5.1 - Protists, Some Virus
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Are Protists eukaryotes or prokaryotes?
eukaryotes
Are protists typically multi-cellular or single celled organisms?
single-celled
Protists are relatively easy to kill ___ ___ _____. (location)
out of humans
One simple protist that is typically sexually transmitted is?
Trichomonas vaginalis
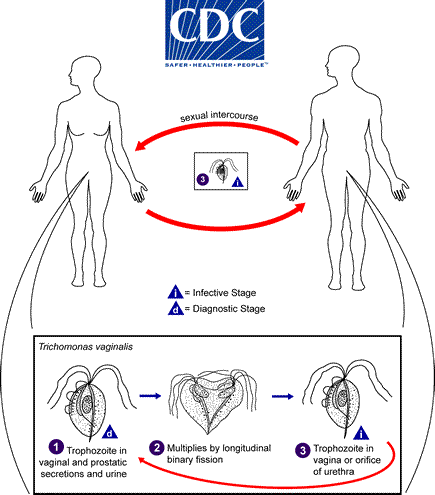
What are the conditions for Trichomonas vaginalis to grow?
vaginal pH increases
How is Trichomonas vaginalis transmitted?
sexually (mucous membrane → mucous membrane)
How many lige cycles (forms/stages) does Trichomonas vaginalis have?
one
Why doesTrichomonas vaginalis only have one life cycle/stage?
never leaves human
At what pH will Trichomonas vaginalis cause irritation or discharge? (it has grown due to this pH; provide < > symbol)
pH > 4.5
Is Trichomonas vaginalis fatal?
no

What’s the species name of a little less simple of a protist?
Giardia lamblia
Giardia lamblia is a _______ protist.
primitive
Does Giardia lamblia have a mitochondria?
no
What are the 2 forms of Giardia lamblia?
Trophozoite and cyst
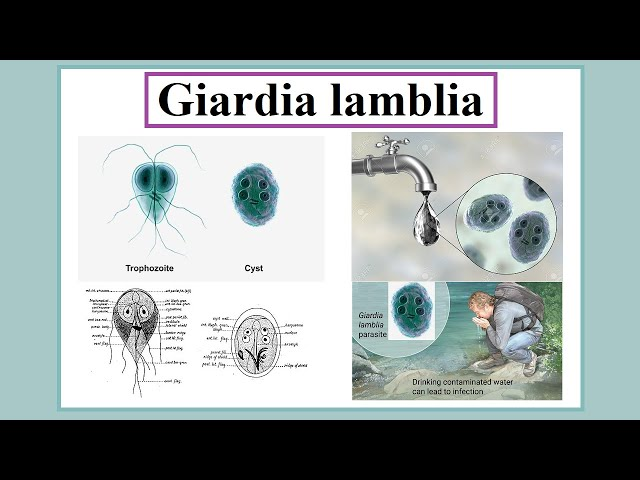
So humans swallow the _____, which germinates into trophozoites in the ______ ______ (name organ).
cyst, small intestine

Giardia lamblia once in it’s trophozoite form in the small intestine leads to → (symptom)
GI infection (explosive diarrhea)
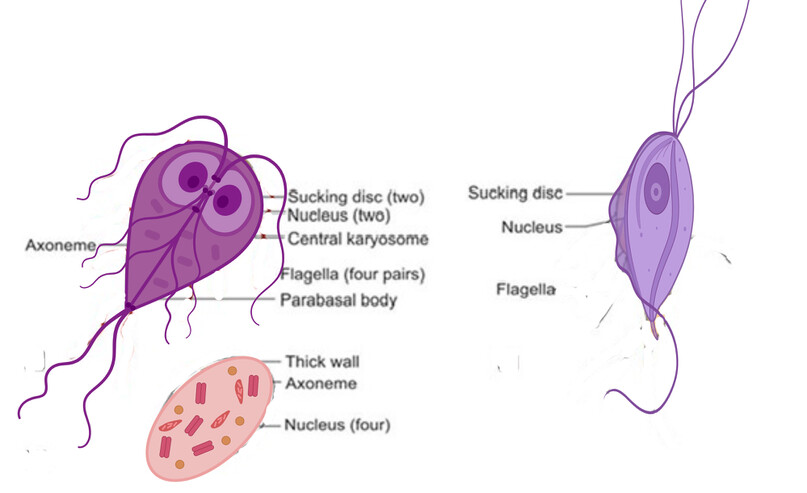
Giardia lamblia in it’s trophozoite form has __ nuclei.
