KIN 222 - Midterm 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:38 AM on 10/26/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
1
New cards
Biomechanics
study of structure and function of biological system by means of the methods of mechanics
2
New cards
Kinematics
study of motion WITHOUT regard to the forces that cause it
3
New cards
Kinetics
study of forces
4
New cards
Quantitative analysis definition and example
- numerical evaluation of motion based on measurement
- hip flexes X degrees, knee flexes Y degrees
- hip flexes X degrees, knee flexes Y degrees
5
New cards
pros/cons of quantitative analysis
pros: objective, accurate, specific
cons: expensive, difficult to get data (special training and equipment required), difficult to apply, need norms
cons: expensive, difficult to get data (special training and equipment required), difficult to apply, need norms
6
New cards
Qualitative analysis definition and example
- non-numerical evaluation of motion based on observation
- hip flexes, knees flex
- hip flexes, knees flex
7
New cards
pros/cons on qualitative analysis
pros: cheaper, time efficient
cons: subjective, general, less accurate, experience changes results
cons: subjective, general, less accurate, experience changes results
8
New cards
statics is the evaluation of objects in a state of ...
evaluation of objects in a state of equilibrium - at rest or constant velocity
9
New cards
dynamics is the evaluation of objects ...
evaluation of objects that are not in a state of equilibrium - acceleration
10
New cards
Evaluating a runner at the start position would be static or dynamic?
static
11
New cards
Evaluating a runner after the start position would be static or dynamic?
dynamic
12
New cards
Scalar definition and examples
- can be described by magnitude
- distance, speed, mass, volume, energy
- distance, speed, mass, volume, energy
13
New cards
Vector definition and examples
- can be described by magnitude and direction
- displacement, velocity, acceleration, force
- displacement, velocity, acceleration, force
14
New cards
linear motion definition and example
- straight or curved motion where all parts move the same distance in an equal amount of time
- ball travelling after a throw
- ball travelling after a throw
15
New cards
Angular motion definition and example
- motion about an axis of rotation where regions do not move the same distance in an equal amount of time
- a rotating sprinkler
- a rotating sprinkler
16
New cards
Gait definition. What are the two primary gait patterns?
- particular pattern of footfalls that are used in locomotion
- walk and run
- walk and run
17
New cards
Describe the gait cycle events
Stance Phase (60% of the stride):
Heel #1 makes contact with ground in frontward position (double support). All weight transfers to #1 (single support) as hip extends. Heel #2 makes contact with ground (double support).
Swing Phase (40% of the stride):
All weight transfers to leg #2(single support). Leg #1 swings from hip extension to flexion
Heel #1 makes contact with ground in frontward position (double support). All weight transfers to #1 (single support) as hip extends. Heel #2 makes contact with ground (double support).
Swing Phase (40% of the stride):
All weight transfers to leg #2(single support). Leg #1 swings from hip extension to flexion
18
New cards
Step
process of moving one limb forward
19
New cards
stride
porcess of making one step with each foot
20
New cards
stride time
time it takes to complete one stride
21
New cards
stride length
distance between heel strikes of the same foot
22
New cards
stride velocity
- vector so includes changes in direction
- stride length/stride time
- stride length/stride time
23
New cards
walking speed
- scalar
- distance/time
- distance/time
24
New cards
stride cadence (this is a frequency)
1/stride time
25
New cards
If time decreases what happens to stride velocity and walking speed?
increases
26
New cards
What is the relationship between stride velocity and stride length, and stride velocity and cadence? What does this relationship show?
There is a linear relationship (increase stride length = increase stride velocity, increase cadence = increase stride velocity). This shows the preferred speed-step length relationship where the pace chosen is the pace with the least metabolic cost
27
New cards
What happens to stride length and cadence as velocity increases during running?
The linear relationship held at walking speed does not continue. Stride length plateaus and cadence increases
28
New cards
What is the difference between a walk and a run?
Walk:
- always one foot in contact with ground
- contact pattern: 1, 2,1
Run:
- an airborne phase between single supports
- contact pattern: 1, 0, 1
- always one foot in contact with ground
- contact pattern: 1, 2,1
Run:
- an airborne phase between single supports
- contact pattern: 1, 0, 1
29
New cards
What is considered to be a functional vital sign?
