Biology test #3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/157
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:12 PM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
1
New cards
*A heterozygous individual has___:*
*two diff. Alleles of a gene*
2
New cards
*An organism's observable traits constitute its___:*
Phenotype
3
New cards
10\.2 Tracking traits:
* 19th century
* 1850
* 19th century
* 1850
\
* 19th century: people thought hereditary material was a fluid
* Hypothesis: fluids from parents blended at fertilization
* However, failed to explain seen patterns
* 1850: Gregory Mendel began experiments breeding pea plants
* Studied 30,000 plants over 10 years
* Gained insight into nature of inheritance
* 19th century: people thought hereditary material was a fluid
* Hypothesis: fluids from parents blended at fertilization
* However, failed to explain seen patterns
* 1850: Gregory Mendel began experiments breeding pea plants
* Studied 30,000 plants over 10 years
* Gained insight into nature of inheritance
4
New cards
**Mendel's Experiments:**
* what did he do?
* what does it mean to breed true?
* why did he use them plats that “breed true”
* what did he conclude?
* \
* what did he do?
* what does it mean to breed true?
* why did he use them plats that “breed true”
* what did he conclude?
* \
* Controlled mating of plants
1. Peas are self fertilizing (viable seeds form if a flowers pollen lands in its own carpel)
2. Mendel removed the anthers to prevent self fertilization
3. He cross fertilized flowers
4. He planted resulting seeds
5. Recorded traits
\
* His experiments often began with plants that “ breed true” for particular traits
* __Breeding true:__ all offspring have same form of trait as parents, generation after generation
* He cross fertilized plants that breed true for diff. Forms of a trait
* Traits of offspring often appear in predictable patterns
* He concluded that hereditary information passes in distinct units
1. Peas are self fertilizing (viable seeds form if a flowers pollen lands in its own carpel)
2. Mendel removed the anthers to prevent self fertilization
3. He cross fertilized flowers
4. He planted resulting seeds
5. Recorded traits
\
* His experiments often began with plants that “ breed true” for particular traits
* __Breeding true:__ all offspring have same form of trait as parents, generation after generation
* He cross fertilized plants that breed true for diff. Forms of a trait
* Traits of offspring often appear in predictable patterns
* He concluded that hereditary information passes in distinct units
5
New cards
**Inheritance in modern terms:**
* what are “hereditary units” ?
* Diploid Cells
* Homozygous
* Heterozygous
* Genotype
* Phenotype
* what are “hereditary units” ?
* Diploid Cells
* Homozygous
* Heterozygous
* Genotype
* Phenotype
\
* Mendel's “hereditary units” are genes
* Individuals in a species share traits bc they have the same genes
* Each gene occurs at a specific loco on a particular chromosome
* Diploid cells have pairs of homologous chromosomes → __they have two copies of each gene__
* __Homozygous:__ having identical alleles of a gene on both homologous chromosomes
* __Heterozygous:__ having different alleles of a gene
* __Genotype:__ the particular set of alleles carried by an individual
* __Phenotype__: an individual’s observable traits
* Mendel's “hereditary units” are genes
* Individuals in a species share traits bc they have the same genes
* Each gene occurs at a specific loco on a particular chromosome
* Diploid cells have pairs of homologous chromosomes → __they have two copies of each gene__
* __Homozygous:__ having identical alleles of a gene on both homologous chromosomes
* __Heterozygous:__ having different alleles of a gene
* __Genotype:__ the particular set of alleles carried by an individual
* __Phenotype__: an individual’s observable traits
6
New cards
Dominant and recessive alleles:
* what makes an allele dominant?
* what makes an allele dominant?
* Phenotype depends on how products of alleles interact
* Product of one allele influences the effect of the other
* An allele is __dominant__ when its effect masks that of a __recessive__ allele paired with it
* Product of one allele influences the effect of the other
* An allele is __dominant__ when its effect masks that of a __recessive__ allele paired with it
7
New cards
T or F: all traits are inherited in a mendelian pattern:
False
8
New cards
**10.3 mendelian inheritance patterns:**
* Segregation of genes into gametes:
* When homo during meiosis, the gene pairs on those chromosomes separate.
* Alleles end up in separate gametes
* When homo during meiosis, the gene pairs on those chromosomes separate.
* Alleles end up in separate gametes
9
New cards
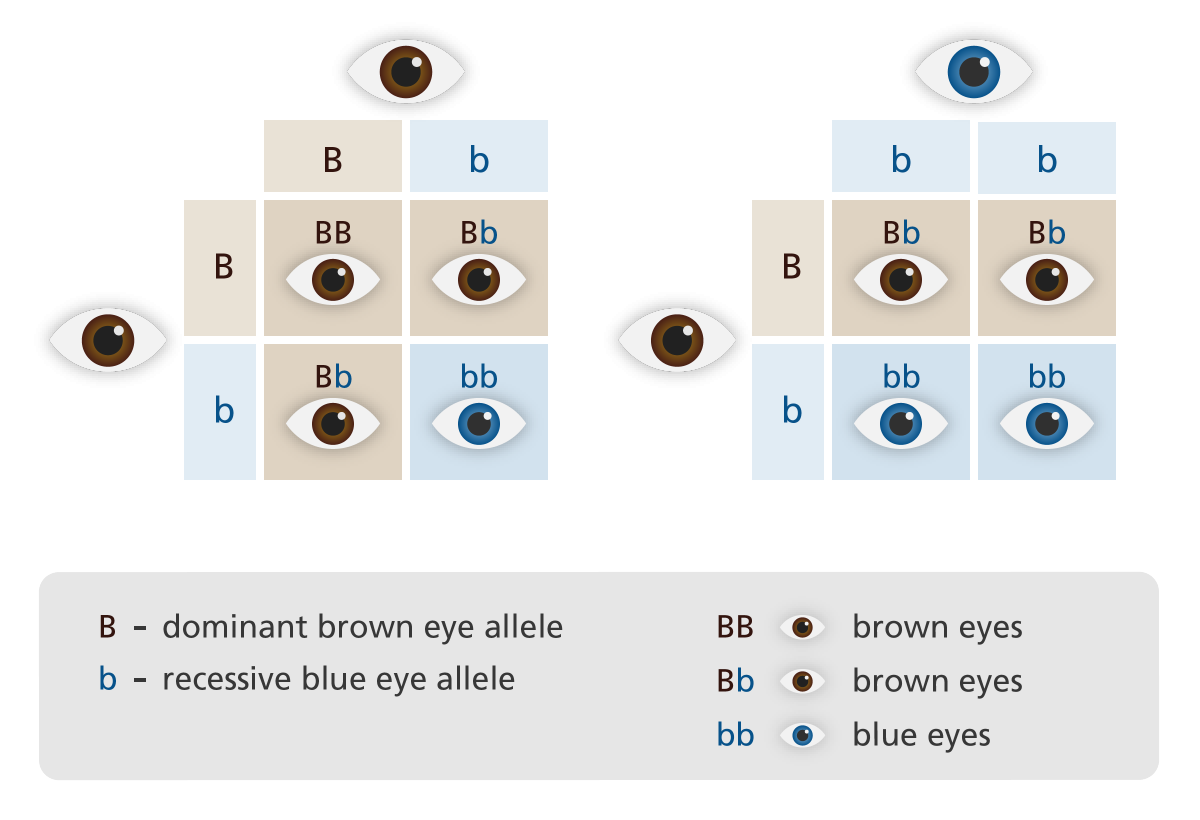
**Segregation of genes into gametes**
* what is a Punnett square?
* what is a Punnett square?
