Acids, Bases and buffer 5.1.3
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What are acids
Proton donors
What are bases
Proton acceptors
what are monobasic acid and example
Release 1 proton
HNO₃
What are dibasic acids and example
Release 2 protons
H₂SO₄
What are tribasic acids and example
Release 3 protons
H₃PO₄
what is a strong acid
Proton donor that fully dissociates
What is a Weak acid
A proton donor that partially dissociates
Strong base definition
A proton acceptor that fully dissociate ( High OH⁻ conc)
Weak base definition
A proton acceptor that Partially dissociate ( low OH⁻ conc)
equation to calculate pH
pH = -log [H⁺]
Equation to calculate concentration of [H⁺]
[H⁺] = 10-ph
How to work out [H⁺] of di basic
X by the amount of protons released
X by 2
what does a larger Ka value mean
Stronger acid and Greater Dissociation
what are the Ka equations
Weak acids → Ka = ( [H⁺] ² / [HA] )
Buffers → Ka = ( [H⁺] [A⁻] / [HA] )
How to work out pKa
pKa = -log (Ka)
How to work out Ka from kpa
Ka = 10-pka
pKa and ka relationship
Lower value of pKa → High value of Ka → more dissociation, stronger acid
General Dissociation of a acid
HA ⇌ H⁺ + A⁻
How to work out pH for a weak acid / monobasic
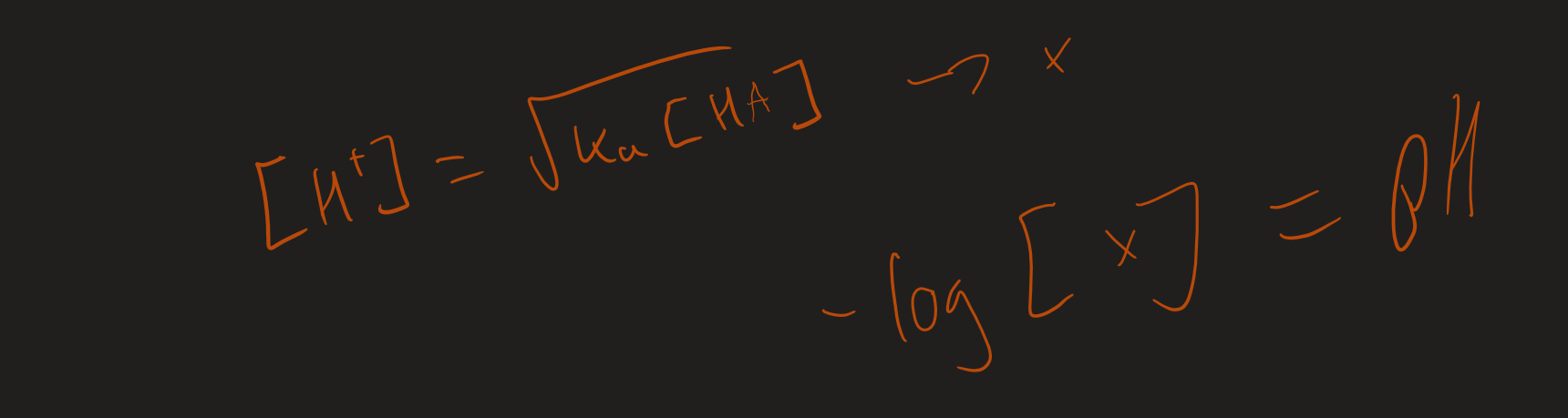
What is the assumption when calculating weak acid
[ H⁺] = [ A⁻] → [ H⁺]²
what are conjugated acid and base pairs ( Image)
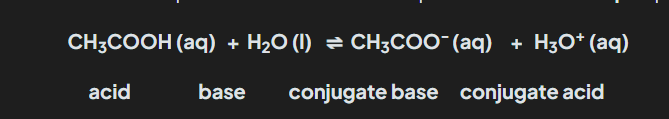
what are conjugated acid and base pairs
