Comp 301 Final Quizlet
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
What is the difference between prologue comments and inline comments? When should each be used?
Prologue comments explain everything a code section does at the beginning of the code artifact. They should be used in every code artifact.
Inline comments are comments within the code that should be used to help maintenance programmers. Should only be used to clarify
What is the aim of coding standards? How restrictive should they be? Why?
The aim of coding standards is to make maintenance easier. Coding standards should be lenient since the quality of software production suffers when programmers have to develop their software within a strict framework.
Explain the concept of stubs and drivers, including their role in TD/BU testing
A stub is an empty artifact called by something, and a driver is a code artifact that calls another artifact. Stubs are used in top down testing to expose design flaws early and can be used to test a routine. Drivers are used in bottom up testing to test the workhorse code early.
Give the strengths and weaknesses of top down, bottom up, and sandwich integration
Top down:
Exposes design flaws early
Does not test workhorse code sufficiently
Bottom up:
Tests workhorse code early
Exposes design flaws late
Sandwich:
Needs both stubs and drivers
Has advantages of both stubs and drivers while addressing their weaknesses
List 3 external quality attributes and 3 internal quality attributes for software and explain how helping one might hurt the other
External quality attributes:
correctness
usability
robustness
Internal quality attributes:
Maintainability
portability
Readability
Fixating on trying to get one attribute to be the best may mean that you have to sacrifice elements of another (e.g. correctness and robustness)
What is the relationship between quality assessment and quality improvement? Why?
Assessment - did we do a good job?
Improvement - how can we do better?
You can assess without improvement but not vice versa
What combination of defect removal techniques yields the highest percentage of defect removal?
high volume beta testing + prototyping + formal code inspections
Explain the concept of a formal code inspection, explaining the roles and what they do
A formal inspection is where a team of about 3-6 people meet to review code.
Roles:
Moderator: handles inspection pace and logistics
Author: writer of code who plays little role
Reviewer: anyone with a direct interest in the code who tries to find defects (not author)
Scribe: Records the assignment of action items and the errors that are detected during the meeting
Management: does NOT go to meeting
Explain the concept, origin, and advantages of pair programming
where one person types the code and the other watches for mistakes
started with the extreme programming movement
improves code quality and shortens project schedules
Define refactoring
Changing software structure to make it easier to understand and cheaper to modify without changing its observable behavior
What is the Cardinal Rule of software evolution?
Evolution should improve the internal quality of the program.
List 5 reasons to refactor code
1. Redundant code
2. Lengthy routines
3. Loops are too long or too deeply nested
4. Poor class cohesion
5. Poor routine name
What is the “fundamental theorem of formatting”?
The formatting should emulate the logical structure of the code.
What are the 4 objectives of a good layout
1. Accurately represents the logical structure of the code
2. Consistently represents the logical structure of the code
3. Improves readability
4. Withstands modification
Which layout style do you prefer and why? (pure blocks, emulated blocks, begin-end pairs, endline layout) Which does McConnell prefer for Java? For C++? (NOT ON TEST)
My favorite is emulated pure block formatting since that style is clean, simple, and easy to understand, and it is what I learned in c++. Pure blocks are also best for Java, emulated pure block or begin end block is best for c++
What is the holy grail of code legibility
Self documenting code
List and explain the three types of comments which are acceptable for completed code
Information that can't be expressed in the code (copyrights, references to requirements etc)
Intent comments - purpose of a section of code
Summary comments - summarize the following code
What is an appropriate comment/code density
1 comment per 10 statements
How are error, fault, mistake, failure, and defect related
They are all types of bugs
What is the purpose, role, and effect of a separate SQA (software quality assurance) group?
Ensures developers are producing high-quality work properly. It allows for debugging early so that a user does not experience errors. It saves you time and money.
