Diencephalon
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
what does the pineal gland do?
it is an endocrine organ. it synthesizes melatonin, controls sleep/wake cycle, and regulates the onset of puberty
two thalami are joined by the
massa intermedia
is the massa intermedia white or gray matter?
gray
what are the three broad areas of the thalamus? what are the separated by?
anterior, lateral, and medial. they are separated by the internal medullary lamina
what are the anterior and medial thalamus involved in?
visceral, emotional, and limbic systems
what is the lateral thalamus involved in?
somatic sensory and motor function
where are the reticular nuclei?
goes all the way around the thalamus
list the input, output, and the function: VPL
input: dorsal column/spinothalamic
output: postcentral gyrus
function: somesthesis (body perception)
list the input, output, and the function: VPM
input: trigeminal system
output: postcentral gyrus
function: somesthesis (body perception)
list the input, output, and the function: MGN
input: inferior colliculus
output: temporal lobe
function: hearing
list the input, output, and the function: LGN
input: retina
output: occipital lobe
function: vision
what are the specific sensory nuclei?
VPL (somesthesis), VPM (somesthesis), MGN (hearing), LGN (vision)
what are the specific motor relay nuclei?
VL, VA (both involved in motor planning; extrapyramidal)
what are the specific association nuclei of the thalamus?
anterior, DM, posterior, pulvinar
list the input, output, and the function: anterior
input: hypothalamus
output: cingulate
function: limbic
list the input, output, and the function: DM
input: amygdala
output: prefrontal cortex
function: limbic
list the input, output, and the function: posterior
input: anterolateral system
output: cingulate and association cortices
function: pain
list the input, output, and the function: pulvinar
input: superior colliculus
output: temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes
function vision
what are the non specific nuclei of the thalamus?
midline, intralaminar, and reticular
list the input, output, and the function: midline
input: reticular formation
output: entire cortex
function: arousal/limbic
list the input, output, and the function: intralaminar
input: motor cortex/basal ganglia
output: striatum and cortex
function: motor integration
list the input, output, and the function: reticular
input: cortex and brainstem
output: thalamus
function: thalamic modulation
pure sensory loss without weakness, pain. contralateral. pain on mild touch, made worse by stress, temperature, etc
thalamic infarction (Dejerine-roussy central pain syndrome)
which thalamic nuclei have inputs from the cerebellum?
VA/VL
the projection fibers that make up the corona radiata also radiate out of the brain stem via the ___
internal capsule
what are the ascending sensory pathways en route to the thalamus?
medial lemniscus, spinothalamic/trigeminothalamic tracts, cerebellothalamic fibers from dentate
what structure is the main highway to/from the cortex?
the internal capsule
which tract is associated with the genu of the internal capsule?
slurred speech, right sided weakness, dysarthria and right hemipledia. normal exam except right facial weakness sparing the forehead, dysarthria, right upgoing plantar response
internal capsular stroke
hallucinations and somolence. not drug,sleep, or psych related. what nucleus could be involved
pulvinar
describe pituitary development
a bulb grows upward from the roof of the mouth (rathke’s pouch) that develops into the anterior pituitary. another bulb grows from the diencephalon that becomes the posterior pituitary gland. in typical development, the rathke/anterior connection disconnects
benign, epithelium lined intrasellar cysts that are remnants of the rathke pouch. can present with headache, visual impairment, or hypothalamic dysfunction, but are usually asymptomatic
rathke’s cleft cyst
adenohypophysis vs neurohypophysis
adenohypophysis - anterior pituitary gland
neurohypophysis - posterior pituitary gland
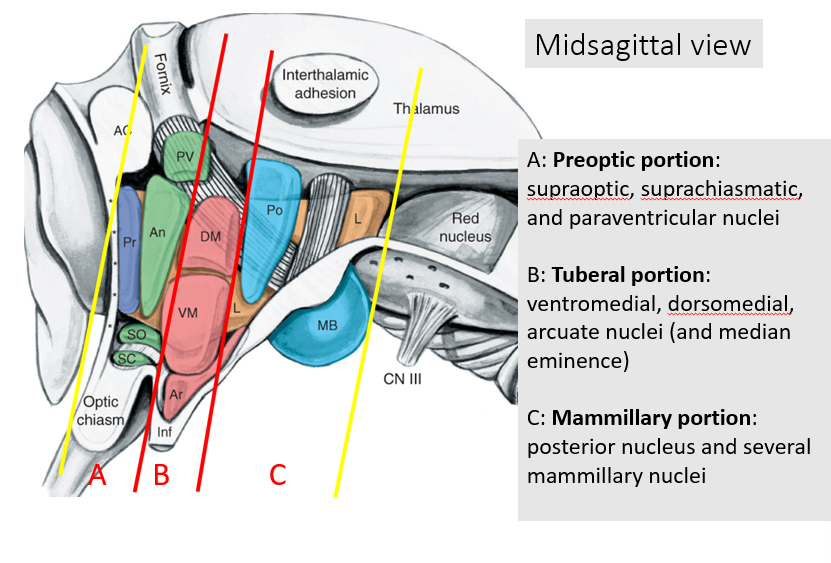
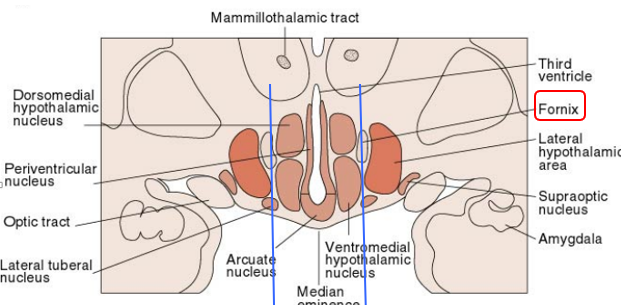
what are the regions of the hypothalamus?
