Rates of Reaction
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Rate of Reaction
The change in concentration of a reactant or a product of a chemical reaction per unit time.
Measures how fast a reactant is used up OR how fast a product is produced.
Change in volume
Gas produced and can be collected in a calibrated tube
Change in colour intensity
Measured with a spectrometer
Change in acidity
When H+ is used or produced – measure with pH meter
Change in electrical conductivity
If aqueous ions are used or produced
Collision Theory
For chemical reactions to occur, molecules must collide
In order for a collision to be successful, it must occur with:
i. Sufficient kinetic energy
ii. Proper orientation
Transition State Theory
Looks at the point where molecules begin to collide and break apart
Explains this process in terms of an activated complex
An unstable, temporary grouping of reactants whose bonds are broken and then reformed
Energy Level Diagrams
Shows how the energy of a reacting system changes as the reaction proceeds.
All reactions must pass through an energy maximum called the transition state and this is where the activated complex
forms.Finally the difference between initial energy of the reactants and the transition state is called the activation energy (Ea ).
The minimum energy that reactant molecules must possess for a reaction to be successful.
The less activation energy needed, the more likely a reaction will proceed.
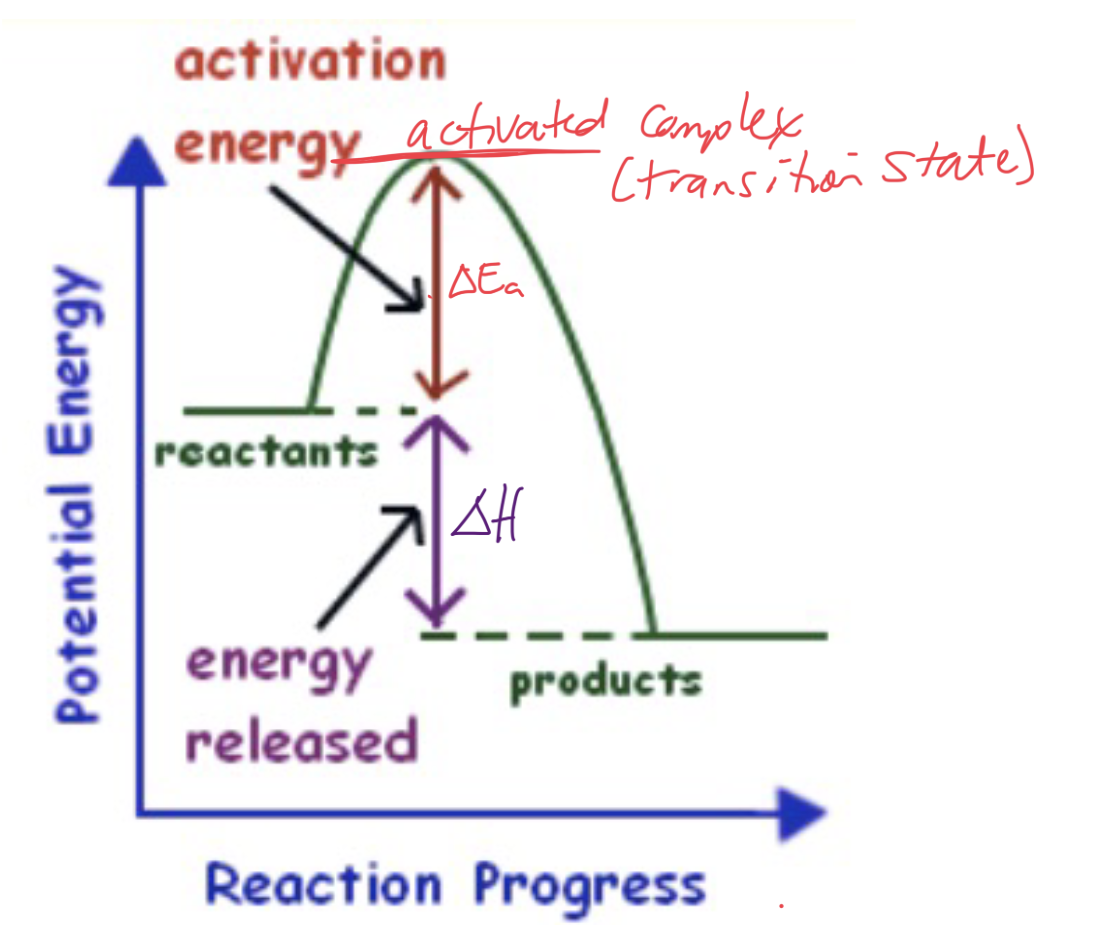
What type of graph and reaction is this?
