PDA Lecture 28: Toxicology: General Management lecture 3
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
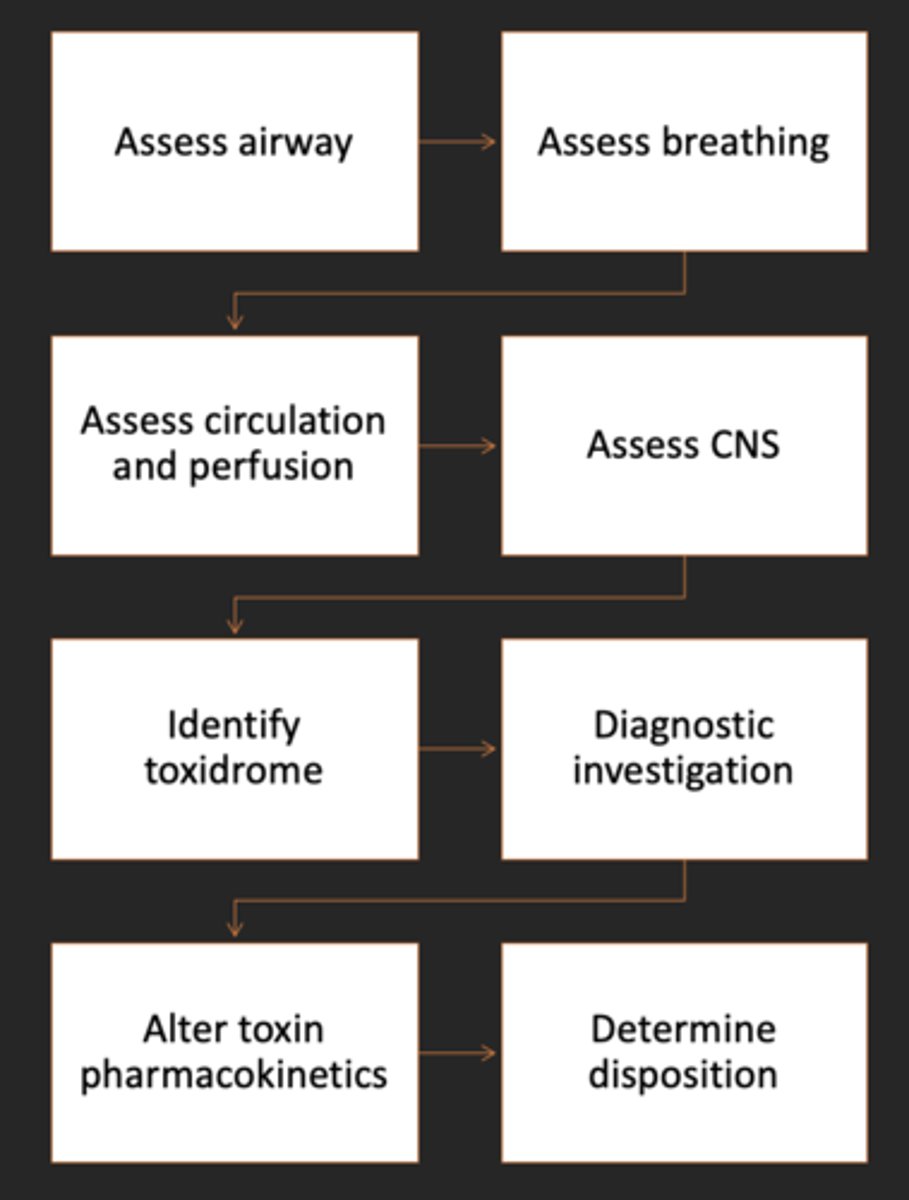
Basic Guide to the Management of Poisoned Patients order
1. Asses airway
2. Assess breathing
3. Assess circulation and perfusion
4. Assess CNS
5. Identify toxidrome
6. Diagnostic investigation
7. Alter toxin pharmacokinetics
8. Determine disposition
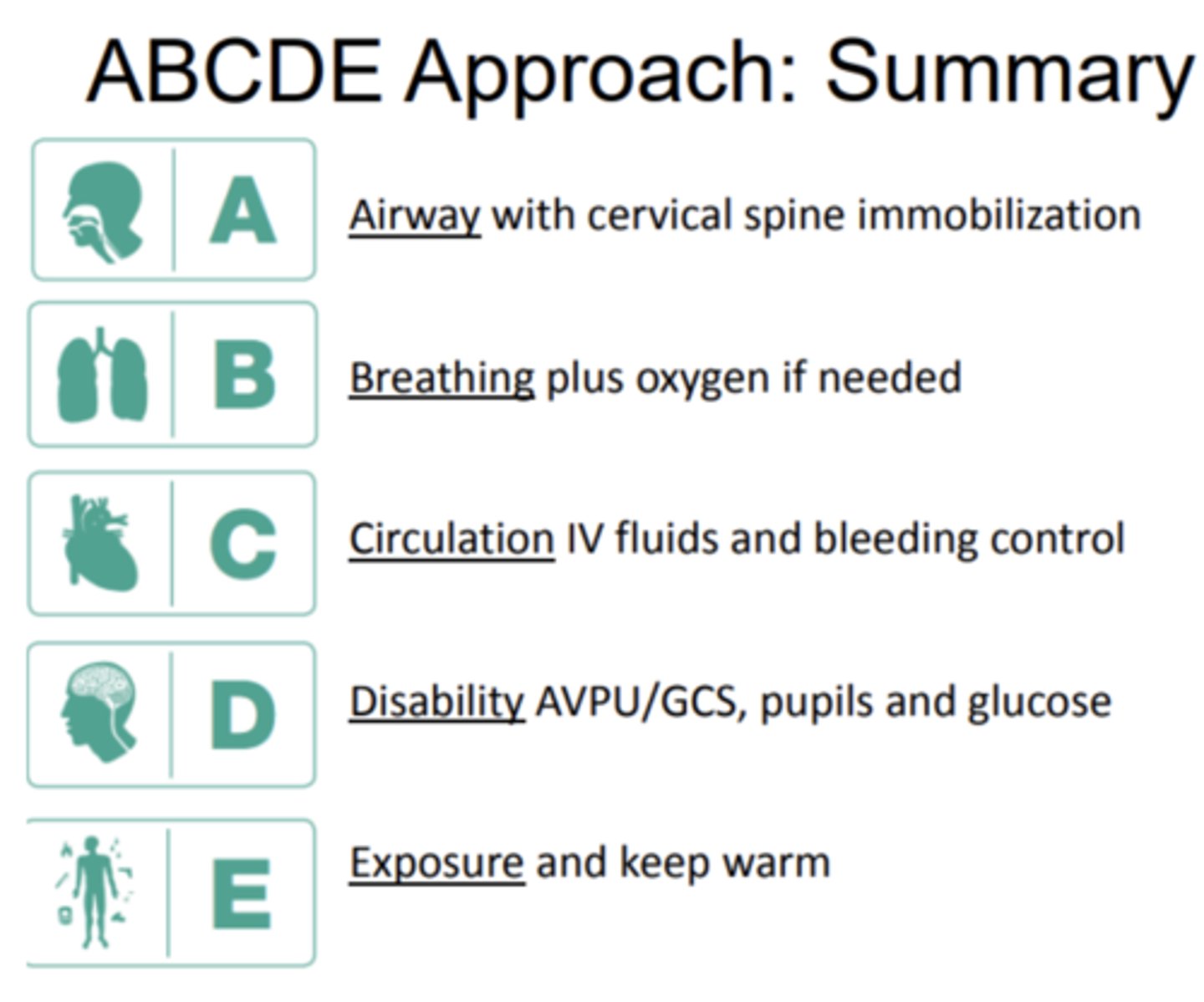
ABCDE Approach
- Airway with cervical spine immobilization
- Breathing plus oxygen if needed