What are the strengths and weaknesses of reviews
Strengths:
Effective way to detect a fault early
Weaknesses:
Large-scale software is extremely difficult to review unless it consists of smaller, largely independent components
Documentation of previous workflows must be complete and updated
Explain the difference between utility, reliability, robustness, performance, and correctness
Utility - the extent to which a user's needs are met under normal circumstances
Reliability - a measure of the frequency and criticality of product failure
Robustness - working in a range of operating conditions, handling an invalid result, handling invalid input.
Performance - the extent to which a product meets resource constraints
Correctness - satisfies its output specifications
What are four suggestions given by Brooks for “designing the bugs out”?
1. Bug proof the definition
2. Test the specification
3. Top Down Design
4. Structured Programming
What are five suggestions Brooks gives for system debugging?
Use debugged components
Build plenty of scaffolding
Control changes
Add one component at a time
Quantize updates
Explain the difference between black box and glass box testing
Black-box testing tests to the specifications, code is ignored
glass-box testing tests by examining the code, specifications ignored
Explain the concept of equivalence class and boundary testing
Equivalence class is a set of test cases that are equally as good as each other
Boundary testing designs test cases on or just to one side of a boundary of an equivalence class to find off by one errors
Explain the concepts of statement, branch, and path coverage during testing, making sure to explain the difference between branches and paths, and which is the best type of testing
Statement coverage is testing every statement at least once
Branch coverage is testing all branches at least once
Path coverage is testing all paths at least once
Selective path coverage is the best type of testing
What is cyclomatic complexity and how is it used
Cyclomatic complexity counts the number of binary decisions plus one
It is used to determine number of test cases needed for branch coverage
What is the difference between unit testing, integration testing, stress testing, and acceptance testing
Unit testing tests individual units of source code
Integration tests combine execution of separate units
Stress testing ensures that the product behaves properly under a heavy load
Acceptance testing hands the product over to the client for them to test/use it
Be able to define:
Unit Testing
Component testing
Integration Testing
Regression Testing
System Testing
Unit Testing: Testing single code sections (class, routine) by original programmers, isolated from larger system.
Component Testing: Testing specific program parts (class, package) by multiple programmers/teams, isolated from system.
Integration Testing: Combining and testing multiple software parts, ongoing until full system completion.
Regression Testing: Repeating passed tests to detect new errors after changes.
System Testing: Final software version testing, including other software/hardware interactions, checking security, performance, etc.
Explain the difference between black box and white box testing
Black box testing refers to tests in which the tester cannot see the inner workings of the item being tested while white box testing refers to tests in which the tester can see the inners workings of the item being tested
Explain the difference between clean and dirty tests, and explain which one you need more of, and why
Clean tests contian expected data that occurs only in normal usage, while dirty tests test if the code breaks with bad data. Need more dirty tests as it finds more defects. 5 to 1
List and briefly explain three types of white box testing
1. Path testing - trying to test all paths of the program
2. Data flow testing - combinations of variable definitions, usages, and destructions
3. Boundary analysis - checking for off-by-one errors
List and briefly explain three types of "test support" tools/techniques
Scaffolding: drivers and stubs make it easy to test code
Test Data Generator: Generator used to try code against a large amount of input data
Coverage monitors: Checks what code is covered by tests and how well it is covered
Explain the concept of “stabilizing the error”
Reproducing an error and narrowing it to its simplest test case. change test case carefully to diagnose the problem
How does unit testing fit in with integration testing
Unit testing should always be done before integration testing.
