bio midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/280
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:04 PM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
281 Terms
1
New cards
How many bones are in the appendicular skeleton?
126
2
New cards
Parts that make up the appendicular skeleton
The pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, the upper and lower limbs.
3
New cards
The Pectoral girdle consists of
The clavicle and scapula
4
New cards
Clavicle
Collar bone that attaches to the sternum and scapula.
5
New cards
Scapula
Shoulder blade that attaches to the clavicle and upper limb bone.
6
New cards
What forms the shoulder?
head of humerus and glenoid cavity of scapula
7
New cards
Pelvic Girdle is composed of
Two os coxa
8
New cards
Each os coxa has?
Allium, Ischium and Pubic bone
9
New cards
The ilium attaches to
The sacrum at the iliac crest.
10
New cards
What joins the 2 pubic bones
Pubic symphysis
11
New cards
Joints of the pelvic girdle
The sacroiliac joint, pubic symphsis, acetabulum
12
New cards
What is the acetabulum?
The socket that attaches to the head of the femur.
13
New cards
Parts of the arm( upper limb)
Humerus, Radius, Ulna, Carpals, Metacarpals and phalanges.
14
New cards
Parts of the leg (lower limbs)
Femur, Tibia, Fibula, Patella, Tarsals, Calcaneous, Metatarsals and plalanges
15
New cards
What makes up the integumentary system?
Skin, Hair, Glands, Nails, Nerves
16
New cards
The skin consists of:
The Dermis and Epidermis
17
New cards
Characteristic of the Epidermis
-Made up of keratinized Squamous epithelium
-Made up of epithelial tissues from the ectoderm.
-Avascular
-Has thick and thin skin.
-Made up of epithelial tissues from the ectoderm.
-Avascular
-Has thick and thin skin.
18
New cards
The Layers of the Epidermis
stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum.
19
New cards
statum basale
Bottom layer of the epidermis that is made of melanocyte and keratinocytes and gets its nutrients from the blood.
20
New cards
stratum spinosum
Epidermis Layer that's several layers thick and has limited cell division happening.
21
New cards
stratum granulosum
Epidermis layer that is 3-5 layers with dark granules and no blood supply.
22
New cards
Stratum Lucidium
epidermis layer with 2-3 flat, dead cell layers that's very apparent in thick skin.
23
New cards
stratum corneum
The glycolipid outermost layer of the epidermis that protects and retains moisture.
24
New cards
Thin SKin
Layer of the skin that has hair follicles, sweat and sebaceous glands.
25
New cards
Thick Skin
Has no hair follicles, no hair or sebaceous glands, found on the palm or sole of feet.
26
New cards
Characteristics of the Dermis
-Made of connective tissue proper.
-Consists of fibroblasts, fibrocytes and matrix.
-Consists of fibroblasts, fibrocytes and matrix.
27
New cards
The Two layers of the Dermis
The reticular layer and the papillary layer.
28
New cards
The Papillary Layer
Vascular layer of the dermis made of loose, areolar connective tissue and has dermal papillae and dermal ridges.
29
New cards
dermal papillae
Upward fingerlike extensions that go in the epidermis.
30
New cards
dermal ridges
Structure below the dermal papillae that forms finger prints and has sweat pores.
31
New cards
The Reticular Layer
Furthest layer that's made of dense irregular tissue that makes up most of the dermis.
32
New cards
What forms after the dermis is torn and white scars (striae) forms?
Stretch Marks
33
New cards
Structures in the Dermis
Hair follicles, Sebaceous and Sudireferous glands, Sensory receptors and Arrector Pili Muscles
34
New cards
Contraction of erector pili forms
Goosebumps
35
New cards
Hypodermis
the connective tissue layer under the dermis that stores fat. and
36
New cards
Where in the skin is Melanin found
Between the stratum basale and Stratum Spinosum.
37
New cards
Structures derived from the epidermis
Hair, Nails and Exocrine glands (sebaceous, sudoriferous, ceruminous and mammary)
38
New cards
Characteristics of Hair
-Made of dead keratinized cells.
-Hair shaft is above skin surface.
-Hair root is below skin surface.
-Hair shaft is above skin surface.
-Hair root is below skin surface.
39
New cards
hair follicle
sac within which each hair grows
40
New cards
hair papilla
Small piece of dermal tissue that protrudes into the hair bulb.
41
New cards
root hair plexus
Hair nerve ending
42
New cards
Nails are made of
keratinized epidermal cells found in the stratum corneum
43
New cards
sebaceous glands
Gland that produces sebum/oil to lubricate the hair and skin.
44
New cards
ceruminous glands
Modified sweat glands that makes ear wax.
45
New cards
mammary glands
Modified sweat glands that produces milk.
46
New cards
suderiferous glands
Gland that produces sweat, which cools the body, works as antibiotic( lysozyme) and removes waste.
47
New cards
cutaneous sense receptors
Nerve endings found in the skin that respond to stimuli.
