9. Biomolecules
1/275
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pretty much every line from NCERT. Suitable for IAT and probably also NEET. Question mode: Flashcards only. Answer mode: Answer with definition. Good luck with exams! I recommend studying from this after you've read the chapter at least once (after that you don't need to since this deck has it all).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
276 Terms
What is the difference between the elements found in living tissues and the elements found in the earth’s crust?
The same elements can be found in both, but the relative abundance of carbon and hydrogen is higher in living tissues relative to the earth’s crust.
Describe the method used to prepare a living tissue for chemical analysis.
We can take any living tissue (a vegetable or a piece of liver, etc.) and grind it in trichloroacetic acid (Cl3CCOOH) using a mortar and a pestle. We obtain a thick slurry.
If we were to strain this through a cheesecloth or cotton we would obtain two fractions.
One is called the filtrate or more technically, the acid-soluble pool, and the second, the retentate or the acid-insoluble fraction.
What is the solvent used to grind living tissue into a thick slurry when preparing it for chemical analysis?
trichloroacetic acid (Cl3CCOOH)
We can grind any living tissue into a thick slurry and strain this through a cheesecloth or cotton, to obtain two fractions of the tissue. What are these fractions?
One is called the filtrate or more technically, the acid-soluble pool.
The second is called the retentate or the acid-insoluble fraction.
What are the basic steps in analysing a living tissue to identify a particular organic compound?
One extracts the compounds, then subjects the extract to various separation techniques till one has separated a compound from all other compounds. In other words, one isolates and purifies a compound.
What are “biomolecules”?
All the carbon compounds that we get from living tissues can be called ‘biomolecules’.
What is the process of Ash Analysis?
One weighs a small amount of a living tissue (say a leaf or liver and this is called wet weight) and dry it. All the water, evaporates. The remaining material gives dry weight. Now if the tissue is fully burnt, all the carbon compounds are oxidised to gaseous form (CO2, water vapour) and are removed. What is remaining is called ‘ash’. This ash contains inorganic elements (like calcium, magnesium etc).
What is the purpose of Ash Analysis?
It enables us to identify and separate inorganic elements found in living tissues.
What sort of inorganic elements and inorganic compounds can be identified through Ash Analysis of living tissue?
Inorganic elements: calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, etc
Inorganic compounds: sulphates, phosphates, rock salt, calcium carbonates, water, etc
When preparing living tissue for chemical analysis by transforming it into a thick slurry and separating the acid-soluble and insoluble fractions, inorganic compounds like sulphate, phosphate, etc., are also seen in the acid-______ fraction.
(soluble / insoluble)
When preparing living tissue for chemical analysis by transforming it into a thick slurry and separating the acid-soluble and insoluble fractions, inorganic compounds like sulphate, phosphate, etc., are also seen in the acid-soluble fraction.
What are amino acids?
Amino acids are organic compounds containing an amino group and an acidic group as substituents on the same carbon chain.
Why are amino acids also called α-amino acids?
The amino group and the acidic group are substituents on the same carbon i.e., the α-carbon.
Why are α-amino acids also called substituted methanes?
Because each hydrogen atom bonded to the carbon atom in methane is substituted with different groups to form α-amino acids. There are four substituent groups occupying the four valency positions.
In α-amino acids, there are four substituent groups occupying the four valency positions. Which are the substituent groups?
These are hydrogen, carboxyl group, amino group and a variable group designated as R group.
How many types of amino acids occur in proteins?
20 (according to NCERT)
22 (according to the real world)

What is this amino acid called?
Glycine
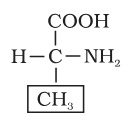
What is this amino acid called?
Alanine
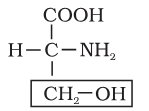
What is this amino acid called?
Serine
Glycine is an amino acid in which the R group is?
H
Alanine is an amino acid in which the R group is?
Methyl
Serine is an amino acid in which the R group is?
hydroxy methyl
What is an example of an acidic amino acid?
Glutamic acid
Aspartic acid
What is an example of a basic amino acid?