- Circulation IV fluids and bleeding control
- Disability AVPU/GCS, pupils and glucose
- Exposure and keep warm
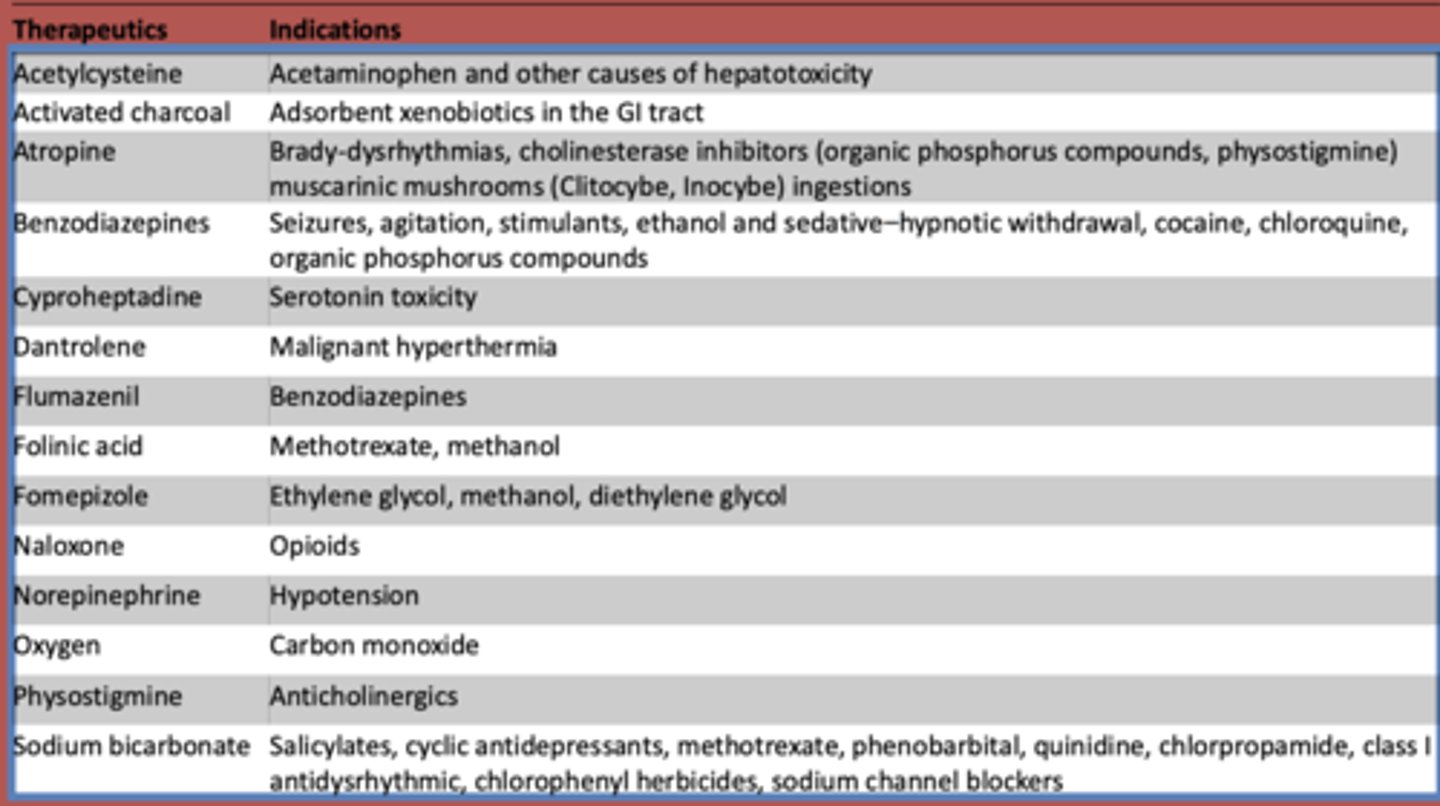
What is used to treat acetaminophen and other other causes of hepatotoxicity?
Acetylcysteine
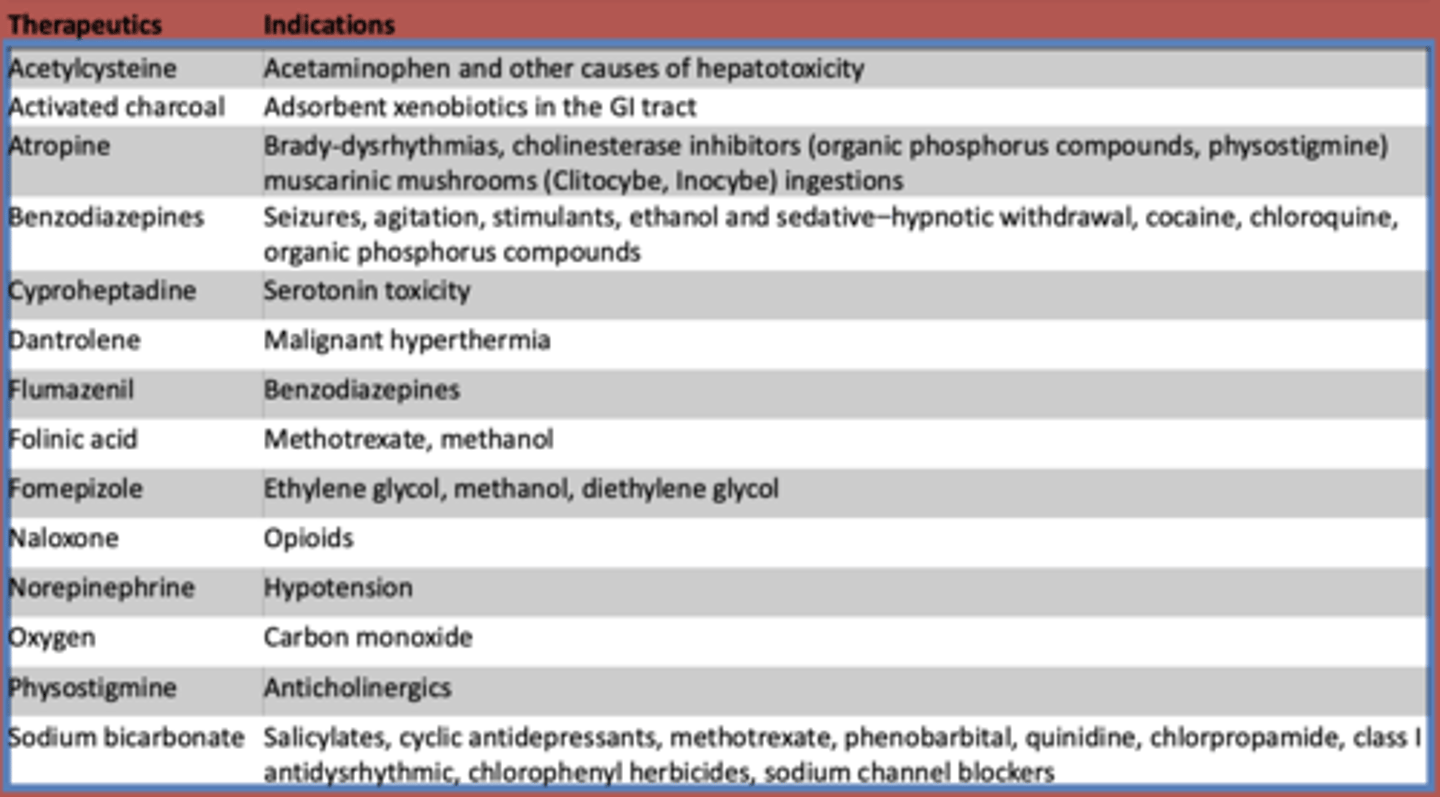
What is atropine used to treat? (3)
- Brady-dysrhythmias
- cholinesterase inhibitors (organic phosphorus compounds, physostigmine)
- muscarinic mushrooms (Clitocybe, Inocybe) ingestions
What are benzodiazepines used to treat?
