Human Bio
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
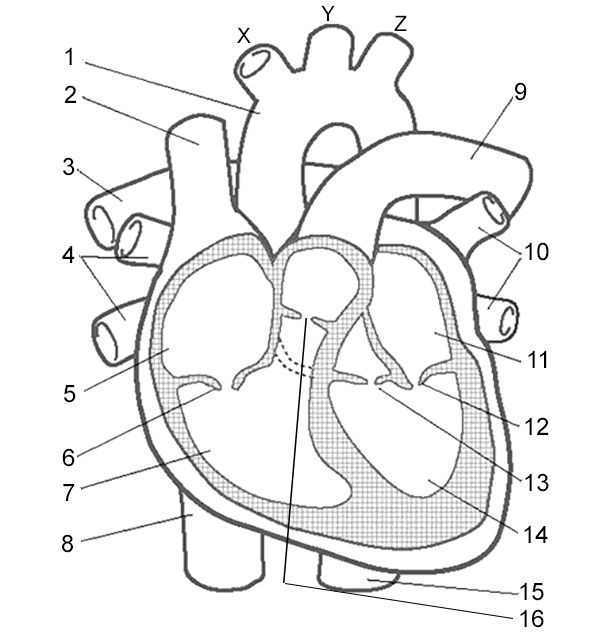
Label 1
Aorta - carries oxygenated blood to the body
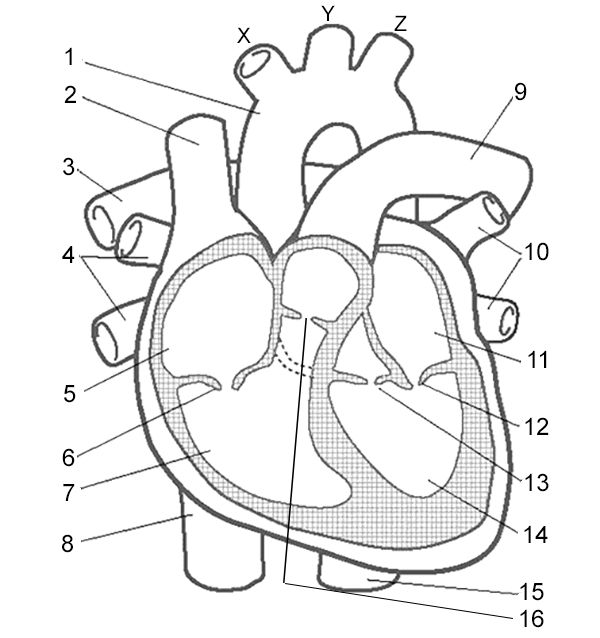
Label 2
Superior Vena Cava - carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body
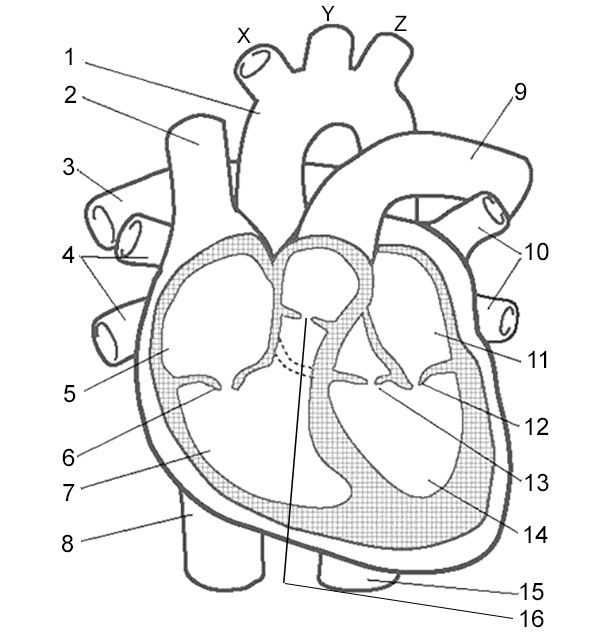
Label 3
Pulmonary Arteries - carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs
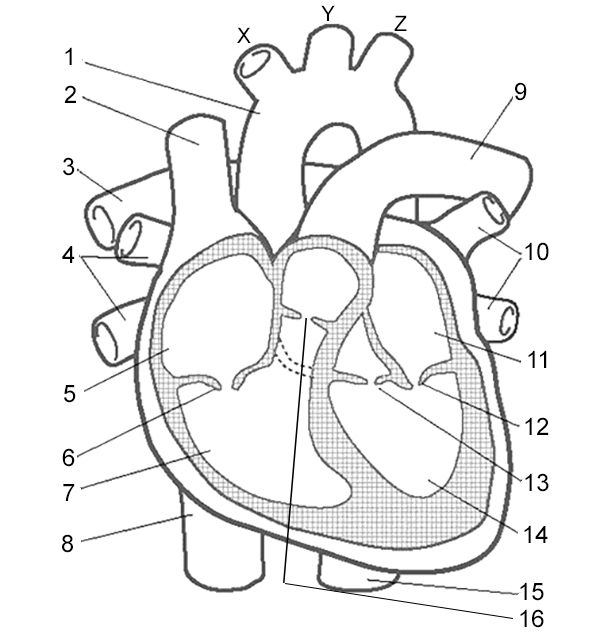
Label 4
Pulmonary Veins - carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
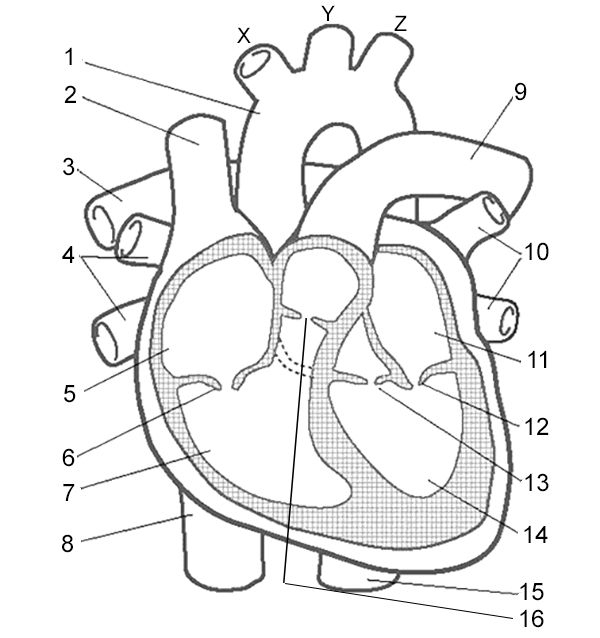
Label 5
Right Atrium - receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava.
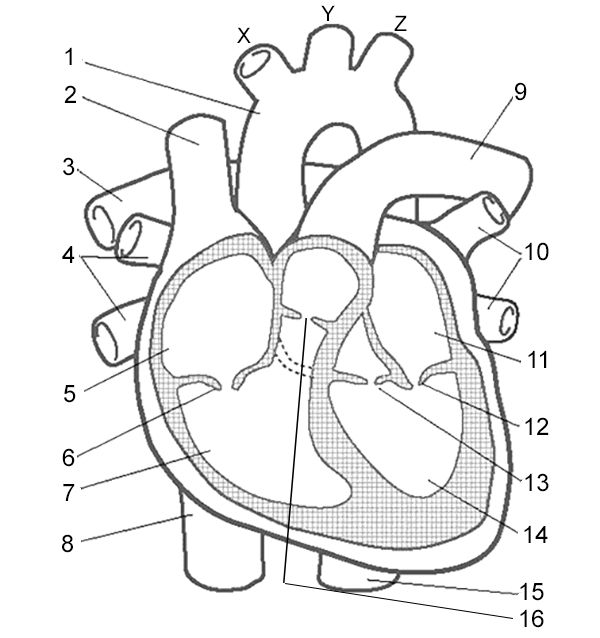
Label 6
Right Atrioventricular Valve - valve that allows blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
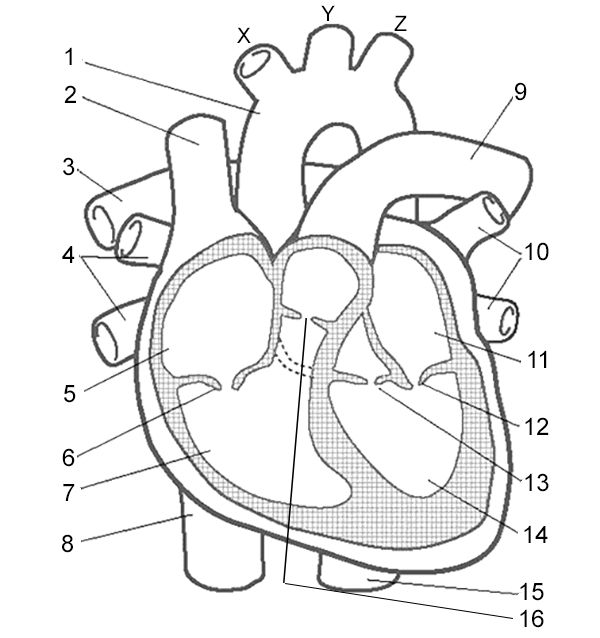
Label 7
Right Ventricle - pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
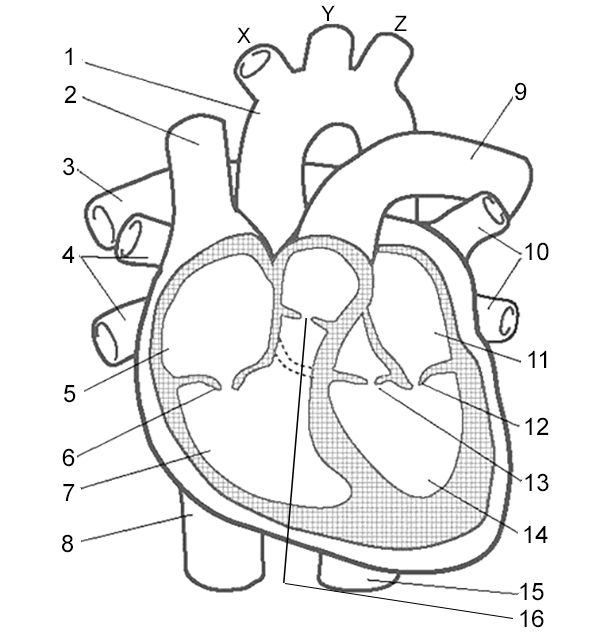
Label 8
Inferior Vena Cava - large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the right atrium.
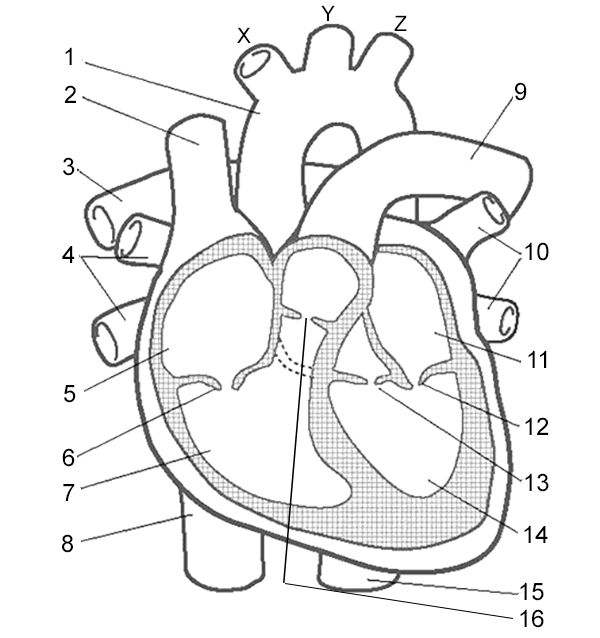
Label 9
Pulmonary Artery - vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation.