What is incremental integration and why should we use it
Adding pieces to a system one at a time. If the new piece causes an error it can be removed and fixed separately and then added back later
What is the role of a "source code comparator" in debugging
pinpoints changes in source code, useful when some changes need to be removed but you can't remember what changes you made
Define and give advantages/disadvantages of any of these testing/integration strategies: big bang, top down, top down vertical slice, bottom up, bottom up vertical slice, sandwich
big bang - everything done all at once
top-down - write and integrate classes at the top of the hierarchy first; exposes design flaws early, doesn’t test workhorse code enough
Top-down vertical slice - integrate from top down in sections
bottom-up - write and integrate classes at the bottom of the hierarchy first; tests workhorse code thoroughly, exposes design flaws late
bottom-up vertical slice - integrate from the bottom up in sections
sandwich - first integrate high-level classes at the top of the hierarchy, then integrate utility classes at the bottom and integrate middle classes later; very well balanced, uses a TON of stubs and drivers
Explain the concept of the daily build and smoke test
works well with any of the integration strategies, all code is compiled into an executable every day and put through a test to see if the product "smokes" when it runs
List and define three different types of post-delivery maintenance.
Corrective - fixing errors
Perfective - making product run better and improving effectiveness of the product
Adaptive - changing product to react to a change in its environment
What is regression testing?
Running tests that have already been passed after making a change
Why is post-delivery maintenance the “most challenging aspect of software productions”
No one wants to do it, and these programmers are looked down upon and usually paid less than other developers who incorporate aspects of all of the other workflows.
How does OOP impact maintenance in a potentially negative way
Polymorphism and inheritance can cause problems
changing base classes changes subclasses
What are the advantages of having formal documents to guide a project
Writing down decisions exposes inconsistencies
The documents will communicate decisions to others
Documents provide a data base and a checklist
Give an example of software tools that might be developed by a toolsmith (probably not on 2023 exam)
Stubs and drivers, scaffolding, data generators for test cases
What does this mean, in terms of documentation: "use parts that must be there to carry as much information as possible"
Make code as self documenting as possible
Explain the concept of egoless programming
a person is willing and able to admit when their code is faulty and needs to be changed
Explain the roles of the members of the chief programmer team
Chief programmer - good manager and skilled programmer who leads a team
Backup programmer - there in case the chief becomes sick or is absent
Secretary - responsible for maintaining documentation
Programmers - writers of code
What is meant by the “synchronize and stabilize” life cycle model
At the end of each day, all of the teams put the partially completed components together. Then, they test and debug the resulting product. Lastly, they freeze the code.
How does pair programming work
Pair programming is when a team of two programmers work together on a single computer. One programmer writes the code while the other checks to make sure that the other is doing it correctly
How does stepwise refinement relate to Miller's law
start with big pieces, divide them into smaller pieces
We can only focus on 7 pieces of info at a time therefore, key issues are prioritized
Give an example of both a process metric and a product metric for software development
process metric - efficiency of fault detection, work velocity
product metric - size, cost, duration, effort, quality complexity
Explain the purpose of a “configuration control” tool
used to automatically manage multiple variations in a product as a result to a change of the product
Do you think that the chief programmer team can work? Why or why not?
The Chief Programmer Team approach can work well for small projects where an individual's expertise can significantly drive progress. However it is almost always worse for larger projects or in environments where team input and diverse skill sets are crucial.
Why does Brooks think the Tower of Babel fell and what does this have to do with software development teams?
According to Brooks, the Tower of Babel fell because of a lack of communication and its consequent, organization. Without communication, large-scale programming projects suffer from schedule disaster, functional misfits, and system bugs.
Give several reasons why LOC is not a good metric for estimating the size of a product
very unreliable
source code is very small part of software development
Different languages result in different amounts of lines
It's unclear exactly what a "line" is
Describe, in general terms, how both FP and FFP are better than LOC.
FFP - files + flow + processes
FP - function points
it's based on measurable quantities that can be determined at the beginning of the software process, FFP and FP have to do with complexity
What is COCOMO and for what is it used
COnstructive COst MOdel, used to estimate software cost
What is the IEEE 1058 and for what is it used
it's a software standard used to create a plan for the production of a software product
Explain the importance of a systematic change control procedure
important when you have a lot of change requests
makes it clear that changes will be considered in the context of what's best for the project as a whole
Name two popular version control systems
1. Git
2. Subversion
What advantages do version control systems bring (probably not on exam)
don't step on anyone's toes when working on a file
backtracking to a previous version is easy
easy to make code branches
What does Brooks mean by essential and accidental elements of a problem
Essential: These are the inherent complexities of a problem, fundamental and unavoidable.