48
New cards
touch receptors
Nerve endings that detect touch on your skin
49
New cards
Example of touch receptors
Meissner's corpuscles
50
New cards
pressure receptors
Nerve endings that respond to pressure on your skin.
51
New cards
Example of Pressure receptors
Pacinian corpules
52
New cards
Thermoreceptors
Nerve endings that detects cold and hot.
53
New cards
Nociceptors
Nerve endings that detect pain
54
New cards
frontal bone
Name this bone.
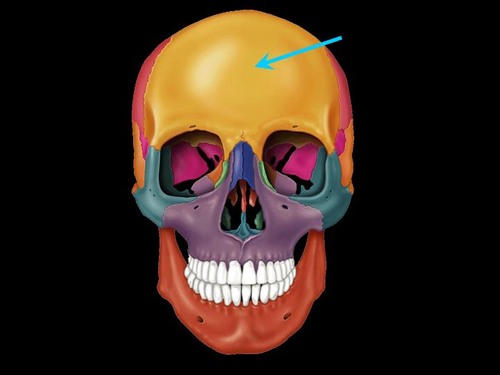
55
New cards
parietal bone
Name this bone.
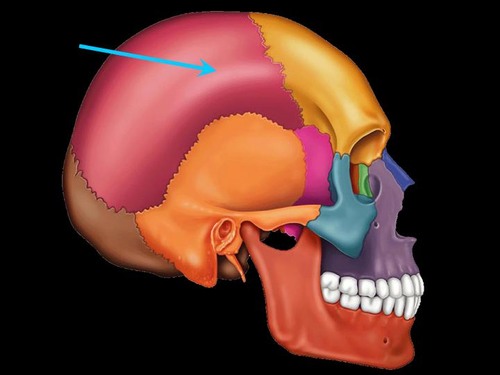
56
New cards
temporal bone
Name this bone.
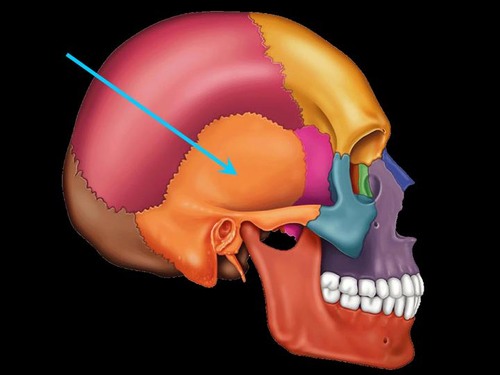
57
New cards
occipital bone
Name this bone.
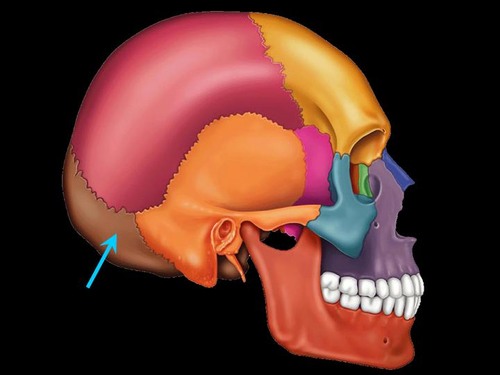
58
New cards
sphenoid bone
Name this bone.
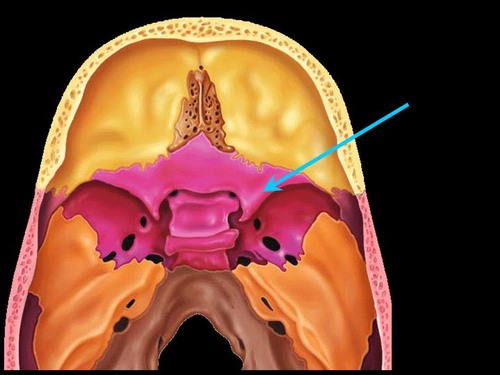
59
New cards
ethmoid bone
Name this bone.
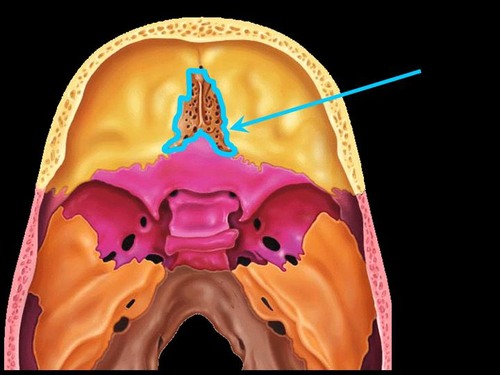
60
New cards
mandible
Name this bone.
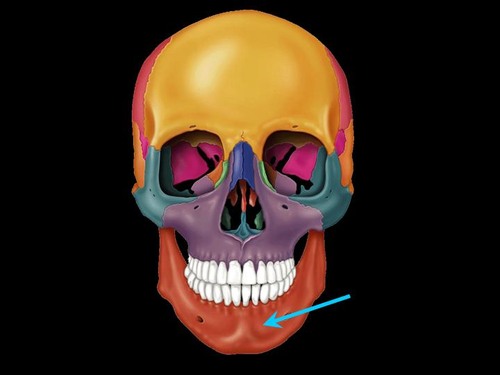
61
New cards
maxilla
Name this bone.