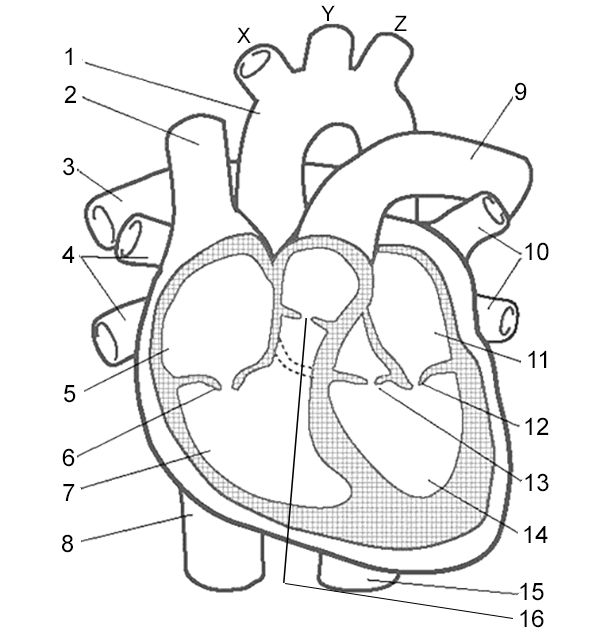
Label 10
Pulmonary Veins - vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
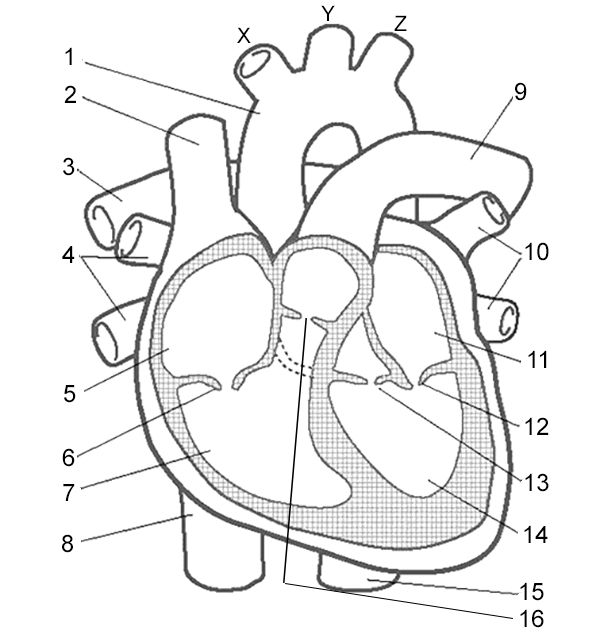
Label 11
Left Atrium - receives oxygenated blood from lungs
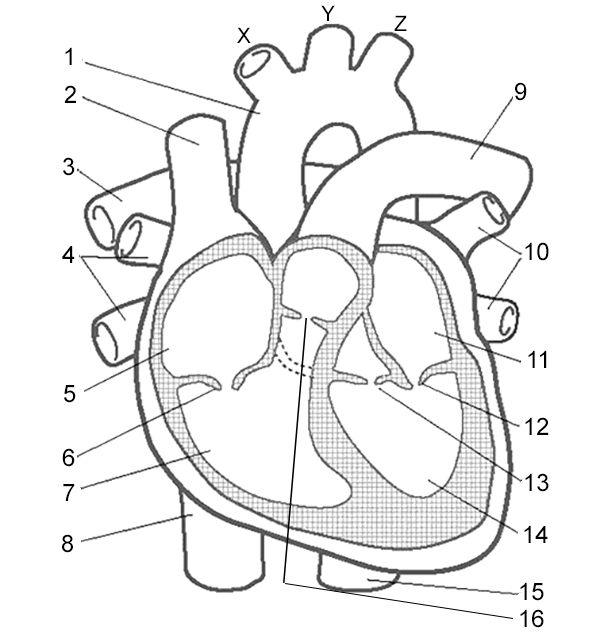
Label 12
Left Atrioventricular Valve - valve that allows blood to flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle.
