Chemistry: Rate & extent of chemical change (Paper 2 Topic 6)
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
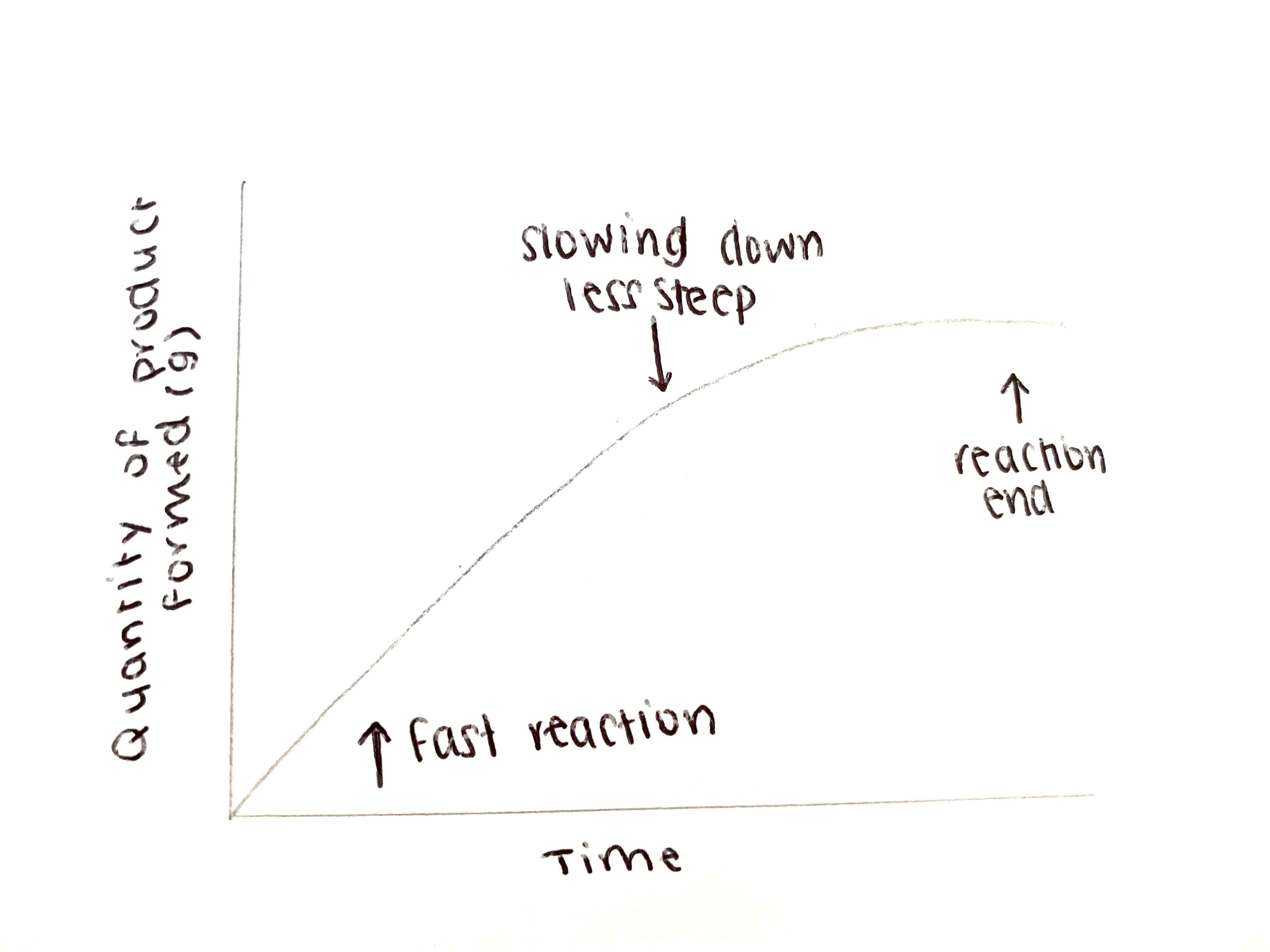
What is the graph for a chemical reaction - Product formed?
