Hx of the GIT
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
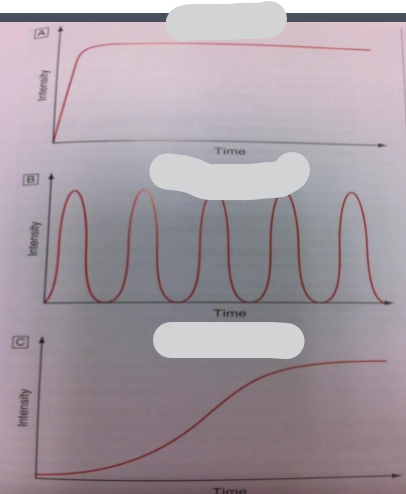
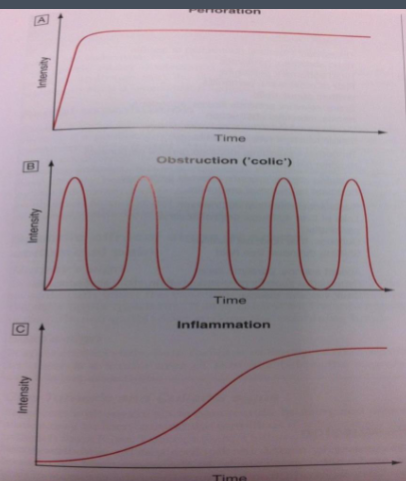
Which graph represents the pain from an obstruction, inflammation or perforation
Name some things that could cause Acute & Severe Abdominal Pain
•Perforated viscus
•Peritonitis
•Acute appendicitis
•Mesenteric ischemia
•Ruptured aortic aneurysm
What is considered Chronic Abdominal Pain
continuous or intermittent abdominal discomfort lasting for at least 3 months
Name some things that could cause Chronic Abdominal Pain
• Gastritis
• Oesophagitis
• Gastro-esophageal reflux disease
• Peptic ulcer disease
• Gallstones
• Pancreatitis
• Inflammatory bowel disease
• Kidney stones
• Constipation /cancer
• Diverticulitis
• Irritable bowel syndrome
For someone with Chronic Abdominal Pain, if their Pain is made worse by eating it may indicate what (5)
• Gastric ulcer
• Chronic pancreatitis
• Gallstone
• Abdominal ischaemia
• Irritable bowel syndrome
For someone with Chronic Abdominal Pain, if their Pain is relieved by eating it may indicate what (1)
Duodenal peptic ulcer disease
For someone with Chronic Abdominal Pain, if their Pain is relieved by defecation it may indicate what (1)
Irritable bowel syndrome
Differentiate between functional & organic Chronic abdominal pain
Functional e.g. Irritable bowel syndrome (no structural defect visible with tests)
Organic: vascular, inflammatory, mechanical (structural defect)
What are 6 Non-GI causes of Abdominal Pain
• Acute coronary syndrome
• Herpes Zoster (shingles)
• Pelvic disorders e.g. ovarian cyst, ectopic pregnancy
• Diabetic ketoacidosis
• Sickle cell crisis
• Pneumonia
What are the 6 Fs that cause Abdominal Distension
• Foetus
• Flatus
• Faeces
• Fluid (Ascites)
• Fat
• Filthy big Tumour
Diarrhoea
Diarrhoea is watery or liquid stools, usually with an increase in stool weight above 200g daily and an increase in daily stool frequency
What to look out for in Diarrhoea
• Duration
• Nocturnal
• Distinguish diarrhoea from faecal urgency or tenesmus (rectal pathology)
• Red-flag symptoms: passing of blood, weight loss
What are some causes of diarrhoea
• Infection: viral, bacterial, parasites
• Inflammatory: IBD: Crohn’s disease, Ulcerative Colitis
• Malabsorption: Coeliac disease
• Pancreatic disease: pancreatitis, tumour
• Large bowel/Colon: Colorectal cancer
• Sigmoid colon: Diverticulitis
• Endocrine: hyperthyroidism, carcinoid syndrome
• Drugs: laxative abuse, antibiotics, NSAIDs, PPIs, alcohol
• Overflow diarrhoea (constipation)
• Irritable bowel syndrome
What can cause constipation
• Diet: low fibre
• Drugs: opiates, CCBs, iron, anticholinergics
• Stricture: (Crohn’s disease)
• Cancer: e.g. carcinoma of colon
• Pelvic mass (foetus, fibroids)
• Hypothyroidism
• Hypercalcaemia
• Idiopathic
Recommended intake of fibre / day
25-30g/day
Jaundice
Yellow pigment of the skin, sclerae and mucosa due to an increase in plasma bilirubin
At what level of bilirubin is jaundice visible
>35μmol/L
Differentiate between Conjugated/Unconjugated bilirubin