Two species that are different from each other by a Proton
Units of Ka
mol dm⁻³
What reaction happens in all aqueous solutions contain
H₂O (l) ⇌ OH⁻(aq) + H⁺(aq)
What factor affects Kw
Temperature only
equation to find pH of pure water
Kw = [ H⁺]²
what is the Kw equation
Kw = [ H⁺]² → ionic water ( aq)
Kw = [ OH-][ H⁺] → Bases
Why is Kw constant
Water dissociates in small amounts
Water concentration is so large effectively constant
What is Kw value at 25⁰C
1.00 × 10¹⁴ mol²dm⁻⁶
What does changing temperature do to kw value
Increases → Kw value increases
decreases → Kw value decreases
What type of reaction is H₂O dissociation
Endothermic
effect of increasing and decreasing temp on dissociation of water
Increase temp → equilibria shifts to right ( products) more dissociation
Decrease temp → equilibria shifts to left ( Reactants)
How to work out concentration of Strong bases
work out [ H⁺] = 10-pH
Kw = [ H⁺][ OH⁻]
[ OH⁻] = Kw / [ H⁺]
equation to use for bases
Kw = [ H⁺][ OH⁻]
Buffer definition
Maintains pH when small amounts of acid / alkali added
Function of acidic and Basic buffers
Acidic → Maintain pH below 7
Basic → Maintain pH above 7
What are the two ways to make acidic buffer
weak acid + its salt
Partially Neutralise weak acid
Acidic buffer ( Image)
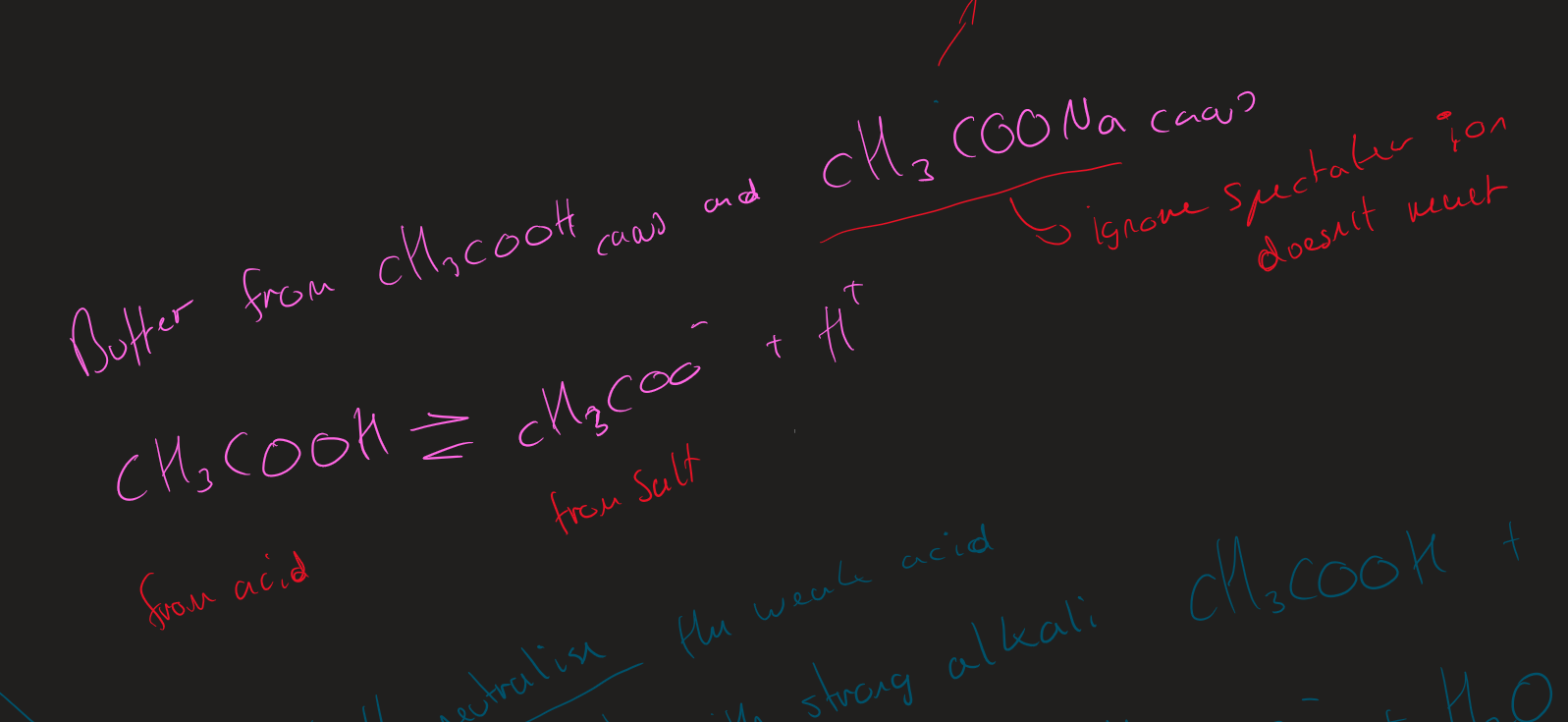
Acidic buffers why is the Ion from the salt
Salt fully dissociates
Larger mols of Ion
How to make a Basic buffer
Weak base + its salt
Acidic buffer adding strong base to weak acid (Image)