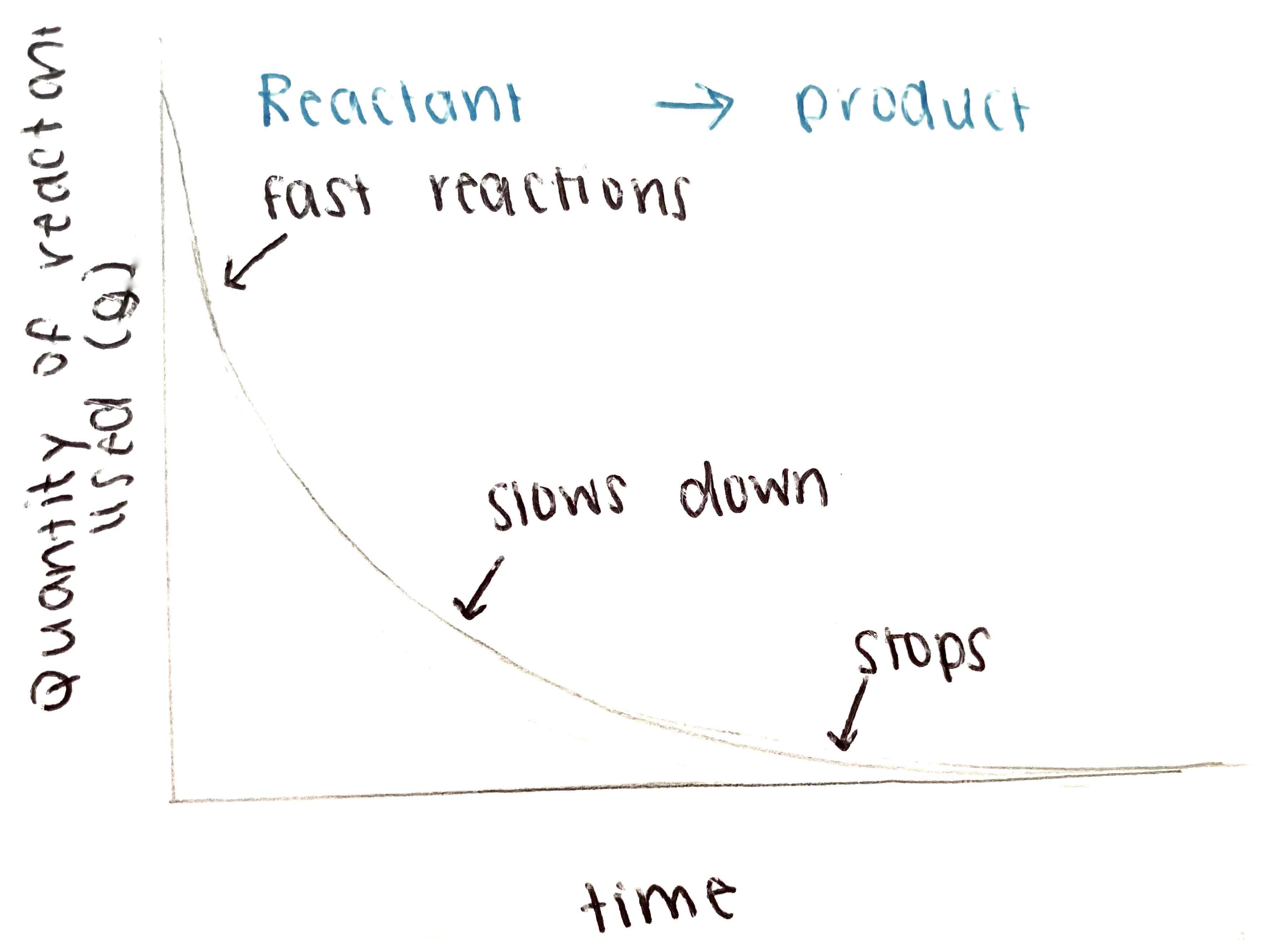
What is the graph for a chemical reaction - Reactants used?