* Plant homozygous for recessive allele (pp) can only make gametes that carry recessive allele (p)
* A cress of the two homozygous plants (PPxpp) has only one outcome: gamete carrying allele P meets with gamete caring allele p
* All offspring will be heterozygous (Pp)
* __Punnett square:__ diagram used to predict genotypic and phenotypic outcomes of a cross
\
* A cress of the two homozygous plants (PPxpp) has only one outcome: gamete carrying allele P meets with gamete caring allele p
* All offspring will be heterozygous (Pp)
* __Punnett square:__ diagram used to predict genotypic and phenotypic outcomes of a cross
\
10
New cards
**Monohybrid crosses**:
\:a cross between individuals that are identically heterozygous for alleles of one gene
* Experiment begins with cross between individuals that breed true
* Cross produces F1 hybrid offspring
* Cross between two of these F1 individuals is monohybrid cross and produces F2 generation
* The frequency at which two traits appear in the second generation provides information about dominance relationship between two alleles
* Dominant trait will have a __3:1 phenotypic ratio__
* Experiment begins with cross between individuals that breed true
* Cross produces F1 hybrid offspring
* Cross between two of these F1 individuals is monohybrid cross and produces F2 generation
* The frequency at which two traits appear in the second generation provides information about dominance relationship between two alleles
* Dominant trait will have a __3:1 phenotypic ratio__
11
New cards
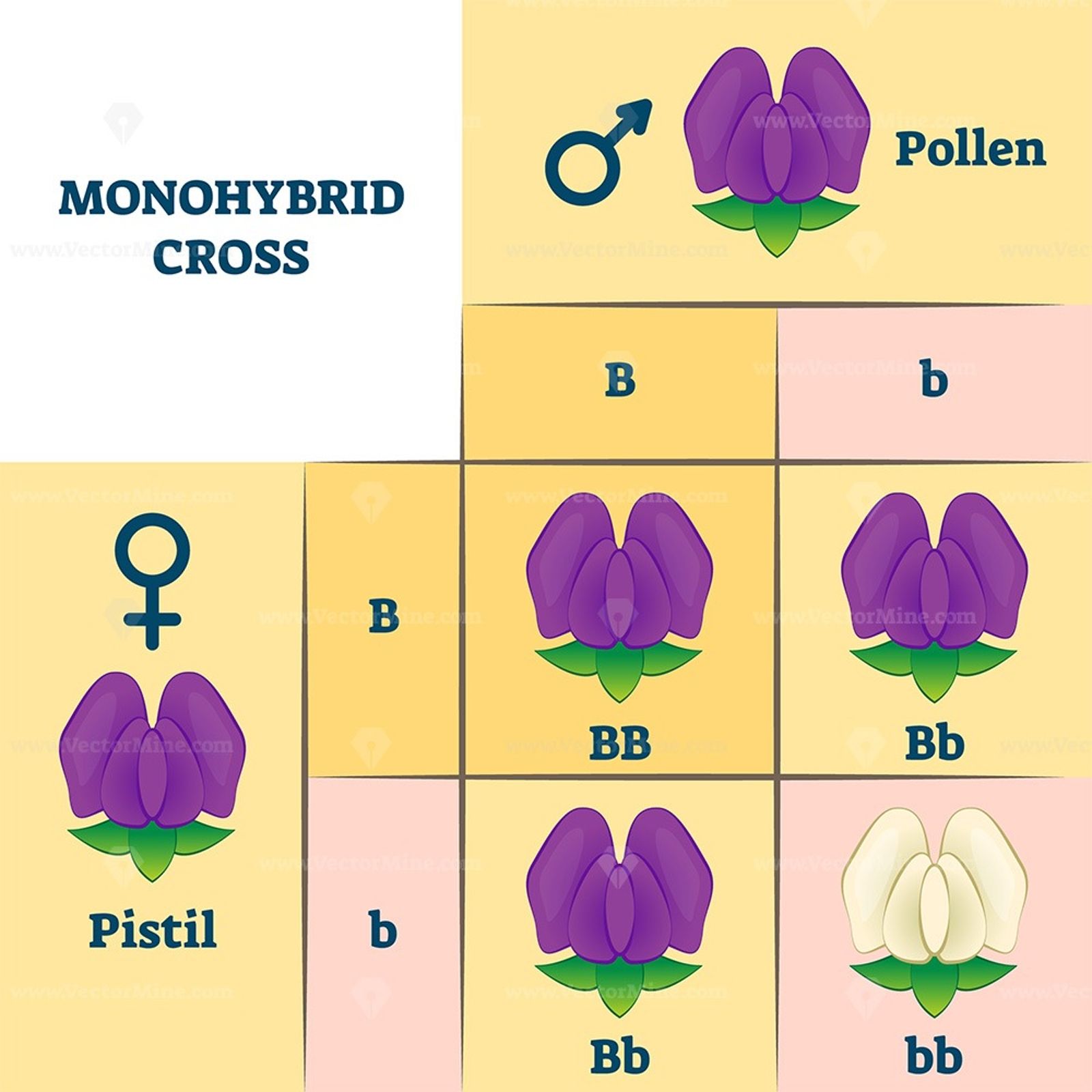
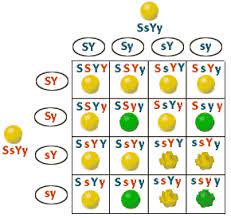
Dihybrid crosses
\: a cross between two individuals that are heterozygous for alleles of two genes (AaBb, for ex)
* Mendel's dihybrid crosses showed that hereditary units for s for different traits (alleles of different genes) often assort independently into gametes
* __9:3:3:1 phenotype ratio__
* Mendel's dihybrid crosses showed that hereditary units for s for different traits (alleles of different genes) often assort independently into gametes
* __9:3:3:1 phenotype ratio__
12
New cards
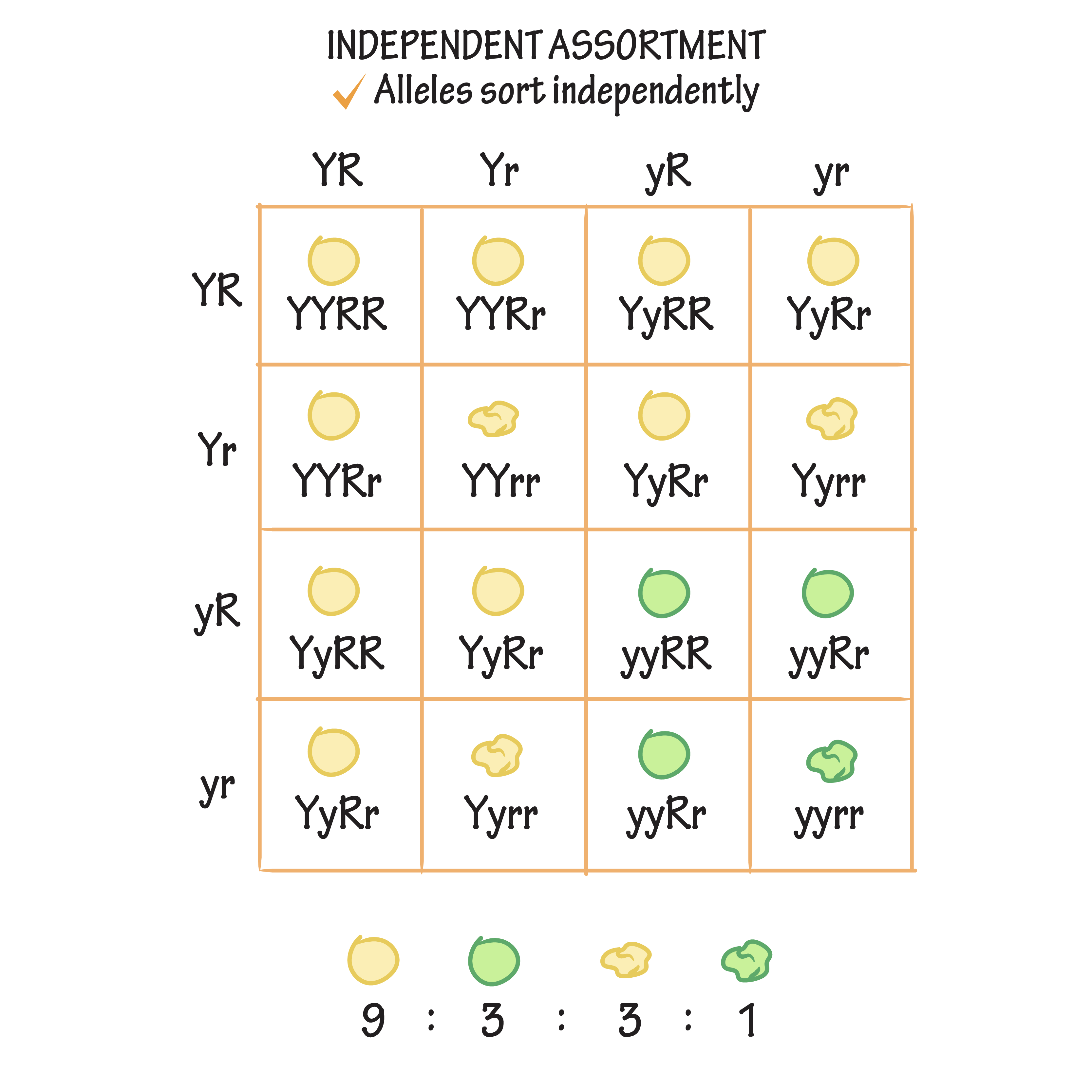
Independent assortment:
\: A gene tends to be distributed independently of how other genes are distributed
* When two genes on the same chromosome are far apart, crossing over occurs more frequently between them
* They tend to assort independently
* Two genes located close together on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together
* When two genes on the same chromosome are far apart, crossing over occurs more frequently between them
* They tend to assort independently
* Two genes located close together on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together
13
New cards
One gene that gives rise to three traits is an example of___:
pleiotropy
14
New cards
**10.4 Non- mendelian inheritance:**
\
* __Mendelian inheritance:__
* One gene gives rise to one trait
* Alleles are either dominant or recessive
* __Non-mendelian inheritance:__
* Incomplete dominance
* Codominance
* Pleiotropy
* Polygenic inheritance
* __Mendelian inheritance:__
* One gene gives rise to one trait
* Alleles are either dominant or recessive
* __Non-mendelian inheritance:__
* Incomplete dominance
* Codominance
* Pleiotropy
* Polygenic inheritance
15
New cards
**Incomplete dominance:**
* Condition in which one allele is not fully dominant over another, so the __heterozygous phenotype is an intermediate blend__ between the two homozygous phenotypes
* Example: snapdragon flower color
* One allele encodes enzymes making red pigment
* Another allele is mutated: enzyme cannot make pigment (flowers are white)
* Heterozygous make only a little pigment, so flowers are pink
* Example: snapdragon flower color
* One allele encodes enzymes making red pigment
* Another allele is mutated: enzyme cannot make pigment (flowers are white)
* Heterozygous make only a little pigment, so flowers are pink
16
New cards
Codominance:
\: inheritance pattern in which two alleles are fully expressed in heterozygotes
* IE: neither allele is dominant or recessive
* Example: ABO blood type in humans
* ABO gene encodes enzyme that modifies a carb on the surface of red blood cells
* A & B alleles encode different enzymes, which modify the carbohydrate differently
* O has a mutation that encodes a faulty enzyme – carbohydrate is unmodified
* IE: neither allele is dominant or recessive
* Example: ABO blood type in humans
* ABO gene encodes enzyme that modifies a carb on the surface of red blood cells
* A & B alleles encode different enzymes, which modify the carbohydrate differently
* O has a mutation that encodes a faulty enzyme – carbohydrate is unmodified
17
New cards
**Pleiotropy:**
\:A single gene affects multiple traits
* Mutation in the genes product affect all the traits
* Mutations in these genes are associated with complex genetic disorders
* Example: sickle-cell anemia
* Mutation in the genes product affect all the traits
* Mutations in these genes are associated with complex genetic disorders
* Example: sickle-cell anemia
18
New cards
Polygenic Inheritance:
\: pattern of inheritance in which multiple genes affect one trait
* Hundreds of genes can be involved
* Ex: Labrador colors
* Hundreds of genes can be involved
* Ex: Labrador colors
19
New cards
**A human example: Skin color**
* Variations in skin color depend on the kinds and amount of melanins produced
* __More than 350 gene products__ affect production and deposition of melanin and melanosomes ( organelles that make melanin )
* Most people have the same # of melanosomes in cells, but they differ in size and shape of melanosomes, and kinds and amounts of melanin they make
* __More than 350 gene products__ affect production and deposition of melanin and melanosomes ( organelles that make melanin )
* Most people have the same # of melanosomes in cells, but they differ in size and shape of melanosomes, and kinds and amounts of melanin they make
20
New cards
**10.5 complex variation in traits**
* nature vs nurture
* environment
* nature vs nurture
* environment
* Variation in traits begins w alleles, but the relationship between alleles and traits can be difficult to determine
* __Environment__ also influences form of many traits
* “Nature vs Nurture”: is behavior based on genetics or the environment
* Today we know that both genetics and environment affect phenotype
* genotype + environment = phenotype
* __Environment__ also influences form of many traits
* “Nature vs Nurture”: is behavior based on genetics or the environment
* Today we know that both genetics and environment affect phenotype
* genotype + environment = phenotype
21
New cards
**Examples of environmental effects on phenotype:**
* Water fleas:
* Low oxygen in water turns on expression of genes that produce hemoglobin, turning them red
* Seasonal changes in coat color
* Plant development
* Changes in temp, night length and availability of water and nutrients trigger changes in gene expression
* Low oxygen in water turns on expression of genes that produce hemoglobin, turning them red
* Seasonal changes in coat color
* Plant development
* Changes in temp, night length and availability of water and nutrients trigger changes in gene expression
22
New cards
**Continuous variation:**
* what is it?
