Unit 1: Diet and Energy
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:00 AM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
1
New cards
Energy
the ability to do work (transfer energy b/w forms)
2
New cards
Everything your body does requires...
energy. Including staying warm, moving, and thinking (the "work" in question).
3
New cards
Heterotroph
an organism that depends on complex organic substances for nutrition
4
New cards
Solar Energy
energy from the sun that is converted into thermal or electrical energy. Every single organism on earth depends on solar energy for life
5
New cards
Mechanical Energy
1. Kinetic- energy of movement
2. Potential- stored energy
2. Potential- stored energy
6
New cards
Chemical Energy
energy stored in chemical bonds
7
New cards
Food is a form of...
Chemical energy. When you digest food, you break the bonds and harvest
the energy to run your cellular processes
the energy to run your cellular processes
8
New cards
First Law of Thermodynamics
• Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change forms
• Photosynthesis is not creating energy, it is converting light energy from the sun to chemical energy in the plant
• All energy in the universe existed when it first began
• Photosynthesis is not creating energy, it is converting light energy from the sun to chemical energy in the plant
• All energy in the universe existed when it first began
9
New cards
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Energy conversions are inefficient and some energy will ALWAYS be lost
10
New cards
Third Law of Thermodynamics
- Energy flows from higher (more ordered or efficient) forms to lower (less ordered or efficient) energy forms
- Disorder, or entropy, increases over time
- Disorder, or entropy, increases over time
11
New cards
Solar energy is converted into...
chemical energy by plants (plant sugars). Animals eat plants or other animals to convert plant sugars into ATP (energy for now) and/or stored chemicals (energy for later)
12
New cards
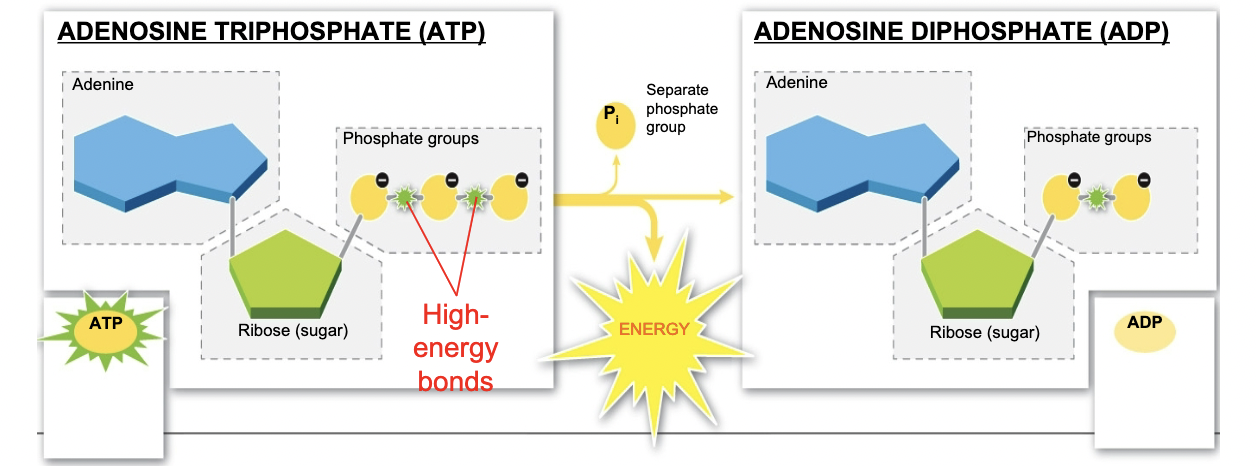
How do cells fuel chemical reactions?
13
New cards
Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy is converted into chemical energy by plants (plant sugars)
- Animals eat plants (or other animals) to convert plant sugars into ATP (energy for now) and/or stored chemicals (energy for later)
