SNC2D1: Optics
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/73
Last updated 6:10 PM on 11/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
1
New cards
Lesson 1: Introduction to Optics
Lesson 2: Reflection of Light in a Plane Mirror
Lesson 3: Curved Mirrors, Ray Diagrams and Image Properties
Lesson 4: Applications of Curved Mirrors and Curved Mirror Equation Calculations.
Lesson 6: Introduction to refraction and refraction ray diagrams.
Lesson 7: Total internal reflection and Critical angle
Lesson 10: Lenses and Ray Diagrams
Lesson 11: Lens Equation
Lesson 12: Introduction to the human eye and eye conditions/corrections
Lesson 2: Reflection of Light in a Plane Mirror
Lesson 3: Curved Mirrors, Ray Diagrams and Image Properties
Lesson 4: Applications of Curved Mirrors and Curved Mirror Equation Calculations.
Lesson 6: Introduction to refraction and refraction ray diagrams.
Lesson 7: Total internal reflection and Critical angle
Lesson 10: Lenses and Ray Diagrams
Lesson 11: Lens Equation
Lesson 12: Introduction to the human eye and eye conditions/corrections
2
New cards
Define "converging"
Going towards the one point.
3
New cards
Define "diverging"
Separating, leaving one point into many different directions.
4
New cards
Define "reflection"
The process of light 'bouncing off' an object.
5
New cards
Recall "The Law of Reflection"
θᵢ = θᵣ
6
New cards
Define "The Law of Reflection"
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Measured at the normal.
7
New cards
Define "The Incident Ray"
The ray moving towards the mirror.
8
New cards
Define "The Reflected Ray"
The ray moving away from the mirror that was reflected.
9
New cards
Define "The Point of Incidence"
The point were the light is reflected.
10
New cards
Define "The Normal Line"
The line perpendicular to the mirror where the Point of Incidence is.
11
New cards
Define "Angle of Incidence"
Represented as 'i', the angle between the ray of incidence and the normal.
12
New cards
Define "Angle of Reflection"
Represented as "r", the angle between the ray of reflection and the normal.
13
New cards
Recall "SALT"
Size, Attitude, Location, Type.
14
New cards
Define "Size"
Bigger, smaller, or same size relative to object.
15
New cards
Define "Attitude"
Upright or Inverted relative to object.
16
New cards
Define "Location"
Same Side (Where—F, C 2F', between O + F'), Behind Mirror
17
New cards
Define "Type"
Real or Virtual.
18
New cards
Define "Real Image"
An image that is formed by rays of light and can be seen/projected onto a surface.
19
New cards
Define "Virtual Image"
An image that is formed by 'fake' rays of light and cannot be seen/projected onto a surface.
20
New cards
Define "Converging Mirrors"
Cause parallel light rays rays to come to a point.
21
New cards
"Converging Mirrors" A.K.A.
Concave mirrors
22
New cards
"Concave Mirrors" A.K.A.
Converging Mirrors
23
New cards
Define "Diverging Mirrors"
Cause parallel lights to spread apart from a point
24
New cards
"Diverging Mirrors" A.K.A.
Convex Mirrors
25
New cards
"Convex Mirrors" A.K.A.
Diverging Mirrors
26
New cards
Recall "Centre of Curvature"
C
27
New cards
Define "Centre of Curvature"
Twice the distance of F, the centre of the sphere of the mirror.
28
New cards
Recall "Centre of Curvature" Variable
C
29
New cards
Recall "Vertex" Variable
V
30
New cards
Define "Vertex"
The point at which the mirror intersects the Principle Axis.
31
New cards
Recall "Principal Axis"
PA
32
New cards
Define "Principle Axis"
The line drawn through the vertex, perpendicular to the mirror.
33
New cards
Define "Focus"
The point halfway between the Centre of Curvature and the Vertex
34
New cards
Recall "Focus" Variable
F
35
New cards
List "Types of Mirror"
Concave, Convex.
