Microbiology Lab Test 1
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What kind of microscope do we use for this class?
compound light microscope
Microscope: What is the function of the Iris diaphragm
increase or decrease the amount of light
Microscope: how many magnification is the eyepiece?
10x
Microscope: how many microns is the objective lens if it is at 10x?
1500 microns
Microscope: how many microns is the objective lens if it is at 100x?
150 microns
Say you’re on objective lens 10x, and the microbe reaches halfway through the eyepiece, how “big” is the microbe?
750 microns
Microscope: always view bacteria in what objective lens?
100x with oil immersion
Microscope: What is the index of refraction?
when the light bends and scattered lost (from the gap between the slide and the lens)
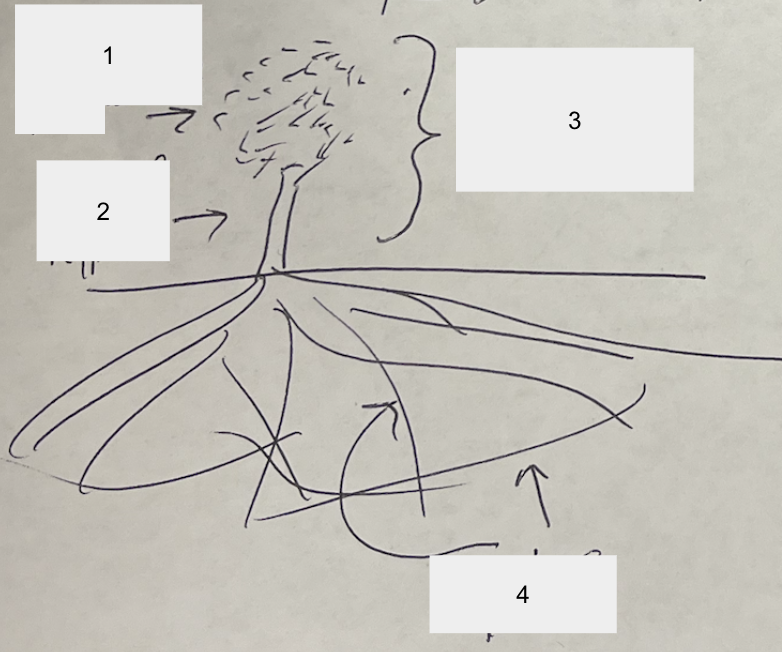
label :D
1: Spore structure
2: Aerial hyphae
3: Fruiting body
4: Hyphae
What is the cell wall of bacterias contain?
peptidoglycan
Are protozoa prokaryotes are eukaryotes?
eukaryote
What does bacteria use to move?
Flagella
What is the brewer’s yeast called? Scientifically
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
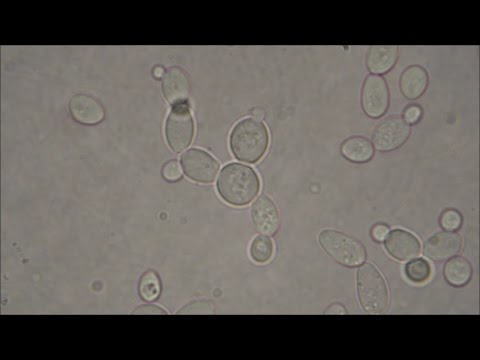
what is this
Bakers’ yeast!
what is this
Penicillium
what is this?
Aspergillus
What does simple stain mean?
1 stain (1 color/dye), any color
Postive simple stains ___?
Negative simple stains __?
microbe
background
3 function for heat fix stain?
drys moisture
makes it microbe stick to the glass
kills the bacteria
For positive simple staining, what stain do you use?
Crystal violet
For negative simple staining, what stain do you use?
Nigrosin Black (remember to not rinse or blot dry) and congo red
Order of gram staining?
Crystal violet
Iodine
Ethanol
Safranin
What shape is a cocci
ball shaped
What shape is lower case bacillus
rod
What shape is spirillum
lazy s shaped
What shape is spirochete?
tight spiral
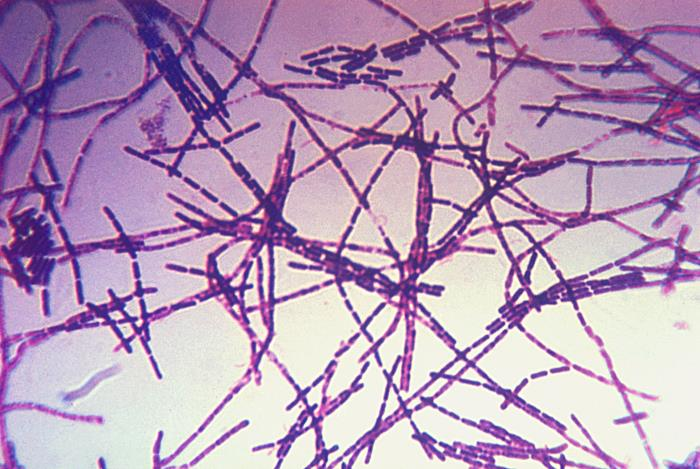
What is this bacterium?
