ICSI Test 4
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:46 PM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
1
New cards
Virus
Ubiquitous, infecting all taxonomic groups
2
New cards
Rhinovirus
Common Cold
3
New cards
Epstein-Barr Virus
Mono
4
New cards
Bacteriophages
Bacteria that infects bacteria cells (can be used as cloning vectors)
5
New cards
T2 phage infects ______
E. Coli
6
New cards
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)
The first virus ever discovered (infects wide range of plants)
7
New cards
Spike proteins
Glycoprotein that connects membrane to capsid (involved in binding to host cells)
8
New cards
Each virus species has a _______
Host range
9
New cards
Tissue tropism
Refers to range of tissue types a virus can infect
10
New cards
Lytic vs. Lysogenic cycle
Lyt- cycle ends when the host cell burst
Lyso-reproduces with the host genome
Lyso-reproduces with the host genome
11
New cards
Papillomavirus DNA Genome
• Infects 80% of adults
• Can cause cancer of cervix, penis, throat and anus (STD)
• Highly contagious
• Gardasail only effective before exposure
• By age 11-12
• Protects against 4 strains, including HPV-16
• Narrow tropism
• Can cause cancer of cervix, penis, throat and anus (STD)
• Highly contagious
• Gardasail only effective before exposure
• By age 11-12
• Protects against 4 strains, including HPV-16
• Narrow tropism
12
New cards
Prions
• Infectious agent with no nucleic acid (infectious protein)
• Comes from preexisting cell
• Mad cow disease, scrapies, brain disease
in sheep, and kuru
• Abnormal form of normally
occurring brain cell protein PrpC
• Binds with normal form of protein
and alters conformation
• Forms harmful aggregates killing cell
• Tissue deterioration and dementia
• Comes from preexisting cell
• Mad cow disease, scrapies, brain disease
in sheep, and kuru
• Abnormal form of normally
occurring brain cell protein PrpC
• Binds with normal form of protein
and alters conformation
• Forms harmful aggregates killing cell
• Tissue deterioration and dementia
13
New cards
Geology
The broadest Earth science
14
New cards
Earth
3/4 covered by water
15
New cards
Earth's Layers- Crust
• Surface layer
• Thin and brittle
• Rocks rich in silicon and oxygen
• Continental crust (usually light in color)
• Granitic rock
• Deep roots
-actually floats in mantle
• Oceanic crust (usually dark/denser in color)
• Fined-grained basalt
• Higher proportion of iron and
magnesium
• Reverse mass
• Ancient sea creatures
embedded in basaltic rock
high in the mountains
• Thin and brittle
• Rocks rich in silicon and oxygen
• Continental crust (usually light in color)
• Granitic rock
• Deep roots
-actually floats in mantle
• Oceanic crust (usually dark/denser in color)
• Fined-grained basalt
• Higher proportion of iron and
magnesium
• Reverse mass
• Ancient sea creatures
embedded in basaltic rock
high in the mountains
16
New cards
Isostasy
Vertical positioning of Earth's crust, due to flotation in the mantle
17
New cards
Earth's Layers- Mantle
• Thick layer of hot rock (thickest layer)
• 82% of Earth mass and 65% of volume
• 2,900 km thick
• Silicon and oxygen, proportionally more magnesium, iron, and
calcium
• Much denser than crust; pressure increases density (squeezed together because of the crust)
• 82% of Earth mass and 65% of volume
• 2,900 km thick
• Silicon and oxygen, proportionally more magnesium, iron, and
calcium
• Much denser than crust; pressure increases density (squeezed together because of the crust)
18
New cards
Earth's Layer's- Core
• Huge ball of hot metal
• Mostly iron with some nickel
• Radius 3,500 km
• Most knowledge comes from seismology
• Mostly iron with some nickel
• Radius 3,500 km
• Most knowledge comes from seismology
19
New cards
Earth's Five Functional Layers (Outer to Inner)
Lithosphere
Asthenosphere
Lower Mantle
Outer Core
Inner Core
Asthenosphere
Lower Mantle
Outer Core
Inner Core
20
New cards
Lithosphere
• Shell of cool, rigid rock (where we walk)
• Crust and upper mantle
• 100 km thick
• Thickest below continent
• Broken into interlocking pieces
• Tectonic plates-ride on the upper mantle
• Crust and upper mantle
• 100 km thick
• Thickest below continent
• Broken into interlocking pieces
• Tectonic plates-ride on the upper mantle
21
New cards
Asthenosphere and Lower Mantle
• Asthenosphere:
• Under lithosphere
• Mantle rock
• Soft and flows VERY slowly (plastic)- not hard rock
• Lower Mantle:
• Below Astheno.
