Lecture 8: Corneal Dystrophies and Degenerations
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
define corneal degeneration
corneal tissue deterioration caused by inflammation, age, or systemic dz
- non familial
- later onset
- deposition of material, thinning of tissue, or vascularization
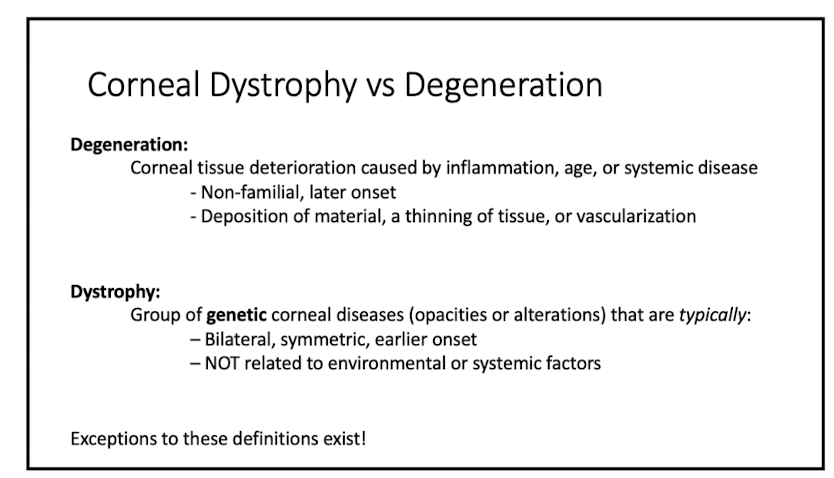
define corneal dystrophy
group of genetic corneal diseases that are:
- bilateral
- symmetric
- early onset
- NOT related to env or systemic factors
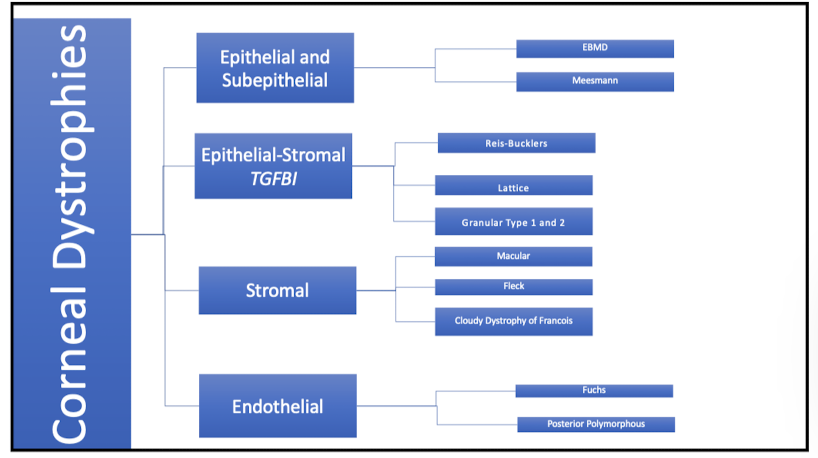
Corneal dystrophies
time it takes for turnover of entire cornea?
