Lecture 15 & 16 (Virus Diseases of Swine)
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
RNA viruses
do DNA or RNA viruses have a higher mutation rate?
non-enveloped viruses
are enveloped or non-enveloped viruses more durable in the environment?
disease severity
what is virulence?
true
t/f: no "long term" decisions are made without lab testing for viral treatment in pigs
-method used for pathogen detection
-PCR
-more sensitive than nasal/oral swabs on population basis
*an effective tool for swine health monitoring
sampling methods:
talk about oral fluid collection in pigs
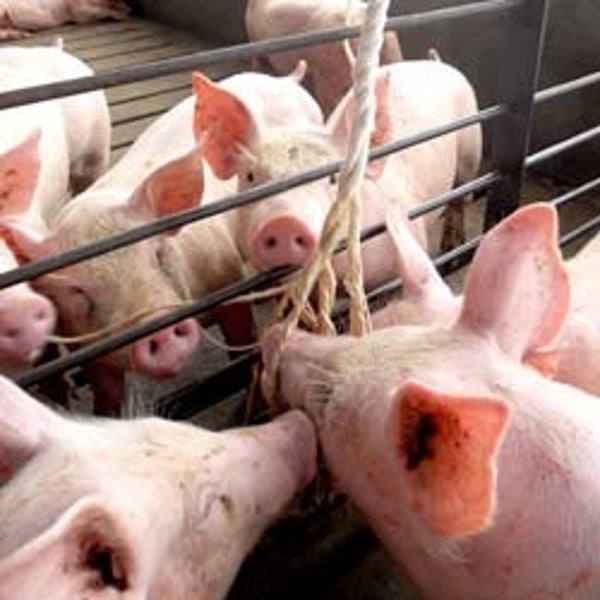

-process tissues → testicles from castration // tails from tail docking
*processing fluids are an effective sample to detect PRRSV in piglets
sampling methods:
talk about processing fluids in pigs
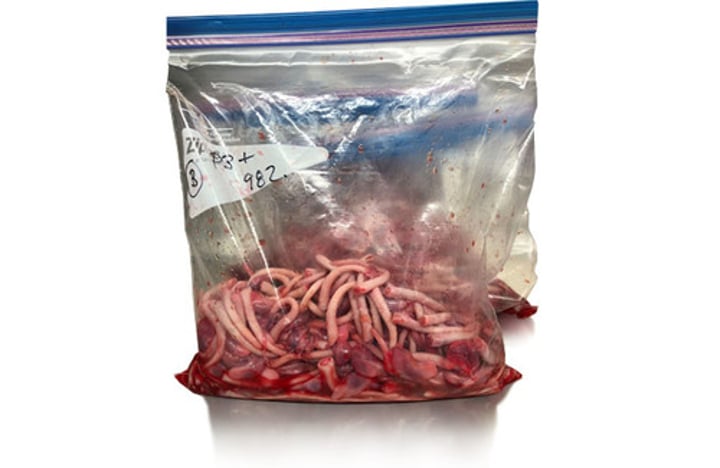

placental umbilical cord serum
*use in utero transmission
what is PUCS?
if we are worried that there is in utero transmission of disease
when would it be important to collect PUCS to send out?
a) in situ hybridization
detect viral nucleic acid (via primer)
a) in situ hybridization
b) immunohistochemistry
b) immunohistochemistry
detect viral antigen in lesion (via antibody)
a) in situ hybridization
b) immunohistochemistry
RNA virus
is Swine Influenza Virus a DNA or RNA virus?
Influenza A Virus in Swine
what does IAV-S stand for?
a) antigenic drift
nucleotide changes
a) antigenic drift
b) antigenic shift
b) antigenic shift
gene recombination
a) antigenic drift
b) antigenic shift
antigenic shift
is the influenza virus an antigenic shift or an antigenic drift?
because they have receptors for both swine viruses, avian viruses as well as human viruses
