Atoms, Molecules, and Life: Key Concepts in Biology and Chemistry
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What is the basic unit of all forms of matter?
The atom
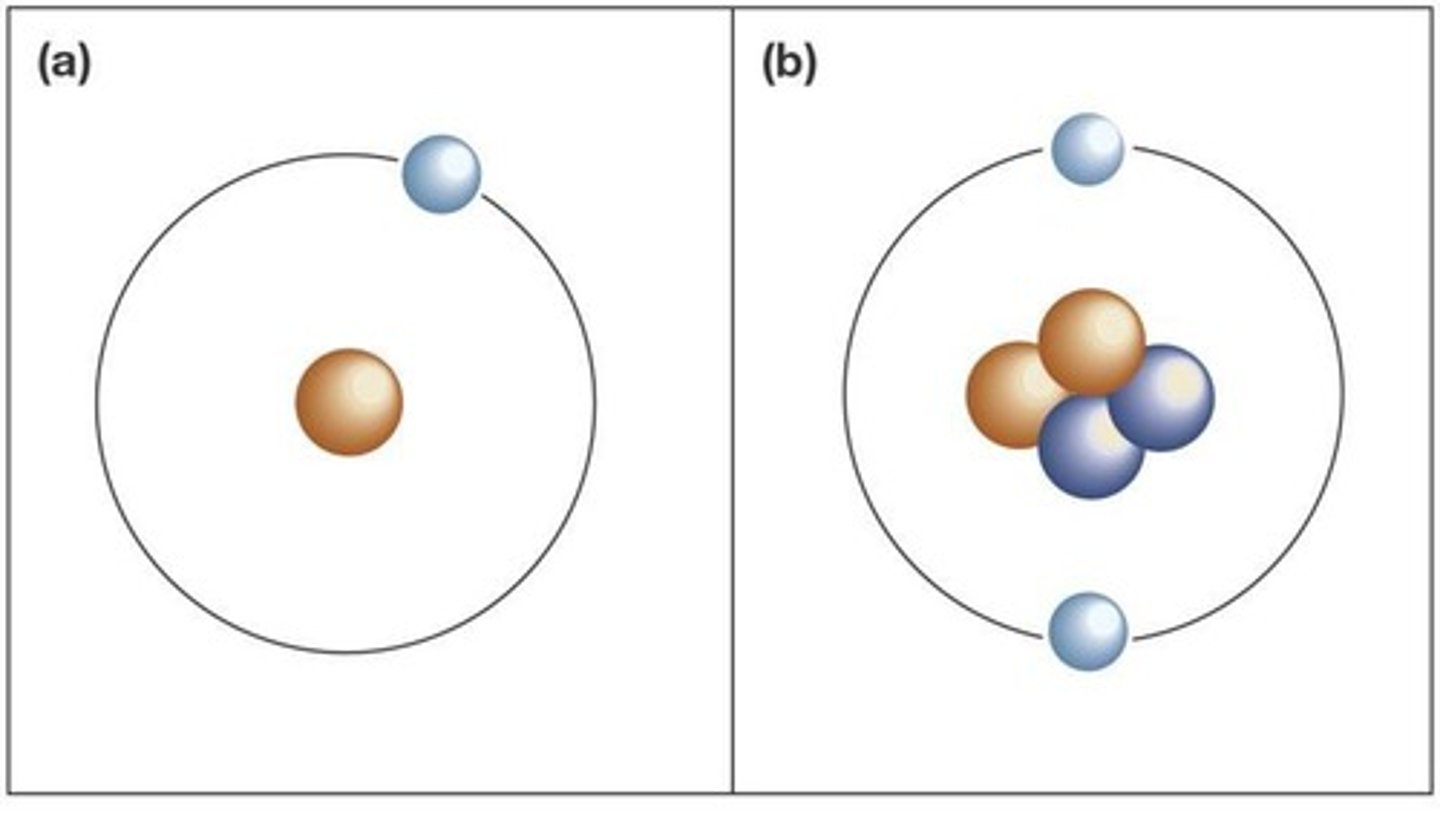
What are the three most stable subatomic particles?