Shape?
What are the little white spots on it?
Disease?
Bacillus anthracis
filamentous (chains)
spores
anthrax
What are the two type of Bacillus anthracis and which one is more deadly?
Cutaneous (skin)
Inhalation (lungs; the more deadly one)
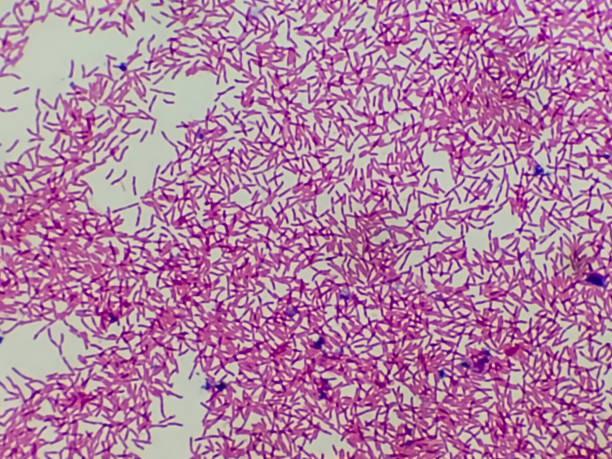
a resident inside a human body; can become deadly. What is this?
E coli
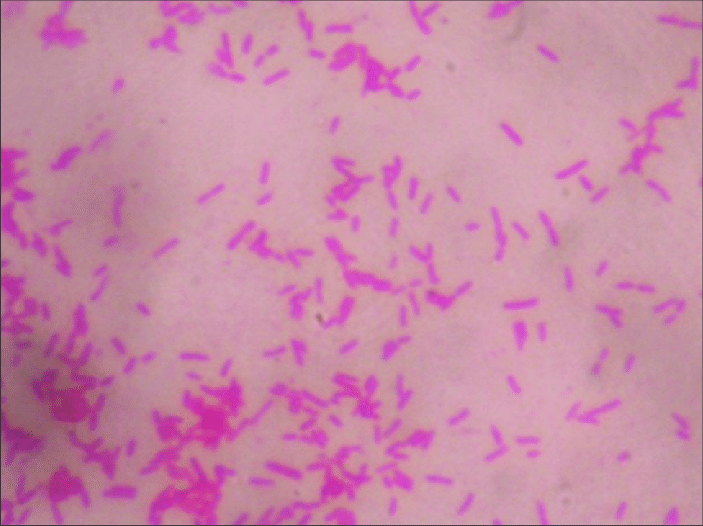
food poisoning, typhoid fever. What is this?
Salmonella
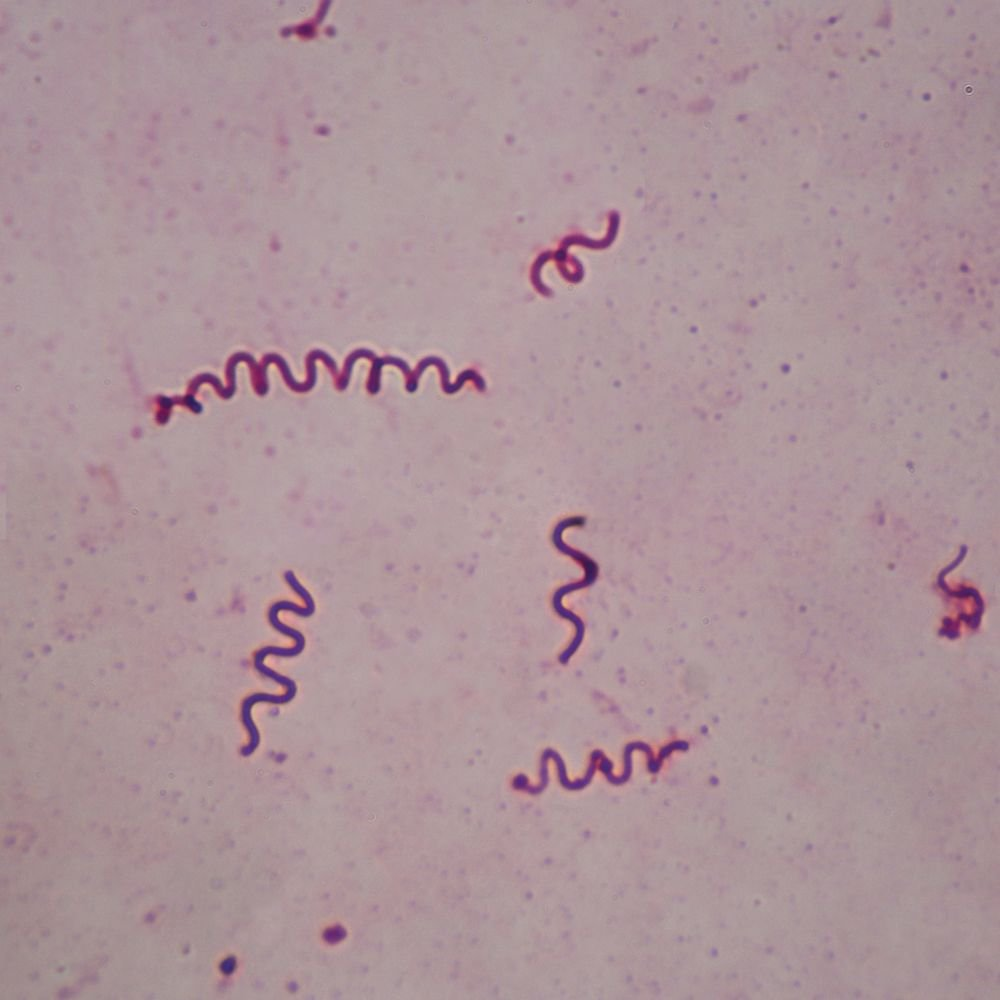
What shape is this?
