Anatomy Nervous System Test
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/155
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:19 PM on 1/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
1
New cards
The nervous system is divided into
Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System
2
New cards
Function of the Nervous System
Master control center for the body, detects impulses from the center
3
New cards
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord
4
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Nerves not in brain/spinal cord
5
New cards
Cranial Nerves
Originate in the brain, 12 to help control body
6
New cards
Spinal Nerves
Originate in the spinal cord
7
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System is divided into
Sensory (Afferent) Division and Motor (Efferent) Division
8
New cards
Sensory (Afferent) Division
Sends impulses from the senses AT the CNS
9
New cards
Motor (Efferent) Division
Sends impulses from the CNS to the muscles and glands (EXITS)
10
New cards
The Motor division divides into the
Autonomic and Somatic Nervous System
11
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System
Involuntary muscle control like digestion, urination, heart pumping
12
New cards
Somatic Nervous System
Voluntary muscle control like muscular skeletal movements
13
New cards
The Autonomic Nervous System is divided into the
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions
14
New cards
Sympathetic Division
Used in emergency situations, fight or flight response
15
New cards
Parasympathetic Division
Reduces the sympathetic response, provides resting functions such as digestion and urination.
16
New cards
Effects of an activated Sympathetic/fight or flight
Heart rate and breathing rate increase, blood pumped to the extremities for physical activities and is diverted from organs
17
New cards
What system does the nervous system work with?
