BASU Exam 3 Chapter 25: Seedless Plants
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Which trait is not shared by chlorophytes, charophytes, and plants?
A) Multicellularity
B) Cell walls with chitin
C) Chloroplasts with chlorophyll a & b
D) Starch as a storage molecule
B) Cell walls with chitin
Which group is the closest relative to land plants?
A) Chlorophytes
B) Rhodophytes
C) Charophytes
D) Brown algae
C) Charophytes
Which of the following adaptations helped plants resist desiccation on land?
A) Development of apical meristems
B) Evolution of a waxy cuticle
C) Presence of lignin in cell walls
D) Formation of multicellular gametangia
B) Evolution of a waxy cuticle
How does the alternation of generations in land plants differ from the life cycle of charophytes?A) Charophytes have both a multicellular haploid and diploid stage
B) Charophytes produce thousands of recombinant spores through meiosis
C) Land plants alternate between a multicellular haploid gametophyte and a multicellular diploid sporophyte
D) The zygote of land plants immediately undergoes meiosis to form four spores
C) Land plants alternate between a multicellular haploid gametophyte and a multicellular diploid sporophyte
What is the function of sporopollenin in land plants?
A) Supports the structural integrity of vascular tissues
B) Assists in fertilization by attracting sperm cells
C) Helps in water and nutrient absorption
D) Protects haploid spores from desiccation
D) Protects haploid spores from desiccation
Which adaptation allows plants to continuously grow toward resources such as water and sunlight?
A) Apical meristem
B) Waxy cuticle
C) Lignin-reinforced cell walls
D) Multicellular gametangia
A) Apical meristem
Why was the evolution of multicellular gametangia important for land plants?
A) It allowed plants to grow taller
B) It made photosynthesis more efficient
C) It protected gametes from desiccation
D) It enabled rapid spore dispersal through air
C) It protected gametes from desiccation
Mycorrhizal associations in early land plants helped with:
A) Protection from herbivores
B) Nutrient and water absorption
C) Carbon dioxide uptake
D) Mechanical support against gravity
B) Nutrient and water absorption
Secondary metabolites in land plants evolved primarily to:
A) Assist in photosynthesis
B) Protect against herbivores and competitors
C) Improve structural rigidity
D) Enhance water retention
B) Protect against herbivores and competitors
Which of the following characteristics is not true of bryophytes?
A) They are seedless and nonvascular
B) They require water for reproduction
C) The diploid sporophyte is the dominant generation
D) They have rhizoids instead of true roots
C) The diploid sporophyte is the dominant generation
What is the function of rhizoids in bryophytes?A) Absorb water and nutrients like true roots
B) Anchor the plant to a substrate
C) Transport water throughout the plant
D) Store starch for later energy use
A) Absorb water and nutrients like true roots
Why do bryophytes require a moist environment for reproduction?
A) Their spores need water to germinate
B) Their gametophytes are unable to survive in dry conditions
C) Their sperm are flagellated and must swim to the egg
D) Their rhizoids only function in wet conditions
C) Their sperm are flagellated and must swim to the egg
Which of the following best describes the sporophyte in bryophytes?
A) It is dominant and provides nutrients to the gametophyte
B) It is independent and photosynthetic
C) It produces both eggs and sperm
D) It is dependent on the gametophyte for food and water
D) It is dependent on the gametophyte for food and water
Where does the bryophyte sporophyte develop?
A) Inside the archegonium of the gametophyte
B) Within the rhizoids of the gametophyte
C) Inside the sporangium
D) Inside a seed coat
A) Inside the archegonium of the gametophyte
What structure in bryophytes produces spores?A) Gametophyte
B) Rhizoids
C) Sporophyte
D) Sporangium
D) Sporangium
What is a distinguishing feature of liverworts (Marchantia)?
A) Large, independent sporophytes
B) Elevated gametophytes that resemble miniature trees
C) Sporophytes that grow tall for better spore dispersal
D) A symbiotic relationship with fungi
B) Elevated gametophytes that resemble miniature trees
Why are hornworts named as such?
A) Their gametophytes have a horn-like structure
B) They grow in dry, desert-like conditions
C) Their sporophytes have a long, tapered horn-like shape
D) They contain toxic secondary metabolites
C) Their sporophytes have a long, tapered horn-like shape
Which of the following statements about mosses is false?
