BIOL20/20N - Exam 1 (Chapters 1-4, & 9)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/267
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
268 Terms
1
New cards
Hippocrates
-"Father of Western medicine"
-Believed that diseases had natural, not supernatural, causes.
-Believed that diseases had natural, not supernatural, causes.
2
New cards
Thucydides
Observed that survivors of the Athenian plague were subsequently immune to the infection
3
New cards
Marcus Vero
-Proposed that disease could be caused by certain minute creatures
-Thought swamps might have tiny, disease-causing animals
-Thought swamps might have tiny, disease-causing animals
4
New cards
Antoine van Leeuwenhoek
First to develop a lens powerful enough to view microbes (or animalcules)
"wee little beasties"
"wee little beasties"
5
New cards
Louis Pasteur
-Fermentation
-Pasteurization
-Vaccines for the treatment of diseases, including rabies, in animals and humans
-Swan-neck flask experiment
-Pasteurization
-Vaccines for the treatment of diseases, including rabies, in animals and humans
-Swan-neck flask experiment
6
New cards
Robert Koch
-First to demonstrate the connection between a single isolated microbe and a known human disease
-Established a protocol to determine the caused of infectious disease. Both scientists contributed significantly to the acceptance of the germ theory of disease
-Koch postulates
-Anthrax
-Cholera
-Tuberculosis
-Established a protocol to determine the caused of infectious disease. Both scientists contributed significantly to the acceptance of the germ theory of disease
-Koch postulates
-Anthrax
-Cholera
-Tuberculosis
7
New cards
fermentation (anaerobic respiration)
Process by which simple sugars are converted into alcohol
8
New cards
Carl Linnaeus
-"Father of Binomial Nomenclature"
-His original classification of the natural world consisted of plants, animals, and minerals
-His original classification of the natural world consisted of plants, animals, and minerals
9
New cards
Three Major Domains
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
10
New cards
Kingdoms of Eukarya
Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
11
New cards
Prokaryotes - Bacteria
-Genetic material (DNA) is not enclosed within a true nucleus
-Most have cell walls that contain peptidoglycan
-Most have cell walls that contain peptidoglycan
12
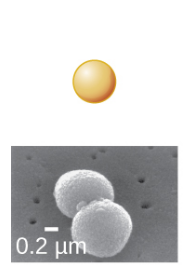
New cards
Coccus
What's the shape of this bacteria?
13
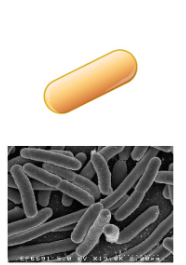
New cards
Bacillus
What's the shape of this bacteria?
14
New cards
Vibrio
What's the shape of this bacteria?
15
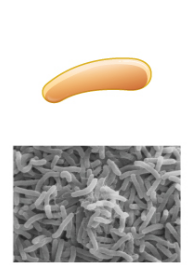
New cards
Coccobacillus
What's the shape of this bacteria?
16
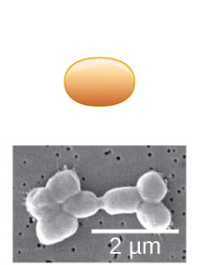
New cards
Spirillum
What's the shape of this bacteria?
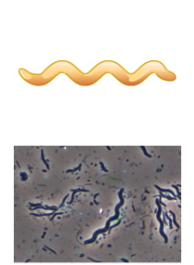
17
New cards
Spirochete
What's the shape of this bacteria?
