Anatomy: Exam 2
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
207 Terms
Describe fibrous joints and give examples of them. What kind of tissue is present?
Characteristics: No joint cavity, bones held by dense connective tissue
Ex: Synarthrosis (sutures), syndesmosis (interosseous membrane), gomphosis (teeth)
Describe cartilaginous joints and give examples of them.
Characteristics: no joint cavity, bones joined by cartilage
Ex: symphysis (pubic symphysis & intervertebral discs), rib to sternum (synchondrosis)
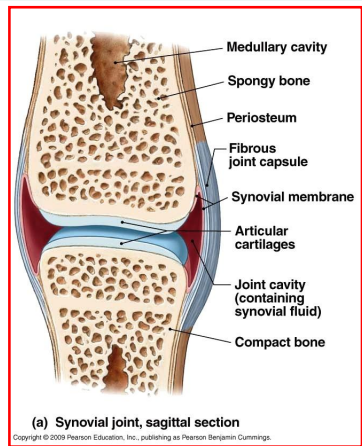
Describe synovial joints and give examples of them.
Characteristics: fluid-filled cavity (unlike the others), enclosed within connective tissue, bones are attached by ligaments
Ex: elbow, knee, etc.
Describe synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis, and diarthrosis. Give examples of each.
Synarthrosis- immobile joint, fibrous or cartilaginous
Ex: tooth to jaw, rib to sternum
Amphiarthrosis- slightly mobile, fibrous or cartilaginous
Ex: tibia to fibula articulation (interosseous membrane)
Diarthrosis- FREELY mobile, ALL synovial joints
Ex: knee joint, elbow joint, etc.
Where is synovial fluid secreted from? What is the function of synovial fluid?
The fluid is secreted from the synovial membrane
Fluid acts as a shock absorber & decreases friction
List the accessory parts of a joint.
Fat- common in the back of the knee (popliteal area)
Menisci- made of fibrous cartilage
Ligaments- examples of ACL & PCL
Bursae- between ligaments & tendons
Tendons- attach muscle to bone
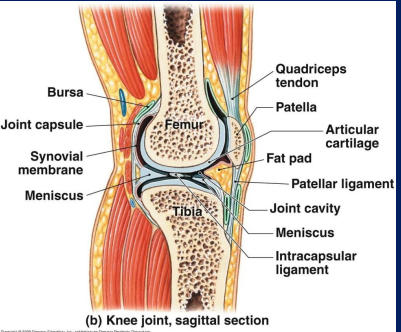
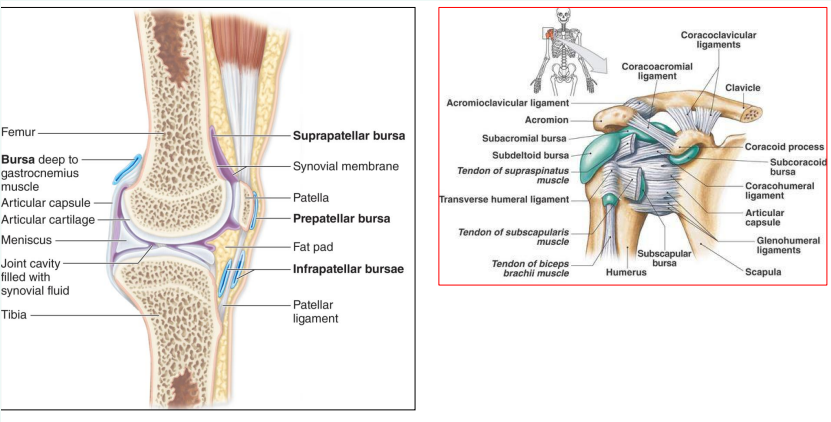
Describe the function of bursae
Synovial fluid-filled saclike structures that minimize friction at joints
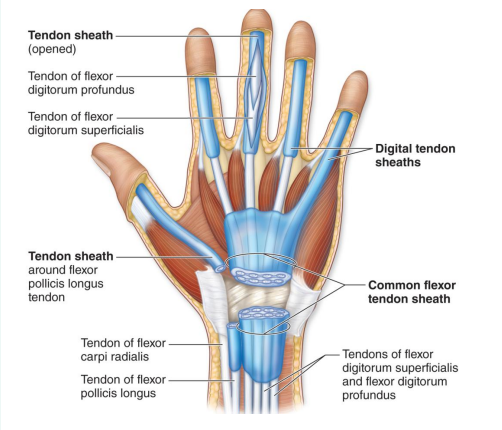
What is the function of the tendon sheath?
Surrounds a tendon to protect it from friction
What is the difference between ligaments and tendons?
Ligaments- connect bone to bone for stability
Tendons- connects muscle to bone for movement
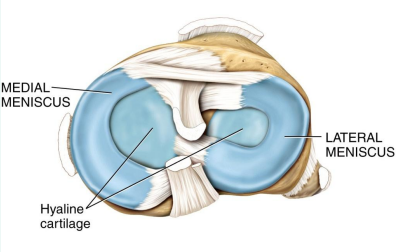
Describe the function of menisci.
Pads of dense fibrocartilage
Allows bones of different shapes to fit together tightly
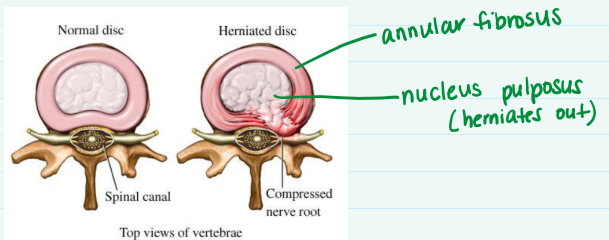
What is the part of intervertebral disc that pulps out in a herniated disc?
Nucleus pulposus
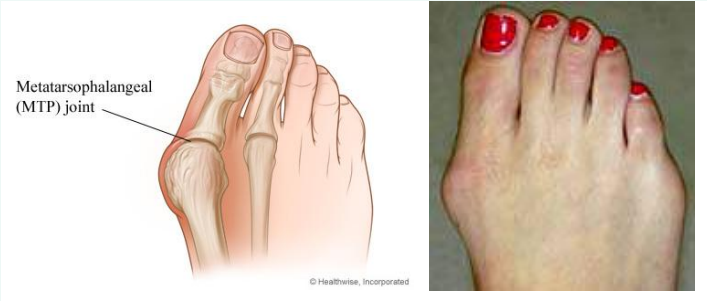
What is a bunion?
Swelling of metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint
Sprain vs. strain
Sprain- tear in a ligament
Strain- overstretching of a ligament
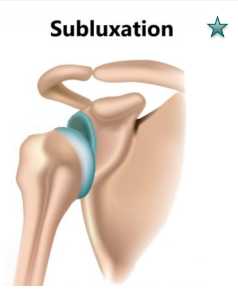
Subluxation vs. full luxation
Subluxation- partial dislocation
Full luxation- full dislocation
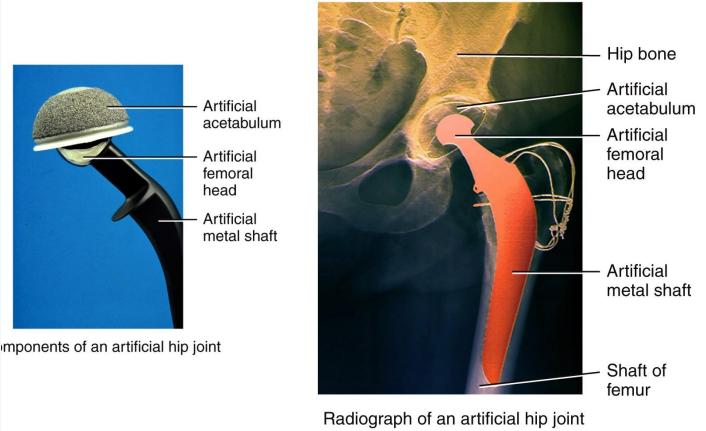
Why is the “ball” part of the artificial joint in a hip replacement rough?
It is rough because it allows bone to grow into it and cement it in place
Osteoarthritis (OA) vs. rheumatoid arthritis
Osteoarthritis- degenerative joint disease where cartilage is lost (linked to age)
Rheumatoid arthritis- autoimmune disease where immune system attacks joints
What are characteristics and function of muscle?