• Strong, rigid mantle rock
• Not as plastic (not plastic)
• Under lithosphere
• Mantle rock
• Soft and flows VERY slowly (plastic)- not hard rock
• Lower Mantle:
• Below Astheno.
• Strong, rigid mantle rock
• Not as plastic (not plastic)
22
New cards
Outer and Inner Core
• Outer Core:
• Hot, liquid metal (mostly iron w/ some nickel)
• Spins as Earth rotates (also convection)
• Creates magnetic field around earth
• Geomagnetic field shields us from solar wind
• High-energy particle coming from the sun
• Inner Core- absolute center of the earth
• Solid sphere of hot metal
• Mostly iron
• 7,000*C
• Pressure keeps from melting
• Hot, liquid metal (mostly iron w/ some nickel)
• Spins as Earth rotates (also convection)
• Creates magnetic field around earth
• Geomagnetic field shields us from solar wind
• High-energy particle coming from the sun
• Inner Core- absolute center of the earth
• Solid sphere of hot metal
• Mostly iron
• 7,000*C
• Pressure keeps from melting
23
New cards
Continental Drift
World's Continents move slowly over Earth's surface
24
New cards
Pangaea
First super continent
25
New cards
Seafloor Spreading
Where the ocean floor opens
-new lithosphere is created at midocean ridge
-oceanic plate that will subduct under the tectonic plate and will melt
-new lithosphere is created at midocean ridge
-oceanic plate that will subduct under the tectonic plate and will melt
26
New cards
Divergent Boundaries
Neighboring plates move away from each other
-Example: East African Rift Zone
-Example: East African Rift Zone
27
New cards
Convergent Boundaries
Plates come together in slow motion collision
28
New cards
Three types of convergence
1)oceanic-oceanic
2)oceanic-continental
3)continental-continental
2)oceanic-continental
3)continental-continental
29
New cards
Oceanic-oceanic
-older plate subducts
-ocean trench
-island arcs parallel trenches
-earthquakes
-ocean trench
-island arcs parallel trenches
-earthquakes
30
New cards
oceanic-continental
-basaltic oceanic plate subducts beneath continental
-deep trench forms offshore
-magma forms at subduction zone and erupts as lava
-volcanic mountain chain
-deep trench forms offshore
-magma forms at subduction zone and erupts as lava
-volcanic mountain chain
31
New cards
Continental-continental
-neither sink below the other
-pushes one another upward
-example: Himalayas
-India rammed into Asia 50 million years ago
-pushes one another upward
-example: Himalayas
-India rammed into Asia 50 million years ago
32
New cards
Faults
Crack that divides into two blocks of rock that have moved relative to each other
33
New cards
What % of Earth's surface is covered by salt water?
71%
34
New cards
7 Continents
Africa, Australia, North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Antarctica
35
New cards
Topography
Shape of earth's surface (mountain belts, plains, plateaus, and canyons)
36
New cards
Continents are AROUND ______ meters ABOVE sea level
840 meters (around)
37
New cards
Pacific Ocean
The largest, deepest, and oldest ocean
38
New cards
Atlantic Ocean
The coldest and saltiest ocean
39
New cards
Indian Ocean
The smallest Ocean
40
New cards
Where is the midocean ridge?
The Atlantic Ocean
41
New cards
Some landforms were created by....