* short tandem repeats
* bell curve
* what is it?
* short tandem repeats
* bell curve
\: a range of small differences in forms of a trait
* Often an outcome of polygenic inheritance, and genes with lots of alleles
* Often associated with __short tandem repeats__: series of 206 nucleotides repeated many times in a row within regions of DNA
* Ex: alleles with more short tandem repeats associated with longer dog faces
* __Bell curve:__ typically results from graphing frequency versus distribution for a trait that varies continuously
* Often an outcome of polygenic inheritance, and genes with lots of alleles
* Often associated with __short tandem repeats__: series of 206 nucleotides repeated many times in a row within regions of DNA
* Ex: alleles with more short tandem repeats associated with longer dog faces
* __Bell curve:__ typically results from graphing frequency versus distribution for a trait that varies continuously
23
New cards
Pedigree analysis is necessary when studying human inheritance patterns bc ___:
*most of us choose our own mates and reproduce when we choose to*
24
New cards
**10.6 Human genetic disorders:**
* Few easily observed human traits follow mendelian inheritance
* Polygenic traits are common, and many phenotypes are influenced by both genetics and the environment
* We decide when and who we mate with → makes studying inheritance patterns challenging
* Polygenic traits are common, and many phenotypes are influenced by both genetics and the environment
* We decide when and who we mate with → makes studying inheritance patterns challenging
25
New cards
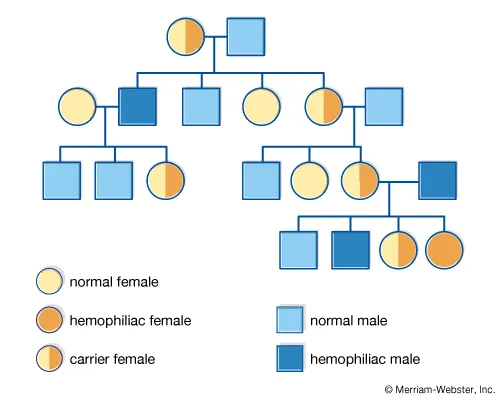
Pedigrees
\:charts illustrating phenotypes through gens. of a family tree
* Used to study inheritance patterns in humans
* Allows for a probability estimation of a phenotype reappearing in future gens
* Shows whether a trait is associated w dominant or recessive alleles
* Shows whether a trait is on an autosome or sex chromosome
\
Will ask to interpret a pedigree on the exam! → examples on slides
* Used to study inheritance patterns in humans
* Allows for a probability estimation of a phenotype reappearing in future gens
* Shows whether a trait is associated w dominant or recessive alleles
* Shows whether a trait is on an autosome or sex chromosome
\
Will ask to interpret a pedigree on the exam! → examples on slides
26
New cards
**Genetic disorders and abnormalities:**
* __Genetic abnormality :__
* an uncommon version of a heritable trait that does not result in medical problems
* Ex: polydactyly → extra fingers
* __Genetic disorder:__
* A heritable condition that results in a syndrome of mild or severe medical problems
* Example: Cystic fibrosis
\
* an uncommon version of a heritable trait that does not result in medical problems
* Ex: polydactyly → extra fingers
* __Genetic disorder:__
* A heritable condition that results in a syndrome of mild or severe medical problems
* Example: Cystic fibrosis
\
27
New cards
**10.7 Inheritance patterns in humans:**
* autosomal dominate trait
* autosomal dominate trait
* Human genetic disorders are characterized by chromosome of origin (sex or autosome) and whether it is recessive or dominant
* __Autosomal dominant trait:__ appears in homozygotes and heterozygotes
* Inheritance clues:
* Two affected parents can have unaffected offspring
* Two unaffected parents cannot have affected offspring
* __Autosomal dominant trait:__ appears in homozygotes and heterozygotes
* Inheritance clues:
* Two affected parents can have unaffected offspring
* Two unaffected parents cannot have affected offspring
28
New cards
**Examples of autosomal dominant disorders:**
\
* Achondroplasia: hereditary dwarfism, caused by mutation of gene for a growth factor receptor
* Alles can be passed on to children
* Achondroplasia: hereditary dwarfism, caused by mutation of gene for a growth factor receptor
* Alles can be passed on to children
29
New cards
**The autosomal recessive pattern:**
* carriers
* carriers
\
* __Autosomal recessive trait__: appears in people homozygous for a recessive allele on an autosome
* __Carriers__: heterozygous individuals who have the allele __but not the trait__
* A child of two carriers has a 25% chance of inheriting allele from parents and developing the trait
* Inheritance clues:
* Two unaffected parents can produce affected child
* Two affected parents only have affected offspring
* __Autosomal recessive trait__: appears in people homozygous for a recessive allele on an autosome
* __Carriers__: heterozygous individuals who have the allele __but not the trait__
* A child of two carriers has a 25% chance of inheriting allele from parents and developing the trait
* Inheritance clues:
* Two unaffected parents can produce affected child
* Two affected parents only have affected offspring
30
New cards
**X linked recessive pattern:**
* : arise from genes on the X chromosome
* Most x chromosome alleles are recessive
* Inheritance clues:
* An affected father never passes allele to a son - all children who inherit fathers X chromosome are female
* Disorder appears more often in males than females - having one x chromosomes, a male must inherit only one allele to be affected by disorder; females must inherit two
* If a mother has trait, all her sons also have it
* Most x chromosome alleles are recessive
* Inheritance clues:
* An affected father never passes allele to a son - all children who inherit fathers X chromosome are female
* Disorder appears more often in males than females - having one x chromosomes, a male must inherit only one allele to be affected by disorder; females must inherit two
* If a mother has trait, all her sons also have it
31
New cards
Nondisjunction at meiosis can result in ___:
aneuploidy
32
New cards
T or F, An individual with three or more complete sets of chromosomes is polyploid:
True
33
New cards
**10.8 changes in chromosomes #:**
* polyploidy
* aneuploidy
* polyploidy
* aneuploidy
* __Polyploidy:__ having three or more of __each type of chromosome__ characteristic of the species
* Common in flowering plants (abt 70%)
* Some insects, fishes, and other animals
* Fatal in humans
* __Aneuploidy__: having too many or too few copies of a __particular chromosome__
* Usually bc of nondisjunction
\
* Common in flowering plants (abt 70%)
* Some insects, fishes, and other animals
* Fatal in humans
* __Aneuploidy__: having too many or too few copies of a __particular chromosome__
* Usually bc of nondisjunction
\
34
New cards
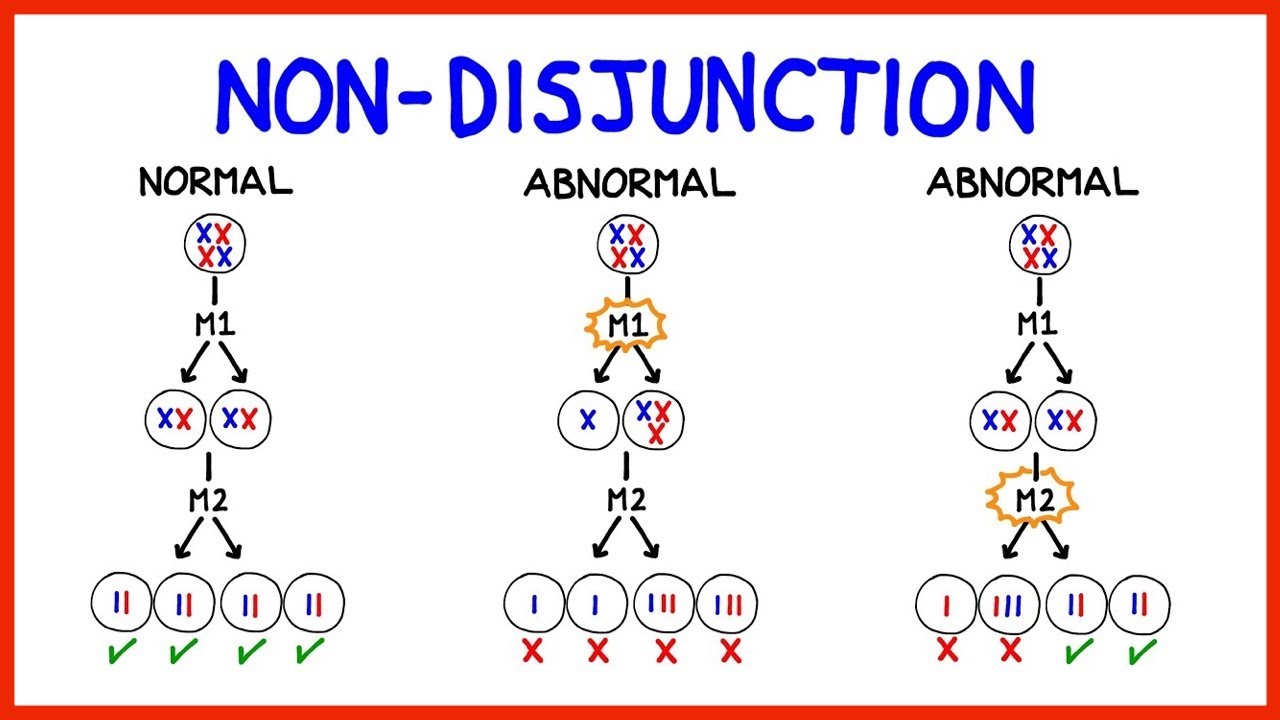
Nondisjunction:
* trisomy
* monosomy
* trisomy
* monosomy
\: the failure of chromosomes to separate normally during meiosis or mitosis
* In meiosis, creates gametes with abnormal number of chromosomes
* If normal gamete (n) fuses with gamete that has an extra chromosome (n +1), the zygote will have three copies of that chromosome - trisomy
* If normal gamete (n) fuses with gamete missing a chromosome (n -1), the zygote will have one copy of that chromosome - monosomy
* In meiosis, creates gametes with abnormal number of chromosomes
* If normal gamete (n) fuses with gamete that has an extra chromosome (n +1), the zygote will have three copies of that chromosome - trisomy
* If normal gamete (n) fuses with gamete missing a chromosome (n -1), the zygote will have one copy of that chromosome - monosomy