*provides an opportunity for recombination
why are pigs considered the "mixing vessel" for influenza viruses?
-hemagglutinin (HA) → enables entry into the cell // main antigen for vaccines
-neuraminidase (NA) → allows virus to exit cell/spread within cells
-nucleoproteins → antigen for ELISA antibody test
what are the 3 important antigens in the swine influenza virus?
a) H1N1
traditional strain in the U.S.
a) H1N1
b) H3N2
c) H1N2
b) H3N2
-relatively new strain in US in 1998
-spread throughout country in 2-3 years
-promiscuous gene group -- TRIG cassette
a) H1N1
b) H3N2
c) H1N2
c) H1N2
-detected first in Indiana
-combination of other two strains
a) H1N1
b) H3N2
c) H1N2
direct transmission via aerosols
how is swine influenza virus transmitted?
b) Swine Influenza
if you have a farm with several coughing ("barking") pigs that have a fever, it's pretty likely you are seeing...
a) Porcine Circovirus 2
b) Swine Influenza
c) Porcine Respiratory and Reproductive Syndrome
d) Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus
b) Swine Influenza
-sudden onset after incubation
-coughing // fever > 105°F // nasal discharge
-anorexia // lethargy // labored breathing
-abortion
a) Porcine Circovirus 2
b) Swine Influenza
c) Porcine Respiratory and Reproductive Syndrome
d) Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus
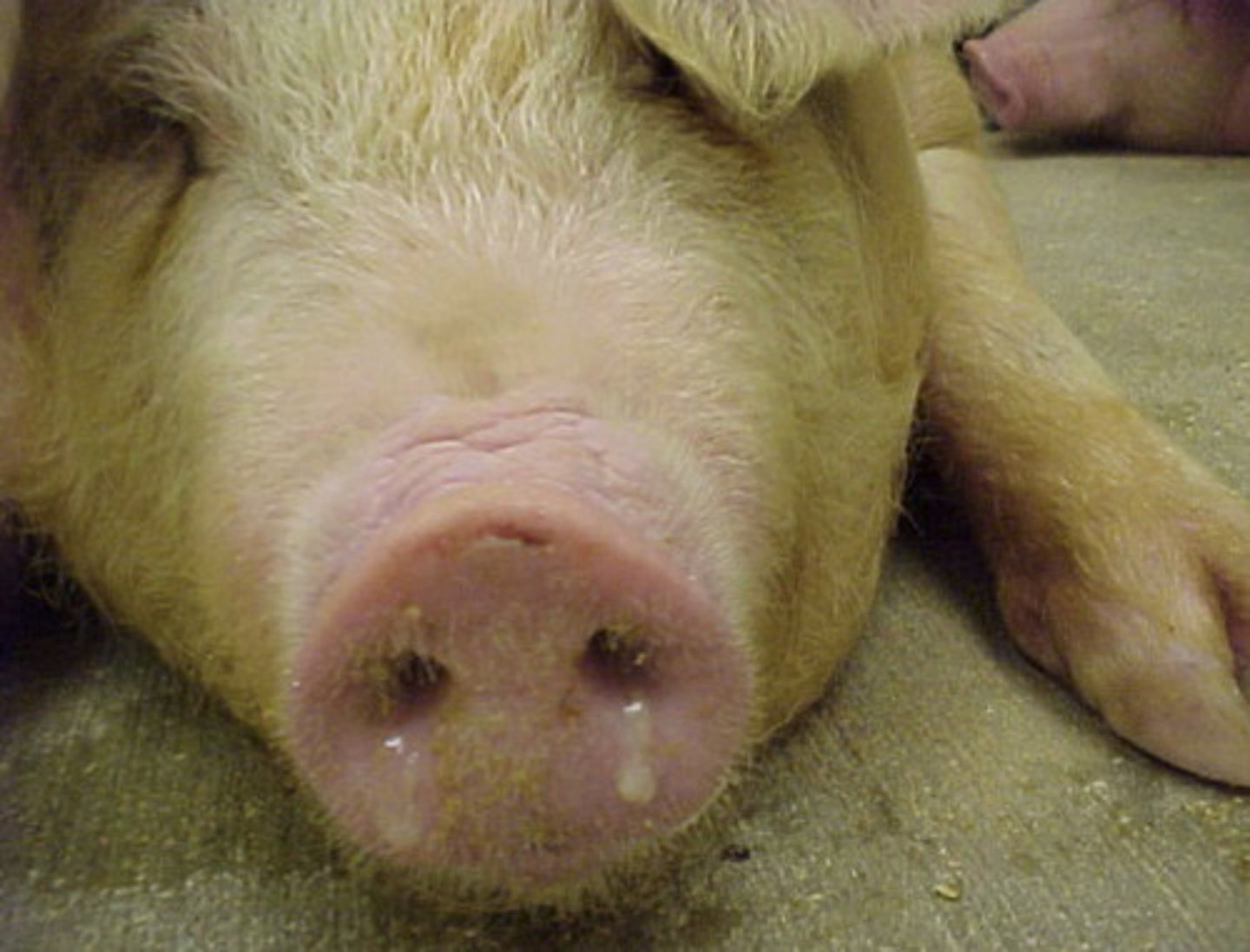

Swine Influenza Virus
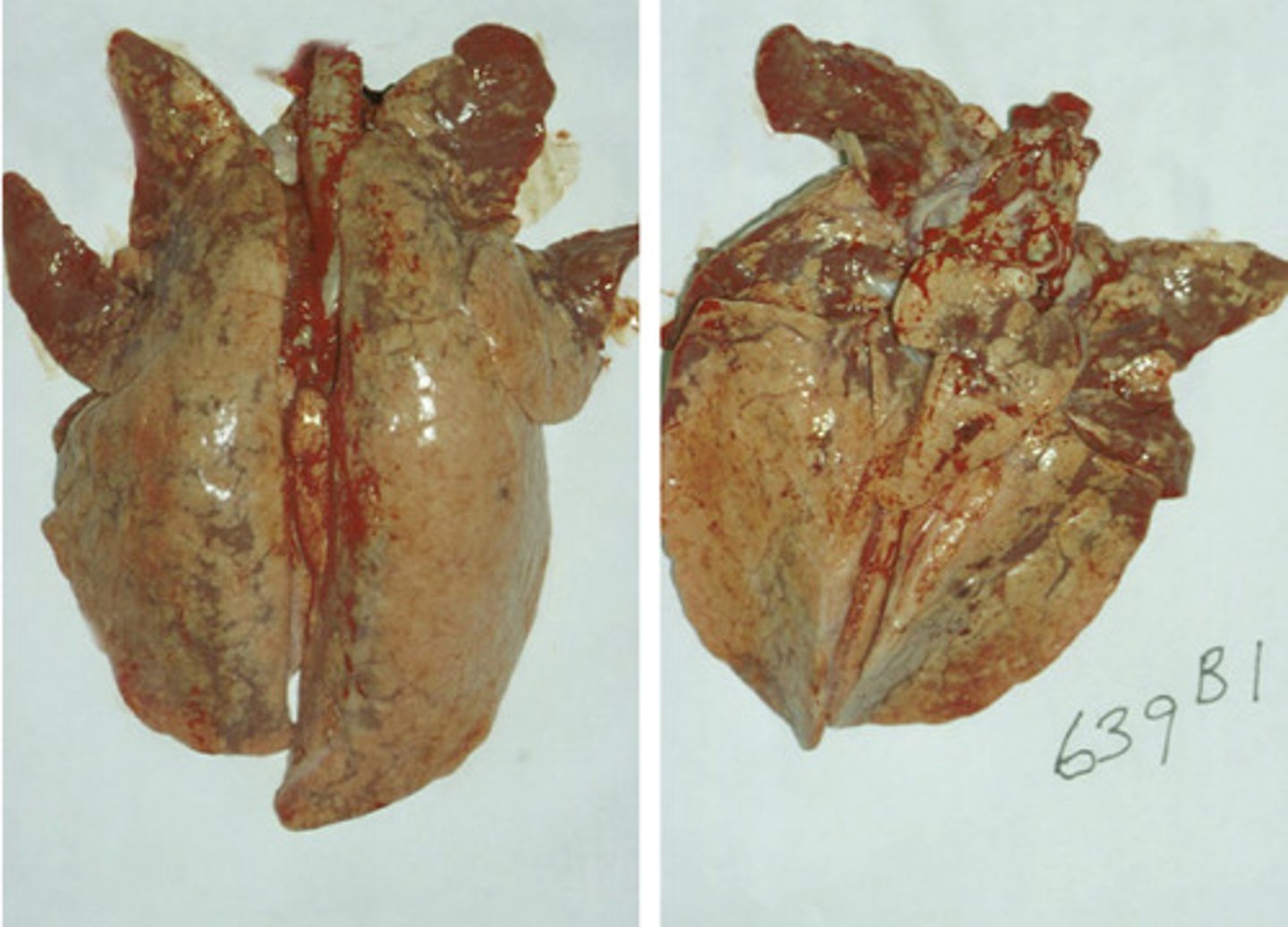
you see lungs that look like this on necropsy:
-lung is often apical or cardiac lobes
-not pathognomonic
-airways with fluid and mucus
-enlarged bronchial lymph nodes
what virus did this pig most likely have?