- Seizures
- agitation
- stimulants
- ethanol and sedative-hypnotic withdrawal
- cocaine
- chloroquine
- organic phosphorus compounds
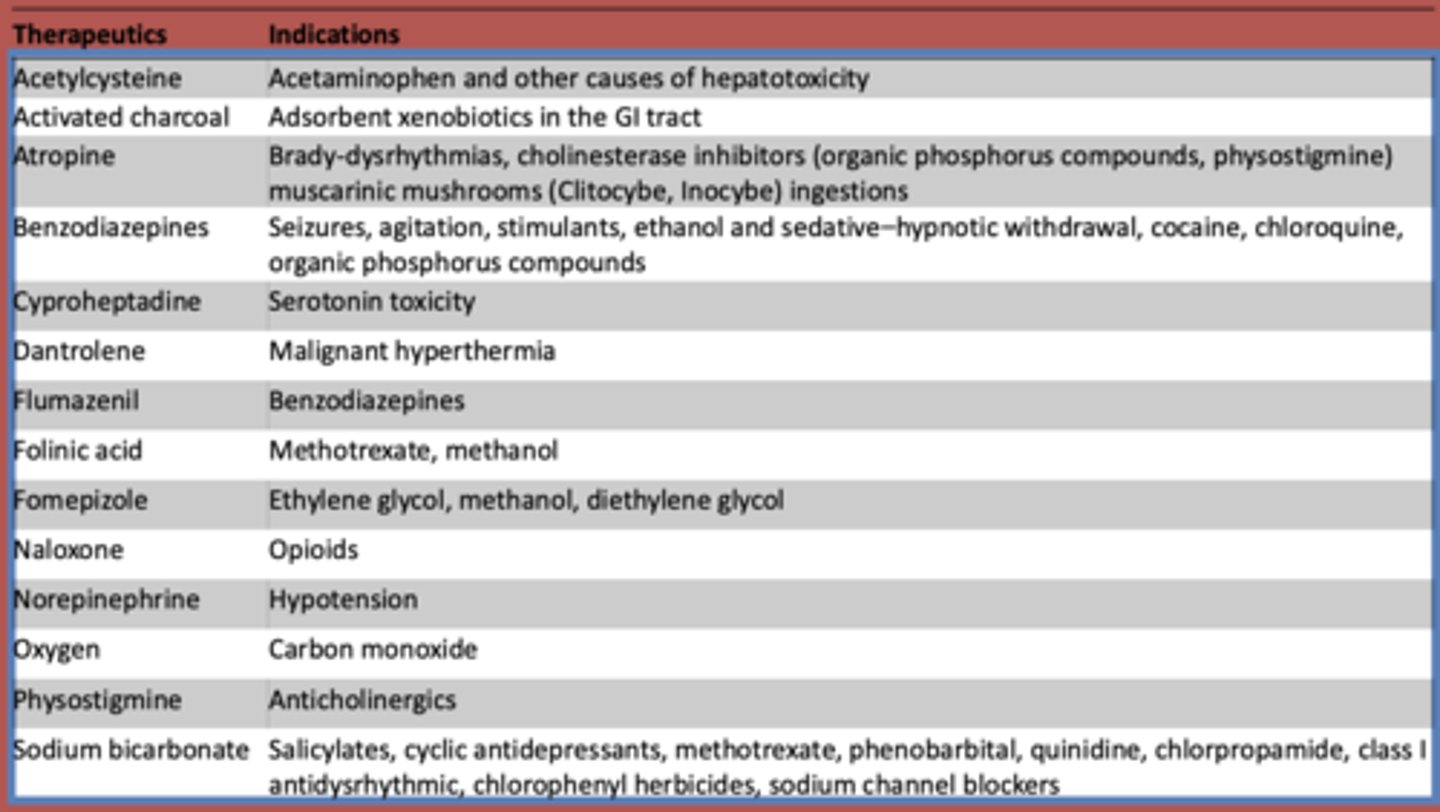
What is cyproheptadine used to treat?
serotonin toxicity
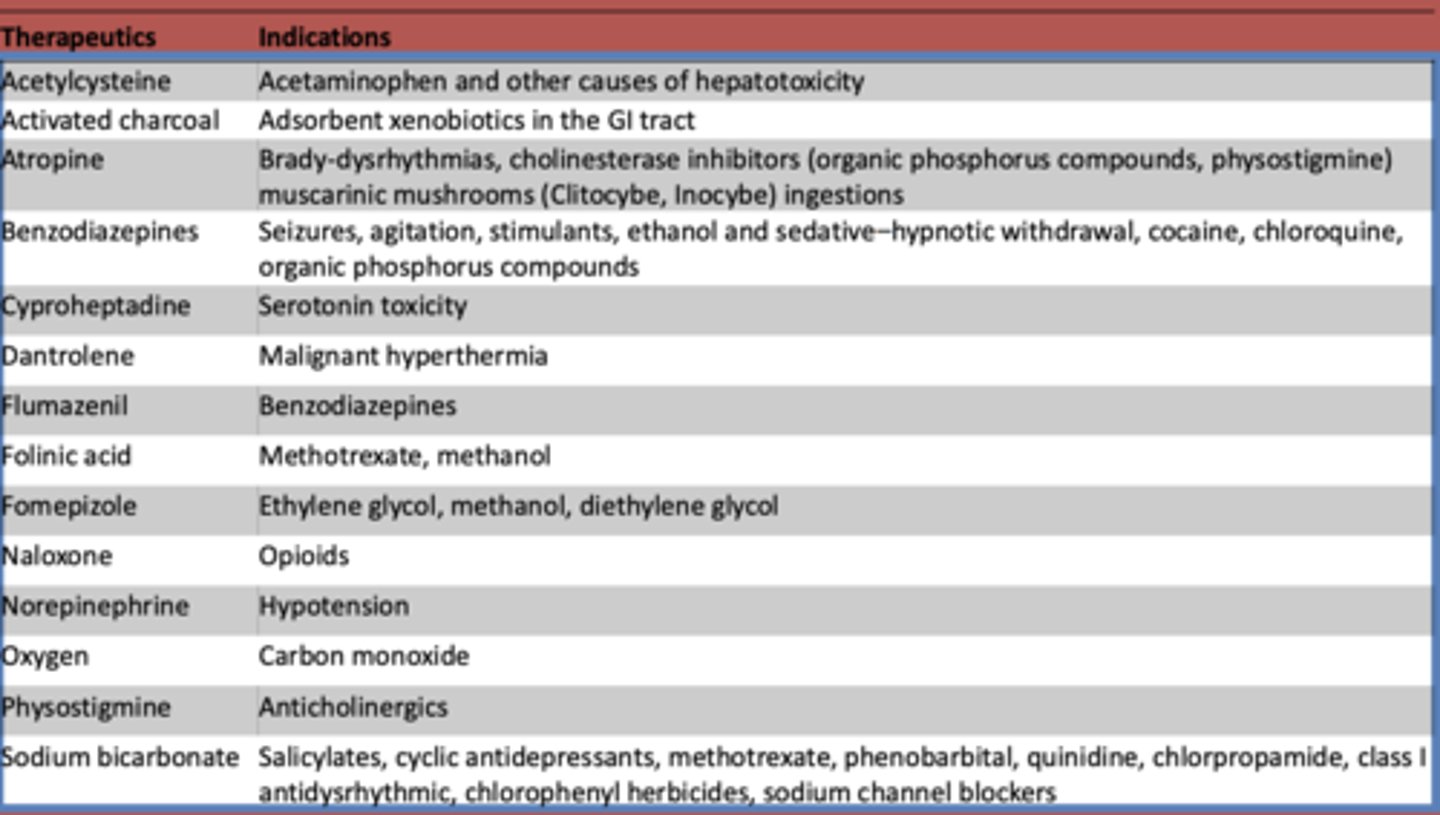
What is dantrolene used to treat?
