Gas laws u13 h. chem
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
kinetic energy
a type of energy anything has if it is moving.
solid has none
liquid has some
gas has a lot
kinetic theory of gases
rules or expectations of how we expect gases to behave. if a gas follows all of these rules, then it is considered an ideal gas (also considered a rare gas).
almost always we find gases w/ exceptions to rules
gases consist of molecules that are very small and are far apart relative to their size. they are in constant random motion, constantly collide with one another and walls of container.
there are no forces of attraction or repulsion between gas molecules
the avg. kinetic energy of gas molecules depends on temp. of gas
more temp. = more kinetic energy
elastic solutions
collisions between gas molecules and the container’s walls is considered this
gas molecules bounce straight off
lots of kinetic energy
inelastic solution
gas molecules when colliding come together
kinetic energy in this is wasted
mmHg
height of mercury in a mercury barometer
1 atm
760 torr
760 mmHg
101.3 kPa
1 torr
0.133322 kPa
Avogadro’s law
states that volume of a container is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas in the container
flexible containers use volume
rigid containers use pressure
more gas = more volume of container
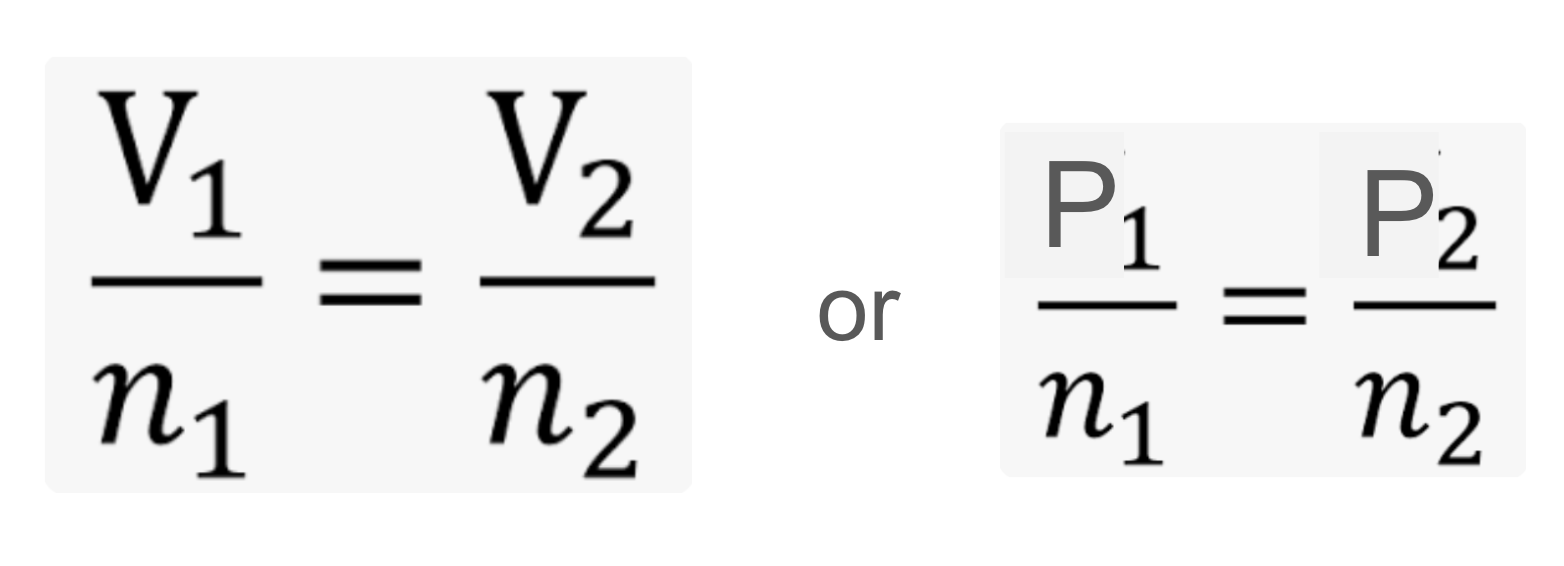
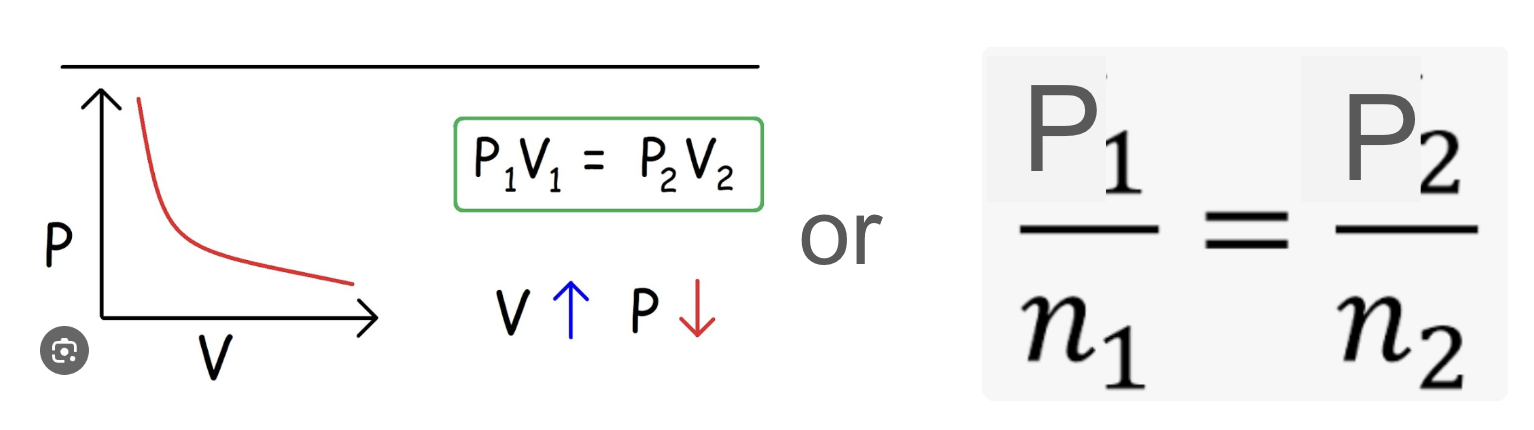
Boyle’s law
states that the pressure of a container is inversely proportional to volume of container
but pressure is directly proportional to num of moles
Charles’ Law
states that the volume of a container is directly proportional to the Kelvin gas in a flexible container (e.g. balloons)
if external pressure stays constant, and temperature increases, the volume of the container will expand because of more kinetic energy so that the internal pressure can be in equilibrium with the external pressure.
