Quiz 10- (Final)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/154
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
1
New cards
**Fatty acids** are stored in adipose tissue as
**triacylglycerols** (TAG) in which fatty acids are linked to glycerol with ester linkages
2
New cards
**Adipose tissue**
located throughout the body, with subcutaneous (below the skin) and visceral (around the internal organs) deposits being most prominent
3
New cards
The fatty acids incorporated into triacylglycerols in adipose tissue are made accessible in three stages
1\.Degradation of TAG to release fatty acids and glycerol into the blood for transport to energy-requiring tissues
2\.Activation of the fatty acids and transport into the mitochondria for oxidation
3\.Degradation of the fatty acids to acetyl CoA for processing by the citric acid cycle
2\.Activation of the fatty acids and transport into the mitochondria for oxidation
3\.Degradation of the fatty acids to acetyl CoA for processing by the citric acid cycle
4
New cards
**Lipid Degradation**
Lipids are hydrolyzed by lipases in three steps to yield fatty acids and glycerol. The fatty acids are taken up by cells and used as a fuel. Glycerol also enters the liver, where it can be metabolized by the glycolytic or gluconeogenic pathways.
5
New cards
Triacylglycerols are stored in **adipocytes** as
a lipid droplet
6
New cards
**Epinephrine** and **glucagon** stimulate
lipid breakdown or lipolysis through 7TM receptors
7
New cards
**Protein kinase A** phosphorylates
**perilipin**, which is associated with the lipid droplet, and **hormone-sensitive lipase**.
8
New cards
Phosphorylation of **perilipin** results in
the activation of **adipocyte triacylglyceride lipase** (ATGL).
9
New cards
Rearrangement of the lipid molecule releases a
coactivator of ATGL.
10
New cards
ATGL initiates
breakdown of lipids
11
New cards
**Chanarin-Dorfmam syndrome** results **if**
ATGL activity is compromised
12
New cards
**Triacylglycerols in Adipose Tissue are Converted into Free Fatty Acids in Response to**
**Hormonal Signals**
13
New cards
**Figure 27.2**
The phosphorylation of perilipin restructures the lipid droplet and releases the coactivator of ATGL. The activation of ATGL by binding with its coactivator initiates the mobilization. Hormone-sensitive lipase releases a fatty acid from diacylglycerol. Monoacylglycerol lipase completes the mobilization process. Abbreviations: 7TM, seven transmembrane; ATGL, adipose triglyceride lipase; CA, coactivator; HS lipase, hormone-sensitive lipase; MAG lipase, monoacylglycerol lipase; DAG, diacylglycerol; TAG, triacylglycerol
14
New cards
**fatty acids are not**
**soluble** in aqueous solutions, they bind to the blood protein **albumin**, which delivers them to tissues in need of fuel.
15
New cards
The **glycerol** released during lipolysis is absorbed by
the **liver** for use in **glycolysis** or **gluconeogenesis**.
16
New cards
Upon entering the cell cytoplasm, fatty acids are **activated by**
attachment to **coenzyme A**
17
New cards
Fatty acids are linked to
coenzyme A before they are oxidized.
18
New cards
Linking a fatty acid to coenzyme A is
a two-step reaction that proceeds through an **acyl adenylate** intermediate.
19
New cards
**The fatty acid** reacts with **ATP** to form
an **acyl adenylate**, and the other two phosphoryl groups of the ATP substrate are released as **pyrophosphate**
20
New cards
The sulfhydryl group of **CoA** then attacks the **acyl adenylate** to form
**acyl CoA** and **AMP**.
21
New cards
Fatty acids are linked to
coenzyme A before they are oxidized.
22
New cards
The reaction is rendered **irreversible** by
The reaction is rendered **irreversible** by
23
New cards
After being activated by linkage to CoA, the **fatty acid** is transferred to
**carnitine** for transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane
24
New cards
**carnitine**
a reaction catalyzed by **carnitine acyltransferase I**,
25
New cards
A **translocase** transports the **acyl carnitine** into
the matrix of the mitochondria.
26
New cards
In the mitochondria, **carnitine acyltransferase II** transfers the fatty acid to
CoA
27
New cards
**Acyl carnitine translocase**
The entry of acyl carnitine into the mitochondrial matrix is mediated by a translocase. Carnitine returns to the cytoplasmic side of the inner mitochondrial membrane in exchange for acyl carnitine.