malignant hyperthermia
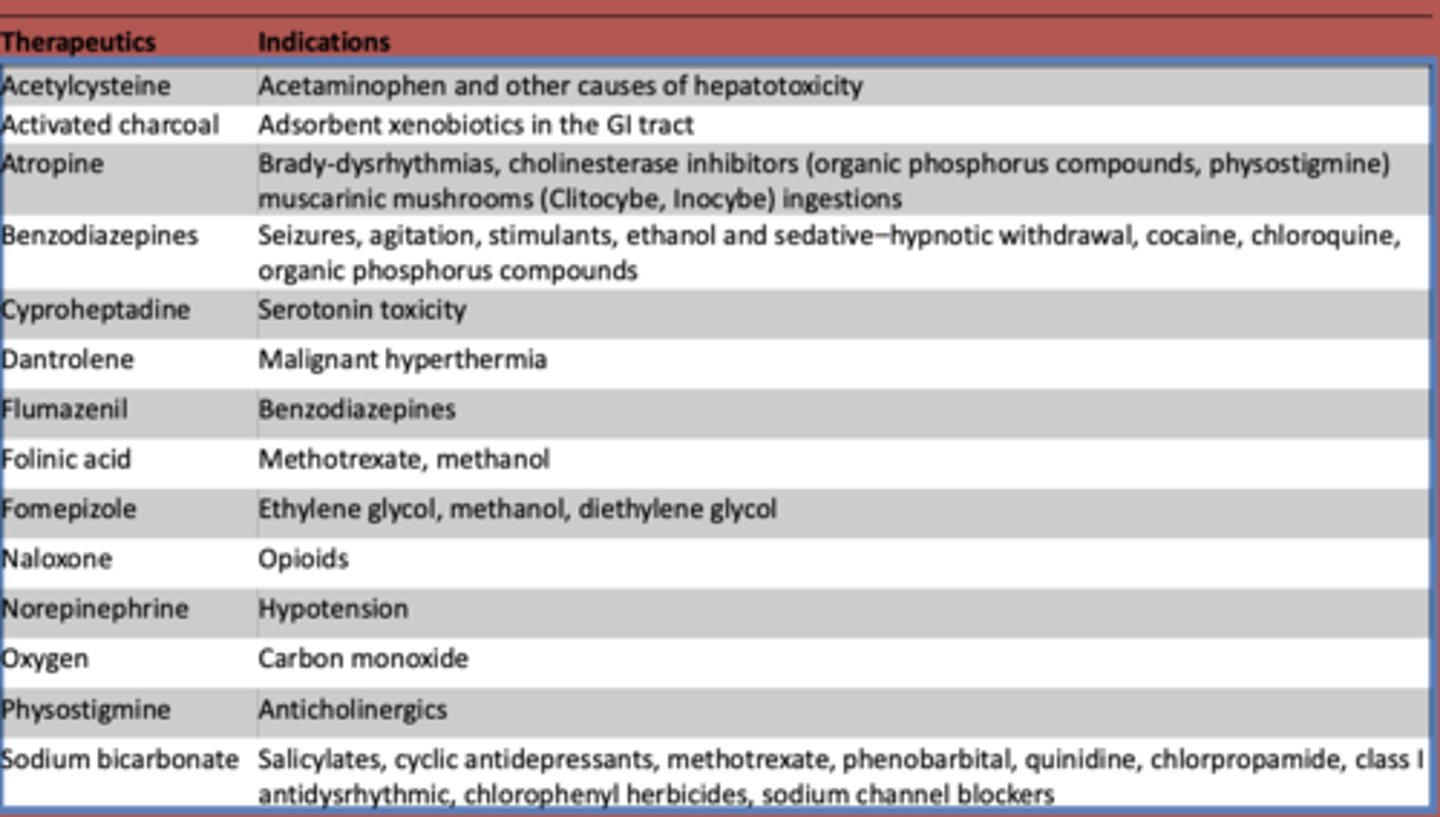
What is flumazeril used to treat?
benzodiazepines
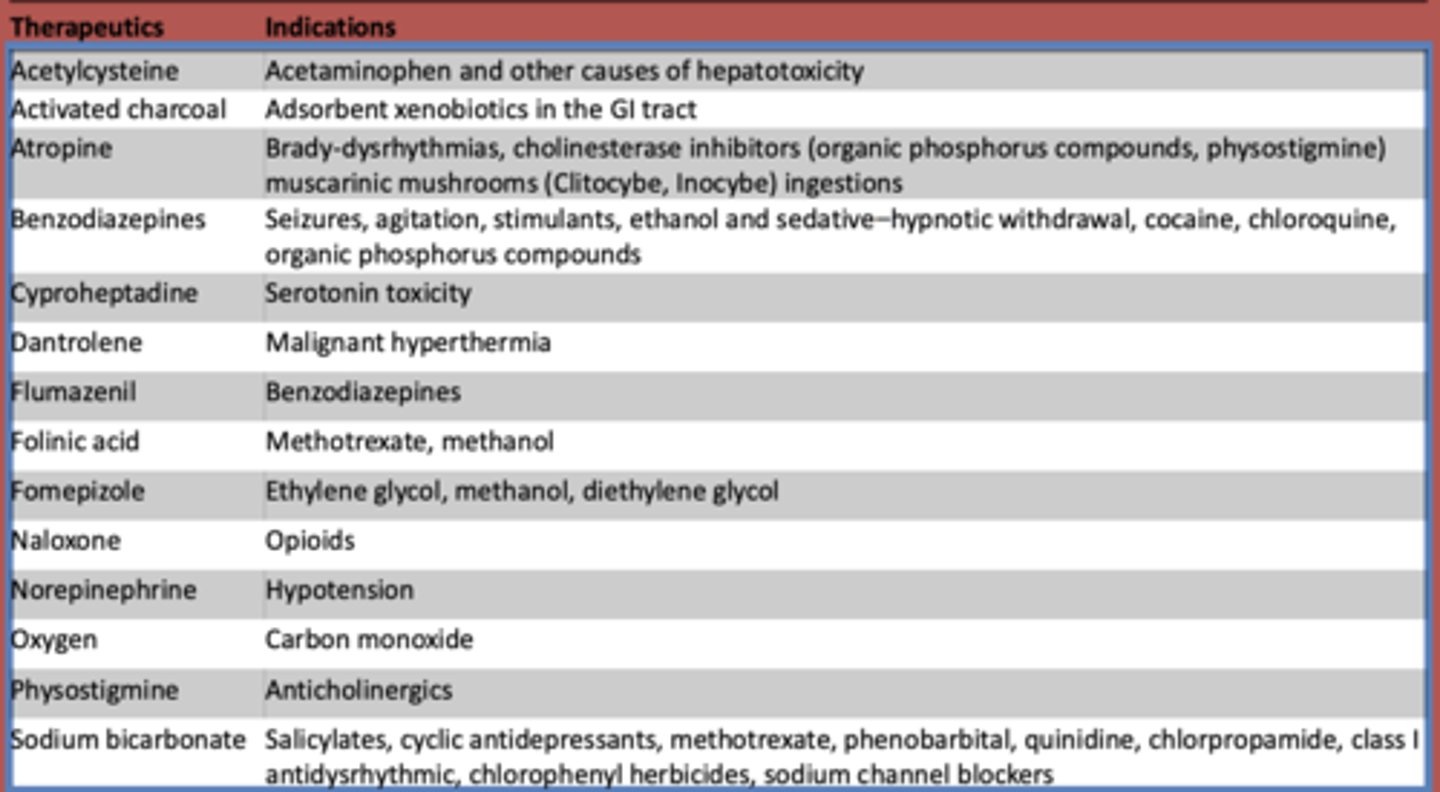
What is folinic acid used to treat?