Characteristics: contractile, excitable, elastic
Functions: movement, support, storage, & thermogenesis
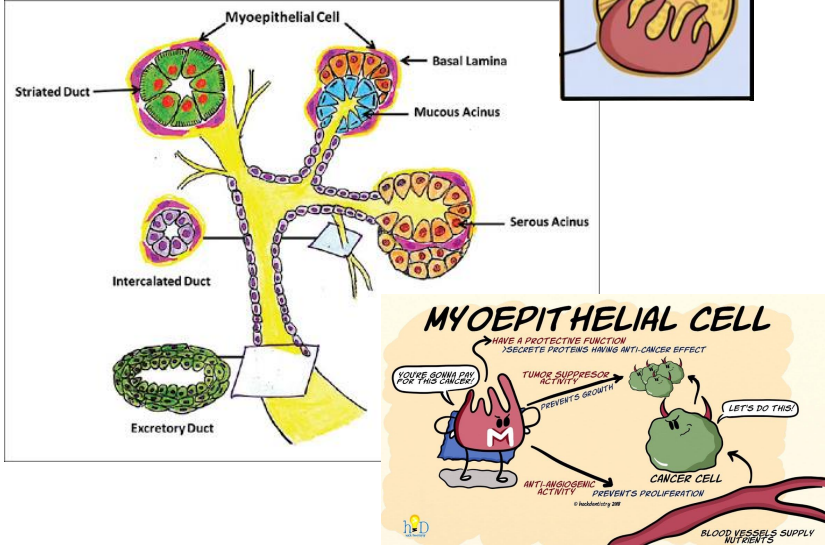
What are basket cells (myoepithelial cells)?
They secrete proteins that have an anti-cancer effect
What are characteristics of skeletal muscle?
Voluntary, striated, multi-nucleated, lots of mitochondria, very vascular, amitotic (does NOT divide)
How can you increase muscle mass if muscle fibers are amitotic?
When there are tears, your muscle fibers (muscle cells) grow larger
This is partially due to satellite cells which are stem cells
Superficial fascia vs. deep fascia
Superficial fascia- provides insulation, attaches skin to muscle
Deep fascia- partitions muscles into groups; connects ligaments, tendons, etc.
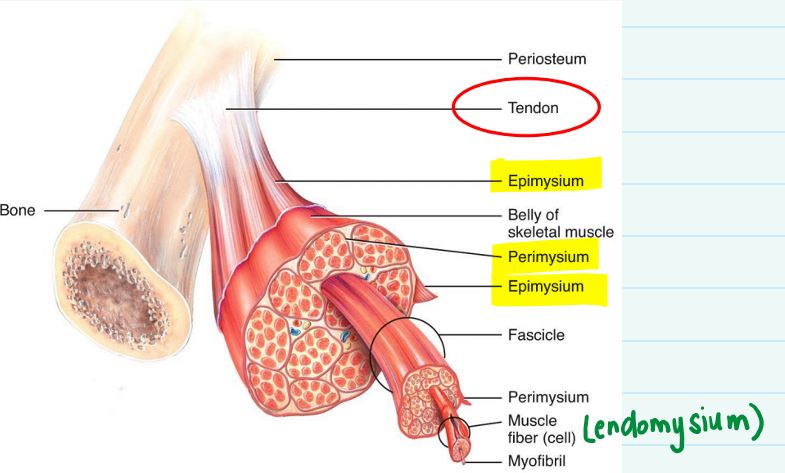
Describe the 3 layers of fascia, and what kind of tissue is in each.
1) Epimysium- surrounds entire group of muscle fascicles
Tough fibrous connective tissue
2) Perimysium- provides pathway for blood vessels & nerves
Areolar connective tissue
3) Endomysium- surrounds each individual muscle fiber
Areolar connective tissue
What are myofibrils and where are they found?
Myofibrils consist of actin & myosin
Found in sarcoplasm (cytoplasm of muscle cells)
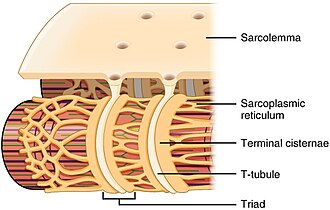
Describe sarcoplasmic reticulum and its function.
Fluid-filled system of sacs that surround each myofibril
Stores and releases calcium
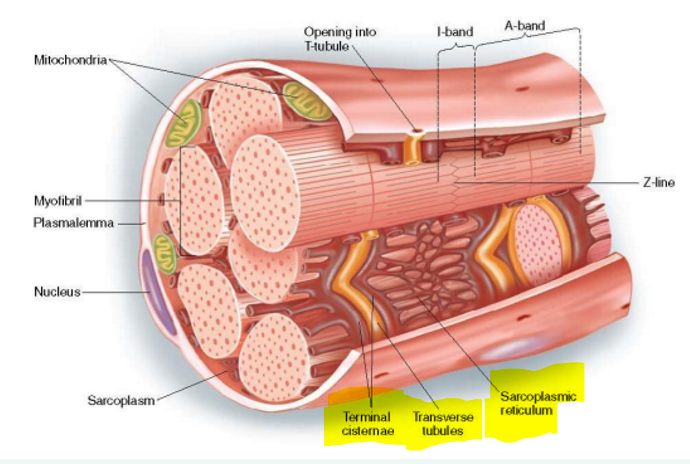
Describe T-tubules and its function.
Invaginations of sarcolemma that help propagate action potentials
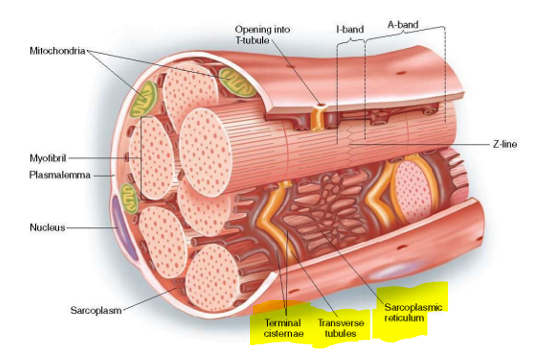
Describe terminal cisterns and its function.
Part of sarcoplasmic reticulum & align with T tubules to form triad
Release calcium to trigger muscle contractions
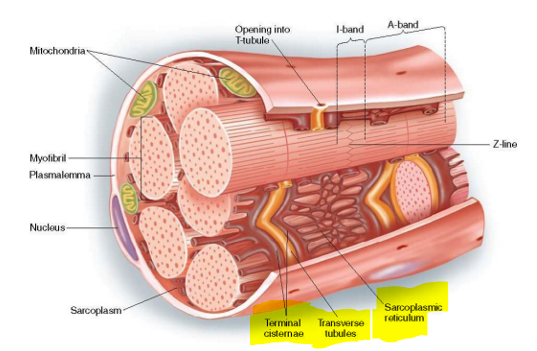
What forms the triad?
Transverse tubules (t-tubules) & two terminal cisternae on either side of it
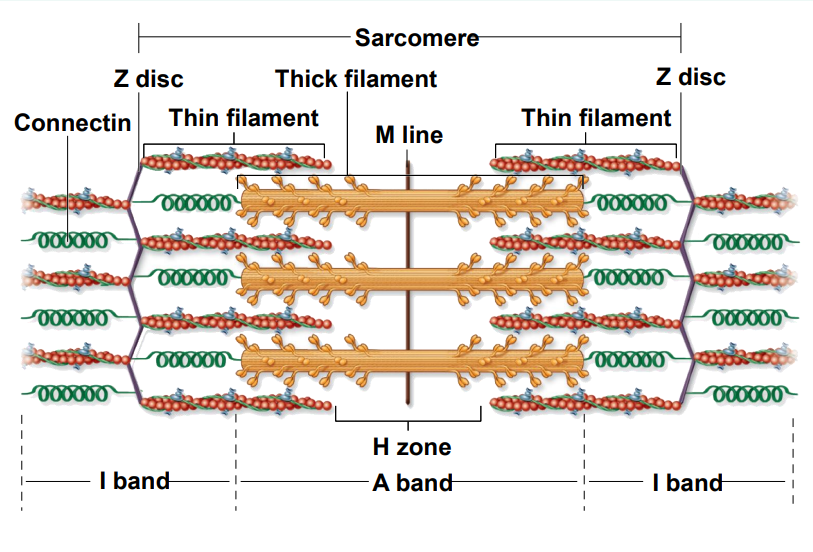
Describe a sarcomere.