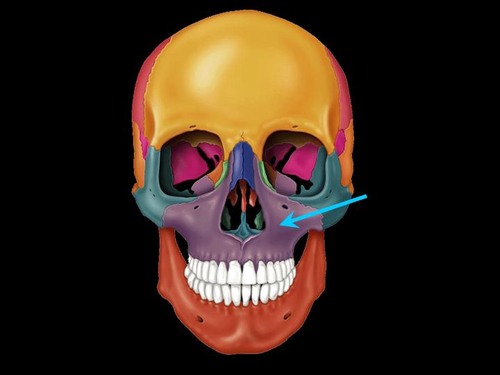
62
New cards
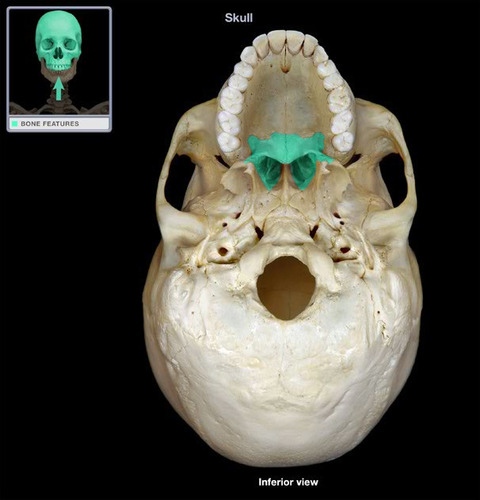
palatine bone
Name this bone.
63
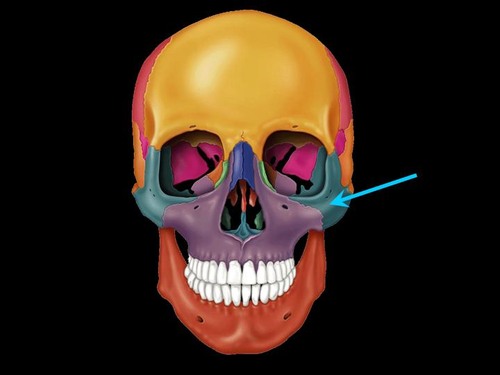
New cards
zygomatic bone
Name this bone.
64
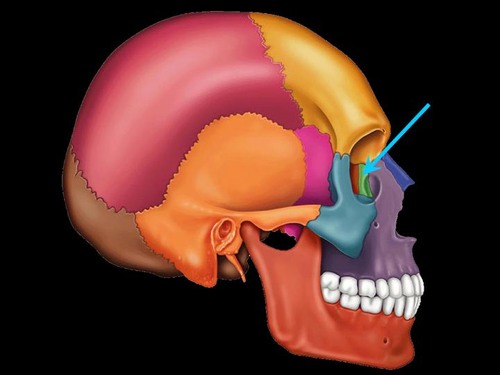
New cards
lacrimal bone
Name this bone.
65
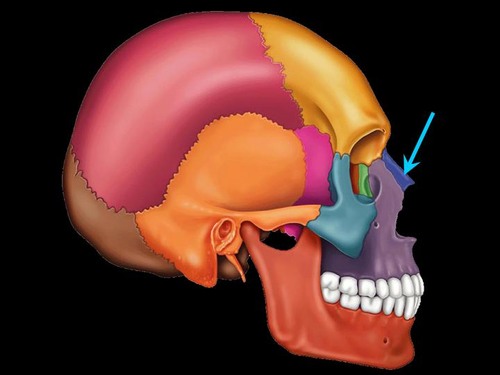
New cards
nasal bone
Name this bone.
66
New cards
vomer
Name this bone.
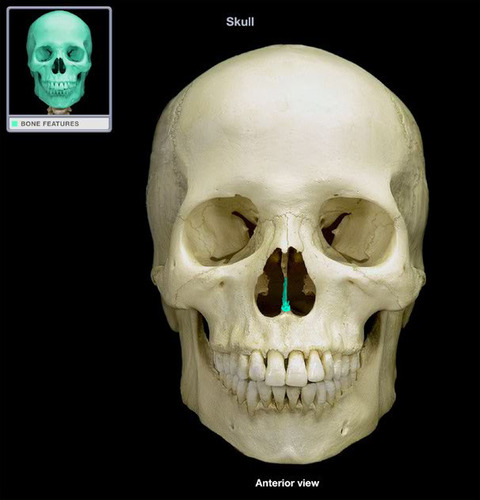
67
New cards
sagittal suture
Name the structure.
