HA Lab Quiz 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/171
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:49 PM on 1/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
1
New cards
anatomical position
To stand erect with arms at the sides and palms of the hands turned forward
2
New cards
Anterior (ventral)
**front** of the body
3
New cards
Posterior (dorsal)
**back** of body
4
New cards
Superior (cranial)
**toward** the head
5
New cards
Inferior (caudal)
**away** from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below
6
New cards
Proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
7
New cards
Distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
8
New cards
Medial
**toward** the midline
9
New cards
Lateral
**away** from the midline
10
New cards
superficial
near the surface
11
New cards
deep
Away from the body surface; more internal
12
New cards
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
13
New cards
midsagittal plane
divides the body into **equal** left and right halves
14
New cards
parasagittal plane
Divides body into **unequal** right and left sides
15
New cards
frontal plane
Divides the body into front and back portions.
16
New cards
transverse plane
divides the body into superior and inferior parts
17
New cards
oblique plane
passes through the body at an **angle**
18
New cards
Dorsal (posterior) cavity contains:
cranial cavity (brain) and spinal cavity (spinal cord)
19
New cards
Ventral (anterior) cavity contains:
contains thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
20
New cards
thoracic cavity
contains the pleural cavity (left/right lungs), mediastinum cavity (the space between the lungs), and the pericardial cavity (heart).
21
New cards
pleural cavities
contains the (left/right) lungs
22
New cards
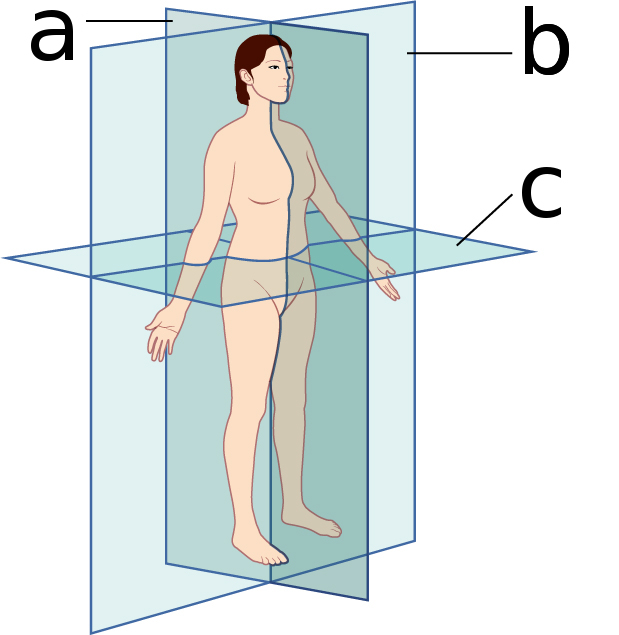
what body plane is ‘a’?
sagittal
23
New cards
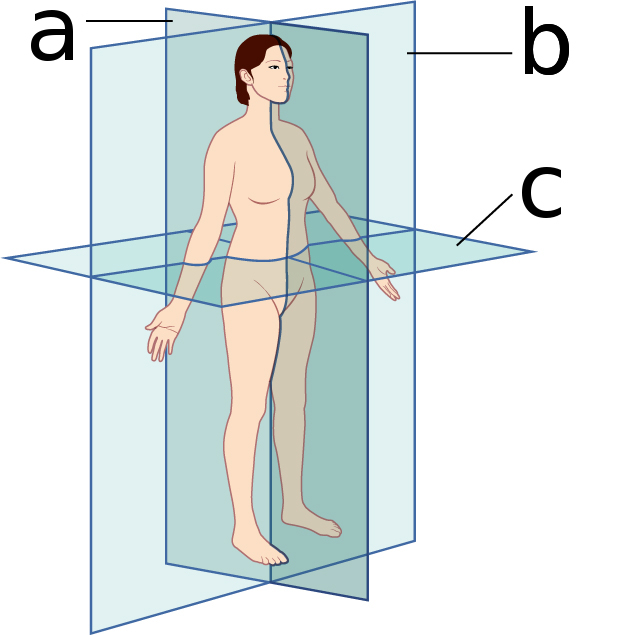
what body plane is ‘b’?
frontal
24
New cards
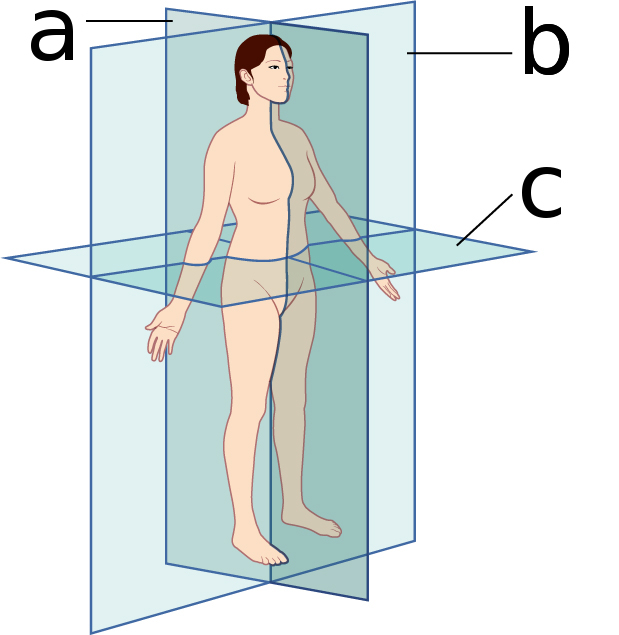
what body plane is ‘c’?