Neutrons, protons, and electrons
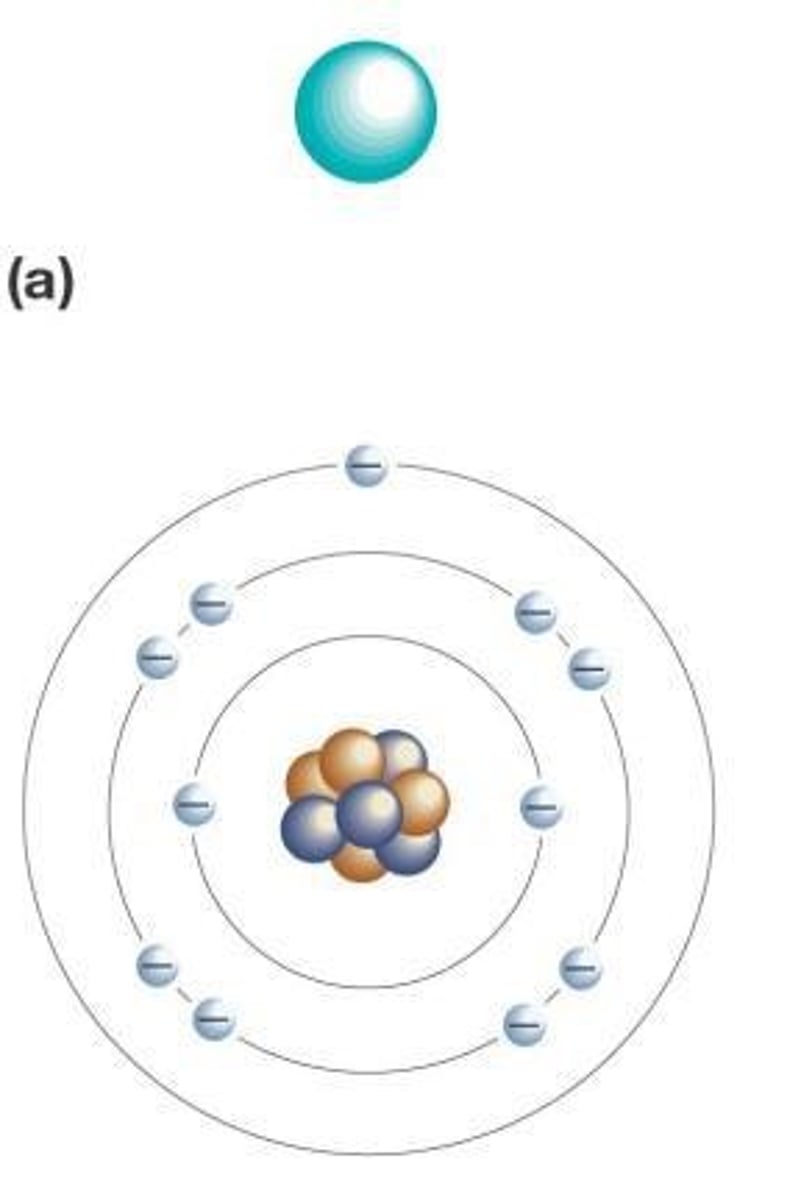
Where are protons located in an atom?
At the core, or nucleus, of the atom
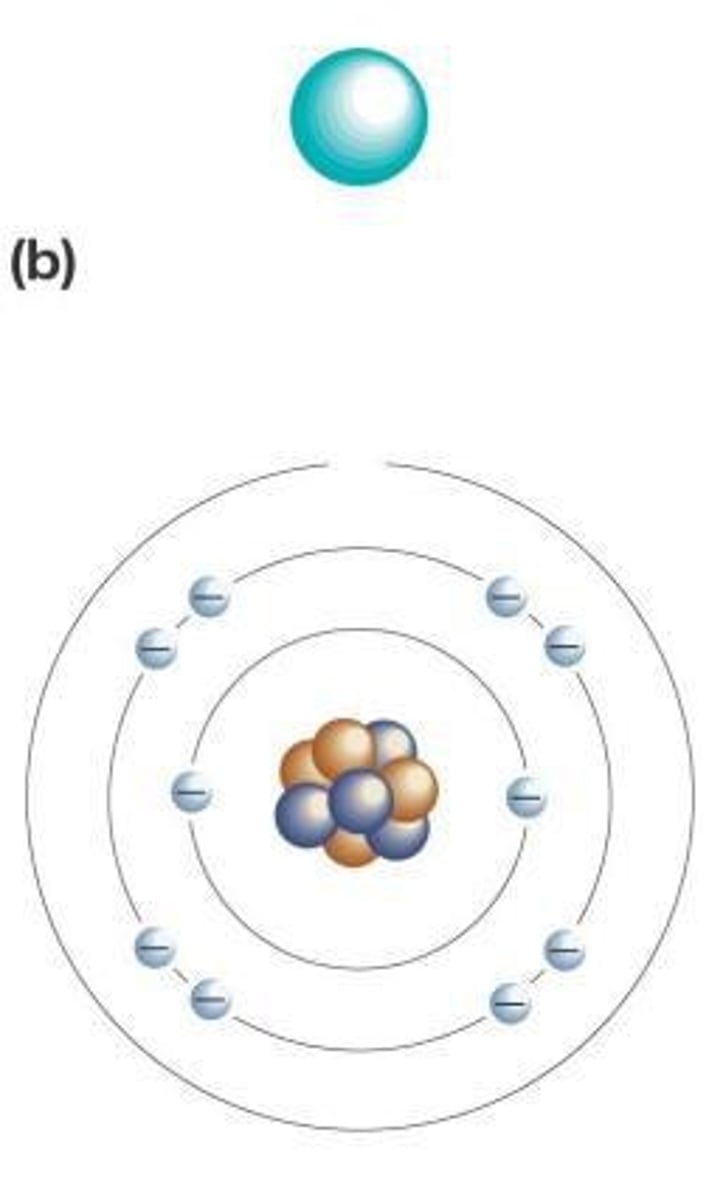
What charge do electrons carry?