Lysine
Arginine
Histidine
What is an example of a neutral amino acid?
Main one: Valine
but there are many others
What are three examples of aromatic amino acids?
Tyrosine
Phenylalanine
Tryptophan
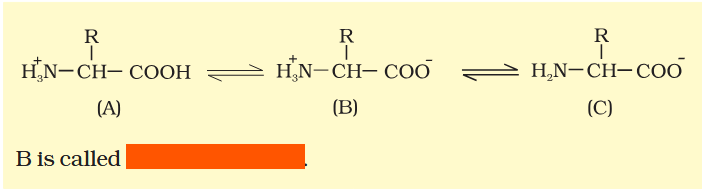
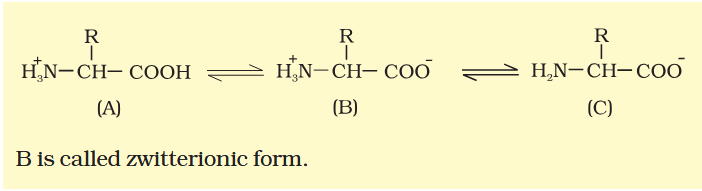
What would an amino acid look like in neutral medium?
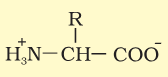
What would an amino acid look like in acidic medium?
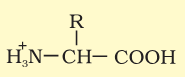
What would an amino acid look like in basic medium?
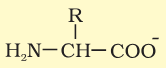

In which medium does an amino acid have this form?
Basic
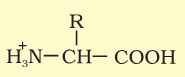
In which medium does an amino acid have this form?
Acidic

In which medium does an amino acid have this form?
Neutral
Lipids are generally water _________.
(soluble / insoluble)
Lipids are generally water insoluble.
What is the structure of a fatty acid?
A fatty acid has a carboxyl group attached to an R group. The R group could be a methyl (–CH3), or ethyl (–C2H5) or higher number of –CH2 groups (1 carbon to 19 carbons).
How many carbons can a fatty acid chain have?
20
(19 excluding the -COOH carbon)
What is the name of the fatty acid that has 16 carbons (including carboxyl carbon)?
Palmitic acid
How many carbon atoms does Palmitic acid have?
16 carbons (including carboxyl carbon)
15 carbons (excluding carboxyl carbon)
What is the name of the fatty acid that has 20 carbons (including carboxyl carbon)?
Arachidonic acid
How many carbons does Arachidonic acid have?
20 carbons (including carboxyl carbon)
19 carbons (excluding carboxyl carbon)
Fatty acids can only be saturated, not unsaturated. True or false?
False, fatty acids can be saturated as well as unsaturated
What is the IUPAC name of glycerol?
trihydroxy propane
What is the general name of fatty acids esterified with glycerol?
fats or oils
What differentiates fats and oils?
their melting point; compounds with higher melting points are called fats and compounds with lower melting points are called oils
What are phospholipids
Some lipids have phosphorous and a phosphorylated organic compound in them. These are phospholipids.
What is the difference between monoglycerides, diglycerides, and triglycerides?
Their structure.
Monoglycerides are compounds where one fatty acid chain links up with a glycerol molecule
Diglycerides are compounds where two fatty acid chains link up with a glycerol molecule
Triglycerides are compounds where three fatty acid chains link up with a glycerol molecule
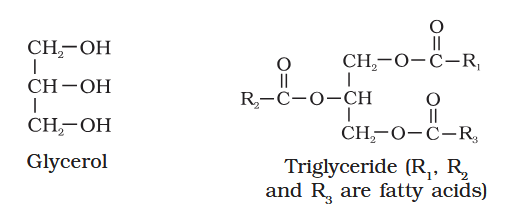
how is one monoglyceride molecule formed?
it is formed from one glycerol molecule and one fatty acid molecule. A water molecule is removed during formation
[sorry I drew the box in the diagram wrong, the fatty acid only contributes H not OH]
![<p>it is formed from one glycerol molecule and one fatty acid molecule. A water molecule is removed during formation</p><p>[sorry I drew the box in the diagram wrong, the fatty acid only contributes H not OH]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bd289d5b-1dbe-48de-a246-82a72a58c016.png)
Where can phospholipids be found?