Measured from Z disc to Z disc
Site of muscle contraction
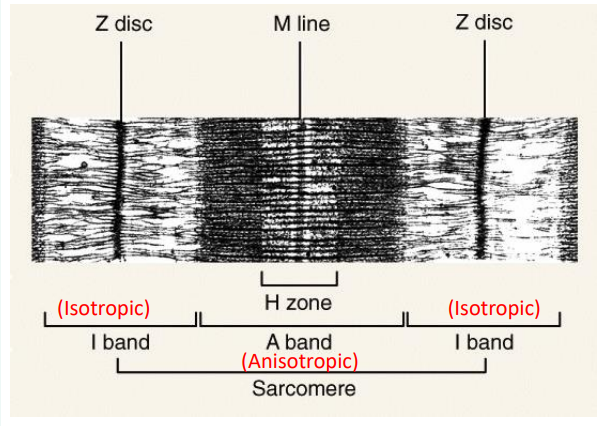
Where do the striations in muscle come from?
Actin & myosin
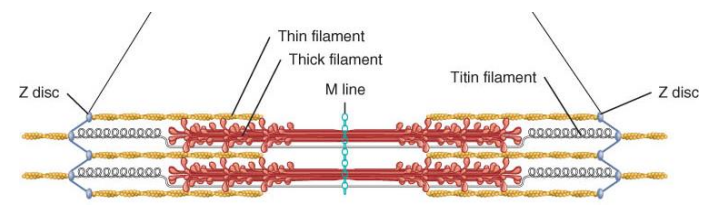
What are the contractile, regulatory, & structural proteins?
1) Contractile- myosin & actin
2) Regulatory- troponin & tropomyosin
3) Structural- titin, myomesin, nebulin, & dystrophin
Structural proteins provide alignment, elasticity, etc.
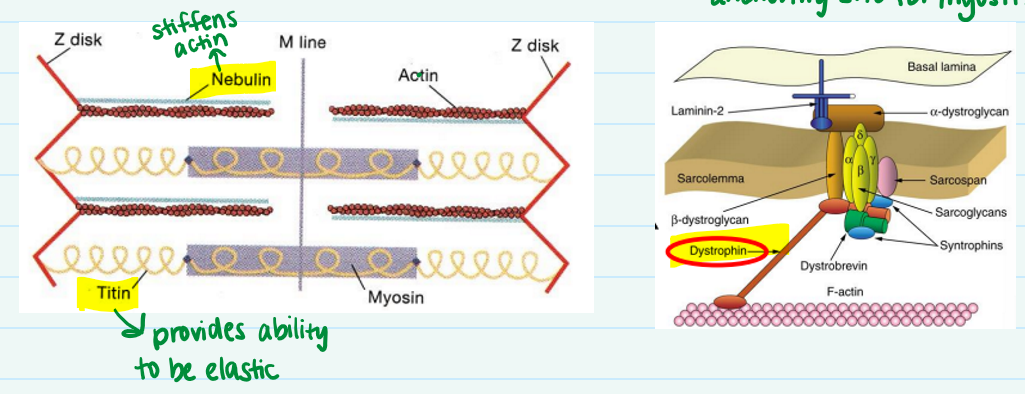
Describe the function of dystrophin, myomesin, titin, & nebulin.
Myomesin- protein that creates anchoring site for myosin
Dystrophin- keeps actin filaments aligned with sarcolemma
Titin- provides ability to be elastic
Nebulin- stiffens actin
Which band or zone is not visible under the microscope? What is the A band composed of?
H zone is NOT present in the microscope view
The A band consists of the overlap of actin & myosin
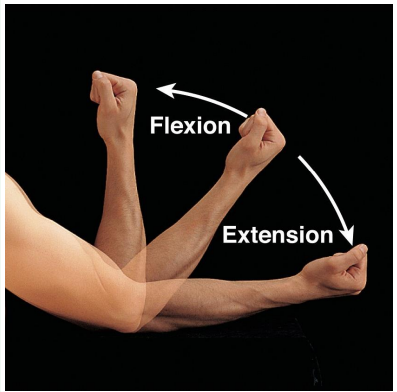
Describe flexion & extension.
Flexion- decrease angle between bones
Extension- increases angle between bones
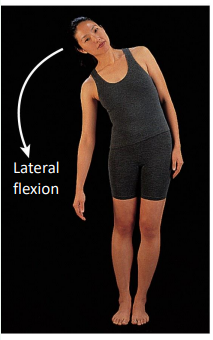
Describe lateral flexion.
Flexion in a frontal plane usually involving the head or trunk
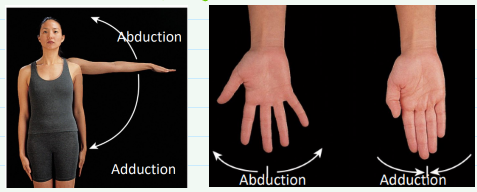
Abduction vs. adduction
Abduction- moving a body part away from the body
Adduction- moving a body part towards midline
Define circumduction, supination, & pronation.
Circumduction- when distal end of body part makes a circle
Supination- movement where palms are anterior
Pronation- palms are posterior
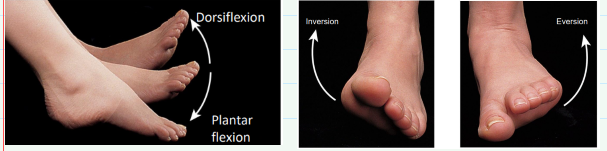
Define inversion, eversion, dorsiflexion, & plantar flexion.
Inversion- sole of foot faces medially
Eversion- sole of foot faces laterally
Dorsiflexion- dorsum of foot moves up towards tibia
Plantar flexion- sole of foot moves posteriorly
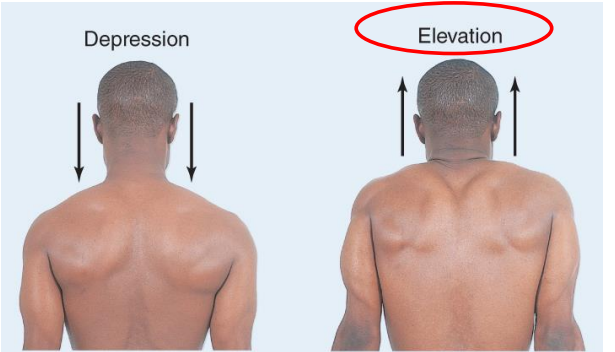
Elevation vs. depression
Elevation- upward movement
Depression- downward movement
Origin vs. insertion of muscle
Origin- stationary position
Insertion- movable end
What layer of fascia arranges muscle?
Perimysium creates compartmentalization of muscle
Arrangement determines range, muscle power, & speed
What is the origin and insertion for muscles of facial expression?
Origin: fascia or bones
Insertion: skin
Describe the function of the genioglossus & geniohyoid.
Genioglossus- allows you to stick out & roll your tongue
Geniohyoid- depresses the mandible
What are the functions of the suprahyoid & infrahyoid?
Functions to stabilize hyoid bone for tongue movement
Which muscle is considered a “white zone”? Explain why.
Linea alba is considered a “white zone” because there’s no blood supply nor nerve tissue
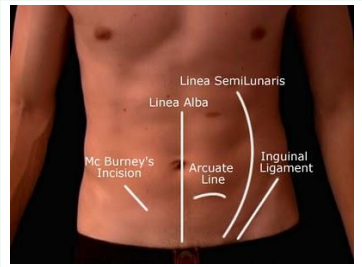
What is the function of the muscles in the anterior abdominal wall?
Contains viscera (organs), compresses cavity, flexes, & rotates column
Why is it easy for males to get an inguinal hernia?
Inguinal canal allows passage of spermatic cord, blood supply, & nerve
Bowel can poke through this canal and cause an inguinal hernia
Which three muscles form the inguinal canal?
