ankle
also called fibular
Pedal region
foot region
Tarsal region
(tarsus) ankle- the union of the crural region with the foot. Tarsal bones are considered part of the foot.
Calcaneal region
heel of foot
Hallux region
big toe
Plantar region
sole of the foot, actually on the inferior body surface
abdominal cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver, and other organs
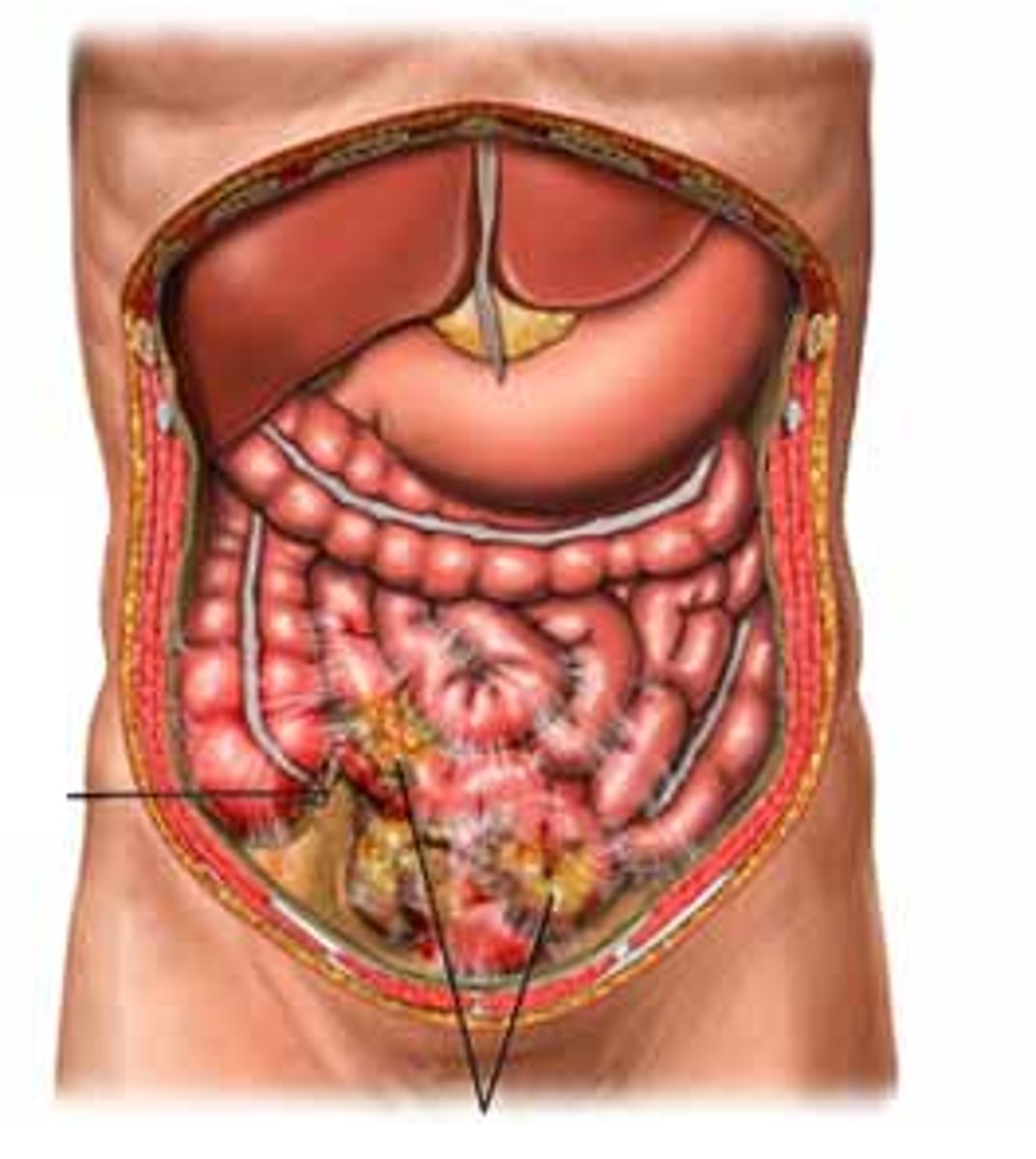
pelvic cavity
contains urinary bladder, portions of large intestine, and internal organs of reproduction
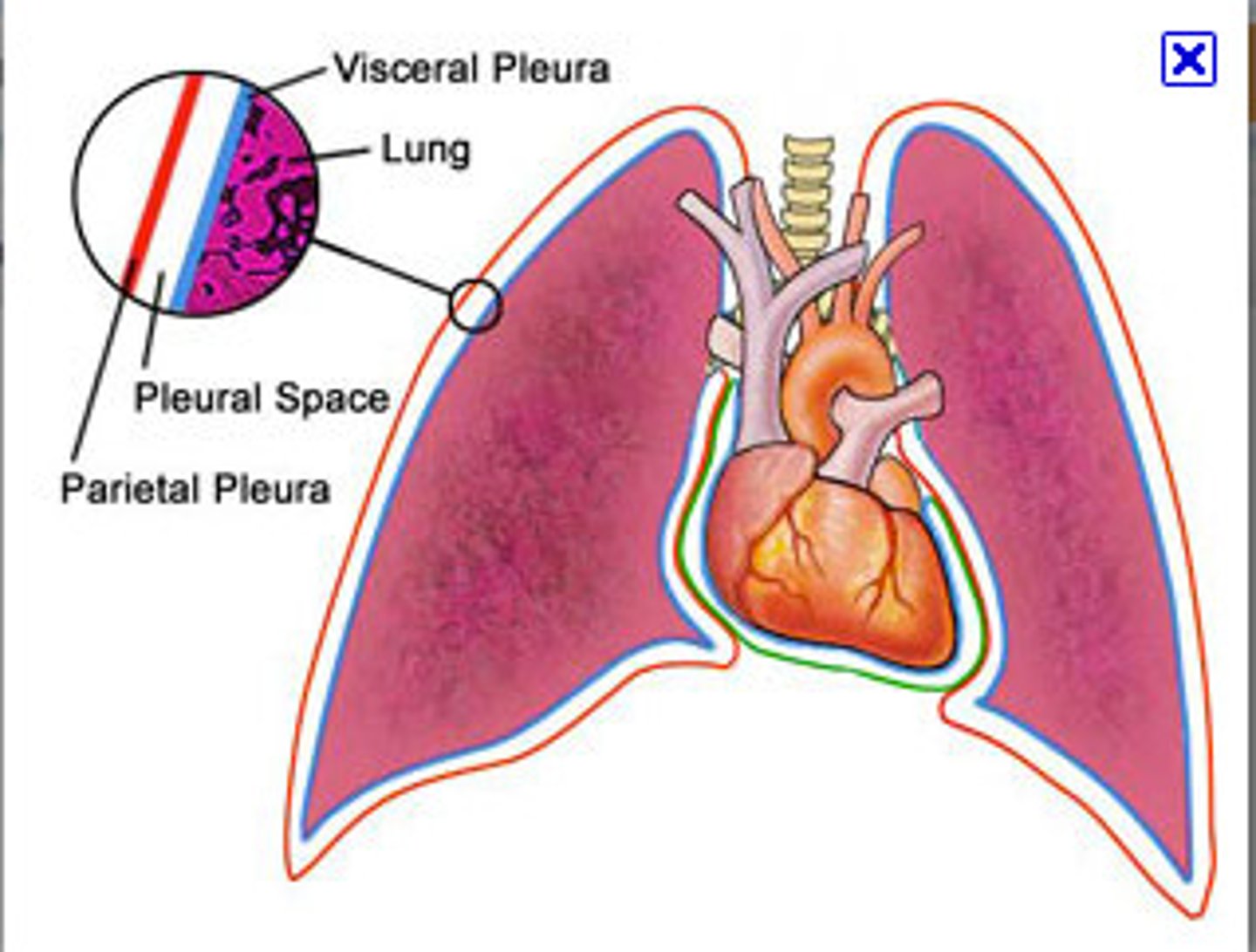
visceral pleura