A) They are the most numerous non-vascular plants
B) They thrive only in moist environments
C) Their sporophytes grow up from female gametophytes for spore dispersal
D) They can inhabit extreme environments such as tundra and deserts
B) They thrive only in moist environments
What important ecological role do mosses play?
A) They are primary producers in cold and high-altitude regions
B) They fix nitrogen in nutrient-poor soils
C) They break down rocks into soil more efficiently than fungi
D) They prevent seed plants from growing in their habitat
A) They are primary producers in cold and high-altitude regions
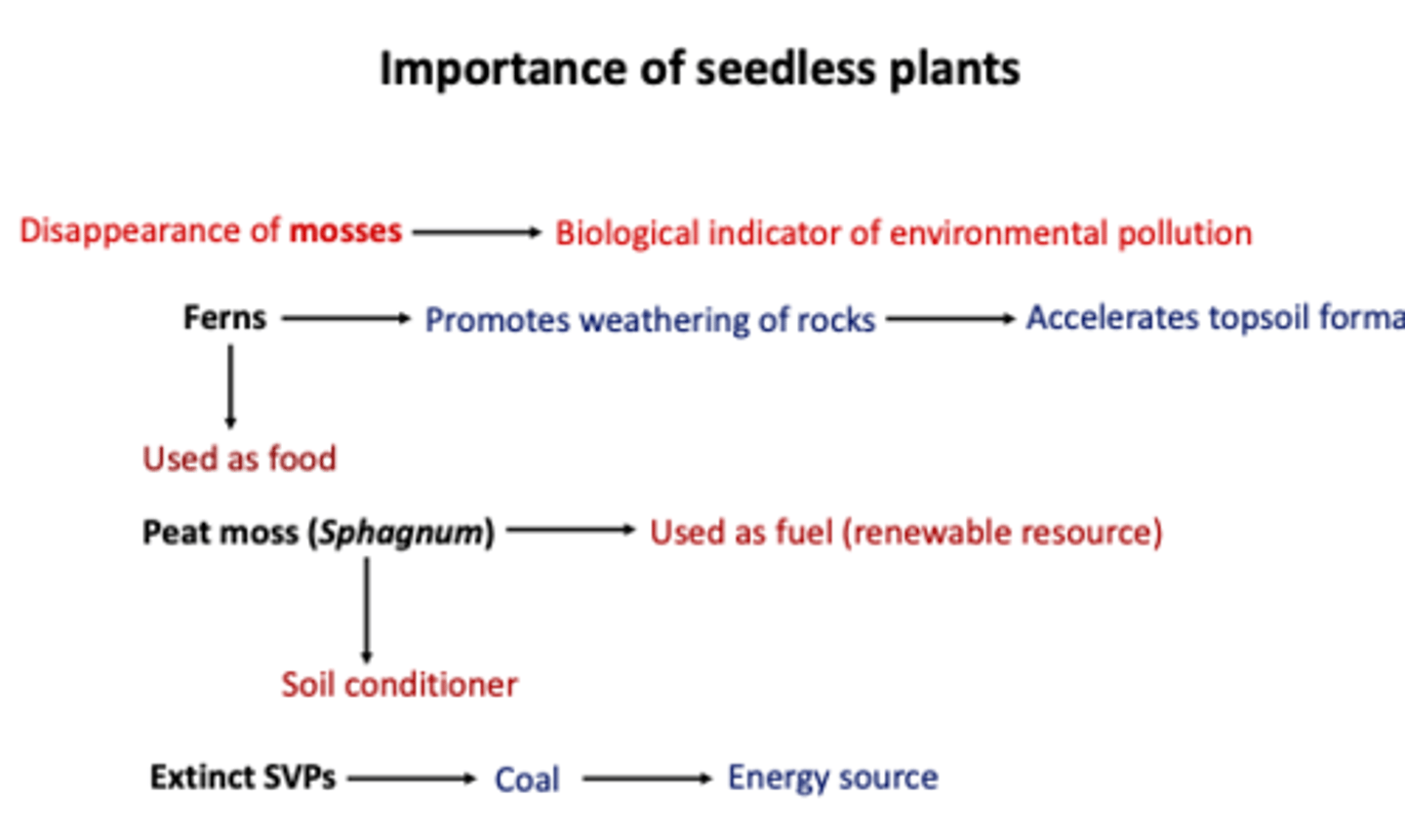
Why are peat moss bogs ecologically significant?