Accidental: These complexities arise from external factors and can potentially be reduced or eliminated.
Why is there no “silver bullet” in software engineering
Hardware progresses much more quickly than software. Software will always be hard to develop because of its inherent complexity, constant change, abstract nature, and dependence on skill.
What were the four values put forth by the agile manifesto
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
Working software over comprehensive documentation
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
Responding to change over following a plan
How does SCRUM fit in with other Lean and Agile methodologies? How do all of these relate to the RUP?
SCRUM is part of Agile. Agile is a part of Lean. All of these come from the RUP, which comes from the waterfall method.
Define sprint
The timeboxing and code development portion of SCRUM.
Define product backlog
A prioritized list of desired product functionality needed for a complete product
Define sprint backlog
List of tasks identified by the Scrum team to be completed during the sprint.
Define daily scrum
Daily Stand up meetings that typically last 15 minutes
Name three different team roles on a scrum team and describe their responsibility.
Scrum Master: Facilitates the process using Scrum practices, and supports the team.
Product Owner: Represents the end users' and stakeholders' interests, prioritizes tasks
Development Team: Does the actual work of developing the product, operating alone or together.
What is involved in a PBI
Features
Defects
Improvements
Knowledge-acquisition
What does it mean to “groom” the product backlog
Split big slices into small slices. Proactively managing, organizing, and administering the product backlog.
What does the DEEP acronym mean, regarding the product backlog
Detailed appropriately
Emergent
Estimated
Prioritized
Describe the process and goals of sprint planning (He hesitated with this one, so it may not be in exam)
To define what can be delivered in the sprint and how that work will be achieved.
The product owner presents the backlog items to the team
The team discusses and understands the work for the sprint
The team forecasts and commits to the items that can be done
Explain the SCRUM system of estimation, including story points and planning poker
Estimation is guessing how much work is left to do.
Story points are units of measurement representing “ideal work days.”
Planning poker is group estimation of how many “ideal work days” it takes to complete a task using only Fibonacci numbers for days.
What is velocity in SCRUM? How is it calculated? Why is it important?
Velocity is how fast the team is doing work. With story points, you can calculate velocity. It is Points per sprint. Velocity is important because if you do not manage it well, your employees will get burned out
Explain the role of the Task Board and the Burndown Chart in a sprint
A task board shows tasks to do, tasks in progress, and tasks completed
A burndown chart visualizes the work velocity of a given sprint
What is the difference between a sprint review and the sprint retrospective
The sprint review reviews the product and a sprint retrospective reviews the process
Define software Engineering
Applying engineering design principles to software development.
What phase of software engineering is most critical, and why
"Requirements" because you MUST be aiming at the client’s target. It is the foundation for the other phases.
Why does post-delivery maintenance account for as much as 75% of the total cost of a software system? How does the development process address this?
Software can be used for decades and the complexity of maintenance and total required maintenance adds up. To reduce the difficulty and cost, software architecture is designed to be more sustainable and maintainable.
Give 2 statistics from one of the texts or notes to indicate why some would say that there is a crisis in software development
1. 18% of projects are cancelled before they are completed
2. Only 29% of projects are successful
What are three advantages of iterative and incremental development which were given in the reading
Robustness
working version in every iteration
testing in every iteration
Describe one unusual technique used in agile/extreme environment
stand-up meetings - a stand up meeting meant to be a short update on what you did, what you learned, and what your struggling with that day
Cite three numerical statistics given by McConnell demonstrating the relative cost of errors, depending on where they are made and where they are discovered in the software development lifecycle
Errors made in requirements, found in ______ cost ____
Requirements, 1
Testing, 10
Maintenance, 100
Explain, in as much detail as possible, the following statement: "The Unified Process is use-case driven"
The use cases are the requirements, and the requirements drive every phase is the software development lifecycle
Diagram and label the waterfall and iterative and incremental (RUP) life cycle models.