Negatively charged
What is an element?
A substance that can't be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions
What is the atomic mass of an element?
The number of protons plus the number of neutrons
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element which have different atomic weights
What determines the chemical behavior of an atom?
The number of electrons in the outermost electron shell
What is a reactive atom likely to do?
Try to fill the valence shell by interacting with other atoms
What is a chemical bond?
An attraction that holds two atoms together
What is a molecule?
Two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
What is an ion?
A charged atom or molecule, which has either lost or gained electrons
What is a cation?
A positively charged atom or molecule that has lost an electron
What is an anion?
A negatively charged atom or molecule that has gained an electron
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, while covalent bonds involve sharing pairs of electrons
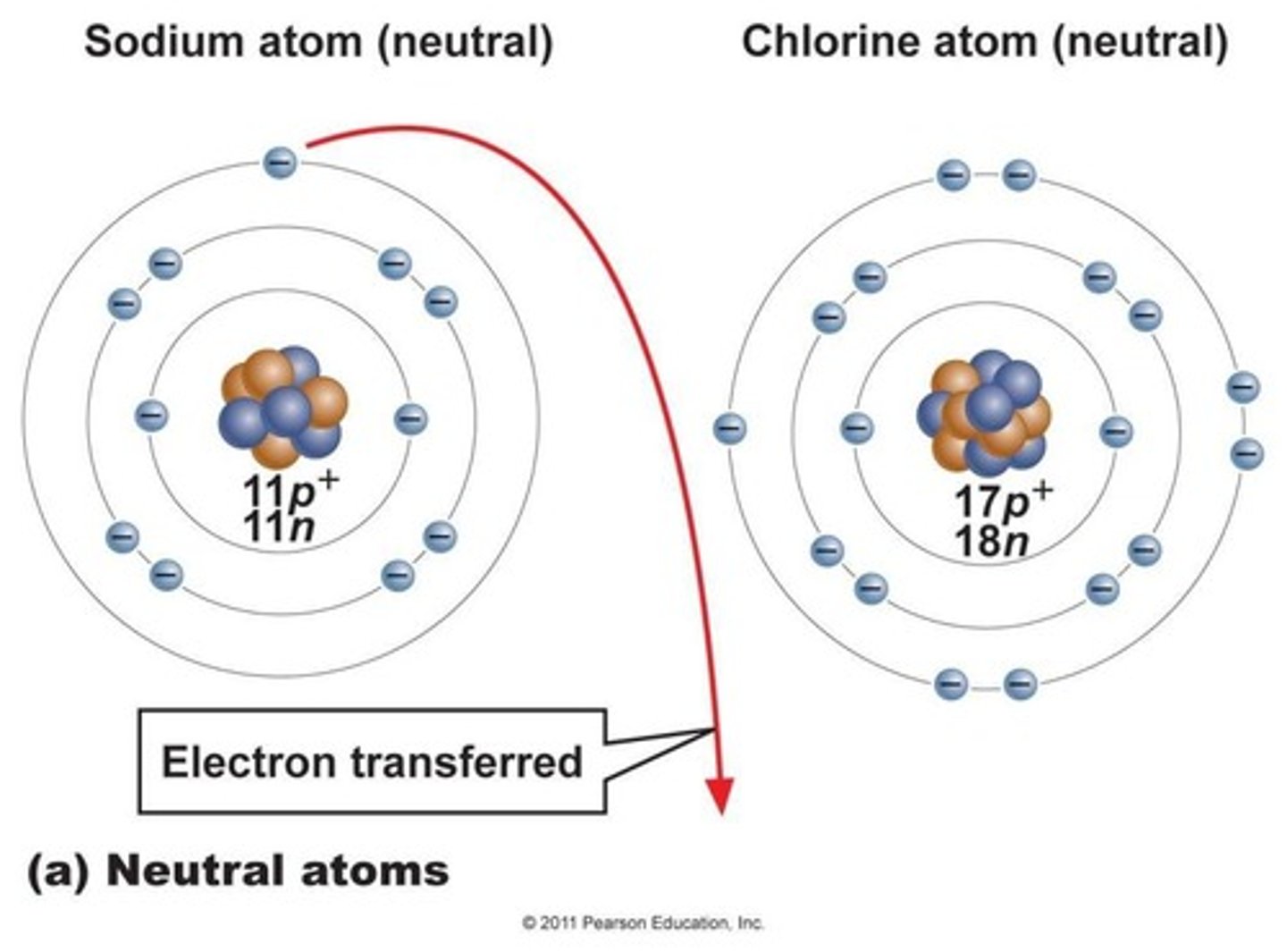
What is a nonpolar covalent bond?