7 days
describe the layers of the epithelium
surface cells
- 2 cells thick
- tight junctions
middle layer
- 2 to 3 layers of wing cells
- desmosomes tightly connect wing cells to each other
last layer
- 1 layer of columnar basal cells
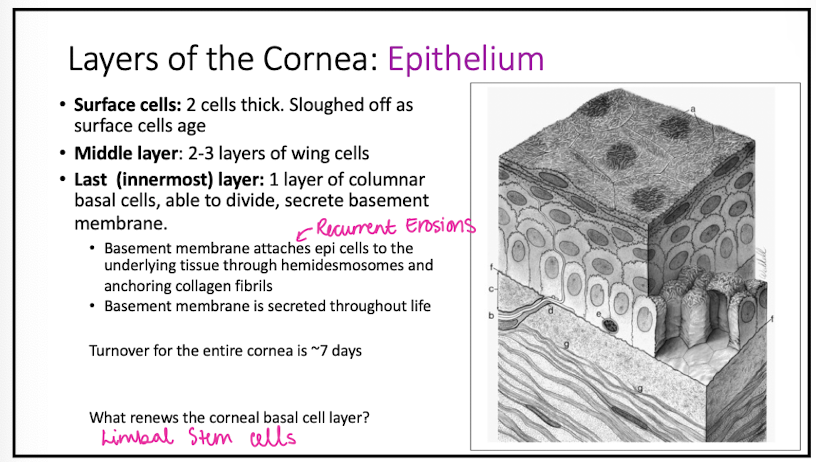
Basement membrane problems lead to
erosions
What type of dystrophy is Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
epi and subepi dystrophy
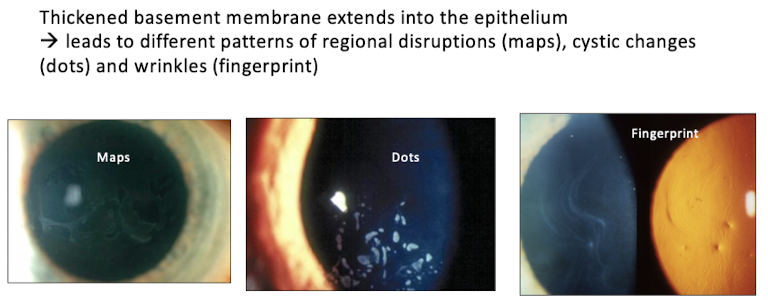
what does EBMD look like
bilateral and asymmetric
1. map like patterns
2. whorl or fingerprint-like lines
3. dot-like epi lesions
4. blebs

EBMD is autosomal _
dominant (but most cases have no documented inheritance so it is better classified as age-related degeneration)
histopathology of EBMD
thickened basement membrane extending into the epi
why is there neg staining in EBMD?
bc the basement membrane is too thick and causes elevation
symptoms of EBMD?