anterior/preoptic - supraoptic, suprachiasmatic, and paraventricular nuclei
tuberal region - ventromedial, dorsomedial, arcuate nuclei
posterior region - posterior nucleus and several mammillary nuclei
___ is a system of blood vessels in the microcirculation at the base of the brain connecting the hypothalamus with the anterior pituitary
hypophyseal portal veins
prolactin, gonadotropic hormones (FSH and LH), TSH, ACTH, and growth hormone are released by
anterior pituitary gland
oxytocin and vasopressin are released by
posterior pituitary
the fornix divides the hypothalamus into what regions
medial and lateral
what is the major output tract of the hippocampus?
the fornix
what are the functions of the hypothalamus?
autonomic ners
central diabetes insipidus, hyperprolactinemia, precocious puberty, and growth defects are all disorders of the
hypothalamus
how does the hypothalamus regulate the autonomic nervous system?
anterior area projects to the brainstem parasympathetic nuclei
posterior area influences sympathetic nuclei through projections to lateral horn
what are the hormone production functions of the hypothalamus?
supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei produce oxytocin and vasopressin, which is transported to the posterior pituitary for release
where are oxytocin and vasopressin produced?
in the hypothalamus (supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei)
circadian rhythm regulation
retina → suprachiasmatic nucleus (hypothalamus) → pineal gland
pineal gland function
produces melatonin, which affe
how does the hypothalamus regulate temperature?
posterior nucleus conserves heat (chills)
anterior nucleus dissipates heat (sweating)
how does the hypothalamus regulate feeding behaviors
arcuate nuc monitors
lateral nuc induces
ventromedial nuc inhibits
paraventricular nuc integrates
what area is the satiety center?
ventral medial hypothalamus
what area is the feeding center?
lateral hypothal

lesions to the ___ result in inability to stop eating, while lesions to the ___ result in refusal to eat
lesions to the ventral medial hypothalamus result in inability to stop eating, while lesions to the lateral hypothalamus result in refusal to eat
the ___ is the “AC” of the brain, while the "___ is the “heater”
anterior hypothalamus, posterior hypothalamus
lesions to the anterior hypothalamus results in
hyperthermia
lesions to the posterior hypothalamus result in
hypothermia (if in cold)
what is pituitary apoplexy?
bleeding into or impaired blood supply of the pituitary gland. can result in sudden sharp headache behind eyes. common during or after pregnancy
hypothyroidism (physical signs)
goiter. weight gain, tiredness, dry skin, depression, constipation due to slowed metabolism.
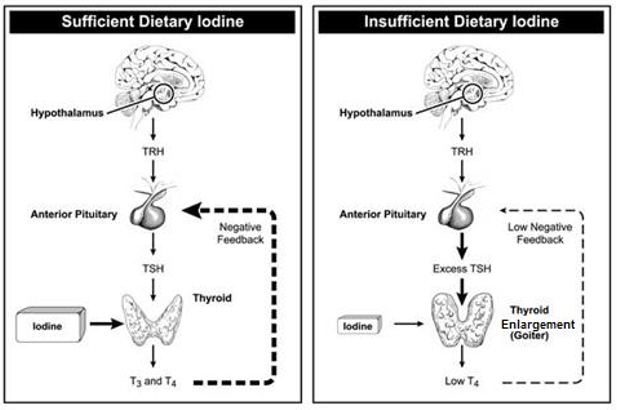
what results in goiter?
not enough iodine signals the thyroid to send less negative feedback to the pituitary, which results in excess TSH and thyroid growth
explain the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid feedback loop
the hypothalamus releases TRH to be received by the anterior pituitary
the anterior pituitary gland releases TSH to be received by the thyroid
if there is enough iodine present, the thyroid produces T3 and T4, which sends negative feedback to the anterior (keeps it from producing excess TSH)
what is acromegaly?
a hormonal disorder that results from too much growth hormone in the body after puberty. enlarged hands and feet, gradual changes in the face (larger jaw, brow, nose, lips, etc.
overeating causes inflammation in the ___, which inhibits neurogenesis
hypothalamus
NPY/AgRP neurons in the ___ nucleus stimulate appetite and lower metabolism/weight gain
arcuate
leptin/ghrelin
leptin - fullness
ghrelin - hunger
diencephalic syndrome
a rare neurological disorder seen in infants and children and characterized by failure to thrive and severe emaciation despite normal intake. strabismus, proptosis