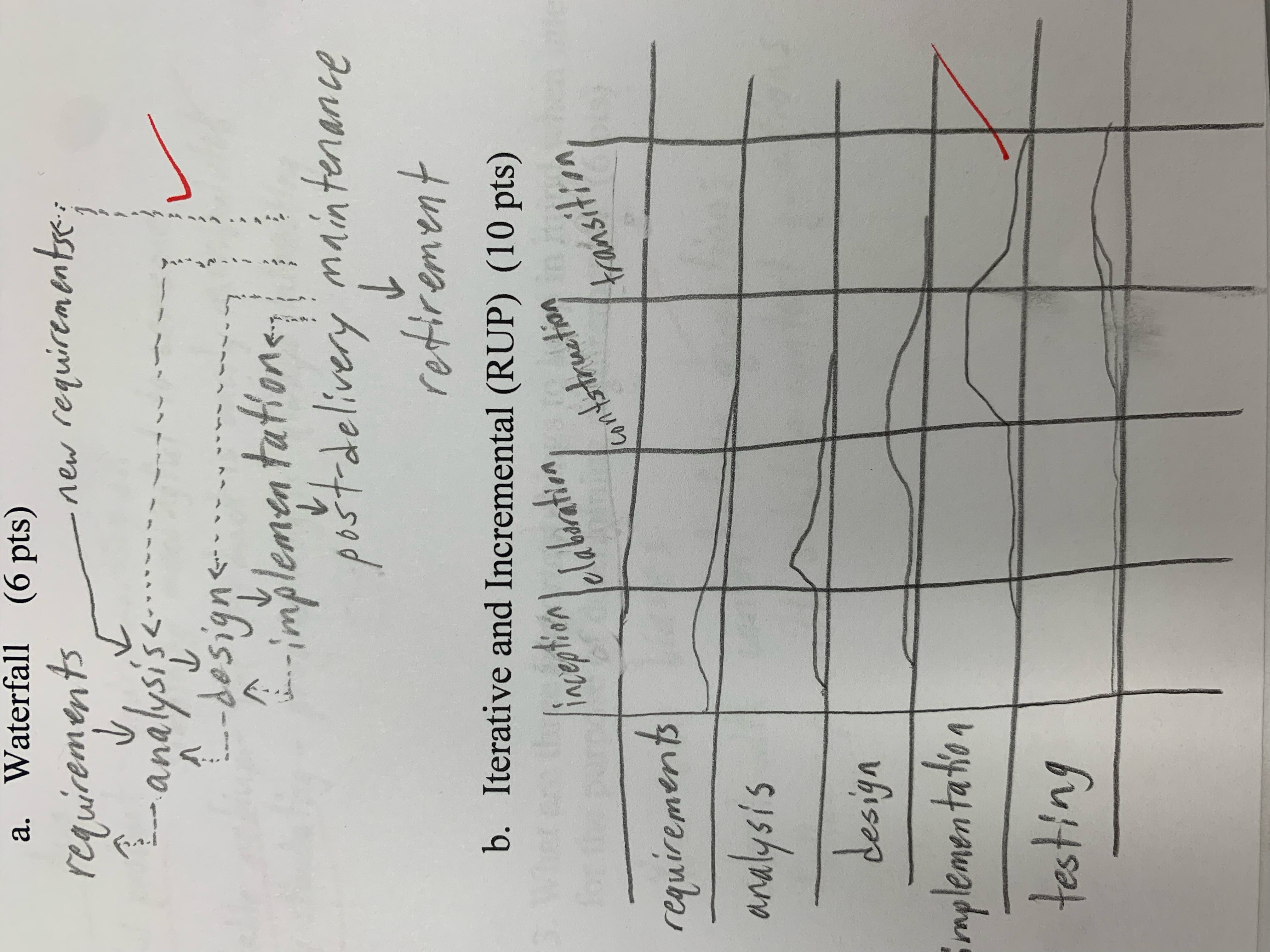
What are the CNM and ISO 9000 standards and what are they trying to address
Software engineering efficiency standards. They are addressing the software crisis
List at least three of the standard requirements elicitation techniques which were described in class.