- Animals eat plants (or other animals) to convert plant sugars into ATP (energy for now) and/or stored chemicals (energy for later)
14
New cards
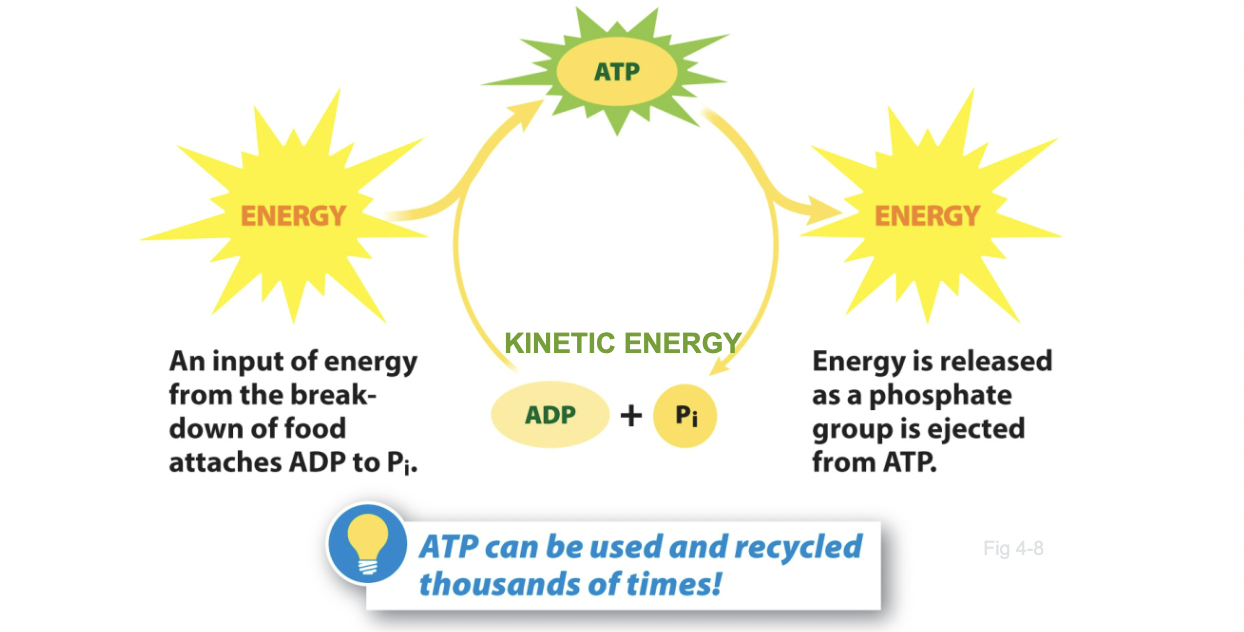
Cells store energy in the bonds of...
ATP
15
New cards
Organic Nutrients
• AKA Biological Macromolecules
• Hydrogen and other elements covalently bonded to Carbon
• Carbon is the backbone of organic molecules necessary for life- forming long chains of hydrogens and carbons
− Hydrocarbon Chains
• Hydrogen and other elements covalently bonded to Carbon
• Carbon is the backbone of organic molecules necessary for life- forming long chains of hydrogens and carbons
− Hydrocarbon Chains
16
New cards
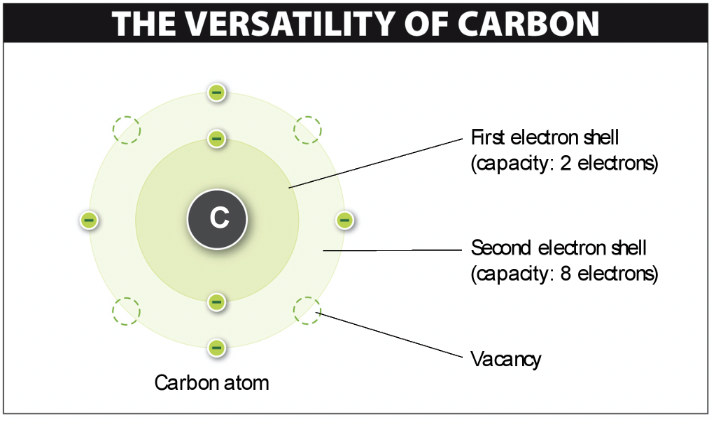
Carbon
• Most versatile element on earth
• Four valence electrons means many covalent bonds
• Four valence electrons means many covalent bonds
17
New cards
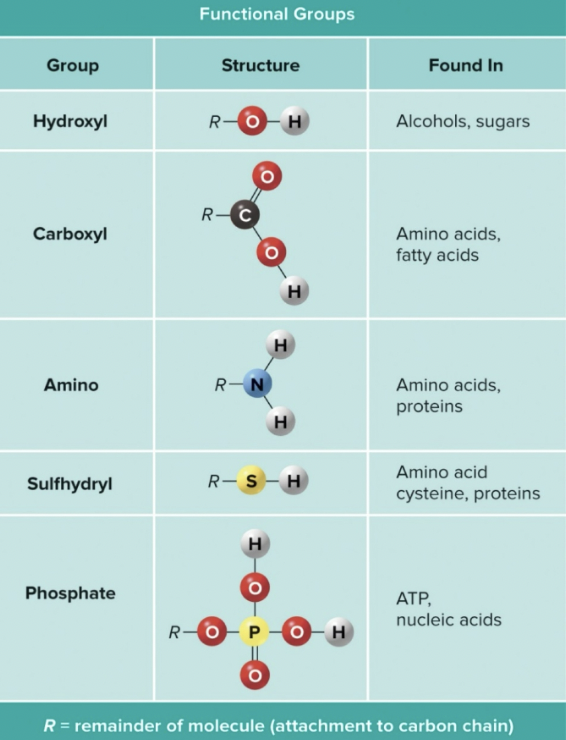
Functional Groups
- Functional groups are attached to hydrocarbon chains to provide chemical reactivity to organic molecules
- Different functional group means the molecule has a different job
- Different functional group means the molecule has a different job
18
New cards
Building Blocks of Organic Nutrients
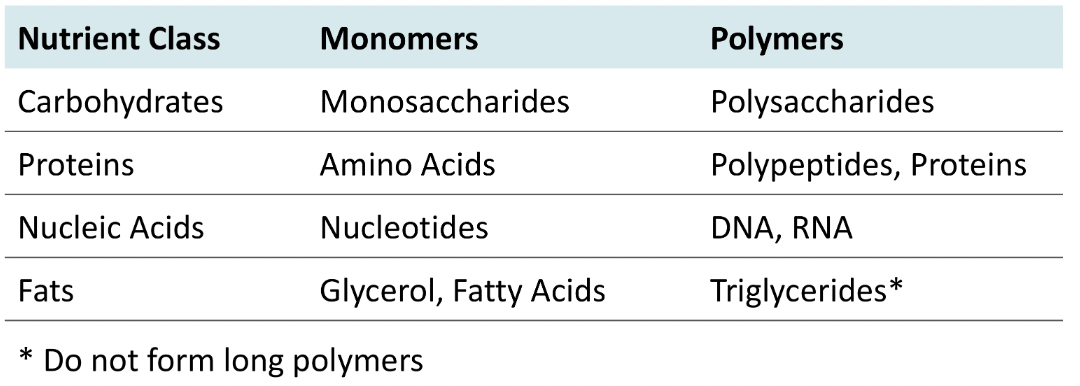
19
New cards
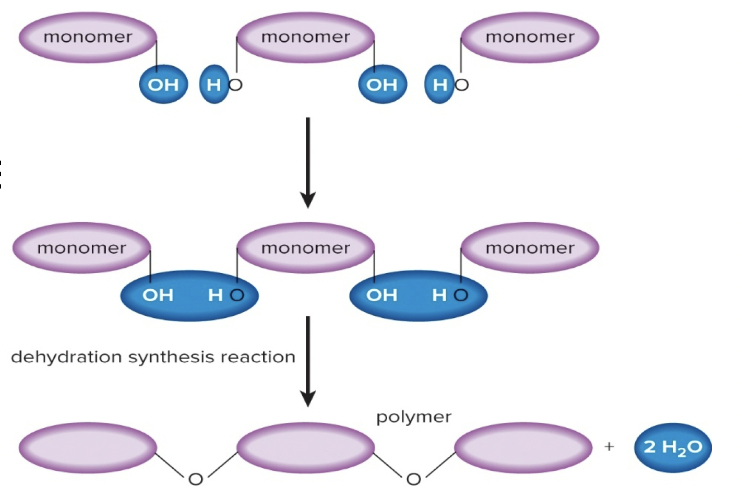
Dehydration Synthesis
Joining monomers to form a polymer by removing a water molecule
20
New cards
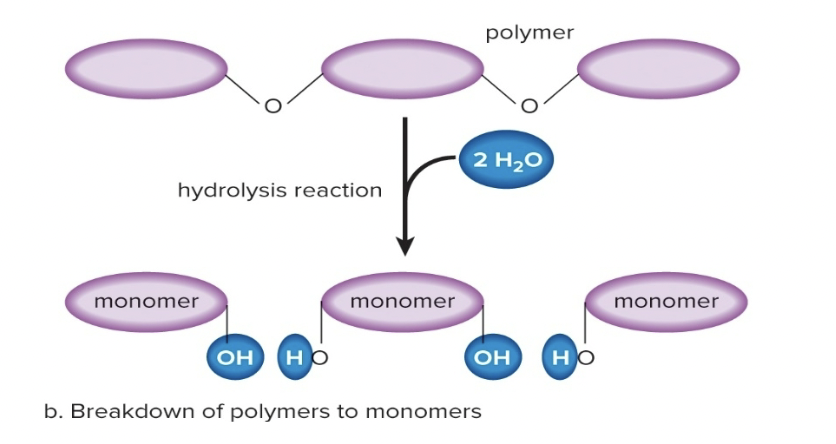
Hydrolytic Reaction (Hydrolysis)
Breaking polymers down into monomers by adding a water molecule
21
New cards
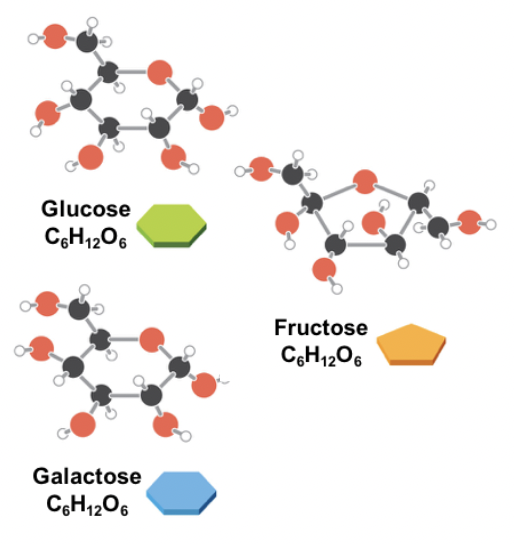
Carbohydrates
- Chains of sugar molecules (carbon rings with 3-7 carbons)
- Quickly accessed as an energy source (preferred energy source)
- Can form long polymers that are easily broken down by digestive enzymes
- Quickly accessed as an energy source (preferred energy source)
- Can form long polymers that are easily broken down by digestive enzymes
22
New cards
Monosaccharide
Single carbohydrate units, AKA simple sugars (Ex: glucose, galactose, fructose)
23
New cards
Disaccharide
Combinations of two monosaccharides, one of which is usually glucose (Ex: maltose, lactose, sucrose)
24
New cards
Polysaccharide
Long chains of glucose molecules, may be either branched or unbranched
25
New cards
Sugars in your blood: 3 fates
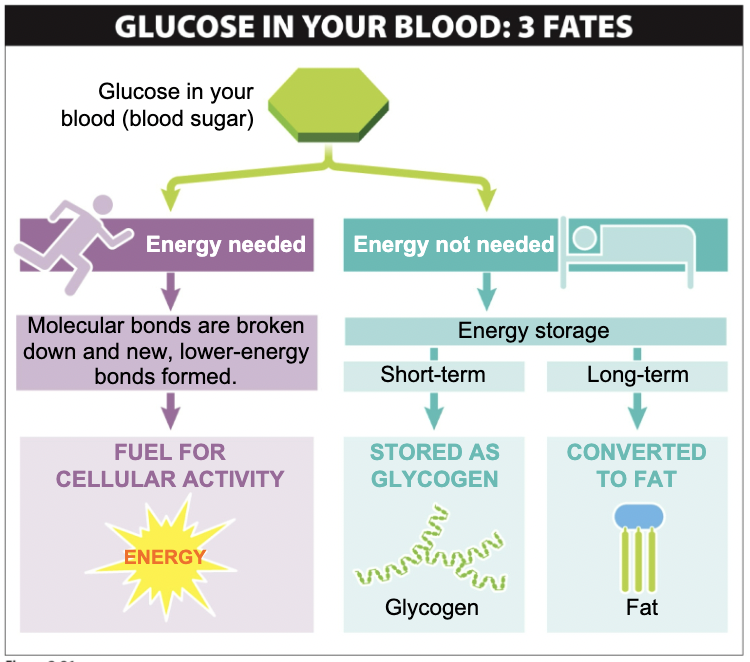
26
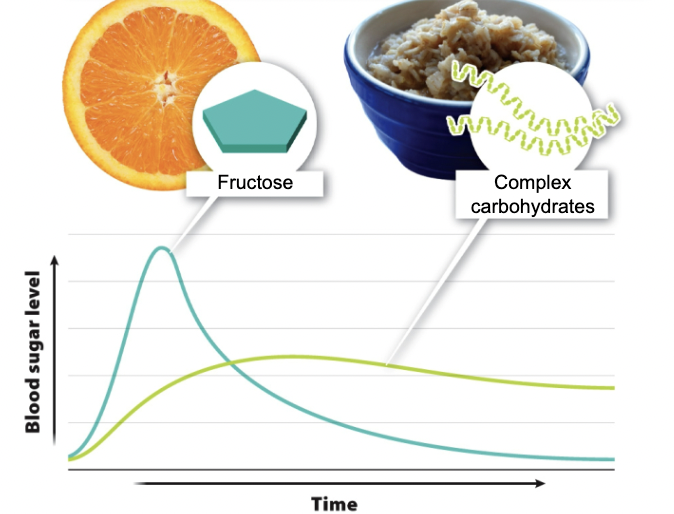
New cards
Depending on their structure, dietary
carbohydrates can...
carbohydrates can...
Lead to quick-but-brief or slow-but-persistent increases in blood sugar.
27
New cards
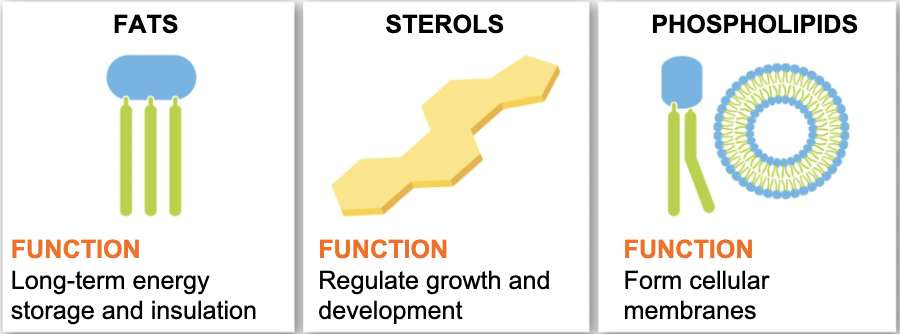
Lipids
Non-polar molecules that do not dissolve in
water
water
28
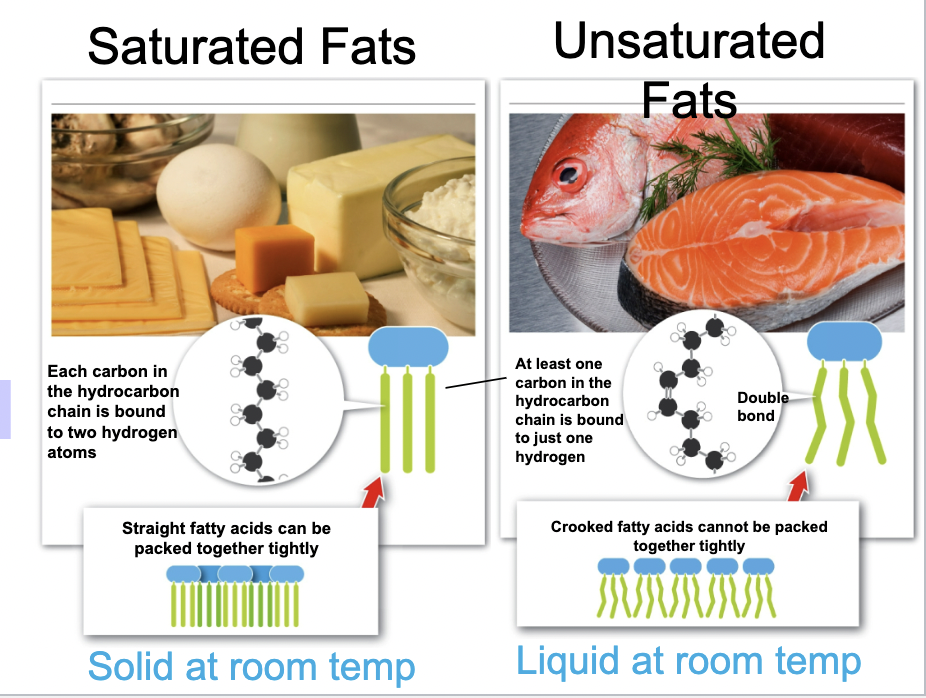
New cards
Saturated fats raise...
Bad cholesterol in the bloodstream which can create blockages and heart disease
29
New cards
Trans Fats
- Man-made fats
- One of the worst things you can eat
- One of the worst things you can eat
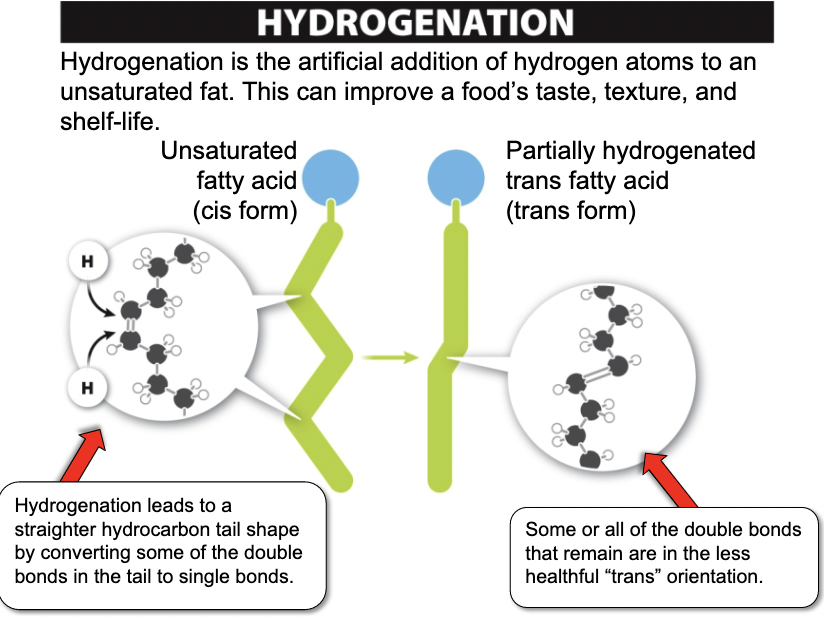
30
New cards
Structure of Fats
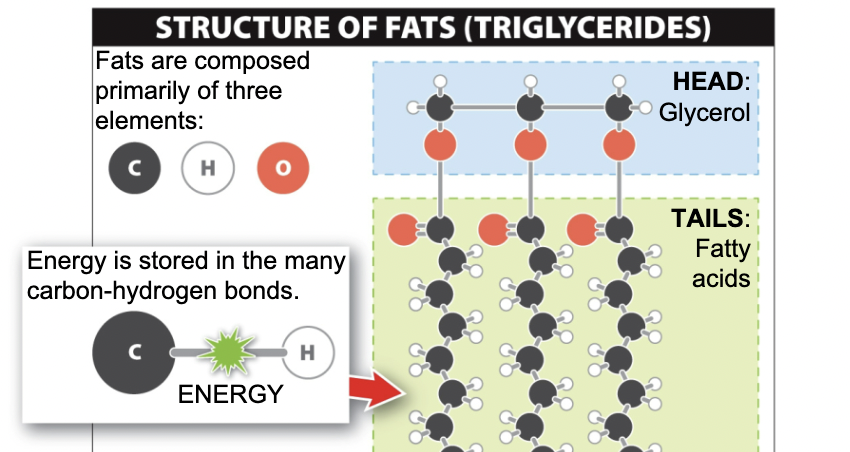
31
New cards
Sterols
• Carbon arranged in four rings instead of chains
• Cholesterol: Component of animal cell membranes−In blood, can attach to vessel walls, causing blockage
• Steroid Hormones−Regulate sexual development, maturation, and sex cell production
−Estrogen: Memory/Mood
−Testosterone: Muscle growth
• Cholesterol: Component of animal cell membranes−In blood, can attach to vessel walls, causing blockage
• Steroid Hormones−Regulate sexual development, maturation, and sex cell production
−Estrogen: Memory/Mood
−Testosterone: Muscle growth
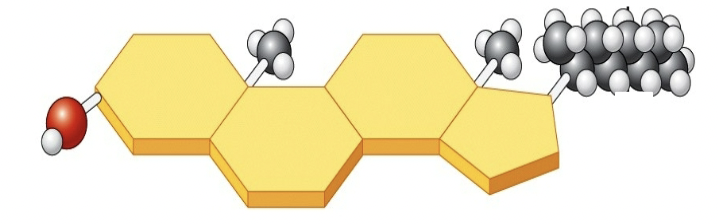
32
New cards
Phospholipids
- Compose the membrane of all living cells
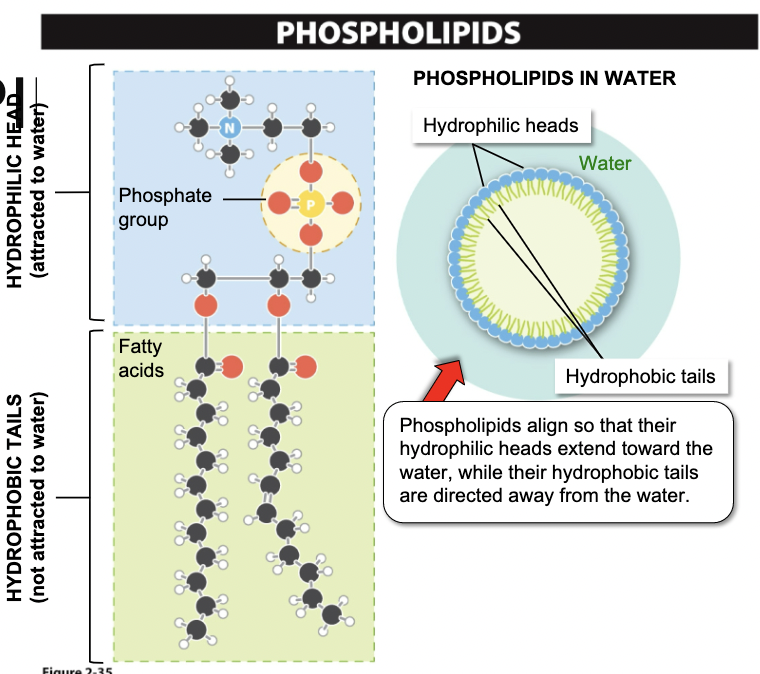
33
New cards
Proteins
• Amino group and carboxyl group bound to a chain of amino acids
• Order, identity and number of amino acids determine protein function
• Order, identity and number of amino acids determine protein function
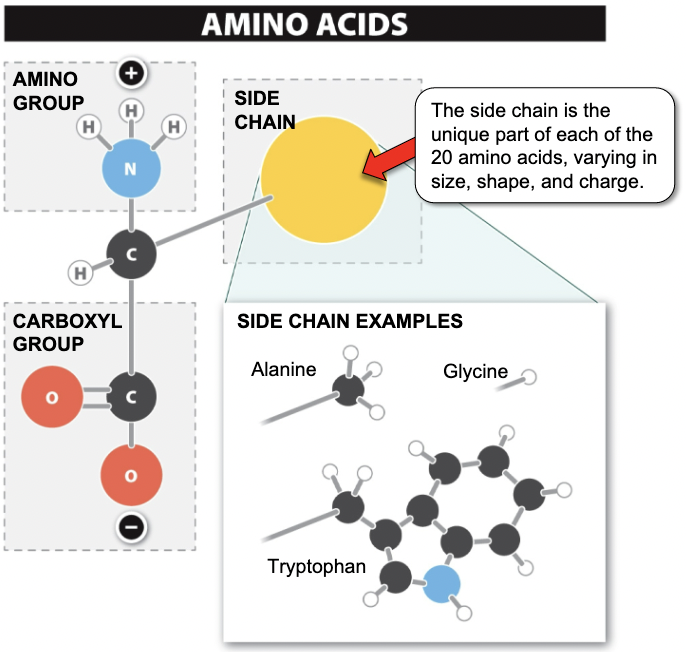
34
New cards
Protein Diversity
- Structure (hair, nails)
- Protection (fight invading microorganisms, coagulate blood)
- Regulation (control cell activity, hormones)
- Contraction (allows muscles to contract, heart to pump)
- Transportation (carry molecules around body)
- Protection (fight invading microorganisms, coagulate blood)
- Regulation (control cell activity, hormones)
- Contraction (allows muscles to contract, heart to pump)
- Transportation (carry molecules around body)
35
New cards
Protein Structure
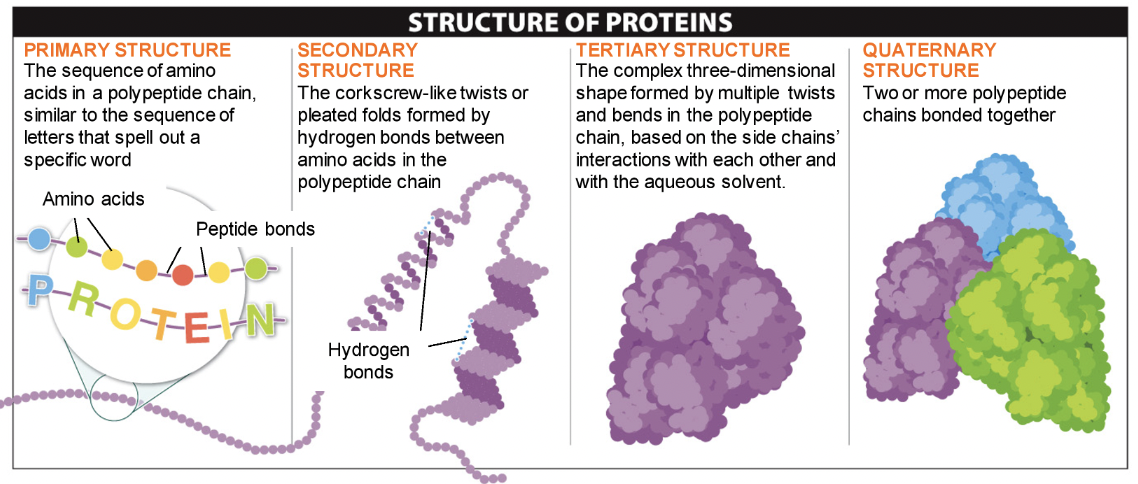
36
New cards
A change in protein shape =
A change in function
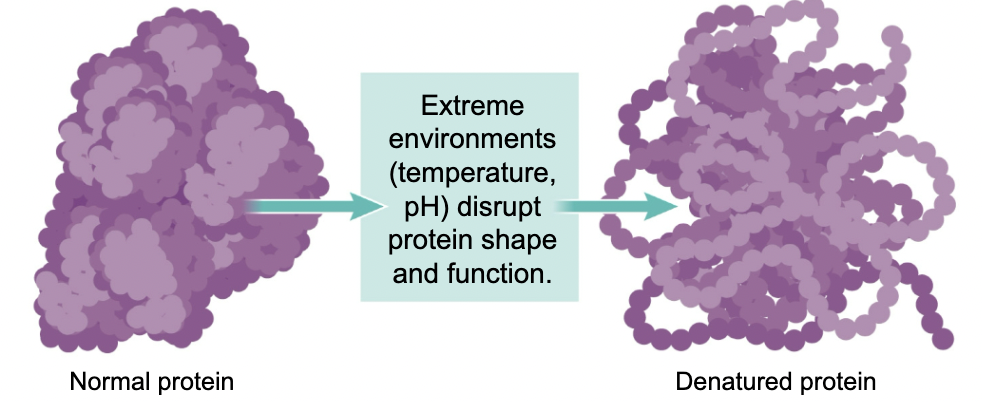
37
New cards
Hair Protein
Keratin
38
New cards
Amino Acids are...
