Exam 2 ( How the Earth Works)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Alfred Wegner (1915)
Had a radical hypothesis of continental drift
Evidence for Pangea
Continental Jigsaw, evidence of fossils across sea
lithosphere
A strong, rigid layer that is made up of plates ( older it is, the thicker it is)
Asthenosphere
Weak sphere, near melting temps. It allows Earths rigid outer shell to move
Mesosphere (lower mantle)
Pressure counteracts temperature creating strong rocks
Outer Core
Liquid layer of iron that generates earth’s magnetic field
Inner Core
Solid Iron because of immense pressure
Plate
A distinct piece of the lithosphere that has boundaries on all sides which are called plate boundaries
Continental Margins
Edges of continents where they meet the oceans/seas. Which lead to active margins and passive margins( not plate boundaries)
Divergent Boundaries
Oceanic Ridges and Seafloor Spreading, Continental rifting
Convergent Boundaries
Oceanic- continental convergence, oceanic, and continental
Divergent Plate Boundaries
Two plates move apart as a result of upwelling material from the mantle to creating new oceanic lithosphere, constructive plate margins
Sea Floor Spreading
True divergent plate boundaries occur along mid-ocean ridges, New ocean crust is formed along the ridge, as the plates move away from each other the older crust moves farther away
Sea Floor Spreading
Moves about 5 centimeters per year, no ocean floor exceeds 180 million years old
Convergent Boundaries
Destructive plate margins, Subduction zone ( one plate bends and sinks under another plate)
Convergent Plates Boundaries
Angles of subduction range from 90 averaging about 45, which depends on the density (Old lithosphere is cold and dense with has a steep angle)
Oceanic - Continental Convergence
Downgoing plate (subducted) and overriding plate ( not sinking)
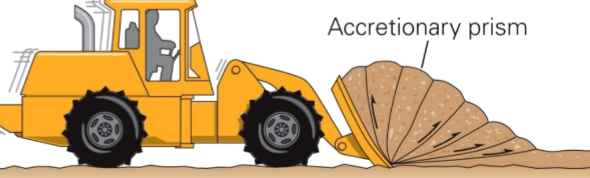
Accretionary Prism ( boundary feature)
A wedge-shaped mass of sediment and rock scraped off the top of a down going plate ( a plow scraping off material
Continental volcanic arc
Volcanoes are associated with the subduction zone because the down plate brings water and the water is heated up and released into the mantle. Which allows it to partially melt, allows magma to form
Partial Melting
The melting of a rock of the minerals with the lowest melting temperatures, while other minerals remain solid
Oceanic-Oceanic (Convergent zone)
Creates volcanic island arcs, Back-arc Basin-Depression are formed behind a volcanic island arc
Continental-Continental ( Convergent zone)
Cannot be subducted, Subduction ends when two continental plates collide, A collisional mountain belt forms where the tow plates collided
Transform Fault Boundaries
Plates slide horizontally past each other without the production or destruction of the lithosphere
Hot Spots
As a plate moves over a hot spot a chain of volcanoes is formed. As these extinct volcanoes sink below sea level, they become seamounts
Earthquake?
A vibration caused by the sudden breaking or frictional sliding of rock in the Earth
Fault?
A fracture on which one body of rock slides past another
Focus?
The location where a fault slips during an earthquake ( Hypocenter)
Epicenter?
The point on the surface of the Earth directly above the focus of an earthquake
Fault trace?
The intersection between a fault and the ground surface
Creep?
Movement along faults occurs gradually and relatively slowly and smoothly
Why do Earthquakes occur?
Elastic Rebound and is produced by the rapid release of elastic energy stored in rock that has been subjected to great stress.
Elastic Robound?
Springing back of a rock once an earthquake has occurred and the rock returns back to its original shape
Footwall (Fault)
The rock mass that lies below the fault plane
Hanging wall (Fault)
The rock or sediment above an inclined fault plane
Transform/Strike-Slip Faults
Motion can be left lateral or right lateral. If you stand on one side and the other side moves left, it becomes a left lateral.