External oblique, internal oblique, & transversus
Frontalis (function, origin & insertion)
Function: elevates eyebrows
Origin: epicranial aponeurosis
Insertion: skin of eyebrows
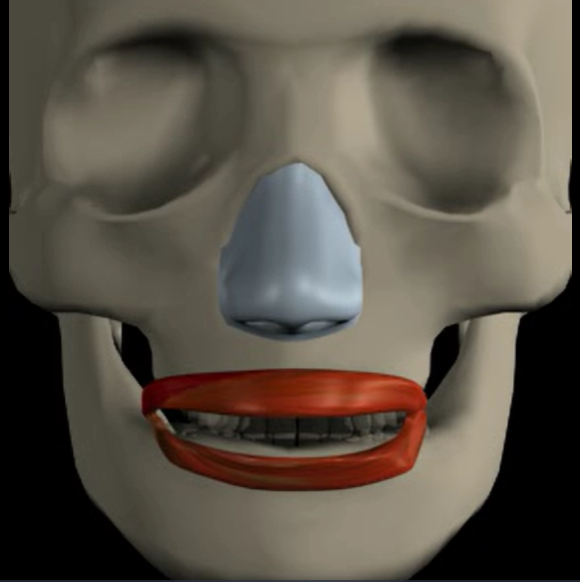
Orbicularis oris (function, origin & insertion)
Function: closes, protrudes lips
Origin: fibers surrounding mouth
Insertion: skin of lips
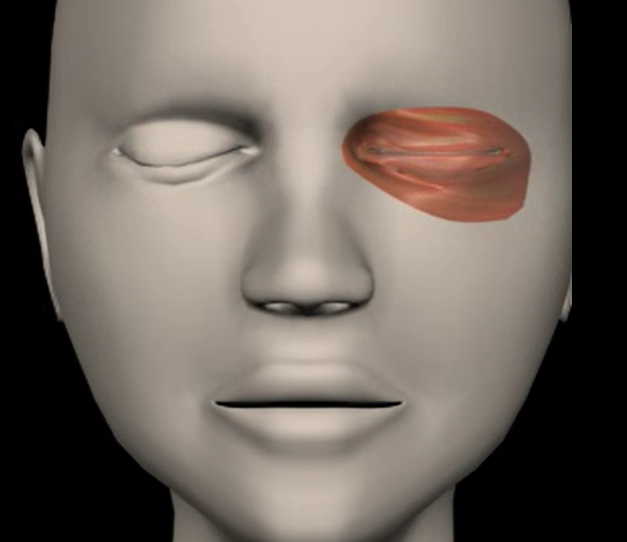
Orbicularis oculi (function, origin & insertion)
Function: closes eye, squint
Origin: frontal & maxillary bones
Insertion: tissue of eyelid
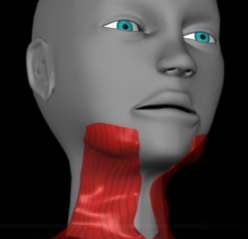
Platysma (function, origin & insertion)
Function: depress mouth corners
Origin: fascia of chest
Insertion: lower margin of mandible
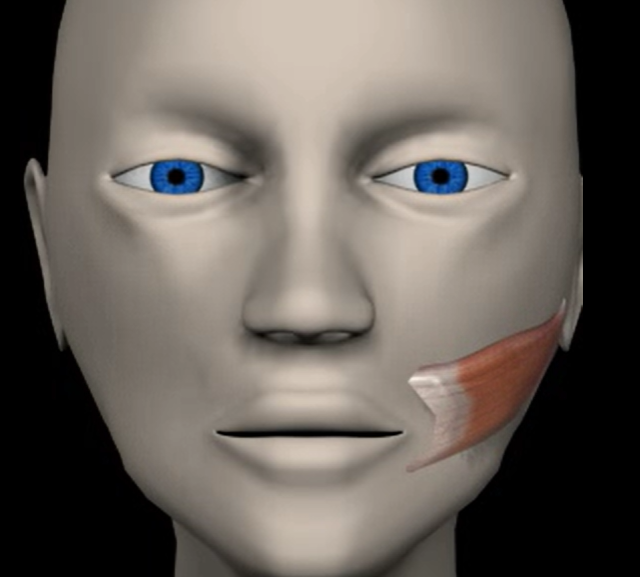
Buccinator (function, origin & insertion)
Function: compress (pull in) cheek
Origin: maxilla and mandible
Insertion: orbicularis oris
Zygomaticus (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: extends mouth corners (into a smile)
Origin: zygomatic bone
Insertion: skin at angle of mouth
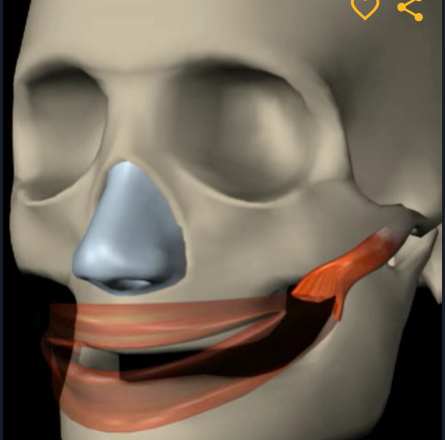
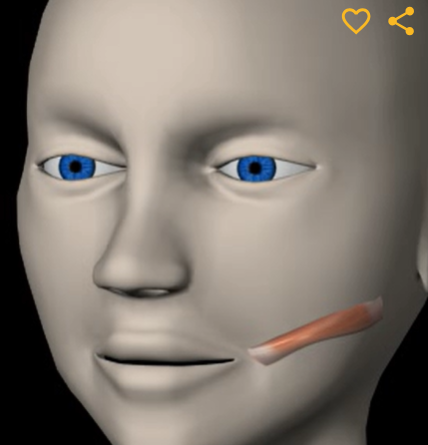
Risorius (function, origin & insertion)
Function: retracts mouth corners
Origin: fascia of masseter
Insertion: skin at angle of mouth

Masseter (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: elevates mandible (closes jaw)
Origin: zygomatic bone
Insertion: angle of mandible
Temporalis (function, origin & insertion)
Function: elevates & retracts mandible
Origin: temporal fossa
Insertion: coronoid process of mandible
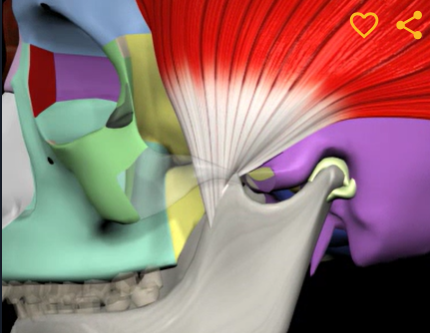
Lateral pterygoid (function, origin & insertion)
Function: protraction of mandible
Origin: greater wing of sphenoid bone
Insertion: condylar process of mandible
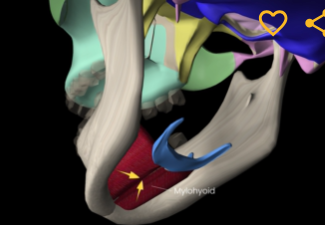