Essential. You cannot make these and you have to obtain them from food or you will die!
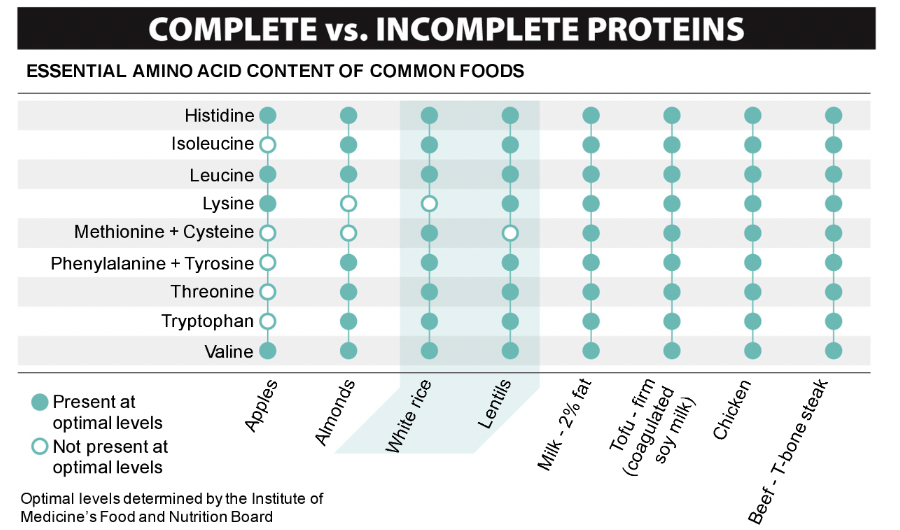
39
New cards
Pathway of Energy
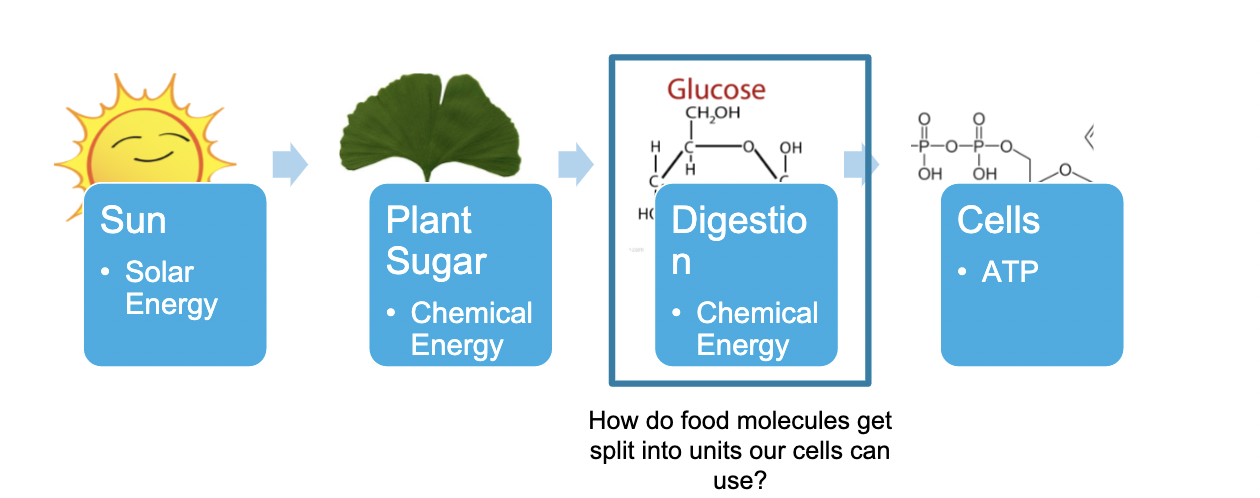
40
New cards
Functions of Digestive System
1. Break down incoming nutrients to be transported to cells of the body
2. Supply cells with water
3. Remove undigested waste material
2. Supply cells with water
3. Remove undigested waste material
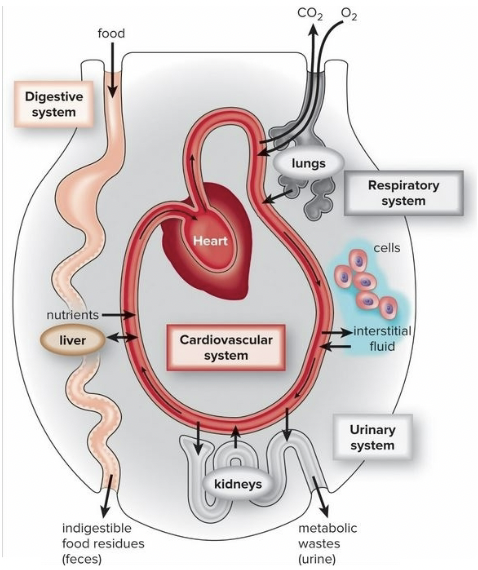
41
New cards
Mechanical Digestion
- Physically breaking food down to increase its surface area
- Mouth and stomach
- Mouth and stomach
42
New cards
Chemical Digestion
- Break down nutrient molecules using enzymes to harvest energy
- Small intestine
- Small intestine
43
New cards
Digestive Tract Organs
Mouth – breaks up food by mechanical and chemical digestion
Esophagus – transports food to stomach
Stomach – mechanical mixing of food
Small intestine – major organ of digestion and absorption
Large intestine – eliminates indigestible materials, reabsorbs water
Esophagus – transports food to stomach
Stomach – mechanical mixing of food
Small intestine – major organ of digestion and absorption
Large intestine – eliminates indigestible materials, reabsorbs water
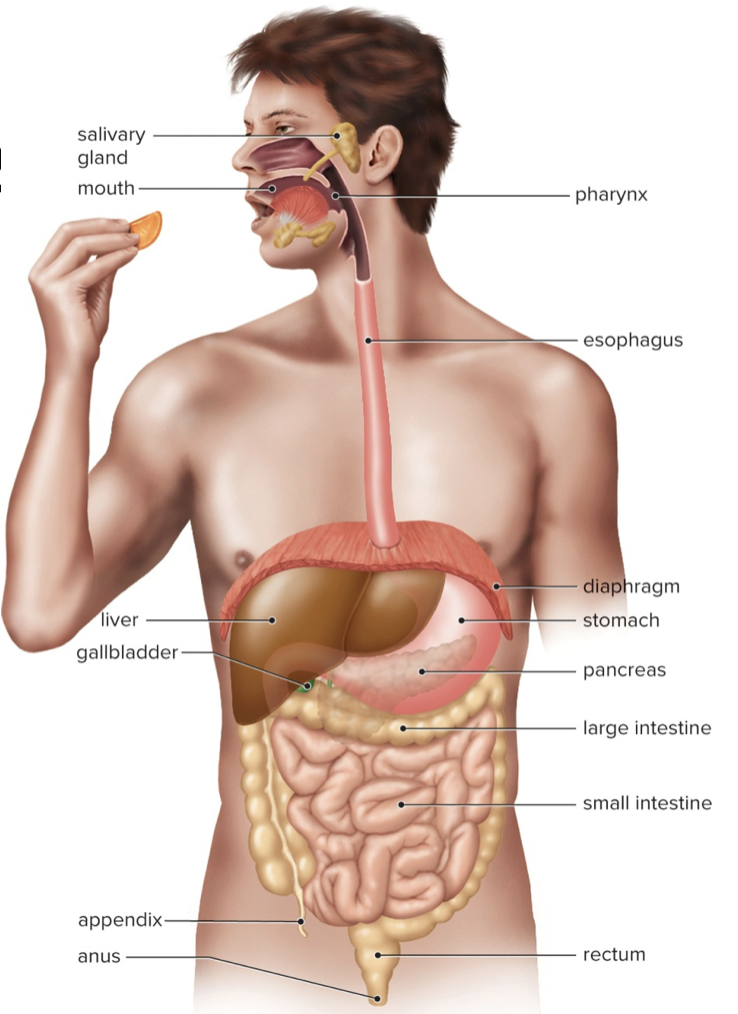
44
New cards
Accessory Organs
Salivary glands – lubricates food and provides enzymes
Liver – produces bile, processes and stores nutrients
Pancreas– produces digestive enzymes for the small intestine, regulates blood sugar levels
Gallbladder – stores bile
Liver – produces bile, processes and stores nutrients
Pancreas– produces digestive enzymes for the small intestine, regulates blood sugar levels
Gallbladder – stores bile
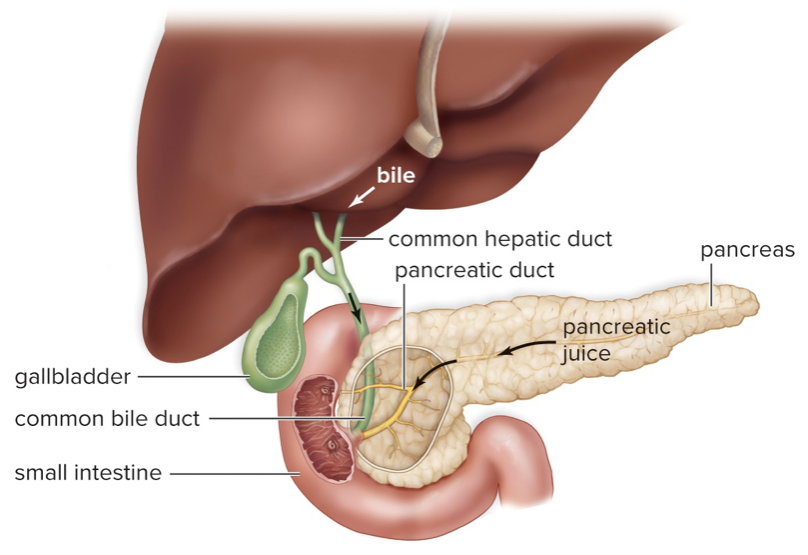
45
New cards
Small Intestine
Folds, Villi: Increase surface area to maximize nutrient absorption
Capillaries inside villi connect small intestine to circulatory system
Lacteals inside villi transport fat-soluble molecules to lymphatic system
Capillaries inside villi connect small intestine to circulatory system
Lacteals inside villi transport fat-soluble molecules to lymphatic system
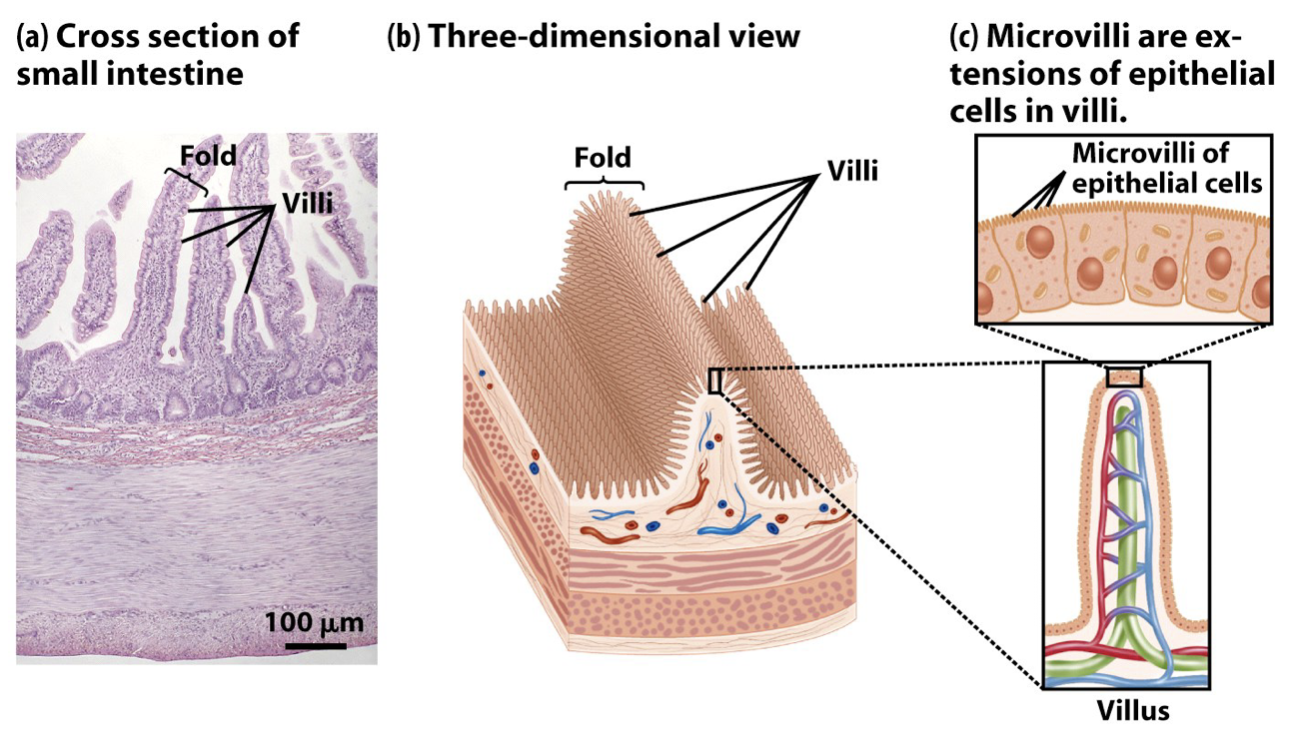
46
New cards
Enzymes
Metabolic catalyst that speed up chemical reactions or allow them to occur at all
Activation Energy: The amount of energy required to make a chemical reaction occur