transverse
25
New cards
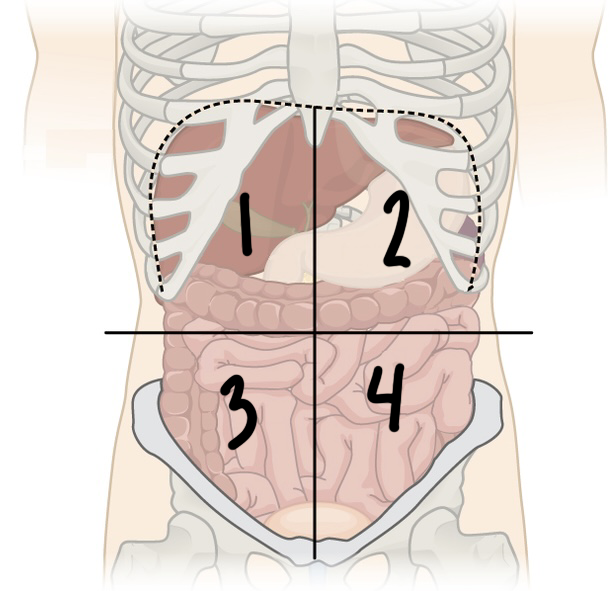
what is ‘1’
RUQ or right upper quadrant
26
New cards
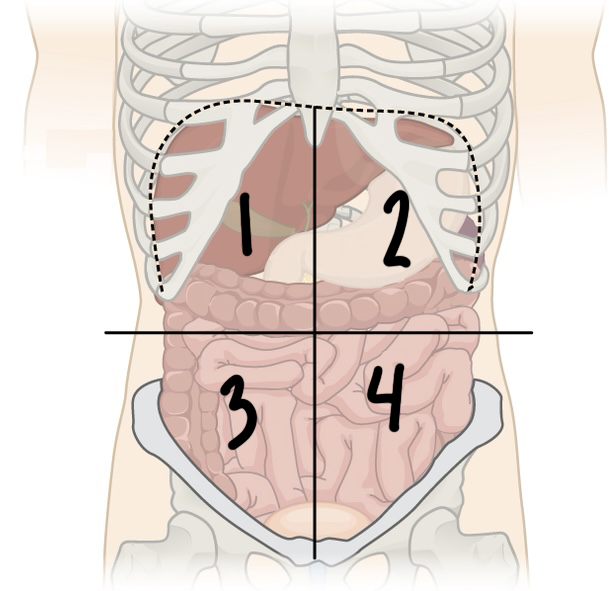
what is ‘4’
LLQ or left lower quadrant
27
New cards
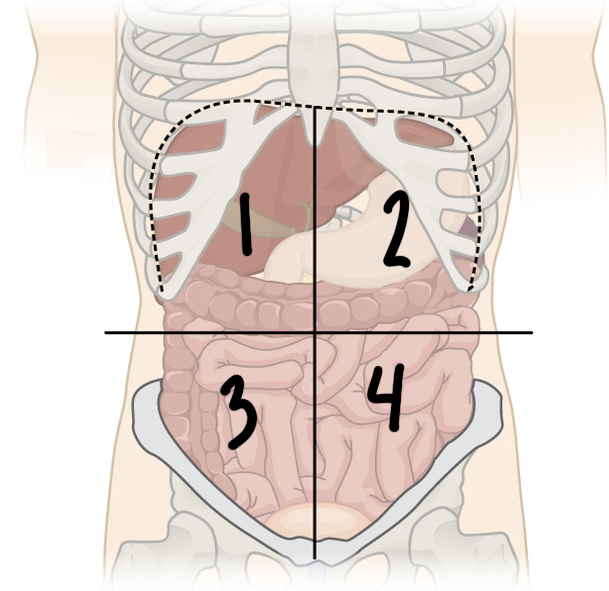
what is ‘3’
RLQ or right lower quadrant
28
New cards
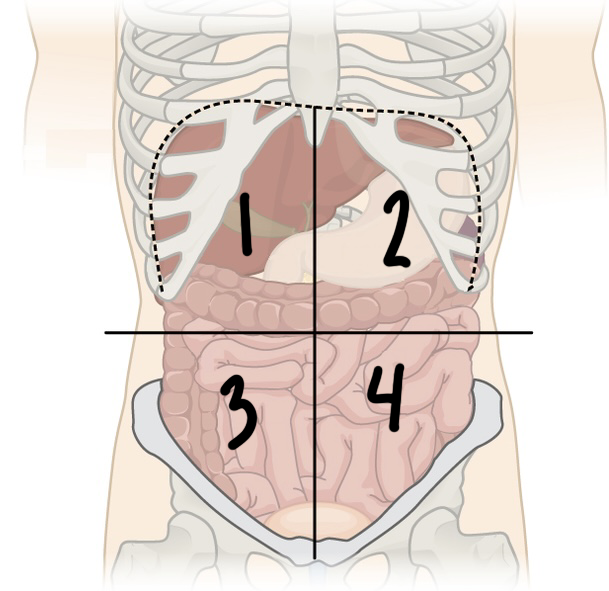
what is ‘2’
LUQ or left upper quadrant
29
New cards
is this a abdominopelvic quadrant or region?
abdominopelvic quadrant
30
New cards

is this a abdominopelvic quadrant or region?