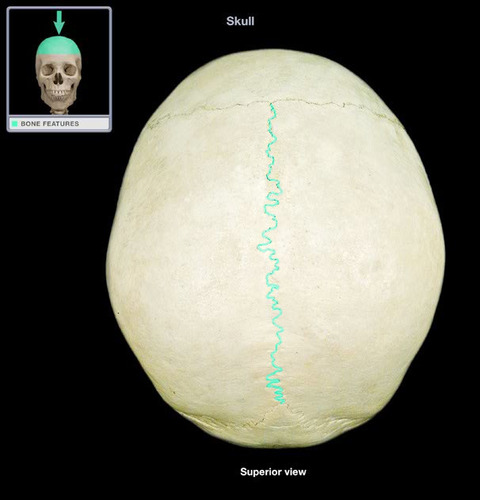
68
New cards
coronal suture
Name the structure.
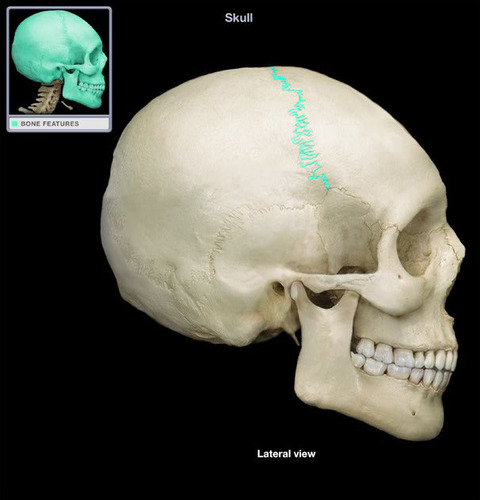
69
New cards
lambdoidal suture
Name the structure.
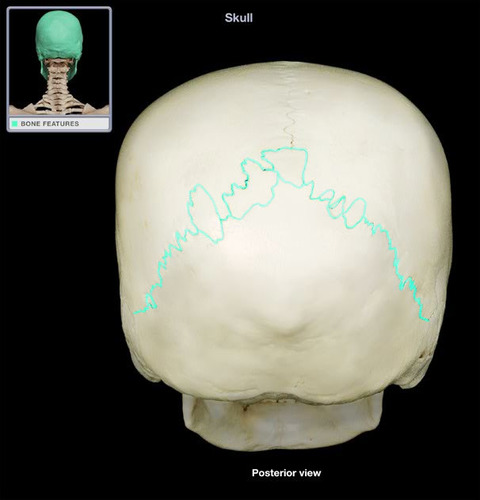
70
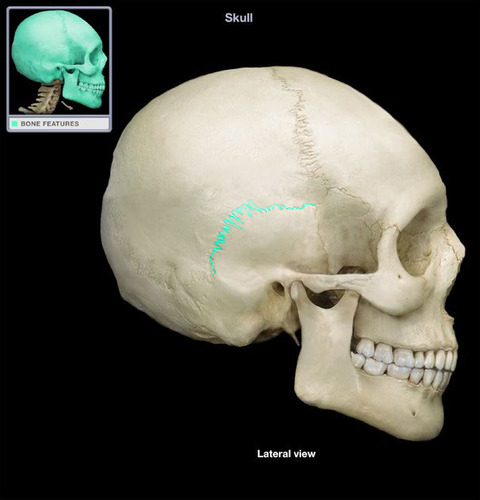
New cards
squamous suture
Name the structure.
71
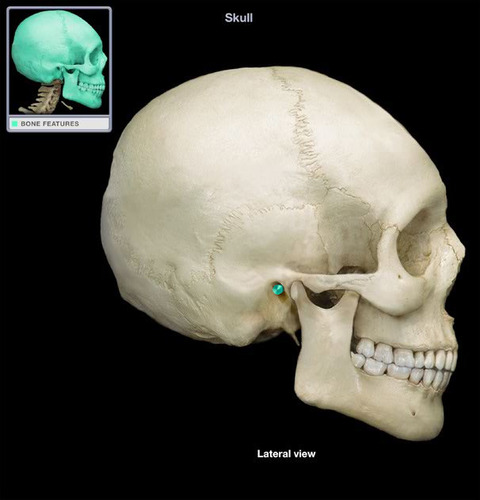
New cards
external auditory meatus
Name this opening.
72
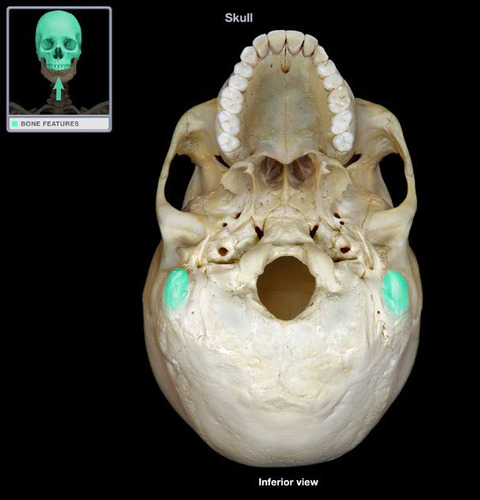
New cards
mastoid process
Name the structure.