Unconjugated bilirubin= water insoluble (fat soluble) does not enter urine
Conjugated bilirubin= water soluble & is excreted in urine (dark colour)
Give 3 causes of Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
Issues in prehepatic region
Increased production e.g. haemolytic anaemia
Impaired uptake by liver e.g. Drugs (rifampicin), congestive cardiac failure
Impaired conjugation e.g. Gilbert’s syndrome, Criglar-Naijar syndrome
3 causes of Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia
Issues in hepatic region
Hepatocellular dysfunction e.g. viral infections, drugs (e.g. statins, sodium valproate, isoniazid, paracetamol overdose), cirrhosis, cancer, haemachromatosis, Wilson’ disease, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Impaired excretion: e.g. Dubin Johnson syndrome, right heart failure
Issues in posthepatic region
Primary biliary cholangitis; drugs (flucloxacillin, nitrofurantoin, choledocholithiasis, compression (cancer head of pancreas, lymph nodes)
What do each of these Oesophagus GI system Symptoms mean:
•Dysphagia
•Odynophagia
•Chest pain
•Heartburn, acid-brash, water brash, belching
•Haematemesis
Dysphagia → Difficulty swallowing.
Odynophagia → Pain when swallowing.
Acid brash → Sour or bitter taste in the mouth from refluxed gastric acid.
Water brash → Sudden filling of mouth with saliva due to oesophageal irritation.
Haematemesis → Vomiting of blood.
What do you call the passage of black, tarry, foul-smelling stool caused by digested blood, typically indicating an upper GI bleed
Melaena
What is Haematochezia & where would the issue be
Haematochezia is the passage of fresh, bright red blood per rectum
Issue in Large bowel/colon
What is tenesmus & where would the issue be
Tenesmus is the persistent, painful feeling of needing to evacuate the bowels even when they are empty, often involving straining and cramping
Issue in Large bowel/colon
If a patient has Pale stools & dark urine, where would the issue be
Hepatobiliary System
Jaundice would be due to an issue where (2)
Hepatobiliary System / Pancreas
3 Signs of infection
Fever, rigors, dehydration
5 causes of anorexia
pancreatitis
IBD
Any tumour
Liver disorders
Inflammation
Name 3 Motor disorders (nerve/ muscle) that could cause GI system Symptoms
Achalasia
Gastro-paresis e.g. ass. with diabetes
Dysphagia e.g. motor-neuron disease
Name 3 causes of Unintentional weight loss
• GI tumour
• IBD (malabsorption)
• Chronic inflammation
3 GI causes of Fatigue
Tumour
Inflammation
Malnutrition/Malabsorption
What could be a GI cause of Raised intra-cranial pressure
Vomiting
Achalasia meaning
Failure of relaxation of the lower gastro- esophageal sphincter
Caused by degeneration of the myenteric plexus
Causes Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
Name some risk factors for Duodenal Ulcers
Males
Blood group O
Helicobacter Pylori
NSAIDs
Aspirin
Steroids
Smoking, alcohol, steroids
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
2 Complications of Duodenal Ulcer
Bleeding
Perforation
What does the Serology (antibodies) of coeliac disease look like (wat antibody is found)
Tissue Transglutaminase IgA antibody