2
The portal of exit for Giardia lamblia is?
feces/rectum
How can Giardia lamblia survive w/out a mitochondria? (how does it synthesize enough ATP)
sits on intestinal wall and absorbs hosts nutrients without needing to make any
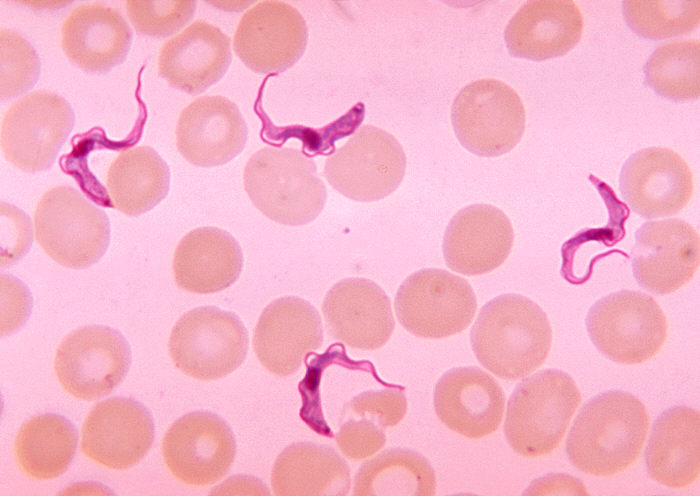
What’s a more advanced Protist species? (hint: worm-like)
Trypansoma brucei
What disease does Trypansoma brucei cause?
African Sleeping Sickness
Does Trypansoma brucei reside in a human: intracellular or extracellular?
extracellular
African Sleeping Sickness caused by Trypansoma brucei is considered an ________ disease.
endemic (only found where vectors’ found)
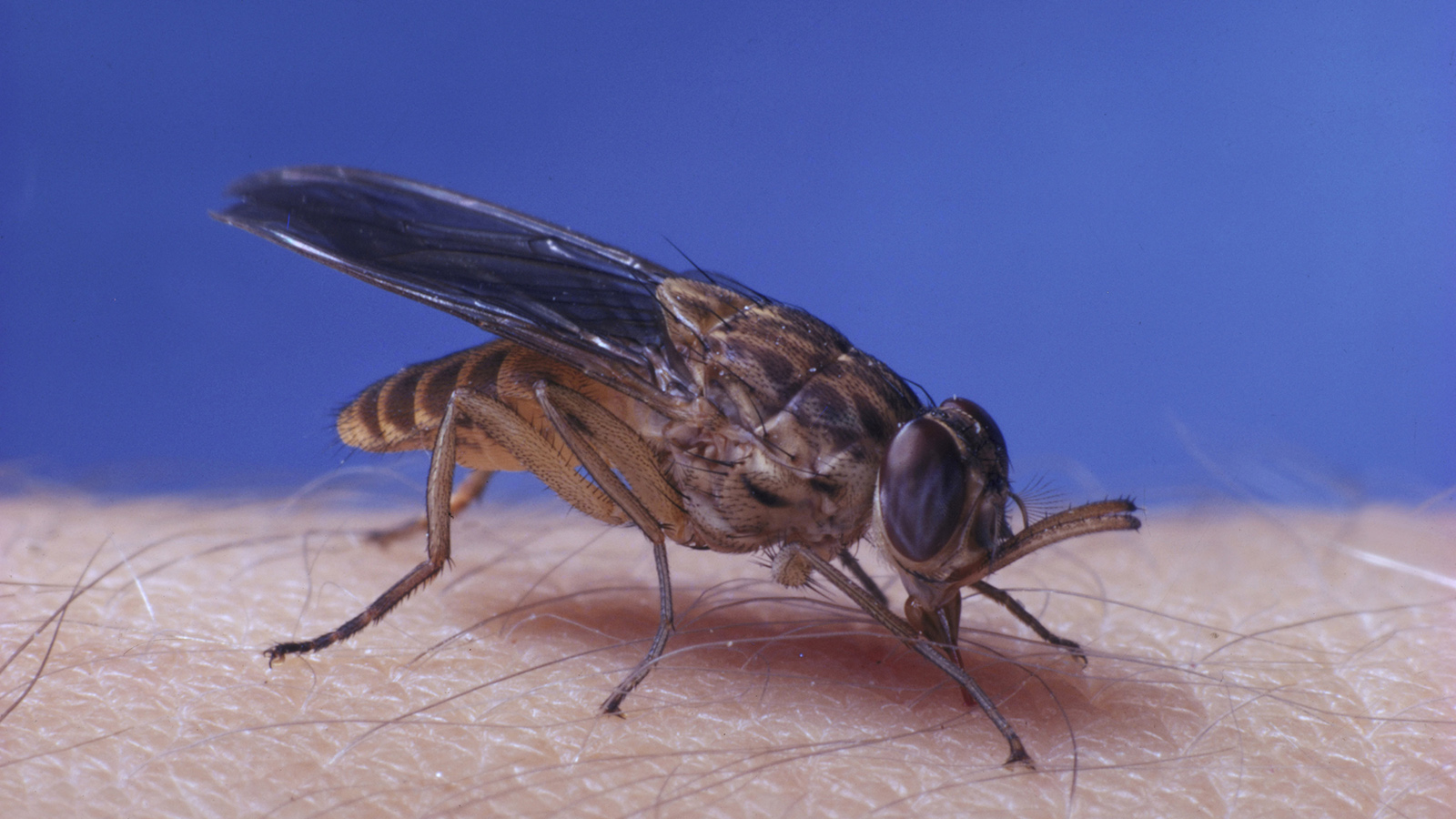

What is the vector for Trypansoma brucei/African Sleeping Sickness?
Tsetse fly
In 2 simple steps Trypansoma brucei first colonizes the ______, then the ____.
blood, CSF
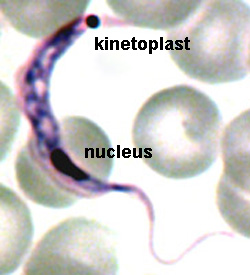
Trypansoma brucei have a kinetoplastid which is an?
enlarged mitochondria