Mylohyoid (function, origin & insertion)
Function: elevates hyoid bone
Origin: mandible
Insertion: hyoid
Digastric (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: depresses mandible
Origin: low margin of mandible
Insertion: connective tissue to hyoid
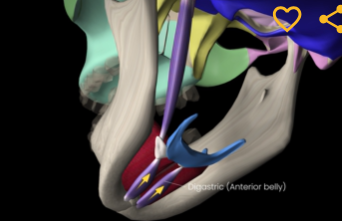
Genioglossus (function, origin & insertion)
Function: protracts & depresses tongue
Origin: mandible
Insertion: hyoid bone & tongue
Styloglossus (function, origin & insertion)
Function: elevates and retracts tongue
Origin: styloid process of temporal bone
Insertion: tongue
Palatoglossus (function, origin & insertion)
Function: elevates posterior tongue
Origin: palatine aponeurosis
Insertion: tongue
Hyoglossus (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: retracts, protracts, & depresses tongue
Origin: hyoid bone
Insertion: lateral portion of tongue
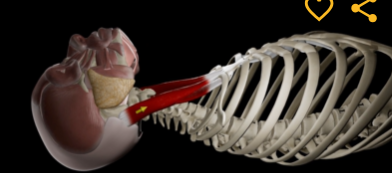
Sternocleidomastoid (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: flexion of neck
Origin: manubrium of sternum & clavicle
Insertion: Mastoid process of temporal bone
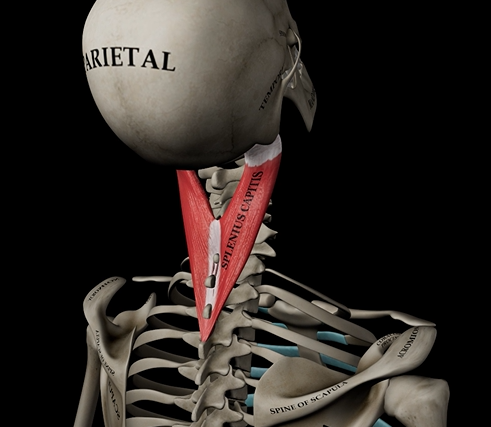
Splenius capitus (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: extension of head & neck
Origin: C7-T3 vertebrae
Insertion: mastoid process of temporal bone
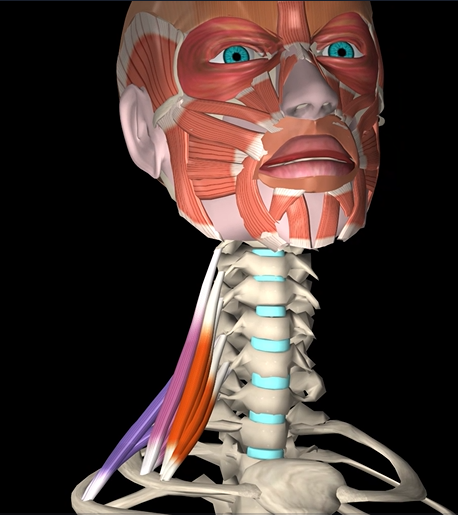
Scalenes (anterior & posterior) (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: lateral flexion of neck
Origin: cervical vertebrae
Insertion: ribs
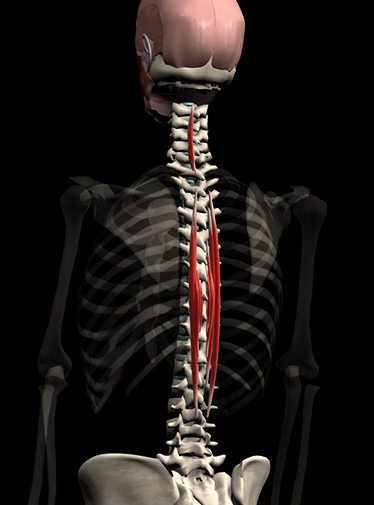
Spinalis (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: extends and laterally flexes spine
Origin: L1, L2, T11, T12, C7, T1, T2
Insertion: T4-T8, C2-C4
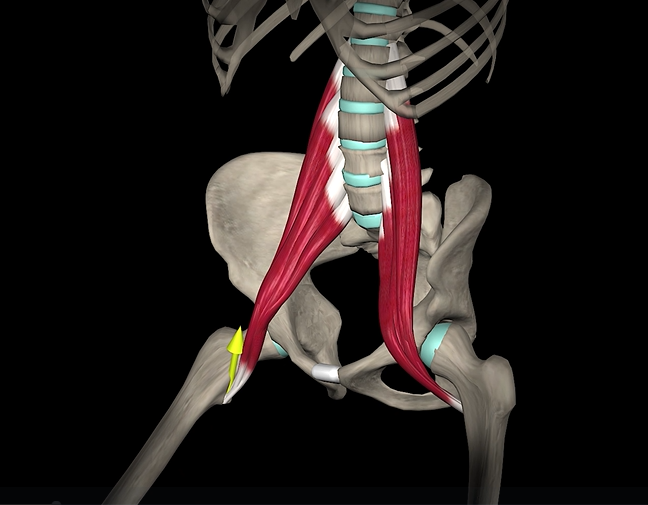
Psoas major (function, origin & insertion)
Function: flexion of hip