similar to RCE: FB sensation, pain upon awakening
onset of EBMD?
2nd decade of life
is tx for EBMD necessary?
only if symptomatic
RCE etiology
poor epi attachment to basement membrane secondary to trauma or EBMD
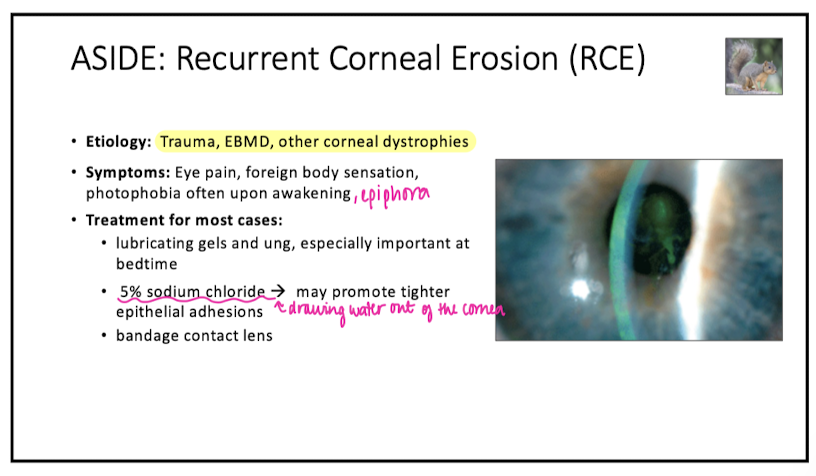
tx for RCE
lubrication
5% sodium chloride
BCL
tx for RCE in recalcitrant cases
doxycycline
amniotic membrane
SK: mechanical debidment of epi
PTK: SK + laser
Describe appearance of Meesman Corneal Dystrophy
tiny intraepi cycts
"meesly lil dots"
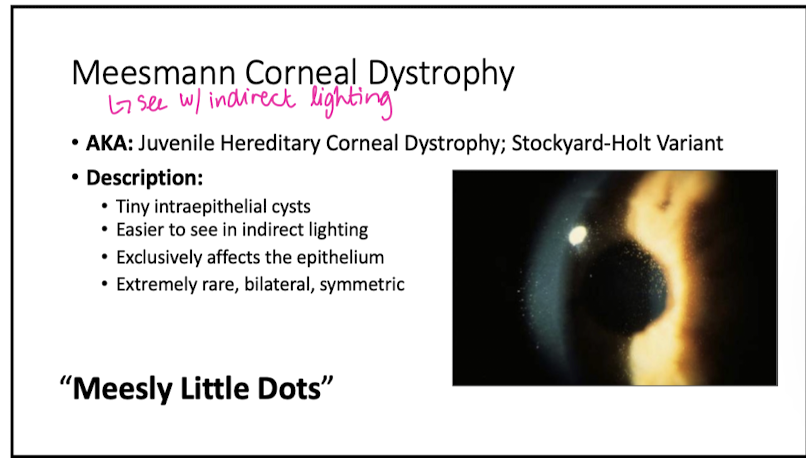
Meesman Corneal Dystrophy
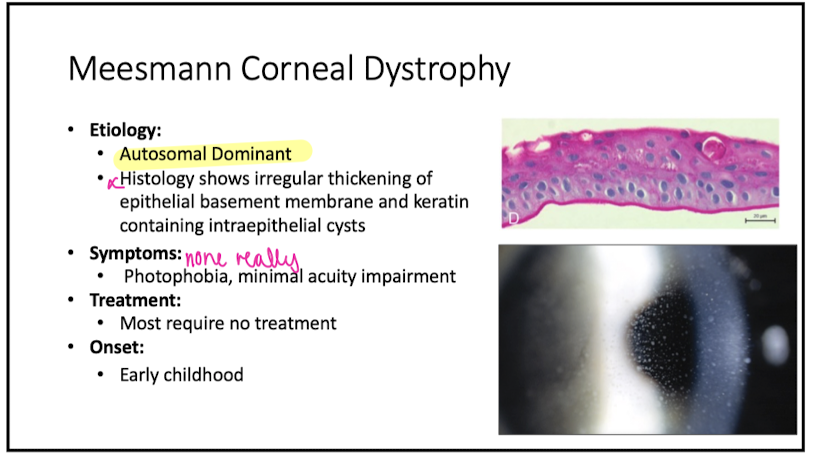
Etiology of Meesman Corneal Dystrophy
irregular thickening of epi basement membrane and keratin containing cysts
What are the 3 epi-stromal TGFB1
Reis-Bucklers
Lattice
Granular Type 1 and 2
Reis-Buckler Sx/Sn
Reis-Buckler Tx
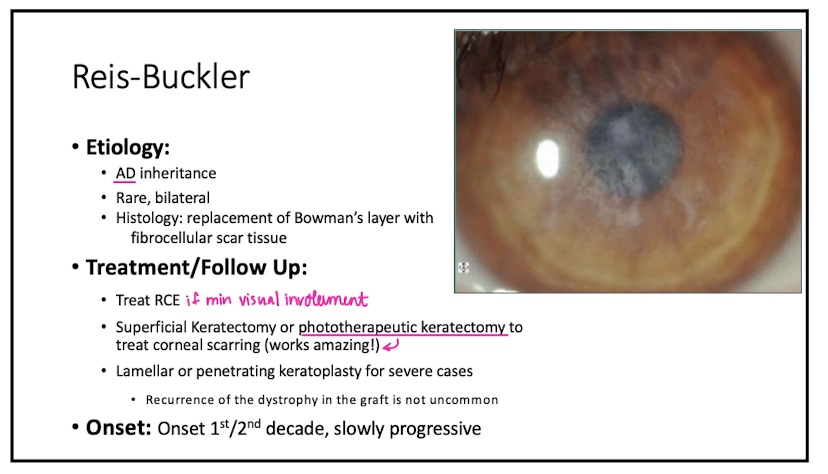
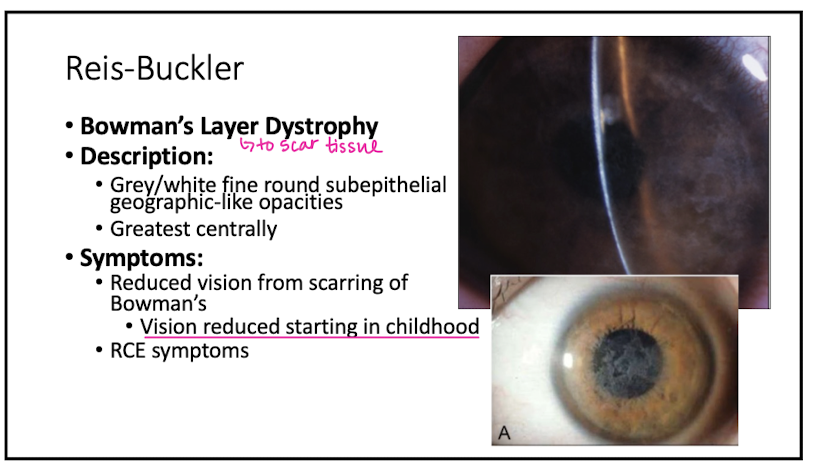
Reis-Buckler is a dystrophy of what layer?