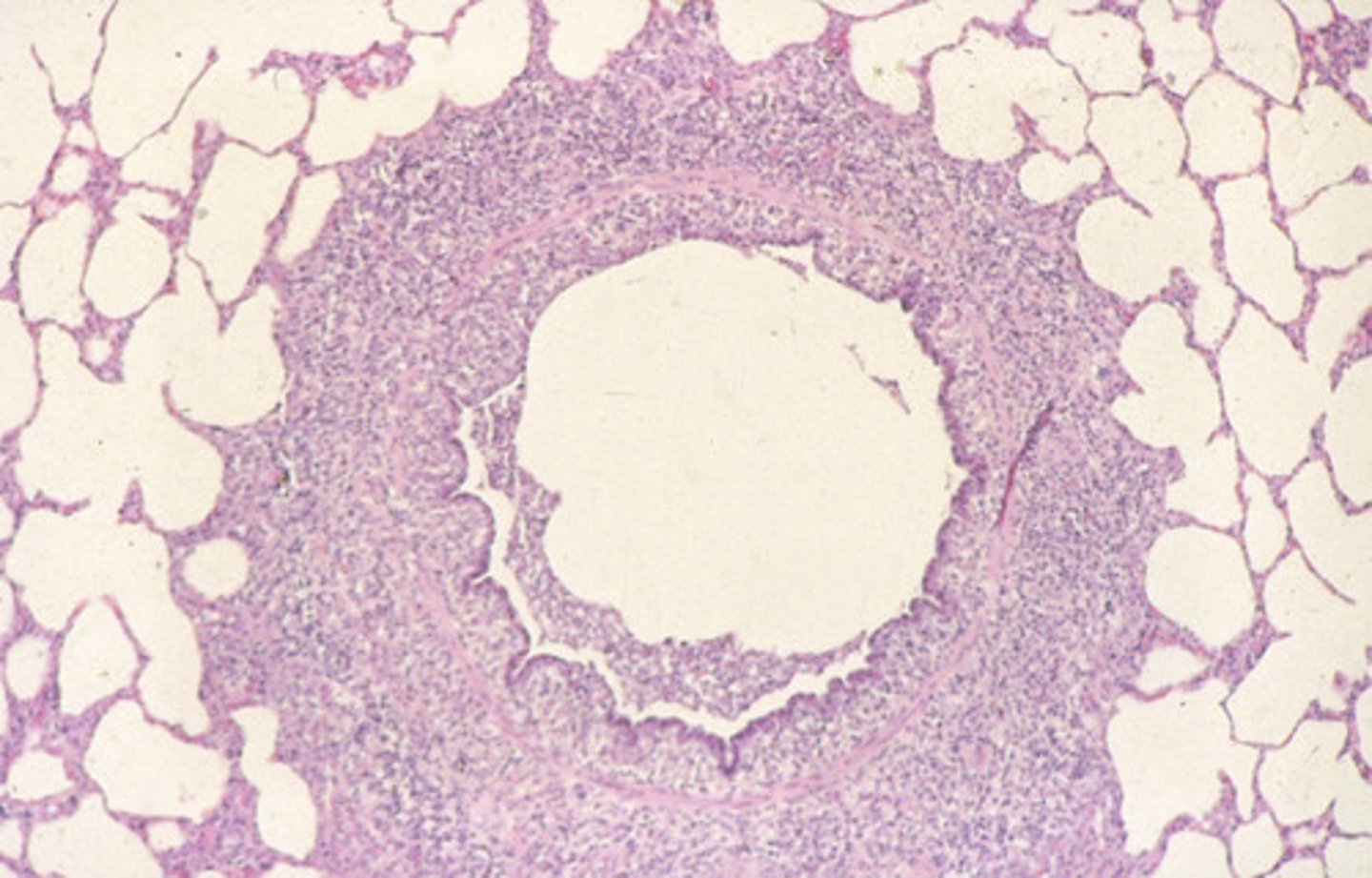
degeneration and necrosis of respiratory epithelium
what causes the cough in a pig that has swine influenza?
-mainly presumptive: acute respiratory outbreak involving the herd
-definitive detection: nasal swab // PCR
-sequencing is common for strain matching
-serology → ELISA
how do you diagnose a pig with swine influenza?
-no specific therapy
-nursing care // draft-free, warm, dry environment
-antibiotics for secondary bacterial infections
-put anti-inflammatories in the water
how do you treat a pig with swine influenza?
-maintain good biosecurity → proper cleaning & disinfecting trucks // quarantine new arrivals
-vaccination → vaccines usually require multiple strains
-maternal derived antibody (MDA) → vaccination of sows to protect pigs
how do you prevent swine influenza?
PRRS virus
what is the most important disease in pigs worldwide?
PRRS virus
this virus infects dendritic cells (macrophages) especially in the lung → pulmonary alveolar macrophages and pulmonary intravascular macrophages
-oro-nasal spread
-body secretions including semen
-blood via injections → change needles often
how is PRRS virus transmitted?
true
t/f: PRRS virus is highly infectious and takes only a few viral particles to infect a pig
PRRS virus
-severe respiratory disease; interstitial pneumonia
-rapid breathing especially after stress
-takes 30-45 days longer to reach market due to virus
-severity of infection diminishes greatly after 8 weeks of age unless co-infected with another agent
in suckling and nursery pigs what virus is this most likely to be?
true
t/f: no sow herd is protected from PRRS with vaccination due to new strains always being created
8 weeks
severity of PRRS infection greatly diminishes after _____ weeks of age unless co-infected with another agent
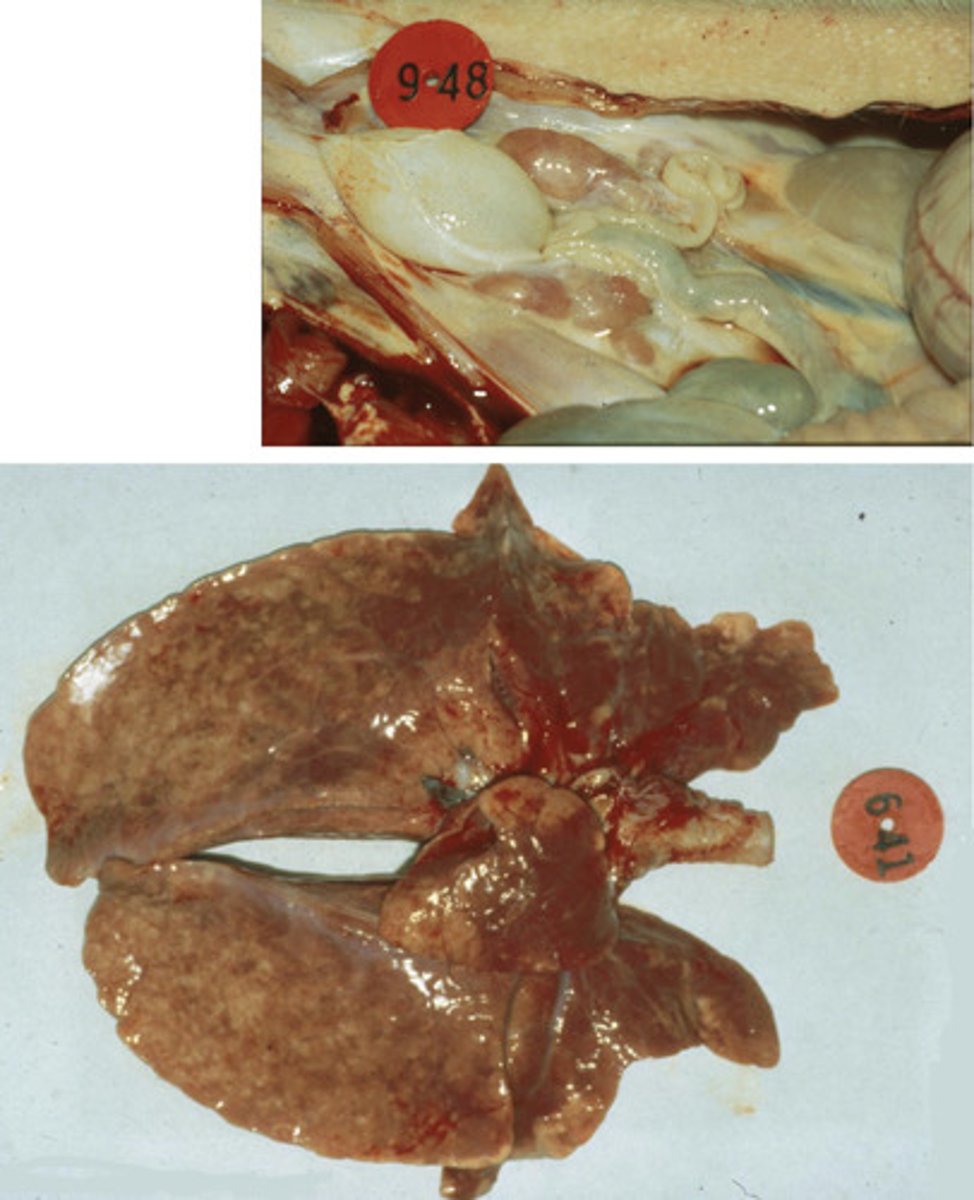
PRRS virus
you see this on a necropsy
-enlarged lymph nodes
-interstitial pneumonia
-tan discoloration of the lungs // rubbery texture
-when you pull the lungs out they fail to collapse due to being filled with edema
what virus did this pig most likely have?