methotrexate, methanol
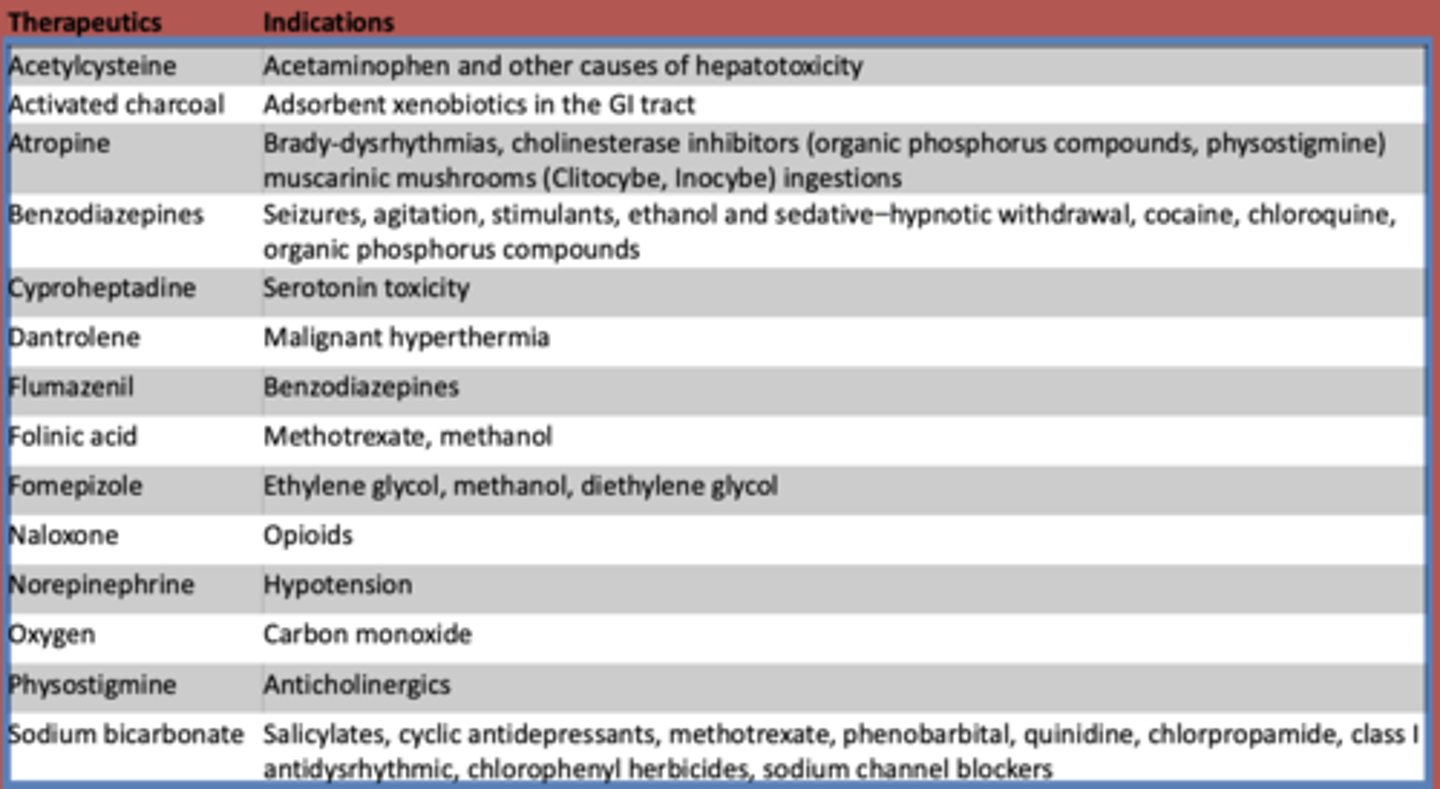
What is fomepizole used to treat?
ethylene glycol, methanol, diethylene glycol
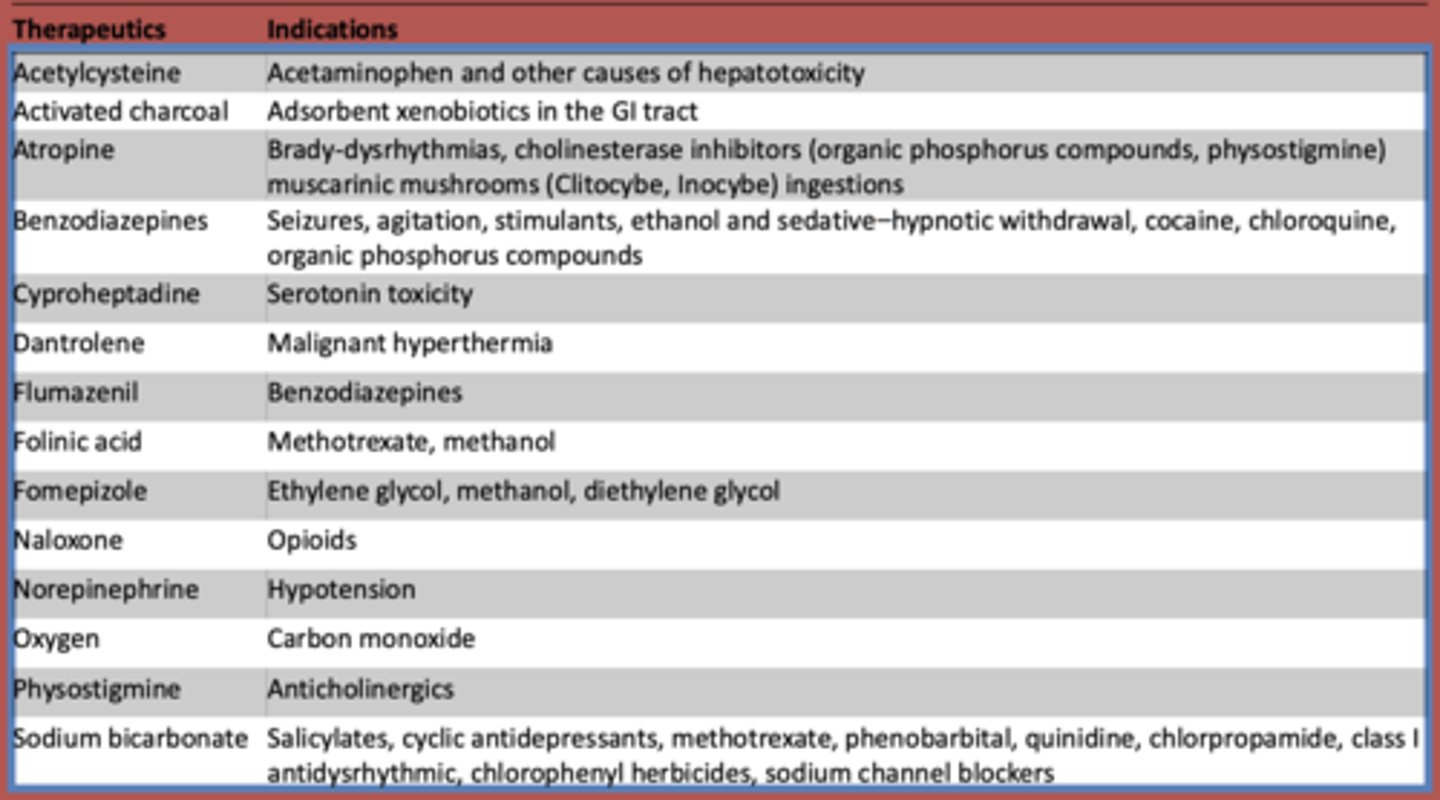
What is naloxone used to treat?
opioids
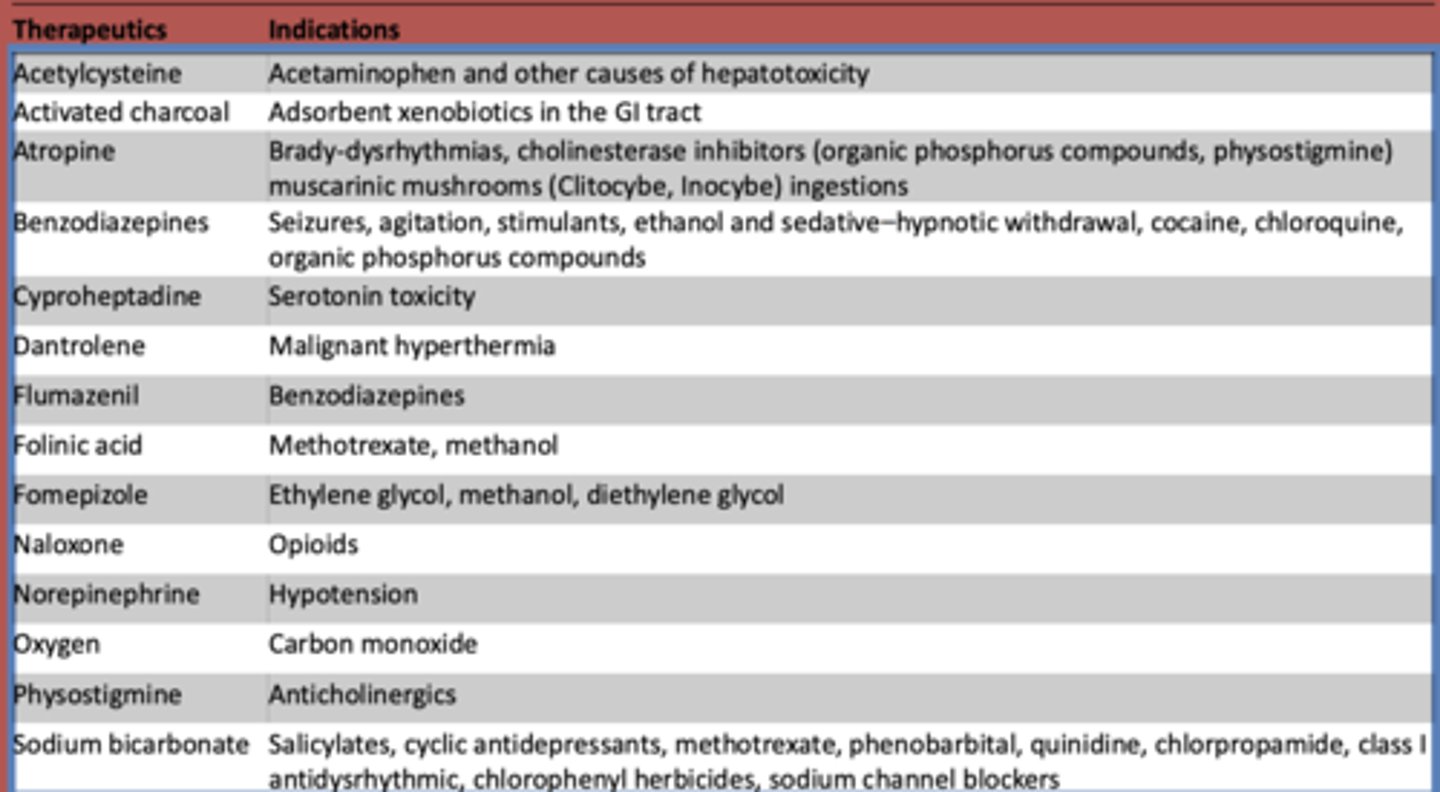
What is norepinephrine used to treat?
hypotension
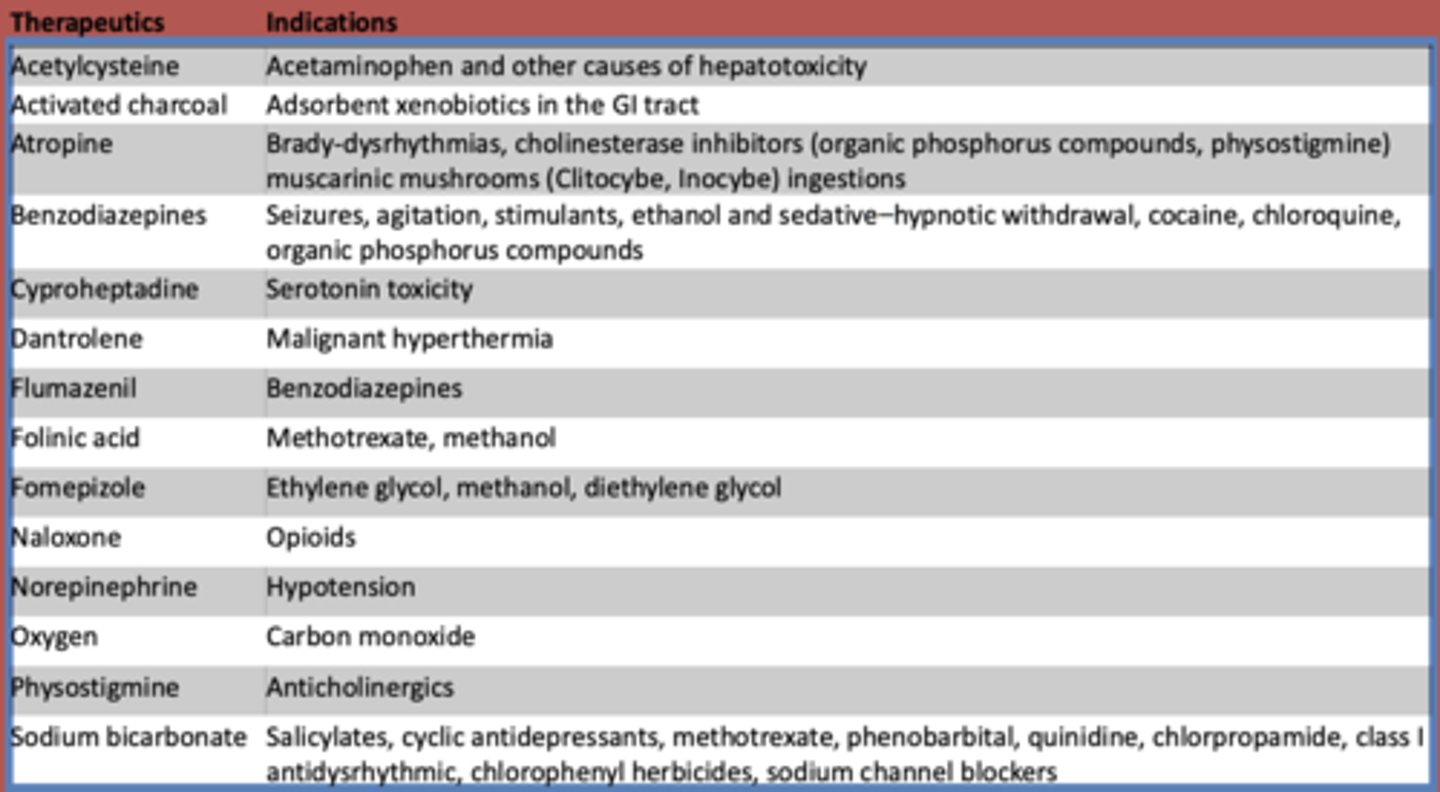
What is oxygen used to treat?
carbon monoxide
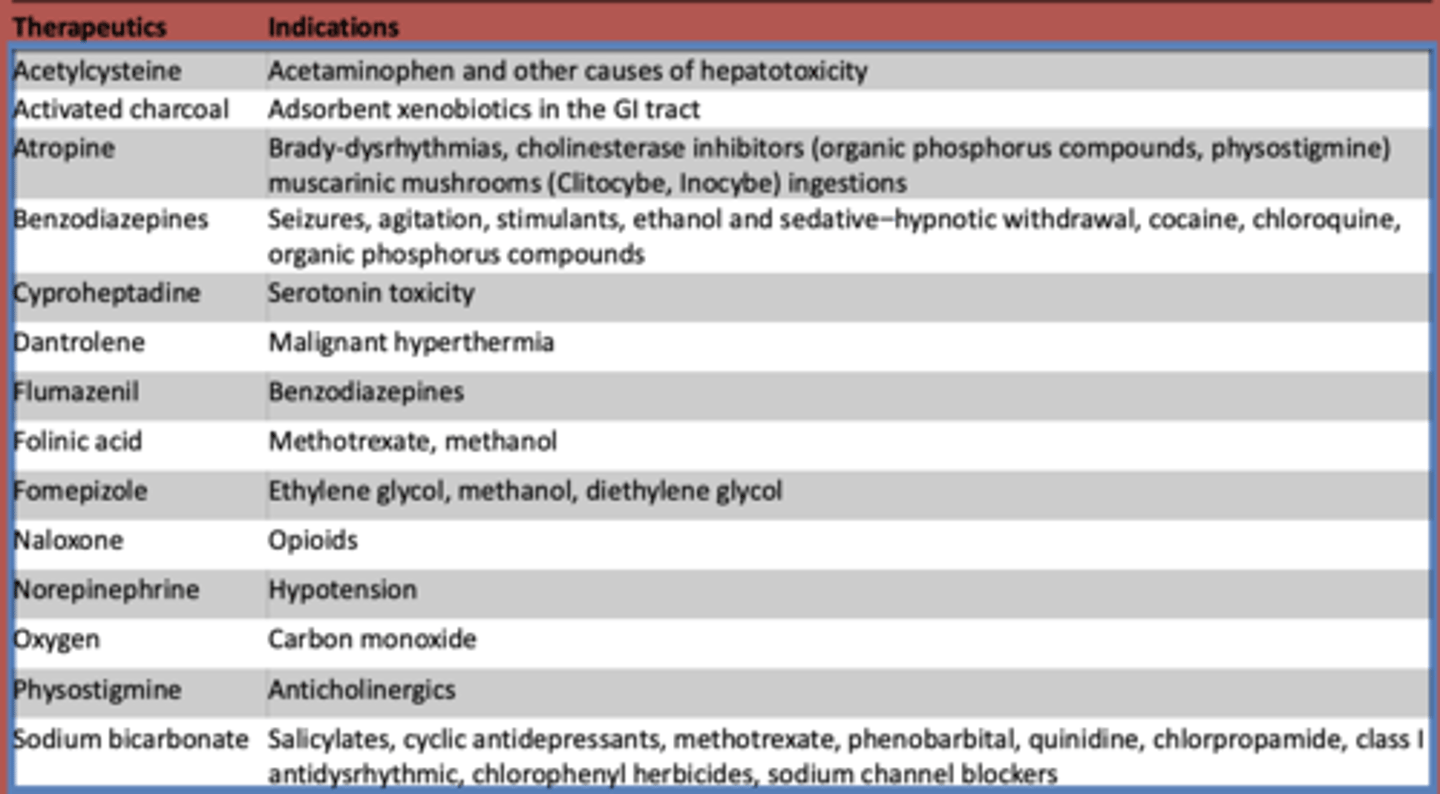
What is used to treat anticholinergic toxidrome?