A covalent bond in which the sharing of the electron pair is equal
What is a polar covalent bond?
A covalent bond in which the sharing of the electron pair is unequal
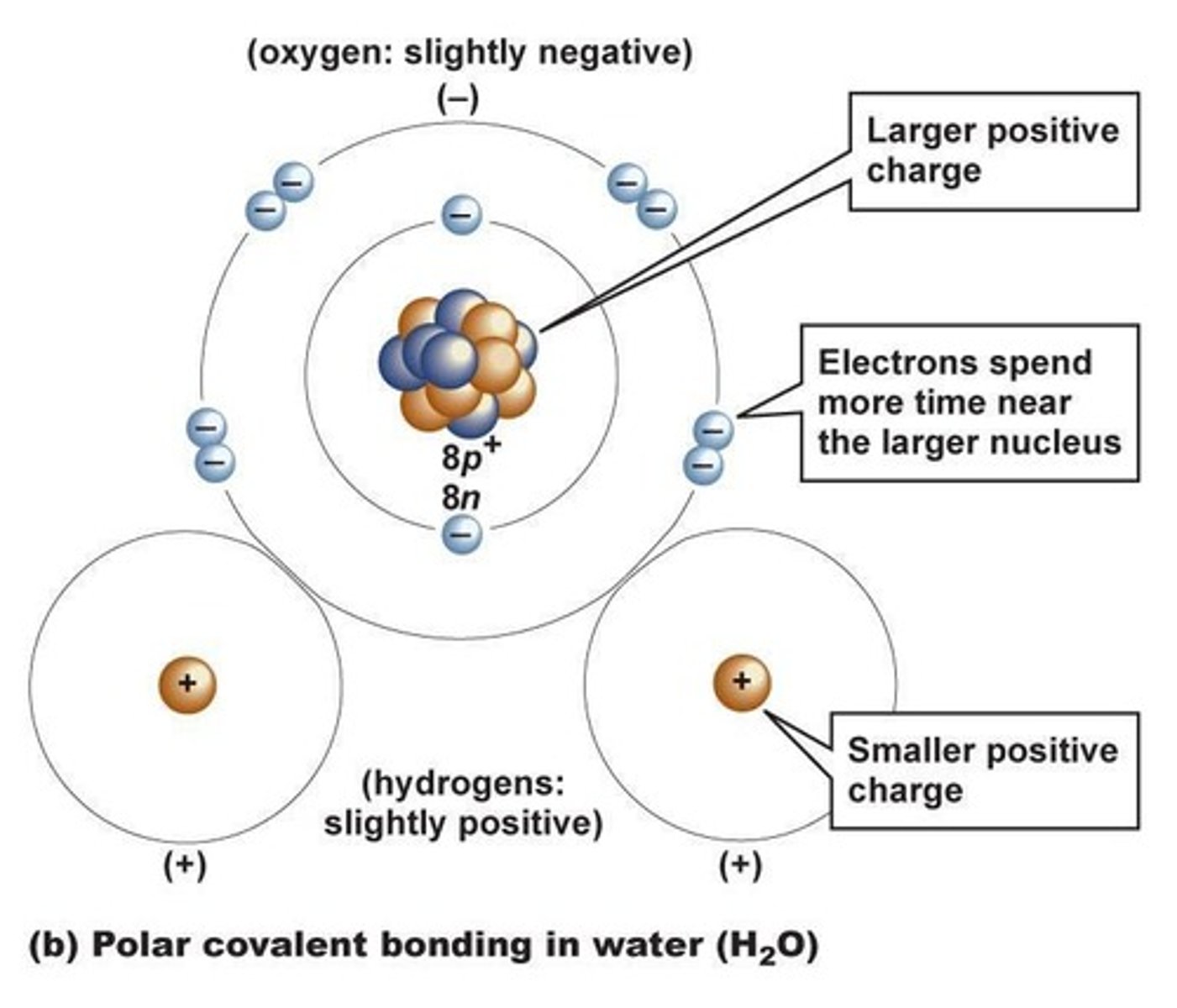
What is electronegativity?