San Andreas Fault ( an active Earthquake zone)
A transform plate boundary (right lateral), displacement occurs along discrete segments 100 to 200 kilometers long
Seismic Waves
Surface waves( complex motion/great destruction/ slowest) and Body waves ( travel deep into Earth’s interior)
Body Waves
P-waves: primary, push/pull motion, fastest
S- waves: Shear, slower, only travel through solids
Earthquake Measurement
Seismogram: depicts earthquake wave behavior
Locating the Epicenter
Data from 3 or more stations pinpoints the epicenter
Ricther Scale
Determined by first calculating the interval between the S and P waves, then determining the amplitude of the largest wave produced, the line intersects where the line is formed
Earthquakes
Factors influencing damage: foundation conditions, building standards
Destruction: structural, tsunami, fire
Destruction
Structural damage, fires, ground shaking, tsunami
Ground and Foundation damage
can trigger mass wasting, lose cohesion: due to shaking of ground, water in pore space cause sand to become mobilized, liquefaction
Liquefaction
The process that occurs when the motion of an earthquake causes sand and clay-rich sediment to become a characteristic of a liquid
Earth’s interior
P-wave shadow zone which is caused by the refraction of P-waves through the earth’s core and S-waves shadow zone: do not penetrate the liquid outer core
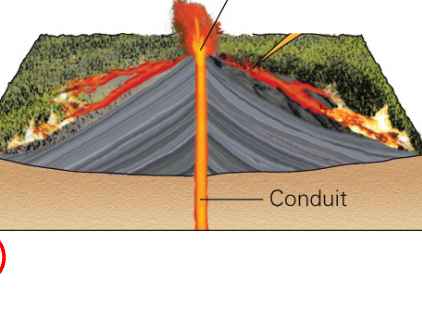
A mountain formed by the accumulation of extrusive volcanic rock
A vent from which melt from inside the Earth spews out onto the planet’s surface
Viscosity
A measure of a material’s resistance to flow
Factors affecting viscosity
Temperature, Composition: Silica content
Gases
dissolved gases increase the fluidity of magma, escaping gases propel the molten rock
Mafic magma
Silica content:Least (-50%), Viscosity: Least, Gas Content: Least(1-2%)
Intermediate magma
Silica content: Intermediate (-60%), Viscosity: Intermediate, Gas Content: Intermediate(3-4%)
Felsic magma
Silica content:Most (-70%), Viscosity: Greatest, Gas Content: Most(4-6%)
Pahoehoe ( basaltic lava flow)
Form relatively smooth skin that wrinkles as the molten subsurface lava continues to advance
lava Tubes: tunnel in hardened lava (horizontal conduit)
Aa ( basaltic lave flow)
Has a surface of rough jagged blocks with sharp edges ( much slower than pahoehoe)
Types of Eruptions and Volcanic Cones
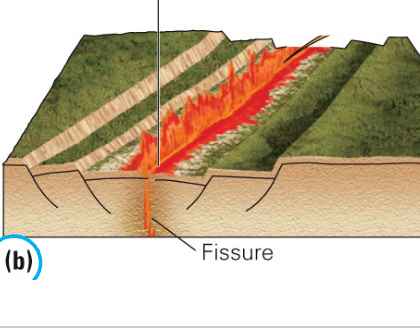
Effusive Eruptions: Shield Volcanoes/Flood Basalts
Explosive Eruptions: Stratovolcanoes/Lava Domes/Cinder Cones
Shield volcanoes
Gentle outpouring of low-silica fluid lavas from a central vent or conduit, Fissure-crack along the flanks of a shield volcano that erupts lava
Ex. Iceland
Strato/ Composite Volcanoes
Combination of effusive and explosive volcanic activity, Occurs landward side of a subduction zone
Ex. Mount Fuji
Stratovolcanoes
Subduction of the Juan de Fuca plate beneath North America has produced the Cascade Range
Lahars
Fast moving volcanic debris flow, Mobilization of debris by water
Ex. Colombia’s nevado del Ruiz
Pyroclastic Debris
Turbulent mixtures of hot gases and pyroclastic material that travel with great velocity and tephra
Tephra
Volcanic rock ejected during an eruption
Nuee Ardente
Pyroclastic flow that consist of hot gases infused with incandescent ash and larger rock fragments
Cinder Cones
Built from ejected lava fragments that take on the appearance of cinders/ small, erupt once, numerous, built of tephra
Calderas
Giant volcanic depressions usually formed after a large eruption, the magma chamber below empties and the volcano collapses into the emptied chamber