73
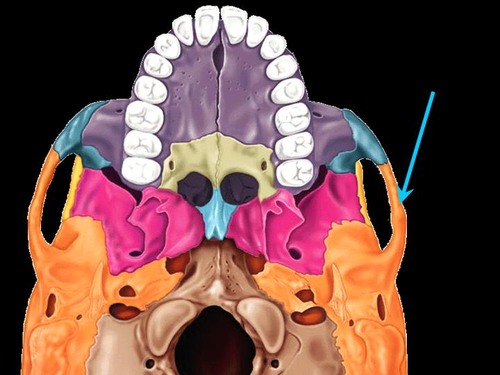
New cards
zygomatic arch
Name the structure.
74
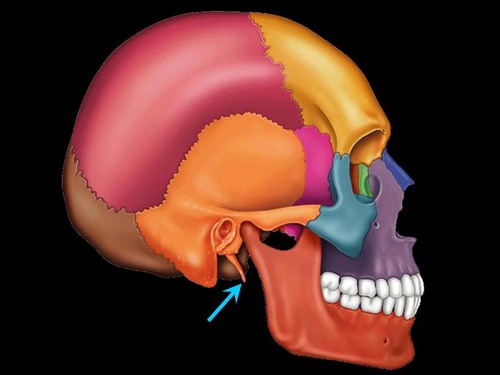
New cards
styloid process
Name the structure.
75
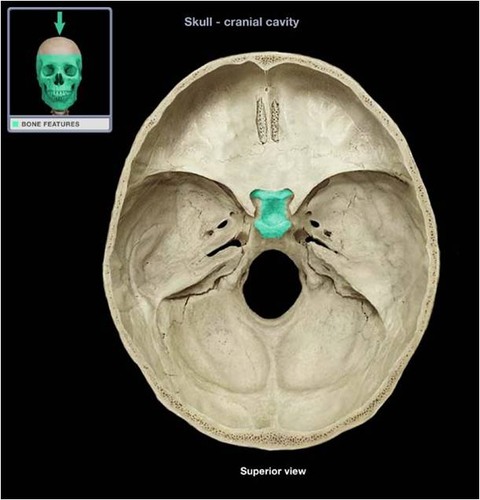
New cards
sella turcica
Name the structure.
76
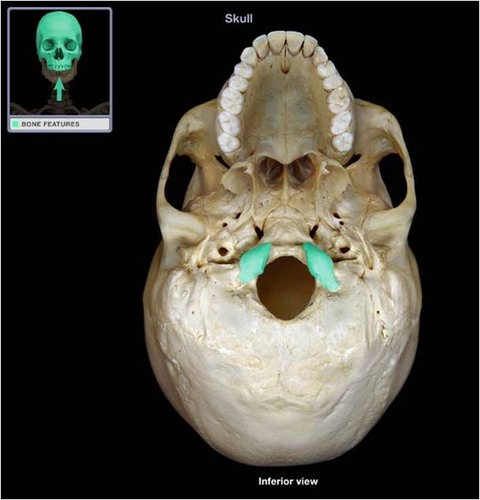
New cards
occipital condyle
Name the structure.
77
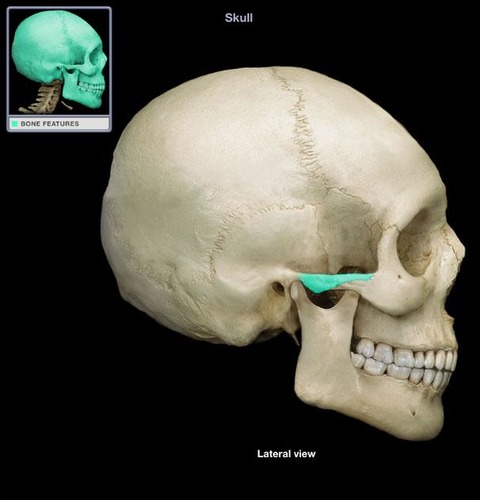
New cards
zygomatic process of temporal bone
Name the structure.