Enzymes lower activation energy
Activation Energy: The amount of energy required to make a chemical reaction occur
Enzymes lower activation energy
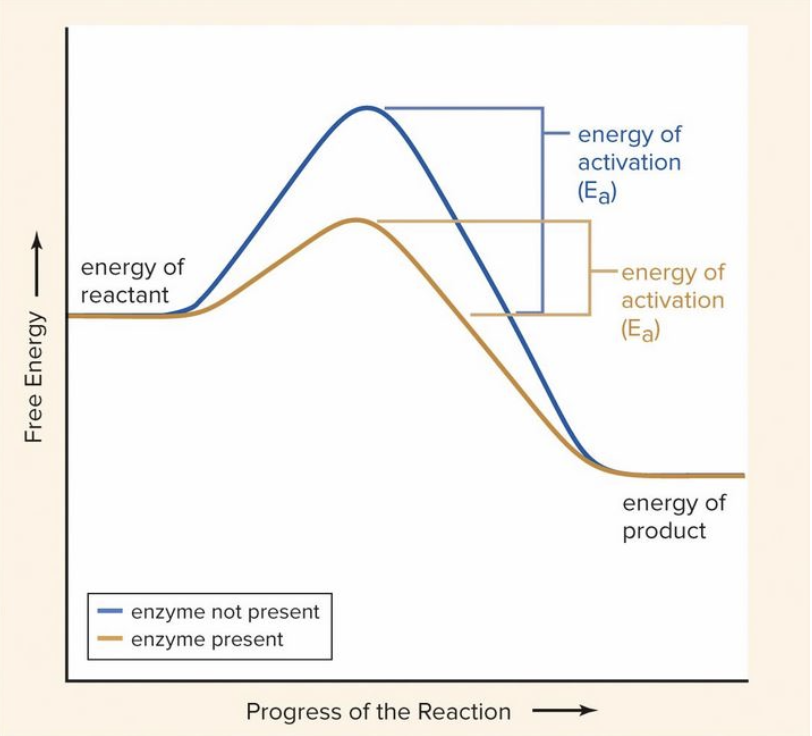
47
New cards
How Enzymes work
1. Substrate (nutrient) binds to active site of enzyme
2. Enzyme changes shape, which changes the shape of the nutrient molecule (thus lowering reaction activation energy)
3. Once reaction is complete, nutrient unbinds from enzyme
2. Enzyme changes shape, which changes the shape of the nutrient molecule (thus lowering reaction activation energy)
3. Once reaction is complete, nutrient unbinds from enzyme
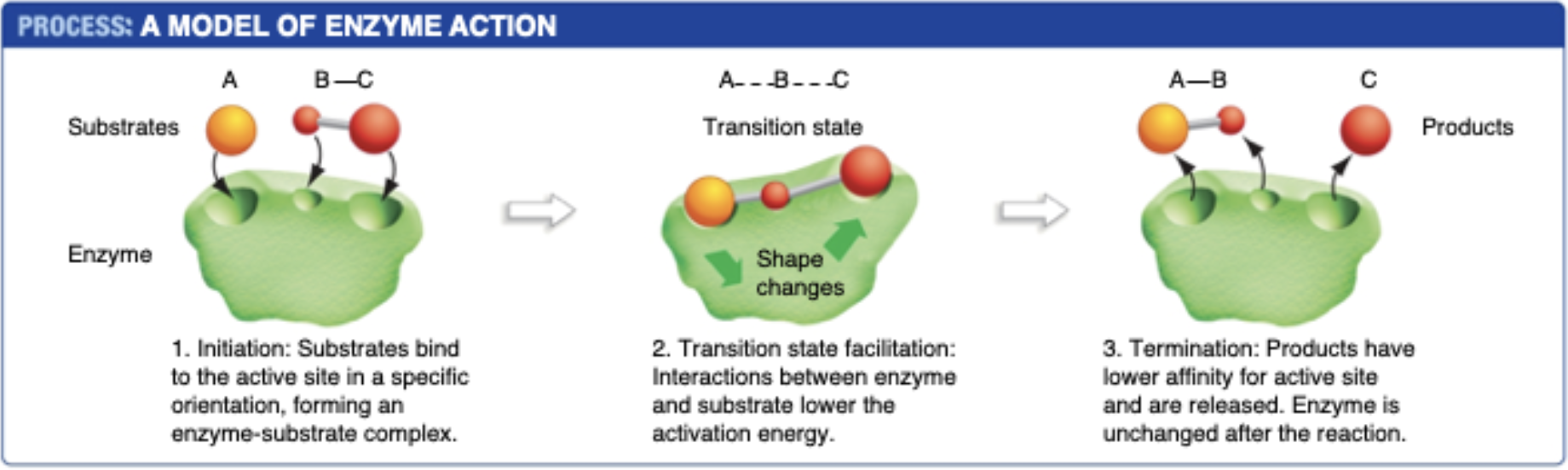
48
New cards
Enzyme Regulation
Conditions can change the shape of the active site and its ability to interact with its substrate
49
New cards
Feedback Inhibition
- Product of the enzyme pathway tells enzyme to stop working
- Only the needed amount of product will be produced
- Only the needed amount of product will be produced
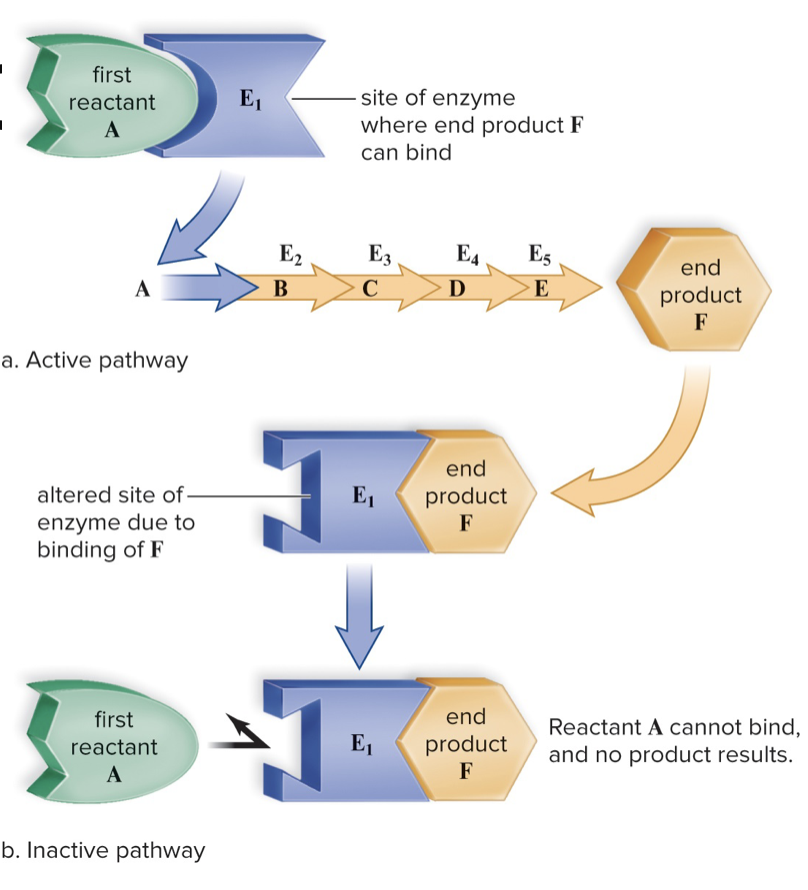
50
New cards
Digestive Enzymes
Break down carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids into molecules that can move into circulatory or lymphatic system
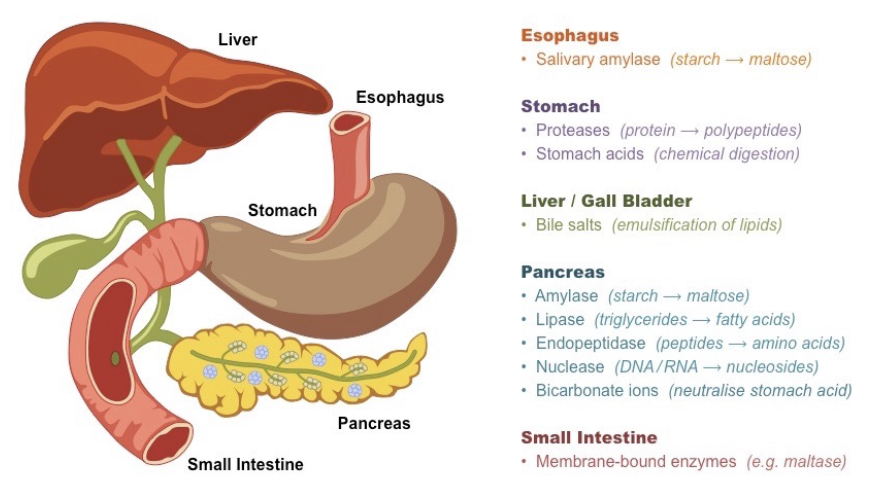
51
New cards
Amylases
- Break down carbohydrates
- Sends simple sugars to blood stream
- Sends simple sugars to blood stream
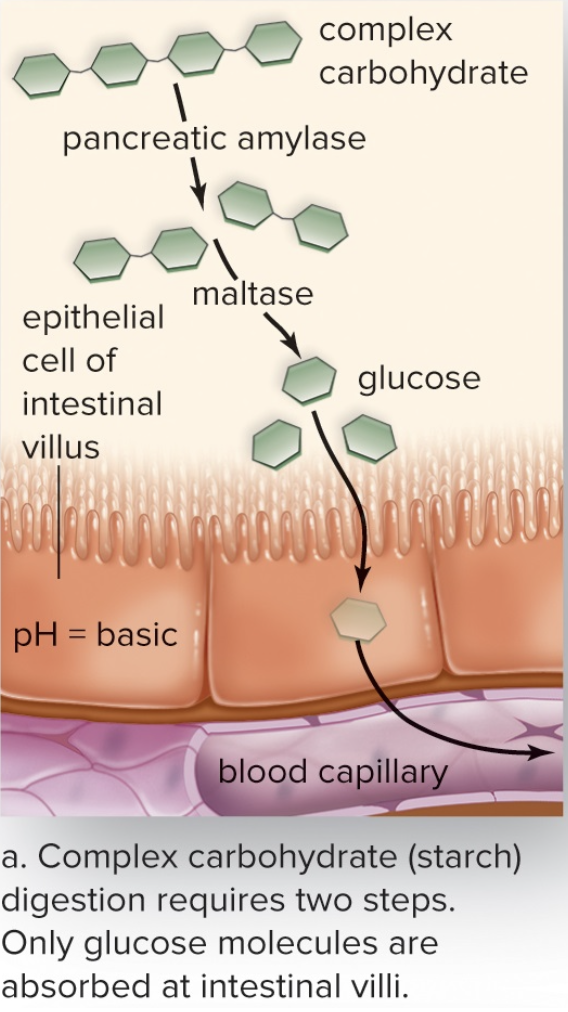
52
New cards
Peptidases
- Break down proteins
- Sends amino acids to blood stream
- Sends amino acids to blood stream
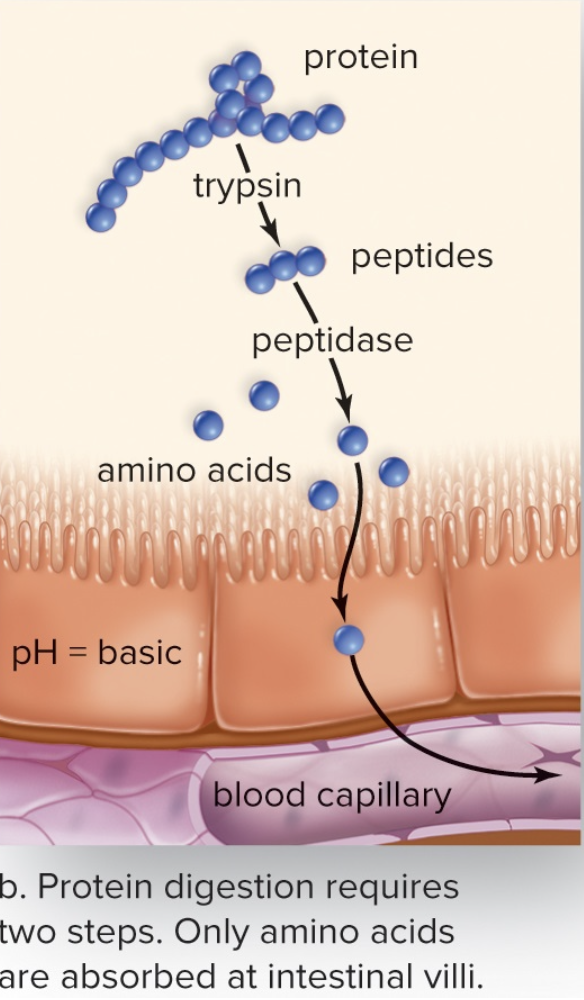
53
New cards
Lipases
- Break down fats
- Sends simple fats (monoglycerides) to lymphatic system
- Sends simple fats (monoglycerides) to lymphatic system
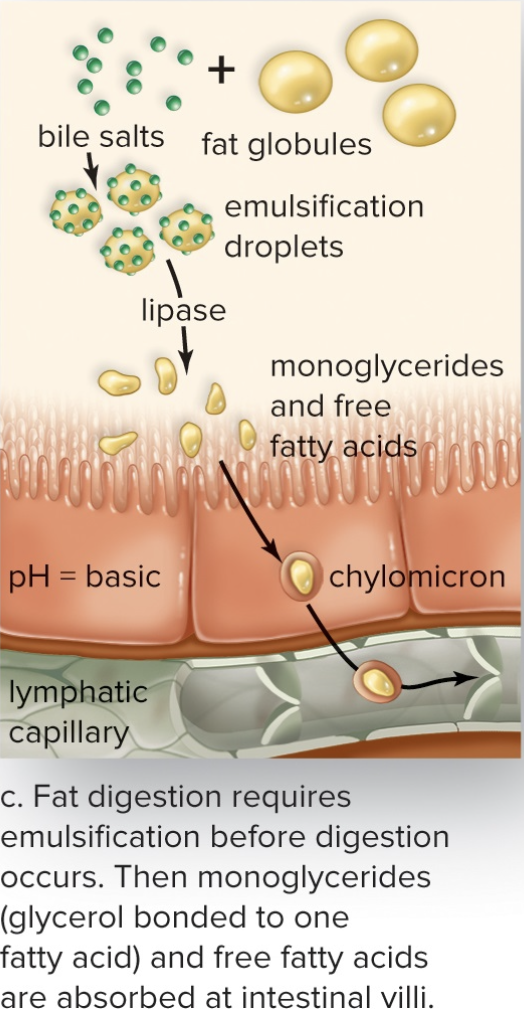
54
New cards
Cells
The smallest unit that still displays all the properties of life
55
New cards
All cells have...
Cytoplasm, Plasma Membrane, DNA, Ribosomes
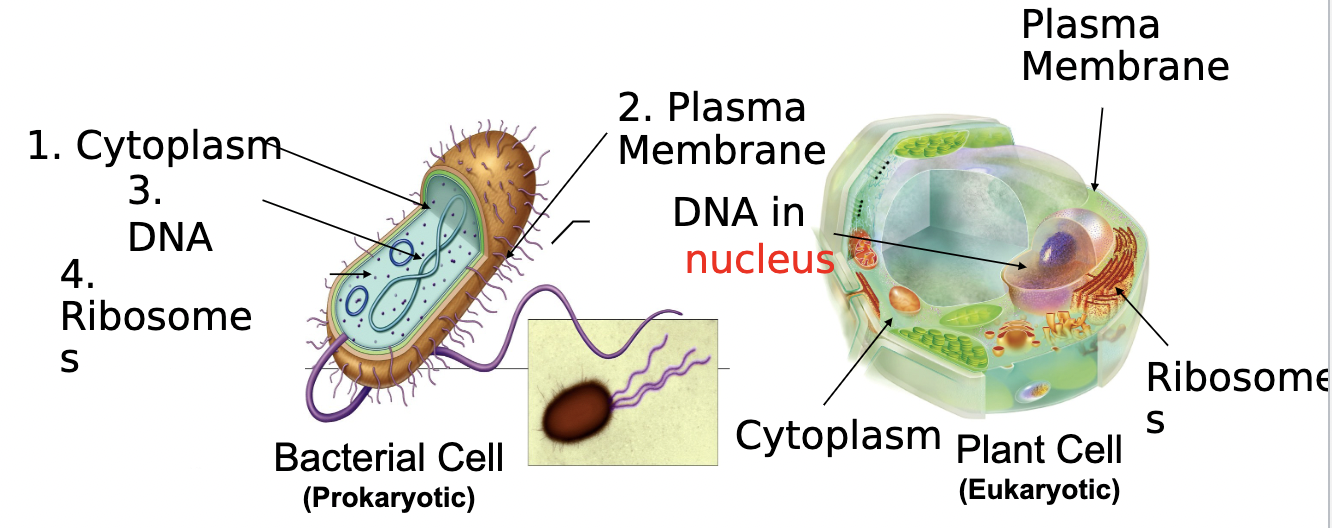
56
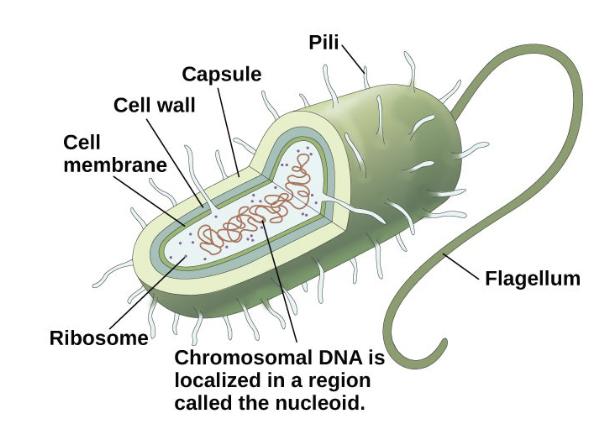
New cards
Prokaryotic Cells
- Simple, single-celled (unicellular) organism
- Lacks a nucleus, or any other membrane-bound organelle
- DNA is found in the nucleoid
- Lacks a nucleus, or any other membrane-bound organelle
- DNA is found in the nucleoid
57
New cards
Prokaryotes: Bacteria and Archaea
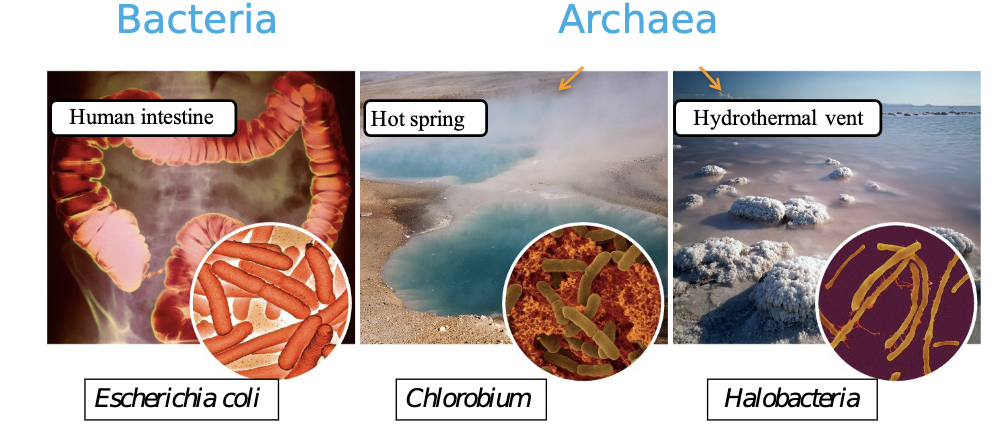
58
New cards
There are how many cells in the body?