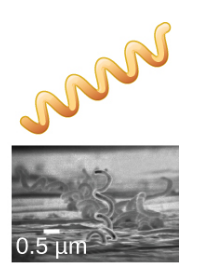
18
New cards
Prokaryotes - Archaea
\-Found in every habitat on earth (including extreme habitats)
**-Lack peptidoglycan cell walls
-No known human pathogen**
**-Lack peptidoglycan cell walls
-No known human pathogen**
19
New cards
Eukaryotes
-Cells contain a nucleus
-Uni- or multicellular
-Uni- or multicellular
20
New cards
Protists
-Eukaryotes that are not plants, animal, or fungi
-Algae and Protozoa
-Algae and Protozoa
21
New cards
Algae
-Plant-like protists
-Cellulose cell walls
-Use photosynthesis for energy
-Cellulose cell walls
-Use photosynthesis for energy
22
New cards
Protozoans
-Animal-like protists
-May be motile via pseudopods, cilia, or flagella
-Some are pathogens
-May be motile via pseudopods, cilia, or flagella
-Some are pathogens
23
New cards
Fungi
-Yeast and Mold
-Cell walls are usually made of chitin
-Cell walls are usually made of chitin
24
New cards
Viruses
-Don't fall under any of the Domains
-Acellular (not composed of cells)
-DNA and RNA core
-Acellular (not composed of cells)
-DNA and RNA core
25
New cards
Bacteriaology
Study of bacteria
26
New cards
Mycology
study of fungi
27
New cards
Protozoology
study of protozoa
28
New cards
Virology
study of viruses
29
New cards
Pathology
study of protozoa and parasitic worms
30
New cards
Brightfield Microscopes
When using this, microorganisms will appear colored against a bright background
31
New cards
Darkfield Microscopes
When using this, the field will be dark and the organism will be outlined by the dark field
32
New cards
Electron Microscopes
-Uses beams of electrons for energy
-Uses a vacuum as a medium
-Uses magnets for objectives
-Image is shown on a screen
-Uses a vacuum as a medium
-Uses magnets for objectives
-Image is shown on a screen
33
New cards
Differences between Light & Electron microscopes
1) Energy; LMs use plain white light while EMs use beams of electrons
2) Medium; LMs use air while EMs use a vacuum
3) Objectives; Glass lens in LMs while magnets in EMs
4) Image display; LMs have ocular lens to see the image while EMs use a screen to show the image
2) Medium; LMs use air while EMs use a vacuum
3) Objectives; Glass lens in LMs while magnets in EMs
4) Image display; LMs have ocular lens to see the image while EMs use a screen to show the image
34
New cards
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) & Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Types of electron microscope
35
New cards
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Used to view thin specimens through which electrons can pass generating a projection image
36
New cards
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Uses a focused beam of high-energy electrons to generate a variety of signals at the surface of solid specimens
37
New cards
Reflection
The bouncing back of a wave when it hits a surface through which it cannot pass
38
New cards
Transmission
Lightwave travels through a material
39
New cards
Absorbance
Material captures the energy of a light wave
40
New cards
Opaque
When most (or all) of the light is absorbed
41
New cards
Transparent
Allowing all the light to pass through
42
New cards
Refraction
The bending of light when it passes through one medium to another
43
New cards
Refractive Index
a measure of the light-bending ability of a medium
44
New cards
D
Which letter represents a refracted ray of light?
45
New cards
C
Which letter represents a reflected ray of light?
46
New cards
Magnification
the ability of a lens to enlarge the image of an object when compared to the real object
47
New cards
Resolution
-Ability to tell that 2 separate points are separate
-Affected by wavelength and numerical aperture
-Affected by wavelength and numerical aperture
48
New cards
Shorter wavelengths have more energy while longer wavelengths have less energy
What is the correlation between energy and wavelength on the light spectrum?
49
New cards
Robert Hooke
-Coined the term "cell"
-Observed dead cork cells under a microscope
-Observed dead cork cells under a microscope
50
New cards
Zaccharias and Hans Janssen
-May have invented the telescope, the simple microscope, and the compound microscope
-Historical evidence is inconclusive
-Historical evidence is inconclusive
51
New cards
1) Eyepiece
2) Revolving nose piece
3) Objective lens
4) Coarse focus
5) Fine Focus
6) Stage
7) Illuminator
8) Condenser and Diaphragm
9) X-Y mechanical stage knobs
10) Rheostat
2) Revolving nose piece
3) Objective lens
4) Coarse focus
5) Fine Focus
6) Stage
7) Illuminator
8) Condenser and Diaphragm
9) X-Y mechanical stage knobs
10) Rheostat
Label the following with the following terms:
Coarse focus
Condenser
Diaphragm
Eyepiece (ocular lens)
Fine focus
Illuminator
Objective lens
Revolving nose piece
Rheostat
Stage
X-Y mechanical stage knobs
Coarse focus
Condenser
Diaphragm
Eyepiece (ocular lens)
Fine focus
Illuminator
Objective lens
Revolving nose piece
Rheostat
Stage
X-Y mechanical stage knobs
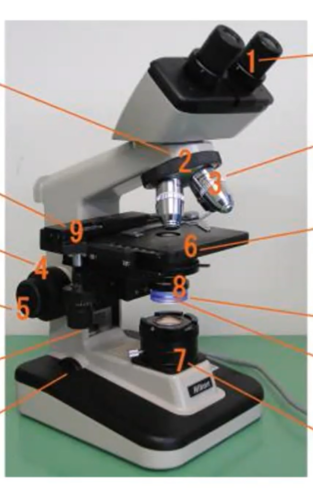
52
New cards
Condenser
Gathers the light coming in from the illuminator and concentrates that light into a light cone on the specimen
53
New cards
Diaphragm
Controls the amount of light passing through the opening of the stage and, consequently, the numerical aperture of the condenser
54
New cards
Rheostat
Controls the intensity of the light source on the microscope
55
New cards
10x, 40x, 100x
What are the magnifications of the 3 objectives in a microscope?