78
New cards
foramen magnum
Name this opening. BONUS
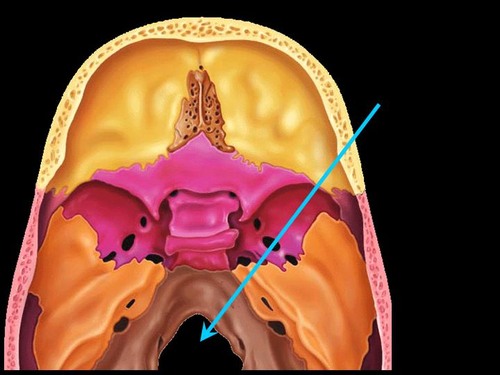
79
New cards
foramen ovale
Name this opening. BONUS
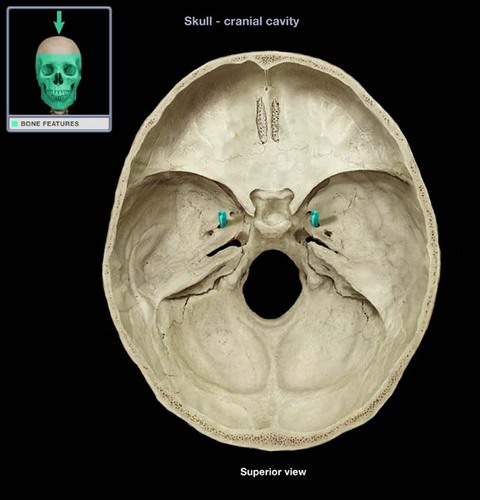
80
New cards
foramen spinosum
Name this opening. BONUS
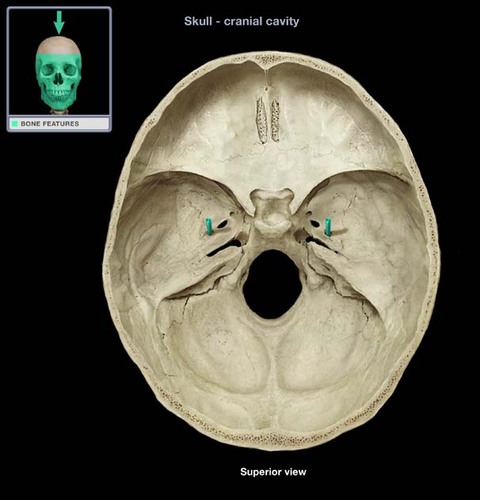
81
New cards
foramen lacerum
Name this opening. BONUS
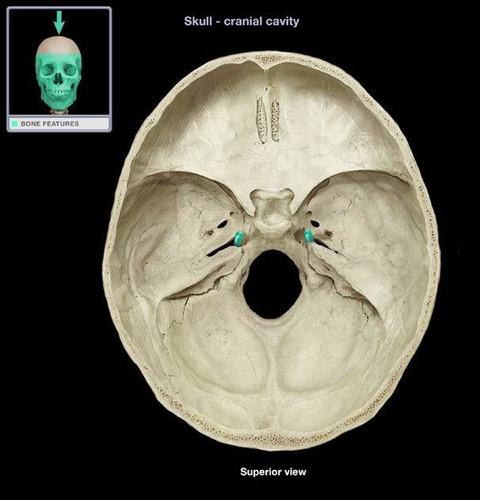
82
New cards
jugular foramen
Name this opening. BONUS
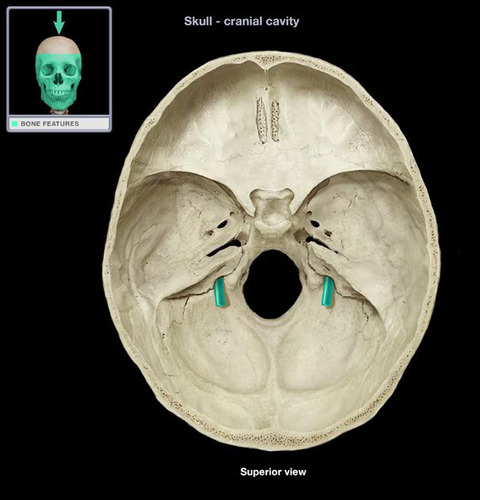
83
New cards
carotid canal
Name this opening. BONUS
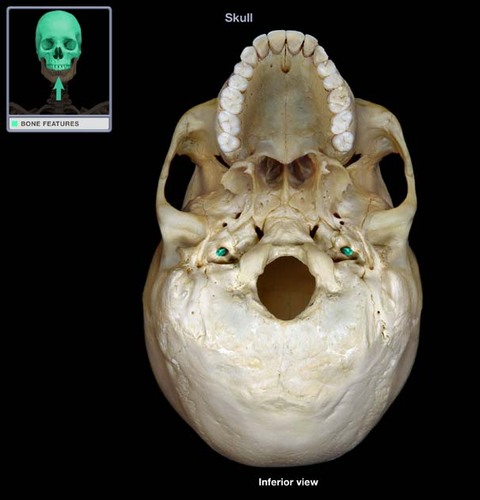
84
New cards
sacrum
Name this bone.
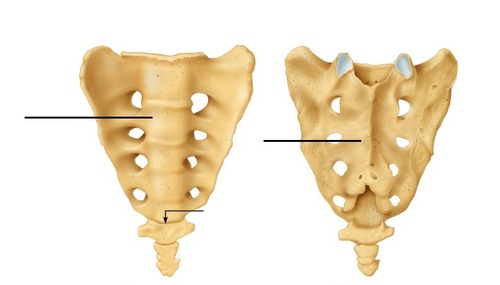
85
New cards
coccyx
Name this bone.