Partially Neutralising weak acid products
Salt + H₂O
Effects of increasing [ H⁺] on Buffer
increase [ H⁺] → Equilibria moves to the left ( Reactants)
reactants with products to form reactant
Effects of increasing [ OH⁻] on Buffer
increase [ OH⁻] → Equilibria moves to Right ( products)
Reacts with [ H⁺] → decreases conc , increases dissociation
Example of Buffers
Blood
What is the pH blood is maintained at
pH 7.35 - 7.45
Equation for blood buffer
H₂CO₃(aq) ⇌ HCO₃⁻ (aq)+ H⁺(aq)
Effects of increasing [ H⁺] on Blood Buffer
Equilibria shifts to the Left → more H₂CO₃ made
prevents blood pH from decreasing
Effects of decreasing [ H⁺] on Blood Buffer
More H₂CO₃ made → dissociates into H⁺
equilibria shifts to right
stops pH from rising ( too alkaline)
ka equation for weak monobasic acids ( only)
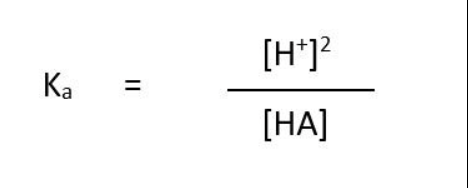
General buffer equation

How to work out pH from buffer solution
work out mols of reactants
limiting mol = [ A⁻] mol
ICE table → limiting reactants gets used up
[ HA] mol = initial - change
use mol value in [ H⁺] = (Ka [ HA] / [ A⁻] )
-log [ H⁺] = pH
how to work out concentration in dilution
( Mol / new volume (dm³)
What are indicators made from
Weak inorganic acids
How to calibrate a pH probe
place bulb of pH meter into distilled water
reading should be 7
How to improve pH experiment
Rinse pH probe in distilled water after each reading
is there a suitable indicator for weak acid/ weak base titrations and why?