56
New cards
Total Magnification
Objective lens X Ocular lens
57
New cards
Oil Immersion Lens
Improves resolutions by reducing refractive index
58
New cards
1000x
What is the total magnification of an object viewed using a 10x ocular lens and a 100x objective lens on a brightfield microscope?
59
New cards
High numerical aperture and short wavelength
What is needed to see a clear image under a microscope?
60
New cards
Stains
Used to increase contrast between the cells and the background, making them easier to see under the microscope
61
New cards
Simple, differential, special
Three types of staining techniques
62
New cards
Simple stains
Will generally make all of the organisms in a sample appear to be the same if the sample contains more than one type of organism
63
New cards
Differential stains
Two organisms in a differentially stained sample may appear to be different colors
E.g. endospore staining, flagella staining, and capsule staining
E.g. endospore staining, flagella staining, and capsule staining
64
New cards
Acidic, Basic, Gram, & Acid-fast
Special stains (4)
65
New cards
Acidic stain
Negatively charged stain
-Stains positively charged molecules and structures like proteins
-Result can be either a positive or negative stain, depending on the cell's chemistry
-Stains positively charged molecules and structures like proteins
-Result can be either a positive or negative stain, depending on the cell's chemistry
66
New cards
Basic stain
-Positively charged stain
-Stains negatively charged molecules and structures like nucleic acids and proteins
-Results in a positive stain
-Stains negatively charged molecules and structures like nucleic acids and proteins
-Results in a positive stain
67
New cards
Crystal violet, Iodine, alcohol, safranin
What is the Gram stain order?
68
New cards
Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM)
-Uses a probe passed horizontally at a constant distance just above the specimen while the intensity of the current is measured
-Can map the structure of surfaces at the atomic level
-Works best on conducting materials but can also be used to examine organic materials such as DNA, if fixed on surface
-Can map the structure of surfaces at the atomic level
-Works best on conducting materials but can also be used to examine organic materials such as DNA, if fixed on surface
69
New cards
Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)
-Can be used in several ways, including using a laser focused on a cantilever to measure the bending of the tip or a probe passed above the specimen while the height needed to maintain a constant current is measured
-Useful to observe specimens at the atomic level and can be more easily used with nonconducting samples
-Useful to observe specimens at the atomic level and can be more easily used with nonconducting samples
70
New cards
AFM
This image was probably achieved with what type of microscope?
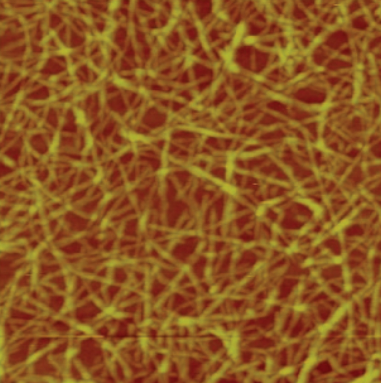
71
New cards
STM
This image was probably achieved with what type of microscope?
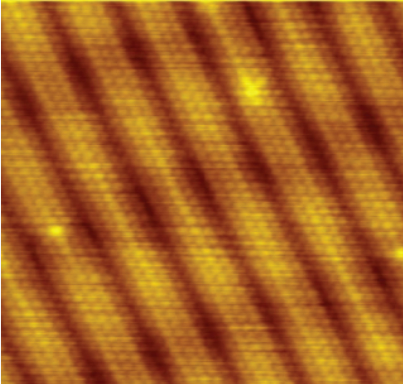
72
New cards
Iodine
What mordant is used in gram-staining?
73
New cards
Alcohol
What decolorizer is used in gram-staining?
74
New cards
Safranin
What is the last thing that is added when doing gram-stains?
75
New cards
Blue/Purple
What color are gram-positive cells?
76
New cards
Red/Pink
What color are gram-negative cells?
77
New cards
Coccus
Describe the bacteria

78
New cards
Diplococci
Describe the bacteria

79
New cards
Streptococci
Describe the bacteria
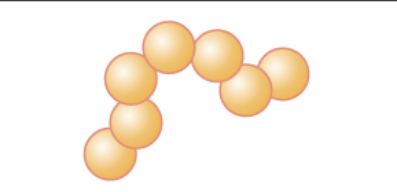
80
New cards
Straphylococci
Describe the bacteria
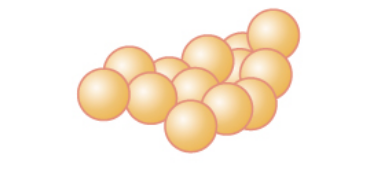
81
New cards
Tetrad
Describe the bacteria

82
New cards
Bacillus
Describe the bacteria

83
New cards
Streptobacilli
Describe the bacteria
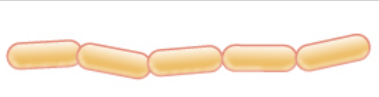
84
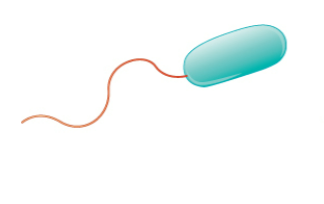
New cards
Monotrichous
Describe the following
85
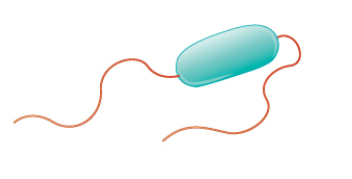
New cards
Ampithrichous
Describe the following
86
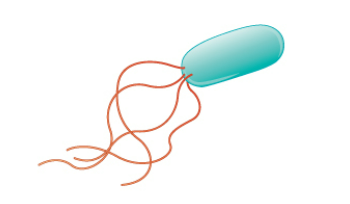
New cards
Lophotrichous
Describe the following
87
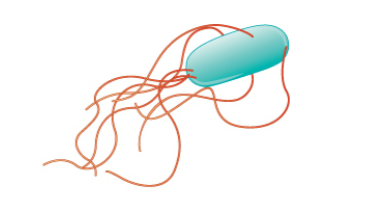
New cards
Peritrichous
Describe the following
88
New cards
Theory of Spontaneous Generation
Stated that organisms arose from nonliving matter as long as it had "breath"
89
New cards
Francesco Redi
Demonstrated that maggots were the offspring of flies, not products of spontaneous generation with his "meat in a jar" experiment
90
New cards
Miasma Theory
Before the discovery of microorganisms, scientists believed diseases came from particles in decomposing matter that spread through the air "poisonous air"
91
New cards
Germ Theory
States that diseases result from microbial infection. Microbes in the air cause disease and can spoil food. The way to prevent these diseases is by washing your hands
92
New cards
John Needham
Heated broth in sealed flasks. When the broth became cloudy with microorganisms, he mistakenly concluded that they developed spontaneously from the broth
93
New cards
Lazzaro Spallazani
Recreated Needham's experiment and obtained results that countered Needham's.
94
New cards
Swan Flask Experiment
Louis Pasteur did this experiment to refute the long-disputed theory of spontaneous generation.
95
New cards
Theory of Biogenesis
states that only living organisms can produce other living organisms
96
New cards
Schleiden
Described plant tissues as being composed of cells
97
New cards
Schwann
Observed cells in animal tissue
98
New cards
Schleiden's and Schwann's Observation
Laid the foundation for the idea that cells are the fundamental components of plants and animals
99
New cards
Rudolf Virchow
Popularized the cell theory in an 1855 essay entitled "Cellular Pathology"
100
New cards
Robert Remak
Came up with the idea that all cells come from pre-existing cells