Spirochete
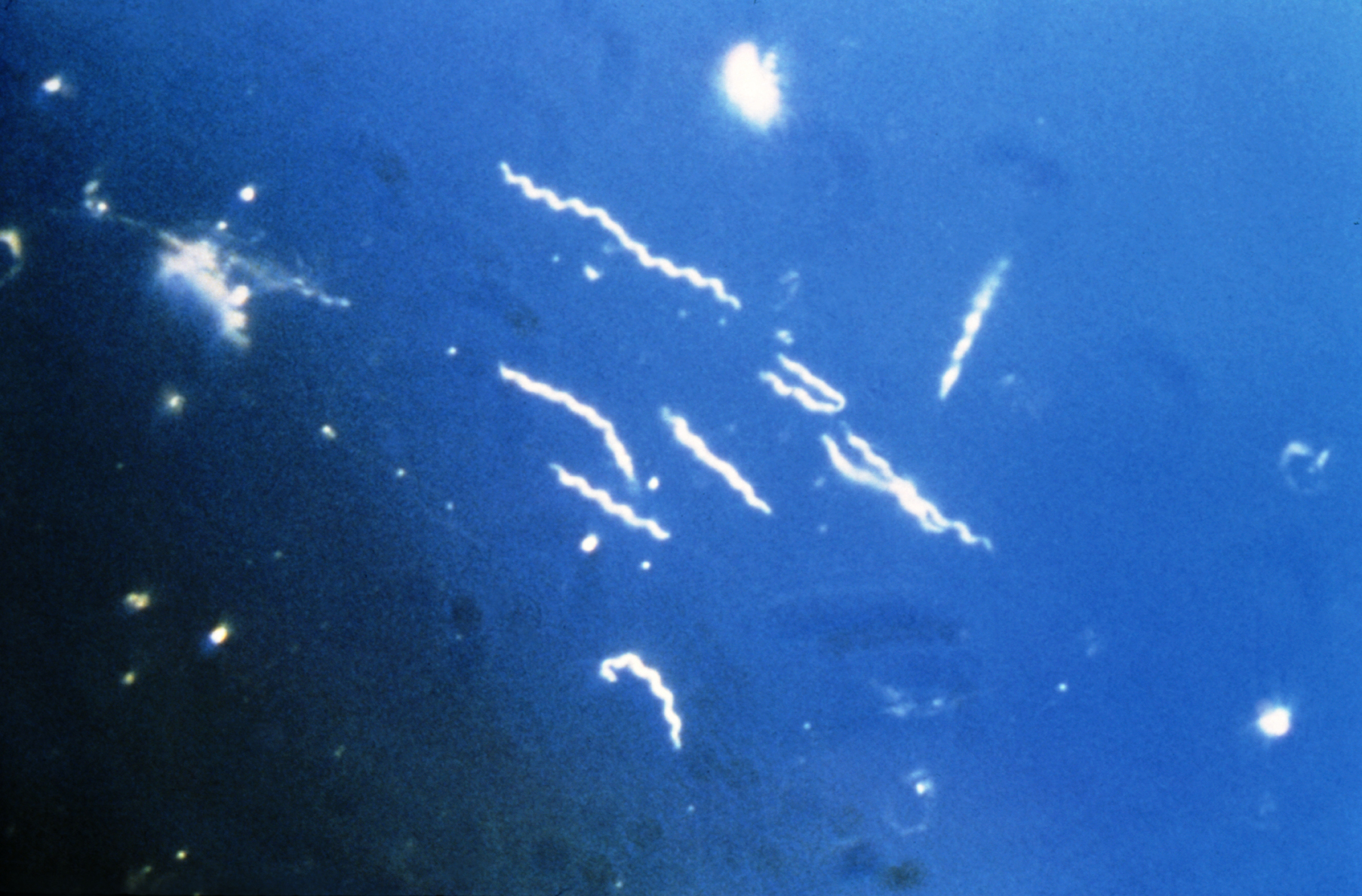
Lyme disease; comes from ticks; causes confusion
Borellia burgdorferi
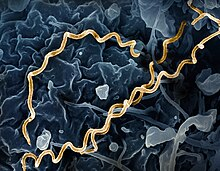
Has 3 phases, a STD. What is the name of the bacteria
Treponema pallidum; syphilis

It is a filamentous bacteria and a massive producer of antibiotics
Streptomyces griseus
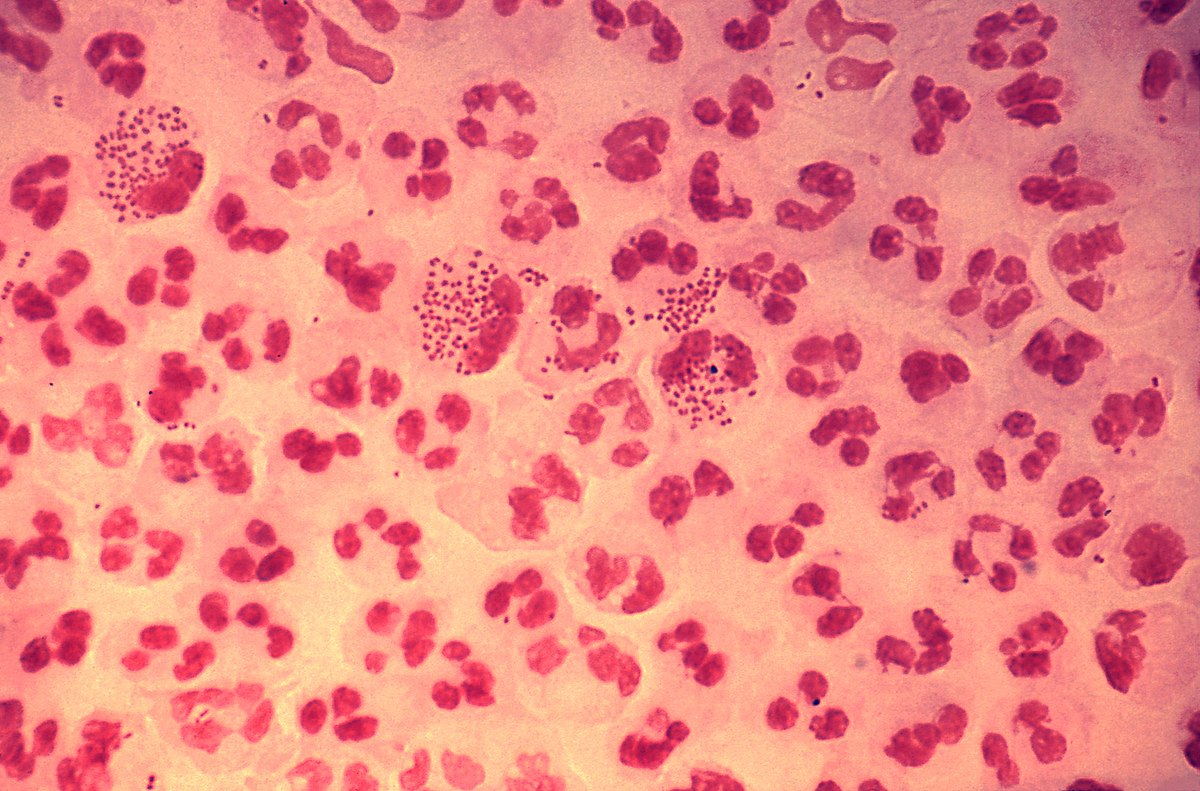
Causes a really bad headache and can be fatal cause death within a day
Neisseria meningitidis (can tell a Neisseria by its 2×2)
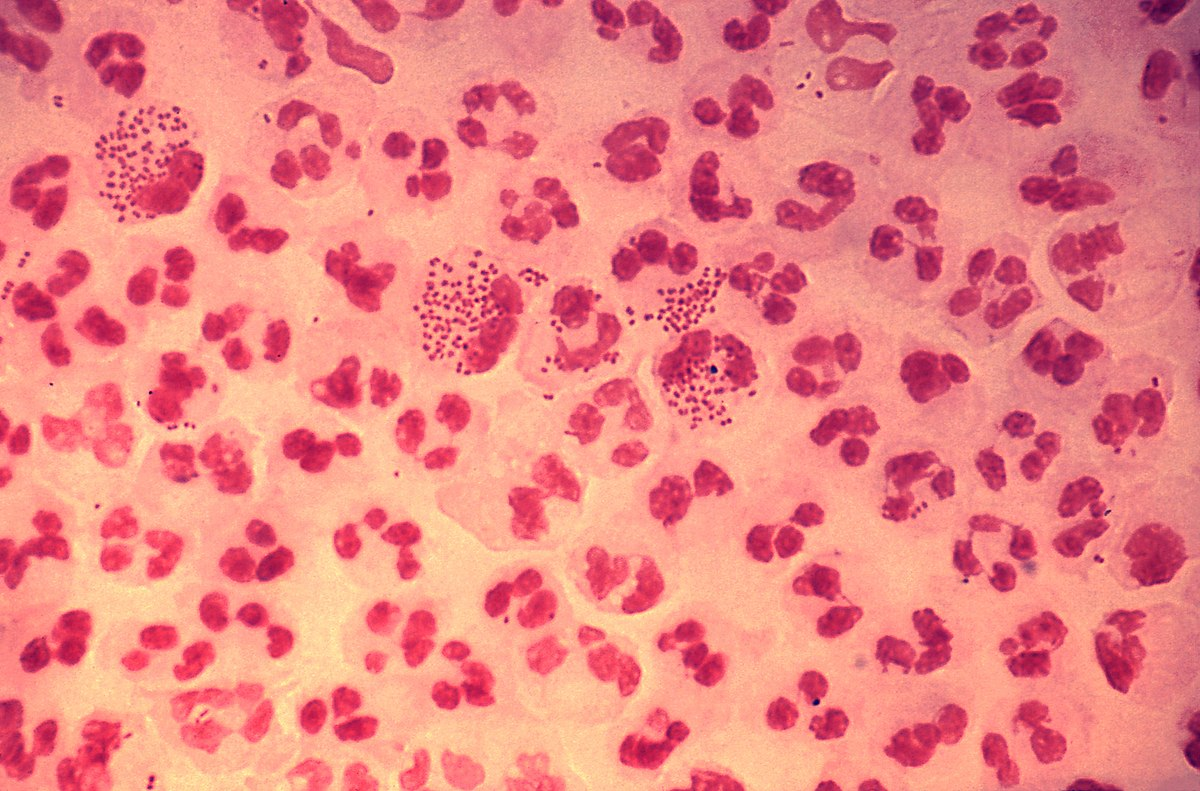
A STD, a diploid (2×2) shaped bacteria