35
New cards
**Down Syndrome:**
\
* A person born with 3 copies of chromosome 21 will have down syndrome (trisomy 21)
* The only autosomal trisomy that allows humans to survive until adult hold
* Affected individuals tend to have certain physical features
* Nondisjunction leading to trisomy 21 increases with age of the mother
* A person born with 3 copies of chromosome 21 will have down syndrome (trisomy 21)
* The only autosomal trisomy that allows humans to survive until adult hold
* Affected individuals tend to have certain physical features
* Nondisjunction leading to trisomy 21 increases with age of the mother
36
New cards
Sex chromosomes aneuploidy
* female abnormalities
* male abnormalities
* how many babies are born with an atypical # of sex chromies
* female abnormalities
* male abnormalities
* how many babies are born with an atypical # of sex chromies
don't need to know the names but should be able to recognize)
\
* Abt 1 in 400 babies are born w an atypical # of sex chromosomes
* Usually associated with learning difficulties, speech delays, and motor skill impairment
* Female sex chromosomes abnormalities:
* Turner syndrome (XO) - one X chromosome only
* XXX syndrome
* Male Sex chromosome abnormalities:
* Klinefelter syndrome (XXY)
* XXY syndrome
\
* Abt 1 in 400 babies are born w an atypical # of sex chromosomes
* Usually associated with learning difficulties, speech delays, and motor skill impairment
* Female sex chromosomes abnormalities:
* Turner syndrome (XO) - one X chromosome only
* XXX syndrome
* Male Sex chromosome abnormalities:
* Klinefelter syndrome (XXY)
* XXY syndrome
37
New cards
*Suppose a single nondisjunction event occurs during anaphase 2 of meiosis in a normal male cell from meiosis 2. Of the resulting sperm,___:*
*two would be normal, one would have an extra chromosome, and one would be missing a chromosome*
38
New cards
An X-linked carrier is a___:
heterozygous female
39
New cards
**10.9 genetic testing:**
* tests for newborns
* tests for parents
* prenatal tests
* Risks??
* tests for newborns
* tests for parents
* prenatal tests
* Risks??
* __Tests for newborns__
* Some disorders can be detected early enough to treat before symptoms develop
* __Tests for prospective parents__
* Probability of a future child inheriting a genetic disorder can be estimated by testing parents for specific alleles
* Karyotypes & pedigrees are also useful
* __Prenatal tests:__
* Genetic screening is also done post-conception
* __Ultrasound imaging__
* Can reveal physical defects that may be the result of genetic disorders
* Obstetric sonography - taken externally
* Fetoscopy - taken inside uterus
* __Sampling fetal cells__
* Amniocentesis - small fluid sample taken from amniotic fluid
* Chorionic villi sampling (CVS) - few cells removed from chorion (membrane surrounding amniotic sac)
* __Risk and intervention:__
* Invasive procedures carry risks to the fetus
* Amniocentesis - no risk of miscarriage
* CVS - 0.3% have underdeveloped or missing fingers and toes
* Fetoscopy - increases risk of miscarriage from 2-10%
* Couples at high risk of having child with genetic disorder may opt for reproductive interventions
* In vitro fertilization: sperm and egg are mixed in a test tube
* One of 8 cells removed from embryo at 48 hours
* Genes analyzed
* If no defects detected, embryo inserted into uterus
* Some disorders can be detected early enough to treat before symptoms develop
* __Tests for prospective parents__
* Probability of a future child inheriting a genetic disorder can be estimated by testing parents for specific alleles
* Karyotypes & pedigrees are also useful
* __Prenatal tests:__
* Genetic screening is also done post-conception
* __Ultrasound imaging__
* Can reveal physical defects that may be the result of genetic disorders
* Obstetric sonography - taken externally
* Fetoscopy - taken inside uterus
* __Sampling fetal cells__
* Amniocentesis - small fluid sample taken from amniotic fluid
* Chorionic villi sampling (CVS) - few cells removed from chorion (membrane surrounding amniotic sac)
* __Risk and intervention:__
* Invasive procedures carry risks to the fetus
* Amniocentesis - no risk of miscarriage
* CVS - 0.3% have underdeveloped or missing fingers and toes
* Fetoscopy - increases risk of miscarriage from 2-10%
* Couples at high risk of having child with genetic disorder may opt for reproductive interventions
* In vitro fertilization: sperm and egg are mixed in a test tube
* One of 8 cells removed from embryo at 48 hours
* Genes analyzed
* If no defects detected, embryo inserted into uterus
40
New cards
Evolution is :
change in a line of decent
41
New cards
12\.1 reflections of a distant past:
\
* Mass extinction occurred 66 mill years ago- wiped out dinos and 75% of all species
* Event marked by worldwide rock layer, k-pg boundary
* Rocks below layer: dinos, above layer: no dinos
* Rich in iridium - rare on earth but common in asteroids
* Giant crater found on yucatan peninsula
* Formed by a 6-mile wide asteroid
* Caused mass extinction
* Mass extinction occurred 66 mill years ago- wiped out dinos and 75% of all species
* Event marked by worldwide rock layer, k-pg boundary
* Rocks below layer: dinos, above layer: no dinos
* Rich in iridium - rare on earth but common in asteroids
* Giant crater found on yucatan peninsula
* Formed by a 6-mile wide asteroid
* Caused mass extinction
42
New cards
**12.2 Old beliefs, New discoveries:**
* the great chain of being
* the great chain of being
* Abt 2,300 years ago, aristotle believed nature was a continuum of organization from lifeless matter Through plants and animals
* His work influenced european scientists
* In the 14th century, euros believed in “ the great chain of being”
* __“ the great chain of being”__ : Each link in the chain was a species and believed to have formed at the same time in one place in a perfect state everything that needed to exist already did
* His work influenced european scientists
* In the 14th century, euros believed in “ the great chain of being”
* __“ the great chain of being”__ : Each link in the chain was a species and believed to have formed at the same time in one place in a perfect state everything that needed to exist already did
43
New cards
**New Evidence:**
* biogeography
* comparative morphology
* biogeography
* comparative morphology
* In 1800’s, euro scientists brought back tens of thousands of plants and animals from around the world
* Each newly discovered species was cataloged
* Began to see patterns in where species lived and similarities in body plans
* __Biogeography:__ the study of pattern in the geographical distribution of species and communities
* Explorer alfred wallace believed shared traits might mean flightless birds share a common ancestor But was unsure how each landed on different continents.
* Naturalists had trouble classifying organisms similar in some features but diff in others
* Desert plants with similar structures can have very different reproductive parts
* __Comparative morphology:__ study of anatomical patterns; similarities and differences among the body plans of organisms
* If every species was created in a perfect state, why were there “useless” parts like wings on birds that do not fly, and the remnant of a tail in humans?