Walking speed. It is used to identify health issues and can predict adverse health outcomes
30
New cards
displacement
- change in an objects position from initial to final location
- vector
= final position - initial position
- vector
= final position - initial position
31
New cards
velocity
- rate of change of an objects displacement over a particular time interval
- vector
= displacement/time or (final position- initial position)/ (final time - initial time)
- vector
= displacement/time or (final position- initial position)/ (final time - initial time)
32
New cards
when velocity = 0
object not moving or object changing direction
33
New cards
Distance
- total length travelled
- scalar
- scalar
34
New cards
when distance = displacement
object moves in straight line
35
New cards
Displacement is always _____ than or _____ to distance
less than or equal
36
New cards
speed
- distance travelled over time or rate of distance travelled over time
- scalar
= distance/time
- scalar
= distance/time
37
New cards
average velocity
average change in displacement over a time interval
38
New cards
instantaneous velocity
rate of change of displacement at a particular instant in time
39
New cards
what happens to displacement when velocity increases and time is constant?
displacement increases
40
New cards
What happens to displacement when time increases and velocity is constant
displacement increases
41
New cards
On a displacement over time graph, what represents velocity? A positive velocity is indicated by? A negative velocity is indicated by? What point on a graph would indicate that the object is changing direction? The greater the slope = ? Lesser?
- slope
- positive slope (line going upward)
- negative slope (line going downward)
- when slope changes from pos to neg or neg/pos. This indicates velocity = 0
- greater velocity
- lesser velocity
- positive slope (line going upward)
- negative slope (line going downward)
- when slope changes from pos to neg or neg/pos. This indicates velocity = 0
- greater velocity
- lesser velocity
42
New cards
How do you calculate velocity on a displacement over time graph?
slope = rise/run
43
New cards
What motion is each segment represent?
1. Accelerating walking in positive direction (speeding up)
2. decelerating walking in positive direction (slowing down)
3. y = 0 stop or change in direction
4. Accelerating in negative direction
5. Decelerating in negative direction
6. stop
2. decelerating walking in positive direction (slowing down)
3. y = 0 stop or change in direction
4. Accelerating in negative direction
5. Decelerating in negative direction
6. stop
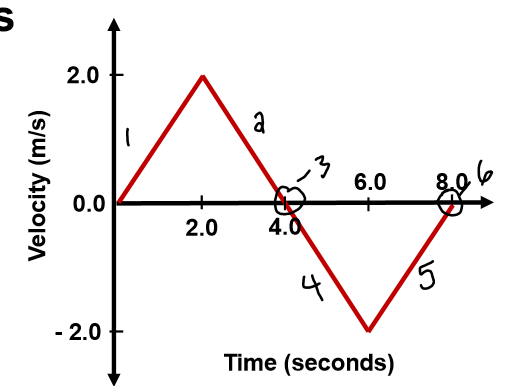
44
New cards
How is displacement calculated on a velocity vs time graph?
By taking the area of the graph and subtracting positive and negative displacements.
Calculate area of a triangle = 0.5 x base x height
Calculate area of a triangle = 0.5 x base x height
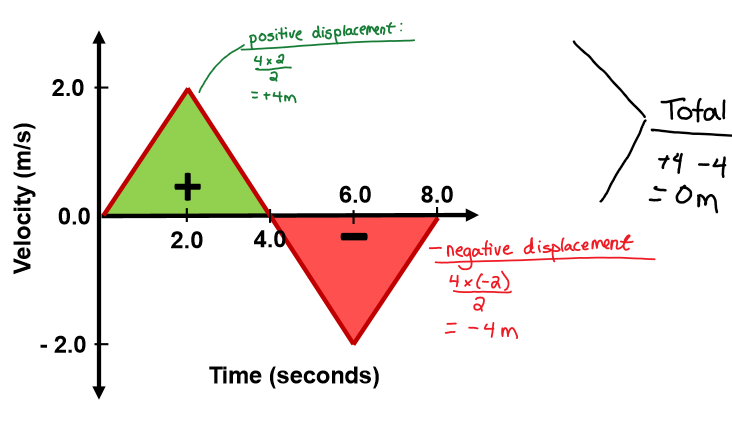
45
New cards
Describe the motion that each velocity vs time graph illustrates
A: slow acceleration , fast acceleration , fast deceleration, slower deceleration
B: deceleration + direction, change direction, acceleration in - direction
C: constant deceleration to a stop
D: moving at a constant velocity
B: deceleration + direction, change direction, acceleration in - direction
C: constant deceleration to a stop
D: moving at a constant velocity
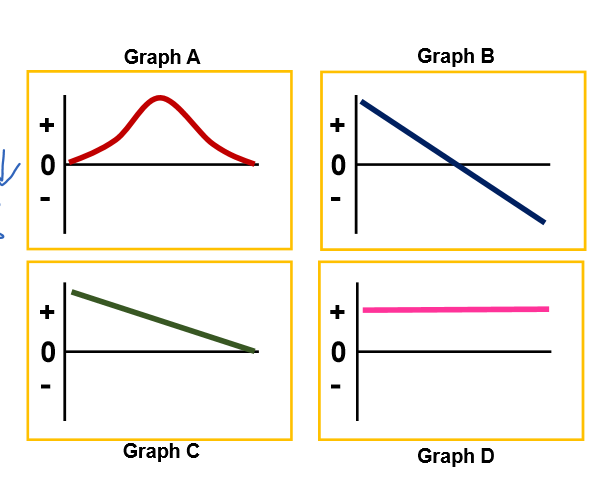
46
New cards
Acceleration
- measure of the rate of change of velocity with respect to time
- vector quantity
- vector quantity
47
New cards
True or False. A change in velocity does not always indicate there is acceleration?
False. If there is a change in velocity (either magnitude or direction) then there is acceleration
48
New cards
If acceleration and velocity are in the same direction
velocity will increase
49
New cards
If acceleration and velocity are in opposite directions
velocity will decrease until the object stops or changes direction
50
New cards
What type of path do projectiles follow?
Parabolic
51
New cards
What are the vertical and horizontal accelerations of projectiles
- vertical -9.81 m/s^2
- horizontal 0, remains constant
- horizontal 0, remains constant
52
New cards
If you kick a ball upwards at 0, 45, and 90 degrees, which will have the greatest vertical and horizontal displacement?
0
- no vertical displacement
- horizontal displacement but slows down from surface friction
45
- less vertical displacement than kicking upwards at 90
- greatest horizontal displacement
90
- greatest vertical displacement
- no horizontal displacement
- no vertical displacement
- horizontal displacement but slows down from surface friction
45
- less vertical displacement than kicking upwards at 90
- greatest horizontal displacement
90
- greatest vertical displacement
- no horizontal displacement
53
New cards
Describe the time and horizontal displacement of a projectile with equal launch and landing height
- time from launch to apex is equal to time from apex to landing
- horizontal displacement equal from launch to apex and apex to landing
- horizontal displacement equal from launch to apex and apex to landing
54
New cards
Describe the time and horizontal displacement of a projectile with a higher launch point than landing point
- time from launch to apex will be shorter than apex to landing
- horizontal displacement will be shorter from launch to apex than apex to land
- horizontal displacement will be shorter from launch to apex than apex to land
55
New cards
Describe the time and horizontal displacement of a projectile with a lower launch point than landing point
- time from launch to apex will be longer than apex to land
- horizontal displacement from launch to apex will be longer than apex to land
- horizontal displacement from launch to apex will be longer than apex to land
56
New cards
When are velocity formulas inaccurate?
when the object is undergoing acceleration
57
New cards
If a person is not undergoing acceleration, what formula can be used and will be accurate
average velocity formulas can be used
58
New cards
frontal plane
anterior and posterior halves
59
New cards
transverse plane
inferior and superior portions
60
New cards
saggital plane
left and right sides
61
New cards
Anteroposterior axis
- goes through the body from front to back
- associated with frontal plane
- associated with frontal plane
62
New cards
Longitudinal axis
- runs from top to bottom
- associated with the transverse plane
- associated with the transverse plane
63
New cards
Mediolateral axis
- side to side
- associated with sagittal plane
- associated with sagittal plane
64
New cards
what are degrees of freedom? What is the max degrees of freedom? How many degrees of freedom do joints have?
- number of independent movements an object can perform
- max 6 degrees of freedom (3 rotations, 3 translations)
- joints have 1-3 however, translation also occurs at many joints, increasing their degrees of freedom
- max 6 degrees of freedom (3 rotations, 3 translations)
- joints have 1-3 however, translation also occurs at many joints, increasing their degrees of freedom
65
New cards
Shoulder joint (Glenohumeral) - what type of joint and how many degrees of freedom?
- ball and socket
- 3 df
- 3 df
66
New cards
Name the glenohumeral joint movements and what plane/axis they occur in
Flexion/extension
- saggital and mediolateral
Abduction/abduction
- frontal and anteroposterior
Medial and lateral rotation
- transverse plane longitudinal axis
- saggital and mediolateral
Abduction/abduction
- frontal and anteroposterior
Medial and lateral rotation
- transverse plane longitudinal axis
67
New cards
Superior and inferior radioulnar joints - what type of joint and how many degrees of freedom
- pivot joint
- 1 df
- 1 df
68
New cards
ulnarhumeral and radiohumeral joint - what type of joint and how many degrees of freedom
- hinge
- 1 df
- 1 df
69
New cards
Acetabulofemoral - what type of joint and how many df?
- ball and socket
- 3 df
- 3 df
70
New cards
Describe the movements of the hip joint and what plane/axis they occur in
Flexion/extension
- sagital
- mediolateral
Adduction/abduction
- frontal
- anteroposterior
medial/lateral rotation
- transverse
- longitudinal
- sagital
- mediolateral
Adduction/abduction
- frontal
- anteroposterior
medial/lateral rotation
- transverse
- longitudinal
71
New cards
Knee (Tibiofemoral) joint - what type of joint and how many df?
- double condyloid (modified hinge)
- 2 df
- significant translation accompanies knee joint motion
- 2 df
- significant translation accompanies knee joint motion
72
New cards
Name the movements of the knee joint and what plane/axis they occur in
Flexion/extension
- sagital
- mediolateral
Medial/lateral rotation
- transverse
- longitudinal axis
- sagital
- mediolateral
Medial/lateral rotation
- transverse
- longitudinal axis
73
New cards
Ankle (talocrural) joint - what type of joint and how many df?
- hinge
- 1 df
- 1 df
74
New cards
ankle joint movements and plane/axis
dorsi/plantar flexion
- sagital
- mediolateral
- sagital
- mediolateral
75
New cards
What symbols are used for angular kinematics?
- theta: angular displacement
- omega: angular velocity
- alpha: angular acceleration
- omega: angular velocity
- alpha: angular acceleration
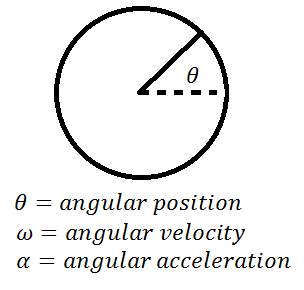
76
New cards
Counter clockwise rotations are? Clockwise?
- positive
- negative
- negative
77
New cards
Angular displacement definition. Vector/scalar? Formula
- differences between the initial and final orientation of a rotating object
- vector
= final orientation - initial orientation
- vector
= final orientation - initial orientation
78
New cards
Angular distance definition. Vector/scalar?
- total of all angular changes measured following a rotating segments exact path
- scalar
- scalar
79
New cards
Angular displacement cannot be greater than _____, angular distance can be ______
- 360 degrees
- any value
- any value
80
New cards
Angular velocity definition. What is it analogous to? Formula.
- rate of change of angular displacement over time
- analogous to linear velocity
- w = (theta final - initial)/time
- analogous to linear velocity
- w = (theta final - initial)/time
81
New cards
The steepness of an angle vs time graph determines the? The direction of the slope determines the?
- magnitude of angular velocity
- direction of angular velocity
- direction of angular velocity
82
New cards
On an angle vs time graph, a change in the direction of the slope indicates a?
a change in the direction of movement
83
New cards
on an angular velocity vs time graph, a change in the sign of angular velocity indicates
a change in direction of movement
84
New cards
Angular motion definition
- evaluation of an objects motion around a fixed axis
- all parts move through the same angle, but do not have equal linear distance
- all parts move through the same angle, but do not have equal linear distance
85
New cards
Name 3 techniques used to measure angular motion
- Video: camera captures frames/sec
- Motion capture: uses specific dots/points on body, then is input into computer
- goniometry: measures the joint angle with specific instruments ex. the bendy wire
- Motion capture: uses specific dots/points on body, then is input into computer
- goniometry: measures the joint angle with specific instruments ex. the bendy wire
86
New cards
local reference system
axes are aligned with a segment and intersect at the joint center
87
New cards
global reference system
axes are aligned with the vertical and horizontal relative to the environment (lab)
88
New cards
How are absolute segment angles calculated?
- use the trigonometric relationship of tangent
- the distal end coordinate values are subtracted from the proximal end coordinate values
- theta = [(y prox - y dist)/ (x prox - x dist)]
- the distal end coordinate values are subtracted from the proximal end coordinate values
- theta = [(y prox - y dist)/ (x prox - x dist)]
89
New cards
What is a relative joint angle? What reference system is used? Where is the vertex located?
- the angle between the longitudinal axis of two segments. Defined as the angle of one segment relative to another segment
- local reference system
- at joint
- local reference system
- at joint
90
New cards
Relative (joint) angle conventions - a system of lower limb conventions has been proposed for two dimensional sagittal plane rotation of the _____, _______, and ______ joints.
This system uses the _______ angles of the trunk, thigh, leg, and foot to calculate relative joint angles
With this system, it is assumed that the _____ side of the body is captured
This system uses the _______ angles of the trunk, thigh, leg, and foot to calculate relative joint angles
With this system, it is assumed that the _____ side of the body is captured
- hip, knee, and ankle
- absolute
- right
- absolute
- right
91
New cards
The relative hip angle is based on the absolute angles of the?
thigh and trunk
92
New cards
When the hip angle is positive, the hip is in what position? Angle = zero? Angle is negative?
- flexed (because it is to the right of the vertical axis)
- neutral
- extended (because it is left of the vertical axis)
- neutral
- extended (because it is left of the vertical axis)
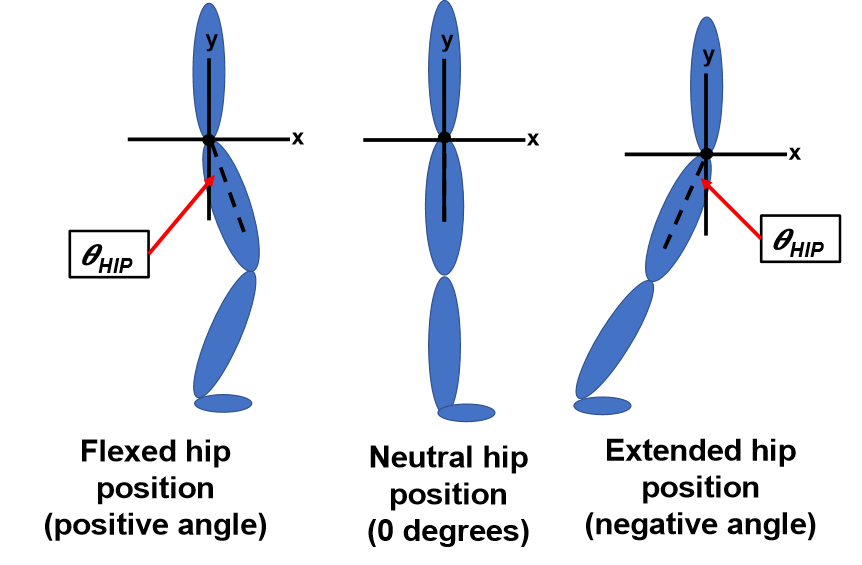
93
New cards
What is the formula for calculating relative hip angle
theta hip = theta thigh - theta trunk
94
New cards
The relative knee angle is based on the absolute angles of the?
thigh and leg
95
New cards
When the knee is in a flexed position the angle is? When the knee is in the extended position? Hyper-extended?
- positive (extend the shin line upwards and it will end up in the positive right quadrant)
- neutral
- negative (extend the shin line upwards and it will be in the negative x quadrant)
- neutral
- negative (extend the shin line upwards and it will be in the negative x quadrant)
96
New cards
What is the formula for calculating relative knee angle?
theta knee = theta thigh - theta leg
97
New cards
The relative ankle angle is based on the absolute angles of the
leg and foot
98
New cards
When the angle is positive, the ankle is in what position? Angle = zero? Negative?
- plantarflexed
- neutral position (ex standing)
- dorsiflexed position
- neutral position (ex standing)
- dorsiflexed position
99
New cards
What is the formula for relative ankle angle?
theta ankle = theta leg - theta foot + 90
100
New cards
Define angular acceleration. It is analogous to?
- rate of change of angular velocity over time
- analogous to linear acceleration
- analogous to linear acceleration