Bowman's
Describe appearance of Reis-Buckler
grey/white, fine, round, subepi opacities geographic like
Symptoms of Reis-Buckler
reduced vision from scarring of Bowman's
Histology of Reis-Buckler
replacement of Bowman's w fibrocellular scar tissue
Tx for Reis-Buckler
treat RCE
PTK or SK
lamellar keratoplasty for severe cases
Onset of Reis-Buckler
1st/2nd decade
Stroma
Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 1
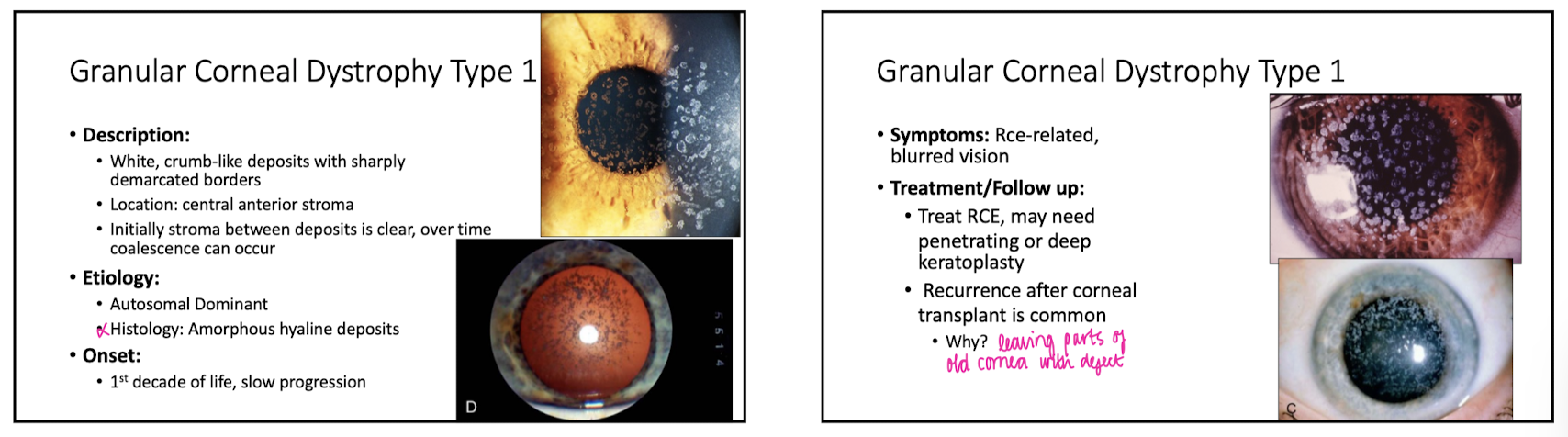
Describe appearance of Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 1
white, crumb-like deposites w sharply demarcated borders
Location of Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 1?
