Electrochemical Equilibria and Membrane Potentials
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Diffusion Potential
Potential difference due to ion concentration gradients.
Equilibrium Potential
Membrane potential where ion concentrations stabilize.
Membrane Potential
Voltage difference across a cell's plasma membrane.
Nernst Equation
Calculates equilibrium potential for specific ions.

Goldman Equation
Calculates membrane potential considering multiple ions.
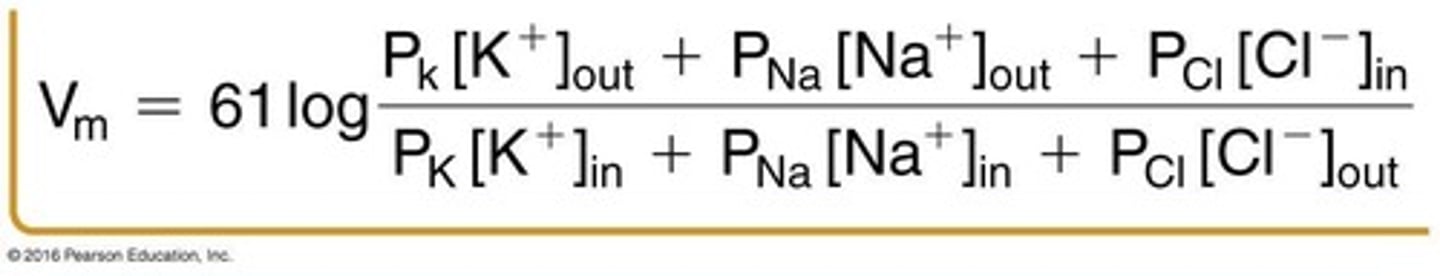
Resting Potential
Stable membrane potential in a non-active cell.
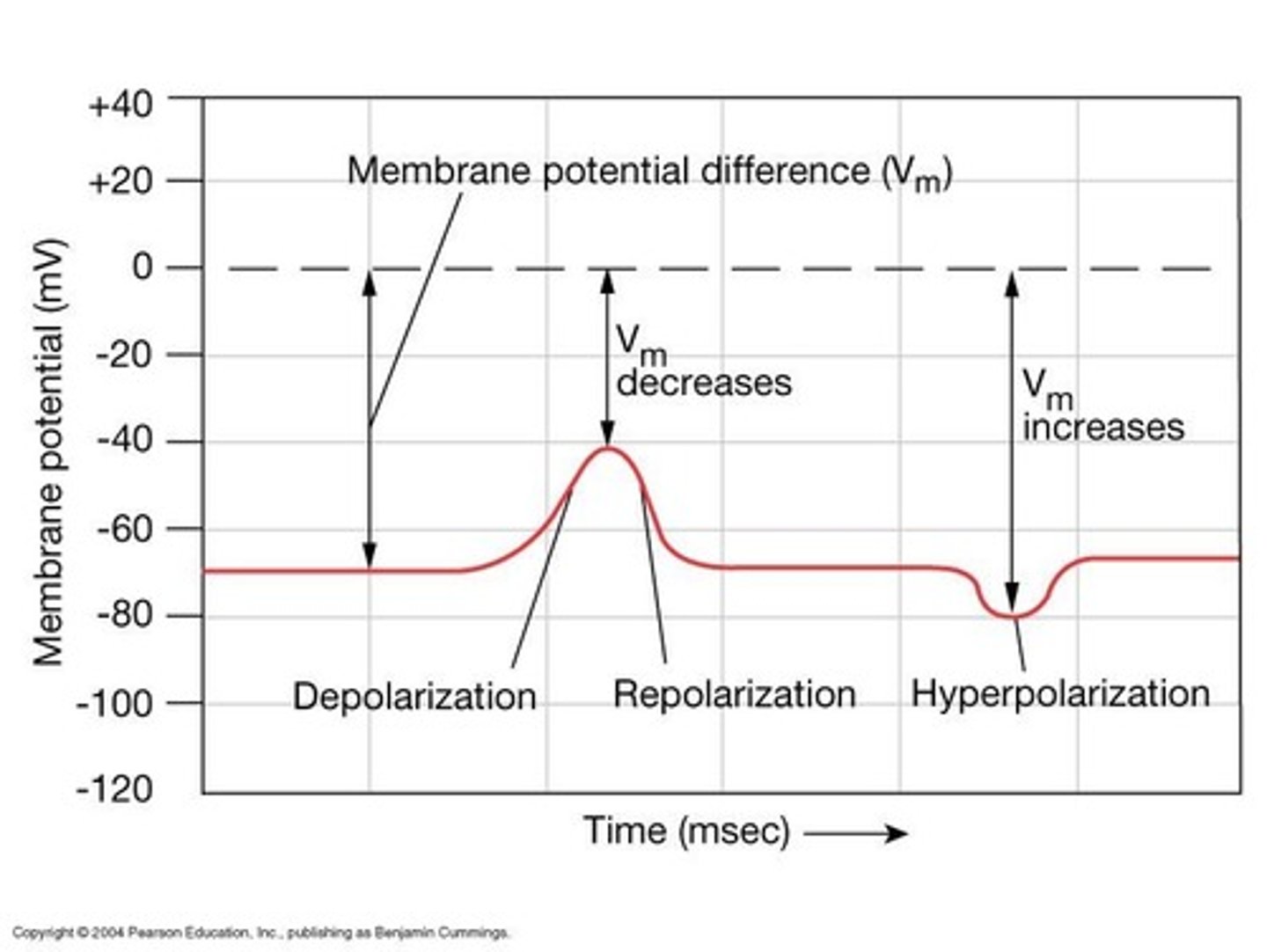
Depolarization
Decrease in membrane potential, making it less negative.
Hyperpolarization
Increase in membrane potential, making it more negative.
Overshoot
Membrane potential exceeds zero during action potential.
Repolarization
Return of membrane potential to resting state.
Graded Potentials
Local changes in membrane potential, not all-or-nothing.
Action Potentials
Rapid, all-or-nothing electrical signals in neurons.
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels
Channels that open during depolarization phase of action potential.
Sodium Permeability
Increases during depolarization phase of action potential.
Potassium Permeability
Increases during repolarization phase of action potential.
Myelinated Axons
Faster action potential conduction due to insulation.
Unmyelinated Axons