physostigmine
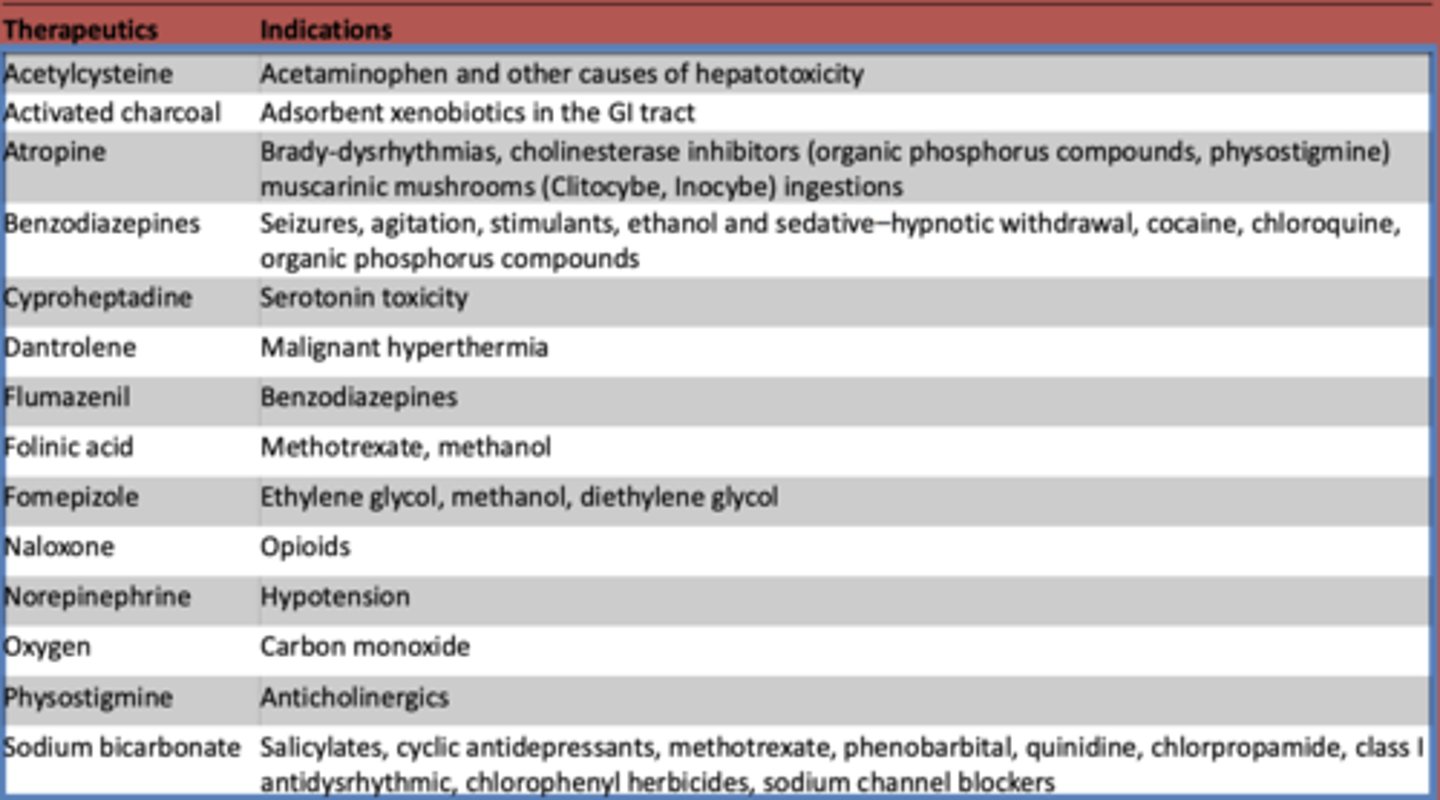
What is sodium bicarbonate used to treat?
- Salicylates
- cyclic antidepressants
- methotrexate
- phenobarbital
- quinidine
- chlorpropamide
- class I antidysrhythmic
- chlorophenyl herbicides
- sodium channel blockers
The management of most patients with toxicologic clinical syndromes cannot be based on ___________________________, but rather relies on the application of ______________________ or pharmacologic care
- specific antidotal therapies
- directed supportive
What is the antidote for acetaminophen overdose?
A. Naloxone
B. Flumazenil
C. N-acetylcysteine
D. Atropine
C. N-acetylcysteine
Altered mental status
deviation from baseline sensorium (normal pts awareness of selves and surroundings)
- can include agitation, delirium, psychosis
Altered mental status is not just......
"awake" or "alert" or "depressed"
You should obtain _______________ with any alternation in mental status
POC glucose
AVPU Scale
Alert
Verbal stimuli
Painful stimuli
Unresponsive
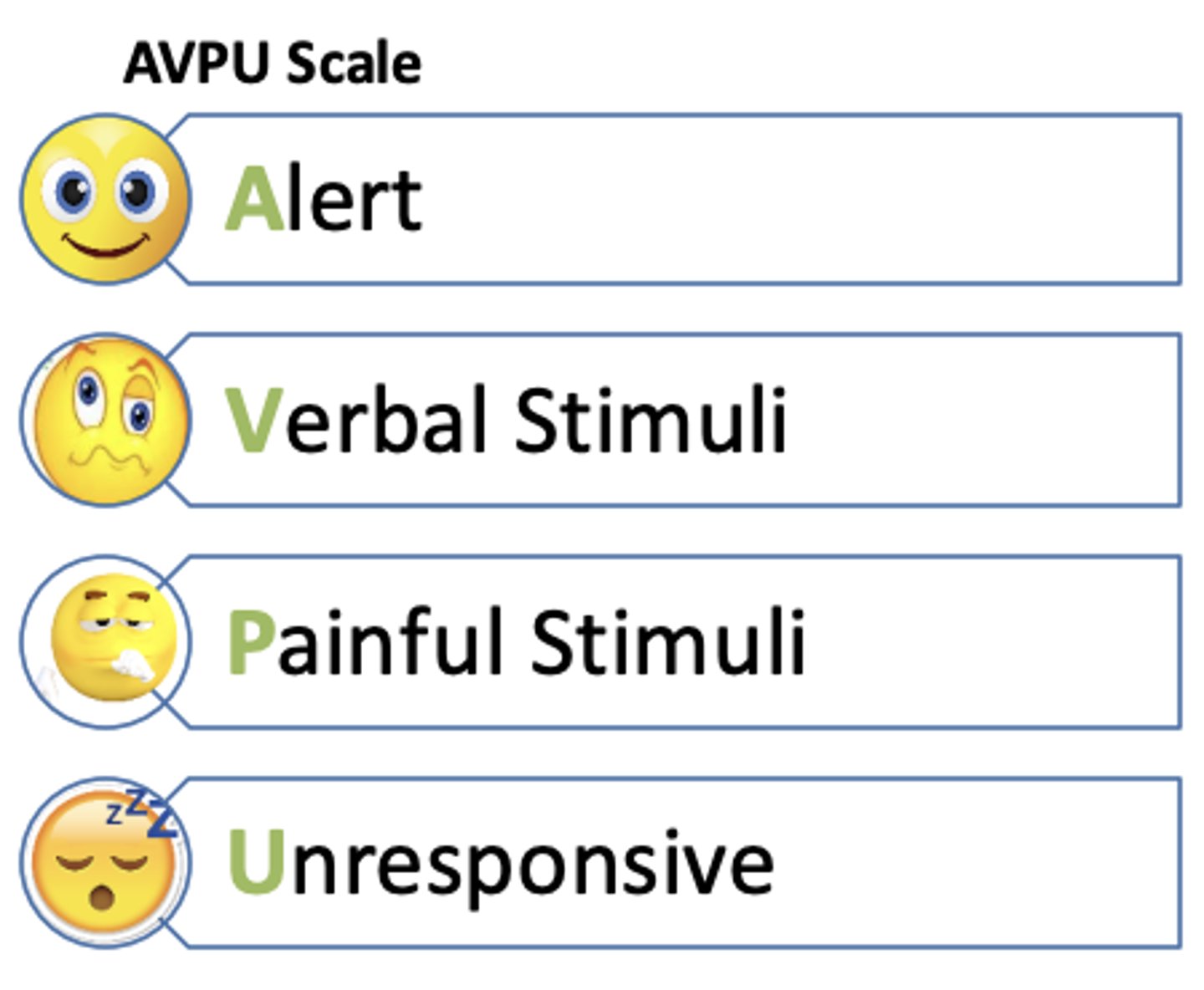
Altered Mental Status + glucose + temperature
Glucose:
- check glucose
- hypoglycemia (<70 mg/dl)
- dextrose 5%
Temperature
- Extreme
- correlation with toxidromes
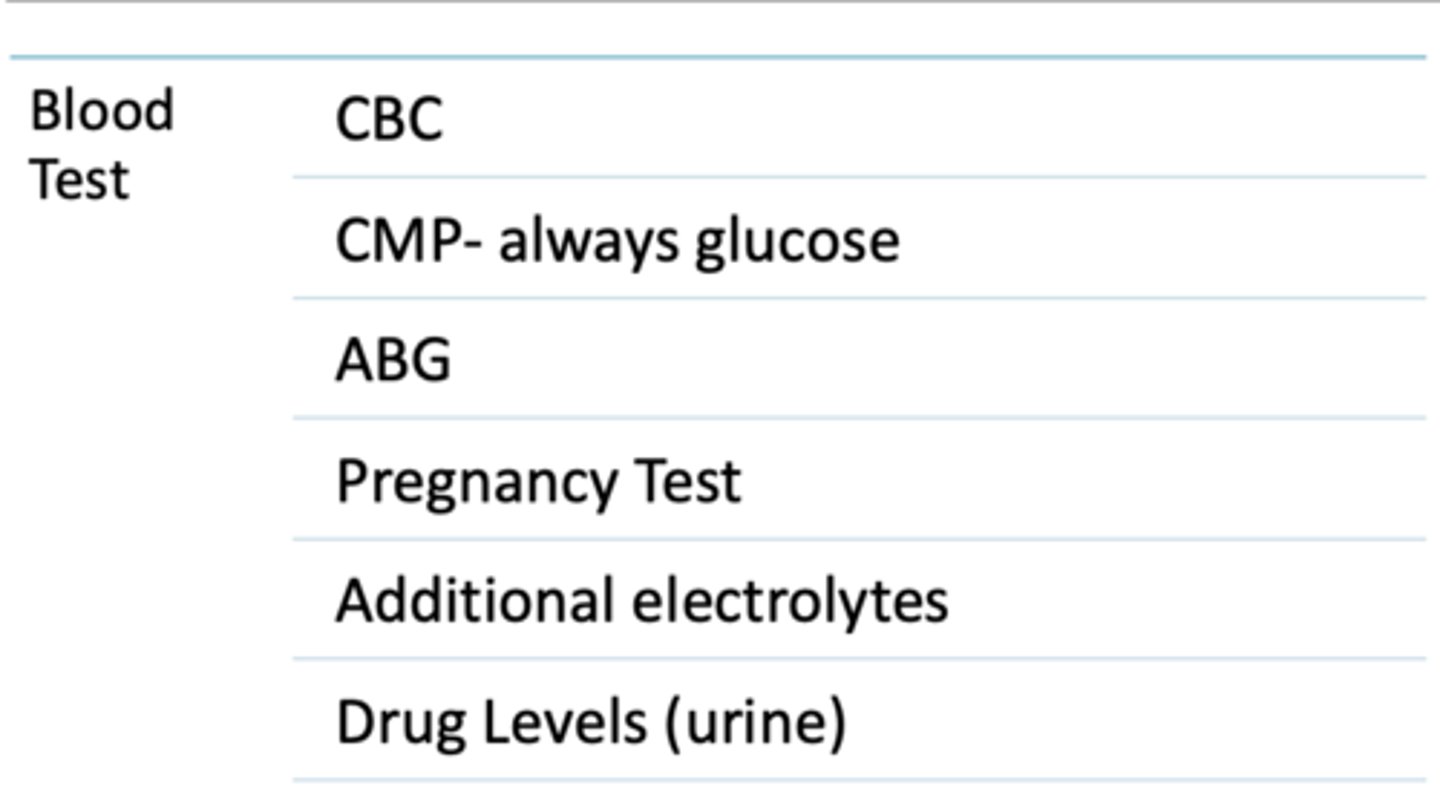
Initial labe assessment tests (6)
- CBC
- CMP-always glucose
- ABG
- pregnancy test
- additional electrolytes
- drug levels (urine)
For suicide ideation, always check: (4)
- Salicylate level
- Acetaminophen level
- Home medications
• Lithium, theophylline, digoxin
- Consider CO
Pregnancy can cause ___________________ changes.
cardiovascular
- elevated blood volume and cardiac output in 2nd and 3rd trimester
- hypotension manifest later- move immediately to left lateral decubitus position. Prevents impairs systemic venous return & compression on vena cave
Use of antidotes in pregnancy
• Limited data available
• Antidotes should not be withheld if they have the potential to reduce potential morbidity and mortality
• Risks and benefits of either decision must be assessed.
When working with children, be careful with....