central anterior stroma
Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 1 is autosomal
dominant
onset of Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 1
1st decade of life
symps of Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 1
RCE related
blurry vision
tx for Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 1
treat RCE
PTK
why is recurrence of Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 1 common after a corneal transplant?
bc only the central cornea is being transplanted so the peripheral corneal cells can still migrate
Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 2
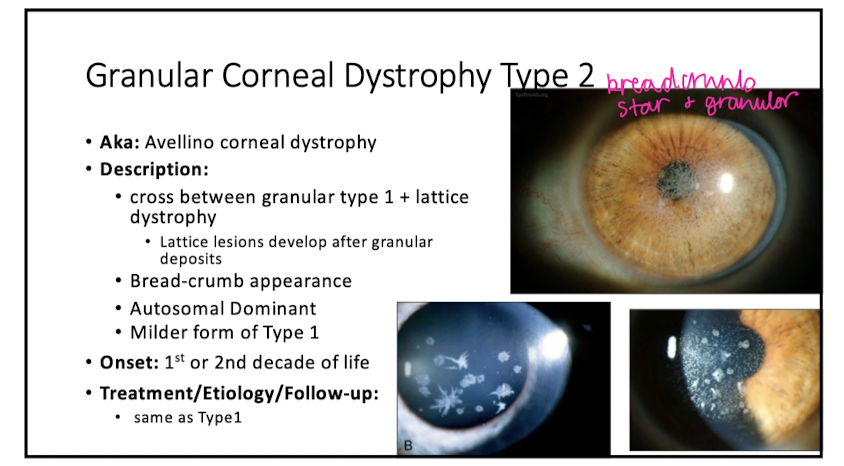
Describe appearance of Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 2
bread-crumb
is a cross b/w granular type 1 and lattice dystrophy
Is Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 2 worse or milder than type 1?
milder
Onset of Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 2
1st or 2nd decade
describe appearance of lattice corneal dystrophy
anterior stromal glass-like filamentous lesions that eventually coalesce into lattice lines
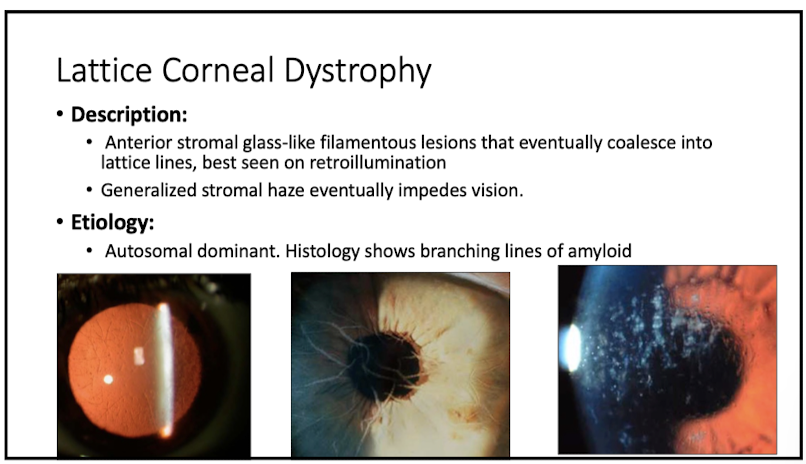
does lattice corneal dystrophy impact vision?
yes, stromal haze impedes vision
histology of lattice corneal dystrophy
branching lines of amyloid
symps of lattice corneal dystrophy
RCE related
reduced VA
what is the most common stromal dystrophy
lattice corneal dystrophy
describe the course of lattice corneal dystrophy
progressive w marked visual decrease by 4th decade
what is lattice type 2 associated w?