Slower action potential conduction without insulation.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in ion concentration across a membrane.
Electrical Potential
Voltage difference caused by ion distribution.
Compartment 1 and 2
Two areas separated by a permeable membrane.
Cl- Diffusion Rate
Chloride ions diffuse faster than sodium ions.
Diffusion
Movement of Cl- from area 1 to 2.
Em
Membrane potential affecting ion movement direction.
Equilibrium
State with no net flux of Cl-.
ECl
Equilibrium potential for chloride ions.
Ion Flux
Movement of ions across a membrane.
Membrane Potential (Em)
Voltage across a cell membrane.
ENa
Equilibrium potential for sodium ions, +58 mV.
EK
Equilibrium potential for potassium ions, -81 mV.
Driving Force
Difference between Em and Eion for ion movement.
Membrane Permeability
Ease of ion passage through membrane channels.
Conductance (gion)
Ease of ion movement through channels.
Channel Selectivity
Preference of channels for specific ions.
Channel Conductance (gs)
Index of ion flux through a channel.
Open Probability (Po)
Likelihood of ion channels being open.
Channel Density (N)
Number of ion channels per membrane area.
Electrochemical Gradient
Combined effect of concentration and electrical gradients.
Resting Membrane Potential
Typical Em value around -70 mV.
Steady State
Condition where sum of ionic currents equals zero.
Permeant Ion
Ion that can cross the membrane.
Dominant Ion
Ion with greater influence on Em.
Cl- Current
Negligible current due to chloride ions in resting state.
Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz Equation
Predicts membrane potential from all permeant ions.
Permeability Ratio (b)
Ratio of K+ to Na+ permeability affecting Em.
Equilibrium Potential (Eion)
Membrane potential where ion's net movement is zero.
Nernst Potential
Equilibrium potential calculated for a specific ion.
Action Potential
All-or-none electrical signal triggered by depolarization.
Threshold
Minimum depolarization needed to trigger an action potential.
Absolute Refractory Period
Time after AP when another cannot be generated.
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive transport of ions across a membrane.
Graded Depolarization
Increase in membrane potential due to Na+ influx.
Graded Hyperpolarization
Increase in membrane potential due to K+ efflux.
Steady State Membrane Potential
Stable membrane potential during constant ion permeability.
Ion Concentration Gradient
Difference in ion concentration across a membrane.
Voltage-gated Ion Channels
Channels that open/close in response to voltage changes.
K+ Dominance
K+ permeability is greater than Na+ at rest.
b Value Change
Alters membrane potential based on ion permeability.
Undershoot
Phase where membrane potential becomes more negative post-AP.
Summation of Graded Potentials
Combining multiple graded potentials to affect membrane potential.
Action Potential (AP)
Rapid change in membrane potential during neuron firing.
Ion Permeability (Pion)
Changes in ion flow affecting membrane voltage.
Depolarizing Stimulus
Initial change that raises membrane potential to threshold.
Voltage-gated Na+ Channels
Open during depolarization, allowing Na+ influx.
Voltage-gated K+ Channels
Open during repolarization, allowing K+ efflux.
After-hyperpolarization
Period following AP where membrane potential is below resting.
Rising Phase
Initial increase in membrane potential during action potential.
Falling Phase
Decrease in membrane potential after peak of action potential.
Refractory Period
Period post-action potential where neuron is less excitable.
Inactivation Gate
Closes Na+ channels rapidly after action potential peaks.
Activation Gates
Open Na+ channels allowing Na+ influx during depolarization.
PNa
Permeability of the membrane to Na+ ions.
PK
Permeability of the membrane to K+ ions.
Cytosol
Intracellular fluid within the neuron.
Extracellular Fluid
Fluid outside the neuron, rich in Na+.
Plasma Membrane
Barrier separating cytosol from extracellular fluid.
Sodium Channel
Channel that selectively allows Na+ ions to pass.
Potassium Channel
Channel that selectively allows K+ ions to pass.
Closed State
Condition of channels when they are not conducting ions.
Open State
Condition of channels when they allow ion flow.
Inactive State
Condition of channels when they cannot open despite depolarization.
Na+ Channels
Voltage-gated channels allowing sodium entry into neurons.
K+ Channels
Voltage-gated channels allowing potassium exit from neurons.
Relative Refractory Period
Only stronger stimulus can initiate action potential.
Ion Permeability
Ability of ions to cross the neuronal membrane.
Dendrites
Branch-like structures receiving signals from other neurons.
Cell Body
Contains nucleus and organelles of the neuron.
Axon
Long projection transmitting electrical impulses away from the cell body.
Myelin Sheath
Insulating layer increasing conduction speed of action potentials.
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in myelin sheath where ion channels are concentrated.
Saltatory Conduction
Rapid transmission of action potentials along myelinated axons.
Trigger Zone
Region where action potential is initiated in the axon.
Local Current Flow
Movement of charge that depolarizes adjacent membrane sections.
Refractory Region
Period preventing backward propagation of action potentials.
Active Region
Area of axon currently undergoing depolarization.
Inactive Region
Area of axon not currently conducting action potentials.
Tetrodotoxin (TTX)
Neurotoxin blocking voltage-gated Na+ channels.
Tetraethylammonium (TEA)
Compound blocking voltage-gated K+ channels.