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
What is the white thing around this bacteria and its’ function?
Capsule; made of polysaccharides and protects the bacteria and stick to surfaces
What is this? and what disease? What is that thing in blue?
Clostridium tetani; tetanus; spores
Causes severe diarrhea, carried by hurricanes. Name of bacteria and disease?
Vibrio cholerae; Cholera
What is the most common type used agar in micro?
Tryptic Soy Agar
What is a RODAC plate?
replicates the microbe of a surface
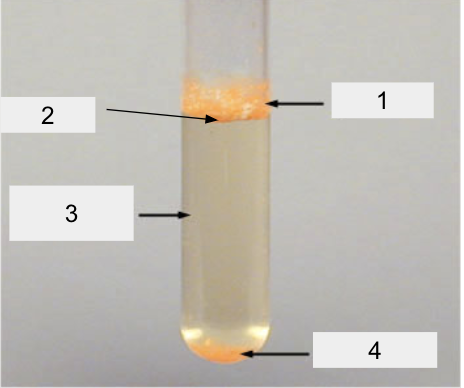
label!
Pellicle
Ring
Turbidity
Sediment
The more hazy the turbidity, the more ____
growth

top to bottom, label the form of isolated colony
spindle
punctiform
circular
irregular
rhizoid
filamentous
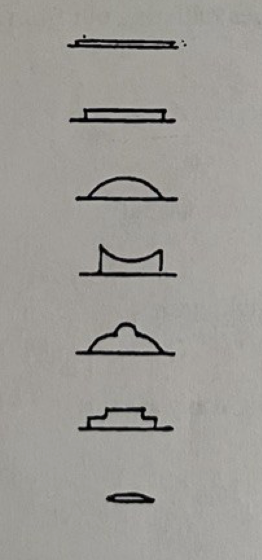
top to bottom, label the elevation of isolated colony
effuse
flat
convex
concave
umbonate
terraced
subsurface
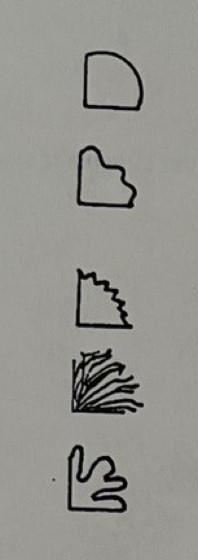
top to bottom, label the margin of isolated colony
entire
undulate
serrate
filamentous
lobate
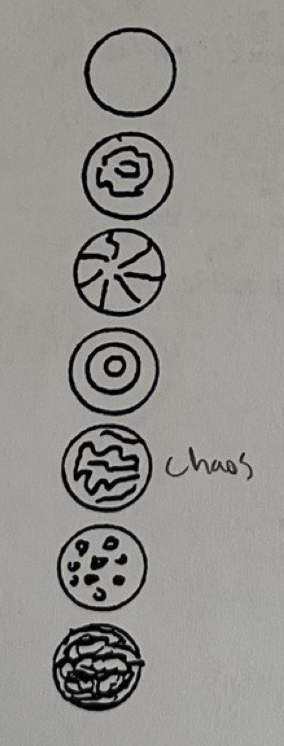
top to bottom, label the surface of isolated colony
smooth
contoured
radiate
concentric
rugose
granular
curled
What does confluent mean?
2 colonies grew over each other
What does TNTC mean?
too numerous to count
For this class, what is countable value do we use?
25-250
What does opaque mean? How about translucent?
You can’t see through the growth; you can see through the growth
you gotta know the dilution, i have no idea what to ask, the amount of 0s, is how many 10^-n you gotta go
For finding Generation Time graph, what goes on the x-axis and y-axis? What graph paper do you use?
x: Time (in mins or hours etc)
y: Cell # __ x 10^n
-semilog paper
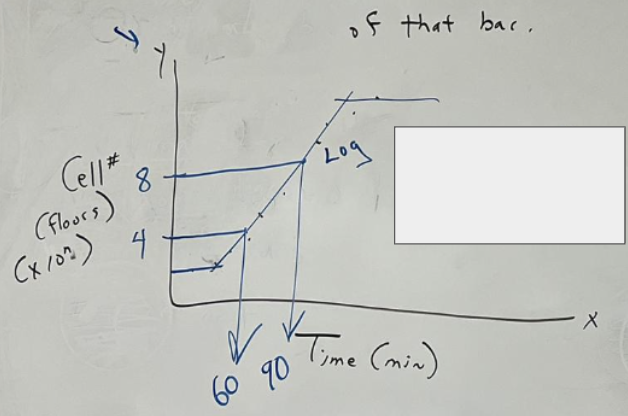
what is the generational time between the time at 60 and 90 mins?
30 mins
what is the term of how bacteria grow?
binary fission
What is the answer to this problem:
10^-4 120 cfu
the work:
120 × 10^-4 bac/ml
1.20 × 10^4 bac/ml
1.2 × 10^6 bac/ml (the answer)
What machine is used to measure turbidity?
Spectrophotometer
What does Optical Density test for? What goes on the x-axis and y?
the amount of light absorbed in the tube;
x: cell #
y: OD
What does % transmission light test for? What goes on the x-axis and y?
amount of light that gets through;
x: cell #
y: % trans
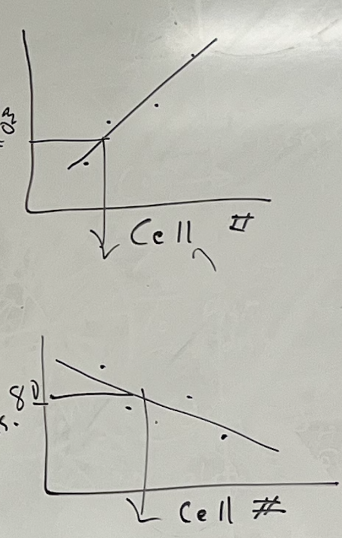
Which one is OD graph, and which one is the % trans?
top one is OD, bottom is % trans
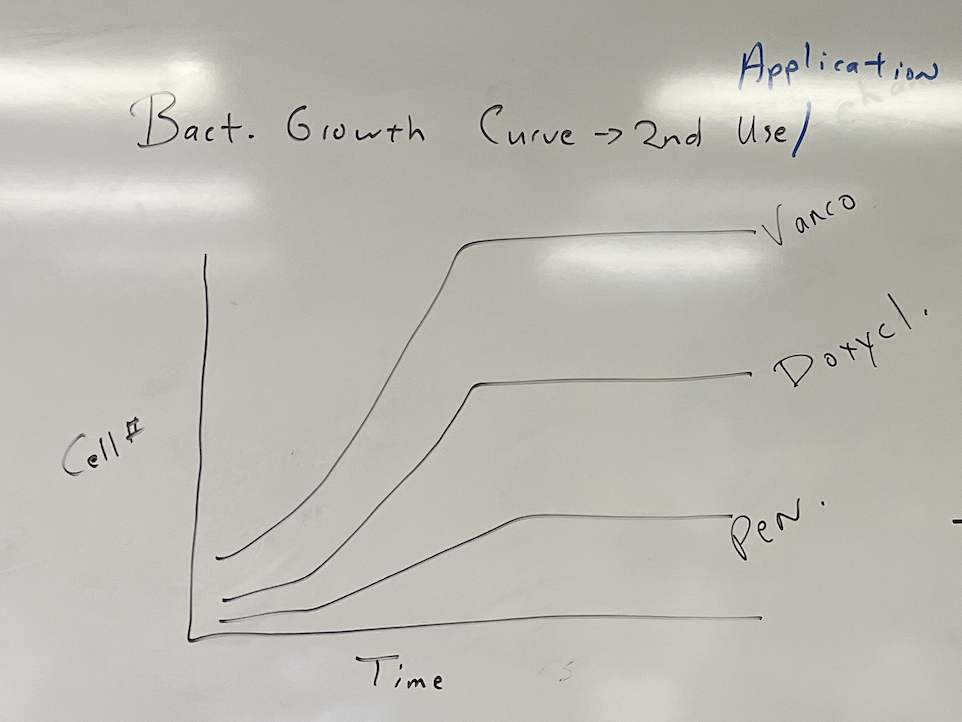
According to this graph, which antibiotic worked the best to fighting this bacteria?
the bottom one
What would TSA test for? And what would it look like?
Staph (opaque) and Strep (translucent)
When you add hydrogen peroxide, would staph or strep bubble?
Staph = Cat+ bubbles
Strep = Cat- no bubbles
Mannitol Salt Agar grows what and stops what?
Grow staph inhibits strep
What are the two types of staph? What color do they turn into on the MSA plate?
Staph epidermis: pink; Staph aureus: gold/yellow
(remember that if its gold/yellow, run coagulase test with rabbit plasma)
With the Chocolate Agar plate, what does it test for after prof do the oxidase test. If it is positive, what color does that bacteria turn to?
testing for the harmless Resident Neisseria; black (candle jar)
What O2 level are Neisseria species?
microaerophillic
Blood Agar test for what?
Streptococcus
(beta, alpha, gamma)
What does Blood Agar with Crystal Violet test for?
grow strep (looks blue/purple), inhibit staph (also in the candle jar)
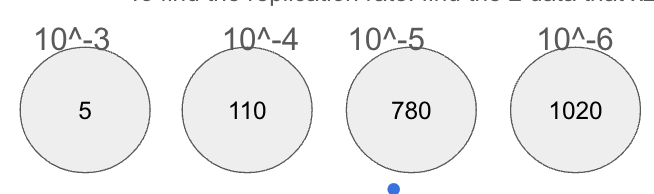
Which plate would you choose? And why?
The 3rd one, because it is between 25-250 cfu
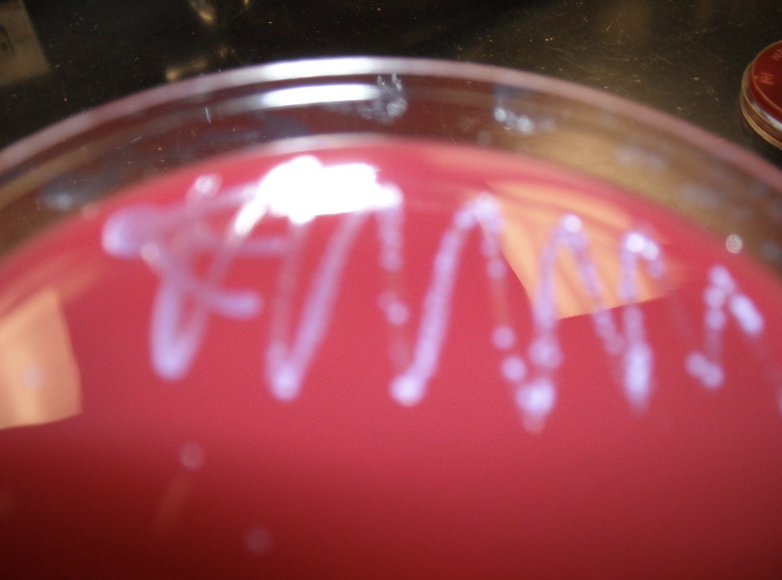
What type of plate is this, and what is the purple?
Blood Agar Crystal Violet, with strep
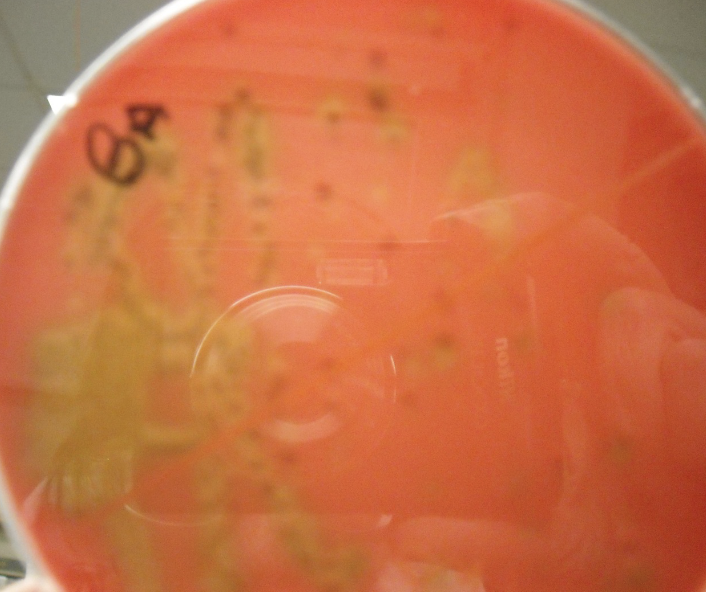
What type of plate is this, and what is the green?
Blood Agar; alpha hemolysis
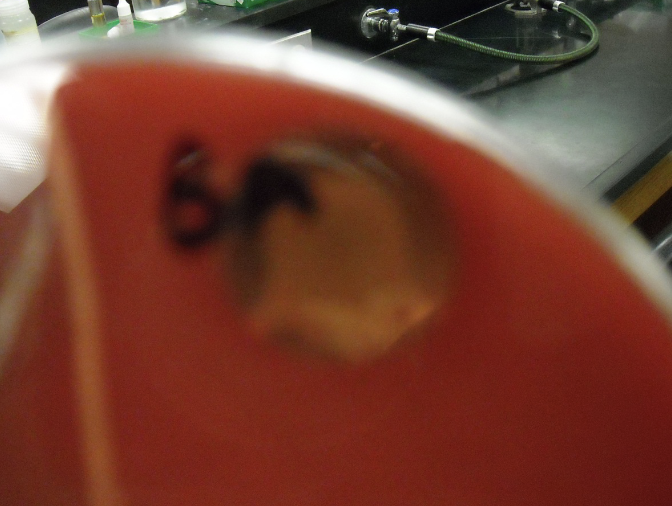

What type of hemolysis
Beta hemolysis
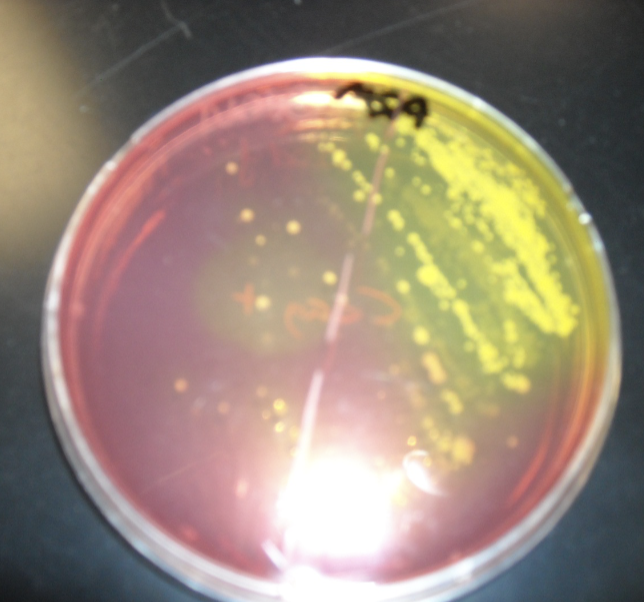
What type of plate and what is the yellow?
Mannitol salt plate; staphylococcus aureus
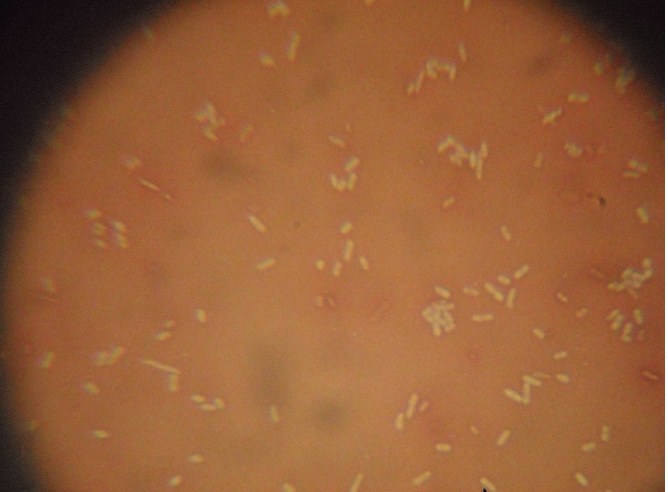
What kind of stain, + or -, what kind of bacteria?
congo red, -, E coli
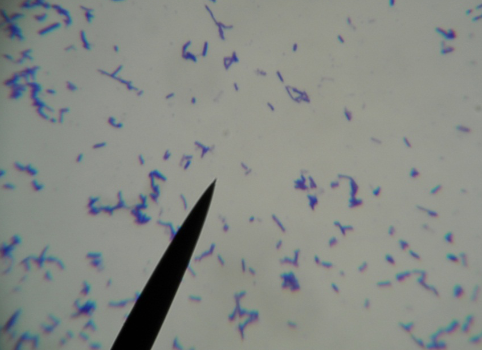
What kind of stain, + or -, what kind of bacteria?
Crystal violet, +, E coli
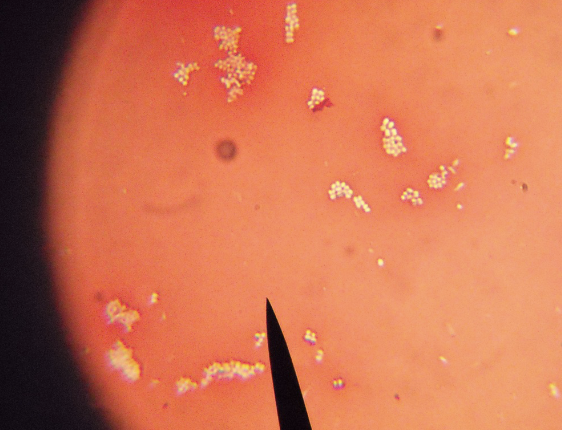
What kind of stain, + or -, what kind of bacteria?
Congo red, -, Micrococcus luteus