The Endocrine System
18
New cards
For the nervous system to do its job it uses
Sensory input, integration, and response
19
New cards
Sensory input
Detects changes/stimuli inside and outside of the body
20
New cards
Integration
Processing and interpreting the information
21
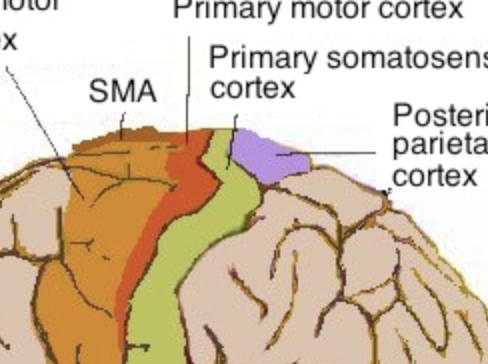
New cards
Response
Activation of muscles (motor output) or glands
22
New cards
The 2 major types of nerve cells are
Neurons and neuroglia
23
New cards
Neurons
Conduct impulses around the body, make up 10% of nerve cells
24
New cards
Neuroglia
Act as nerve glue & support, insulate, and protect neurons, make up 90% of nerve cells
25
New cards
What do all neurons have in common?
A main cell body and processes extending outward.
26
New cards
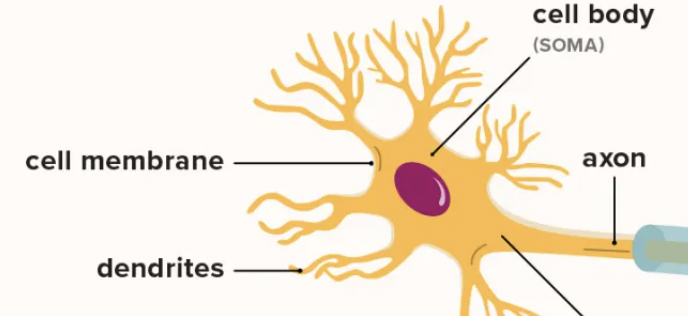
The cell body contains the
Nucleus, cytoplasm, organelles
27
New cards
Processes of a neuron are divided into
Dendrites and Axons
28
New cards
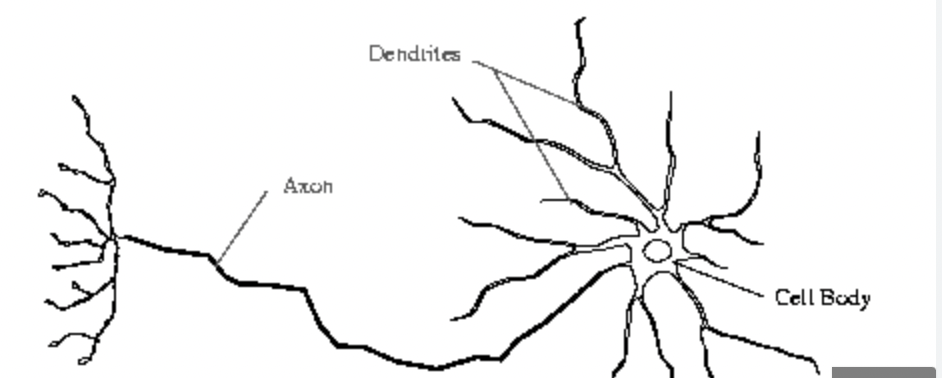
Dendrites
Bring impulses TOWARDS the cell body
29
New cards
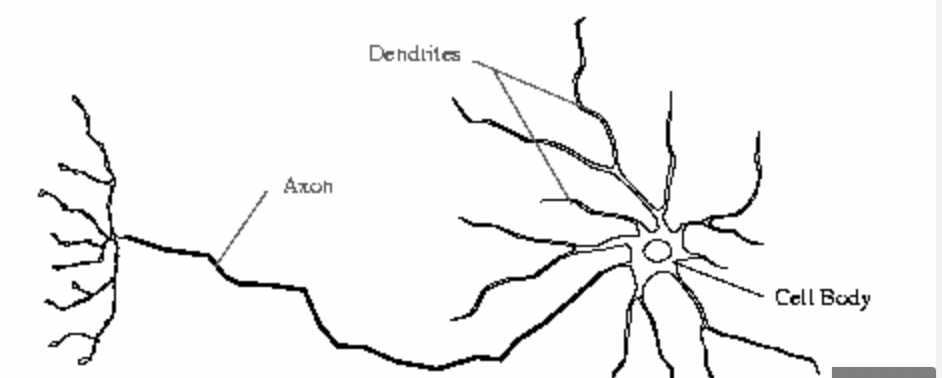
Axons
Send impulses AWAY from the cell body
30
New cards
What do processes end with?
Axon terminals
31
New cards
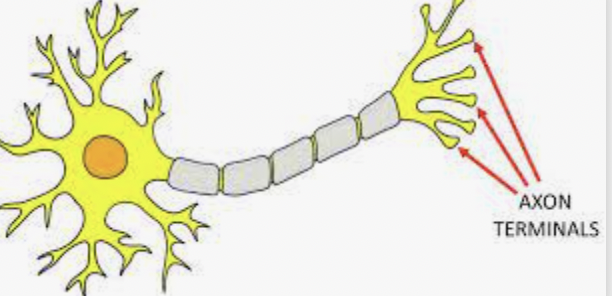
Axon terminals
Release neurotransmitters to pass the impulse to the next neuron
32
New cards
MS disease
Myelin sheath degenerates, motor function issue
33
New cards
Neurons are classified by
number of processes extending from the cell body and their function
34
New cards
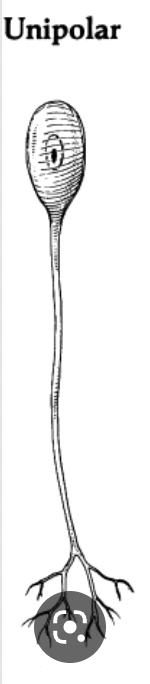
One process
Unipolar neurons
35
New cards
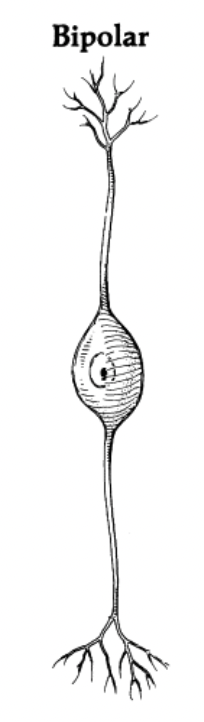
Two processes
Bipolar neurons
36
New cards
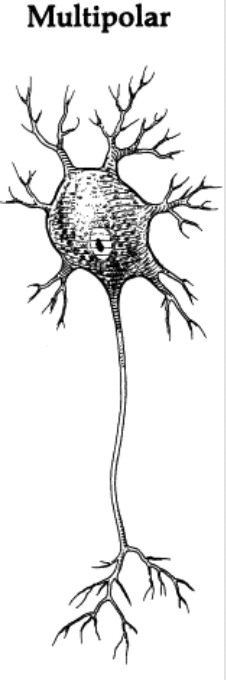
many processes
Multipolar neurons
37
New cards
Afferent neurons
Carry impulses AT the CNS
38
New cards
Efferent neurons
Carry impulses away from the CNS (EXITS)
39
New cards
Interneurons
Connect afferent and efferent neurons.