An atom's ability to attract and hold electrons
What is a hydrogen bond?
A bond formed by the charge attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one atom and attracted to a second atom
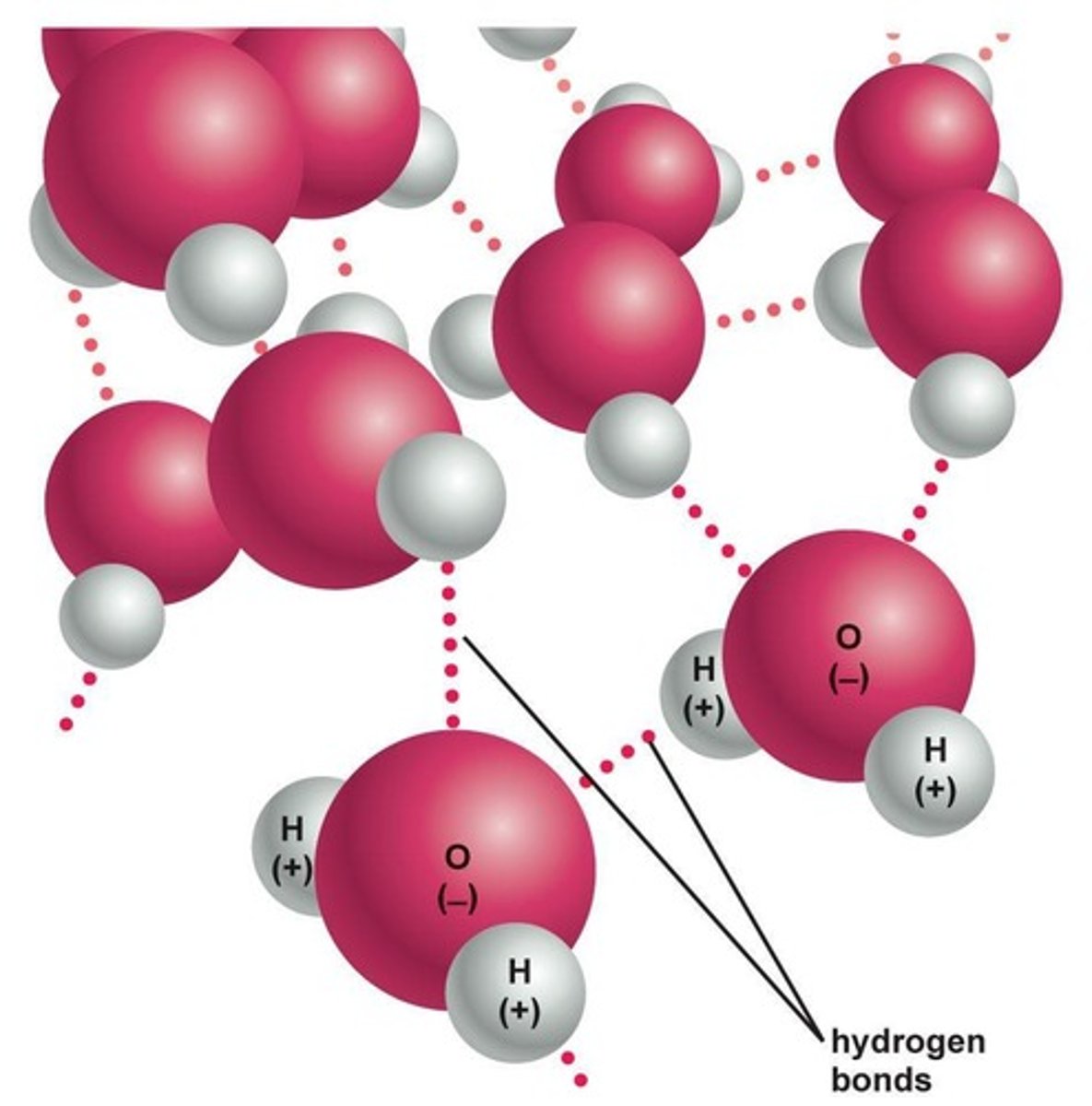
What percentage of cells is water?