the inner layer of pleura that surrounds each lung
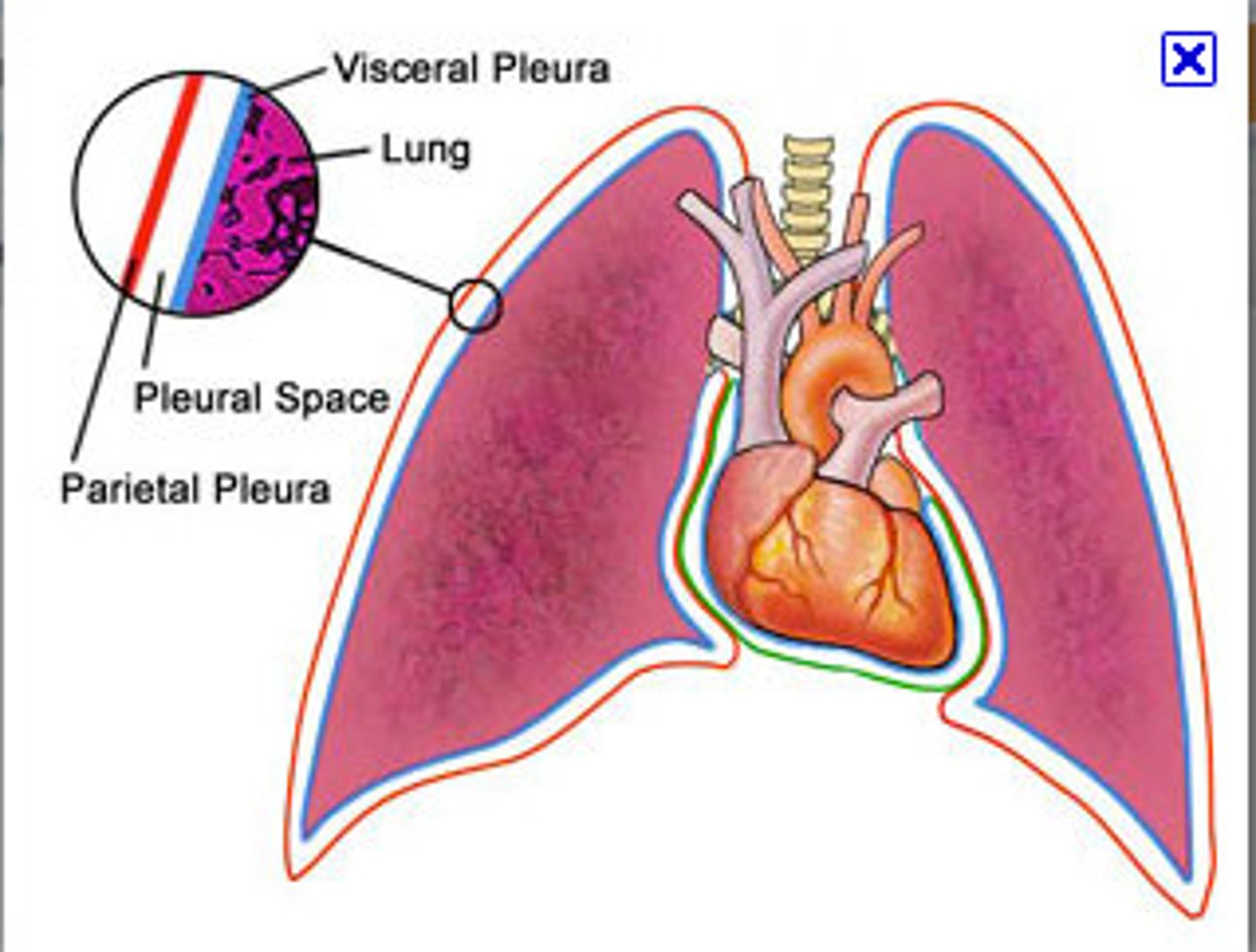
pleura
double-layered membrane surrounding each lung
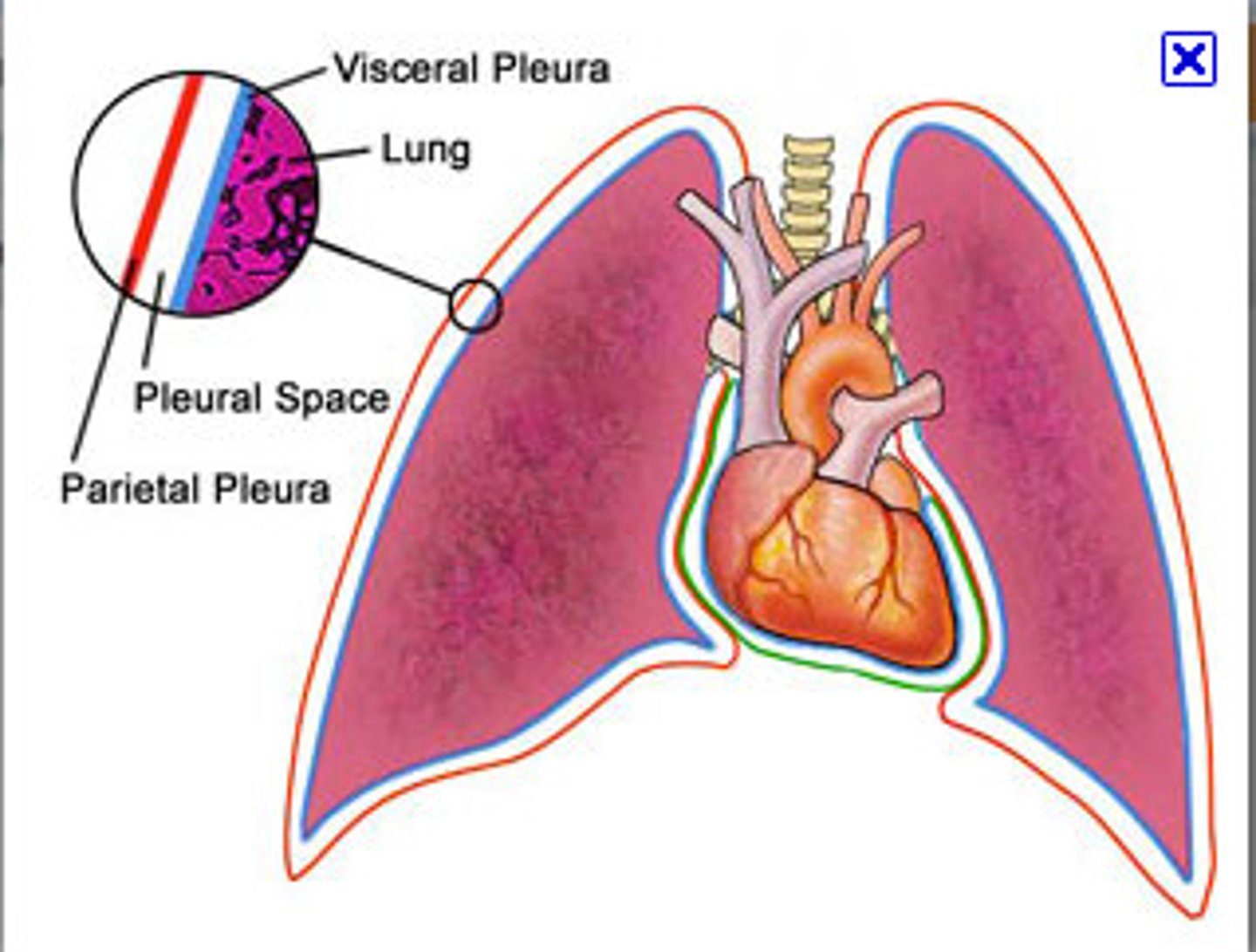