abdominopelvic region
31
New cards
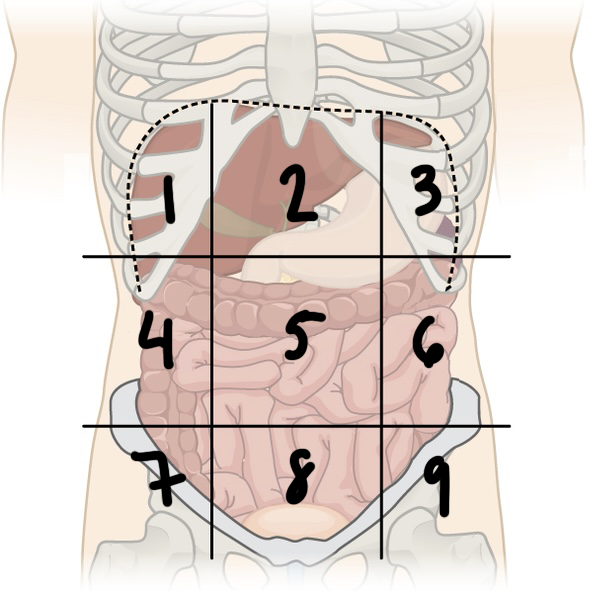
what is ‘2’
epigastric region
32
New cards
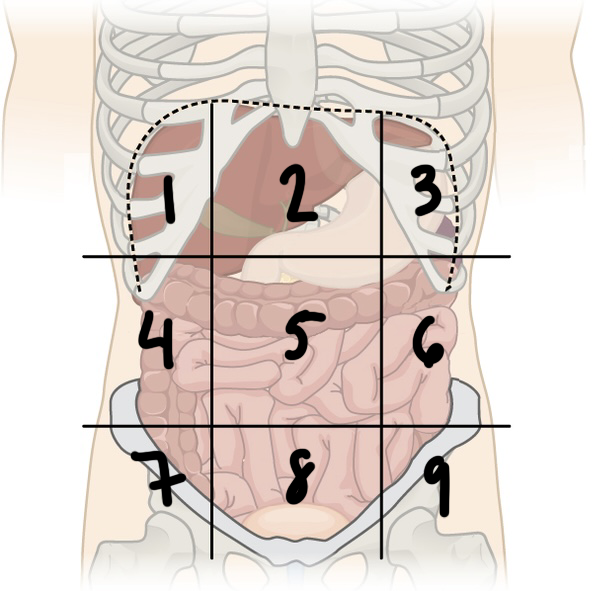
what is ‘1’
right hypochondriac region
33
New cards
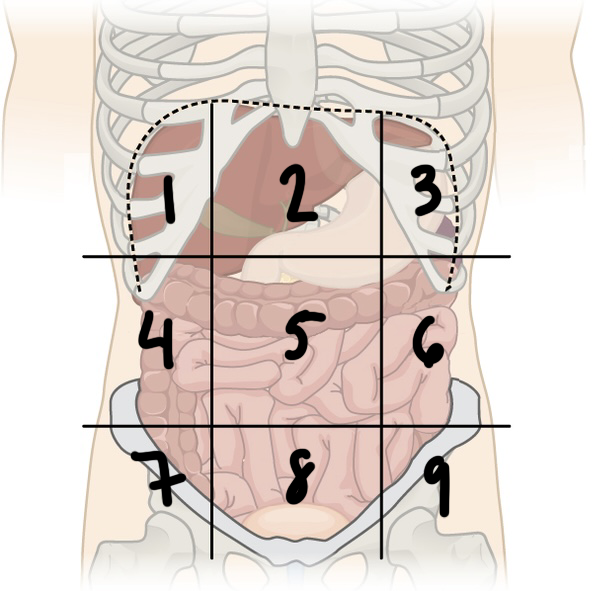
what is ‘3’
left hypochondriac region
34
New cards
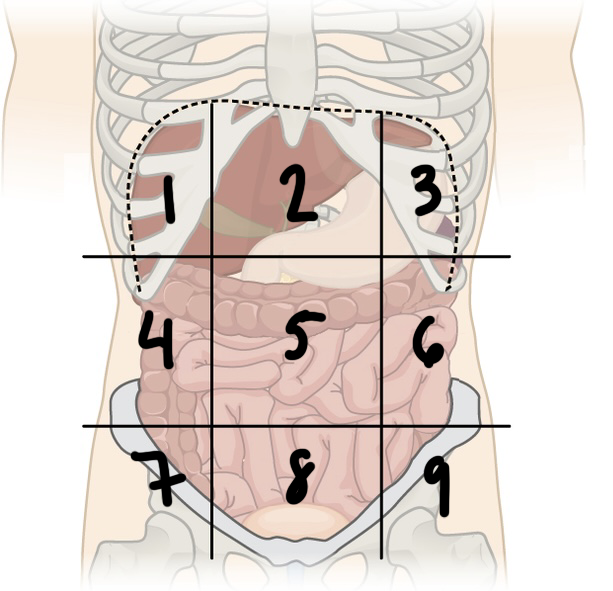
what is ‘5’
Umbilical region
35
New cards
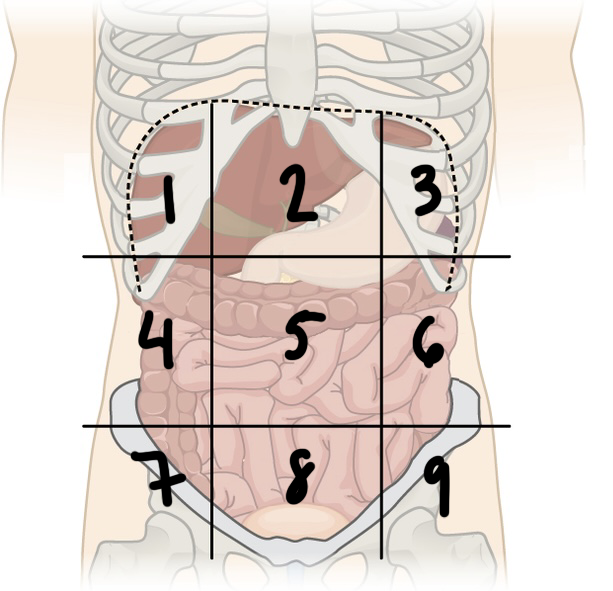
what is ‘6’
left lumbar region
36
New cards
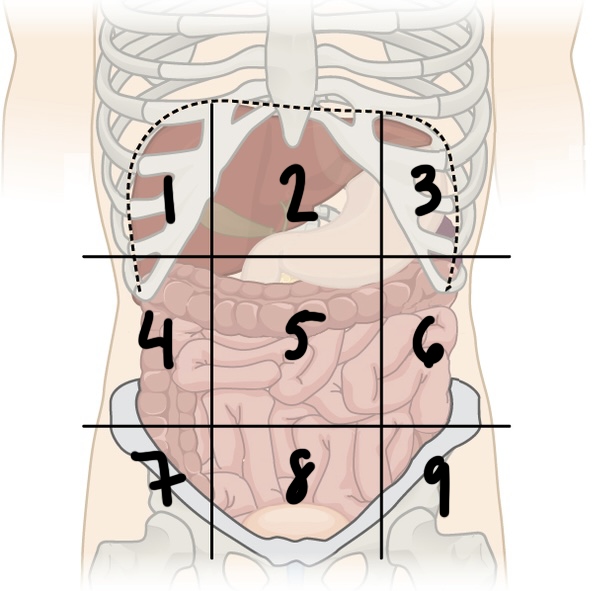