70-95%
What bonds hold the atoms of a single water molecule together?
Covalent bonds
What type of bond forms between water molecules?
Polar covalent bonds
What property describes substances that have an affinity for water?
Hydrophilic
What is the term for substances that do not have an affinity for water?
Hydrophobic
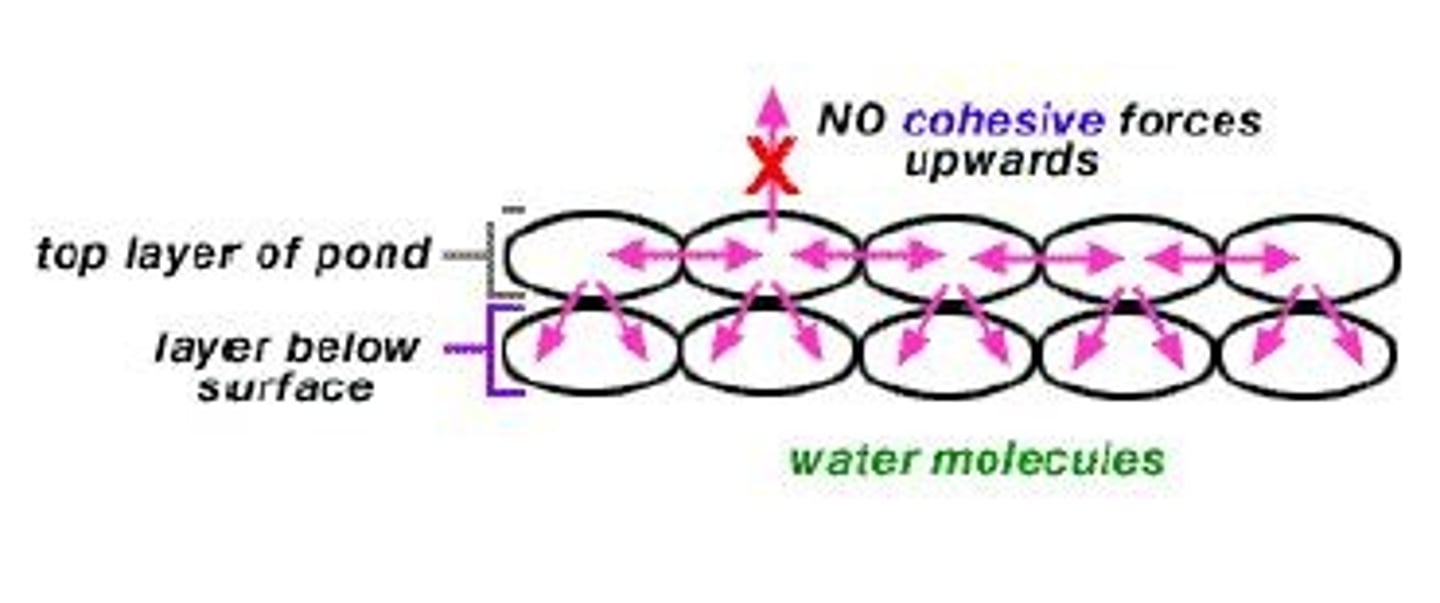
What is cohesion in relation to water?
Attraction between like molecules, resulting in surface tension.