Trypansoma brucei causes a ____-_____ pathogen
blood-borne
Disease Process of African Sleeping Sickness
Once inside the brain they cause disruption of the _______ ______.
Circadian Rhythm

Disruption of a persons’ circadian rhythm causes →
sleeping during the day
Disease Process of African Sleeping Sickness
The infection eventaully progresses to ____, _____, and ______. (3)
seizures, coma, death
Disease Process of African Sleeping Sickness
How does the Trypansoma brucei never get caught by the immune system?
switches it’s surface antigens routinely (plays antigenic cat & mouse)
A very advanced protist species is ______ __., otherwise known as Malaria.
Plasmodium sp.
Malaria is an _____ disease.
endemic
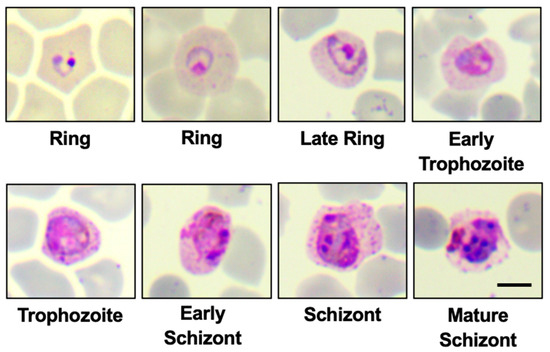
What are the 4 life stages of Plasmodium sp.?
Trophozoite, Gametocyte, Sporozoite, Merozoite
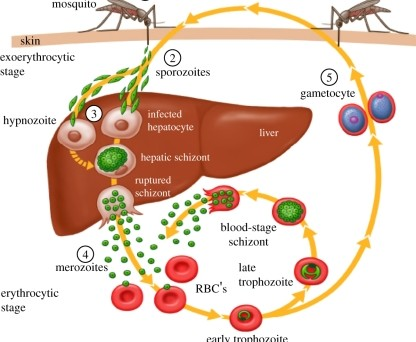
Disease Process of Malaria
Mosquito bites infected human, and draws up _______.
gametocytes (of Plasmodium sp.)