treatment:
-supportive → aspirin and ibuprofen
-control secondary bacterial infections with antibiotics
biosecurity:
-people shower in and out
-air filtration in facilities
controlled exposure with serum from infected pigs (LVI - live virus inoculation)
what is the treatment and control for PRRS virus?
a) type 1 PCV
cause of infectious congenital tremors; porcine cell line contaminant
a) type 1 PCV
b) type 2 PCV
c) type 3 PCV
b) type 2 PCV
cause of PMWS (post-weaning multi-systemic wasting syndrome)
a) type 1 PCV
b) type 2 PCV
c) type 3 PCV
c) type 3 PCV
recent (2016); 35-40% genetic homology to PCV2
a) type 1 PCV
b) type 2 PCV
c) type 3 PCV
PCVAD (associated disease) or PCVD (disease)
what is PCV2 now referred to as?
it's non-enveloped and very stable in the environment
this characteristic of PCV2 makes it very durable
infects lymphocytes → atrophy of lymph nodes → immune suppression
talk about pathogenesis of PCV2
70 days; 3-5 months
the PCV2 virus sheds for at least ______ days via nasal secretions and/or feces and is viremic (virus in blood) for ________ months
PCV2
all PMWS cases are __________ positive
true
t/f: not all PCV2 positive pigs have PMWS
the virus did not have distinctive case presentation
why was it difficult to diagnose PCV2 early on?
-wasting
-microscopic lesions: lymphoid depletion → granulomatous infiltration
-detection of PCV2 in lesions → antigen by immunochemistry
what are the 3 criteria for diagnosing PCVAD
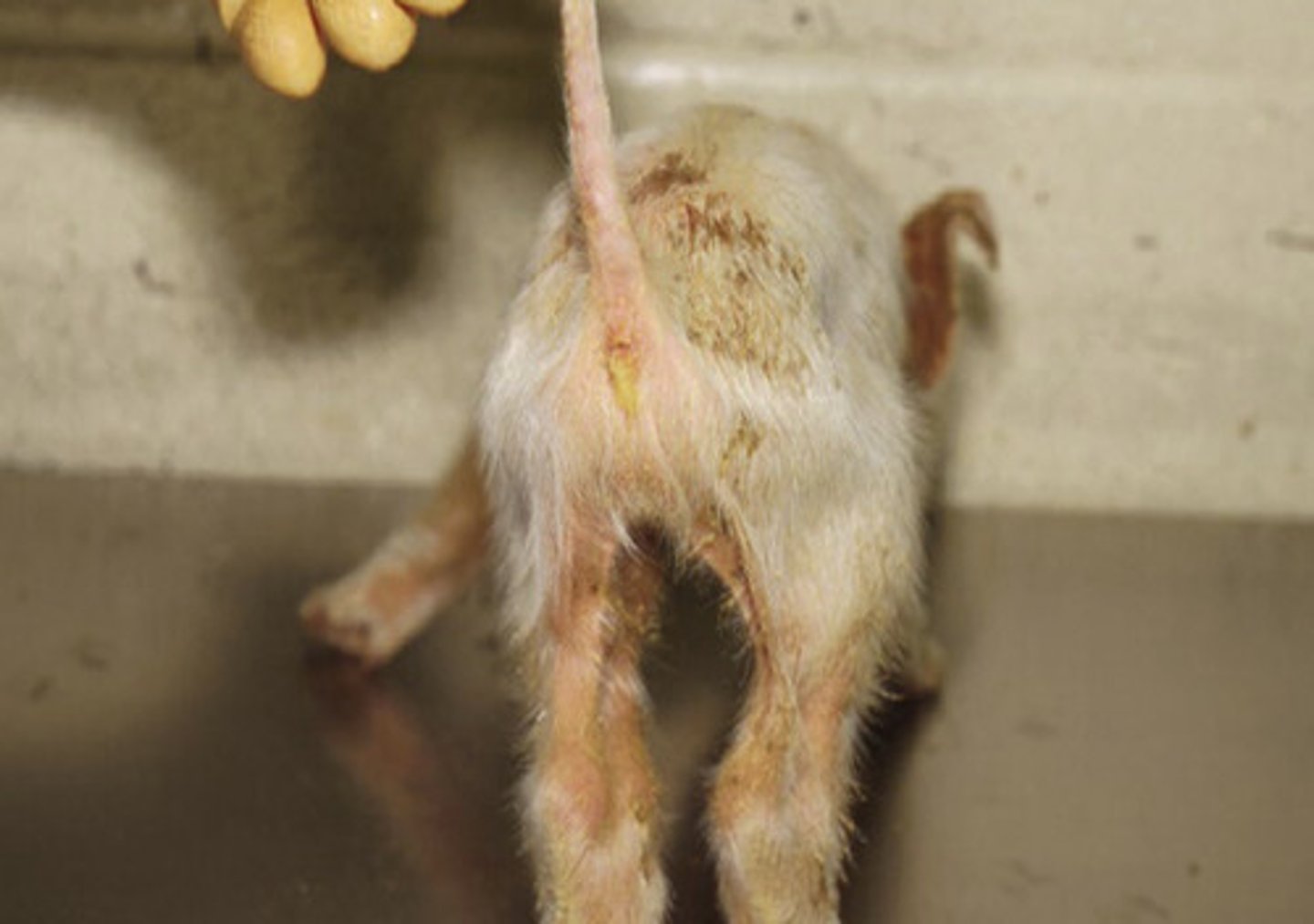
PCV2
these pigs are wasting quickly - cachexia - and water consumption declines so they are becoming dehydrated
what virus do these pigs most likely have?