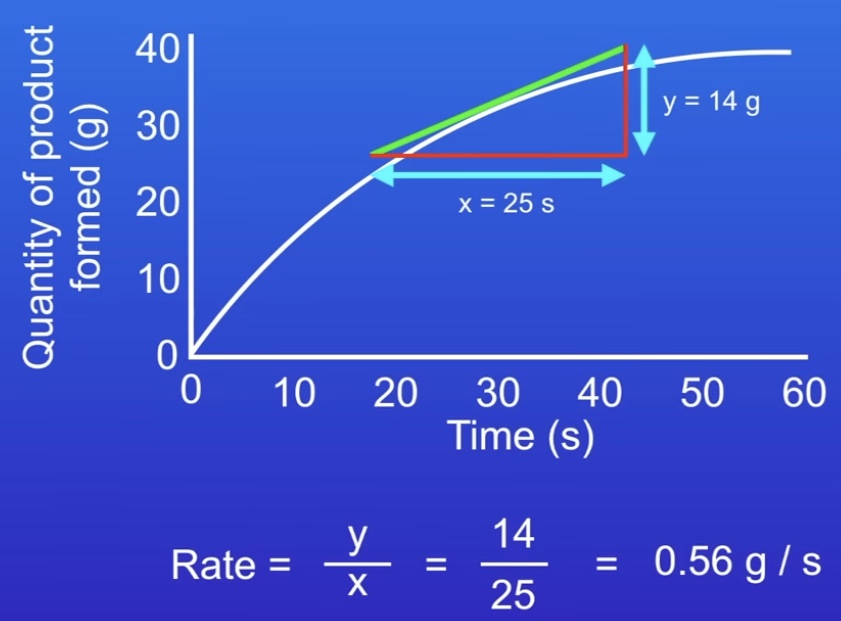
what is the formula to calculate mean rate of reaction?

How do we calculate the rate of reaction?
Drawing a tangent
Straight line at a point
Difference in y divided by difference in x
What is Collision Theory?
Chemical reactions an only take place when reacting particles collide with each other
The collisions must have sufficient energy
Rate of a chemical reaction is determined by freq of successful collisions
Frequency - No. of successful collisions per second
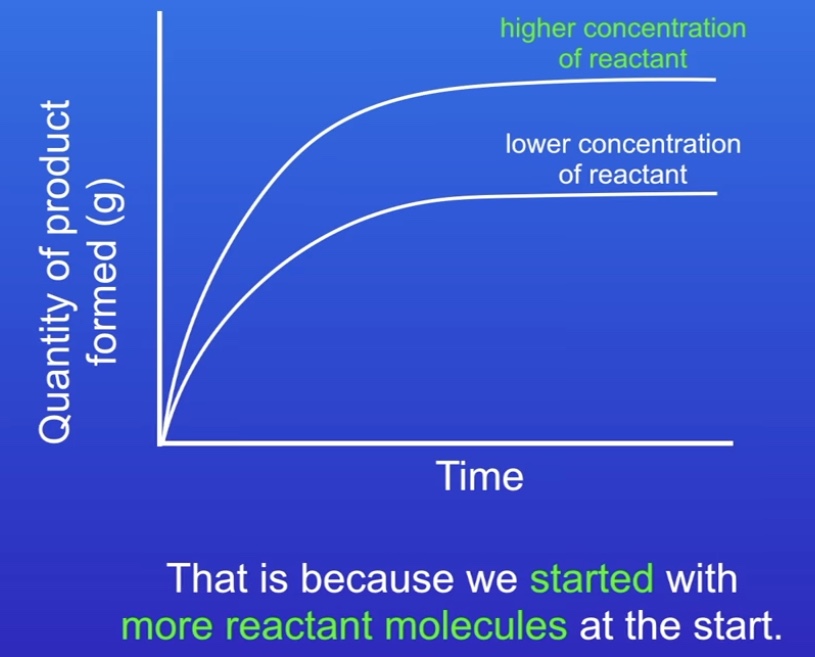
What is the effect of concentration on the rate?
Higher concentration:
The number of collisions (per sec) will be higher
Therefore higher frequency
Higher freq means quicker rate of reaction
(Rate is proportional to frequency)
What is a hypothesis?
Proposal that could explain a fact or observation
Must be testable
What is the Investigating rate of reaction practical (liquid) process?
Measure 10cm3 of sodium thiosulphate into conical flask
Put flask onto black cross
Add 10cm3 of hydrochloric acid
Swirl solution, start stopwatch
Observe through top of flask, stop timer when cross is invisible
Repeat with lower concentrations of sodium thiosulphate solution
Calculate mean values
What affects the accuracy of this experiment?
A measurement is reproducible if it can be repeated
Different people have different eyesights
May not get the same result
Same size cross should reduce mistakes
What is the investigating rate of reaction practical (Gas) process?