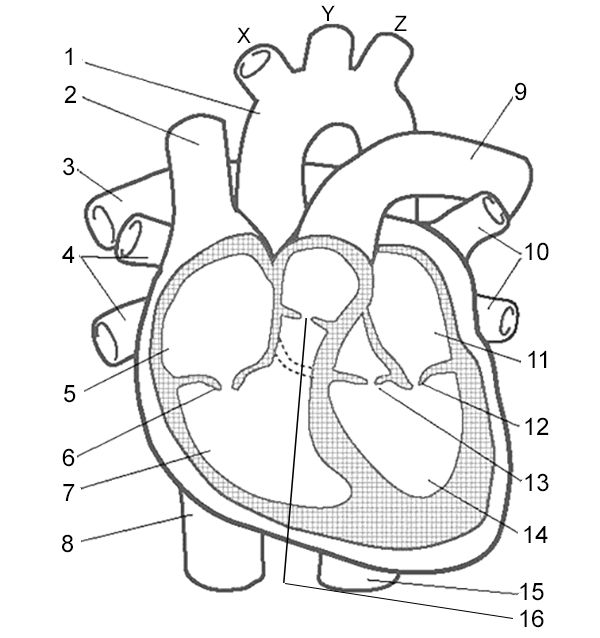
Label 13
Left Semilunar Valve - receives oxygenated blood from left ventricle and pumps it to body
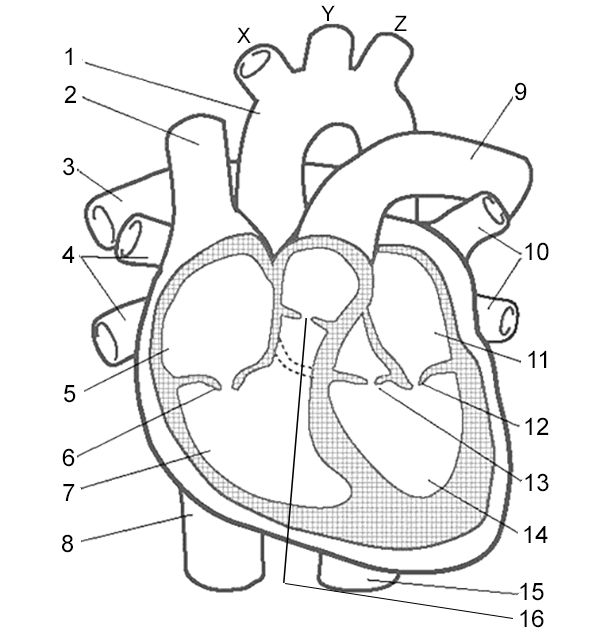
Label 14
Left Ventricle - receives oxygenated blood from left atrium and pumps it to aorta
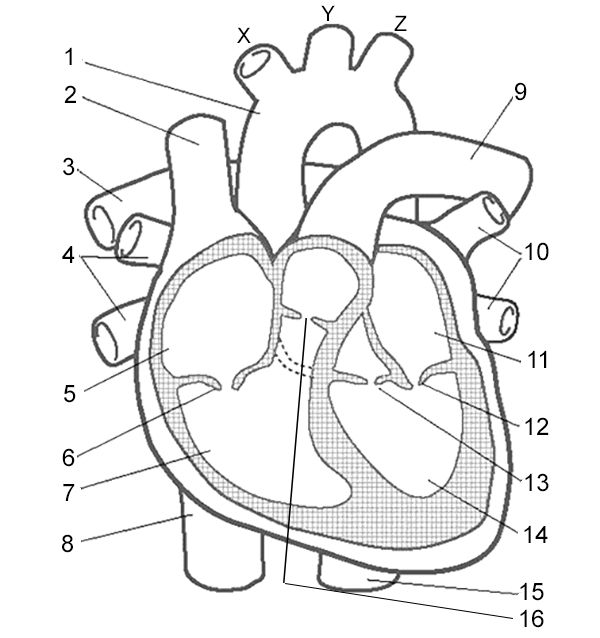
Label 16
Right Semilunar Valve - receives deoxygenated blood from right ventricle and pumps it to lungs
Heart
The muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients while removing carbon dioxide and waste.