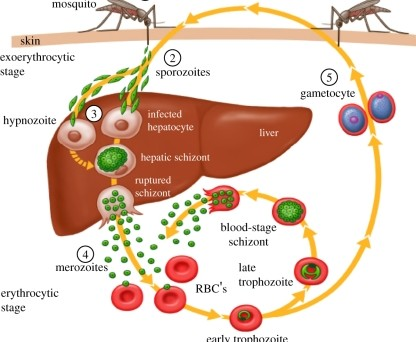
Disease Process of Malaria
Gametocytes fuse into a _______ within the mosquitos’ gut.
sporozoite
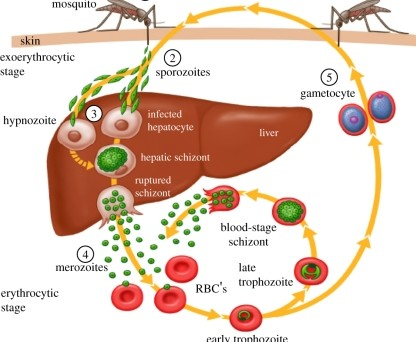
Disease Process of Malaria
2.1 - Sporozoites migrate to mosquitos _____ ______.
salivary glands
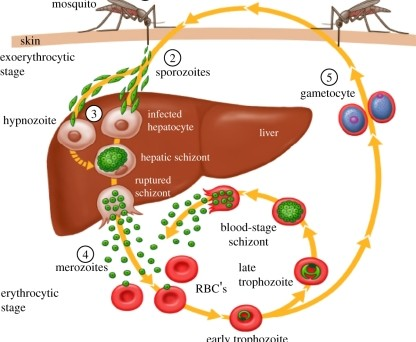
Disease Process of Malaria
Mosquito bites new victim, ____ _______.
transmitting sporozoites
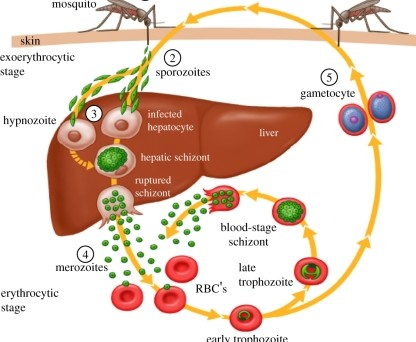
Disease Process of Malaria
Sporozoites travel to ______ and infect the _________ (liver cells).
liver; hepatocytes
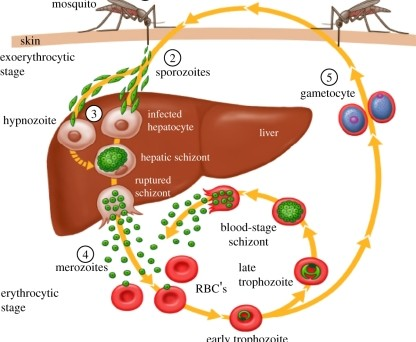
Disease Process of Malaria
The sporozoites will replicate within the hepatocytes, and change into _______ form.
merozoite
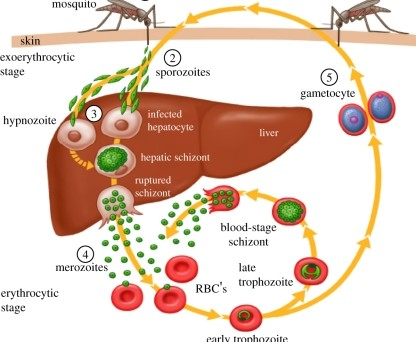
Disease Process of Malaria
5.1 - Once all the merozoites are produced, they are released all at once which →
lyses liver cells
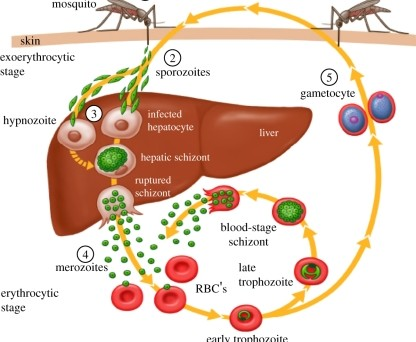
Disease Process of Malaria
Merozoite now attatches & invades ____.