1. Interviewing
2. Storyboarding
3. Prototyping
List and briefly describe five different pluses and/or minuses of programming as an activity, according to the essay by Brooks
Plus:
1. Useful product - working on something meaningful to someone
2. Tractable medium - product is easily manipulated
3. Mentally stimulating - always interesting
Minus:
1. Debugging - tedious work
2. Dependent on others - reliant on past components
What are three important things to keep in mind when interviewing a stakeholder for the purposes of determining requirements
Your own biases
Start with context-free questions
Follow-up with solution-context questions
What is the most challenging part of programming, according to McConnell
Conceptualizing the problem
What are there no planning, testing, and documentation phases in software development
Planning, testing, and documentation should be ongoing processes throughout development
What is the difference between a program and a programming systems product
A program is a single piece of code written for 1 device and 1 user (you). A programming systems product is multiple code components used by many users on many devices. A programming systems product cost 9x more than a program.
Explain what a Communication Diagram is used for, diagram an example showing the most common possibilities and explaining the meaning of the symbols.
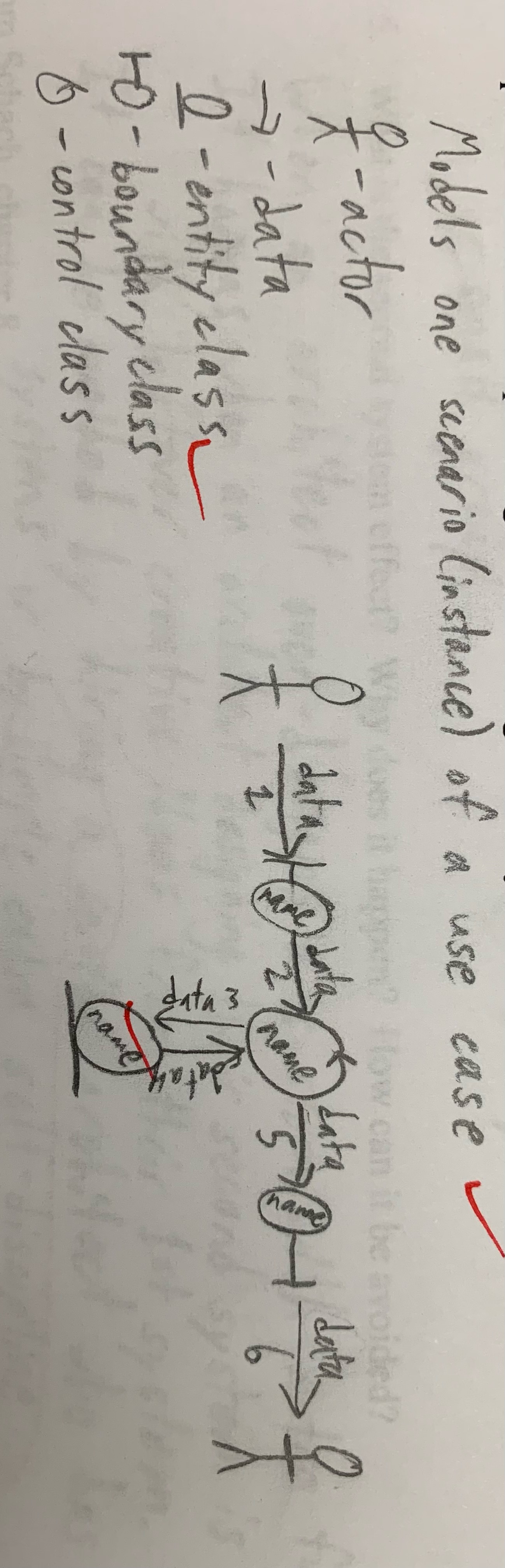
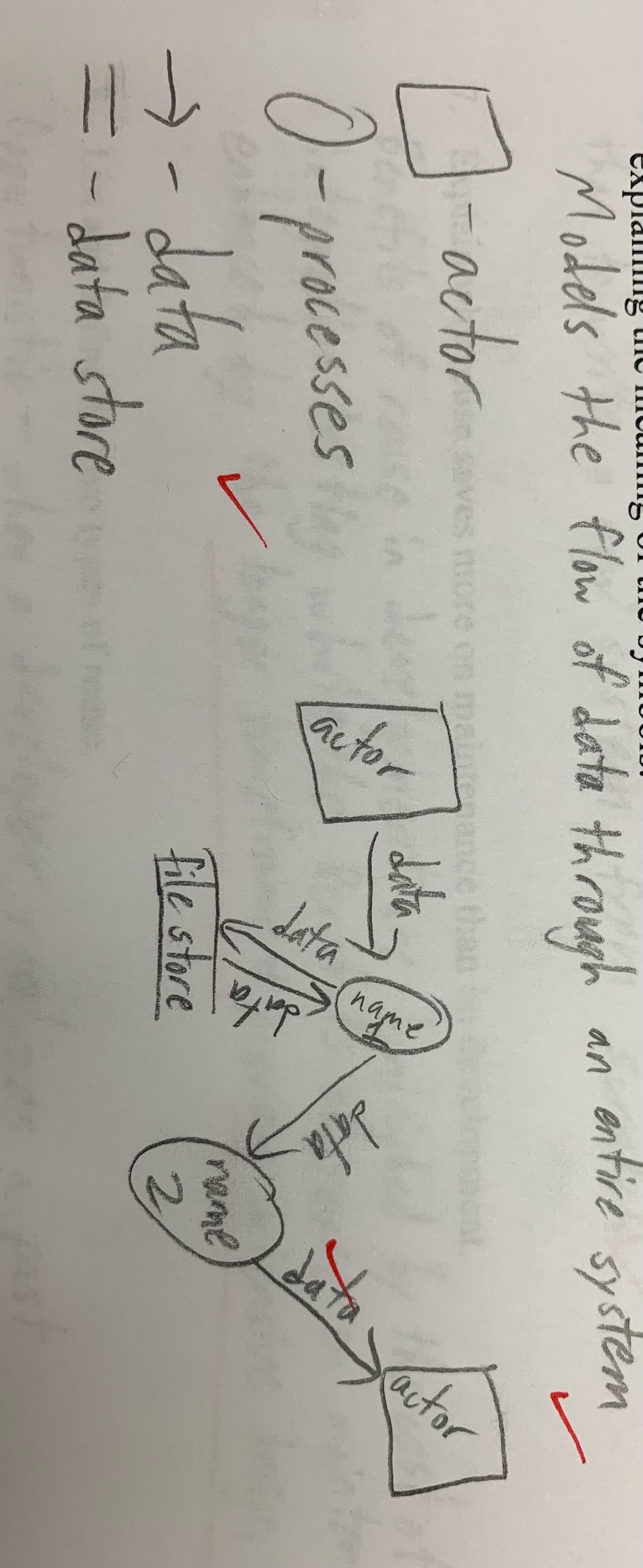
Explain what a Data Flow Diagram (DFD) is used for, diagram an example showing the most common possibilities and explaining the meaning of the symbols.