Origin: lumbar vertebrae
Insertion: lesser trochanter of femur
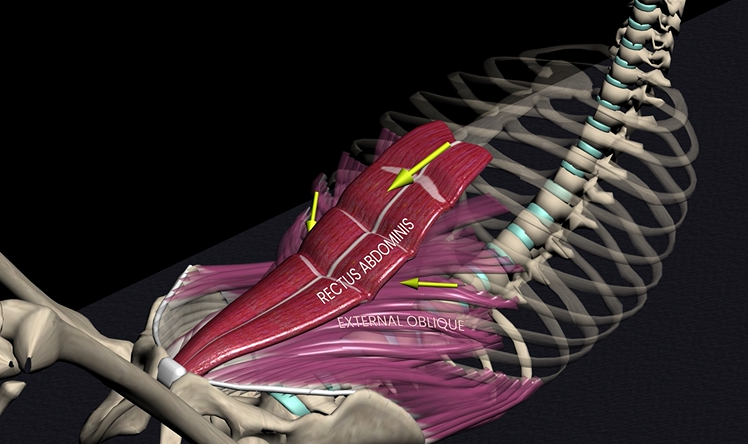
Rectus abdominus (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: spinal flexion
Origin: pubic symphysis
Insertion: costal cartilage & sternum
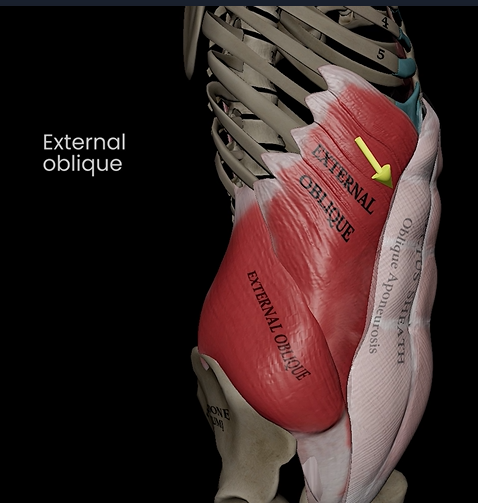
External oblique (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: flexes, lateral flexion, & rotation of trunk
Origin: external surface or ribs
Insertion: linea alba & pubic crest
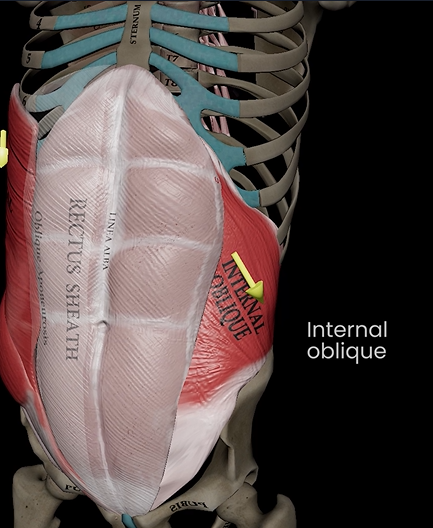
Internal oblique (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: flexes, lateral flexion, & rotation of trunk
Origin: lumbar fascia & iliac crest
Insertion: linea alba & pubic crest
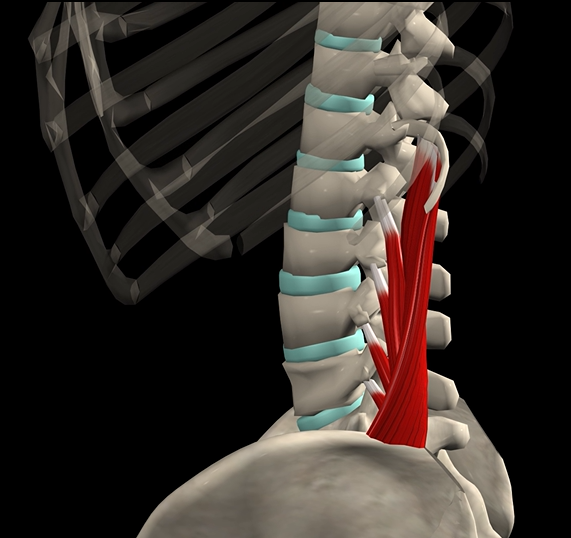
Quadratus lumborum (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: extension of spine
Origin: iliac crest
Insertion: lumbar vertebrae
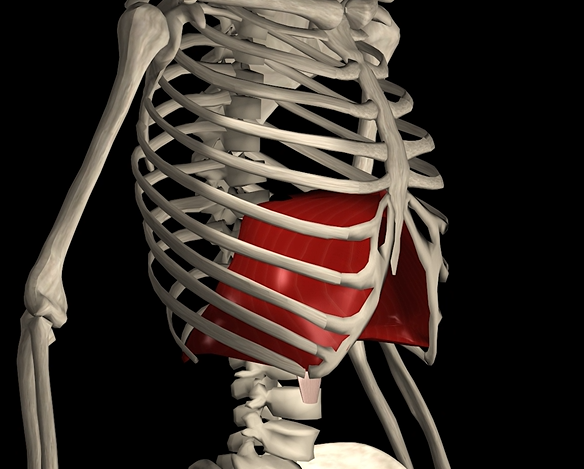
Diaphragm
Function: expands and contracts chest cavity
Origin: sternum, ribs, & vertebrae
Insertion: central tendon
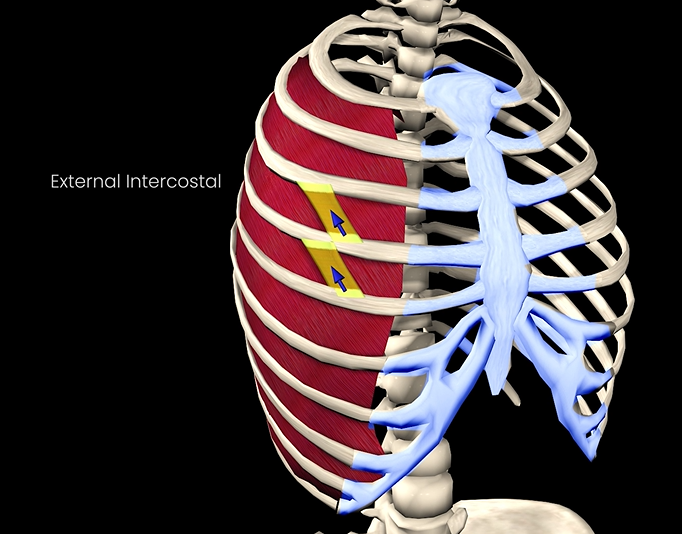
External intercostals
Function: elevates ribcage
Origin: inferior border of rib above
Insertion: superior border of rib below
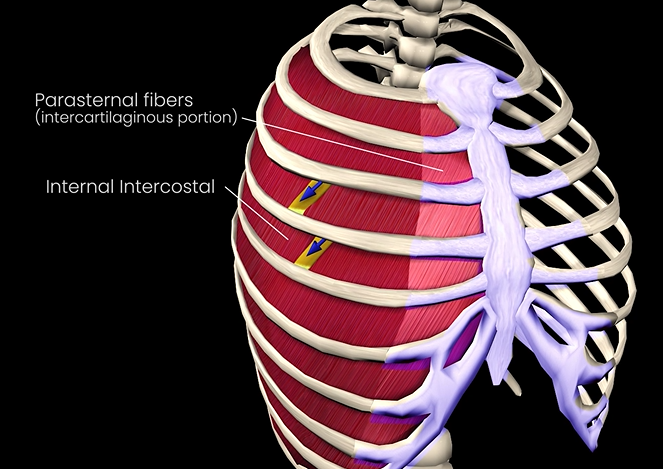
Internal intercostals
Function: depresses ribcage
Origin: superior border of rib below
Insertion: inferior border of rib above
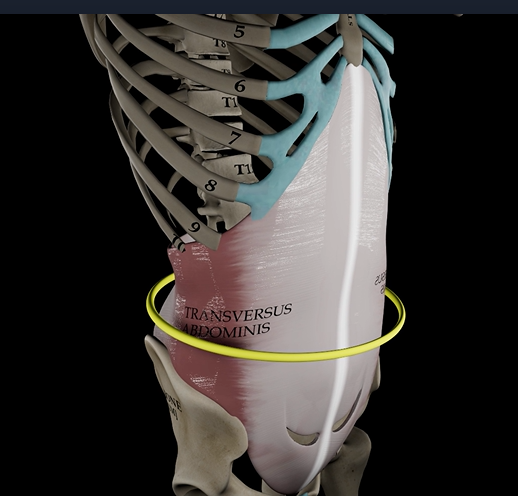
Transversus abdominus (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: compresses abdomen
Origin: inguinal ligament & iliac crest
Insertion: linea alba & pubic crest
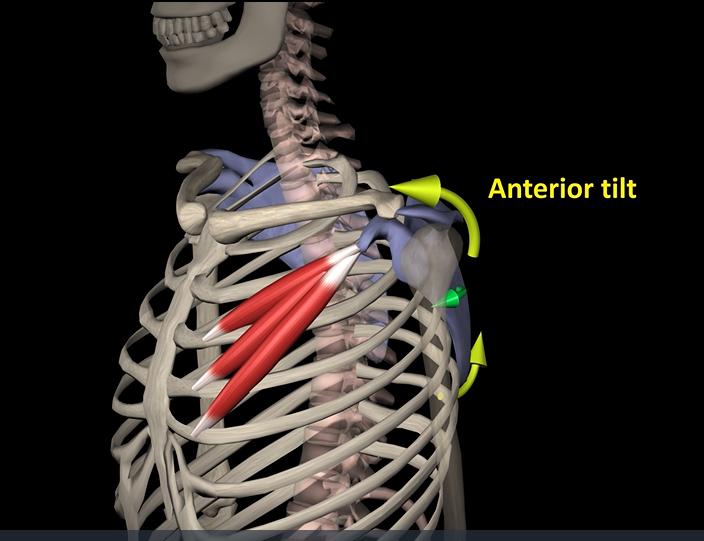
Pectoralis minor (function, origin, insertion)
Function: protracts scapula
Origin: ribs
Insertion: coracoid process of scapula
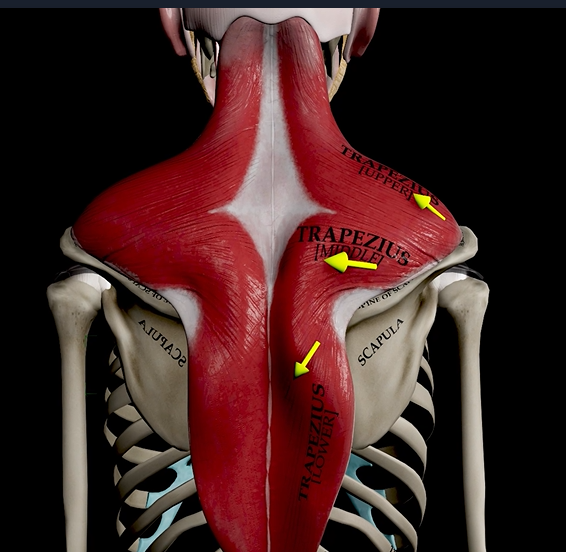