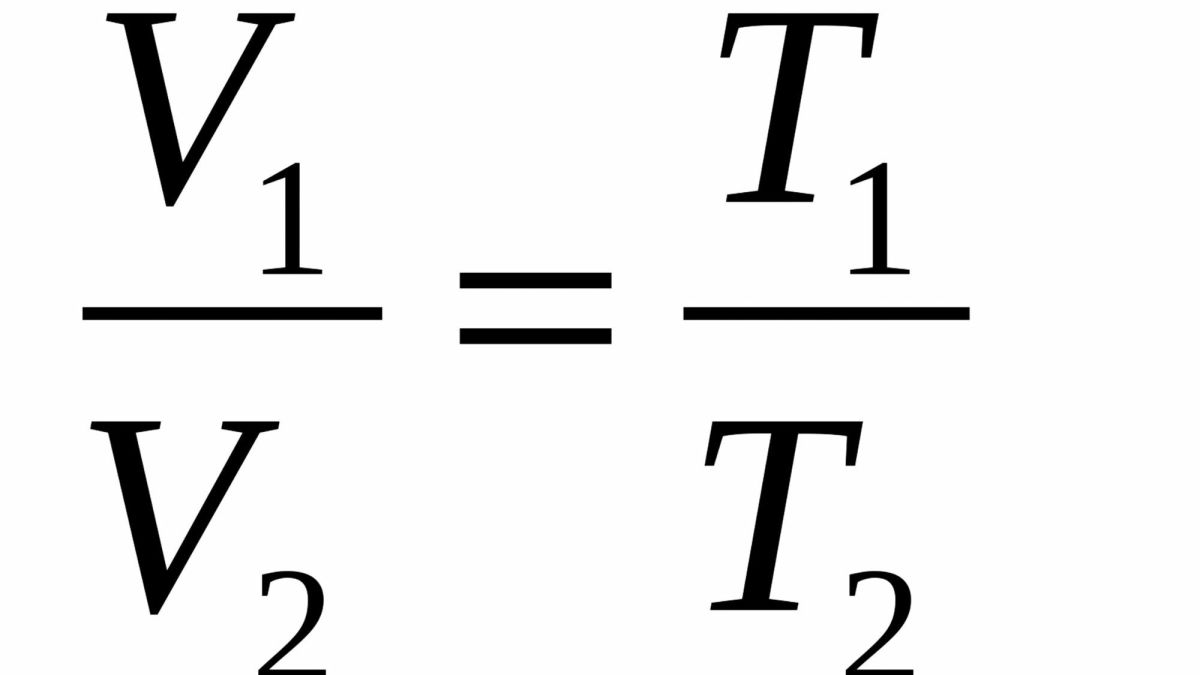
Gay-Lussac’s law
similar to Charles’s law, but instead explains rigid containers.
if walls of container do noto expand, when heated, pressure builds and container may explode!
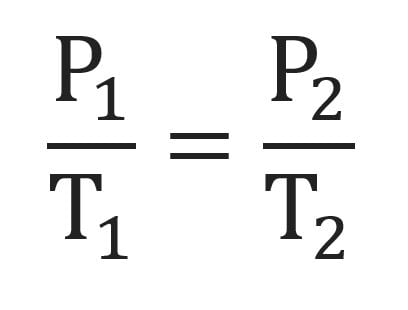
combined gas law
formula you use when there is a situation in which the pressure, volume, and temperature all change.
this happens when there is a container with flexible walls, and where the external pressures may change (e.g. balloon going up into the atmosphere).
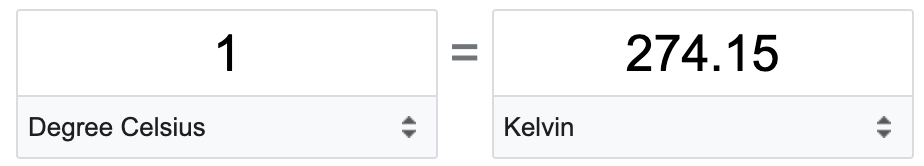
TEMPERATURE FOR THIS FORMULA MUST BE IN KELVINS (K)!!!
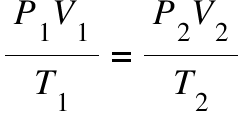
converting Celsius into Kelvins