40
New cards
What are axons wrapped in?
Myelin, which is like a waxy insulation.
41
New cards
How is myelin formed?
Schwann cells (type of neuroglia) wrap itself around the axon, like a coil, helping it move faster with support and protection.
42
New cards
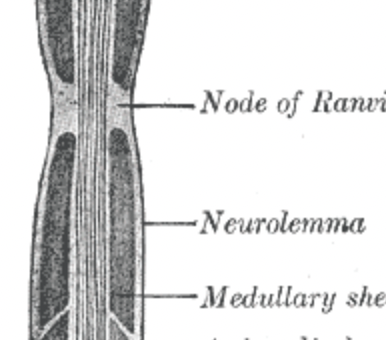
Neurilemma
Outer layers of the Schwann cell
43
New cards
What does myelin do?
Helps the nerve impulses to travel more quickly.
44
New cards
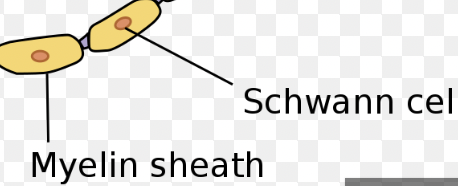
Myelin sheath
All of the myelin wrappings collectively.
45
New cards
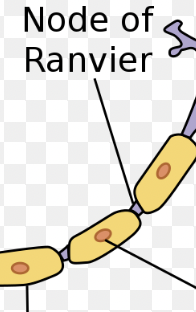
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps formed because the myelin sheath has many Schwann cells.
46
New cards
Where are Neuroglial cells found
In both the CNS and PNS.
47
New cards
Neuroglial cells in the CNS
Astrocytes, Microglia, Ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes
48
New cards
Astrocytes
Support and ANCHOR neurons to surrounding capillaries, giving blood to surrounding tissues
49
New cards
Microglia
Provide immune response to to CNS
50
New cards
Meningitis
Meninges infection, microglia help
51
New cards
Ependymal cells
Secrete and circulate cerebrospinal fluid
52
New cards
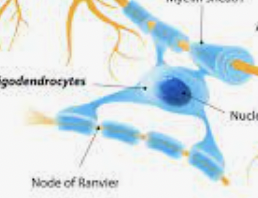
Oligodendrocytes
Provide myelin insulation to neurons in the Central Nervous System.
53
New cards
Neuroglial cells in the Peripheral Nervous System
Satellite cells, Schwann cells
54
New cards
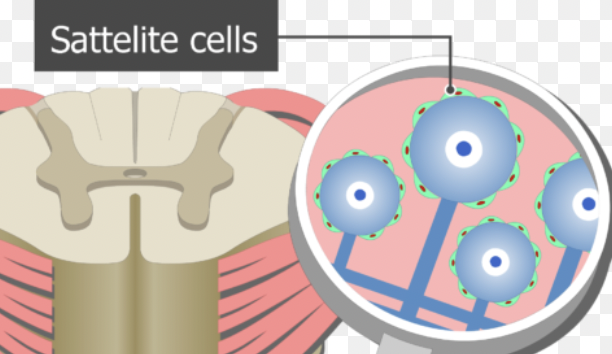
Satellite cells
SUPPORT and anchor neurons in the PNS.