1) tectonic process
2) WATER (running, more powerful than the others)
3) wind
4) ice
5) gravity
2) WATER (running, more powerful than the others)
3) wind
4) ice
5) gravity
42
New cards
Compression
Pushing together, converging plates
43
New cards
Tension
pulling apart of rock, diverging plates
44
New cards
Shear Stress
Slide past each other
45
New cards
Rocks respond to stress by
Fracture, deform elastically, and deform plastically
46
New cards
Fracture
Breaks under a lot of pressure
47
New cards
Deform elastically
Bounces back to original shape and size
48
New cards
Deforms plastically
Stress exceeds elastic limit
49
New cards
4 types of mountains
Folded, Upwarped, Fault-block, and Volcanic
50
New cards
Folded Mountains
• Most common type of mountain
• Tallest mountain range on Earth
• Tectonic collisions cause compressive stress
and crumples the rock
• Mountain ranges in the middle of a continent
mean that plates have collide there in the
past
• Canadian Rockies (young)
• Himalayas still converging and still growing
• Appalachian Mountains (plate convergence 300 million years ago) when the African plate hit the North American plate
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r9Uu-Gp2ztg
• Tallest mountain range on Earth
• Tectonic collisions cause compressive stress
and crumples the rock
• Mountain ranges in the middle of a continent
mean that plates have collide there in the
past
• Canadian Rockies (young)
• Himalayas still converging and still growing
• Appalachian Mountains (plate convergence 300 million years ago) when the African plate hit the North American plate
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r9Uu-Gp2ztg
51
New cards
Upwarped Mountains
• Black Hills of South Dakota (great example)
• Domelike shape, produced by compression
• Single anticline
• Forms when magma pushes its way up and moves crust upward
• Made of older igneous and metamorphic bedrock
• Sedimentary rock erodes from top
• Domelike shape, produced by compression
• Single anticline
• Forms when magma pushes its way up and moves crust upward
• Made of older igneous and metamorphic bedrock
• Sedimentary rock erodes from top
52
New cards
Fault-Block Mountains
• Mountain formed by tensional stress and has at least one side bounded by a normal fault
• Broad uplifting over a large area
• Huge blocks of crust are pushed upward along steep fault planes, while other sections drop down
• Rise steeply above surrounding landscape
• Teton Range and Sierra Nevada
-appears out of nowhere
• https://www.coursera.org/lecture/mountains-101/2-3-types-of-mountains-q9lb3
• Broad uplifting over a large area
• Huge blocks of crust are pushed upward along steep fault planes, while other sections drop down
• Rise steeply above surrounding landscape
• Teton Range and Sierra Nevada
-appears out of nowhere
• https://www.coursera.org/lecture/mountains-101/2-3-types-of-mountains-q9lb3
53
New cards
Volcanoes
• Mountain or hill formed by the extrusion
of lava, ash, and rock fragments (depending on how much pressure there is)
• Conical shape
• Summit has bowl-shaped depression called
crater
• Connected to subsurface magma chamber by
a vent
• Crater that exceeds 1 km is called a caldera
of lava, ash, and rock fragments (depending on how much pressure there is)
• Conical shape
• Summit has bowl-shaped depression called
crater
• Connected to subsurface magma chamber by
a vent
• Crater that exceeds 1 km is called a caldera
54
New cards
Caldera
When a volcano breaks
55
New cards
Three kinds of volcanoes
Shield, Cinder cones, and composite cones
56
New cards
Shield Volcano
Built by a steady supply of basaltic lava (built by oceanic crust)
57
New cards
Cinder Cones
Very steep, but rarely exceed 300m
-built from ejected materials: ash cinder, glass, and lava fragments
-single vent, pile up at steep angle
-built from ejected materials: ash cinder, glass, and lava fragments
-single vent, pile up at steep angle
58
New cards
Composite Cone
High, steep sided summit and gently sloping flanks
-alternating layers of lava, ash, and mud
-example: Mount St. Helens
-alternating layers of lava, ash, and mud
-example: Mount St. Helens
59
New cards
Volcanoes
• Most form near divergent or convergent plates
• Ring of Fire encircles most of the Pacific Ocean
• Convergent boundaries
• 75% of Earth’s volcanoes
• 600 are active (most are underwater)
• Some are created by hot spots
• Stationary, exceptionally hot region deep in Earth’s
interior
• Mantle rock over hotspot softens and is moved upward by
convection
• Warmed rock melts under less pressure and erupts near
surface
• Mostly under sea floor
• Seamount ---> volcanic island ---> plate shifts island away
from hotspot
• Ring of Fire encircles most of the Pacific Ocean
• Convergent boundaries
• 75% of Earth’s volcanoes
• 600 are active (most are underwater)
• Some are created by hot spots
• Stationary, exceptionally hot region deep in Earth’s
interior
• Mantle rock over hotspot softens and is moved upward by
convection
• Warmed rock melts under less pressure and erupts near
surface
• Mostly under sea floor
• Seamount ---> volcanic island ---> plate shifts island away
from hotspot
60
New cards
Plains and Plateaus
• Plains are broad flat areas that do not rise far above sea level
• Extend from base of mountain range
• Built by accumulated sediment
• Between Rocky Mountains and Mississippi river
• Georgia Coastal Plain
• Much of midwestern US
• Plateau flat areas uplifted > 600 m above sea level
• Tectonic forces
• Extend from base of mountain range
• Built by accumulated sediment
• Between Rocky Mountains and Mississippi river
• Georgia Coastal Plain
• Much of midwestern US
• Plateau flat areas uplifted > 600 m above sea level
• Tectonic forces
61
New cards
Earth's Water
• Almost all of Earth’s water is salt water
• < 3% of water is fresh water
• Most held in ice and snow in polar regions and tops of
mountains (we cannot use most of this water)
• Groundwater-under the surface
• Surface water
• Atmosphere- think clouds
• Biosphere- water in living things
• Water is always moving in a cycle (hydrologic cycle)
• < 3% of water is fresh water
• Most held in ice and snow in polar regions and tops of
mountains (we cannot use most of this water)
• Groundwater-under the surface
• Surface water
• Atmosphere- think clouds
• Biosphere- water in living things
• Water is always moving in a cycle (hydrologic cycle)
62
New cards
Ocean Basin
• Deep depression in lithosphere between continental margin (edge of a continent) and midocean ridge
• 30% of Earth’s surface
• Made of oceanic crust (basaltic)
• Contains abyssal plains, seamounts, and ocean trenches
• 30% of Earth’s surface
• Made of oceanic crust (basaltic)
• Contains abyssal plains, seamounts, and ocean trenches
63
New cards
Abyssal Plain
• Flattest places on Earth
• Averages 4,000 m below sea level
• Less than 1 ft vertical change over 1,000
sq ft (.01%)
• Dark, dense, near freezing
• Pressure increases with depth
• Most animals eat dead organic matter
• Averages 4,000 m below sea level
• Less than 1 ft vertical change over 1,000
sq ft (.01%)
• Dark, dense, near freezing
• Pressure increases with depth
• Most animals eat dead organic matter
64
New cards
Ocean Trenches
• Deep furrow in the sea floor adjacent to active
continental margins
• Can exceed 10,000 meters
• Edge of one tectonic place disappears due to
subduction
• Subducting lithosphere can become stuck b/c of
friction
• Earthquake
• Creates heat
continental margins
• Can exceed 10,000 meters
• Edge of one tectonic place disappears due to
subduction
• Subducting lithosphere can become stuck b/c of
friction
• Earthquake
• Creates heat
65
New cards
Midocean Ridge
• Rises from seafloor indicating divergent plate
boundary
• 65,000 m long
• 21% of Earth’s surface
• “ridge” is somewhat misleading because
system is hundreds of meters wide and rift
valley exist along ridge crest
boundary
• 65,000 m long
• 21% of Earth’s surface
• “ridge” is somewhat misleading because
system is hundreds of meters wide and rift
valley exist along ridge crest
66
New cards
Agents of Change
mediums where surface processes occur (includes liquid water, ice, gravity, and wind)
67
New cards
Weathering
The breakdown of rock that occurs at or near Earth's surface
68
New cards
What are the two types of weathering
Chemical and mechanical (physical)
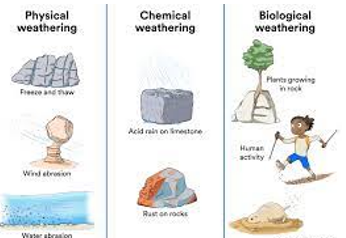
69
New cards
Mechanical Weathering
The breakdown of rock by physical means
70
New cards
Erosion
The physical REMOVAL of weathered bits of rock from one place and their transport by liquid water, ice, gravity, and wind to another place
71
New cards
Soil is...
1) a mixture of organic and nonliving materials
2) rock fragments with decaying matter
3) necessary for plant growth
4) found in thousands of different kinds
5)composed of layers (shorthand is just to identify "topsoil" and "subsoil"; in reality, subsoil is composed of various layers or "horizons").