* Each newly discovered species was cataloged
* Began to see patterns in where species lived and similarities in body plans
* __Biogeography:__ the study of pattern in the geographical distribution of species and communities
* Explorer alfred wallace believed shared traits might mean flightless birds share a common ancestor But was unsure how each landed on different continents.
* Naturalists had trouble classifying organisms similar in some features but diff in others
* Desert plants with similar structures can have very different reproductive parts
* __Comparative morphology:__ study of anatomical patterns; similarities and differences among the body plans of organisms
* If every species was created in a perfect state, why were there “useless” parts like wings on birds that do not fly, and the remnant of a tail in humans?
44
New cards
**New Ideas:**
* Discoveries in biogeography and comparative morphology began accumulating in the 19th cent
* Evidence implied that Earth had changed over time, but this went against prevailing beliefs at the time
* Arguments began among scientists to make sense of the new information
* Evidence implied that Earth had changed over time, but this went against prevailing beliefs at the time
* Arguments began among scientists to make sense of the new information
45
New cards
New Ideas- Lamarckian Inheritance
* In early 1800s, __jean-baptiste lamarck__ (naturalist) had an idea that species gradually improved generation to generation due to a __drive towards perfection__
* Believed environmental pressures produce change in an individual's body → resulting in change in their offspring
* Lamarck’s understanding of inheritance was incomplete, but he was the first to propose a mechanism for evolution: change in a line of descent
* A line of descent is also called a _______
* Believed environmental pressures produce change in an individual's body → resulting in change in their offspring
* Lamarck’s understanding of inheritance was incomplete, but he was the first to propose a mechanism for evolution: change in a line of descent
* A line of descent is also called a _______
46
New cards
**New Ideas: Catastrophism:**
* Georges Cuvier
* Catastrophism
* Georges Cuvier
* Catastrophism
* __Georges cuvier:__ compare morphology expert
* Rejected lamarck's ideas
* __Catastrophism:__ earth's landscape and been shaped by violent geologic events
* Believed many animals went extinct during geologic events and new species were created following each event
* Argued that the evidence for species changing did not exist
* Rejected lamarck's ideas
* __Catastrophism:__ earth's landscape and been shaped by violent geologic events
* Believed many animals went extinct during geologic events and new species were created following each event
* Argued that the evidence for species changing did not exist
47
New cards
**New Ideas: uniformitarianism**
* who?
* \
* who?
* \
* __Charles lyell:__ geologist
* Believed global catastrophe was not necessary to explain earth's landscape
* __Uniformitarianism__: gradual, everyday geological processes shaped landscape
* Geological processes that sculpt formations in the present could have sculpted rock formations in the past – if they took place over millions of years
* This challenged prevailing belief of Earth being 1,000 years old, but most naturalists accepted Lyell’s idea
* Believed global catastrophe was not necessary to explain earth's landscape
* __Uniformitarianism__: gradual, everyday geological processes shaped landscape
* Geological processes that sculpt formations in the present could have sculpted rock formations in the past – if they took place over millions of years
* This challenged prevailing belief of Earth being 1,000 years old, but most naturalists accepted Lyell’s idea
48
New cards
**Mary Anning:**
\
* Avid fossil hunter and discoverer of many important specimens
* Corresponded with charles lyell and adam sedgwick, who taught charles darwin
* Avid fossil hunter and discoverer of many important specimens
* Corresponded with charles lyell and adam sedgwick, who taught charles darwin
49
New cards
*The process in which environmental pressures result in the differential survival and reproduction of individuals of a population is called___:*
natural selection
50
New cards
A trait is adaptive if it ___:
increases fitness
51
New cards
**12.3 Natural Selection:**
\
* Charles Darwin: (naturalist) was influenced by Lamarck, Culvier, and Lyell's findings
* In 1831, darwin went on a 5 year expedition on the beagle
* Found many unusual fossils, saw many diverse species
* Upon return home (England), he studied his notes and fossils
* Recognized that life changed over time, and thought about the forces that would cause that change
* Charles Darwin: (naturalist) was influenced by Lamarck, Culvier, and Lyell's findings
* In 1831, darwin went on a 5 year expedition on the beagle
* Found many unusual fossils, saw many diverse species
* Upon return home (England), he studied his notes and fossils
* Recognized that life changed over time, and thought about the forces that would cause that change
52
New cards
**Descent with modification:**
* Darwin fossils glyptodonts
* Glyptodonts are extinct, but share many traits with today's armadillos
* Armadillos live only where glyptodonts once lived
* Glyptodonts are extinct, but share many traits with today's armadillos
* Armadillos live only where glyptodonts once lived
53
New cards
**Struggle with limited resources:**
* thomas malthus
* what did darwin realize?
* thomas malthus
* what did darwin realize?
* Darwin read an essay by __Thomas Malthus__: proposed disease, famine, and war limited the size of the human population
* When people reproduce beyond capacity of environment, they run out of food and compete for resources
* Only some survive the struggle for existence
* Darwin realized wider application beyond humans
* When people reproduce beyond capacity of environment, they run out of food and compete for resources
* Only some survive the struggle for existence
* Darwin realized wider application beyond humans
54
New cards
**Variation in traits:**
* What differences in traits distinguish closely related species from one another?
* Finch species on isolated islands of galapagos
* Finches had no opportunity to breed with those mainland populations
* Galapagos finches resembled finch species on mainland, but had unique traits suited to their particular environments
* Finch species on isolated islands of galapagos
* Finches had no opportunity to breed with those mainland populations
* Galapagos finches resembled finch species on mainland, but had unique traits suited to their particular environments
55
New cards
**Fitness:**
* fitness
* adaption
* fitness
* adaption
* Darwin was familiar with variation in traits that selective breeding could produce
* Darwin similarly reasoned that environments could “select” certain traits
* Having a particular trait could give one species an advantage over other species
* Individuals of a natural pop. vary in fitness
* __Fitness:__ the degree of adaptation to a specific environment
* __Adaption:__ trait that enhances fitness
* Darwin similarly reasoned that environments could “select” certain traits
* Having a particular trait could give one species an advantage over other species
* Individuals of a natural pop. vary in fitness
* __Fitness:__ the degree of adaptation to a specific environment
* __Adaption:__ trait that enhances fitness
56
New cards
**Natural selection:**
* Darwin realized that individuals best adapted to their environment were most likely to survive and leave more offspring than less fit rivals
* __Natural selection__: differential survival and reproductive of individuals of a population based on differences in shared, heritable traits → need to be able to pick out this definition
* __Natural selection__: differential survival and reproductive of individuals of a population based on differences in shared, heritable traits → need to be able to pick out this definition
57
New cards
**Great minds think alike:**
* alfred wallace
* alfred wallace
* Darwin developed hypothesis of evolution by natural selection but did not publish his finds yet
→ kept collecting evidence for a decade
* __Alfred Wallace__: was also writing Darwin at the time regarding patterns in geographic distribution
* In 1858, hypothesis of evolution by natural selection was presented at a scientific meeting
* Darwin published “On the origin of species”, with detailed evidence to support his hypothesis
→ kept collecting evidence for a decade
* __Alfred Wallace__: was also writing Darwin at the time regarding patterns in geographic distribution
* In 1858, hypothesis of evolution by natural selection was presented at a scientific meeting
* Darwin published “On the origin of species”, with detailed evidence to support his hypothesis
58
New cards
**Phylogeny primer:**
* __Phylogenies:__ show hypothesized relationships
* Indicate __common ancestors__ and shared lineages
* Are built using __homologous characters__: characters that are similar due to a shared common ancestry
* Can show evolutionary change in characters
* Indicate __common ancestors__ and shared lineages
* Are built using __homologous characters__: characters that are similar due to a shared common ancestry
* Can show evolutionary change in characters
59
New cards
T or F Wrinkly textures in rock that formed from ancient biofilms living in marine sediments are fossils:
True
60
New cards
*The # of a species on an island usually depends on the size of the island and its distance to the mainland. This statement would likely be made by___:*
a biogeographer
61
New cards
**12.4 fossil evidence:**
* __Fossils:__ remains or traces of organisms that lived long ago
* Most fossils include: mineralized bones, teeth, spores, shawls, and seeds
* Trace fossils: footprints, nests, burrows, eggshells, feces - evidence of activities
\
* Most fossils include: mineralized bones, teeth, spores, shawls, and seeds
* Trace fossils: footprints, nests, burrows, eggshells, feces - evidence of activities
\
62
New cards
**Fossilization:**
* It begins when an organism or traces become covered in sediment, mud, or ash