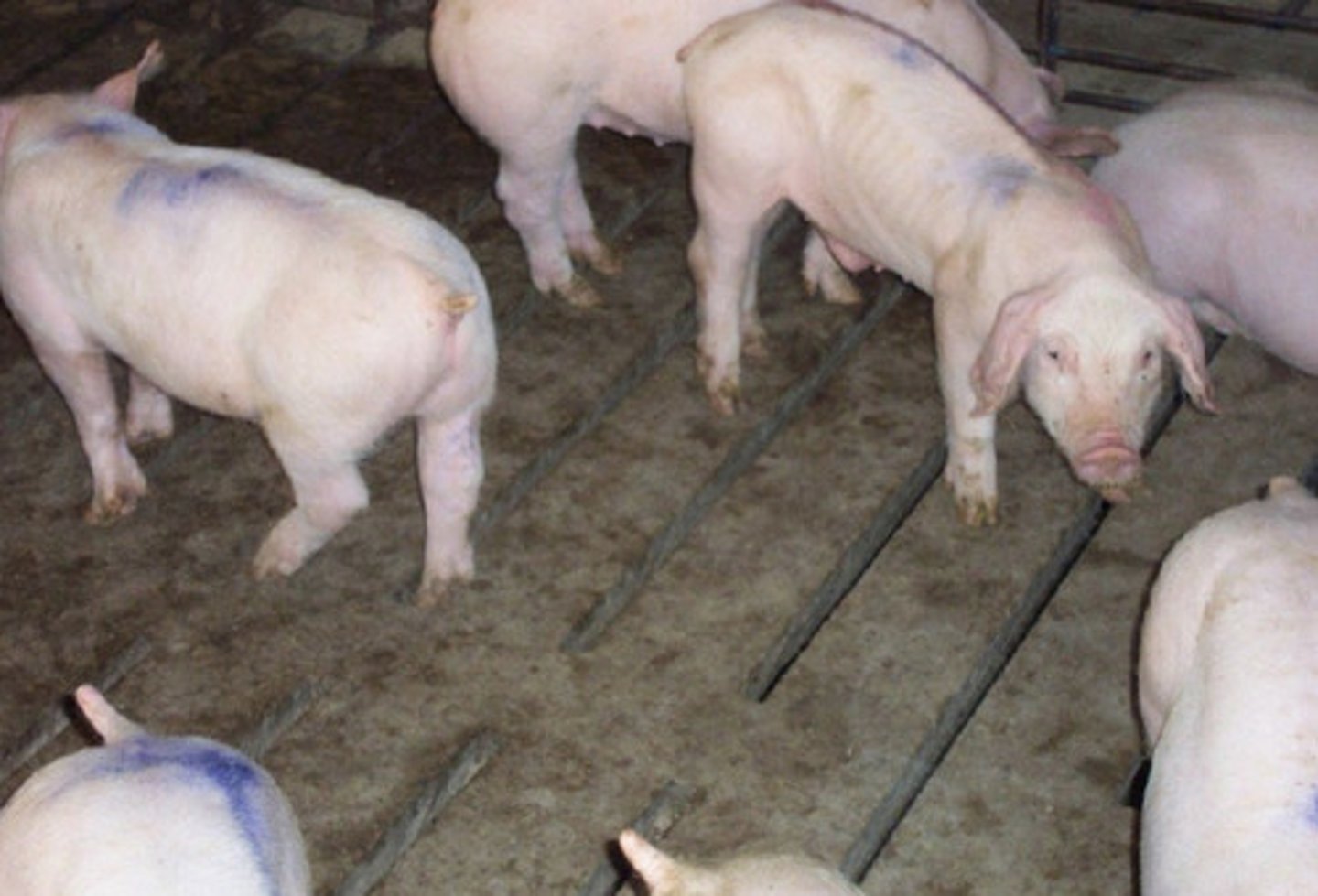

a) Porcine Circovirus 2
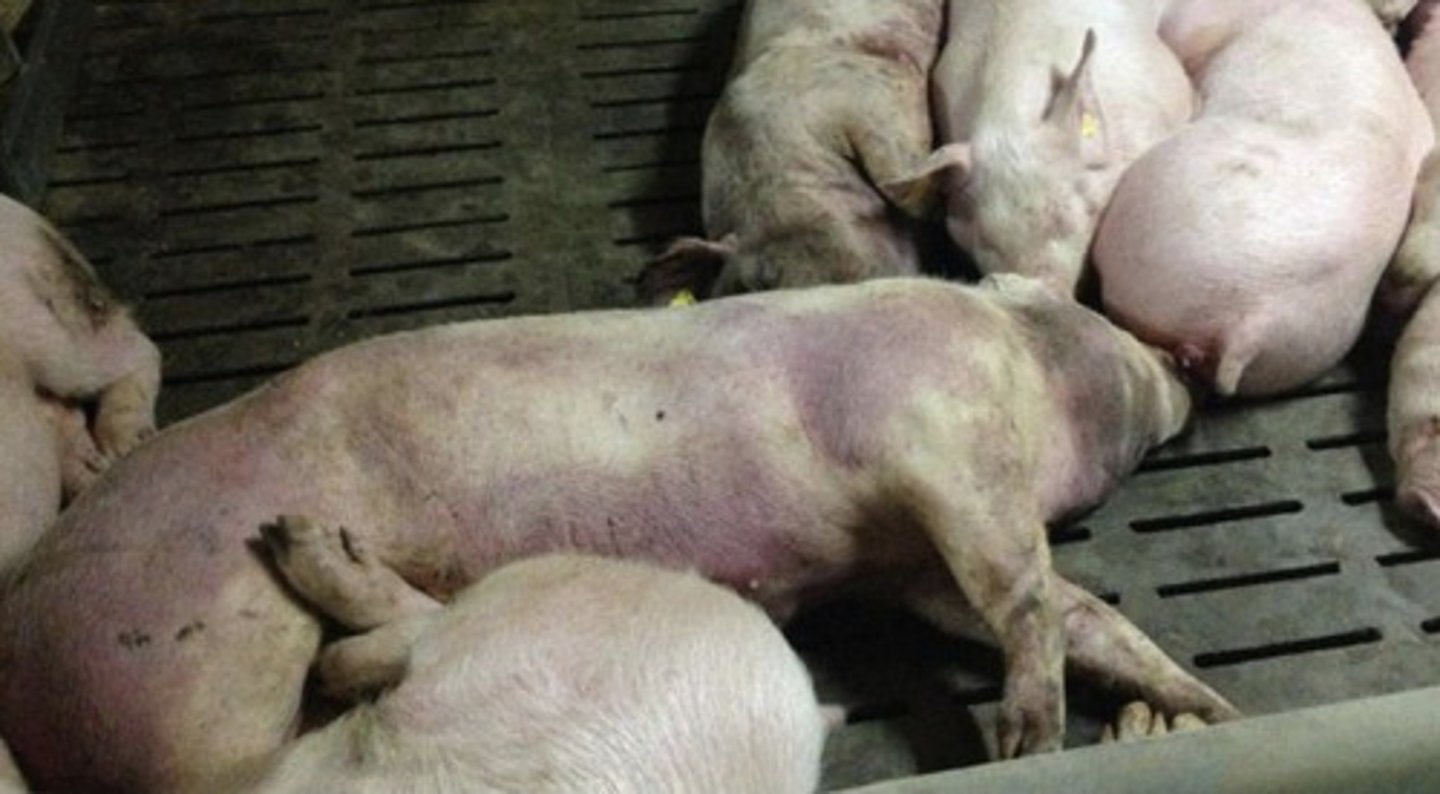
Porcine Dermatitis and Nephropathy Syndrome may be caused by:
a) Porcine Circovirus 2
b) Swine Influenza
c) Porcine Respiratory and Reproductive Syndrome
d) Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus
Coronaviruses and Rotavirus (both RNA viruses)
these two types of viruses can cause viral diarrhea in baby pigs
PED/TGE
what viral disease is this?
-100% mortality in pigs <2 weeks of age
-severe villous atrophy
-slow regeneration from crypts
-malabsorption → dehydration and hypoglycemia
-all ages develop diarrhea // vomiting commonly observed
PED
[PED/TGE] emerged in the USA from China in 2014
TGE
[PED/TGE] is no longer present
100%
with PED/TGE there is a _____% mortality rate in pigs less than 2 weeks old
-feed back intestines from affected pigs to all sows/boars
-euthanize all baby pigs at birth until sows with immunity start to farrow
-clean & disinfect everything (all surfaces)
-vaccinate prior to farrowing for at least 5-6 months
how do you manage a PED/TGE outbreak?
Deltacoronavirus
what is the milder form of PED/TGE
Porcine Parvovirus (PPV)
-Type 1
-this virus is very common in herds
-shed in feces for 3 weeks after infection
-durable in the environment
-shed in semen for up to 3 weeks after infection
-causes mummified fetuses
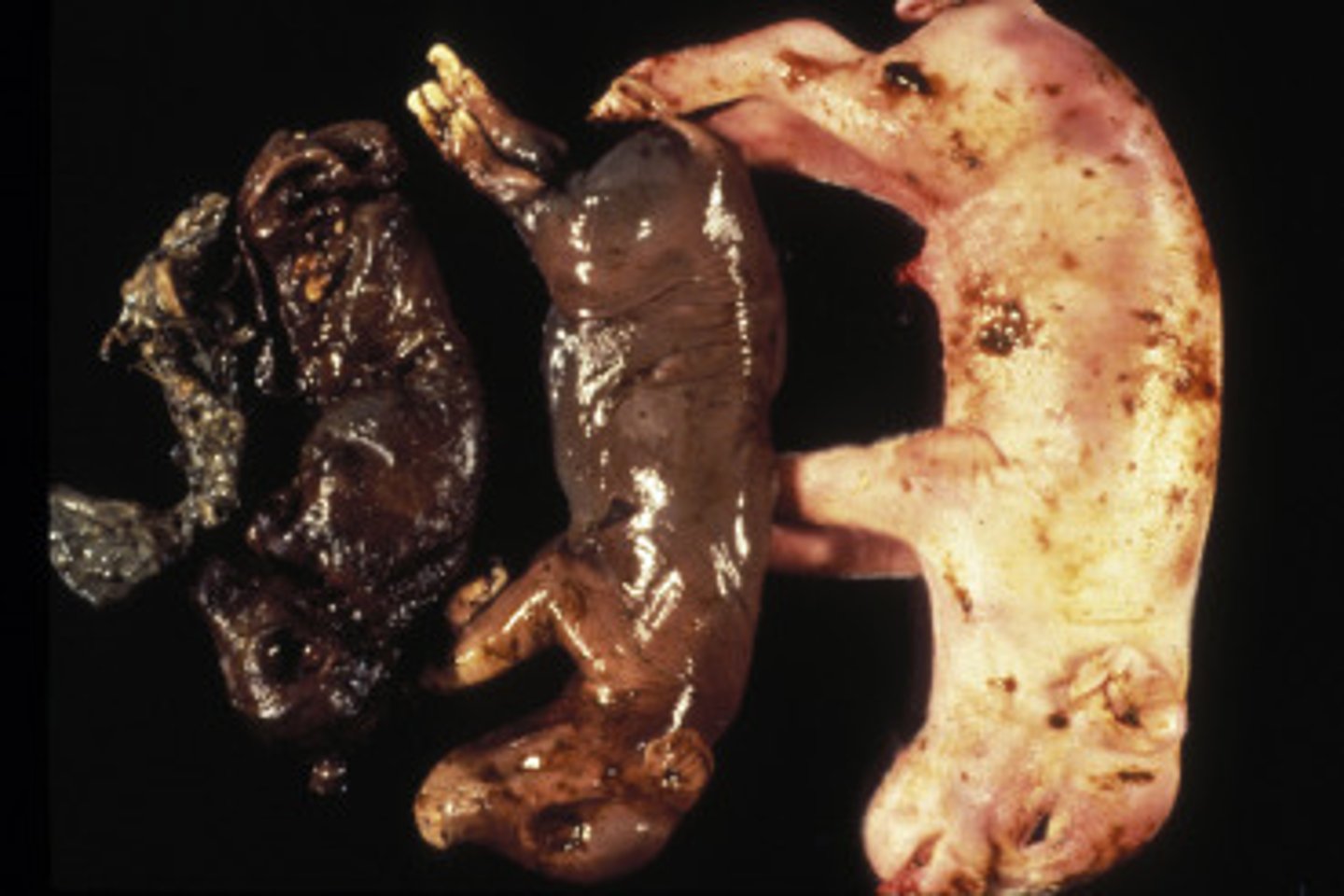
embryos being absorbed
with Porcine Parvovirus:
infection that occurs less than 35 days into gestation results in...
fetal mummification
in Porcine Parvovirus:
infection that occurs within 35-70 days gestation results in...
Senecavirus A (Seneca Valley Virus)
-this virus causes vesicles like foot and mouth disease
-late summer problem
-main concern is cases at sow slaughter plants
-if diagnosed at farm, sales are stopped until cleared
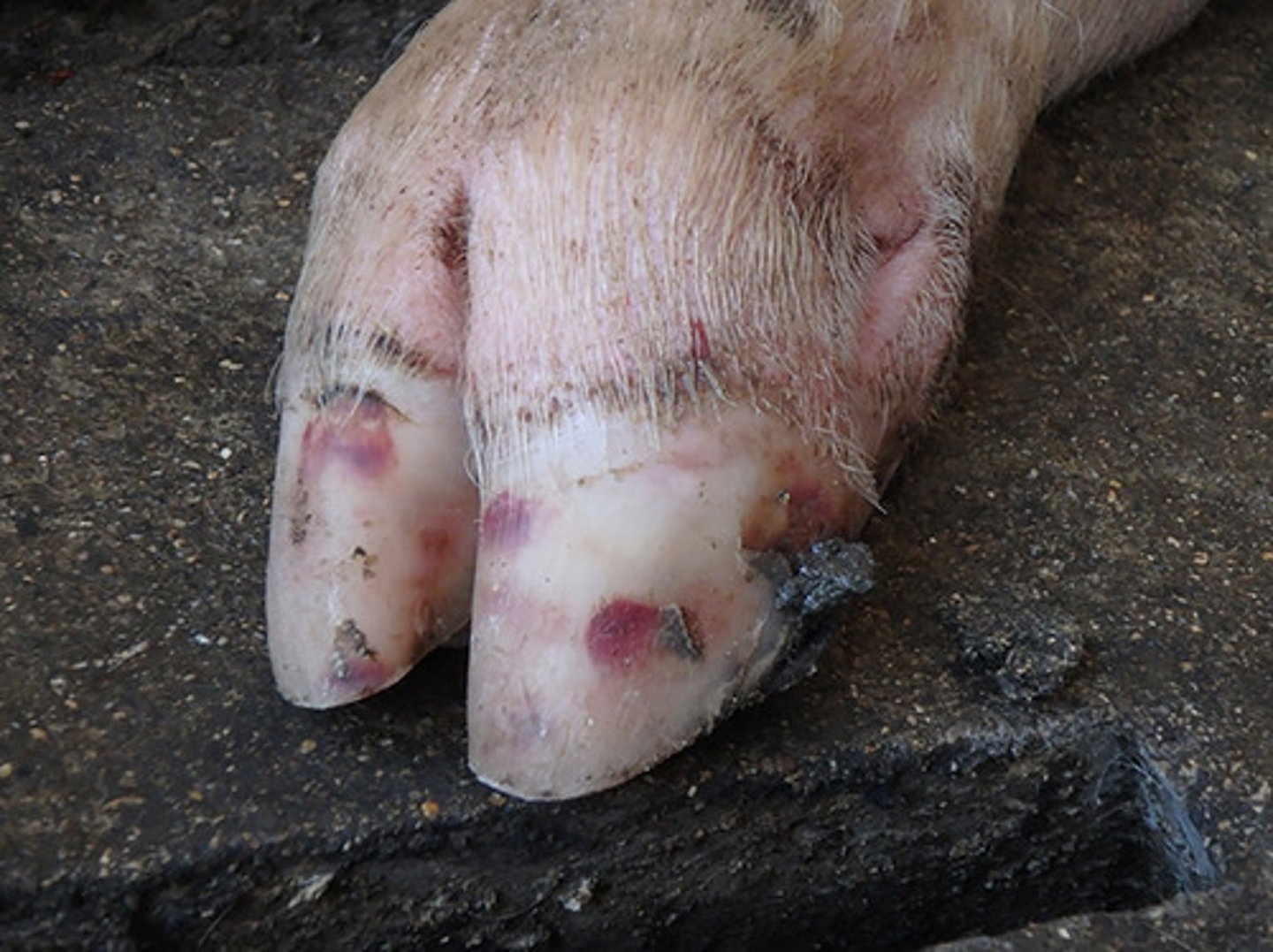
Pseudorabies virus
-this virus is nearly eradicated in USA (feral pigs only)
-DNA virus // herpes virus causes latency
-respiratory disease in any age pigs in addition to CNS signs in neonates and reproductive disease in sows