parietal pleura
outer layer of pleura lying closer to the ribs and chest wall
visceral peridcardium
covers the heart
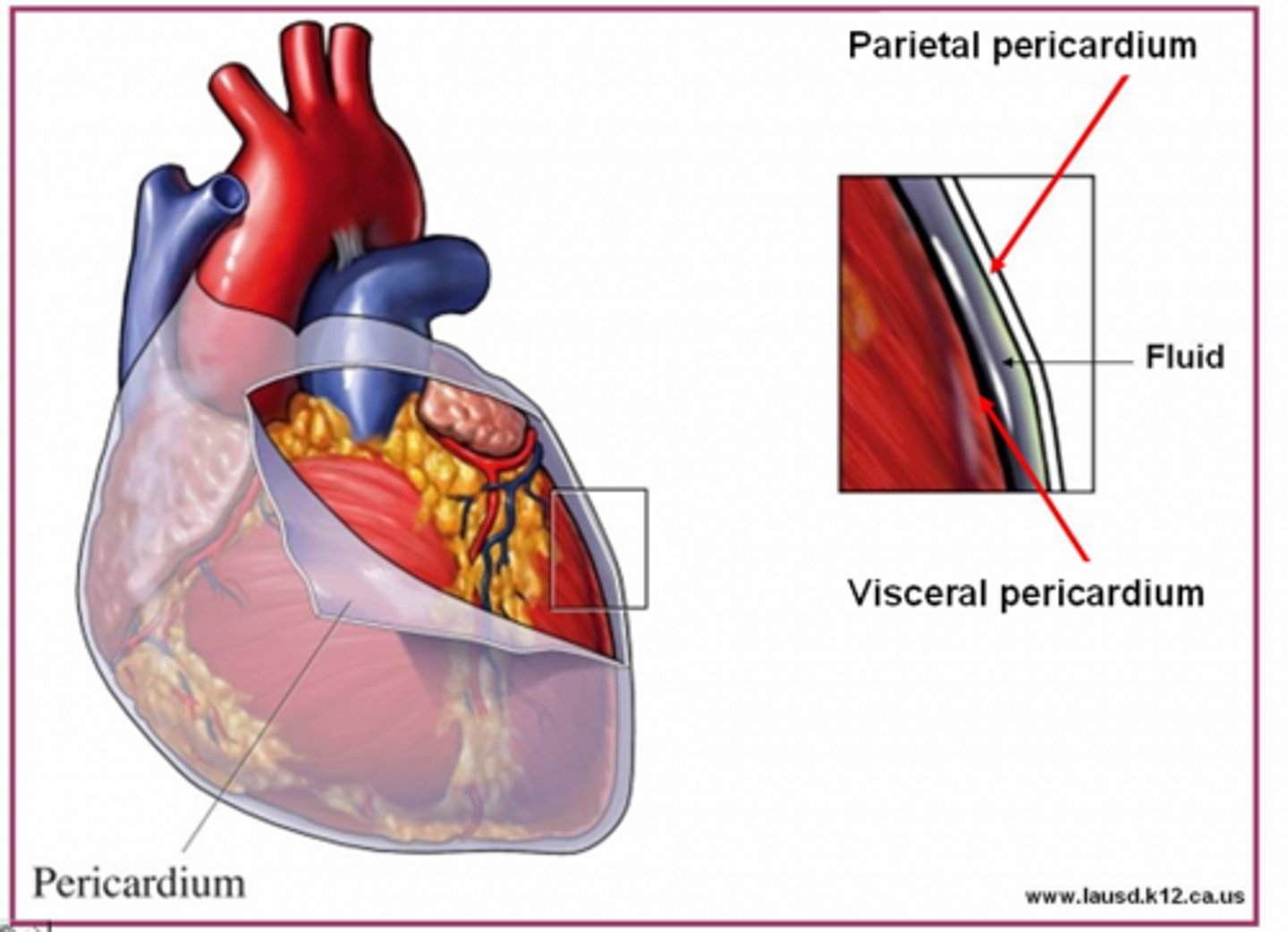
parietal pericardium