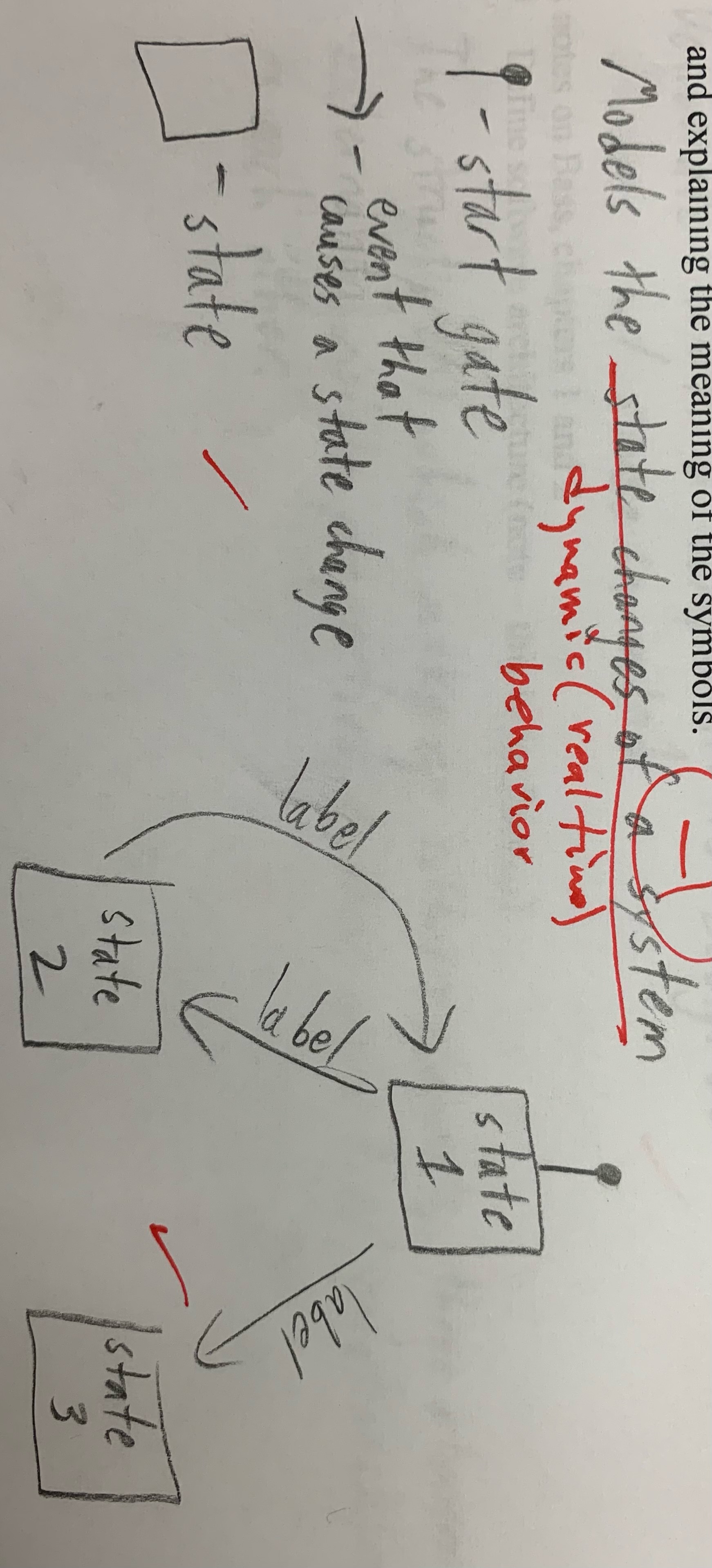
Explain what a Statechart (STD) is used for, diagram an example showing the most common possibilities and explaining the meaning of the symbols.
What is conceptual integrity? Why is it so important? How is it achieved
Conceptual integrity is the unity of ideas and implementation within a project. It is important because it makes a computer easy to build, use, and maintain. It is achieved through consistent design by a small group.