55
New cards
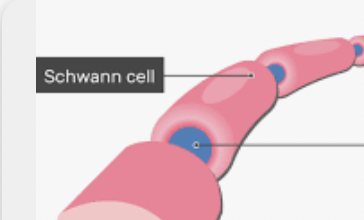
Schwann cells
Provide myelin insulation to neurons in the PNS.
56
New cards
What is a nerve impulse
An electrical signal that travels along a neuron
57
New cards
How do nerve impulses arise
It arises from a movement of ions causing a change in electrical charges.
58
New cards
How is intracellular space charged?
Negatively charged (resting potential)
59
New cards
How is extracellular space charged?
Positively charged (resting potential)
60
New cards
What happens when a neuron is stimulated by the environment or another neuron?
Sodium rushes into the neuron, and quickly reverses the charges (Depolarization), this process quickly moves down the length of a neuron.
61
New cards
What is depolarization known as?
Action potential
62
New cards
What happens as the impulse passes?
Potassium diffuses out of the neuron (Repolarization)
63
New cards
Refractory period
Spike down caused by ions moving back to original spots
64
New cards
What does sodium potassium pump do after repolarization?
Restores ion concentrations to normal, resting potential returns. (All or Nothing event) → Homeostasis
65
New cards
What are some problems with the Na K pump if it doesn’t work?
Congestive heart failure
66
New cards
Synapse
Where two neurons meet
67
New cards
Synaptic cleft
The space between the two neurons at a synapse because the neurons don’t touch.
68
New cards
What happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminal?
It can’t cross the gap between the two neurons, so it stimulates vesicles to release neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft.
69
New cards
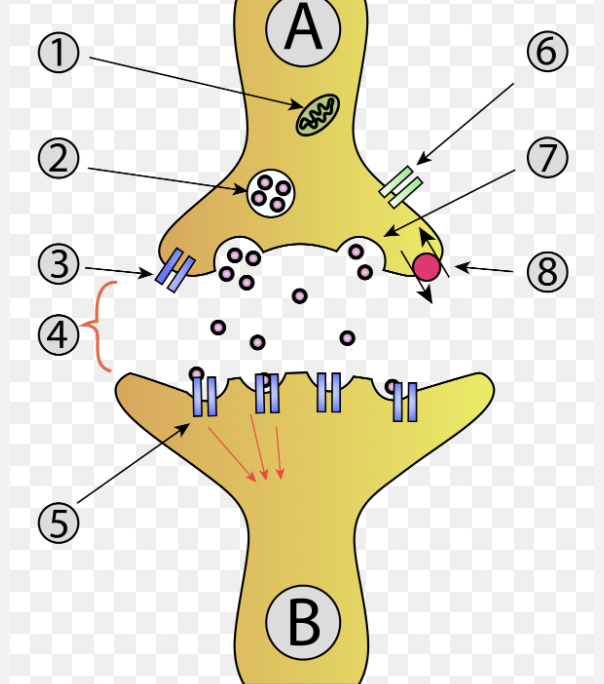
How do neurotransmitters open the next neuron?
They cause channels to open, continuing the action potential from one neuron to the next.
70
New cards
What is an example that uses this process?
When you take drugs that cause hormones to be released like Caffiene.
71
New cards
What chemical helps impulses travel?