* Overtime, groundwater seeps into the remains filling around and inside
* Minerals dissolved in the water gradually replace minerals found in bone and other hard tissue (can crystalize inside cavities to form detailed imprints of internal and external structures)
* Extreme pressure turns the mineral to rock
* Overtime, groundwater seeps into the remains filling around and inside
* Minerals dissolved in the water gradually replace minerals found in bone and other hard tissue (can crystalize inside cavities to form detailed imprints of internal and external structures)
* Extreme pressure turns the mineral to rock
63
New cards
**Sedimentary Rock**
* __Most fossils are found in sedimentary rock__
* These rocks form as rivers, sand, volcanic ash, and other materials from land to sea
* Mineral particles in the materials settle on seafloors in horizontal layers
* After millions of years, the layers are buried and compacted into rock
* Geologic processes can tilt sedimentary rock and lift it above sea level where erosion can leave it exposed
* Deeper the layer, older the fossil
* These rocks form as rivers, sand, volcanic ash, and other materials from land to sea
* Mineral particles in the materials settle on seafloors in horizontal layers
* After millions of years, the layers are buried and compacted into rock
* Geologic processes can tilt sedimentary rock and lift it above sea level where erosion can leave it exposed
* Deeper the layer, older the fossil
64
New cards
**The fossil record:**
\
* We have fossils for 250,000 know species
* This is likely to be a __small portion of past species:__
* Most remains are lilley not fossilized
* Remains that escape scavenging may decompose in presence of moisture and oxygen
* Fossils are often crushed or scattered by erosion
* Many fossils are inaccessible
* Many species can’t fossilize
* We have fossils for 250,000 know species
* This is likely to be a __small portion of past species:__
* Most remains are lilley not fossilized
* Remains that escape scavenging may decompose in presence of moisture and oxygen
* Fossils are often crushed or scattered by erosion
* Many fossils are inaccessible
* Many species can’t fossilize
65
New cards
**Finding a Missing Link :**
* Discovery of cetaceans (dolphins, whales) provide an example of how scientists reconstruct evolutionary history
* Skeletons of modern cetaceans have remnants of pelvis and hind limbs (many years ago, they walked on land)
* Modern cetaceans are related to artiodactyls (antelopes, sheep)
* Cetaceans developed gigantic bodies for deep ocean swimming
* Skeletons of modern cetaceans have remnants of pelvis and hind limbs (many years ago, they walked on land)
* Modern cetaceans are related to artiodactyls (antelopes, sheep)
* Cetaceans developed gigantic bodies for deep ocean swimming
66
New cards
**The time it takes for half of the atoms in a radioisotope sample to decay is called the ___. :**
half life
67
New cards
**Radiometric Dating: ****
* Radioisotopes decay at a constant rate into daughter elements
* __Half life:__ the time it takes for half the atoms in a sample of a radioisotope to decay
* Each radioisotope has a characteristic half life
* __Half life:__ the time it takes for half the atoms in a sample of a radioisotope to decay
* Each radioisotope has a characteristic half life
68
New cards
**Dating a fossil: (know the concept)**
* radiometric dating
* radiometric dating
* Age of fossils that still contain organic material can be aged via carbon isotopes
* Almost all carbon on earth (and in organisms) is in form of 12C
* Carbon 14 (14C) is a radioisotope, so it decays at a constant rate, and forms at a constant rate in atmosphere
* Ratio of 14C to 12C in atmospheric CO2 is stable
* Living things acquire carbon through their life in this ratio
* When a living thing dies, it stops taking in Carbon and the ratio of 14C to 12C in its remains declines over time as 14C decays but 12 stays the same
* This ratio of 14C to 12C in organism remains can be used to calculate how long ago it died
* 14C half-life= 5,730 years
* __Radiometric dating:__ a method that can reveal the age of a material by measuring its isotope content
* Carbon dating can only be used on biological material less than 60,000 years
* Age of older fossils can be estimated by radiometric dating of volcanic rocks above and below the fossil
* Almost all carbon on earth (and in organisms) is in form of 12C
* Carbon 14 (14C) is a radioisotope, so it decays at a constant rate, and forms at a constant rate in atmosphere
* Ratio of 14C to 12C in atmospheric CO2 is stable
* Living things acquire carbon through their life in this ratio
* When a living thing dies, it stops taking in Carbon and the ratio of 14C to 12C in its remains declines over time as 14C decays but 12 stays the same
* This ratio of 14C to 12C in organism remains can be used to calculate how long ago it died
* 14C half-life= 5,730 years
* __Radiometric dating:__ a method that can reveal the age of a material by measuring its isotope content
* Carbon dating can only be used on biological material less than 60,000 years
* Age of older fossils can be estimated by radiometric dating of volcanic rocks above and below the fossil
69
New cards
**Dating a Rock:**
* Original source of most rocks is magma →Lava
* Lots of elements found in magma, including uranium → a radioactive element's → half life of 4.5 billion years
* When magma cools, the uranium starts decaying into lead
* Ratio of uranium to lead atoms can be measured to calculate how long ago the lava cooled
* Oldest known rock = 4.4 billion years old
* Lots of elements found in magma, including uranium → a radioactive element's → half life of 4.5 billion years
* When magma cools, the uranium starts decaying into lead
* Ratio of uranium to lead atoms can be measured to calculate how long ago the lava cooled
* Oldest known rock = 4.4 billion years old
70
New cards
*The discovery of immense ridges and trenches stretching thousands of kilometers across the sea floor in the 1950s led to acceptance of the theory of___:*
plate tectonics
71
New cards
**12.5 Changes in the history of Earth:**
* Many processes shape the earth's surface
* All continents were once part of a supercontinent known as __pangea__ that split into fragments and drifted apart aby 200 mil years ago
* Continental drift explains why magnetic poles of gigantic rock formations point in different directions in different continents
* All continents were once part of a supercontinent known as __pangea__ that split into fragments and drifted apart aby 200 mil years ago
* Continental drift explains why magnetic poles of gigantic rock formations point in different directions in different continents
72
New cards
**Plate tectonics:**
* Continental drift was not immediately accepted as there was no known mechanism for continents to move
* 1950s→ deeps sea explorers found huge ridges and trenches stretching thousands of kilometers, leading to a mechanism for continental drift
* __Plate tectonics theory__ : Earth’s outer layer of rock is cracked into huge plates, the slow movement of which moves continents to new locations over geologic time
* 1950s→ deeps sea explorers found huge ridges and trenches stretching thousands of kilometers, leading to a mechanism for continental drift
* __Plate tectonics theory__ : Earth’s outer layer of rock is cracked into huge plates, the slow movement of which moves continents to new locations over geologic time
73
New cards
**Plate tectonics: fossil evidence:**
\
* Fossil record provides evidence in support of plate tectonics
* Identical sequence of rock layers in south America, Africa, India, Antarctica, and Australia
* Fossils from multiple species occur in these layers on multiple continents
* Fossil record provides evidence in support of plate tectonics
* Identical sequence of rock layers in south America, Africa, India, Antarctica, and Australia
* Fossils from multiple species occur in these layers on multiple continents
74
New cards
**Supercontinents:**
* At least 5 formed and split up again, since about 4.55 billion years ago
* One was named __Gondwana__ (abt 540 million years ago); merged w/ another supercontinent to form pangea about 300 million years ago
* One was named __Gondwana__ (abt 540 million years ago); merged w/ another supercontinent to form pangea about 300 million years ago
75
New cards
**Tectonics and life's History:**
* Continents colliding brought together populations and species living on different landmasses and separated ocean species
* Recycling between mantle and crust prevents elements crucial to life (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus) from being permanently tied up in rocks
* Recycling between mantle and crust prevents elements crucial to life (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus) from being permanently tied up in rocks
76
New cards
**The geologic time scale:**
* : chronology of earth's history
* Correlates layers of rock with long time intervals
* Composition of each layer hold info about environmental conditions, and fossils are recorded of life in the same period
* Layers differ in composition and fossil content, which imply transitions in Earth’s history
* Earth has been shaped by both gradual and catastrophic events
* Correlates layers of rock with long time intervals
* Composition of each layer hold info about environmental conditions, and fossils are recorded of life in the same period
* Layers differ in composition and fossil content, which imply transitions in Earth’s history
* Earth has been shaped by both gradual and catastrophic events
77
New cards
*Through ___, a body part of an ancestor is modified differently in different lines of descent.:*
: divergent evolution
78
New cards
**12.6 evidence in form and function:**
* __Species with closer evolutionary relationships have more traits in common__
* Comparative morphology provides evidence of such relationships in body form and function
* Comparative morphology provides evidence of such relationships in body form and function
79
New cards
**Homologous structures:**
* homologous: similar in position, structure, and evolutionary origin but not necessarily in function.