36
New cards
List "Rules for Concave Mirror Ray Diagram"
Parallel to PA & reflected through F, Through F & reflected parallel to PA, Through C & reflected along same path
37
New cards
List "Rules for Convex Mirror Ray Diagram"
Parallel to PA & reflected backwards with virtual line through F, Towards virtual F & reflected parallel to PA with parallel virtual line parallel to PA, Towards virtual C & reflected on same path with virtual line to C.
38
New cards
Curved Mirror Equation
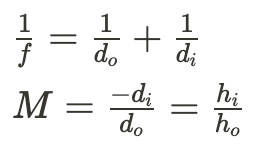
39
New cards
Recall "Negative F Mirror"
Diverging/Convex Mirror
40
New cards
Recall "Positive F Mirror"
Converging/Concave Mirror
41
New cards
Recall "Negative dᵢ"
Image is virtual
42
New cards
Recall "Positive dᵢ"
Image is real
43
New cards
Recall "Negative M"
Image is inverted
44
New cards
Recall "Positive M"
Image is upright
45
New cards
Recall "Index of Refraction" Variable
n
46
New cards
Define "Index of Refraction" Variable
The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium
47
New cards
Recall "Speed of Light in Medium" Variable
V
48
New cards
Recall "Speed of Light in Vacuum" Variable
c
49
New cards
Recall "The Speed of Light"
3.00 • 10^8 m/s
50
New cards
Result of "Light Travelling from less dense to more dense medium"
Bends towards normal
51
New cards
Result of "Light travelling from more dense to less dense medium"
Bends away from normal.
52
New cards
Define "Total Internal Reflection"
Where light reflects in a medium instead of exiting out of it.
53
New cards
Define "Critical Angle"
The greatest angle light is able to exit a medium with.
54
New cards
Recall "Two conditions for total internal reflection"
The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle. The light must be travelling from a more to less dense medium.
55
New cards
Define "Convex Lenses"
Lenses that cause parallel light rays to go towards one point.
56
New cards
Define "Concave Lenses"
Lenses that cause parallel light rays to disperse from one point.
57
New cards
"Convex Lenses" A.K.A.
Converging Lenses
58
New cards
"Concave Lenses" A.K.A.
Diverging Lenses
59
New cards
"Converging Lenses" A.K.A.
Convex Lenses
60
New cards
"Diverging Lenses" A.K.A.
Concave Lenses
61
New cards
List "Rules for Lens Ray Diagrams"
A ray parallel to the Primary Focus and is refracted so it passes through F. A ray that passes through F' and is refracted as a parallel line. A ray that passes through the optical centre without bending.
62
New cards
Define "Hyperopia"
The condition where someone can see far away but not close. Caused because the focal point is too far away to the retina.
63
New cards
"Hyperopia" A.K.A.
Farsightedness
64
New cards
Define "Myopia"
The condition where someone can see close but not far away. The focal point is too close to the retina.
65
New cards
"Myopia" A.K.A.
Nearsightedness
66
New cards
Define "Lens for Hyperopia"
Convex/Converging Lens
67
New cards
Define "Lens for Myopia"
Concave/Diverging Lens.
68
New cards
Define "Incandescence"
The light produced by hot objects. Most energy is given off as heat.
69
New cards
Define "Luminescence"
Light given off by objects that have not been heated.
70
New cards
Define "Fluorescent"
Tubes that contain mercury vapour that emit UV light until it is coated in phosphos. Some energy is given off as heat.
71
New cards
Define "Phosphorescence"
Light emitted by phosphor that glow in the dark.
72
New cards
Define "Discharge Tubes"
Neon Lights, produced by an electric current when their energy is released
73
New cards
Define "Light Emitting Diodes"
LED. Very durable, small electric current required.
74
New cards
Define "Chemiluminescence"
Light released during chemical reactions. When it occurs in organisms it is called Bioluminescence.