Calcium ions
72
New cards
What are the 3 layers of connective tissue that protect the brain and spinal cord called? (blood-brain barrier)
Meninges
73
New cards
Layers of meninges from top to bottom
Skin, Periosteum, Bone, Dura Mater, Arachnoid Membrane, Pia Mater
74
New cards
Dura mater
Thick, tough layer
75
New cards
Arachnoid membrane
Thin, cobweb-like layer
76
New cards
Pia Mater
Thin layer containing lots of blood vessels
77
New cards
What is between the Arachnoid layer and the pia mater?
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
78
New cards
What does the cerebrospinal fluid do
Protects the brain by preventing it from contacting the skull & maintains the blood brain barrier.
79
New cards
What does the blood brain barrier do?
Controls homeostasis for the brain and prevents infection.
80
New cards
Where is CSF produced
Spaces within the brain called ventricles
81
New cards
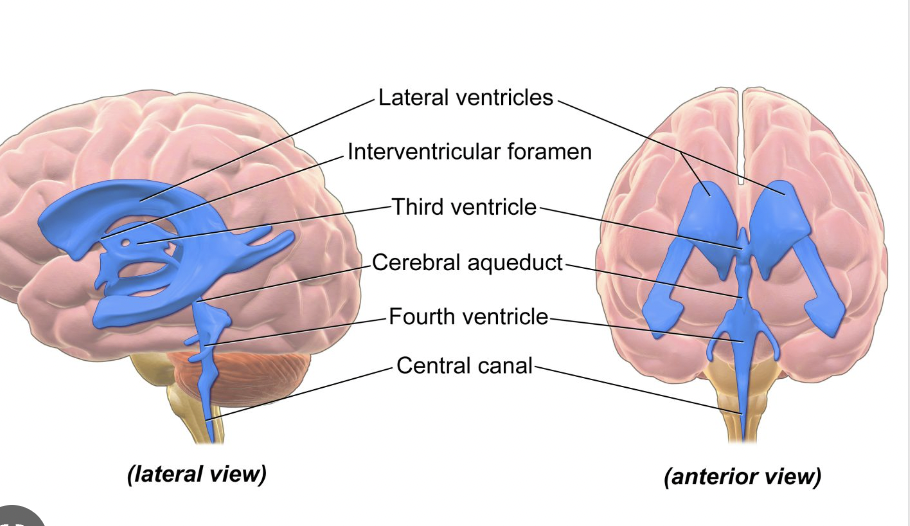
What are the four ventricles?
Lateral (Right and Left), 3rd and 4th ventricles.
82
New cards
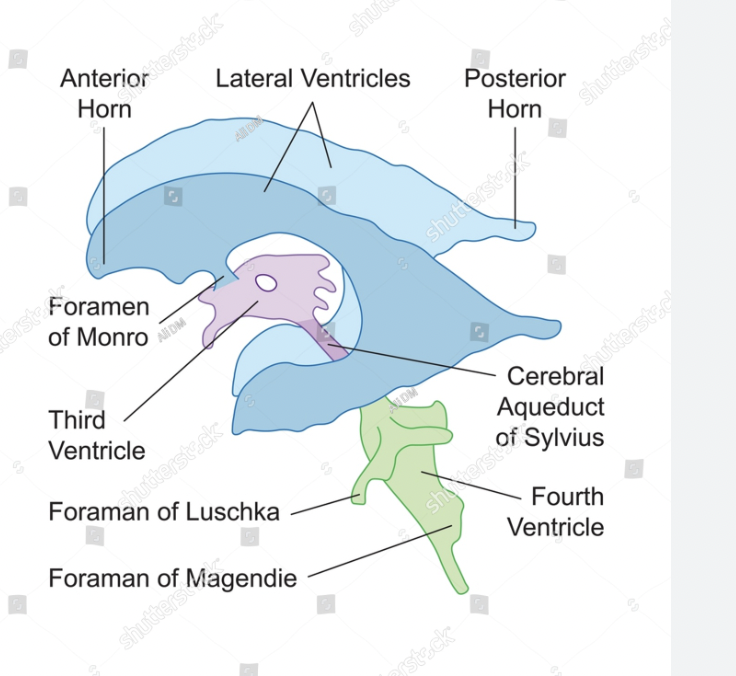
How are the lateral ventricles connected to the third ventricle?
The thin interventricular (inter= between ventricles) foramen → Foramen of Monro (hole)
83
New cards
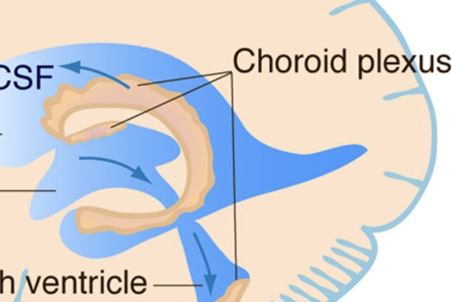
What are choroid plexuses
Clusters of capillaries in the ventricles that secrete CSF, causing it to flow around the ventricles, then be absorbed by arachnoid granulations in the blood.
84
New cards
What is CSF constantly doing in the ventricles?
Being produced, circulated, and reabsorbed. (Continuously and closed)
85
New cards
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain, divided into two hemispheres (right and left)
86
New cards
How are the two hemispheres of the brain connected?
A bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum.
87
New cards
What is the surface of the cerebrum covered with?
Ridges (gyri) and grooves (sulci)
88
New cards
What are the deep grooves that divide portions of the brain?
Fissures
89
New cards
What are the brain’s 3 major layers from superficial to deep?
Cerebral cortex, cerebral medulla, basal nuclei
90
New cards
Cerebral cortex
Gray matter, made of cell bodies and dendrites
91
New cards
Cerebral medulla
White matter, made of myelinated axons.
92
New cards
Basal nuclei
Islands of gray matter
93
New cards
How is the cerebrum divided?
It is divided into 4 lobes based on their functions, and are named for parts of the skull protecting them.
94
New cards
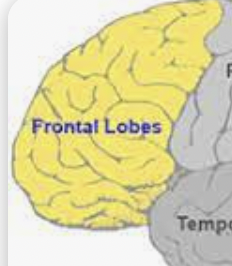
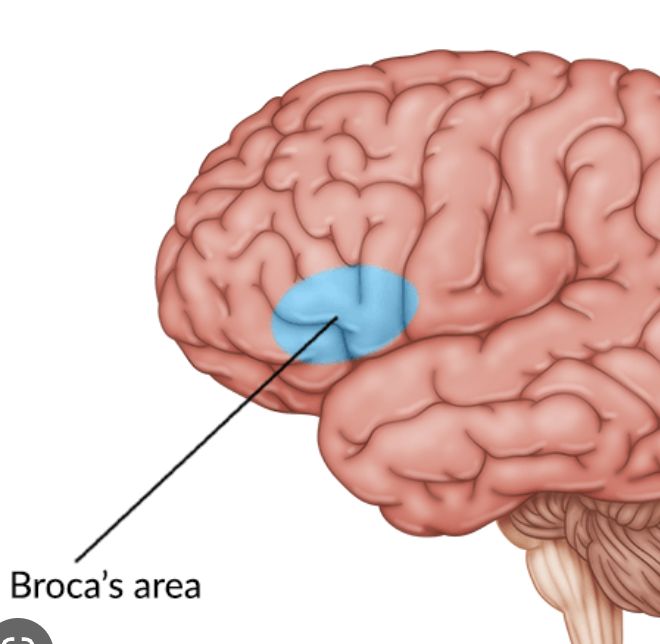
Frontal lobe
Controls voluntary movements like walking, reasoning + decision making. memory, predicting consequences. planning, verbal communication in Broca’s area
95
New cards
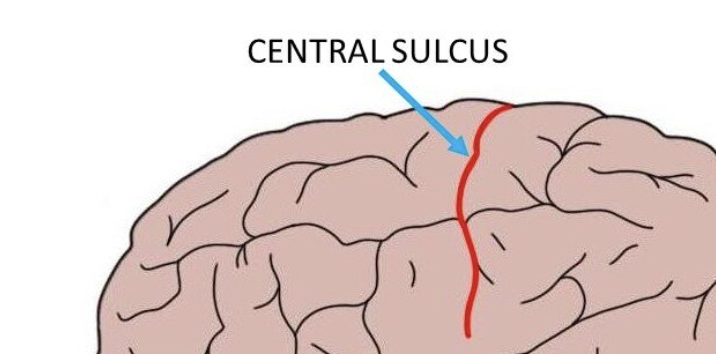
How is the frontal lobe separated from the parietal lobe?