6)a finite (limited) resource. (As in, fertile soil)
2) rock fragments with decaying matter
3) necessary for plant growth
4) found in thousands of different kinds
5)composed of layers (shorthand is just to identify "topsoil" and "subsoil"; in reality, subsoil is composed of various layers or "horizons").
6)a finite (limited) resource. (As in, fertile soil)
72
New cards
Components of soil
Air
water
rocky material
Humus (5% or less, gives the black/brown color)
water
rocky material
Humus (5% or less, gives the black/brown color)
73
New cards
Soil is classified by texture
Sand (2-0.05mm)
Silt(0.05-0.002mm)
Clay (smaller than 0.002mm)
GEORGIA HAS MORE CLAY
Silt(0.05-0.002mm)
Clay (smaller than 0.002mm)
GEORGIA HAS MORE CLAY
74
New cards
Loam
The best soil, it's a mixture of sand, silt, and clay
75
New cards
Soil Horizons
1) O Horizon-below the grass, smallest layer
2) A Horizon-topsoil, brown/black color
3) E Horizon-leaching layer
4) B Horizon- subsoil
5) C Horizon- substratum, contains groundwater
6) R Horizon- bedrock
2) A Horizon-topsoil, brown/black color
3) E Horizon-leaching layer
4) B Horizon- subsoil
5) C Horizon- substratum, contains groundwater
6) R Horizon- bedrock
76
New cards
Stream
any body of flowing water confined within a channel (has sides)
77
New cards
Running water is most widespread agent of ____
Erosion (example: grand canyon)
78
New cards
Gradient
Slope of a stream
79
New cards
Velocity
How quickly water moves at a given point
80
New cards
Discharge
volume of water that a stream transports in a given amount of time
81
New cards
Load
the amount and type of sediment that a stream carries (dissolves, suspended, and bed)
82
New cards
Evolution of a stream
•Streams change over time.
–Initially, streams are straight and the water flows fast. (finding the route of least resistance)
–Later, streams are meandering (curve of a river)
–Stream channels deepen and widen.
–Initially, streams are straight and the water flows fast. (finding the route of least resistance)
–Later, streams are meandering (curve of a river)
–Stream channels deepen and widen.
83
New cards
Downcutting
•River erodes channel more deeply overtime
–Erosion works on sides widening the channel
–Can create valley
•V-shaped valleys
–Steep slopes
–Very common
–Erosion works on sides widening the channel
–Can create valley
•V-shaped valleys
–Steep slopes
–Very common
84
New cards
Glaciers
•Glaciers are enormous masses of moving ice.
–formed by snow that doesn't melt
–compacted by overlying snow, becoming crystalline with a liquid base.
-between the rock and the glacier, there will be a little bit of water that they are riding on
•Two kinds: alpine and continental
–formed by snow that doesn't melt
–compacted by overlying snow, becoming crystalline with a liquid base.
-between the rock and the glacier, there will be a little bit of water that they are riding on
•Two kinds: alpine and continental
85
New cards
Glacial Erosion
•Means of erosion:
–Abrasion
–Plucking
-can be apart of the glacier
•Evidence of glacial erosion:
–U-shaped valleys
–Striations
–Horns
–Glacial lakes- where the water in the U shaped valley meets in the middle and forms a lake
–Abrasion
–Plucking
-can be apart of the glacier
•Evidence of glacial erosion:
–U-shaped valleys
–Striations
–Horns
–Glacial lakes- where the water in the U shaped valley meets in the middle and forms a lake
86
New cards
Groundwater-Change Agent
-Cave-empty underground space large enough for a human to enter
-created by dissolving action of groundwater (especially limestone)
-chemically weathering and erosion
-readily dissolves in acidic groundwater
-stalatites (from the top of the cave) vs stalagmites (from the bottom of the cave)
-Calcium carbonate and other minerals precipitate out of solution
-Over time, roof can collapse forming in a sinkhole
-created by dissolving action of groundwater (especially limestone)
-chemically weathering and erosion
-readily dissolves in acidic groundwater
-stalatites (from the top of the cave) vs stalagmites (from the bottom of the cave)
-Calcium carbonate and other minerals precipitate out of solution
-Over time, roof can collapse forming in a sinkhole