RBC
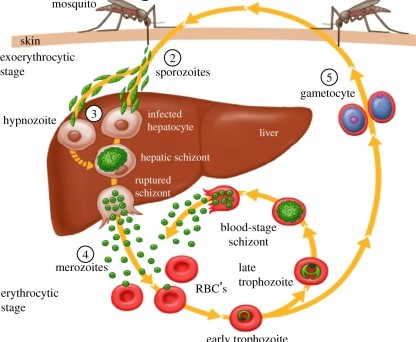
Disease Process of Malaria
6.1 - Withn the RBC, the merozoite germinates into a ______. In this form it will expand and consume resources.
trophozoite
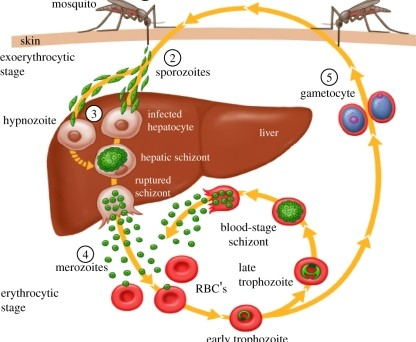
Disease Process of Malaria
6.2 - The trophozoite then divies into 6-12 ______ and causes the RBC to _____. Cycle Repeats
merozoites, lyse
Restating Part 6 of Malaria: (4 steps)
merozoite pulls itself into RBC and germinates
turns into trophozoite (in RBC)
takes over whole RBC
divides into new merozoites and lyses RBC
There is treatment for Malaria, but ____ _____ makes it difficult.
drug resistance
Also, treatment for Malaria DOES NOT prevent from ________.
re-infection
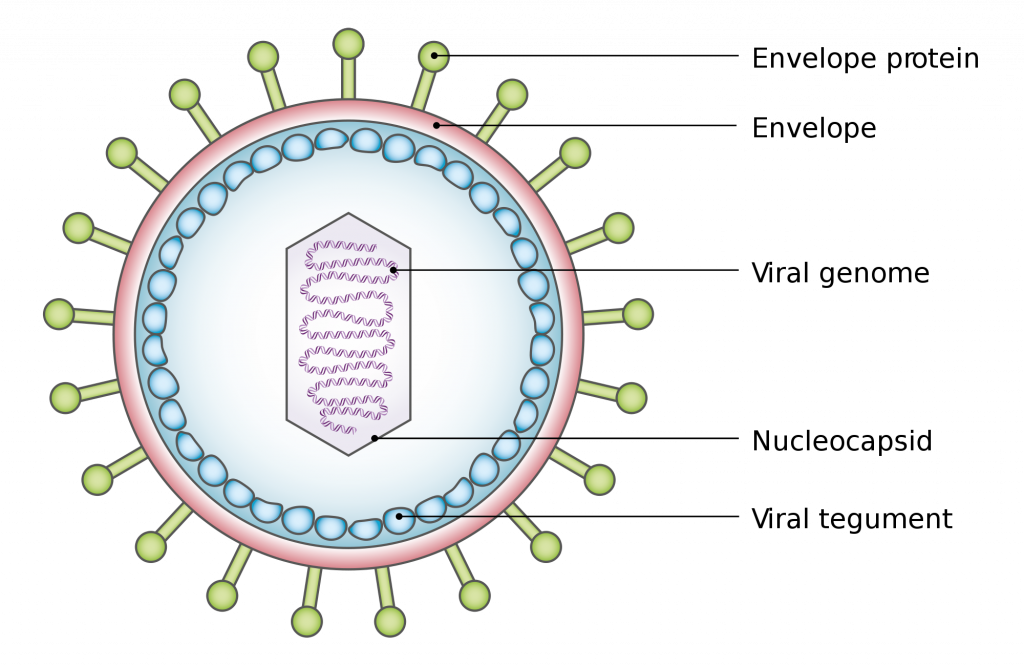
What 2 Features all Viruses have?
nucleic acid, protein shell (capsule)
What’s 1 feature viruses may or may not have?
envelope

If a virus does have an envelope, it will always have ____.