The central sulcus
96
New cards
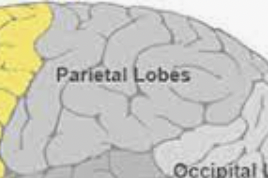
Parietal lobe
Sensations like pain, temperature, and touch, visual spatial processing and body position.
97
New cards
Occipital lobe
Visual processing, vision and memory of objects.
98
New cards
How is the temporal lobe separated from the frontal lobe?
Lateral sulcus
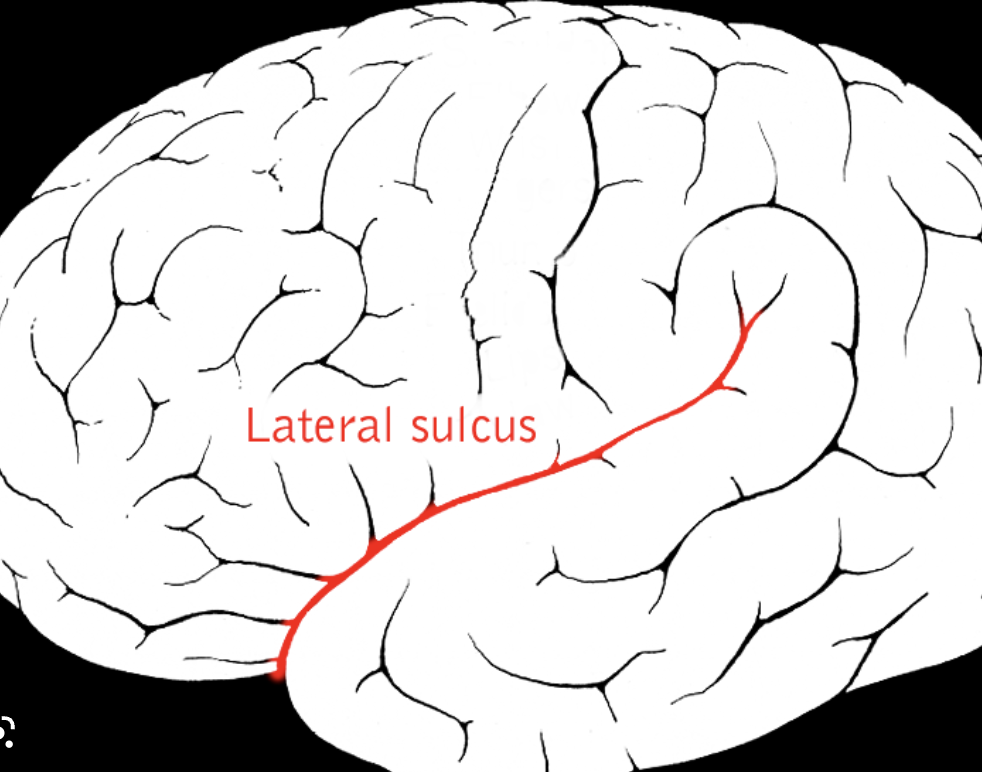
99
New cards
Temporal lobe
Controls memory, comprehension and pronunciation of words. smell and sound, emotional association of memories.
100
New cards
Diencephalon
Small nondescript region within the cerebrum