Measure 50cm3 dilute hydrochloric acid into conical flask
Attach to bung and delivery tube
Add 3cm strip of magnesium to acid
Start stopwatch
Record amount of gas in measuring cylinder every 10s
Repeat with different concentrations of hydrochloric acid
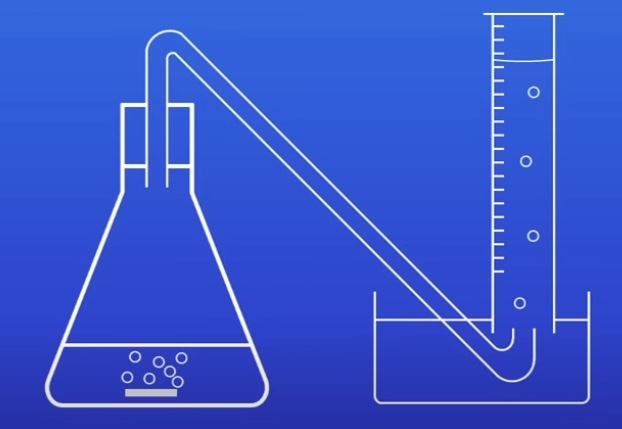
What are the Investigating rate of reaction practical results?
The greater the concentration of a chemical in a reaction, the faster the reaction takes place
This finding is reproducible (2 experiments)
What is the Ratio of surface area:volume effect on rate?
Smaller sized blocks have a larger surface area:volume ratio
More particles on the surface
More collisions per second
Higher rate
What effect does temperature have on rate?
Particles need activation energy to react
If 2 particles with little energy collide, a reaction will not occur
Increasing the temp increases the energy of the particles
Increases freq of collisions & rate
Rate of reaction is proportional to the temperature
What is a catalyst? Why are they commonly used?
Increase the rate of chemical reactions without being used up
Saves money bc reactions occur quickly without temp increase
Not used up, saves money
Increase the rate by providing a different pathway for the reaction that has a lower activation energy
3 key facts about catalysts
Not included in chemical equation (Not used up)
Different reactions need different catalysts
Enzymes are catalysts in living organisms
What is a common reversible reaction?
Heat is added to go ‘forwards’ (endothermic) & released to go ‘backwards’ (exothermic)
If it is exothermic one way, its endothermic the other
The same amount of energy is transferred

What is equilibrium?
If a reversible reaction is in a container, the reactants and products can’t escape
Eventually the reverse reactions will occur at the same rate
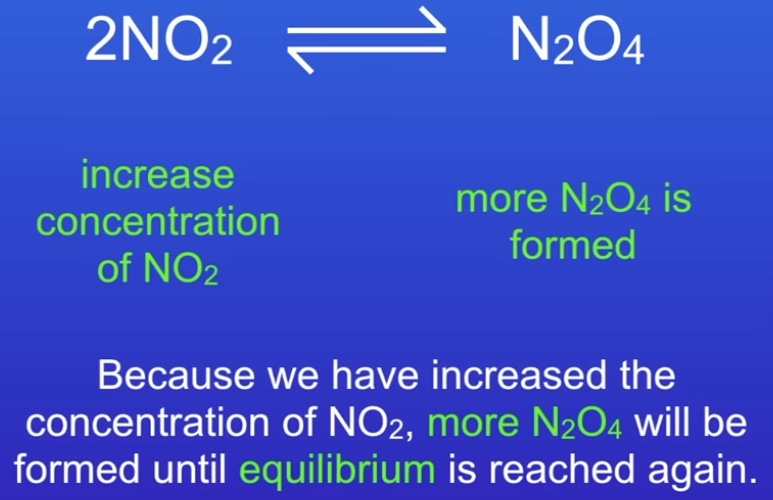
What is Le Chatelier’s Principle?
If a reaction is at equilibrium and a change is made to the conditions, the reaction responds to counteract the change
(Ep 9 ‘concentration…’ freesciencelessons rates of reaction)
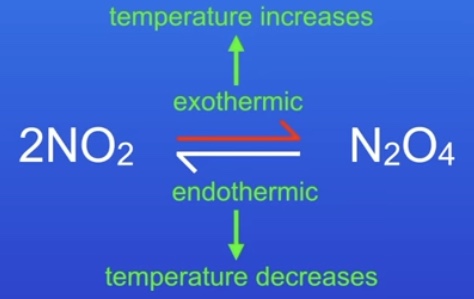
What affect does temperature change have on equilibrium?
(ep 10 ‘temperature…’ freesciencelessons rates of reaction)
What affect does pressure change have on equilibrium?
Increase pressure, position of equilibrium shifts to side with less molecules
Decrease pressure, position of equilibrium shifts to side with more molecules
If reaction is equal on both sides, pressure change has no effect