- 30 trillion human cells
- 39 Trillion bacteria, archaea, and fungi cells
- That’s more cells than there are stars in the milky way galaxy
- 39 Trillion bacteria, archaea, and fungi cells
- That’s more cells than there are stars in the milky way galaxy
59
New cards
Eukaryotic
Nucleus and membrane bound organelles
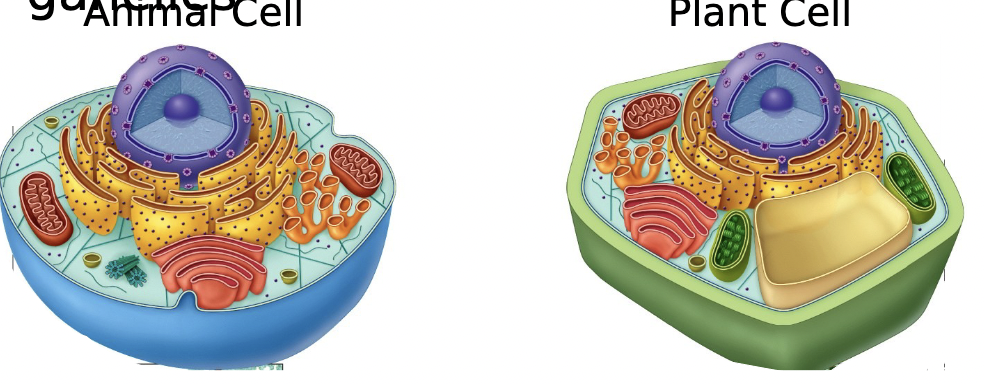
60
New cards
Eukaryotic Cells & Membrane Bound Organelles
- Membrane-bound compartments inside cells with specific functions
- What is the advantage of compartmentalization?
- What is the advantage of compartmentalization?
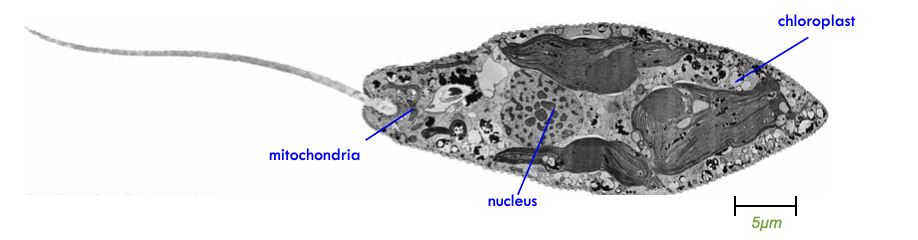
61
New cards
Mitochondria
- Act as all-purpose energy converters
- Harvest energy to be used for cellular functions
- Harvest energy to be used for cellular functions
62
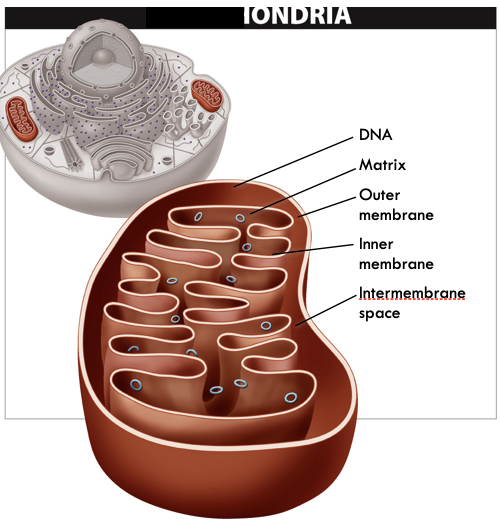
New cards
Mitochondria Structure
- “Bag-within-a-bag”
- Two areas inside: Intermembrane space, Mitochondrial matrix
- Two areas inside: Intermembrane space, Mitochondrial matrix
63
New cards
Origin of Mitochondria
- Symbiosis: Individuals of two different species live in physical contact, often for mutual benefit
- Endosymbiosis: Occurs when an individual of one species lives inside an individual of another species
- Endosymbiosis: Occurs when an individual of one species lives inside an individual of another species
64
New cards
Endosymbiosis
Hypothesis
Mitochondria originated from bacterial cell that took up residence inside another cell (developed by Lynn Margulis)
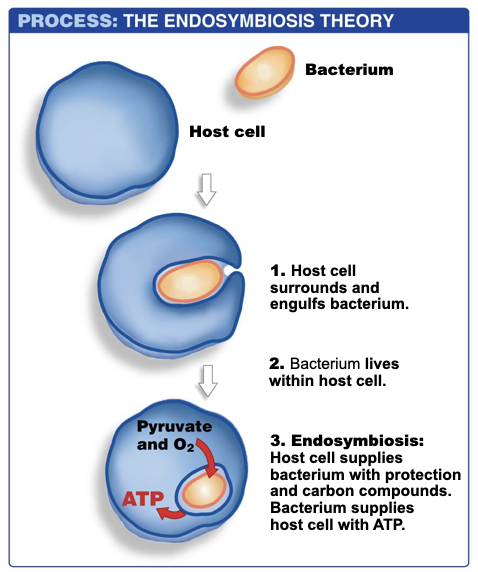
65
New cards
Plasma Membrane
- Defines the boundary of the cell
- Determines the nature of its contact with the environment
- Can exclude, allow in, or remove different substances
- Regulates internal environment of cell
- Made of a phospholipid bilayer
- Determines the nature of its contact with the environment
- Can exclude, allow in, or remove different substances
- Regulates internal environment of cell
- Made of a phospholipid bilayer
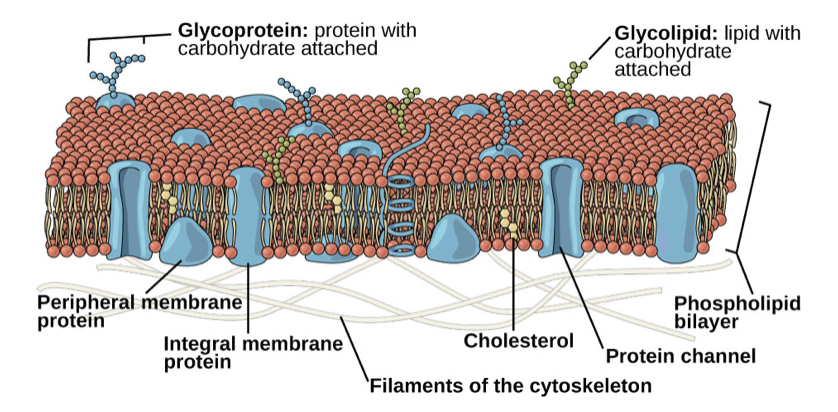
66
New cards
Phospholipid Bilayer Structure in a Cell
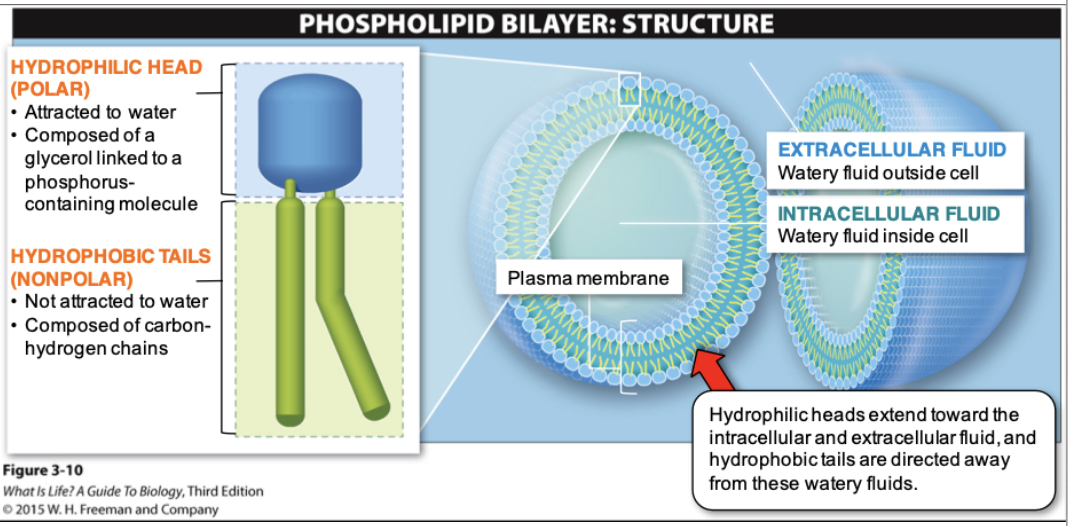
67
New cards
Fluid-Mosaic Model
- Describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components that are able to flow and change position, while maintaining the basic integrity of the membrane
- Phospholipids
- Cholesterol—regulates fluidity based on temperature
- Proteins—serve as channels or pumps, enzymes, structural attachments
- Carbohydrates—on exterior of cell surface
- Phospholipids
- Cholesterol—regulates fluidity based on temperature
- Proteins—serve as channels or pumps, enzymes, structural attachments
- Carbohydrates—on exterior of cell surface
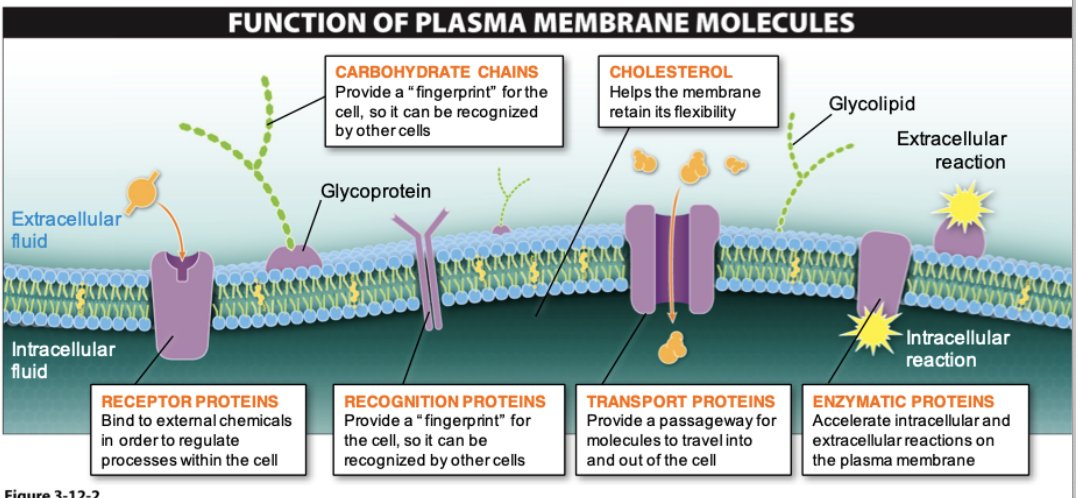
68
New cards
Molecules must move across membranes
- Cells take in food/nutrients, export wastes, and communicate with their environment
- Passive Transport: No energy required
- Diffusion (simple or facilitated)
- Osmosis (water only)
- Active Transport: Energy Required
- Bulk Transport: Special vesicles used to move large quantities at the same time
- Passive Transport: No energy required
- Diffusion (simple or facilitated)
- Osmosis (water only)
- Active Transport: Energy Required
- Bulk Transport: Special vesicles used to move large quantities at the same time
69
New cards
Passive Transport: Diffusion
- Solute: What molecule is being dissolved
- Solvent: What molecule is dissolved in
- Concentration Gradients: Differences in number of molecules solute per mL solvent across a membrane