Trapezius (function, origin, & insertion)
Function: elevates, rotates, and retracts scapula
Origin: occipital bone
Insertion: acromion and spine of scapula
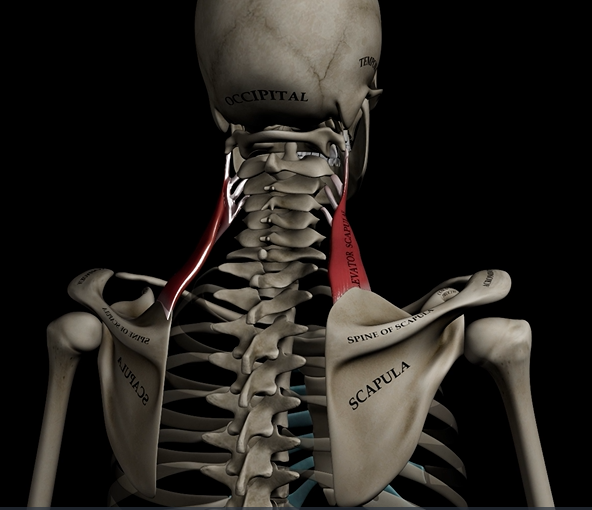
Levator scapulae (function, origin & insertion)
Function: elevates & adducts scapula
Origin: C1-C4
Insertion: medial border of scapula
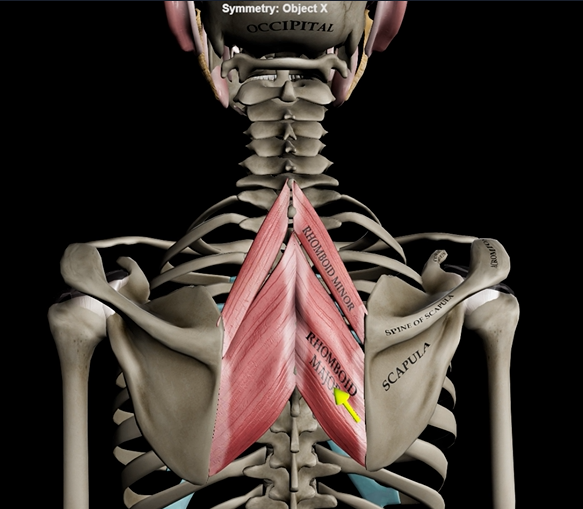
Rhomboideus major/minor
Function: retracts & adducts scapula
Origin: T1-T5
Insertion: medial border of scapula
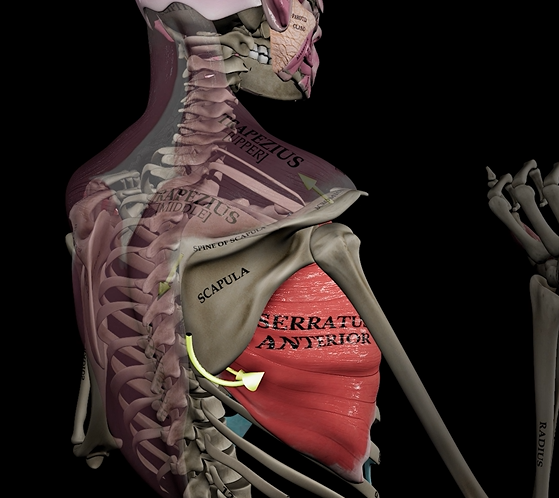
Serratus anterior
Function: rotates and abducts scapula
Origin: ribs
Insertion: scapula
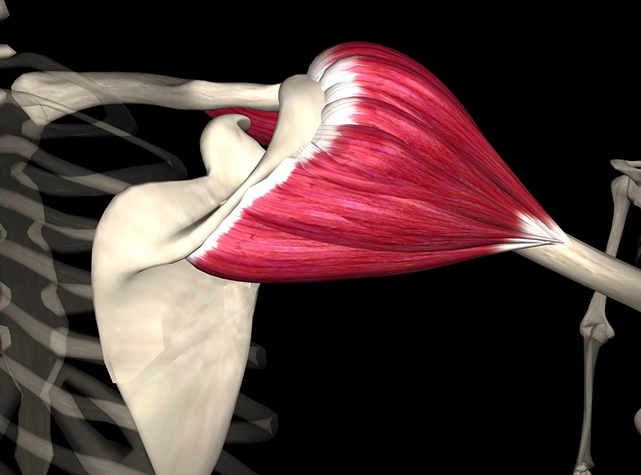
Deltoid
Function: flexes and abducts shoulder
Origin: clavicle and scapula
Insertion: deltoid tuberosity of humerus
Pectoralis major
Function: adducts & medially rotates shoulder
Origin: clavicle & sternum
Insertion: intertubercular sulcus of humerus
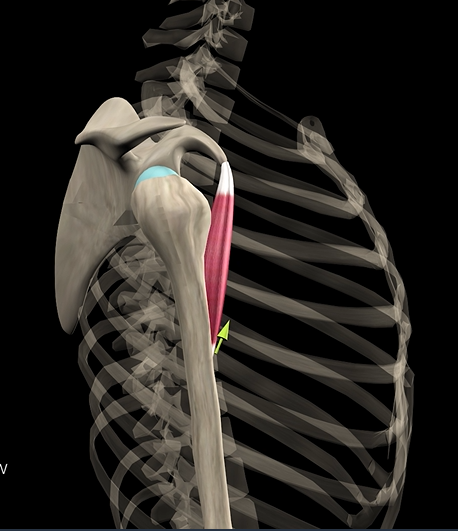
Coracobrachialis
Function: flexes & adducts shoulder
Origin: coracoid process
Insertion: humerus
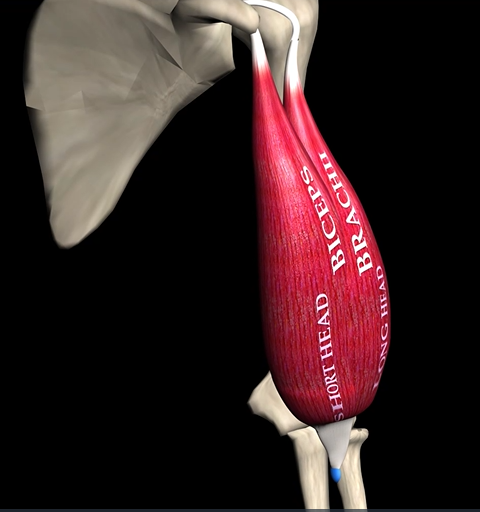
Biceps brachii (2 heads)
Function: flexes shoulder
Origin: coracoid process & supraglenoid tubercle
Insertion: radial tuberosity
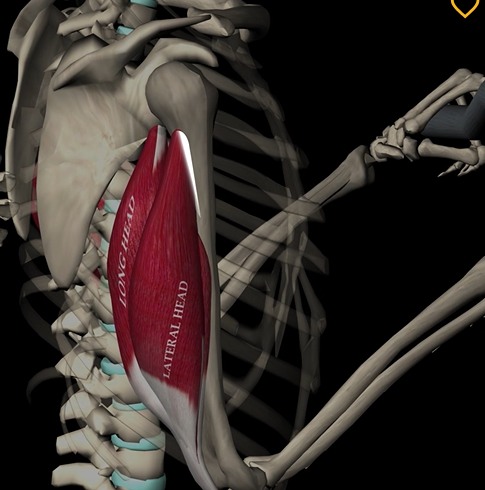
Triceps brachii
Function: extends elbow
Origin: posterior humerus
Insertion: olecranon of ulna
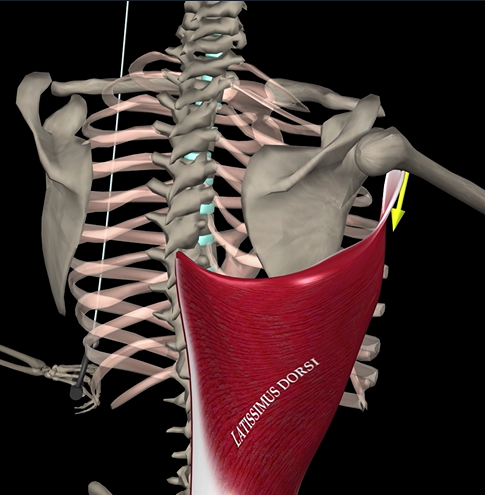
Latissimus dorsi
Function: extends, adducts, and rotates arm
Origin: vertebrae, ribs, iliac crest
Insertion: intertubercular sulcus of humerus
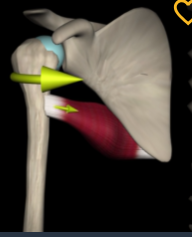
Teres major
Function: medially rotates humerus
Origin: inferior angle of scapula
Insertion: intertubercular sulcus of humerus
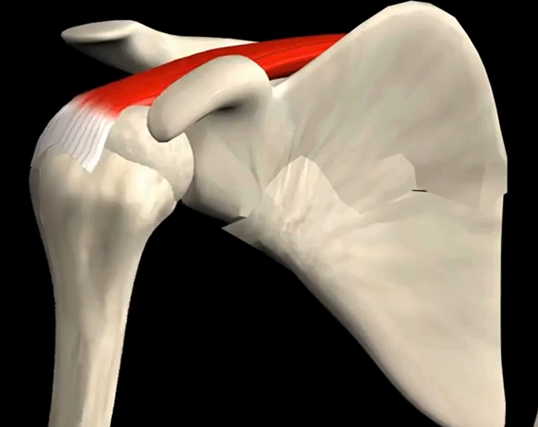
Supraspinatus
Function: abducts humerus