* Descendants of a common ancestor may evolve in different ways depending on environmental pressures
* __Divergent evolution__: the divergence of lineages descended from a common ancestor
* Can give rise to homologous structures
* __Homologous structures__: body parts that may appear different in different lineages but are derived from a common ancestral form
* Descendants of a common ancestor may evolve in different ways depending on environmental pressures
* __Divergent evolution__: the divergence of lineages descended from a common ancestor
* Can give rise to homologous structures
* __Homologous structures__: body parts that may appear different in different lineages but are derived from a common ancestral form
80
New cards
**Analogous structures:**
* convergent evolution
* convergent evolution
* Structures that appear similar in different species are not always homologous
* __Convergent evolution__: evolutionary pattern in which similar body parts evolve separately in different lineages
* Convergent evolution can give rise to __analogous structures__: similar body parts that evolved independently in different lineages
\
\
* Wing surfaces:
* Wings of insects, bats, and birds perform the same function, but adaptations differ
* Bat and bird wings: limbs are homologous, but other structures that make them useful for flight are not
* Plant forms:
* Saguaro cactus (North America) and African milk barrel plant (Africa) have homologous and analogous structures
* __Homologous structure:__ accordion-like pleats in plant body swell when well watered, shrink as water is used
* __Analogous structure:__ cactus spines are modified leaves, while milk barrel spines are dried flower stalks
* __Convergent evolution__: evolutionary pattern in which similar body parts evolve separately in different lineages
* Convergent evolution can give rise to __analogous structures__: similar body parts that evolved independently in different lineages
\
\
* Wing surfaces:
* Wings of insects, bats, and birds perform the same function, but adaptations differ
* Bat and bird wings: limbs are homologous, but other structures that make them useful for flight are not
* Plant forms:
* Saguaro cactus (North America) and African milk barrel plant (Africa) have homologous and analogous structures
* __Homologous structure:__ accordion-like pleats in plant body swell when well watered, shrink as water is used
* __Analogous structure:__ cactus spines are modified leaves, while milk barrel spines are dried flower stalks
81
New cards
T/F : Most mutations are adaptive:
False
82
New cards
All of these data types can be evidence of shared ancestry except similarities in ___:
*form due to convergent evolution*
83
New cards
**12.7 molecular evidence for evolution:**
* Over generations, mutations change the DNA sequence of a lineage
* Most mutations are neutral (no effect)
* Mutations accumulate independently in genomes of separate lineages
* The more recently two lineages diverges, the less there has been given mutations to rise
* Similarities in nucleotide sequences of a shared gene, or in the amino acid sequence of a shared protein, are used as evidence of evolutionary relationships
* Most mutations are neutral (no effect)
* Mutations accumulate independently in genomes of separate lineages
* The more recently two lineages diverges, the less there has been given mutations to rise
* Similarities in nucleotide sequences of a shared gene, or in the amino acid sequence of a shared protein, are used as evidence of evolutionary relationships
84
New cards
**Comparing proteins**
* Evolutionary biologist often compare proteins sequence among species and use the number of amino acid differences to determine relatedness
* Most mutations that affect phenotype are selected against
* Occasionally, one is adaptive
* Longer since divergence = more amino acid difference
* Most mutations that affect phenotype are selected against
* Occasionally, one is adaptive
* Longer since divergence = more amino acid difference
85
New cards
**Comparing DNA**
* Recently diverged species may have many proteins with identical amino acid sequences
* Even if the amino acid sequence is identical between species, the nucleotide sequence of the gene that encodes that protein may differ
* Relative relatedness among species is measured by DNA similarities
* Even if the amino acid sequence is identical between species, the nucleotide sequence of the gene that encodes that protein may differ
* Relative relatedness among species is measured by DNA similarities
86
New cards
**Similarities in development:**
* Generally the more closely related animals are, the more similar their development
* Ex: all vertebrates go through a stage where the embryo has a tail and divisions called somites along the back
* Many master regulator genes (genes that control cascades of gene expression) retain similar sequences and functions
* Ex: all vertebrates go through a stage where the embryo has a tail and divisions called somites along the back
* Many master regulator genes (genes that control cascades of gene expression) retain similar sequences and functions
87
New cards
**HOx Genes**
* : group of highly conserved master regulators
* conserved= has remained essentially unchanged throughout evolution
* Trigger formation of specific body parts
* Insects have Hox gene called antennapedia that causes legs to form wherever it is expressed
* Humans and other vertebrates have a version of this gene (Hoxc6 ) that causes ribs to develop in embryos
* conserved= has remained essentially unchanged throughout evolution
* Trigger formation of specific body parts
* Insects have Hox gene called antennapedia that causes legs to form wherever it is expressed
* Humans and other vertebrates have a version of this gene (Hoxc6 ) that causes ribs to develop in embryos
88
New cards
*___ is the OG source of new alleles.:*
Mutation
89
New cards
**13.1 Farming superbugs:**
* Every time a cell divides, it is an opportunity for a mutation to occur
* Intestinal bacteria E. coli can divide every 17 minutes
* Leads to rapid diversification
* Human use of antibiotics is providing a selective pressure that results in E. coli and salmonella resistant to these antibiotics
* Most common on farms where antibiotics are used in food animals
* Intestinal bacteria E. coli can divide every 17 minutes
* Leads to rapid diversification
* Human use of antibiotics is providing a selective pressure that results in E. coli and salmonella resistant to these antibiotics
* Most common on farms where antibiotics are used in food animals
90
New cards
**13.2 Alleles in populations:**
* population
* dimorphic
* polymorphic
* population
* dimorphic
* polymorphic
* __Population:__ a group of interbreeding individuals of the same species in the same area
* Individuals in a pop. have the same genes, so they share certain features
* Morphological traits (morpho = “form”)
* Physiological traits such as details of metabolism
* Sexual reproduction produces offspring with different allele combinations - almost every shared Trait varies among members
* Trait with 2 distinct forms (two alleles) : __dimorphic__
* Trait with three or more distinct forms (3 or more alleles): __polymorphic__
* Most other traits are more complex (polygenic + polymorphic + environment)
* Individuals in a pop. have the same genes, so they share certain features
* Morphological traits (morpho = “form”)