dilutions and dosing
Avoid secondary exposures by...
wearing a gown, gloves and shoe covers
Remove patient's clothing and place it in...
bags and seal them
Was the patient with __________ and copious amounts of _________. Wash ______, regardless of time of exposure
- soap
- water
- twice
T/F: Attempt to neutralize contaminations
FALSE
do not use an acid with a base, or a base with an acid
Why should you avoid using greases or creams?
It increases the contact and makes removal difficult
Other decontaminations for eyes (4)
- Irrigate for no less than 20 min (eyelids fully retracted)
- Check for contact lens
- Anesthetic drops (proparacaine or tetracaine) may be needed
- Check with pH strip to assess irrigation status
• Goal 6.5 to 7.6
• Paper strips may goal to 8
General Assessments of Poisoning
- Identification
- Label
- Route
- Medical literature
- Pt assessment
- Toxicity assessment
General Assessments of Poisoning
Identification:
Label:
Route:
Medical literature:
Pt assessment:
Toxicity assessment:
Identification: What product was taken, which ingredients
Label: look for "signal words" in label
Route: identify route of exposure
Medical literature: potential effects
Pt assessment: pt is asymptomatic vs pt is presenting symptoms
Toxicity assessment: adequate time has occrured to assess the potential for the development of toxicity
___________________ can provide direct evidence of some drugs/poisons
Toxic screen
Drug screening should not affect _____________________
initial management (4-8 hours)
There is a questionable value for ____________________, ____________________ screening purposes
- nonspecific, general
Quantitative determination of serum concentrations may be important for some poisonings, including..... (5)
◦ Acetaminophen
◦ Ethanol
◦ Iron
◦ Salicylates
◦ Digoxin
What cases are sent to the ICU? (8)
• End organ involvement
• Lab values extremely out of range
• Seizures
• Unresponsive
• Hemodynamically unstable
• Pre-existing medical conditions of concern
• Suicide/Suicidal
• Long term monitoring (especially cardiac & respiratory)