Origin: supraspinous fossa of scapula
Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
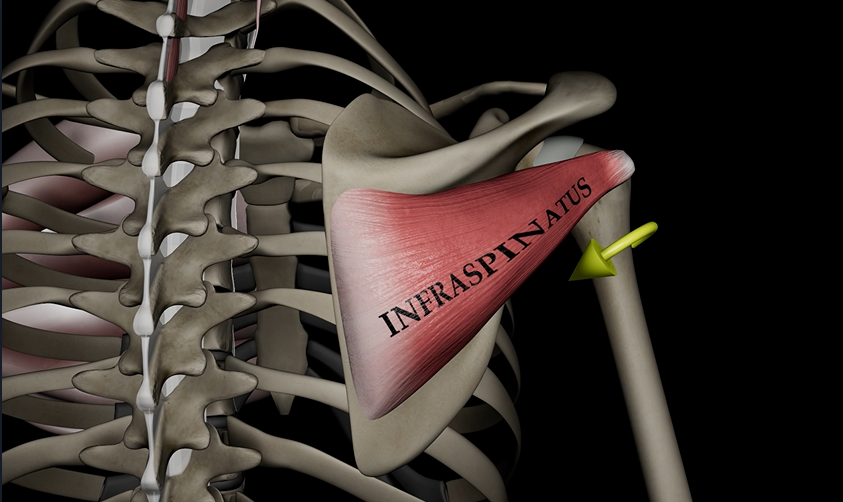
Infraspinatus
Function: lateral rotates humerus
Origin: infraspinous fossa
Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
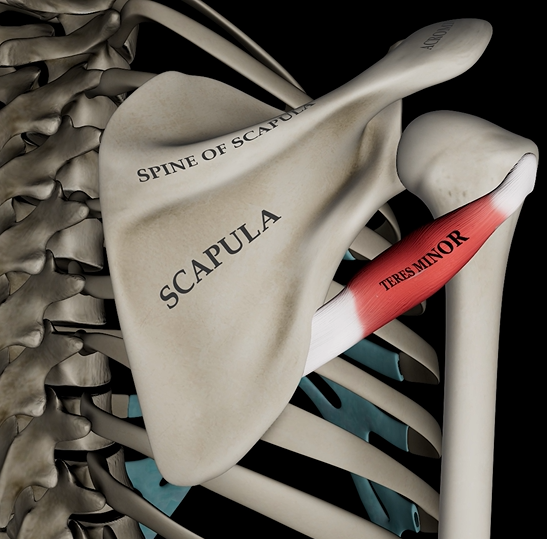
Teres minor
Function: laterally rotates humerus
Origin: lateral side of scapula
Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
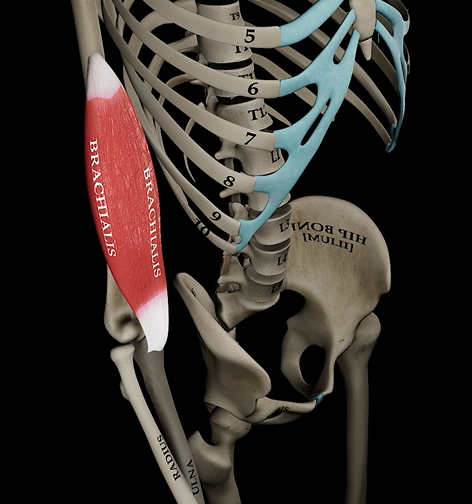
Brachialis
Function: flexes elbow
Origin: anterior humerus
Insertion: coronoid process of ulna
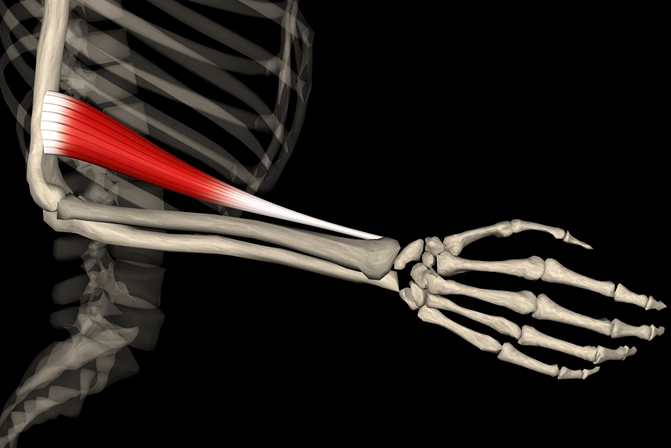
Brachioradialis
Function: flexes elbow
Origin: distal end of humerus
Insertion: radial styloid process
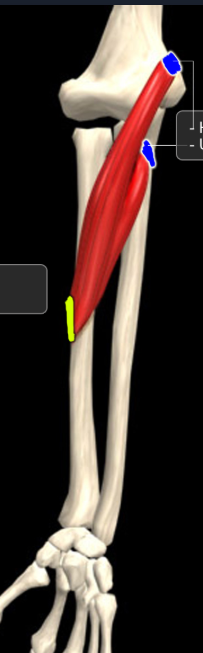
Pronator teres
Function: pronates forearm
Origin: humerus and coronoid process of ulna
Insertion: radius
Pronator quadratus
Function: pronates forearm
Origin: distal, anterior ulna
Insertion: distal, anterior radius
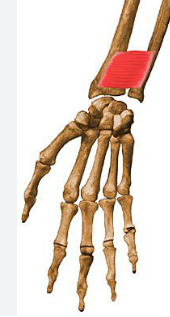
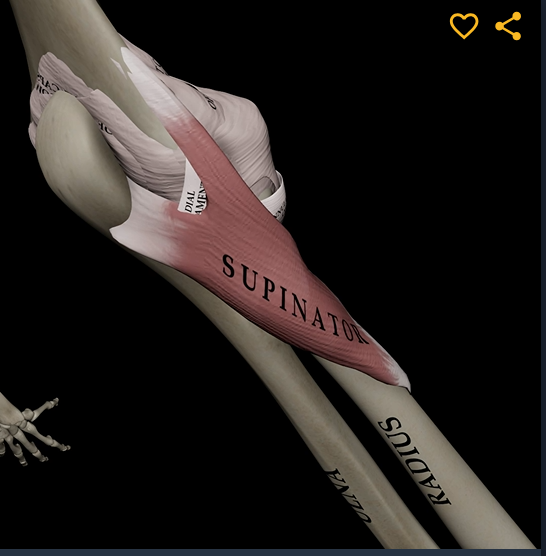
Supinator
Function: supinates forearm
Origin: lateral epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: proximal end of radius
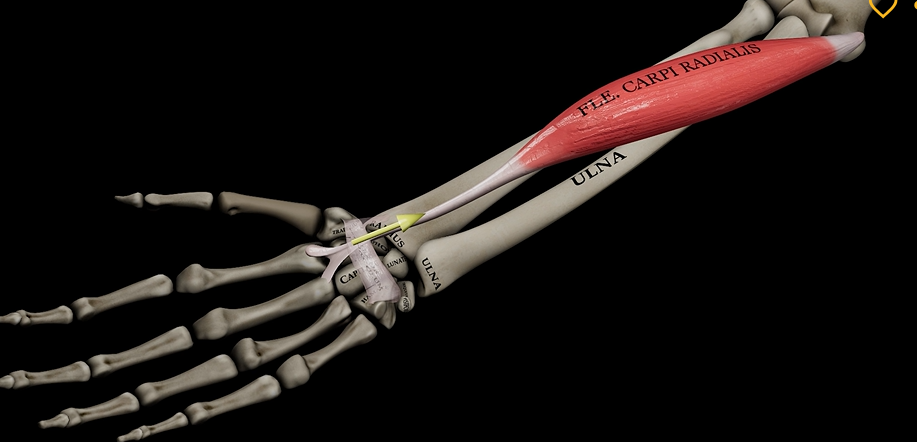
Flexor carpi radialis
Function: flexes wrist
Origin: medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: metacarpals
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Function: flexes wrist
Origin: medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: metacarpals

Palmaris longus
Function: flexes hand
Origin: medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: palmar aponeurosis

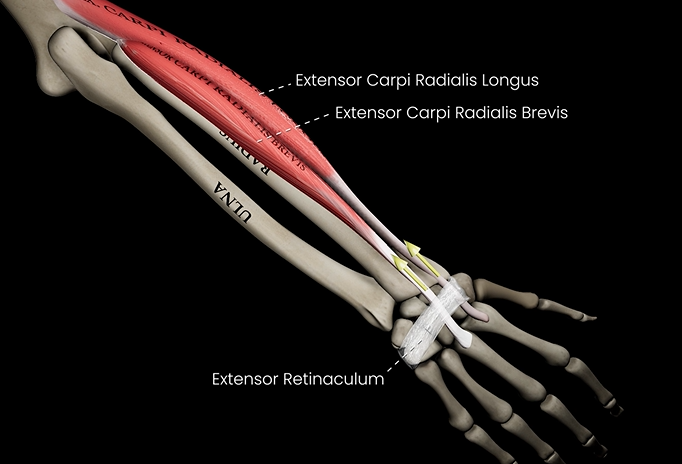
Extensor carpi muscles
Function: extends wrist
Origin: lateral epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: metacarpals