A) They store large amounts of carbon and are harvested for fuel
B) They produce oxygen at a higher rate than trees
C) They act as natural fertilizers for surrounding plants
D) They help disperse fungal spores across large distances
A) They store large amounts of carbon and are harvested for fuel
What is a unique feature of some peatlands that contain Sphagnum moss?
A) They support the growth of large vascular plants
B) They have preserved corpses for thousands of years
C) They are highly resistant to desiccation and fire
D) They function as breeding grounds for amphibians
B) They have preserved corpses for thousands of years
True or False: Hornworts can form symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria.
True
Which characteristic distinguishes seedless vascular plants from bryophytes?
A) Gametophyte-dominant life cycle
B) Lack of vascular tissue
C) Presence of seeds
D) Branched sporophytes that are independent of gametophytes for nutrition
D) Branched sporophytes that are independent of gametophytes for nutrition
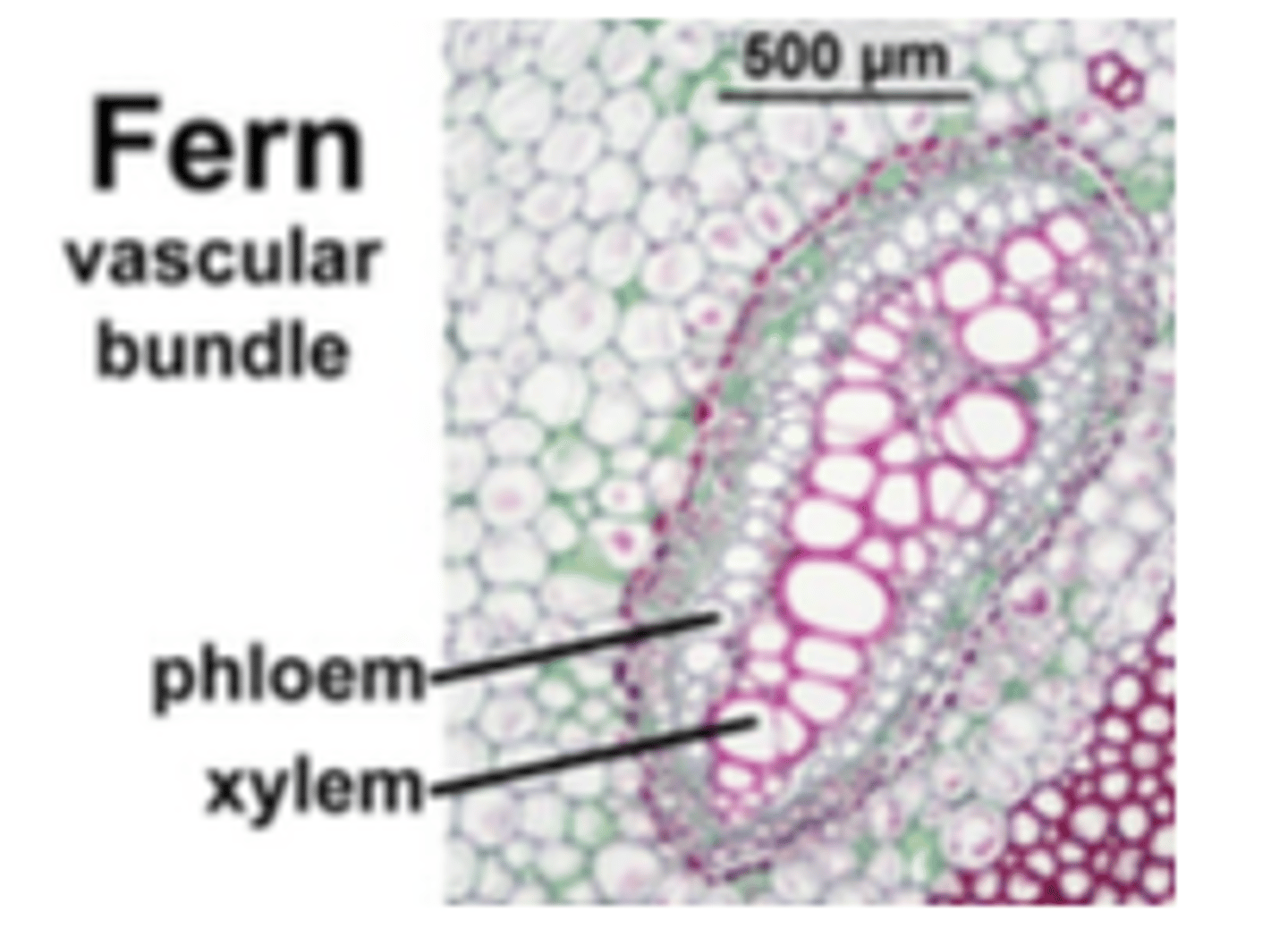
What is the function of xylem in vascular plants?A) Transporting water and minerals
B) Transporting sugars and amino acids
C) Protecting against herbivory
D) Storing starch for energy
A) Transporting water and minerals
Which of the following is true about microphylls?