* Physiological traits such as details of metabolism
* Sexual reproduction produces offspring with different allele combinations - almost every shared Trait varies among members
* Trait with 2 distinct forms (two alleles) : __dimorphic__
* Trait with three or more distinct forms (3 or more alleles): __polymorphic__
* Most other traits are more complex (polygenic + polymorphic + environment)
91
New cards
Sources of variation in traits:
\
\
\
* __Mutation is the source of new alleles__
* Other events __shuffle these alleles among offspring__
* Humans have more than 20,000 genes, all w/ multiple alleles
* You are the only person who will ever have your particular combination of alleles
* Except for identical twins!
\
* __Mutation is the source of new alleles__
* Other events __shuffle these alleles among offspring__
* Humans have more than 20,000 genes, all w/ multiple alleles
* You are the only person who will ever have your particular combination of alleles
* Except for identical twins!
\
92
New cards
An evolutionary view of mutations:
* how many new mutations is a child born with?
* beneficial
* neutral
* harmful
* how many new mutations is a child born with?
* beneficial
* neutral
* harmful
* Mutations are the raw material of evolution
* Every human child is born with an average of __64 new mutations__ (64 DNA sequence variations that did not occur in the parents )
* __Beneficial mutation:__ improves the chance of survival or reproduction
* Natural selection acts on these traits
* Tend to be more popular in pop. over time
* __Neutral mutation:__ has no effect on survival or reproduction
* Natural selection does not act on trait
* __Harmful mutation__: reduces chance of surviving and reproducing
* Tend to become less common in a population over time
* Every human child is born with an average of __64 new mutations__ (64 DNA sequence variations that did not occur in the parents )
* __Beneficial mutation:__ improves the chance of survival or reproduction
* Natural selection acts on these traits
* Tend to be more popular in pop. over time
* __Neutral mutation:__ has no effect on survival or reproduction
* Natural selection does not act on trait
* __Harmful mutation__: reduces chance of surviving and reproducing
* Tend to become less common in a population over time
93
New cards
Allele Frequency:
* gene pool
* allele frequency
* microevolution
* evolution is not…
* gene pool
* allele frequency
* microevolution
* evolution is not…
* __Gene pool__: all the alleles of all the genes in a population
* __Allele frequency:__ abundance of a particular allele in a population's gene pool
* Expressed in proportions:
* if half the population is homozygous for an allele: frequency is 50%, or 0.5
* If half the population is heterozygous for an allele: frequency is 25% or 0.25
* __Microevolution:__ change in allele frequency
* Always occurring in natural populations, as natural selection and other processes that cause evolution are always in play
* __Evolution is not purposeful - there is no goal__
* __Allele frequency:__ abundance of a particular allele in a population's gene pool
* Expressed in proportions:
* if half the population is homozygous for an allele: frequency is 50%, or 0.5
* If half the population is heterozygous for an allele: frequency is 25% or 0.25
* __Microevolution:__ change in allele frequency
* Always occurring in natural populations, as natural selection and other processes that cause evolution are always in play
* __Evolution is not purposeful - there is no goal__
94
New cards
The observation that female lions prefer male lions with darker manes is an example of ___:
sexual selection
95
New cards
**13.3 Patterns of natural selection:**
* natural selection - one of several mechanisms by which microevolution occurs
* Natural selection affects allele frequency in a population by operating on forms of a trait that vary in the population
* Occurs in different patterns depending on species and selection pressures:
* __Directional selection__
* __Stabilizing selection__
* __Disruptive selection__
* Natural selection affects allele frequency in a population by operating on forms of a trait that vary in the population
* Occurs in different patterns depending on species and selection pressures:
* __Directional selection__
* __Stabilizing selection__
* __Disruptive selection__
96
New cards
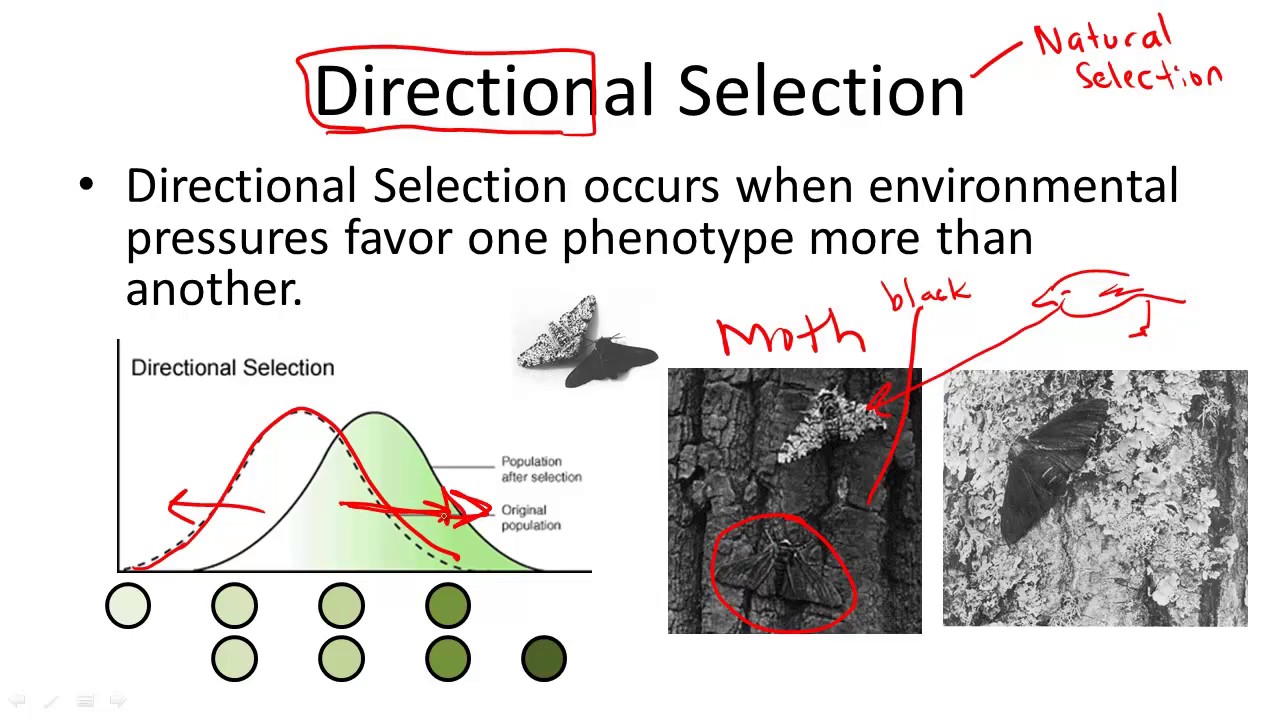
Directional selection:
\: pattern of natural selection in which a form of a trait at one end of a range of variation is adaptive
* Examples: warfarin resistance in rats, peppered moth color
* Examples: warfarin resistance in rats, peppered moth color
97
New cards
**Directional selection: warfarin resistance in rats**
* Warfarin poisoning of rats began on the 1950s
* Warfarin inhibits function of enzyme that regenerates vitamin k, a coenzyme producing blood clotting factors
* By 1980, 10% of rats in urban areas were resistant to warfarin
* Rats resistant to warfarin have mutation in gene that prevents warfarin binding
* Exposure drives microevolution in rats
* Warfarin inhibits function of enzyme that regenerates vitamin k, a coenzyme producing blood clotting factors
* By 1980, 10% of rats in urban areas were resistant to warfarin
* Rats resistant to warfarin have mutation in gene that prevents warfarin binding
* Exposure drives microevolution in rats
98
New cards
**Directional selection: color forms of the peppered moth**
\
\
* Peppered moths in england rest on trees during the day
* In 1850, when air was clean and lichens grew on tree trucks, most peppered moths were light colored with black speckles; better camo than black ones
* By 1900, black moths became much more common
* Smoke from coal burning factories killed lichens on trees and trucks darkened with soot
* Black moths were better camo from predatory birds
* In 1850, when air was clean and lichens grew on tree trucks, most peppered moths were light colored with black speckles; better camo than black ones
* By 1900, black moths became much more common
* Smoke from coal burning factories killed lichens on trees and trucks darkened with soot
* Black moths were better camo from predatory birds
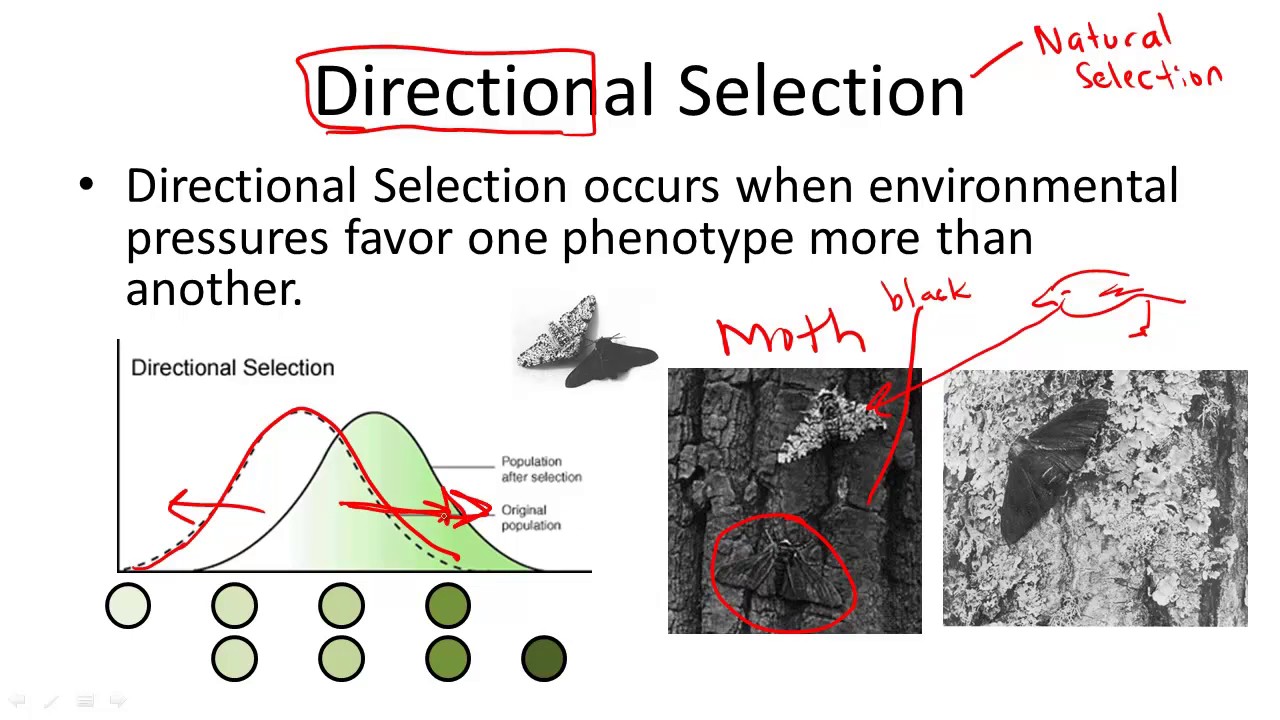
99
New cards
Stabilizing selection:
\
\: pattern of natural selection in which an intermediate form of a trait is adaptive, and extreme forms are selected against
* Examples: body mass in populations of sociable weaver birds, human baby birth weight
\: pattern of natural selection in which an intermediate form of a trait is adaptive, and extreme forms are selected against
* Examples: body mass in populations of sociable weaver birds, human baby birth weight
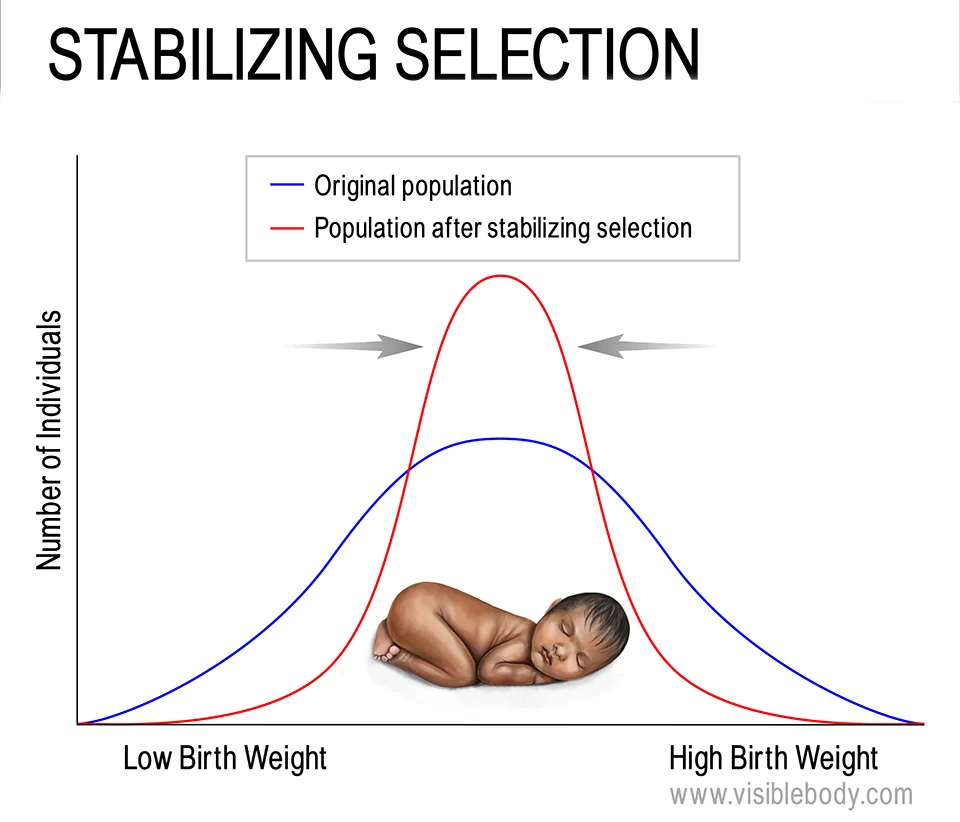
100
New cards
**Stabilizing selection: sociable weaver**
* Stabilizing selection maintains an intermediate body mass in populations of sociable weaver bird
* Trade off between risks of starvation and predation
* Big birds less likely to starve then small
* Big birds spend more time eating in open areas where vulnerable to predators, and are not as agile when escaping
* Intermediate body size is adaptive trait in this environment
* Trade off between risks of starvation and predation
* Big birds less likely to starve then small
* Big birds spend more time eating in open areas where vulnerable to predators, and are not as agile when escaping
* Intermediate body size is adaptive trait in this environment