- Solvent: What molecule is dissolved in
- Concentration Gradients: Differences in number of molecules solute per mL solvent across a membrane
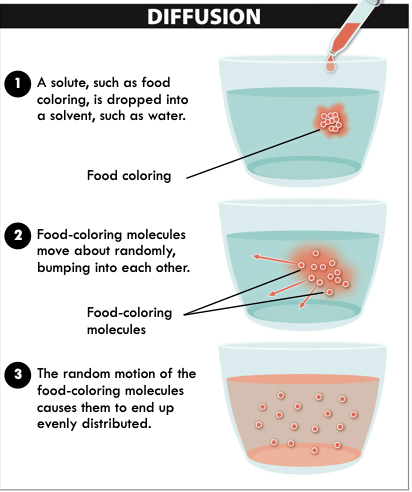
70
New cards
Concentration Gradient
- Molecules will move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration until the concentrations are the same
- This happens without input of energy
- This happens without input of energy
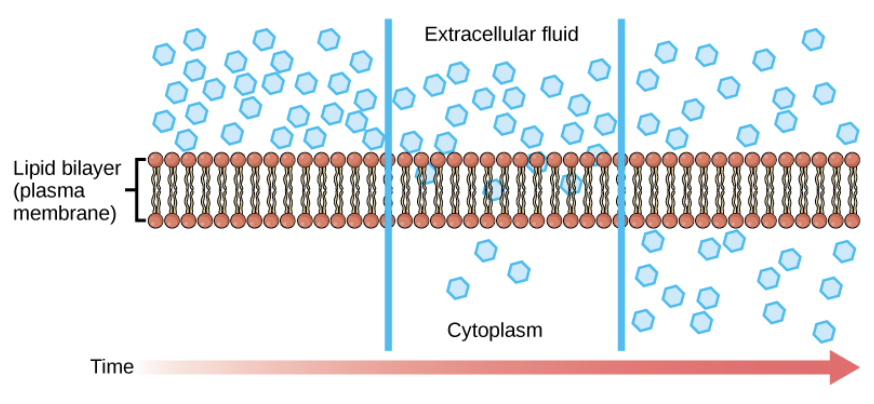
71
New cards
Passive Transport:
Simple Diffusion
Small molecules that carry no charge can pass directly through the membrane
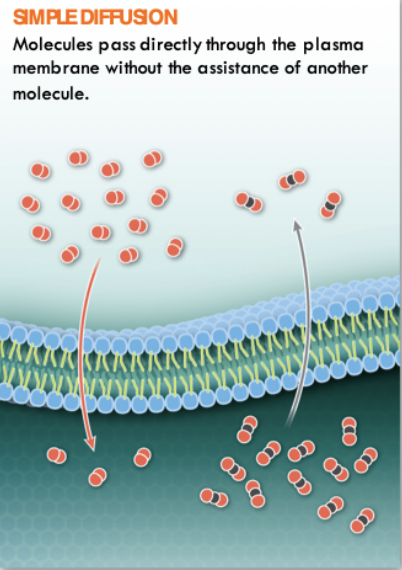
72
New cards
Passive transport:
Facilitated Diffusion
Large or charged molecules must pass through a channel or carrier molecule to get across PM
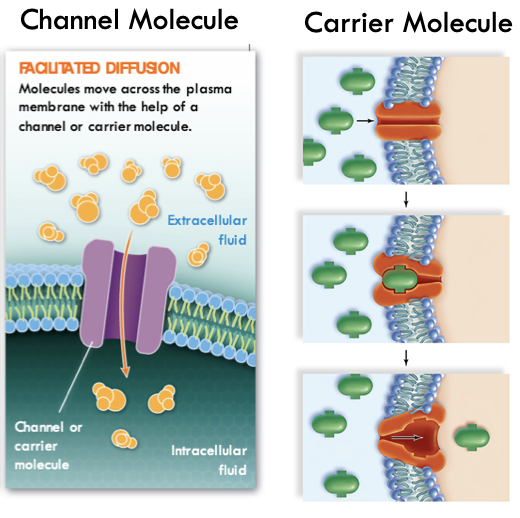
73
New cards
Osmosis
- Passive transport of water
- Water diffuses across a membrane via channel molecule to equalize the concentration of solute inside and outside the cell
- Water diffuses across a membrane via channel molecule to equalize the concentration of solute inside and outside the cell
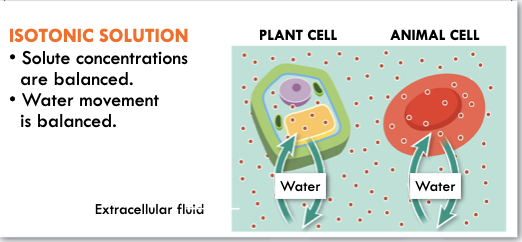
74
New cards
Osmosis Part 2
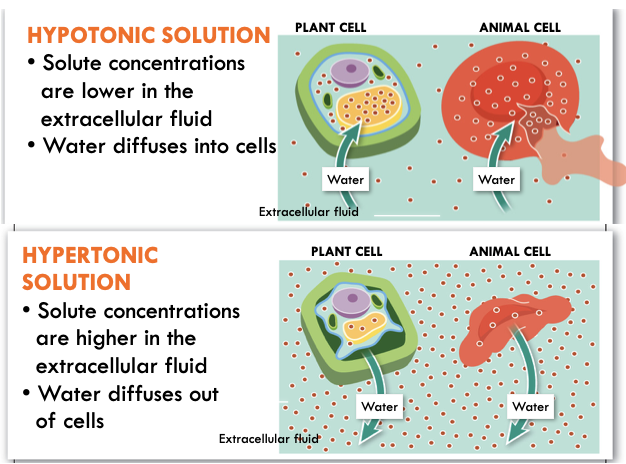
75
New cards
Active Transport
- Movement of molecules across the plasma membrane that requires energy
- Molecules being pumped against their chemical gradients
- Molecules being pumped against their chemical gradients
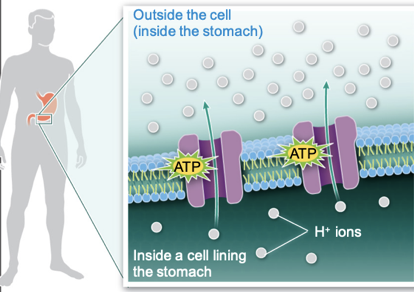
76
New cards
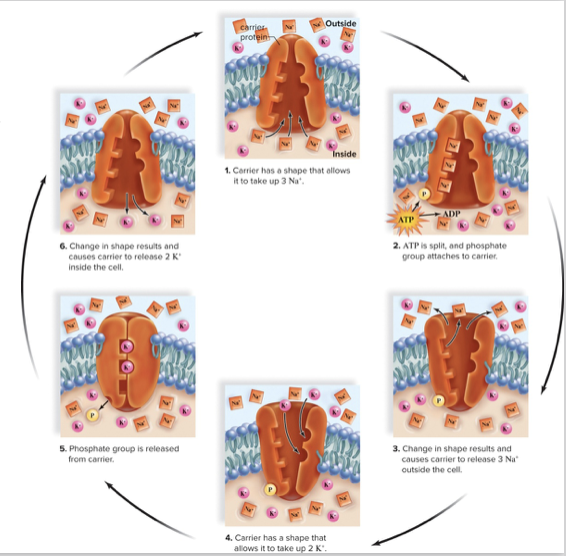
Sodium-Potassium Pump
- Important active transport example
- Creates a charge gradient (or resting potential) that helps maintain cell conditions
- Creates a charge gradient (or resting potential) that helps maintain cell conditions
77
New cards
Bulk Transport:
Endocytosis
- A type of active transport that moves large particles into a cell
- The plasma membrane of the cell forms a pocket around the target particle
- The pocket pinches off from the membrane
- The particle becomes contained in a newly created vacuole formed from the plasma membrane
- The plasma membrane of the cell forms a pocket around the target particle
- The pocket pinches off from the membrane
- The particle becomes contained in a newly created vacuole formed from the plasma membrane
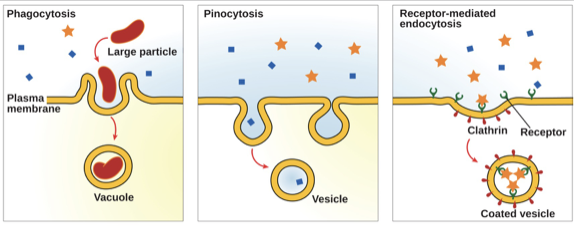
78
New cards
Once Molecule is inside the cell
- Cellular respiration converts sugar molecules to ATP
- Needs Oxygen
- Releases water and Carbon Dioxide
- Needs Oxygen
- Releases water and Carbon Dioxide
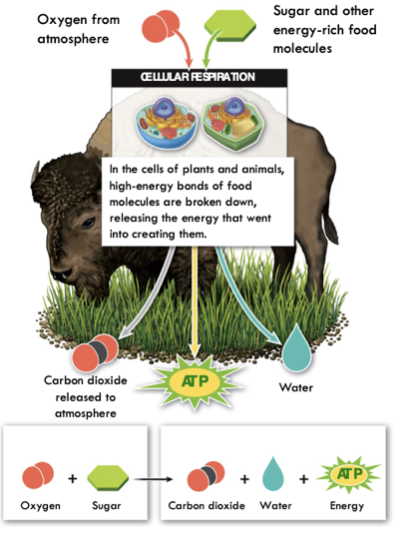
79
New cards
Three steps of cellular respiration
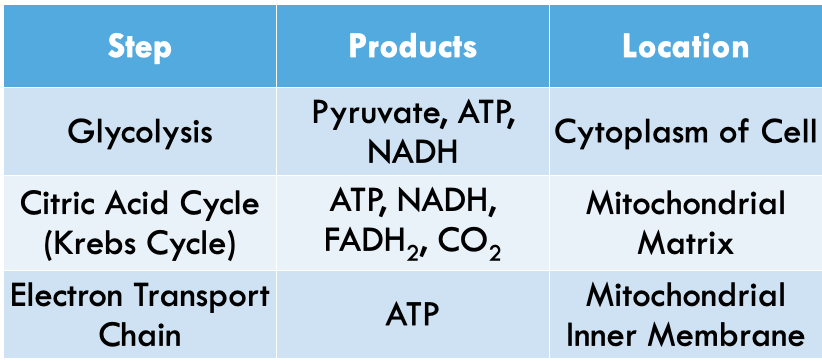
80
New cards
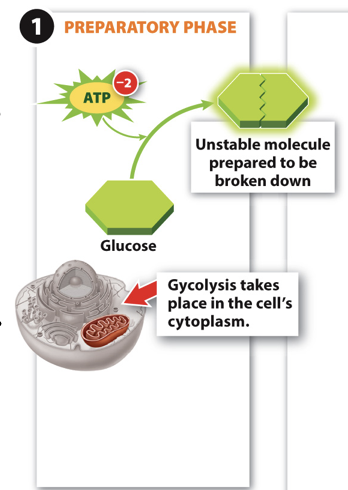
Glycolysis Step 1
- Step 1: ATP is used to destabilize a glucose molecule.
- Makes energy in bonds easier to harvest
- Makes energy in bonds easier to harvest
81
New cards
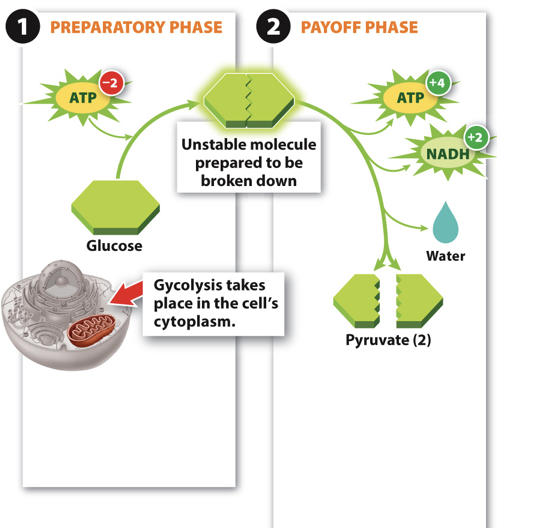
Glycolysis Step 2
- Step 2: Glucose broken in to two pyruvate molecules.
- Energy stored in ATP
- Electrons stored in NADH
- Energy stored in ATP
- Electrons stored in NADH
82
New cards
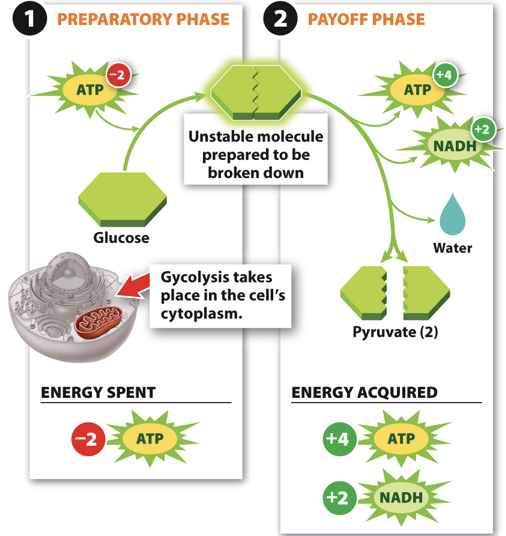
Glycolysis uses...
- Uses 2 ATP
- Results in 4 ATP (2 Net ATP) and 2 NADH and 2 Pyruvate
- For small organisms, this is all they do!
- Larger organisms must harvest more energy from the pyruvate
- Results in 4 ATP (2 Net ATP) and 2 NADH and 2 Pyruvate
- For small organisms, this is all they do!