Energy Diagram for Exothermic Reaction
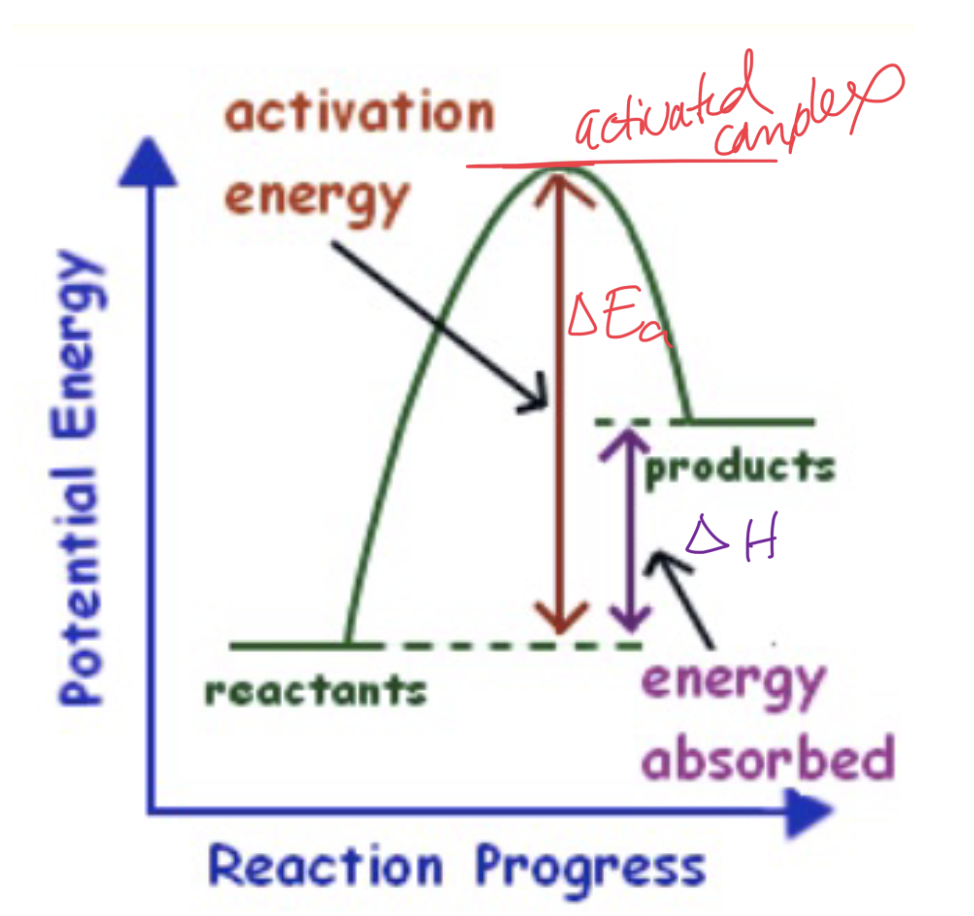
What type of graph and reaction is this?
Energy Diagram for Endothermic Reaction
How does temperature affect rate of reaction?
When temperature is increased the rate of reaction is
increased.Molecules are moving faster, with more kinetic energy so
there is a greater likelihood of successful collisions.There is a greater number of molecules with sufficient
energy and proper orientation.Increasing temperatures does NOT affect the potential energies of reactants and products or the position of the transition state. Therefore, the energy level diagram is
NOT affected.
How does concentration affect rate of reaction?
When concentration of reactants increases, the rate of
reaction increases.More reactant molecules means more collisions so there
is a greater likelihood of successful collisions.There is a greater number of molecules with sufficient
energy and proper orientation.Increasing concentration does NOT affect the potential energies of reactants or the transition state, therefore the energy level diagram is NOT affected.
Can be increased by:
Adding more reactant
moleculesReducing the volume
of the container
How does surface area affect rate of reaction?
When surface area of reactants increases, the rate of reaction increases.
If a reaction involves a solid only the atoms or ions at the surface can interact with other reactants.
Increasing the surface area of a solid reactant by breaking it apart, therefore increases its concentration.
Increasing surface area does NOT affect the potential energies of reactants or the transition state, therefore the energy level diagram is NOT affected.
How does a catalyst affect rate of reaction?
The use of a catalyst increases the rate of reaction.
A catalyst interacts with the reactants, but is not altered or destroyed in the interaction.
Catalysts do NOT increase the number of collisions between reactant molecules.
A catalyst provides an alternative pathway for the reaction, which has a lower activation energy, by partially or completely breaking the bonds of the reactants.
How does a inhibitor affect rate of reaction?
The use of an inhibitor decreases the rate of reaction.
Inhibitors raise the activation energy.
How does the nature of reactants affect rate of reaction?
Some general conditions predispose a reaction to be fast or slow
Gases tend to react faster because…
substances in this state react faster because Particles are apart and moving rapidly
Ionic compounds will react faster with each other if they are in aqueous solution because…
these compounds react faster because
ions separate and float around more freely for collisions
ionic reactions are faster than molecular because…
These reactions occur faster because
between ions simply involve a positive charge and a negative charge attracting
but, between molecules, electrons have to
be transferred, and the rearrangement of atoms and bonds from one
location to another occur
stronger bonds react slower because…
these bonds react slower because double bonds are stronger than single bonds.
The more bonds that must be broken the slower the reaction, so…
smaller molecules will react faster than larger molecules, since larger molecules have more atoms which requires more bonds.
What is rate law?
A math expression that allows the calculation of reaction rate as a function of reactant concentration
what is the order of reaction?
An exponent used to describe the relationship between the initial concentration of a particular reactant and the rate of the reaction
What is the total order of reaction?
The sum of the exponents in the rate law equation
What are reaction mechanisms?
Most reactions can be shown to be a series of steps, each generally involving one collision
Bimolecular
The step involves a 2 particle collision
Trimolecular
The step involves a 3 particle collision
Unimolelcular
The step involves a single particle breaking up
What are reaction intermediates?
This is neither a reactant nor a product, but is formed and consumed during the reaction sequence.
Rate Determining Step
The overall rate of any process which consists of several consecutive steps depends on the rate of the slowest step.
To increase the overall rate of reaction the rate determined step must be increased.