systemic amyloidsis- bilateral cranial and peripheral neuropathy , dry skin, bilateral facial palsy, protruding lips
what are the 3 stromal corneal dystrophies
macular dystrophy
fleck dystrophy
central cloudy dystrophy of francois
macular corneal dystrophy
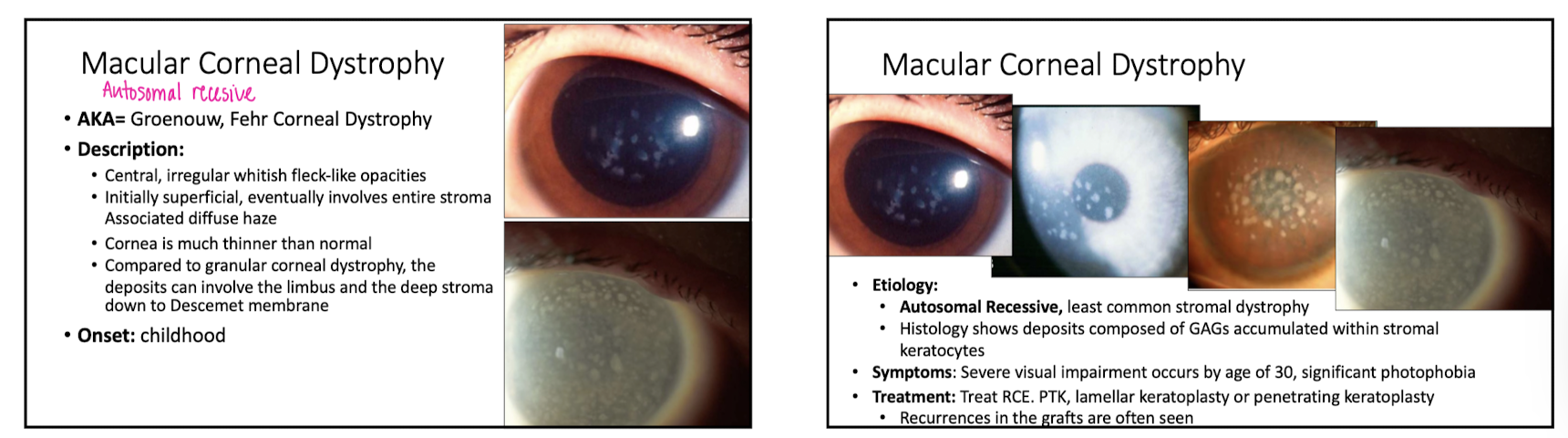
describe appearance of macular corneal dystrophy
central, whiteish opacities
what happens to the cornea in macular corneal dystrophy?
it is thinner than normal
how is macular corneal dystrophy diff from granular corneal dystrophy
the deposits involve the limbus and stroma all the way to Descemet's
onset of macular corneal dystrophy
childhood
macular corneal dystrophy is autosomal _
recessive (it's the only one)
histology of macular corneal dystrophy
deposits composed of GAGs accumulated within stromal keratocytes
symps of macular corneal dystrophy
severe visual impairment occurs by 30yo
photophobia
tx for macular corneal dystrophy
treat RCE
PTK or lamellar keratoplasty
"Marilyn Monroe Always Gets Her Men in LA. County" mnemonic
Macular dystrophy: will see mucopolysaccharide: stains w alcian blue
Granular dystrophy: will see hyaline materials: stains w masson-trichrome
Lattice dystrophy: will see amyloid: stains w congo red
describe appearance of Fleck Corneal Dystrophy
small, translucent, gray-white, dandruff flakes

location of Fleck Corneal Dystrophy
scattered throughout the stroma
histology of Fleck Corneal Dystrophy
accumulation of GAGs and lipids in keratocytes
onset of Fleck Corneal Dystrophy
congenital or 1st year of life
describe appearance of Central Cloudy Dystrophy of Francois
polygonal, cloudy opacities separated by clear lines
leather like appearance in the stromal part of central cornea
Descement’s Membrane
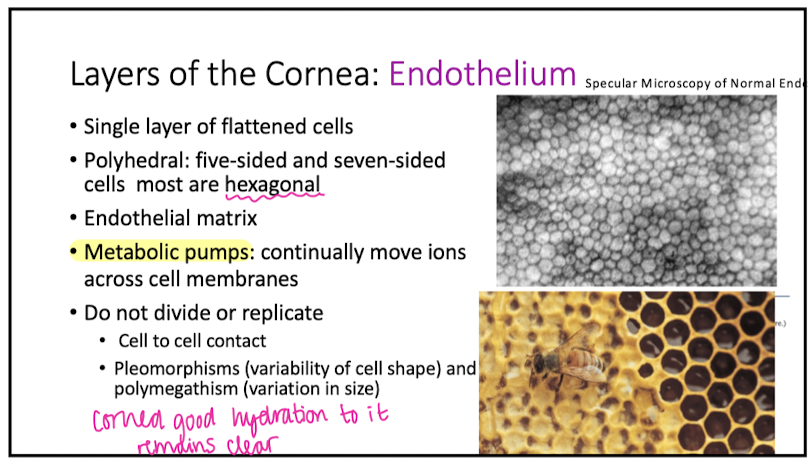
Endothelium
why are collagen fibers in the stroma not continuous with those in Descemet's as they are with Bowman's?