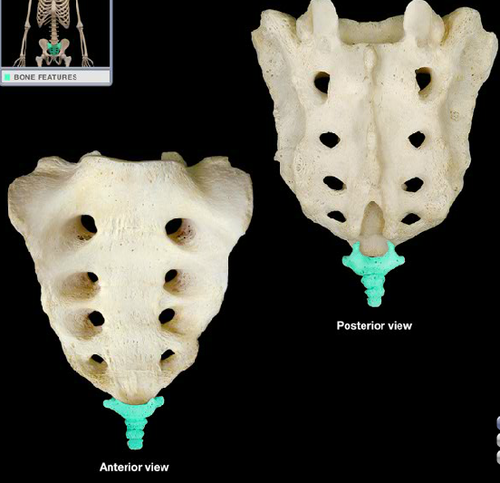
86
New cards
spinous process
Name the structure.
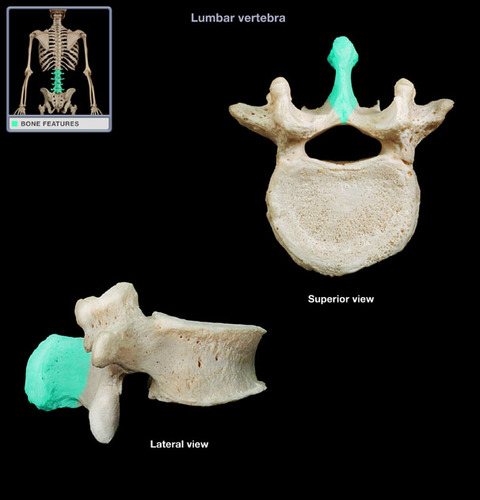
87
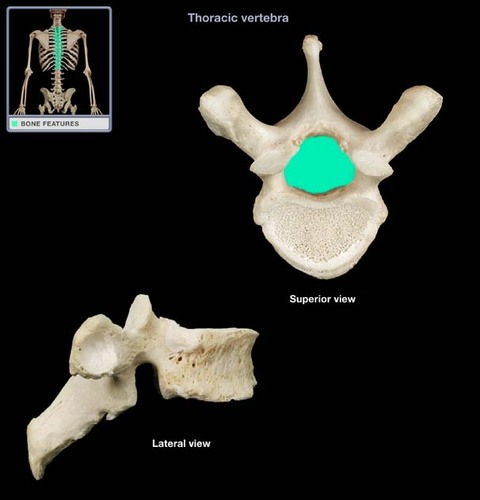
New cards
vertebral foramen
Name this opening.
88
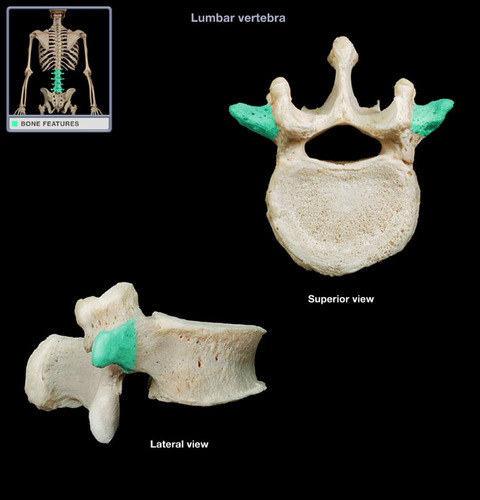
New cards
transverse process
Name the structure.
89
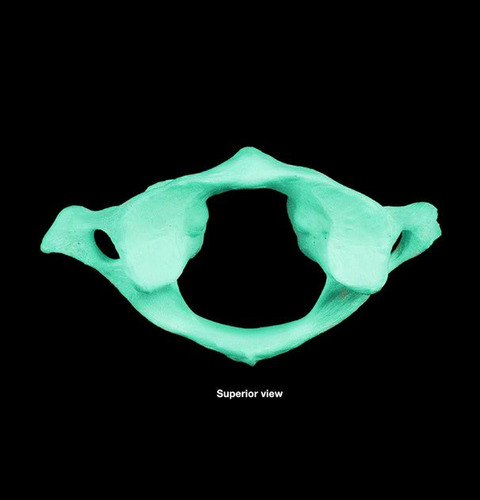
New cards
atlas
Name the bone.
90
New cards
axis
Name the bone.
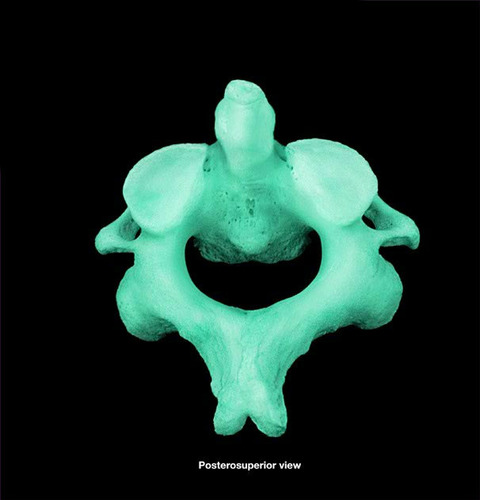
91
New cards
dens
Name the structure.