In cell membranes
What is a prime example of a phospholipid?
Lecithin
What sort of biomolecule is Lecithin?
phospholipid
Some tissues especially the neural tissues have lipids with more complex structures. Keep this in mind.
Okay.
What are heterocyclic rings?
Ringed compounds which have elements other than carbon in the rings.
What are homocyclic rings?
Ringed compounds which have only carbons in the ring.
Are nitrogenous bases homocyclic or heterocyclic?
heterocyclic
When a nitrogenous base is attached to a sugar, what is it called?
a nucleoside
When a nitrogenous bas is attached to a sugar, and a phosphate group is also esterified with the sugar, what is it called?
a nucleotide
Some examples of nitrogenous bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil, and thymine.
What are the names of their respective nucleosides?
Adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, uridine, thymidine
Some examples of nitrogenous bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil, and thymine.
What are the names of their respective nucleotides?
Adenylic acid, guanylic acid, cytidylic acid, uridylic acid and thymidylic acid
Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA are polymers of _________.
(nucleosides / nucleotides)
nucleotides
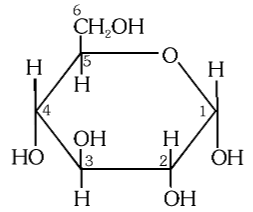
What is this structure called?
α-D-glucose
What is the structure of α-D-glucose?
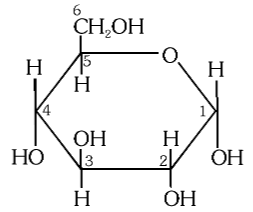
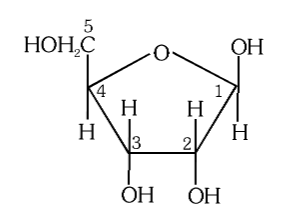
What is this structure called?
ribose
What is the structure of ribose?
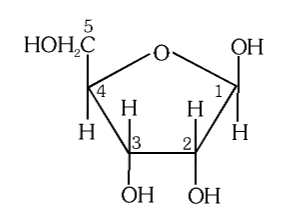

What is this structure called?
deoxyribose
What is the structure of deoxyribose?
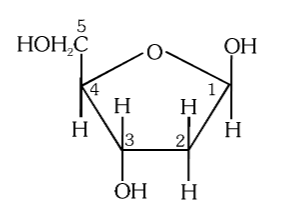
What is the structure of palmitic acid?
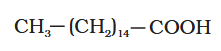

What is this structure called?
Palmitic acid
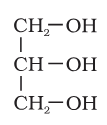
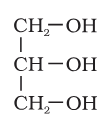
What is the structure of glycerol?
What is this compound called?
glycerol
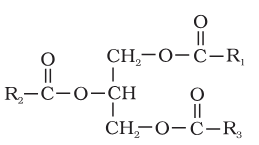
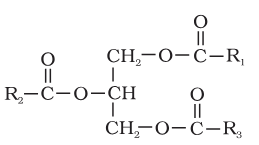
What is the structure of triglyceride?
What is this compound called?
triglyeride
What is the structure of Lecithin?
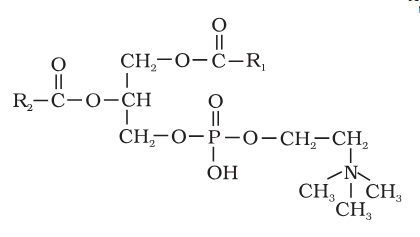
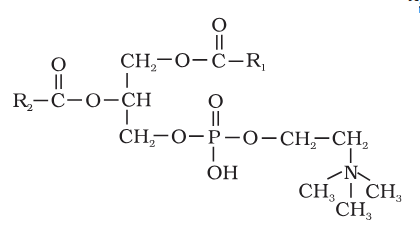
What is this compound called?
Lecithin
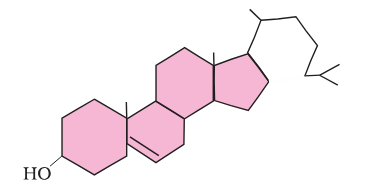
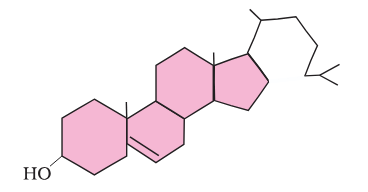
What is this compound called?
cholesterol
What is the structure of cholesterol?
What is the structure of adenine?
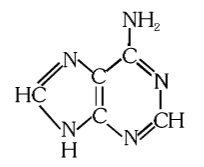
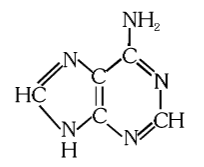
What is this compound called?
adenine
What is the structure of guanine?
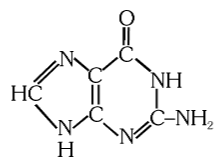
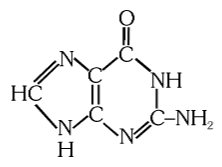
What is this compound called?
guanine
What is the structure of cytosine?
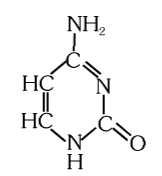
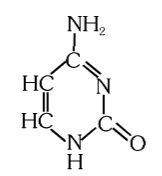
What is this compound called?
cytosine
What is the structure of thymine?
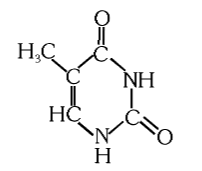
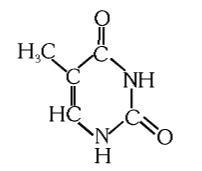
What is this compound called?
thymine
What is the structure of uracil?

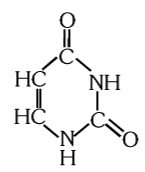
What is this compound called?
uracil
What is the structure of adenosine?
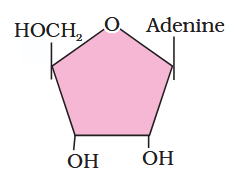

What is this compound called?
adenosine
What is the structure of uridine?
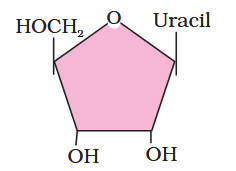
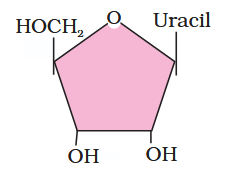
What is this compound called?
uridine
What is the structure of adenylic acid?
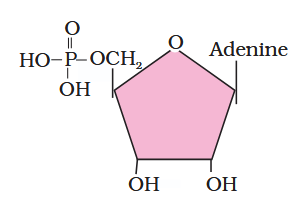
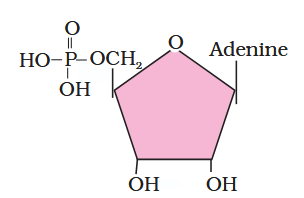
What is this compound called?