28
New cards
Muscle, kidney, and heart use
fatty acids as a fuel
29
New cards
Pathological conditions result if
the acyltransferase or the translocase is deficient.
30
New cards
Fatty acid degradetion consists of four steps that are repeated. name thaw
1\.**Oxidation** of the **β carbon**, catalyzed by **acyl CoA dehydrogenase**, generates ***trans*****-Δ2-enoyl CoA** and **FADH2**.
\
**2.Hydration** of *trans*-Δ2-enoyl CoA by **enoyl CoA hydratase** yields l**-3-hydroxyacyl CoA**
\
3\.**Oxidation** of l-3-hydroxyacyl CoA by **l-3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase** generates **3-ketoacyl CoA** and **NADH**.
4\.Cleavage of the 3-ketoacyl CoA by **β-ketothiolase** forms **acetyl CoA** and **a fatty acid chain two carbons shorter**.
\
**2.Hydration** of *trans*-Δ2-enoyl CoA by **enoyl CoA hydratase** yields l**-3-hydroxyacyl CoA**
\
3\.**Oxidation** of l-3-hydroxyacyl CoA by **l-3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase** generates **3-ketoacyl CoA** and **NADH**.
4\.Cleavage of the 3-ketoacyl CoA by **β-ketothiolase** forms **acetyl CoA** and **a fatty acid chain two carbons shorter**.
31
New cards
Fatty acid degradation is also called
***β*** **oxidation**
32
New cards
**What is The reaction sequence for the degradation of fatty acids**
Fatty acids are degraded by the repetition of a four-reaction sequence consisting of oxidation, hydration, oxidation, and thiolysis
33
New cards
**The first three rounds in the degradation of palmitate.**
Two carbon units are sequentially removed from the carboxyl end of the fatty acid.
34
New cards
**Principal Reactions Required for Fatty Acid Degradation**
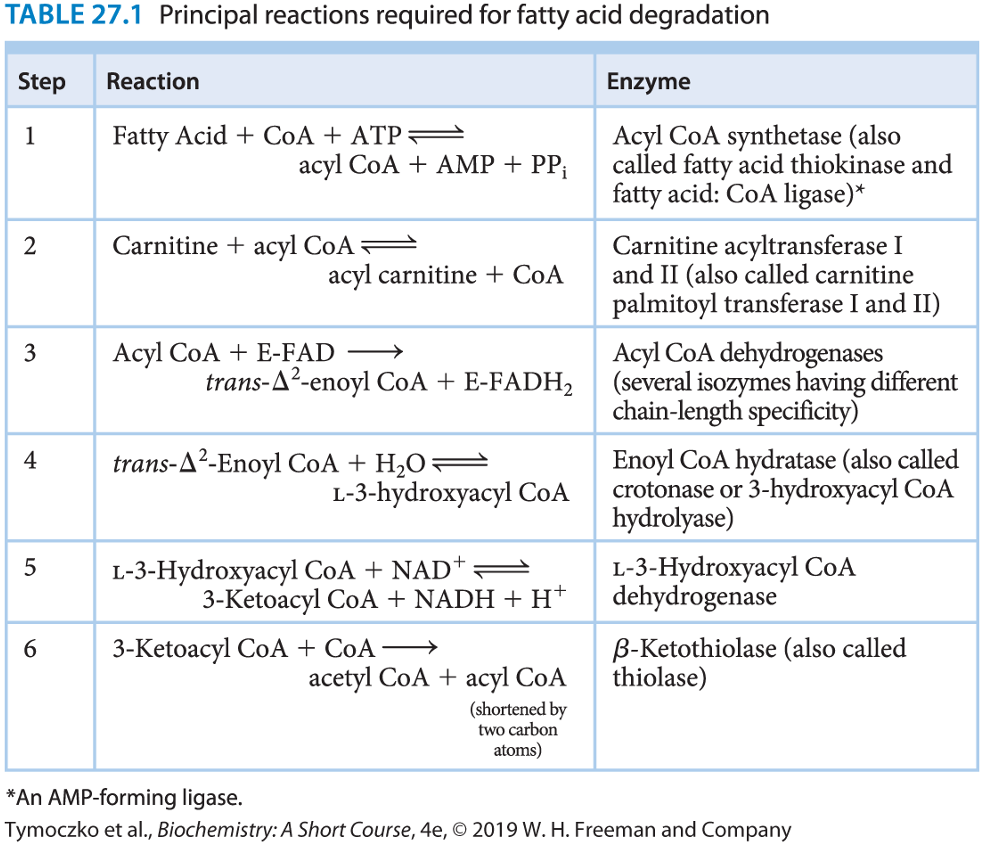
35
New cards
The reaction for one round of β oxidation is
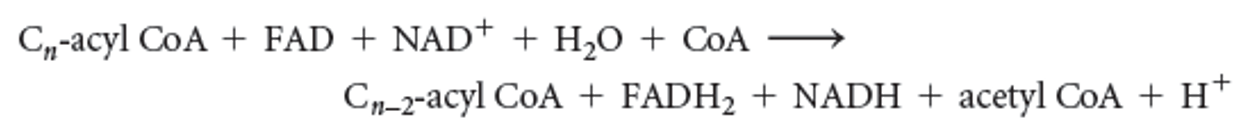
36
New cards
The complete reaction for C16 palmitoyl CoA is
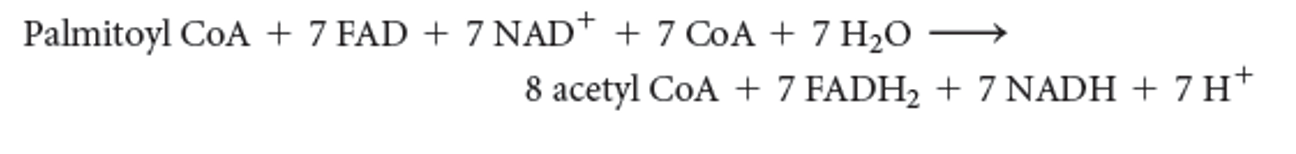
37
New cards
Processing of the products of the complete reaction by cellular respiration would generate
108 molecules of ATP, or net 106 molecules of ATP
38
New cards
Describe the repetitive steps of β oxidation. Why is the process called β oxidation?
39
New cards
An **isomerase** and a **reductase** are required for the oxidation of
**unsaturated** **fatty acids**
\