- Larger organisms must harvest more energy from the pyruvate
83
New cards
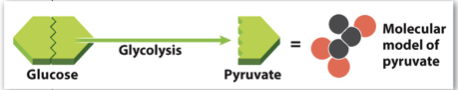
Prep Reactions:
Acetyl-CoA production
- Before proceeding to the citric acid cycle, the molecules needed for that process must be modified
- This occurs in the mitochondrion before the citric acid cycle begins
- This occurs in the mitochondrion before the citric acid cycle begins
84
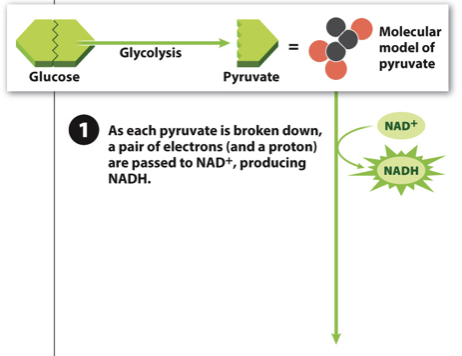
New cards
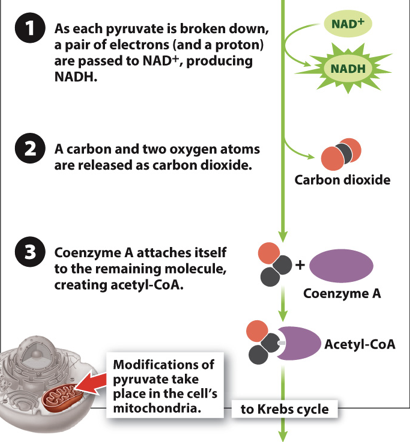
Acetyl-CoA production Step 1
- Step 1: Break down pyruvate, and in the process donate two electrons to NAD+, creating NADH
85
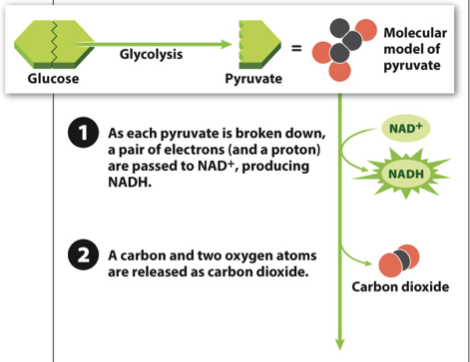
New cards
Acetyl-CoA production Step 2
- Step 2: CO2 is formed and released
- The CO2 diffuses out of the cell into the blood stream, and you eventually breathe it out
- The CO2 diffuses out of the cell into the blood stream, and you eventually breathe it out
86
New cards
Acetyl-CoA production Step 3
Step 3: A molecule called coenzyme-A attaches itself to the remaining portion of pyruvate
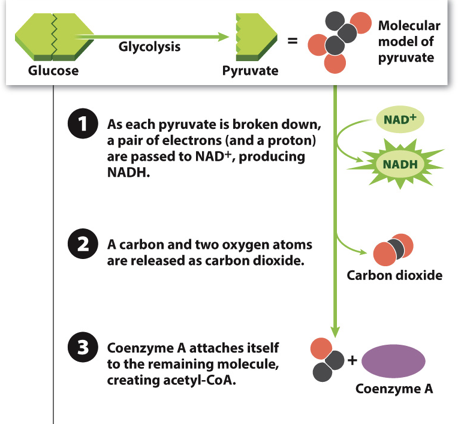
87
New cards
What results from Acetyl-CoA production?
- Resulting molecule, called Acetyl – CoA, is sent to the Citric Acid Cycle
- This happens twice per original glucose molecule
- This happens twice per original glucose molecule
88
New cards
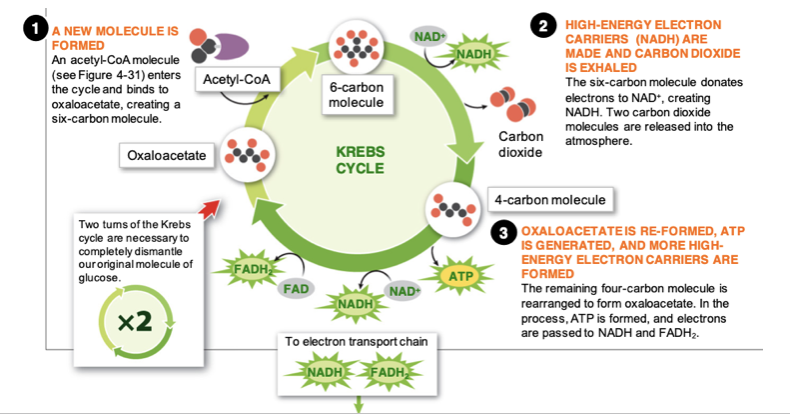
Citric acid cycle (krebs cycle)
1) acetyl-CoA molecule enters the cycle and binds to oxaloacetate, creating a six-carbon molecule.
2) The six-carbon molecule donates electrons to NAD+, creating NADH. Two carbon dioxide molecules are released into the atmosphere.
3) The remaining four-carbon molecule is rearranged to form oxaloacetate. In the process, ATP is formed, and electrons are passed to NADH and FADH2.
2) The six-carbon molecule donates electrons to NAD+, creating NADH. Two carbon dioxide molecules are released into the atmosphere.
3) The remaining four-carbon molecule is rearranged to form oxaloacetate. In the process, ATP is formed, and electrons are passed to NADH and FADH2.
89
New cards
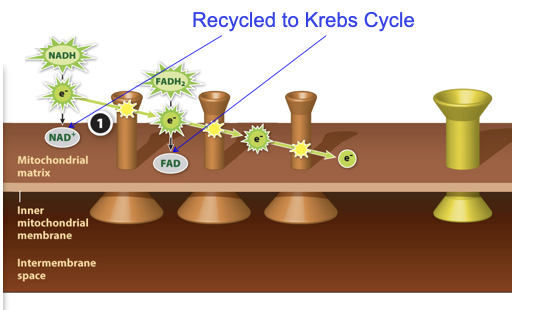
Mitochondrial electron transport chain
Recall:
- Glycolysis stores high-energy electrons in NADH
- The Citric Acid Cycle stores high-energy electrons in NADH and in FADH2
- How to extract that energy?
Transport chain used to harvest energy stored in electrons in NADH and FADH2
- Glycolysis stores high-energy electrons in NADH
- The Citric Acid Cycle stores high-energy electrons in NADH and in FADH2
- How to extract that energy?
Transport chain used to harvest energy stored in electrons in NADH and FADH2
90
New cards
Mitochondrial electron transport chain Step 1
At each step in the electron transport chain’s sequence of handoffs, the electrons fall to a lower energy state, releasing a little bit of energy.
91
New cards
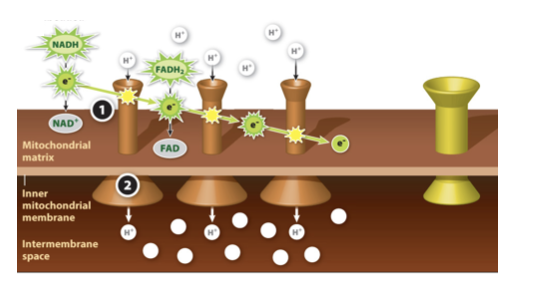
Mitochondrial electron transport chain Step 2
The energy is used to power proton pumps, which pack hydrogen ions from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space.
92
New cards
Mitochondrial electron transport chain Step 3
At the end of the chain, the lower energy electrons are handed off to oxygen, which then combines with free H+ ions to form water.
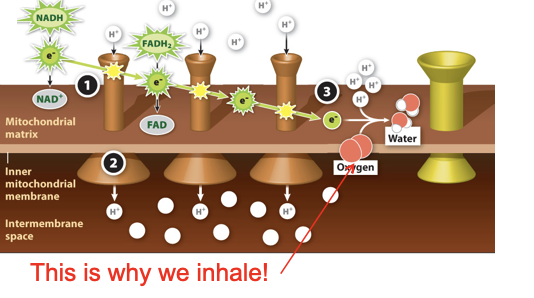
93
New cards
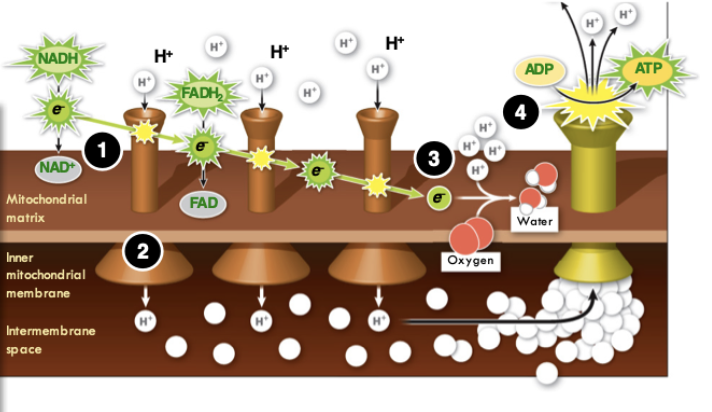
Mitochondrial electron transport chain Step 4
The protons rush back to the mitochondrial matrix with great kinetic energy, which can be used to build ATP
94
New cards
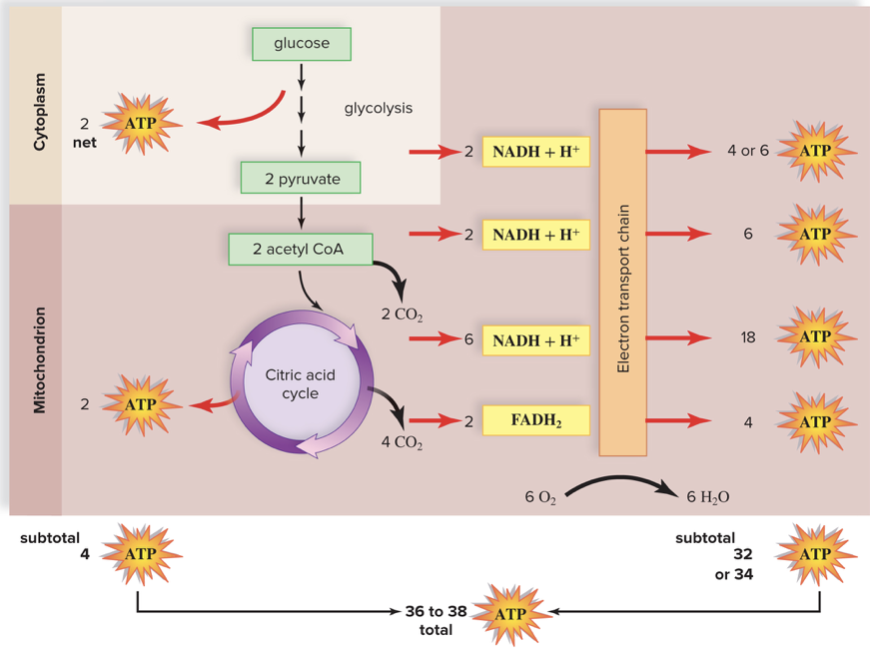
How much ATP per glucose molecule?
36-38 total
95
New cards
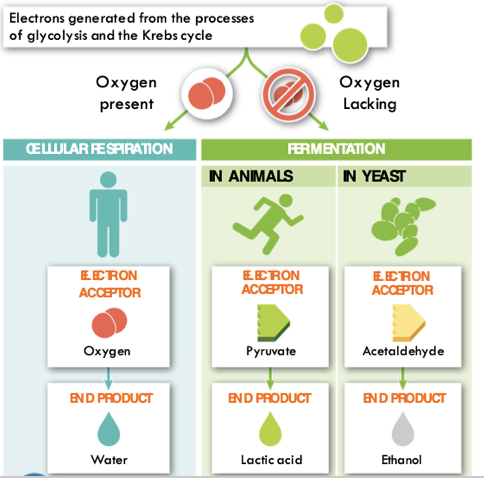
Alternative pathways of energy acquisition
- Aerobic Respiration requires oxygen
- Anaerobic Respiration (Fermentation) does not require oxygen
- Cells performing anaerobic respiration must use another molecule as the final electron acceptor
- Anaerobic Respiration (Fermentation) does not require oxygen
- Cells performing anaerobic respiration must use another molecule as the final electron acceptor
96
New cards
What happens if our bodies fall behind in delivering oxygen?
Lungs ➡ Bloodstream ➡ Cells ➡ Mitochondria
- Many organisms have a backup method for breaking down sugar when oxygen is not present
- Many organisms have a backup method for breaking down sugar when oxygen is not present
97
New cards
Alternative
energy pathways
Lactic acid build up in muscles causes cramping and burning
98
New cards
Fermentation in Yeast
- Sugars from grapes yields wine
- Sugars from barley yields beer
- Sugar from potatoes yields vodka
- Sugars in dough yields bread
- Sugars from barley yields beer
- Sugar from potatoes yields vodka
- Sugars in dough yields bread
99
New cards
Alternative energy
sources
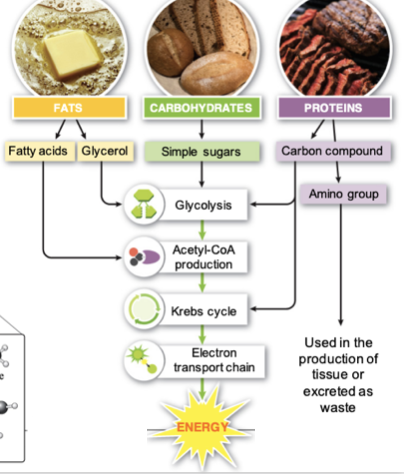
100
New cards
Energy drinks contain...
- No carbohydrates, proteins or fats
- contain vitamins, minerals, food additives, and stimulants
- NOT considered food by the FDA
- contain vitamins, minerals, food additives, and stimulants
- NOT considered food by the FDA