No suitable indicator
there’s no rapid pH change
Example of weak alkali
NH₃ ( aq)
Measuring pH experiment how to know what was in the flask and burette on graph
If pH starts above 7 → alkali in flask / acid in burette
if pH starts below 7 → acid in flask/ alkali in burette
What is the equivalence point ?
shows when the substances are neutralised
How to know choose a suitable indicator
endpoint is close to equivalence point and is within the rapid pH change
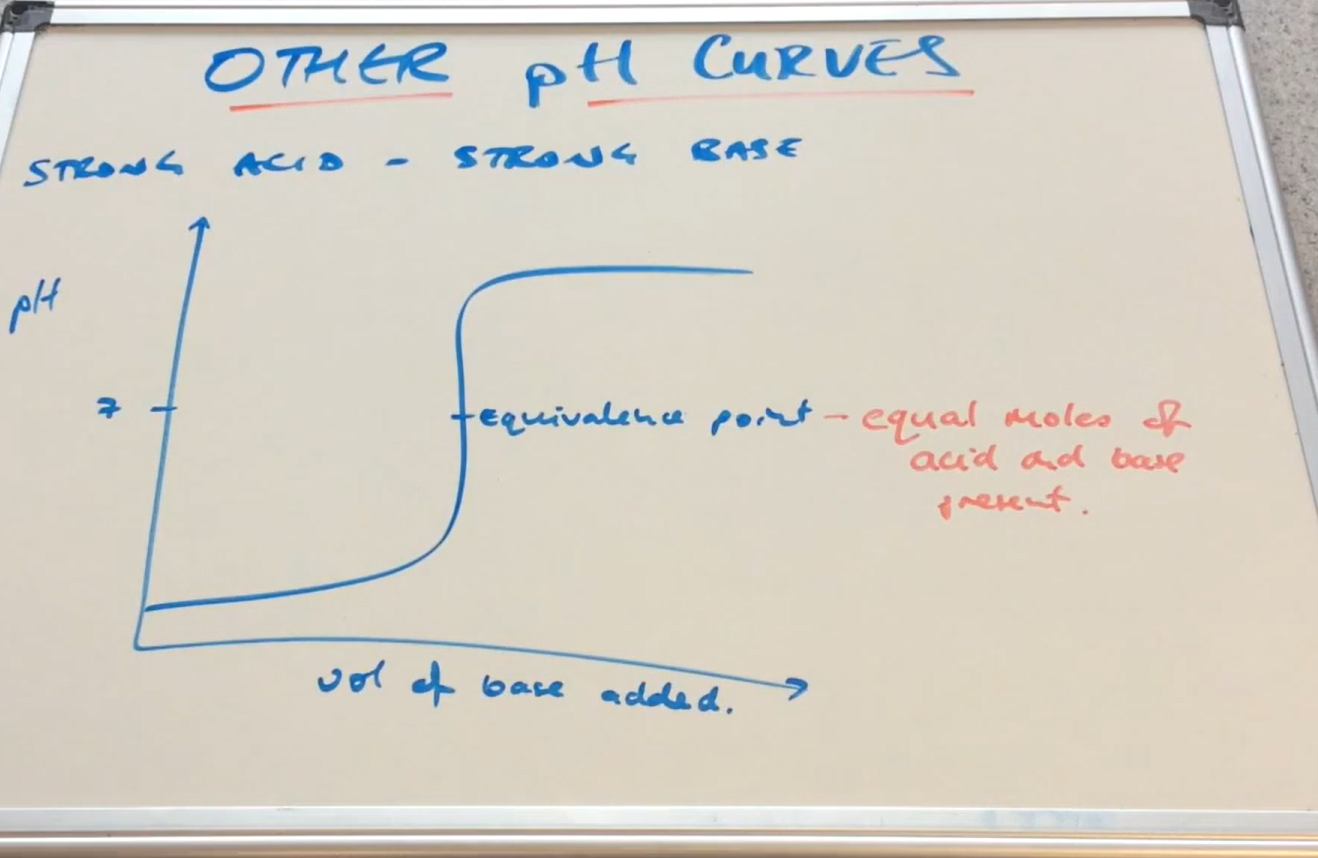