•β oxidation alone cannot degrade unsaturated fatty acids. When monounsaturated fatty acids such as palmitoleate are degraded by β oxidation, *cis*-Δ3-enoyl CoA is formed, which cannot be processed by acyl CoA dehydrogenase.
\
•β oxidation alone cannot degrade unsaturated fatty acids. When monounsaturated fatty acids such as palmitoleate are degraded by β oxidation, *cis*-Δ3-enoyl CoA is formed, which cannot be processed by acyl CoA dehydrogenase.
40
New cards
*Cis*-Δ3-enoyl CoA isomerase converts the double bond into
*trans*-Δ2-enoyl CoA, a normal substrate for β oxidation.
41
New cards
When polyunsaturated fatty acids are degraded by βoxidation what is required?
•***cis*****-Δ3-enoyl CoA isomerase** is also required. 2,4-Dienoyl CoA is also generated but cannot be processed by the normal enzymes.
42
New cards
2,4-Dienoyl CoA is converted into *trans*-Δ3-enoyl CoA by
2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase, and the isomerase converts this product to *trans*-Δ2-enoyl CoA, a normal substrate
43
New cards
Unsaturated fatty acids with **odd-numbered double bonds** require only
the **isomerase**
44
New cards
**Even-numbered double bonds** require
both the **isomerase** and **reductase**
45
New cards
**The oxidation of linoleoyl CoA**
The complete oxidation of the diunsaturated fatty acid linoleate is facilitated by the activity of enoyl CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase.
\
\
46
New cards
β Oxidation of fatty acids with odd numbers of carbons generates
propionyl CoA in the last thiolysis reaction
47
New cards
**Propionyl CoA carboxylase**, a biotin enzyme, adds
a carbon to propionyl CoA to form methylmalonyl CoA
48
New cards
Succinyl CoA, a citric acid cycle component, is subsequently formed from
methylmalonyl CoA by **methylmalonyl CoA mutase**, a vitamin B12-requiring enzyme.
49
New cards
**The conversion of propionyl CoA into succinyl CoA**
Propionyl CoA, generated from fatty acids having an odd number of carbon atoms as well as from some amino acids, is converted into the citric acid cycle intermediate succinyl CoA
50
New cards
An **isomerase** and a **reductase** are required for the
oxidation of **unsaturated** **fatty acids**.
51
New cards
When monounsaturated fatty acids such as palmitoleate are degraded by β oxidation…. what happens?