bc it's easy to peel off Descemet's and endothelium away from stroma
how is Descemet's able to curl into the anterior chamber?
bc it is elastic
do cells in the endo divide or replicate?
NO
what do metabolic pumps in the endo do?
move ions across cell membranes
what are the 2 posterior corneal dystrophies?
Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy
Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy
Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy is characterized by...
central corneal guttata
Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy is also associated w _ edema that may progress to involve the _
stromal
epithelium
symps of Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy
reduced vision, worse in AM
pain from ruptured epi bullae
what are guttata
droplet-like accumulations of non-banded collagen on the posterior surface of Descemet's
grading scale for guttata
Grade 0: negative
Grade 1: 0-12 central guttae
Grade 2: Greater than 12 central nonconfluent guttae
Grade 3: 1-2 mm of confluent central guttae
Grade 4: 2-5 mm of confluent central guttae
Grade 5: Greater than 5 mm of confluent central guttae or G4 with stroma or epithelial edema (G5)
onset of Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy
4th decade of life or later
do more males or females get Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy
females 3:1
how to prevent Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy?
you can't
but stop smoking
can Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy progress?
yes
tx for Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy
5% NaCl
DSAEK
DMEK- best for Fuch's
DWEK
Rho Kinase Inhibitors
pt comes in w guttata, what do u do nect?
1. grade it: for a few guttae, just move on but for a lot, do the next steps
2. ask about blurry vision worse in AM
3. check for corneal edema on slit lamp
4. get baseline pachy reading
5. refer when pt is bothered by reduced VA or when stromal haze is noted
describe appearance of Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy
several clinical presentations
1. geographic gray opacities
2. vesicular lesions
3, parallel gray-white endo bands (snail tracks)
pathogenesis of Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy
abnormal endo cells that take on properties of epi cells
descemet's thickening
onset of Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy
early childhood
what does a severe variant of Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy involve?
angle abnormalities and iridocorneal adhesions (rare tho)
list the corneal dystrophies that involve TGFB1 gene
EBMD
Reis-Buckler
Granular Type 1 and 2
Lattice
list the 3 corneal stromal deposits
Ocular Chrysiasis: Gold
Ocular Argryosis: Silver
Wilson's Disease: Kayser-Fleischer ring Copper
describe appearance of Ocular Chrysiasis: Gold
deposition of gold in ocular tissues
dust-like granules scattered in stroma and epi
etiology of Ocular Chrysiasis: Gold
from gold salt tx used for rheumatoid arthritis
describe appearance of Ocular Argryosis: Silver
gray, diffuse opacities in the deep corneal stroma and descemet's
symp of Ocular Argryosis: Silver
reduced dark adaptation
etiology of Ocular Argryosis: Silver
secondary to chronic exposure to silver
tx for Ocular Argryosis: Silver
d/c silver intake or limit exposure
describe appearance of Wilson's Disease
brownish-yellow copper ring
location of Kayer-Fleischer Ring
peripheral descemet's membrane
what is Kayer-Fleischer Ring associated w
sunflower cataract
Wilson's Dz is autosomal _
recessive
Wilson's Dz is caused by a mutation on what chromosome?
13