what is ‘4’
right lumbar region
37
New cards
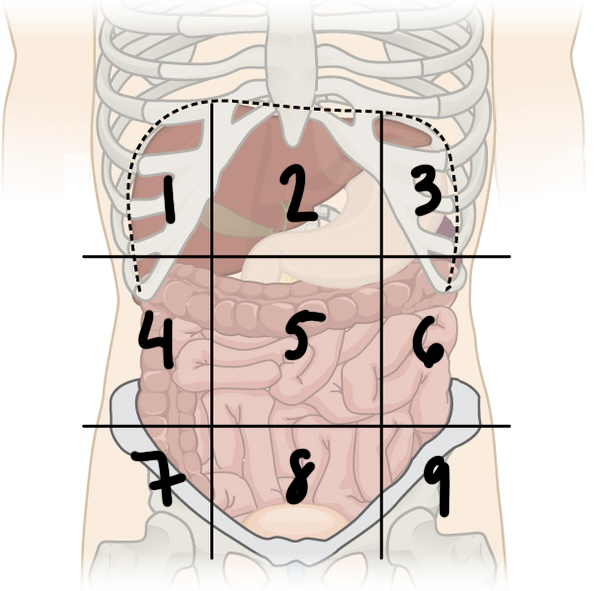
what is ‘9’
left iliac region
38
New cards
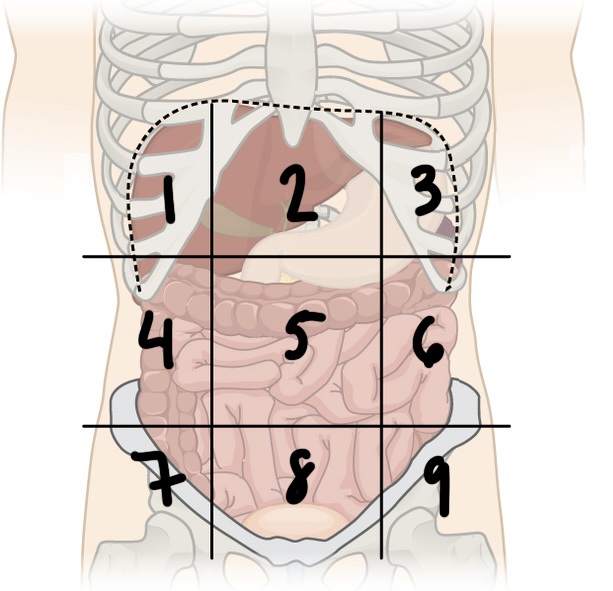
what is ‘8’
hypogastric region
39
New cards
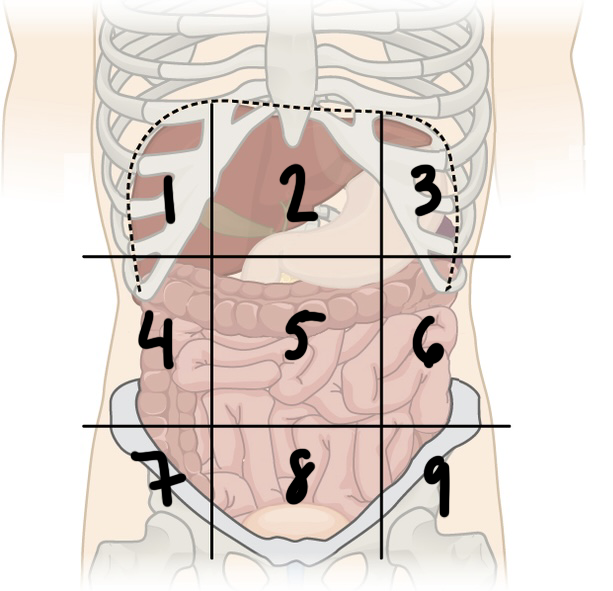
what is ‘7’
right iliac region
40
New cards
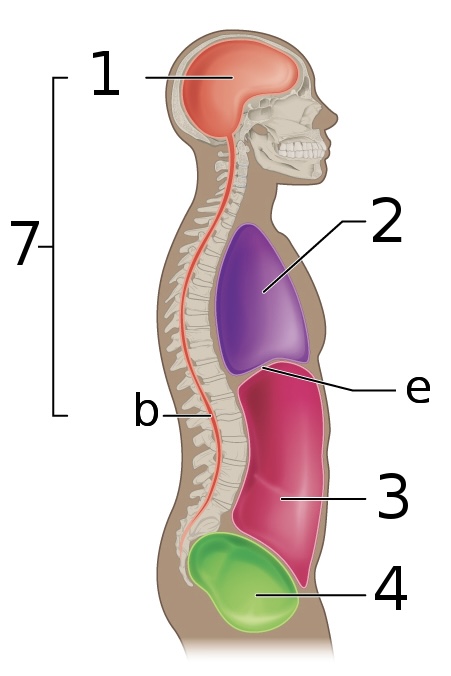
what is ‘2’ (has 3 cavities)
thoracic cavity
41
New cards
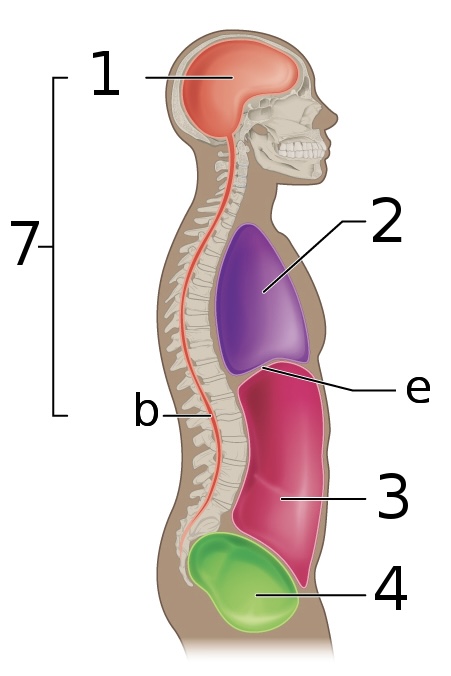
what is ‘e’
Diaphragm
42
New cards
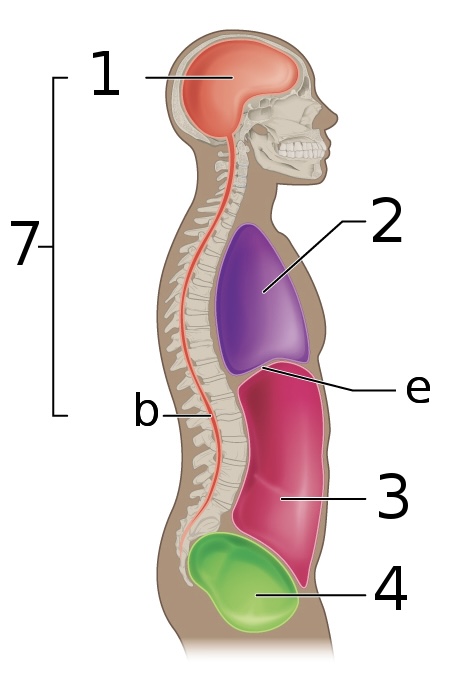
what is ‘7’
dorsal cavity
43
New cards
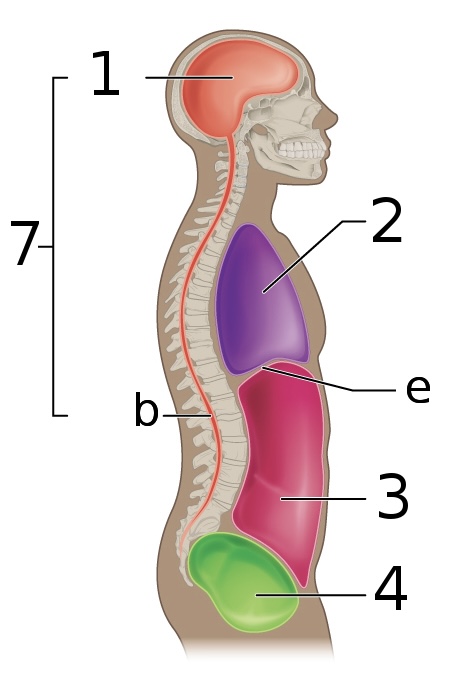
what is ‘1’
Cranial cavity
44
New cards
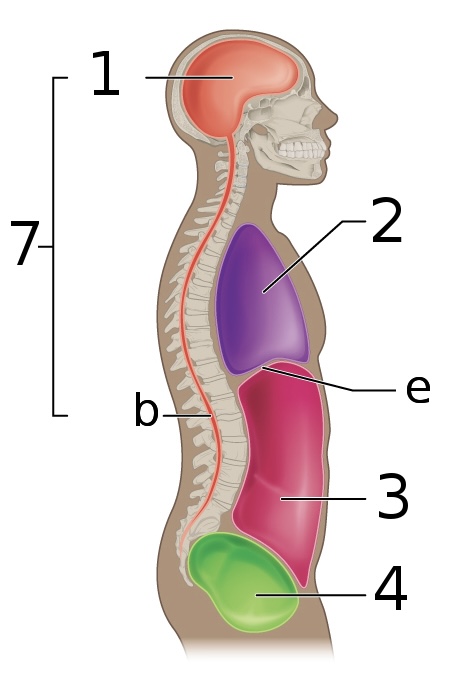
what is ‘3’
Abdominal cavity
45
New cards
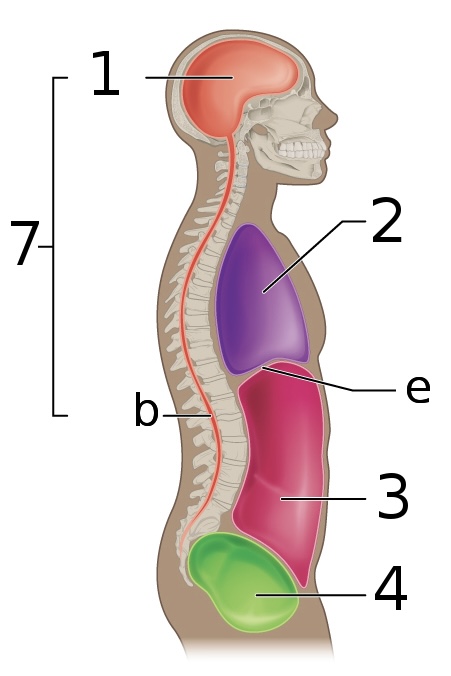
what is ‘b’
spinal cavity
46
New cards
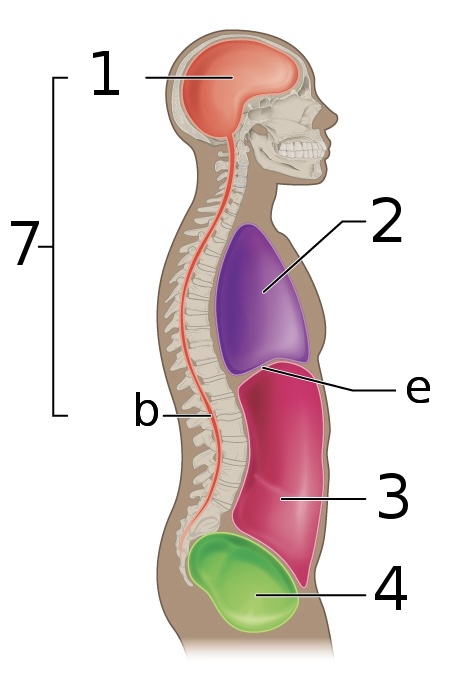
what is ‘4’
pelvic cavity
47
New cards
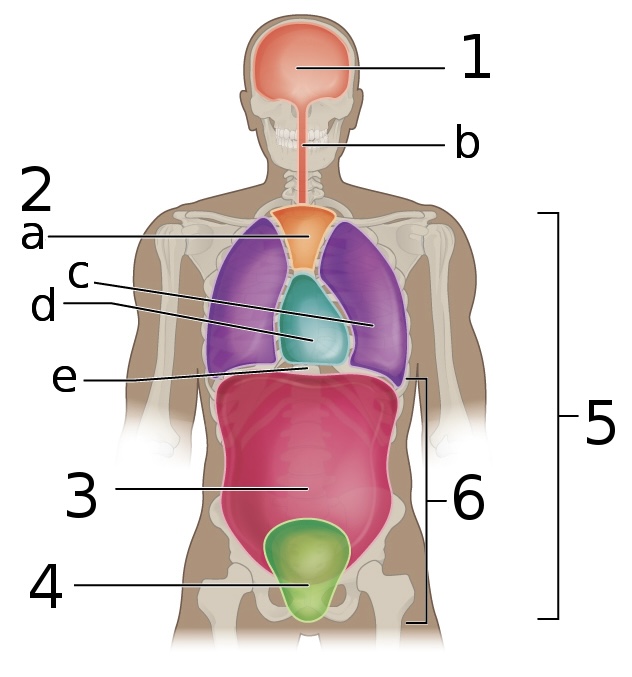
what is ‘1’
Cranial cavity
48
New cards
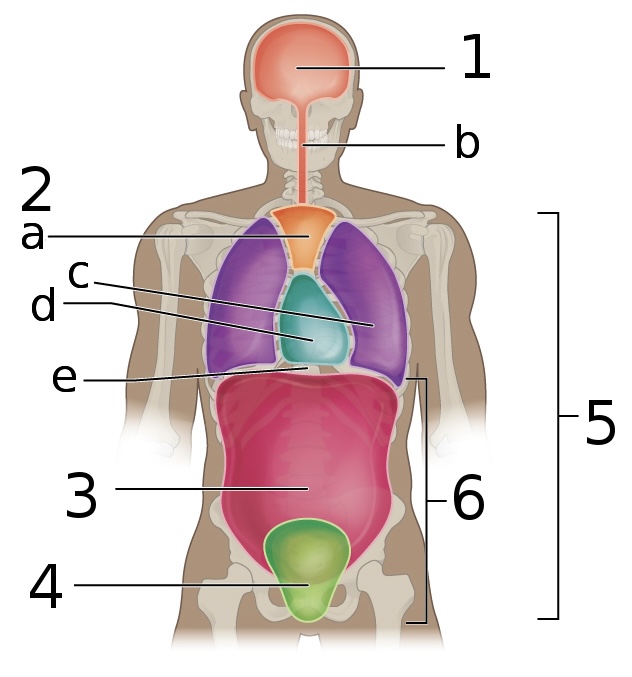
what is ‘a’
Mediastinum
49
New cards
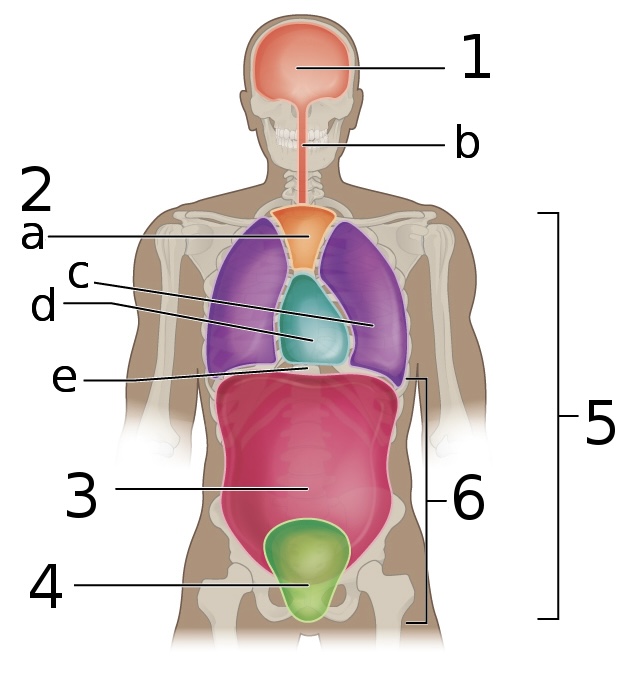
what is ‘c’
pleural cavity
50
New cards
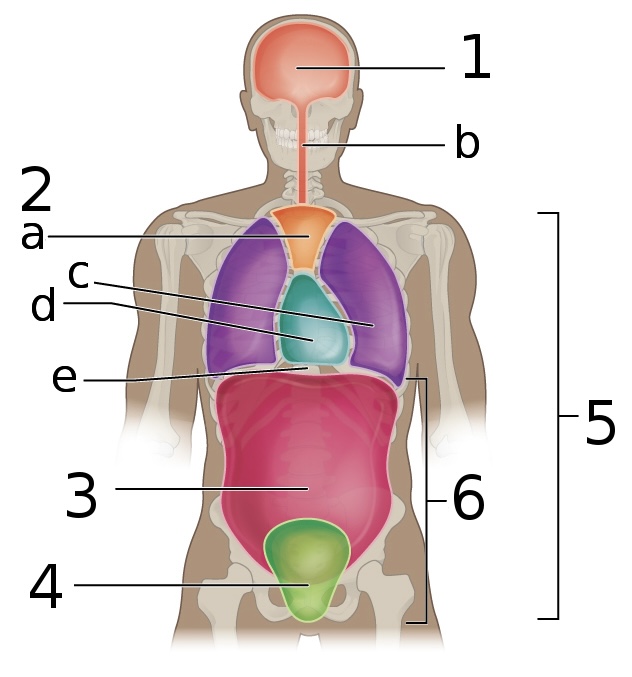
what is ‘d’
Pericardial cavity
51
New cards
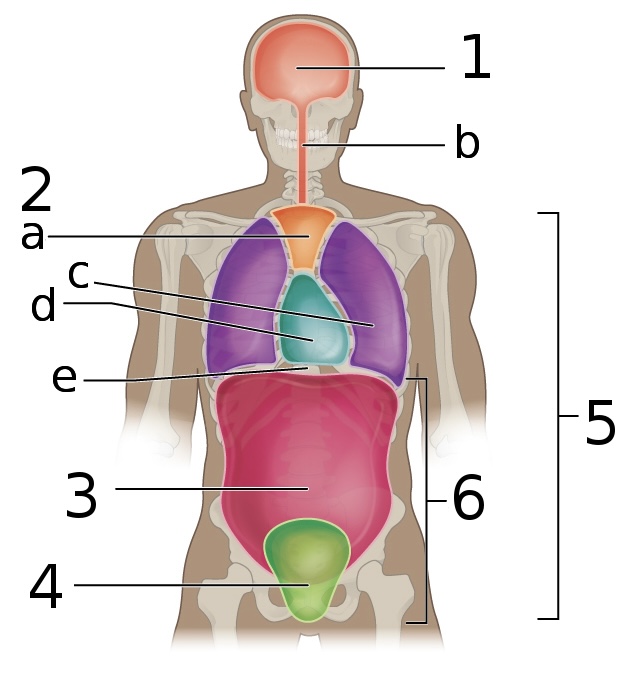
what is ‘5’
ventral cavity
52
New cards
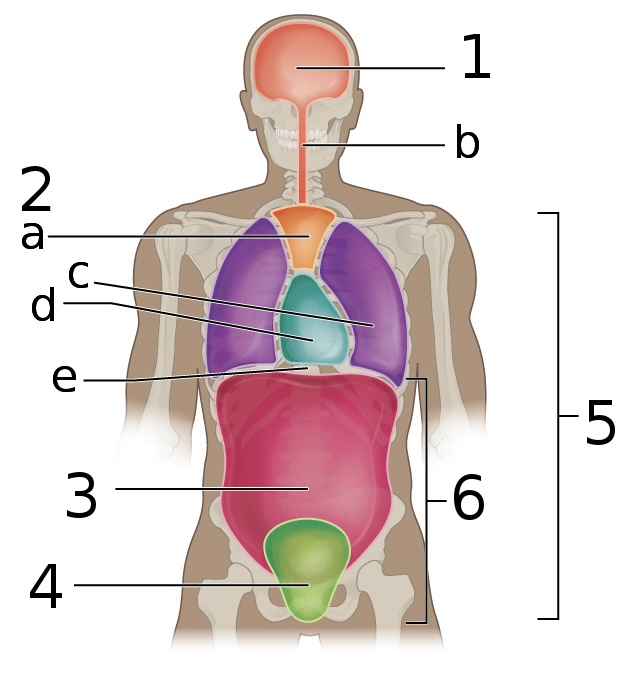
what is ‘6’
Abdominopelvic cavity
53
New cards
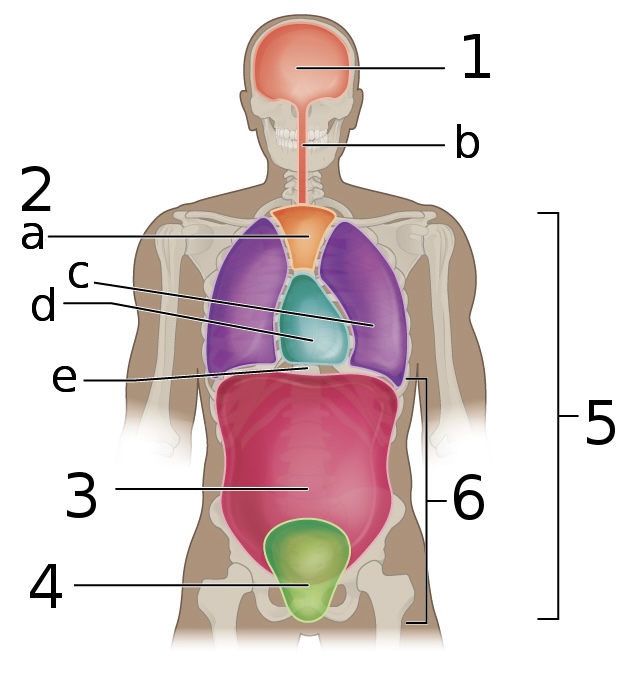
what is e’
Diaphragm
54
New cards
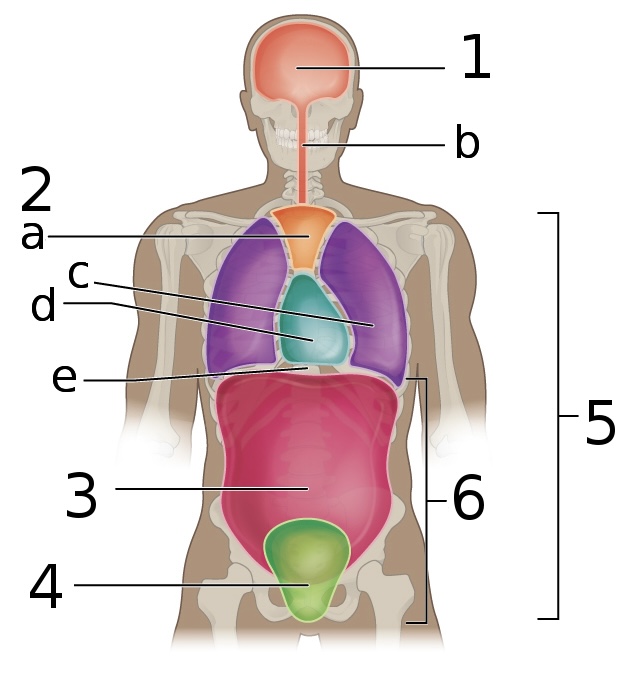
what is ‘3’
Abdominal cavity
55
New cards
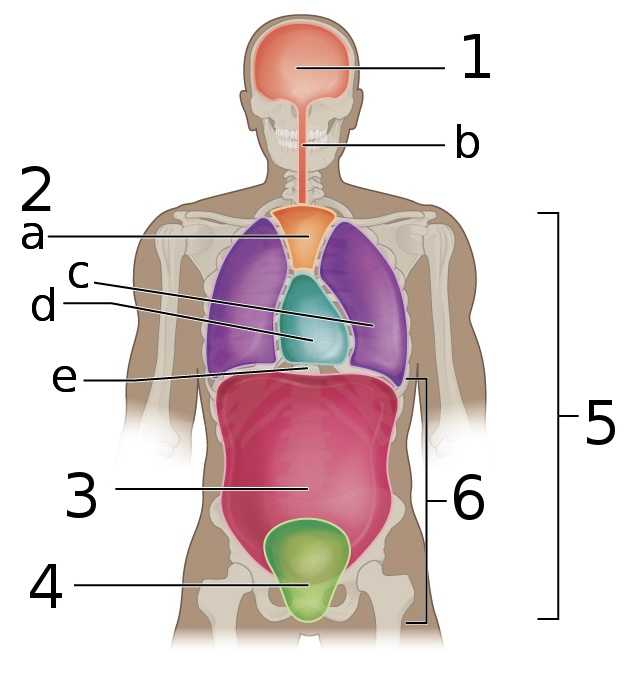
what is ‘4’
Pelvic cavity
56
New cards
Eyepiece (microscope)
Where you look into the microscope
57
New cards
Body Tube (microscope)
Where light passes from the objective lens to the eyepiece
58
New cards
arm (microscope)
Used to carry microscope
59
New cards
nosepiece(microscope) function
holds the objective lenses, it rotates
60
New cards
objective lens function
There may be two or three of these mounted on the nosepiece. Each one magnifies at a different power.
61
New cards
stage (microscope) function
supports the slide being viewed
62
New cards
stage clips function
Two pieces of metal that keep the slide from moving
63
New cards
Lamp (microscope) function
provides light so that it is easier to see the object that you are viewing
64
New cards
diaphragm (microscope) function
controls the amount of light that passes through
65
New cards
base (microscope) function
support for the microscope
66
New cards
Coarse adjustment function
begin focusing with this part of the microscope, It moves the stage up and down, NEVER USE on high power
67
New cards
Fine adjustment function
use this to make the object appear clearer
68
New cards
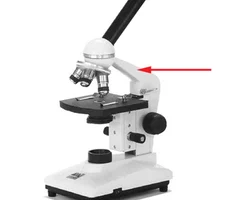
what apart of the microscope is this
arm
69
New cards
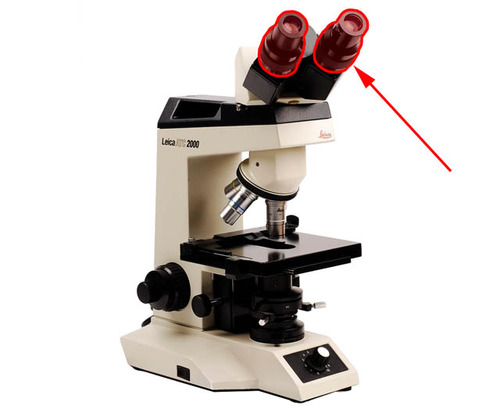
what apart of the microscope is this
eyepiece
70
New cards
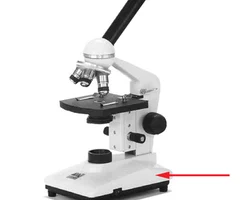
what apart of the microscope is this
base
71
New cards

what apart of the microscope is this
rotating nosepiece
72
New cards
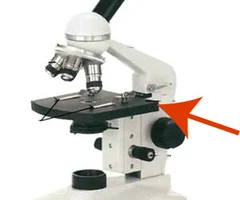
what apart of the microscope is this
stage
73
New cards
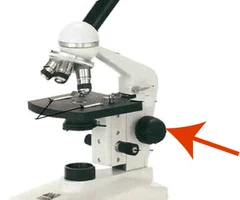
what apart of the microscope is this
coarse adjustment knob
74
New cards
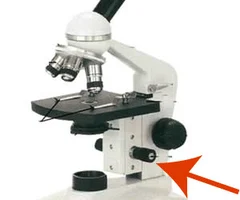
what apart of the microscope is this
fine adjustment knob
75
New cards
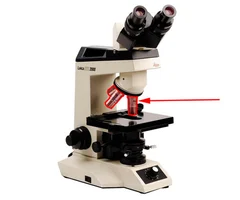
what apart of the microscope is this
objective lens
76
New cards

what apart of the microscope is this
stage clip
77
New cards

what apart of the microscope is this
body tube
78
New cards
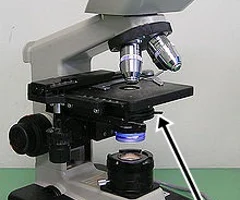
what apart of the microscope is this
Diaphragm
79
New cards
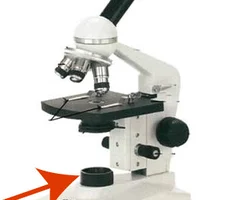
what apart of the microscope is this
lamp
80
New cards
how many ‘N’ or chromosomes does a human have
2N or 46
81
New cards
cardiovascular system function
transports nutrients, chemical messengers, gases and wastes in blood
82
New cards
respiratory system function
adds oxygen to the blood and removes carbon dioxide from blood.
83
New cards
digestive system function
breaks down food into units that can be absorbed by the body
84
New cards
urinary system function
removes wastes, maintains body fluid volume, pH and electrolyte levels.
85
New cards
integumentary system function
provides a protective barrier for the body, contains sensory receptors for pain, touch, temperature
86
New cards
lymphatic system function
returns fluid to cardiovascular system, detects, filters, and eliminates disease causing organisms.
87
New cards
skeletal system function
protects major organs, provides levers and support for body movement
88
New cards
muscular system function
moves bones and maintains posture
89
New cards
nervous system function
controls cell function with electrical signals
90
New cards
endocrine system function
controls cell function with hormones
91
New cards
reproductive system function
produces gametes, female organs provide environment for development of fetus
92
New cards
lungs function
Main organs of the respiratory system that filters air
93
New cards
Trachea function
Allows air to pass to and from lungs apart of the respiratory system
94
New cards
thyroid gland function
endocrine gland that surrounds the trachea in the neck
95
New cards
Testes function
produce sperm
96
New cards
Vagina function
Female organ of intercourse; birth canal
97
New cards
heart function
A hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
98
New cards
spleen function
Organ near the stomach that produces, stores, and eliminates blood cells
99
New cards
stomach function
A muscular and elastic sac that serves mainly to store food, break it up mechanically, and begin chemical digestion of proteins and fat.
100
New cards
large intestine function
The last section of the digestive system, where water is absorbed from food and the remaining material is eliminated from the body