Chapter 4- Histology
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Histology
the study of tissue
simple epithelium
single layer of epithelial cells
stratified epithelium
multiple layers of epithelial cells
squamous
flat, wide, irregular cells with flat nucleus, “squash”
cuboidal
tall as wide, “cube”, cells, nucleus in the center
columnar
slender, taller than wide, nucleus basal, “column”
what are the four types of tissue
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
function of epithelial tissue
protection, selective permeability, secretions, sensations

what tissue is is
simple squamous epithelium
what is the structure of simple squamous epithelium
1 layer, flat
what is the function of the simple squamous epithelium
rapid diffusion
where is the simple squamous epithelium located
alveoli, capillaries, endothelium of vessels, serous membranes of body cavities
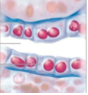
What tissue is this
simple cuboidal epithelium
what is the structure of simple cuboidal epithelium
1 layer of cube cells
what is the function of simple cuboidal epithelium
absorption, secretion
where is the location of simple cuboidal epithelium
thyroid, kidney, glands
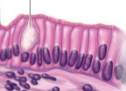
what tissue is this
simple columnar epithelium with nonciliated microvilli
what is the structure of the simple columnar epithelium
1 layer, column shaped cells, microvilli to increase surface area
what is the function of the simple columnar epithelium
absorption
where is the simple columnar epithelium located
digestive tract
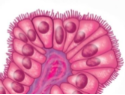
what tissue is this
simple columnar epithelium ciliated
what is the function of the simple columnar epithelium ciliated
movement of mucus and oocyte
what is the structure of simple columnar epithelium ciliated
1 layer, column shaped cells, cilia
where is the simple columnar epithelium ciliated located
larger bronchioles, uterine tube
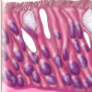
what tissue is this
pseudostratified columnar epithelium ciliated
what is the structure of pseudostratified columnar epithelium ciliated
single layer, cells look like layers but are scattered
what is the function of pseudostratified columnar epithelium ciliated
moves mucus
where is the pseudostratified columnar epithelium ciliated located
respiratory tract
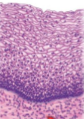
what tissue is this
stratified squamous epithelium nonkeratinized
what is the structure of stratified squamous epithelium nonkeratinized?
2+ layers of flat squished cells
what is the function of stratified squamous epithelium nonkeratinized
protection from abrasion
where is the stratified squamous epithelium nonkeratinized location
epidermis of skin

what tissue is this
stratified squamous epithelium keratinized
what is the structure of stratified squamous epithelium keratinized?
2+ layers, flat shaped
what is the function of stratified squamous epithelium keratinized?
abrasion, secretions
where is the stratified squamous epithelium keratinized location
epidermis of skin
what is the structure of stratified cuboidal epithelium
2 layers, cube shaped
what is the location of stratified cuboidal epithelium
sweat glands
what is the function of stratified cuboidal epithelium
secretion, abrasion
what is the structure of stratified columnar epithelium
2-3 layers, column shaped cells
what is the location of stratified columnar epithelium
salivary glands, male urethra
what is the function of transitional epithelium
distention
what is the structure of transitional epithelium
multiple cells of all varying shapes
where is the location of transitional epithelium
uterus, urinary bladder, part of male urethra
osteo-
bone
adipo-
fat
fibro-
fibers
chrondro-
cartilage
-cyte
cell
-blast
build
-clast
destroy

what tissue is this
areolar connective tissue
what is the structure of areolar connective tissue
collagen, elastic fibers, scattered fibroblasts, blood vessels
what is the function of areolar connective tissue
packing and attachment
where is location of areolar connective tissue
subcutaneous skin, surrounds nerve and muscle cells, outer layer of blood vessels
what is the structure of adipose ct
lipids, adipocytes squished together
where is the location of adipose ct
subcutaneous layer of the skin
what is the structure of reticular ct
fibroblasts, reticular meshwork, leukocytes
what is the function of reticular ct
lymphatic organs
where is the location of reticular ct
spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow

what tissue is this
dense regular connective tissue
what is the function of dense regular connective tissue
strength and flexibility
what is the structure of dense regular connective tissue
densely packed, parallel arrays of collagen, fibroblasts in between layers
where is the location of dense regular connective tissue
tendons, ligaments

what tissue is this
dense irregular connective tissue
what is the structure of dense irregular connective tissue
collagen in many directions, fibroblasts among fibers
what is the function of dense irregular connective tissue
tensile strength in many directions
where is the location dense irregular connective tissue
dermis, capsules around organs, outer layer of muscles and nerves
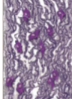
what tissue is this
elastic connective tissue
what is the structure of elastic connective tissue
elastic fibers, fibroblasts in between
what is the function of elastic connective tissue
stretch and recoil
where is the location of elastic connective tissue
vocal chords,large medium sized ovaries

what tissue is this
hyaline cartilage
what is the structure of hyaline cartilage
smooth, scatter chondrocytes
what is the function of hyaline cartilage
smooth surface, support soft tissue
where is the location of hyaline cartilage
fetal skeleton, articular, cartilage, trachea, larynx, nose

what tissue is this
fibrocartilage
what is the structure of fibrocartilage
parallel collagen fibers, large chondrocytes
what is the function of fibrocartilage
resists compression
where is the location of fibrocartilage
intervertebral discs, pubic symphyses, menisci
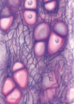
what tissue is this
elastic cartilage
what is the structure of elastic cartilage
elastic fibers in web like mesh
what is the function of elastic cartilage
structure and shape with flexibility, closely packed lucumae
where is the location of elastic cartilage
ear epiglottis
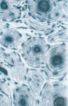
what tissue is this
compact bone
what is the structure of compact bone
osteons, lamellae, central canal
what is the function of compact bone
support, protection, lever for skeletal muscles, calcium storage
where is the location of compact bone
bone
what is the structure of spongey bone
lamellae, no central canal, bone marrow
what is function of spongy bone
compact bone, hemopoisis
where is spongey bone located
middle layer of flat bones, inner layer among long bones

what tissue is this
skeletal muscle
what is the structure of skeletal muscle
cylindrical and long, multinucleated, voluntary
what is the function of skeletal muscle
movement of skeleton or skin
what is the location of skeletal muscle
attached to bone
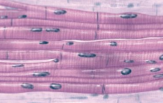
what tissue is this
cardiac muscle
what is the structure of cardiac muscle
branded, y-shaped, striated, involuntary, intercalated dics
what is the function of cardiac muscle
heart beat
what is the location of cardiac muscle
myocardium
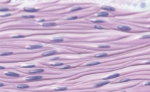
what tissue is this
smooth muscle