*cis*-Δ3-enoyl CoA is formed, which cannot be processed by acyl CoA dehydrogenase
52
New cards
When polyunsaturated fatty acids are degraded by βoxidation.. what happens
***cis*****-Δ3-enoyl CoA isomerase** is also required. 2,4-Dienoyl CoA is also generated but cannot be processed by the normal enzymes.
53
New cards
2,4-Dienoyl CoA is converted into *trans*-Δ3-enoyl CoA by
2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase, and the isomerase converts this product to *trans*-Δ2-enoyl CoA, a normal substrate
54
New cards
Unsaturated fatty acids with **odd-numbered double bonds** require
only the **isomerase**
55
New cards
**Even-numbered double bonds** require
both the **isomerase** and **reductase**
56
New cards
**The oxidation of linoleoyl CoA**
The complete oxidation of the diunsaturated fatty acid linoleate is facilitated by the activity of enoyl CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase
57
New cards
β Oxidation of fatty acids with odd numbers of carbons generates
propionyl CoA in the last thiolysis reaction
58
New cards
**Propionyl CoA carboxylase**, a biotin enzyme, adds a carbon to
propionyl CoA to form methylmalonyl CoA
59
New cards
Succinyl CoA, a citric acid cycle component, is subsequently formed from methylmalonyl CoA by
**methylmalonyl CoA mutase**, a vitamin B12-requiring enzyme.
60
New cards
Ketone-body synthesis takes place in
the liver
61
New cards
Ketone-body synthesis mechanism
•Ketone bodies—acetoacetate, D-3-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone—are synthesized from acetyl CoA in liver mitochondria and secreted into the blood for use as a fuel by some tissues such as heart muscle.
62
New cards
D-3-Hydroxybutyrate is formed upon the
•reduction of acetoacetate. Acetone is generated by the spontaneous decarboxylation of acetoacetate.
63
New cards
64
New cards
In tissues using ketone bodies, D-3-hydroxybutyrate is oxidized to
acetoacetate, which is ultimately metabolized to two molecules of acetyl CoA.
65
New cards
**Formation of Ketone Bodies**
**.** The ketone bodies—acetoacetate, d-3-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone—are formed from acetyl CoA primarily in the liver. Enzymes catalyzing these reactions are (1) 3-ketothiolase, (2) hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA synthase, (3) hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA cleavage enzyme, and (4) d-3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. Acetoacetate spontaneously decarboxylates to form acetone.
66
New cards
**Utilization of D-3-Hydroxybutyrate and Acetoacetate as a Fuel**
d-3-Hydroxybutyrate is oxidized to acetoacetate with the formation of NADH. Acetoacetate is then converted into two molecules of acetyl CoA, which then enter the citric acid cycle.
67
New cards
Fats are converted into
acetyl CoA, which is then processed by the citric acid cycle
68
New cards
Oxaloacetate, a citric acid cycle intermediate, is a precursor to
Oxaloacetate, a citric acid cycle intermediate, is a precursor to
69
New cards
acetyl CoA derived from fats cannot lead to the net synthesis of oxaloacetate or glucose because
although two carbons enter the cycle when acetyl CoA condenses with oxaloacetate, two carbons are lost as CO2 before oxaloacetate is regenerated.
70
New cards
Why might D-3-hydroxybutyrate be considered a superior ketone body compared with acetoacetate?
71
New cards
Ketone bodies are
moderately strong acids
72
New cards
excess production can lead to
acidosis
73
New cards
An overproduction of ketone bodies can occur when
•diabetes, a condition resulting from a lack of insulin function, is untreated. The resulting acidosis is called diabetic ketosis.
74
New cards
If insulin is absent or not functioning
glucose cannot enter cells. All energy must be derived from fats, leading to the production of acetyl CoA.
75
New cards
fatty acid release from adipose tissue is enhanced in the absence of
insulin function
76
New cards
**How Diabetic Ketosis Results When Insulin is Absent**
In the absence of insulin, fats are released from adipose tissue, and glucose cannot be absorbed by the liver or adipose tissue. The liver degrades the fatty acids by b oxidation but cannot process the acetyl CoA because of a lack of glucose-derived oxaloacetate (OAA). Excess ketone bodies are formed and released into the blood. Abbreviation: CAC, citric acid cycle.