-will have fever but no other obvious clinical signs initially
inclusion body rhinitis
-this is a common disease in early nursery pigs
-causes high pitched sneezing
-a form of porcine cytomegalovirus
-on histopath you will see blue inclusions
Porcine Picornaviruses
with this virus you will see nervous clinical signs in nursery/grower pigs (3 to 15 WOA) → listless // ataxia // abnormal postures // recumbency
-reproductive failure
-sporadic outbreaks
Hemagglutinating Encephalomyelitis Virus (HEV)
-this virus is a form of coronavirus
-cross-reacts with FIP
-causes vomiting and wasting disease
-rare/sporadic cases
Porcine Respiratory Coronavirus (PRCV)
this is a mild respiratory disease in young pigs // widespread // natural deletion mutant of TGE virus so it cannot attach to intestinal epithelium
-recovered pigs are immune to TGE virus
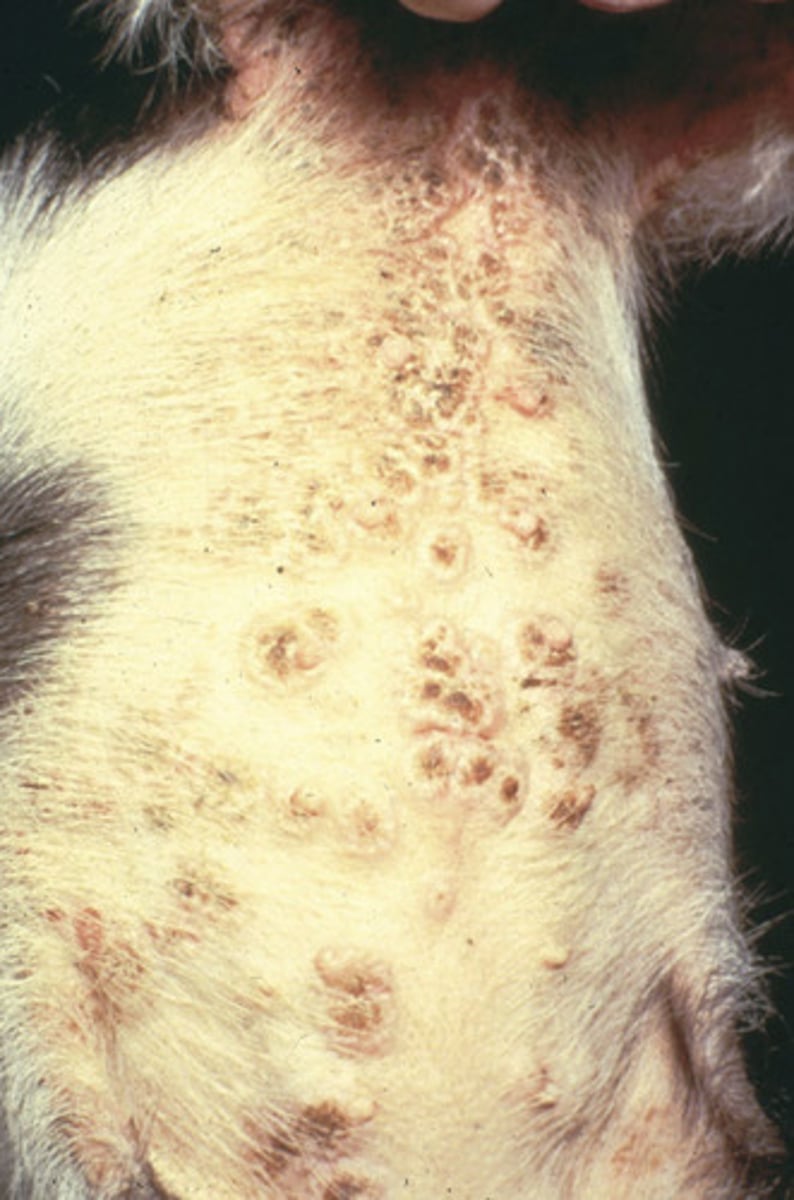
Swine Pox Virus
-this virus occurs in young pigs
-vesicles to pustules to scabs mainly ventral on sow udders but can spread
-lesions heal in 3-4 weeks
a) vesicular stomatitis
-endemic in SW USA but not in swine
-periodic outbreaks - every 10 years or so
a) vesicular stomatitis
b) vesicular exanthema
b) vesicular exanthema
-eradicated from the USA in 1956
-same virus that causes San Miguel sea lion virus disease
a) vesicular stomatitis
b) vesicular exanthema
Foot and Mouth disease
-this is a vesicular disease
-pigs replicate lots of virus
-if suspected, call the state vet
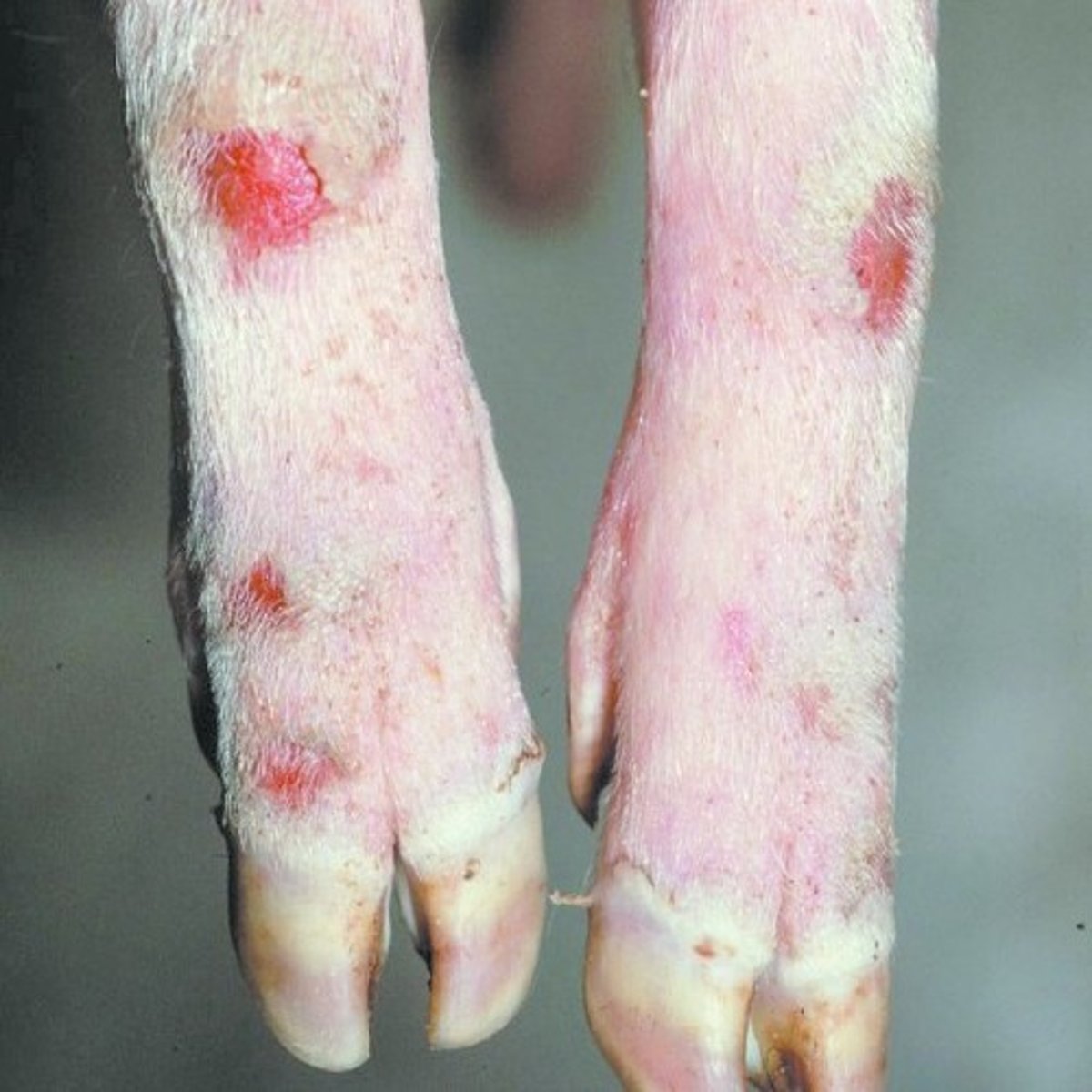
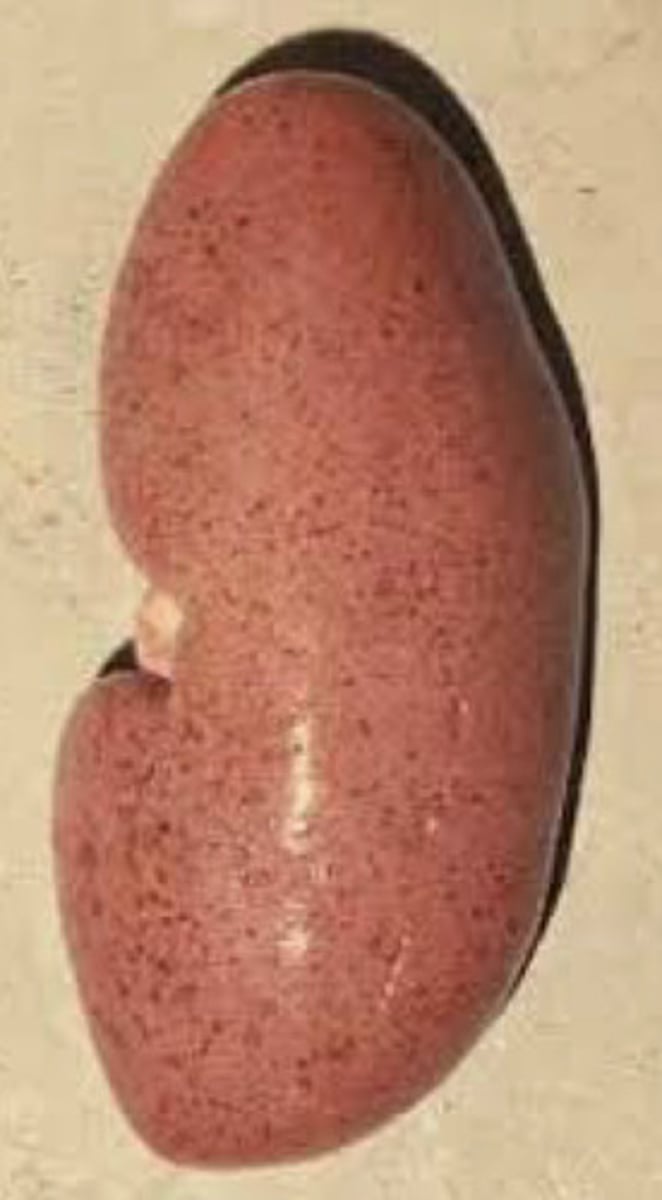
African Swine Fever
-high mortality rate
-major outbreak in China in the past 2 years
-no effective vaccines
-foreign disease → risk for US introduction
-if suspected, call the state vet

Classical Swine Fever (Hog Cholera)
-eradicated from US in early 1970's
-this virus has similar lesions to African Swine Fever but not as severe
-if suspected, call the state vet

Japanese Encephalitis
-this virus is mosquito born
-common cause of encephalitis in humans in Asia
-pigs are amplifying host but not clinically affected
-pregnant swine: fetal infection → fetal death
Atypical Porcine Pestivirus
-this virus was recently implicated as the cause of Shaker Pig disease
-congenital tremor
-pigs shake right after birth → if too severe will be unable to suckle
-outbreak may last 2-3 months
-diagnose via PCR
Porcine Circovirus type 3
-this virus is 35-40% nucleotide homologous to PCV2
-originated from bats in China
-fetal death is well documented
-diagnose via PCR
Porcine sapovirus
-this virus was first detected in 1980
-diarrhea in suckling pigs during mid-lactation
-clinically similar to rotavirus and coccidiosis
-reduced weaning weights - 1#/pig
-no or slight increase in mortality
-diagnose via PCR
Porcine parainfluenza virus type 1
this virus clinically causes mild respiratory issues and vaccination is not warranted
Torque Teno Virus (TTV)
this virus is fairly common but has not been shown to cause disease and is implicated as the contributor in Acute Pulmonary Edema PCV2 cases
Hepatitis E virus
this virus is widespread in US swine herds: pigs are the reservoir host
-causes liver inflammation in humans
-present in undercooked pork meat