Science 9: Space Exploration SE1 Vocabulary
1/31
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Celestial Bodies
All objects seen in the sky (the Sun, Moon, stars, and planets)
Constellations
Groupings of stars that form patterns, which appear like objects, and are given names (such as Orion, the Hunter)
Sky Coordinates
Locate a celestial body relative to a fixed Earth (as though the celestial bodies are circling Earth)
Azimuth
The angle measured clockwise from North when measuring altitude-azimuth coordinates
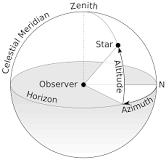
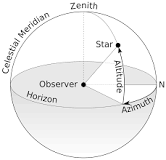
Altitude
The angle measured above the horizon in degrees when meausring altitude-azimute coordinates
Astrolabe
A device used to measure the altitude of an object
Compass
A device used to measure an object’s azimuth
Solstice
Either of the two times during the year when the sun is most northerly or southerly from the equator (shortest and longest day of the year)
Equinox
The days where days and nights are of equal length
Zenith
The point in the sky directly above an observer (90 degree altitude)
Geocentric Model
Earth centered Universe model, proposed by Aristotle
Heliocentric Model (Sun-centred)
A model of the universe that places the Sun at the centre with Earth, the planets, and Moons revolving around it
Universal Gravitaton
Newton’s law states that all objects attract all other objects, and provides an explanation for the planets’ elliptical orbits
Elliptical Orbit
An oval-shaped path due to gravitational interactions among celestial bodies
Aristotle
Greek philosopher that proposed Earth centered model (384-322 BC)
Ptolem
Greek philosopher attempted to explain retrograde motion by including small epicycles (AD 90-168)
Copernicus
Astronomer that proposed heliocentric system (orbiting sun)
Galileo
Improved the telescope in 1600s
Kepler
Predicted that the planets moved in elliptical orbits rather than circular orbits, explained retrograde motion (1571-1630)
Refracting Telescope
Invented by Lippershey/Galileo, uses lenses to gather more light than the human eye could collect on its own and focuses it. Used for planetary viewing.
Reflecting Telescope
Invented by Newton, uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. Used for deep sky viewing.
Radio Telescope
Invented by Jansky/Reber in the 1930s, detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Can penetrate dust clouds and access areas unavailable to optical telescopes, can be used day and night.
Resolving Power
Magnification
Focal Length of Objective Lens/Focal Length of the Eyepiece Lens
Interferometry
A technology that connects 2 or more telescopes to combine their images
Adaptive Optics
A technology for ground based telescopes that adjusts the mirrors of a telescope or the image they product to cancel the effects of atmospheric distortion
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength
Spectroscope
A scientific instrument that splits light into its different wavelengths, which humans see as different colours
Spectral lines
Dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum used to identify elements
Spectroscopy
Spectral analysis can be used to identify the chemical composition of distant stars. By comparing the black lines to the unique spectrum of each element, we can determine the composition of stars
Diffraction grating
A series of closely spaced slits
Spectral analysis
Spectral analysis can be used to identify the chemical composition of distant stars. By comparing the black lines to the unique spectrum of each element, we can determine the composition of stars