Strong acid - strong Base pH curve graph( Image)
Strong acid - Weak base pH curve graph ( Image)
pH isn’t 13 / 14 then its a weak base
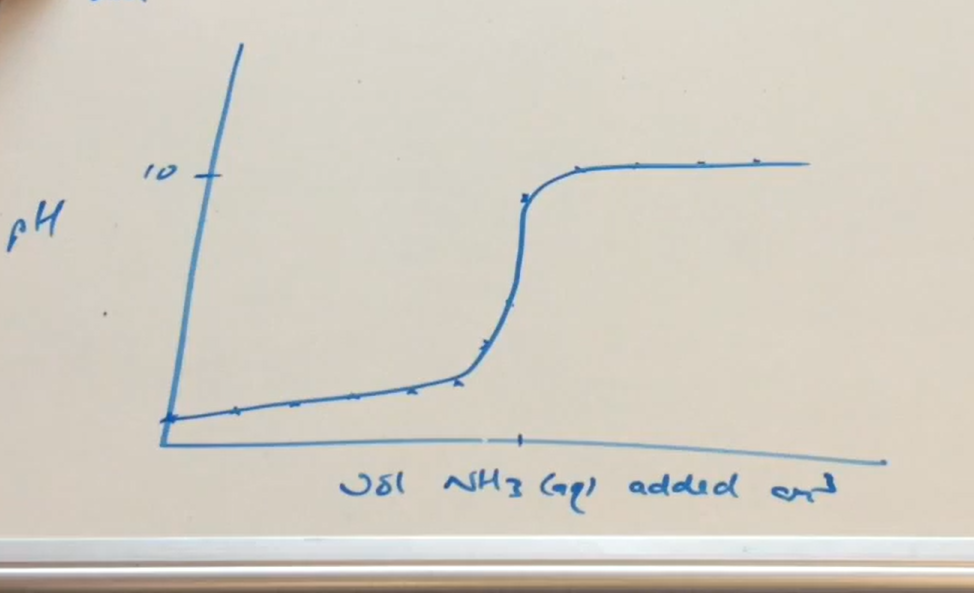
Why can pH at the equivalence point be below 7 in a equation with Ammonium salt as product ( SA-WB)
NH₄X ⇌ NH₄⁺ + X⁻
NH₄⁺ ⇌ NH₃ + H⁺ ( in a solution)
H⁺ decreases pH
How to work out volume of base needed for neutralisation on pH curve graph
use the rapid pH change line
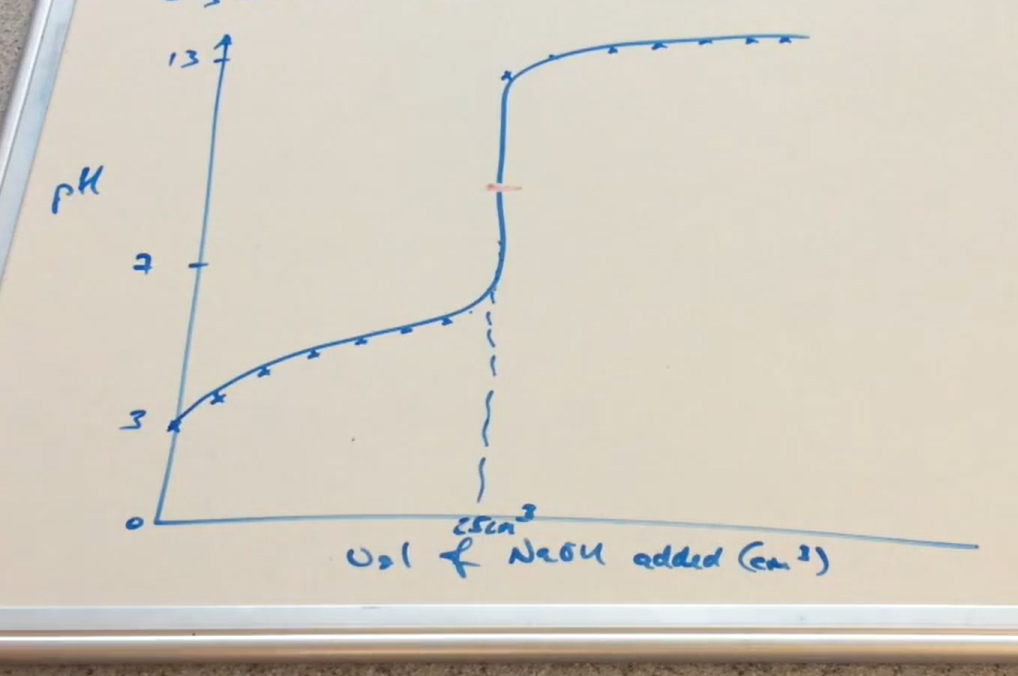