spikes
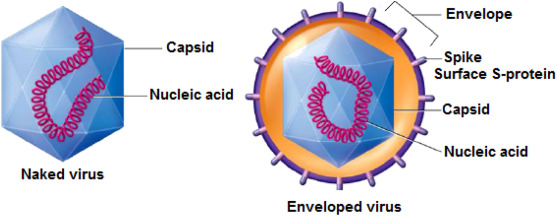
A virus with an envelope is called →
enveloped virus
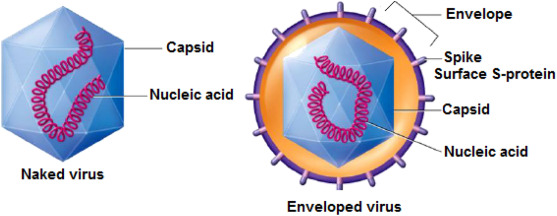
A virus with no envolope is called →
naked virus
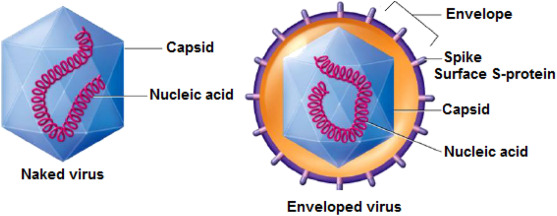
Can a naked virus still opt to have spikes, even though they have no envelope?
yes
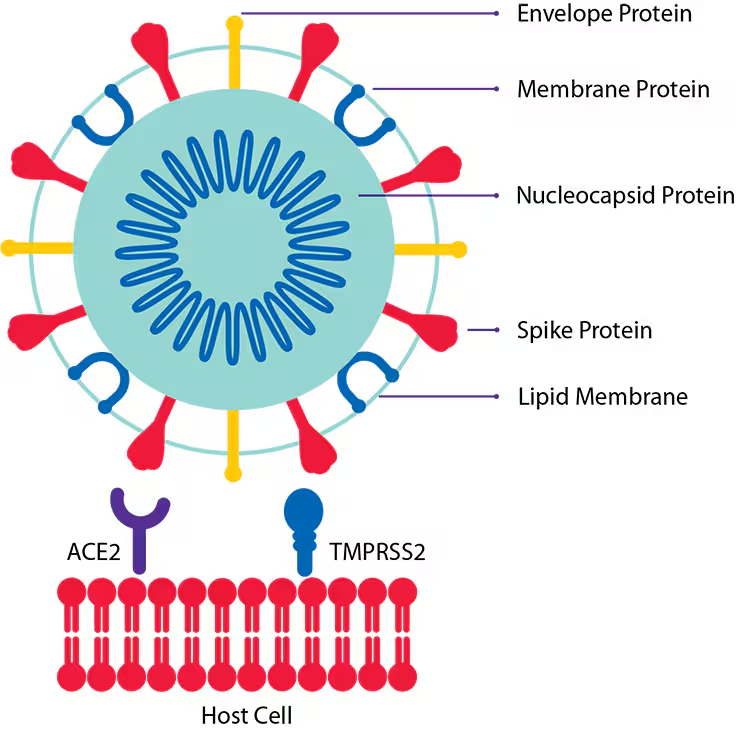
The purpose of spikes is for →
attatchment to human cells
The envelope of a virus is typically dervied/made from the ______ ____ ______.
human cell membrane (few viruses use from golgi body or ER)
What type of Nucleic Acid can Viruses have? (2)
DNA or RNA (most have RNA)
What is the ultimate goal for all viruses?
bring viral genetic code into host cell
What’s a pro of Naked Viruses?
can withstand harsh environments outside of human
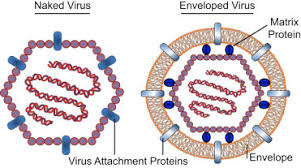
What’s are some cons of Naked Viruses? (2)
made of all antigen (capsid = antigen)
can only exit host cell by lysing it, alerts immune system (not discrete)
What are some pros of Enveloped Viruses? (2)
can leave/exit via budding
less antigens (spikes are only antigen portion)
What’s a con of the Enveloped Virus?
delicate and easily killed outside of human
Viruses DNA/RNA can be _____ or ______ stranded.
single, double (ss = single stranded; ds = double stranded)
So for DNA specifically, the types of nucleic acid strategies are: (2)
dsDNA
ssDNA
For RNA’s nucleic acid strategies there are: (3)
dsRNA
(-) ssRNA
(+) ssRNA
The significance about (+) ssRNA is that they offshot and become a →
retrovirus (ex. HIV)
Of all the nucleic acid strategies, the most common that infect humans are: (4)
dsDNA, (-)ssRNA, (+)ssRNA, retrovirus