outer layer of pericardium surrounding heart
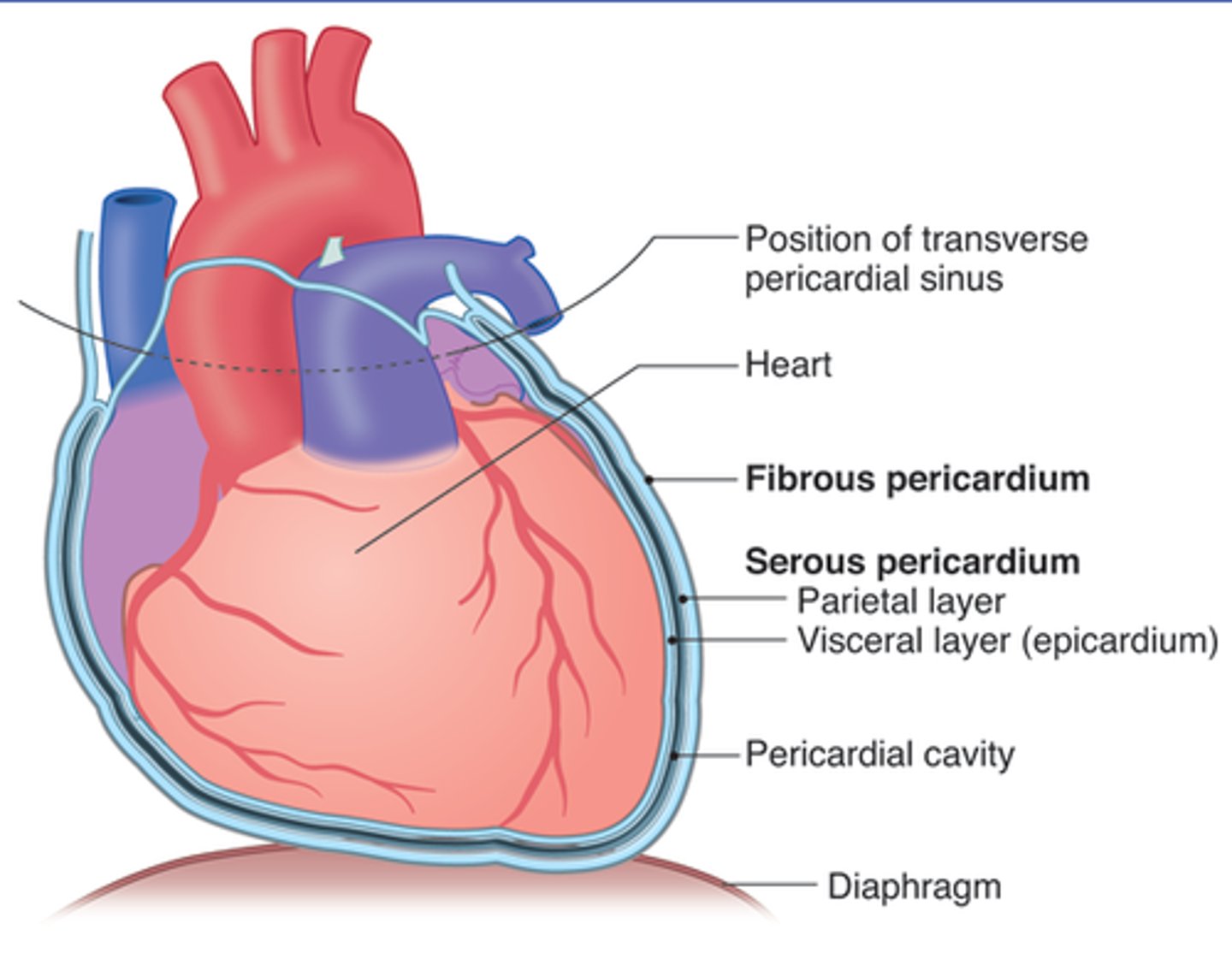
Percardium
the membrane enclosing the heart, consisting of an outer fibrous layer and an inner double layer of serous membrane.