Weak acid - strong base pH curve ( Image)
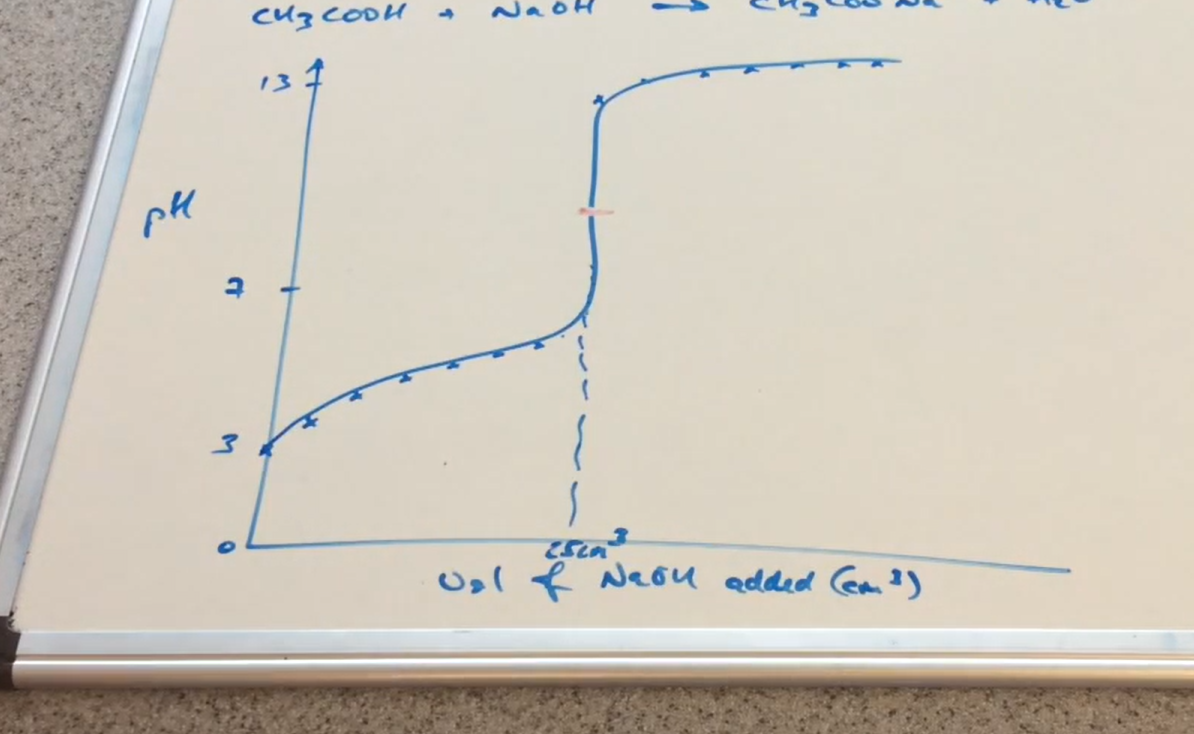
Why can pH at the equivalence point be above 7 in a equation with a Salt as product ( WA-SB)
Salt dissociate to form
HA ⇌ A⁻ + H⁺ ( in water)
A⁻ accepts H⁺ so acts as base
Weak acid - Weak base pH curve graph (Image)
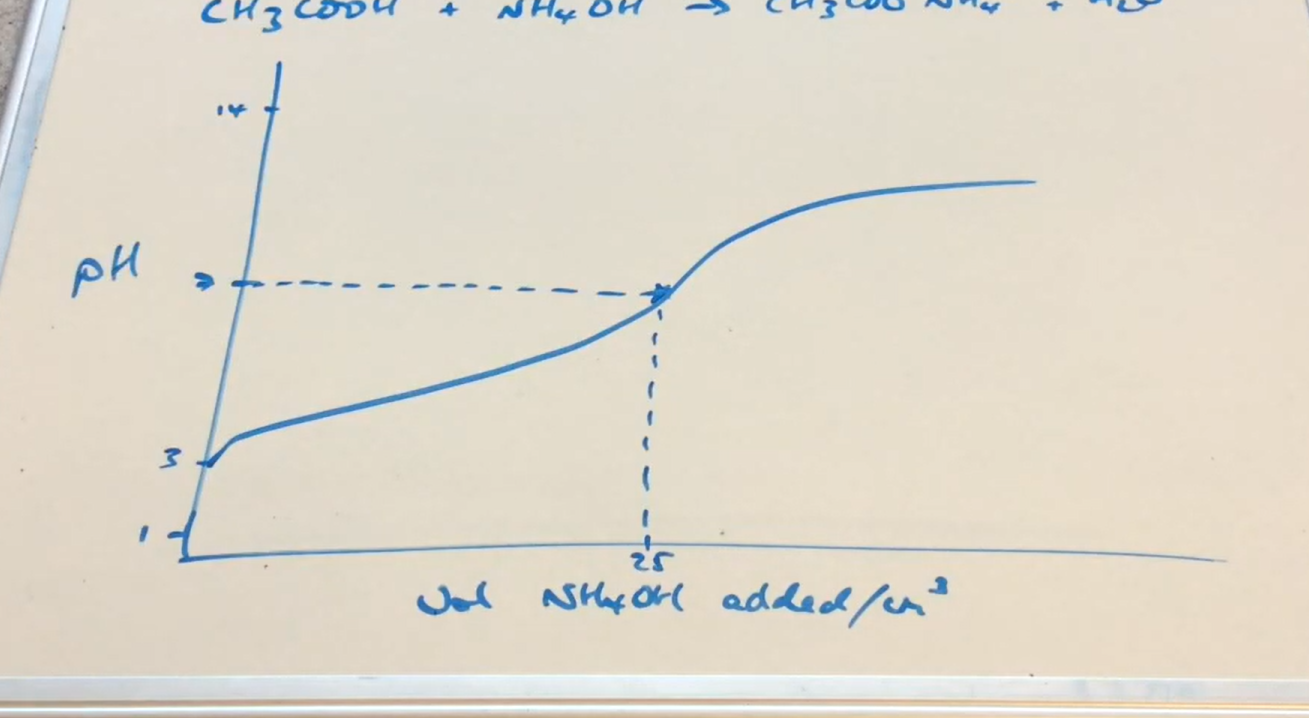
Weak acid- Weak base pH curve why is point of equivalence pH 7
Salt dissociates into weak acid and weak base
Which constant to use acids and bases/ water
bases/ water → KW
Acids → Ka
acid dissociation constant equation
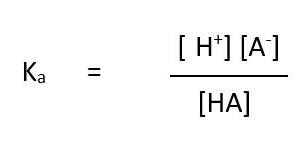
General equation for all weak acids
HA ⇌ H⁺ + A⁻
How to prove that a Acid is weak using a pH meter
if SA → full dissociates so [ HA ] = [ H⁺]
pH = - Log [ H⁺] ( stated)
if pH is greater then its a weak acid
How to do write a conjugate acid-base pairs equation between a SA and WA
SA acts as a acid and donates proton
WA acts as base and accepts proton ( cation)