A) They have a highly branched vascular system
B) They are small, spine-shaped leaves with a single vascular strand
C) They increase photosynthetic efficiency more than megaphylls
D) They are found in almost all vascular plants
B) They are small, spine-shaped leaves with a single vascular strand
What is a key advantage of megaphylls over microphylls?
A) Increased resistance to herbivores
B) More efficient water absorption
C) Greater photosynthetic productivity
D) Reduced transpiration rate
C) Greater photosynthetic productivity
Is diploid sporophyte or haploid gametophyte dominate for SVPs?
diploid sporophyte
Do Seedless Vascular Plants have true roots and true leaves?
Yes
Do only Lycophytes or Pterophytes only have microphylls?
Lycophytes
Match what is true?
a) Microphylls: Leaves with a highly branched vascular system& Megaphylls: Small, spine-shaped leaves supported by a single strand of vascular tissue
b) Microphylls: Small, spine-shaped leaves supported by a single strand of vascular tissue & Megaphylls: Leaves with a highly branched vascular system
b) Microphylls: Small, spine-shaped leaves supported by a single strand of vascular tissue & Megaphylls: Leaves with a highly branched vascular system
What is the primary function of sporophylls?
A) They are leaves modified to bear sporangia
B) They produce seeds in gymnosperms
C) They store starch for energy
D) They transport water in vascular plants
A) They are leaves modified to bear sporangia
How do lycophyte sporophylls differ from those of ferns?
A) Lycophyte sporophylls form a cone-like structure called a strobilus
B) Fern sporophylls produce seeds instead of spores
C) Lycophyte sporophylls lack sporangia
D) Fern sporophylls are entirely non-photosynthetic
A) Lycophyte sporophylls form a cone-like structure called a strobilus
What is a characteristic of homosporous spore production?
A) It involves separate male and female gametophytes
B) It only occurs in gymnosperms
C) It produces a single type of spore that develops into a bisexual gametophyte
D) It prevents sexual reproduction in seedless plants
C) It produces a single type of spore that develops into a bisexual gametophyte
Which statement best describes the difference between megaspores and microspores?A) Megaspores are produced by microsporophylls
B) Megaspores develop into female gametophytes, while microspores develop into male gametophytes
C) Microspores are larger than megaspores in all plants
D) Megaspores and microspores are identical in function
B) Megaspores develop into female gametophytes, while microspores develop into male gametophytes
Where are spores typically produced in ferns?A) Inside the ovule
B) Within specialized cones
C) On sori located on the underside of sporophylls
D) In the antheridium of the gametophyte
C) On sori located on the underside of sporophylls
Which group of Lycophytes is homosporous?
A) Quillworts
B) Club mosses
C) Spike mosses
D) All Lycophytes are heterosporous
B) Club mosses
For Lycophytes, are they are small population living in tropical and temperate environments or are they are large population living in many environments?
they are small population living in tropical and temperate environments
Which is false when talking about Whisk Ferns?
•dichotomous branching
• no true leaves or roots
• Homosporous
• Strobili
• Photosynthesis occurs in stem
• Strobili
Which is false when talking about Horsetails?
• jointed stems with tiny leaves
• Strobili
• no true leaves or roots
• Homosporous
• Photosynthesis occurs in stems
• no true leaves or roots
Which is false when talking about Ferns?