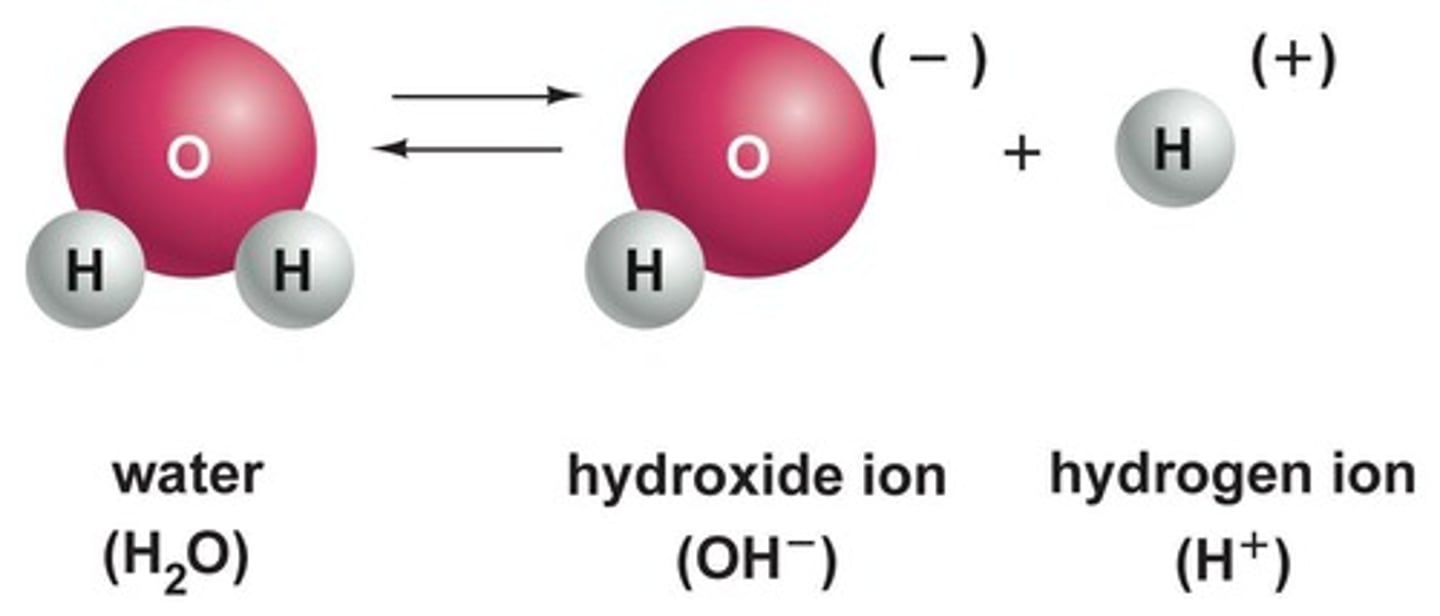
What happens to water molecules when they dissociate?
They form hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-).
What is the pH of a neutral solution?
pH = 7
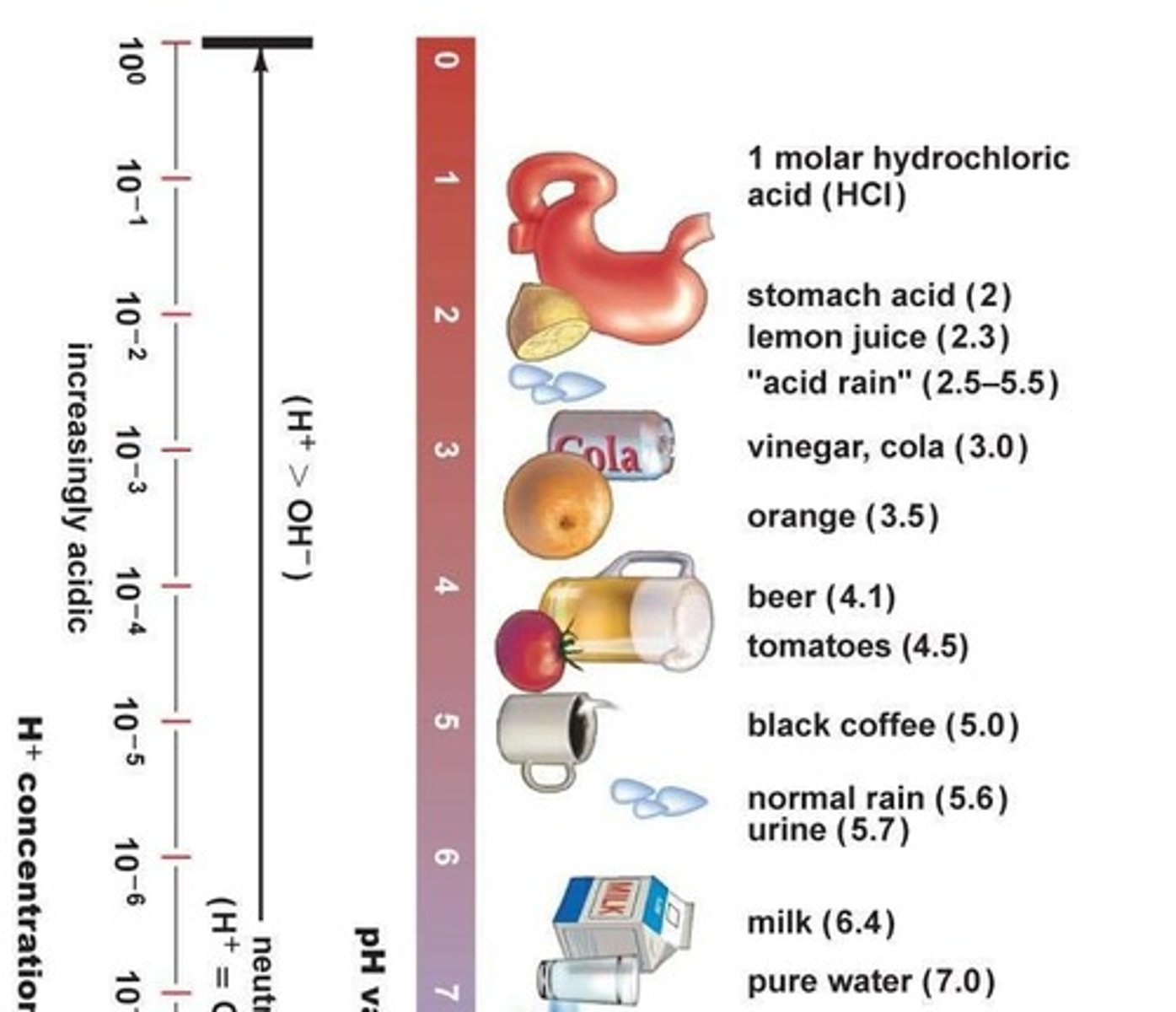
What defines an acidic solution in terms of H+ and OH- ions?