adenylic acid
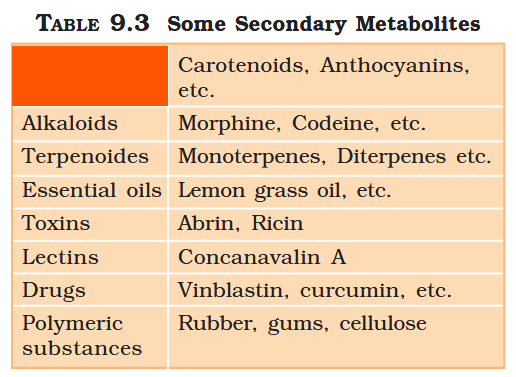
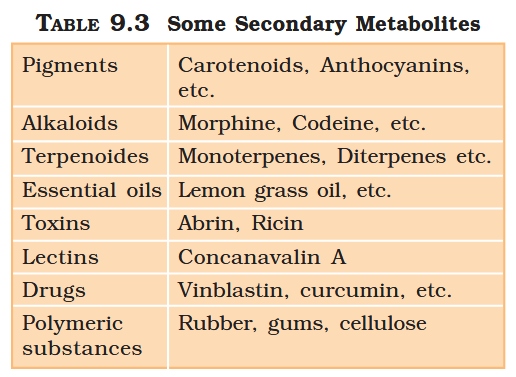
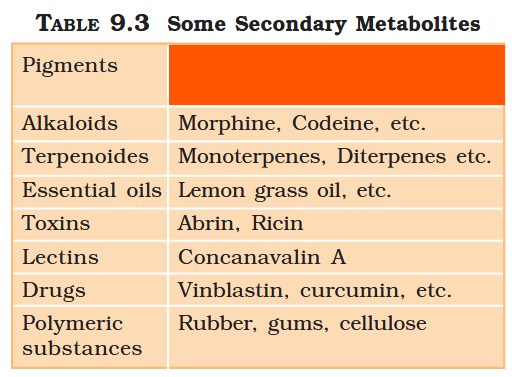
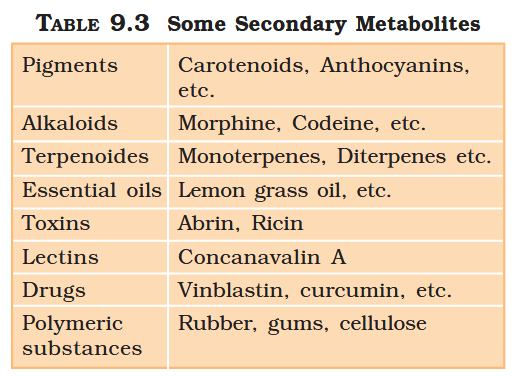
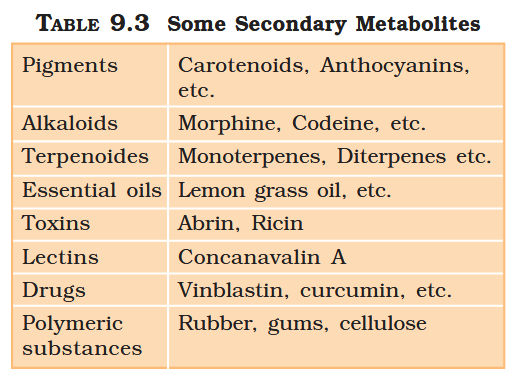
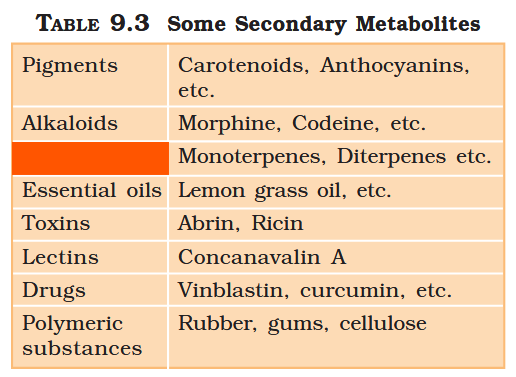
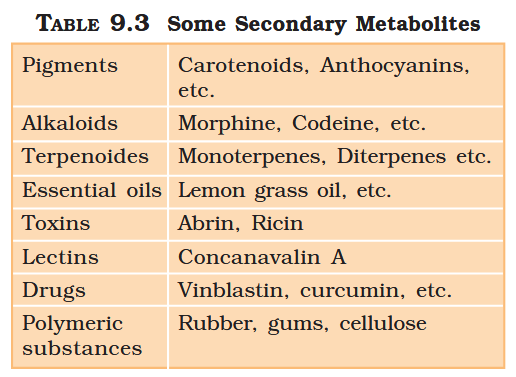
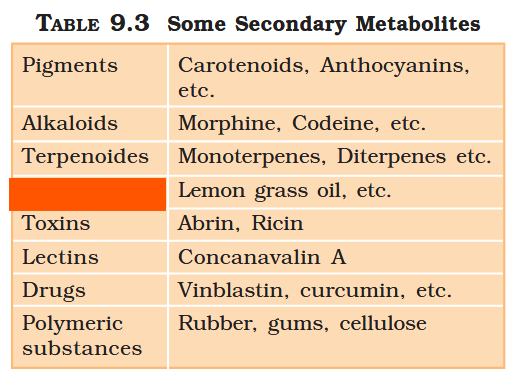
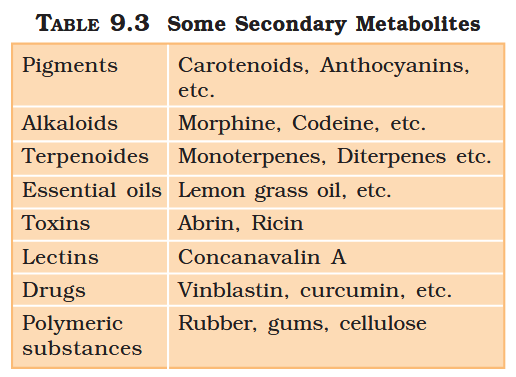
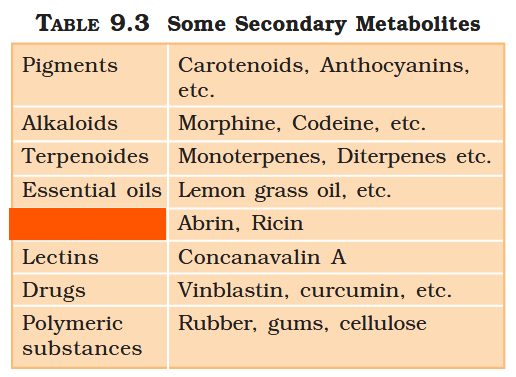