77
New cards
Glucose is the
predominant fuel for the br
78
New cards
During starvation, protein degradation is initially the source of
carbons for gluconeogenesis in the liver. The glucose is then released into the blood for the brain to use.
79
New cards
After several days of fasting
the brain begins to use ketone bodies as a fuel
80
New cards
Ketone body use curtails protein degradation and thus prevents
•tissue failure. Moreover, ketone bodies are synthesized from fats, the largest energy store in the body.
81
New cards
After depletion of triacylglycerols.. what happens
protein degradation accelerates, and death inevitably results from a loss of heart, liver, or kidney function. A person’s survival time is mainly determined by the size of the triacylglycerol depot.
82
New cards
**Fuel Reserves in a Typical 70-kg (154-lb) Man**
Most glycogen is in the muscle
\
Most TAG is in adipose
\
Most proteins in the body reside in muscles
\
Brain stores almost nothing
\
Most TAG is in adipose
\
Most proteins in the body reside in muscles
\
Brain stores almost nothing
83
New cards
**Fuel choice during starvation**
The plasma levels of fatty acids and ketone bodies increase in starvation, whereas that of glucose decreases.
\
A week out, ketone bodies are being used for the majority of energy needs in the body.
\
A week out, ketone bodies are being used for the majority of energy needs in the body.
84
New cards
Saturated and trans unsaturated fatty acids are synthesized commercially to enhance
the shelf life and heat stability of fats for food preparation
85
New cards
Studies suggest that excess consumption of these fats promote
obesity, atherosclerosis, and type 2 diabetes
86
New cards
The first stage of fatty acid synthesis is
transfer of acetyl CoA out of the mitochondria into the cytoplasm. Citrate is transported into the cytoplasm and cleaved into oxaloacetate and acetyl CoA
87
New cards
The second stage of **Fatty Acid Synthesis is**
1\.the activation of acetyl CoA to form malonyl CoA.
88
New cards
The third stage of fatty acid synthesis is
the repetitive addition and reduction of two carbon units to synthesize C16 fatty acid. Synthesis occurs on an acyl carrier protein, a molecular scaffold
89
New cards
Citrate, synthesized in the mitochondria, is transported to the
cytoplasm and cleaved by **ATP-citrate lyase** to generate acetyl CoA for fatty acid synthesis
90
New cards
Fatty acid synthesis requires
reducing power in the form of **NADPH**
91
New cards
Some NADPH can be formed from the
oxidation of oxaloacetate, generated by ATP-citrate lyase, by the combined action of cytoplasmic **malate dehydrogenase** and **malic enzyme**.
92
New cards
**Malate dehydrogenase reaction**
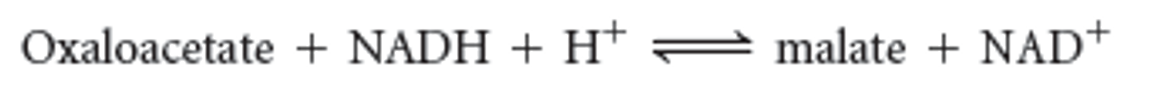
93
New cards
**Malic enzyme reaction**
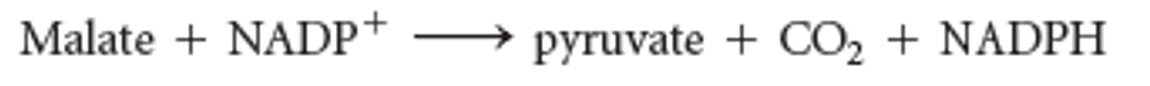
94
New cards
Pyruvate formed by malic enzyme enters the mitochondria where it is converted into
oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase.
95
New cards
The sum of the reactions catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase, malic enzyme, and pyruvate carboxylase is:
The sum of the reactions catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase, malic enzyme, and pyruvate carboxylase is
96
New cards
**Additional NADPH is synthesized by**
**the pentose phosphate pathway**
97
New cards
**Malonyl CoA** is synthesized from acetyl CoA by
**acetyl CoA carboxylase 1**, a biotin-requiring enzyme
98
New cards
The formation of malonyl CoA occurs in two steps
99
New cards
Fatty acid synthase, a complex of enzymes, catalyzes
the formation of fatty acids.
100
New cards
Fatty acid synthesis occurs on
the **acyl carrier protein** (ACP), a polypeptide with structure similar to CoA. Intermediates are linked to the sulfhydryl group of the **phosphopantetheine** group attached to ACP.