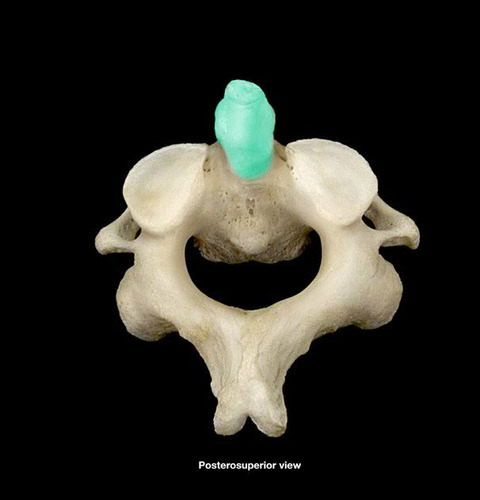
92
New cards
hyoid bone
Name the bone.
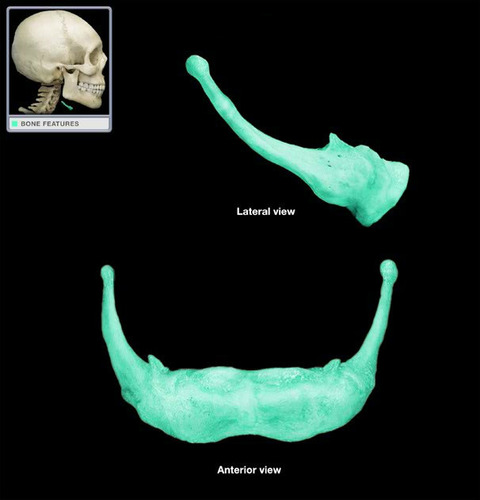
93
New cards
manubrium
Name this bone.
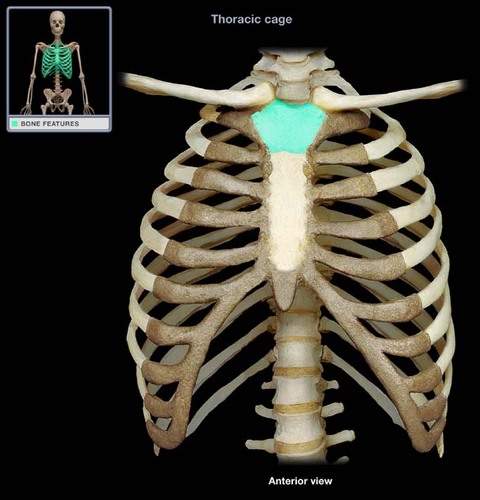
94
New cards
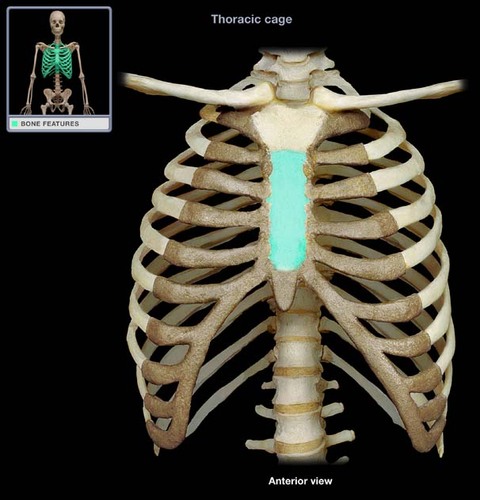
body of the sternum (gladiolus)
Name this bone.
95
New cards
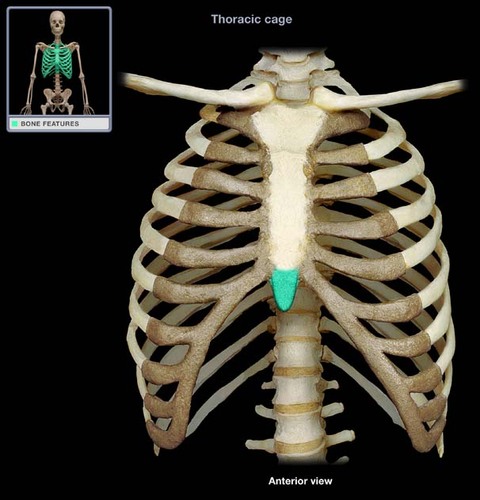
xiphoid process
Name the structure.
96
New cards
auditory ossicles
malleus, incus, stapes
97
New cards
Function of the hyoid bone
Attach muscles of the tongue, neck and pharynx.
98
New cards
Each vertebral column has
A body, Lamina, Pedicle, Vertebral arch, Vertebral foramen, Spinous process, transverse process, superior and inferior articular processes.
99
New cards
5 Regions of the Vertebral column
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccyx
100
New cards
How many vertebrae in the cervical region
7