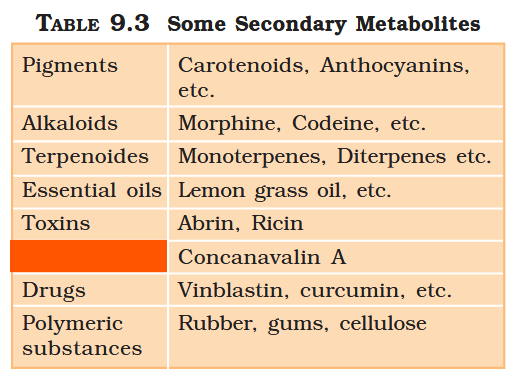
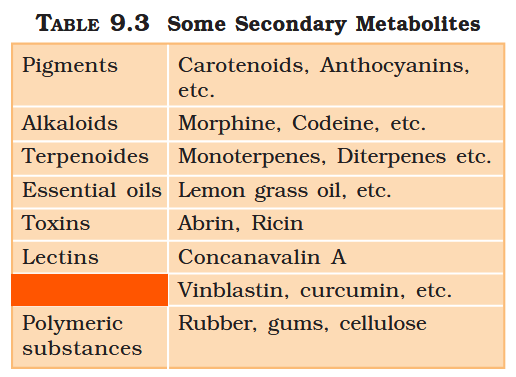
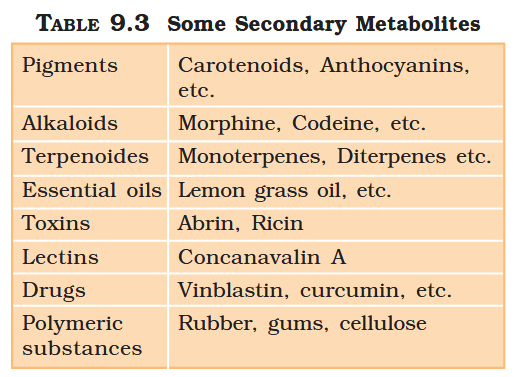
What are primary metabolites?
Biomolecules which have identifiable functions and play known roles in normal physiologial processes.
What are secondary metabolites?
Biomolecules for which the role / function is not known in their host organisms, but some of which are useful to “human welfare”, or have ecological importance.