• most widespread & diverse Monilophytes
• homosporous
• large megaphylls
•dichotomous branching
• sori on underside of sporophylls
• mostly in understory or as epiphytes
•dichotomous branching
Where are sori found in ferns?
A) On the stems
B) On the underside of sporophylls
C) Inside strobili
D) In specialized roots
B) On the underside of sporophylls
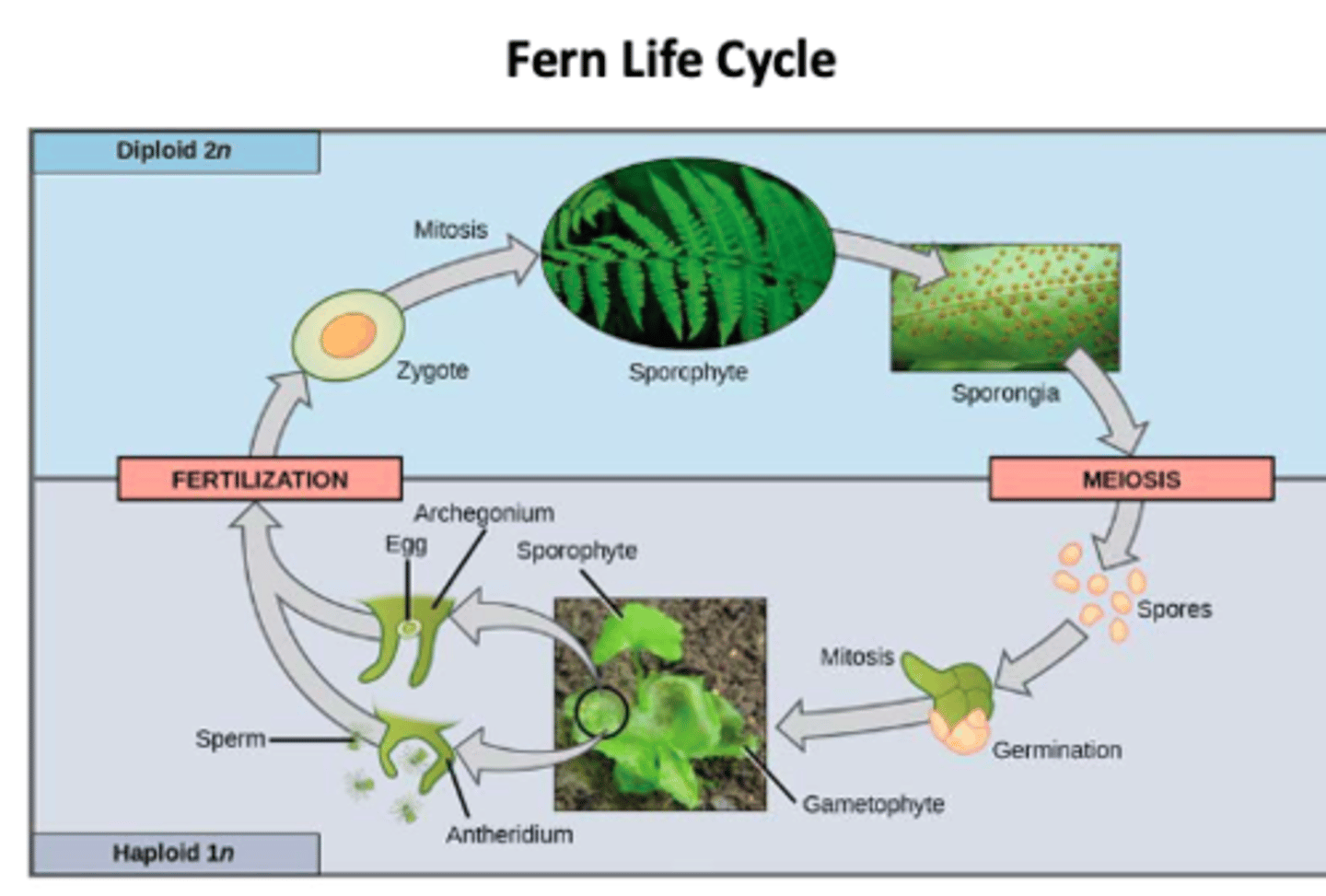
Fern Life Cycle:
Important of seedless plants: