Synapses and summation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what is a synapases ?
its’s a junction between 2 more more neurones
what is a synaptic cleft ?
a small gap 20 nm between the neurones.
Cholinergic synapses
a synapse that uses acetylcholine as it’s neurotransmitter.
what is a neurotransmitter?
a chemical used as a signalling molecules between two neurones in a synapse.
type of neurotransmitter
acetylcholine
Presynaptic neurone
ends in swelling called presynaptic bulb
what does the presynaptic neurone contain ?
mitochondria, vesicles, large amount of SER and voltage agates Ca+ channels.
Postsynaptic neurone
located at the other side of the synaptic cleft , also specialised in key ways
key ways of Postsynaptic neurone specialised
contain receptors that are complementary to specific neurotransmitter
contain many Na+ ion channels.
Transmission across a synapse
An action potential arrives at the presynaptic bulb
The voltage gated calcium ion channels open
Calcium ions diffuse into the presynaptic bulb
Calcium ions cause vesicles full of neurotransmitter to move and fuse with the cell surface membrane
Acetylcholine is released via exocytosis
Acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft
Acetylcholine binds with complimentary receptors on the postsynaptic membrane
This causes sodium ion channels to open
Sodium ions diffuse across the postsynaptic membrane
A generator potential is created (also called an excitatory post synaptic potential, or EPSP)
Multiple generator potentials will cause a rise in potential that goes over the threshold
A new action potential is created in the post synaptic neurone
Regulating transmission across synapses
If acetylcholine remains in the cleft, it will continue to trigger responses in the post synaptic neurone. To regulate the impulses generated, we need to be able to remove acetylcholine when it is no longer needed.
Acetylcholinesterase in an enzyme found in the synaptic cleft, which breaks down the neurotransmitter into ethanoic acid and choline.
These two molecules are recycled. The re-enter the presynaptic bulb and are converted back into adeldholine using the ATP generated from the many m/tochandria.
increase the duration of the neurotransmitter not the volume of the neurotransmitter
by blocking the synaptic cleft
Synapses and communication
how is excitatory post synaptic potential (EPSP) produce ?
A relatively small amount of acetylcholine will diffuse across the synaptic cleft and produce an excitatory post synaptic potential (EPSP). One of these is not enough to overcome the threshold potential.
what does the term summation mean ?
It often takes many EPSPs to reach the threshold potential. The combined effect of many of these EPSPs is known as summation.
what does summation result in ?
Summation can result from several action potentials from the same presynaptic neurone (temporal summation) or from action potentials arriving from different presynaptic neurones (spatial summation).
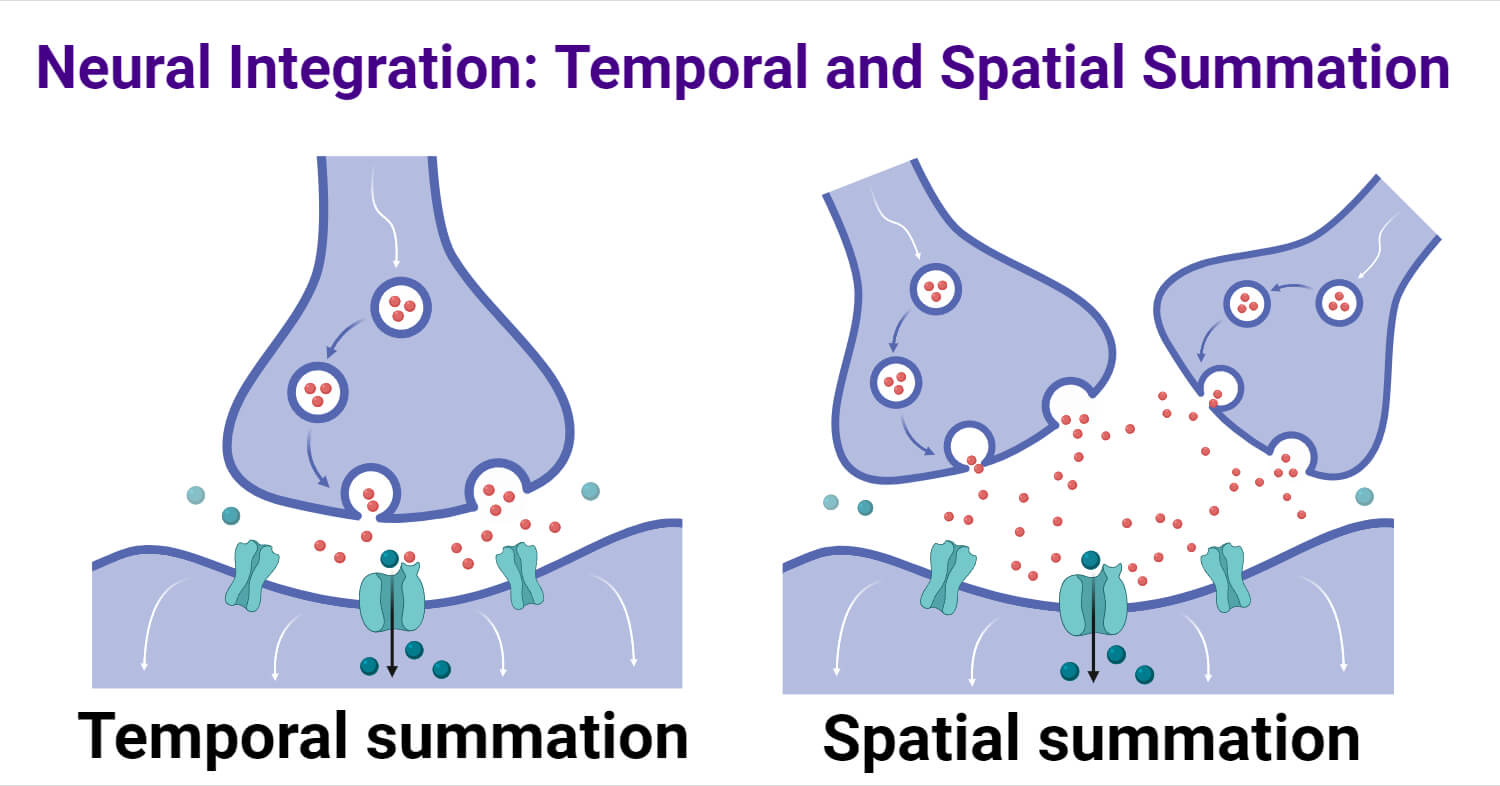
Temporal summation:
The repeated action potentials in the pre-synaptic neurone are required to generate an action potential in the post synaptic neurone.
Spatial summation:
The post-synaptic neurone requires action potentials from serval re-synaptic neurones.
Action potentials have a fix strength.
The frequency of transmission changes.
-> as we increase frequency = increase intensity of signals
what can presynaptic neurone produce ? what will it effect ?
In addition to this stimulation process, some presynaptic neurones can produce inhibitory postsynaptic potentials.
These can dampen the effect of summation and prevent an action potential from occurring in the postsynaptic neurone.