H+ ions are greater than OH- ions.
What defines a basic solution in terms of H+ and OH- ions?
OH- ions are greater than H+ ions.
What is the role of buffers in biological systems?
Buffers prevent large, sudden changes in pH.
What is specific heat?
The amount of energy required to change the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius.
What is the specific heat of water?
1 calorie/gram
What is the heat of vaporization?
The quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 gram to be converted to gas.
What happens to the temperature of water when it evaporates?
The average temperature of the remaining liquid decreases.
Why does ice float on water?
Ice is less dense than liquid water.
What are the three properties of water that help keep temperature stable?
High specific heat, high heat of vaporization, and high heat of fusion.
What is the effect of hydrogen bonding on the formation of hydrogen ions in pure water?
Hydrogen bonding reduces the formation of hydrogen ions.
What is the significance of the pH scale being logarithmic?
A change of one pH unit represents a tenfold change in the concentration of H+.
What is the heat of fusion?
The amount of heat required to convert a solid into a liquid at its melting point.
What is the definition of an acid?
A substance that donates protons (H+) in a solution.
What is the definition of a base?
A substance that accepts protons (H+) in a solution.
What is hydrophobic interaction?
The tendency of nonpolar substances to clump together in water.
What is the effect of temperature changes on living organisms?
Water helps moderate the effects of temperature changes.
What is biology?
The science of living organisms and life processes.
Define life according to the Student Dictionary of Biology.
An evanescent phenomenon dependent for its continued existence on cyclic enzymatic reactions in an environment consisting principally of protein and water.
What are the characteristics of life?
1. Complex, organized structure 2. Response to stimuli 3. Homeostasis 4. Ability to acquire material and energy 5. Growth 6. Reproduction 7. Ability to evolve.
What does 'homeostasis' refer to in living organisms?
The ability to maintain structure and regulate the internal environment.
What is metabolism?
The sum total of all chemical reactions that occur within an organism.
What is an emergent property? Give an example.
A property that emerges from the interaction of components, e.g., NaCl (sodium chloride) is formed from sodium (a solid metal) and chlorine (a poisonous gas).
What is a biosphere?
That part of Earth inhabited by living organisms, including both living and nonliving components.
Define an ecosystem.
A community together with its nonliving surroundings.
What is a community in biological terms?
Two or more populations of different species living and interacting in the same area.
What distinguishes a species?
Very similar, potentially interbreeding organisms in the same area.
What is a population?
Members of one species inhabiting a specific area.
Define a multicellular organism.
An individual living thing composed of many cells.
What is an organ system?
Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific bodily function.
What is an organ?
A structure usually composed of several tissue types that form a functional unit.
Define tissue.
A group of similar cells that perform a specific function.
What is a cell?
The smallest unit of life.
What is an organelle?
A structure within a cell that performs a specific function.
Define an atom.
The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element.
What are subatomic particles?
Particles that make up an atom, such as electrons, neutrons, and protons.
What is the characteristic of life demonstrated when a plant leans towards the sun?
Response to stimuli.
What is the significance of DNA in reproduction?
DNA contains the genetic information, the 'blueprint' for the offspring.
What is evolution in biological terms?
A change in the genetic makeup of a population over time.
What are the two prokaryotic domains?
Bacteria and Archaea.
What is the eukaryotic domain?
Eukarya.
What distinguishes prokaryotic cells from eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and organelles.
What are the three basic nutritional methods of organisms?
1. Photosynthesis 2. Absorption 3. Ingestion.
Define heterotroph.
An organism that must rely on other organisms for energy.