Dikes (intrusive igneous activity)
Magma injected into fracture perpendicular to bedding plane
Sills (intrusive igneous activity)
Magma injected into fractures along a bedding plane
Laccoliths (intrusive igneous activity)
Similar to a sill but magma more viscous
Batholith (intrusive igneous activity)
Largest igneous body
Volcanic Hazards
Flows, Ash, Blast, Landslides, and Earthquakes
Mountain Building
True mountains form by convergent plate tectonic activity
Non-tectonic mountains are usually formed by eroding a high plateau
Orogeny
The processes that collectively produce a mountain belt
Rock Deformation
All the changes in the original shape and/or size of the rock body: changes in location or rotation
Brittle (Deformation)
Cracking and fracturing of material subjected to stress
Ductile (Deformation)
The flowing of material subjected to stress with cracking
Folds
Layers of rocks that are deformed by tectonic compression, form geometry (hinge, limbs, axial plane)
Hinge
A line along which curvature is the greatest
Monocline
Result of the reactivation of steeply dipping fault zones in basement rock, caused by a blind fault
Domes
Folded or arched layers with the shape of an overturned bowl that is produced by unwrapping (Black Hills)
Basins
A fold shaped like a right-side bowl that is produced by downwrapping (Bedrock in Michigan)
Normal fault
Associated with fault-block mountains, divergent plate boundaries, tensional forces
Fault Block Mountains
The tensional stress applied to rocks causes a fault system of normal faults called Horst and Graben
Horst
The high block between two grabens
Graben
A down-dropped crustal block bounded on either side by a normal fault dripping toward the basin
Fault Block Mountains
Mountains that are produced by continental rifting or extension of the crust that bounded by high angle normal faults that flatten at depth
Reverse and Thrust Fault
Compressional forces, convergent plate boundaries ( Reverse: > 45o) (Thrust: <45o)
Mountain Building
Volcanic Island Arcs (Oceanic) and Andean( continental volcanic arc)
Accretion and Orgogenesis
Accretion of terranes along a subduction zone can form mountains
Terrane
A crustal block, bounded by faults, whose geologic history is distinct from the history of the adjoining crustal block
The North American Cordillera
Comprised of numerous accreted terranes
Continental- Continental Convergence
Continental collisions are when two tectonic plates made up of continental crust converge on each other, during collision intense compression and shear cause the crust to thicken through folding and faulting
isostasy
Concept of a floating crust in gravitational balance
Isostatic Adjustment
Establishing a new level of gravitational equilibrium, the process of uplift and erosion will continue until the mountain block reaches normal crustal thickness
Mass Wasting
It is the downslope motion of rock, regolith, snow, and ice (Gravity)
Landslide
Is a general term having the same meaning as mass wasting
Slope Stability
mass wasting will occur if the force of gravity pulling on the block exceeds the resistance holding the block in place
Controls and Triggers of Mass Wasting
The role of water, oversteepend slopes, undercutting, planes of weakness, removal of vegetation
The role of water
Mass wasting can occur when heavy rains saturate the soil- saturation reduces the internal resistance of materials
Oversteepend Slopes
Erosion and cut & fill may cause landslides
Removal of Vegetation
Plants protect against erosion because roots bind soil together
Roots help hold rock and soil in place