Valves
structures in the heart that open and close to make sure blood only flows in one direction
Circulatory System
The organ system responsible for the transportation of blood, nutrients, gases, hormones, and removal of waste throughout the body
Respiratory System
The organ system responsible for breathing and the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body
Blood
Transport link between the cells of all body systems
Double Circulation
The blood passes twice through the heart making one complete round through body
Veins
Thin, inelastic wall, low blood pressure, contains valves, takes blood towards heart
Arteries
Thick, muscular, elastic walls, high blood pressure, takes blood away from heart
Capillaries
Link arteries and veins, 1 layer of cells, carry blood close to cells in body, deliver nutrients and take away waste
Diastole
Heart muscles relax and chambers fill with blood
Systole
Heart muscles contract and pump blood
Pulmonary Circulation
Responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs
Systematic Circulation
Pathway of blood flow that delivers oxygenated blood from left ventricle to body
Leucocytes
White blood cells, 1%, defend body against infections and foreign invaders, formed in bone marrow
Plasma
55%, mixture of water with dissolved substances, transports cells, nutrients, wastes, hormones, proteins, and antibodies
Erythorcytes
Red blood cells, 40-45%, biconcave shape, no nucleus, transport oxygen, formed in bone marrow, destroyed by macrophages after 100-120 days
Thrombocytes
Platelets, small cell fragments, adhere to lining and form scaffold (blood to form a clot)
ABO Blood System Types
Type A, Type B, Type AB, Type O
Type A Blood
Antigen A, antibody B, can donate to A AB, can receive from A O
Type B Blood
Antigen B, Antibody A, can donate to B AB, can receive from B O
Type AB Blood
Antigen A + B, neither antibodies, can donate to AB, can receive from A B AB O
Type O Blood
Neither antigen, Antibody A + B, can donate to A B AB O, can receive from O
Antigen
Sugar and protein molecules on the surface of red blood cells that can stimulate an immune response
Antibody
In response to exposure to an antigen
Rhesus Factor Grouping
Rh antigens = Positive, No Rh antigens = negative
Positive
Rh antigen, cannot produce anti Rh
Negative
no Rh antigens, can produce anti Rh
Universal Donor
O- as it has no antigens present on red blood cells which means no agglutination would be caused in any recipient
Universal Recipient
AB+ as there are no anti A or anti B in blood so no agglutination would be caused in any recipient
Lymphatic System Function
Collect some fluid that escapes from blood capillaries and return it to circulatory + plays role in internal defence against disease causing organisms
Tissue Fluid vs Plasma
Plasma contains more protein molecules
Lymph
Clear, colourless fluid that circulates through the lymphatic system
Lymphatic System Structure
Network of lymph capillaries joined to larger lymph vessels and lyph nodes along length of some lymph vessels
Substances that CANNOT pass through capillary walls
anything other than oxygen, water, proteins, fats
Semi Permeable Membrane
Allows some substances to pass through but restricts movements of larger molecules
How do substances move from blood into cells
Diffusion - substances moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
How are lungs well suited to their function
Large surface area, moist environment, and rich blood supply
Inspiration
Diaphragm contracts, intercostal muscles contract, ribs move up and out, volume in chest cavity increases, pressure in lungs decreases, air moves high to low pressure into lungs
Expiration
Diaphragm relaxes, intercostal muscles relax, ribs move down and in, volume in chest cavity decreases, pressure inside lungs increases, air moves high to low pressure out of lungs
Inhalation Order
Nasal cavity, pharynx, epiglottis, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli